QC Lab - Volumetric Apparatus
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
burette & pipette
üUsed in delivering definite volume (open both at top and bottom)
volumetric flask & graduated cylinder
üUsed to contain definite volume (open at top and closed at bottom)
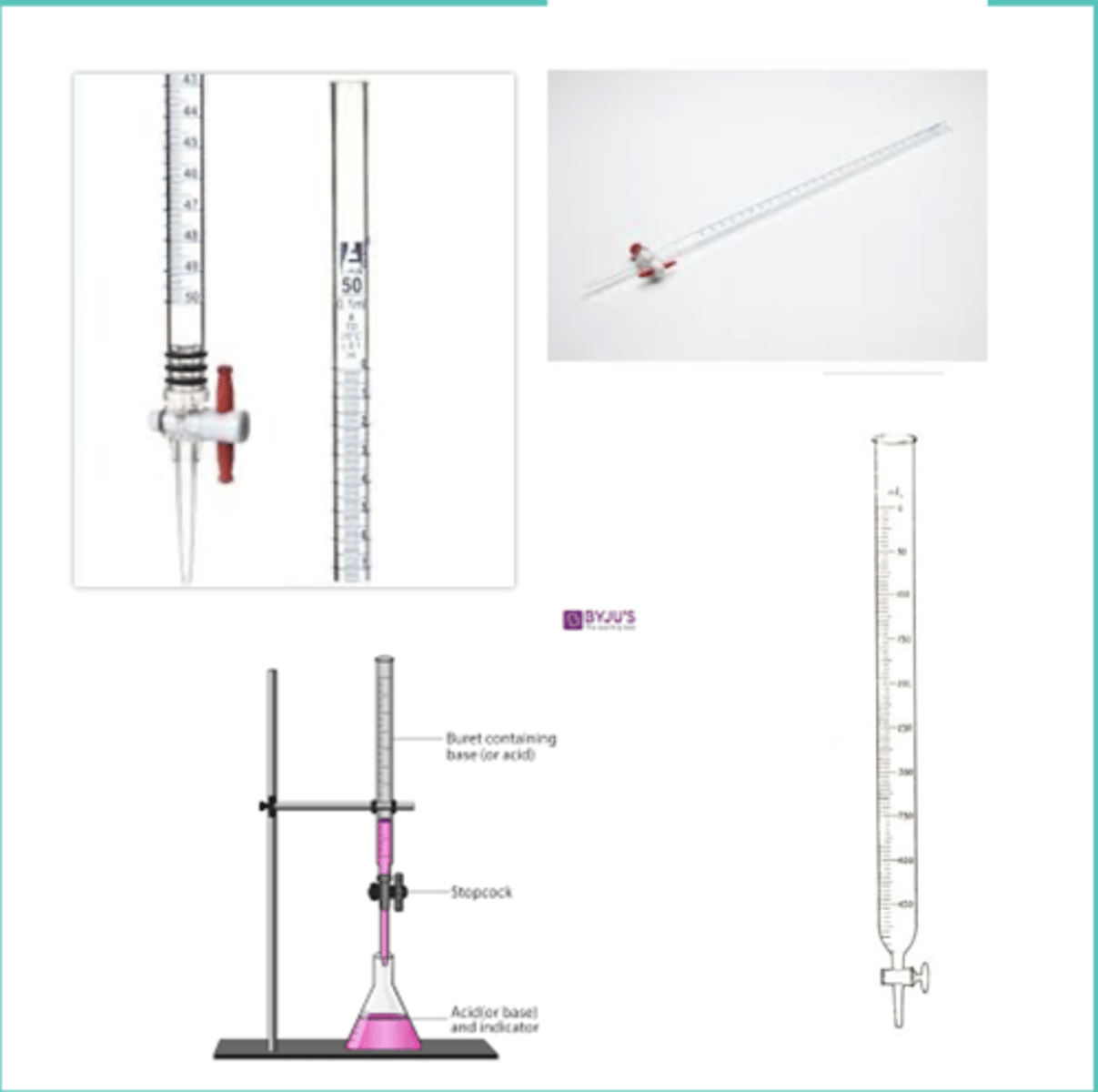
burette
oLaboratory apparatus used in quantitative chemical analysis used in the measurement of variable quantities
oClosed at the bottom by a glass or Teflon stopcock to control the outflow of liquid
- horizontal: closed
- vertical: open
- use iron stand in even surface and burette clamp firmly attached
- graduations: top (0 ml) to tip (bottom)
titer/titre
total volume of liquid added from the burette
filled until 0ml = final volume reached by liquid inside the burette
- can be used even when not filled to 0 mL
- FBR - IBR
meniscus
üCurve seen at the top of a liquid in response to its container
üCan be either concave or convex, depending on the surface tension of the liquid and its adhesion to the wall of the container
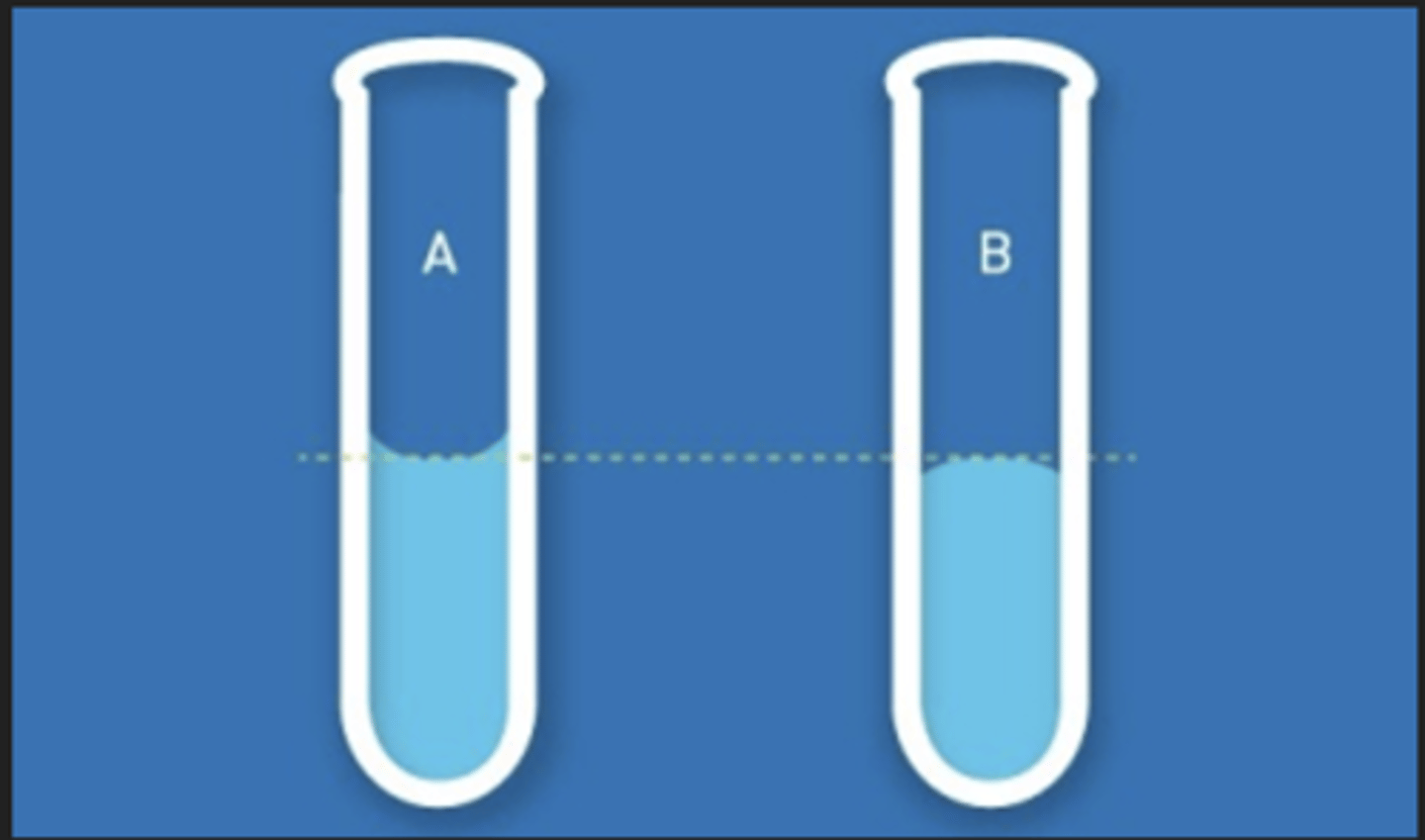
convex meniscus
- backwards meniscus
- molecules are more strongly attracted to each other than container
- mercury
concave meniscus
- occurs when molecules of liquid are more strongly attracted to their container than to each other
- most liquids (water)
colorless
- lower meniscus
highly colored/opaque
- upper meniscus (there is no lower meniscus)
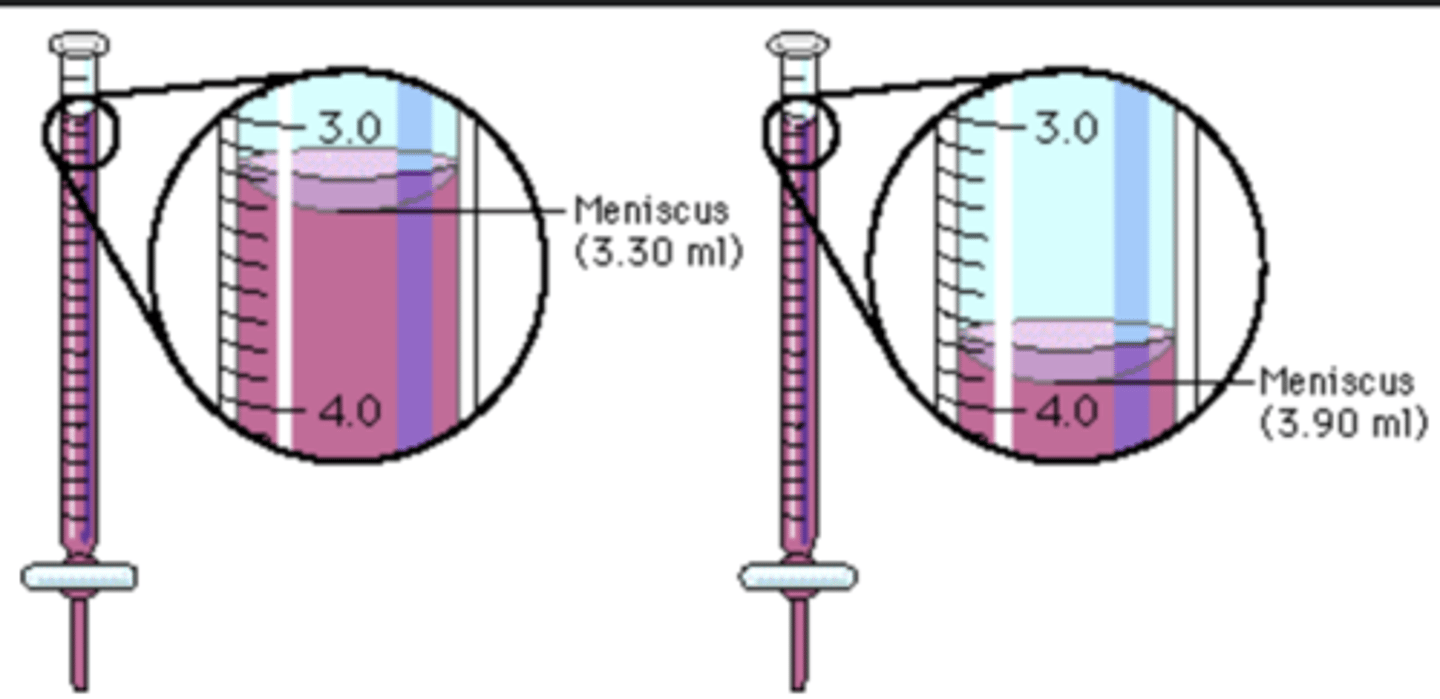
burette reading
Apparatus must be placed on an even surface
Eye must be on the same level as the meniscus
For colorless solutions, reading should be made at the lower meniscus
For highly colored solutions, reading should be made at the upper meniscus
proper use of burette
Clean burettes with dishwashing liquid and burette brush
Before filling the burette with the VS, it should first be rinsed several times with small portions of the desired solution, discarding each wash. Use <5mL of the solution to wash the inside walls of the burette.
pipette
Small tubes that transfer liquids from one container to another in exact and measurable amounts (w/rubber aspirator)
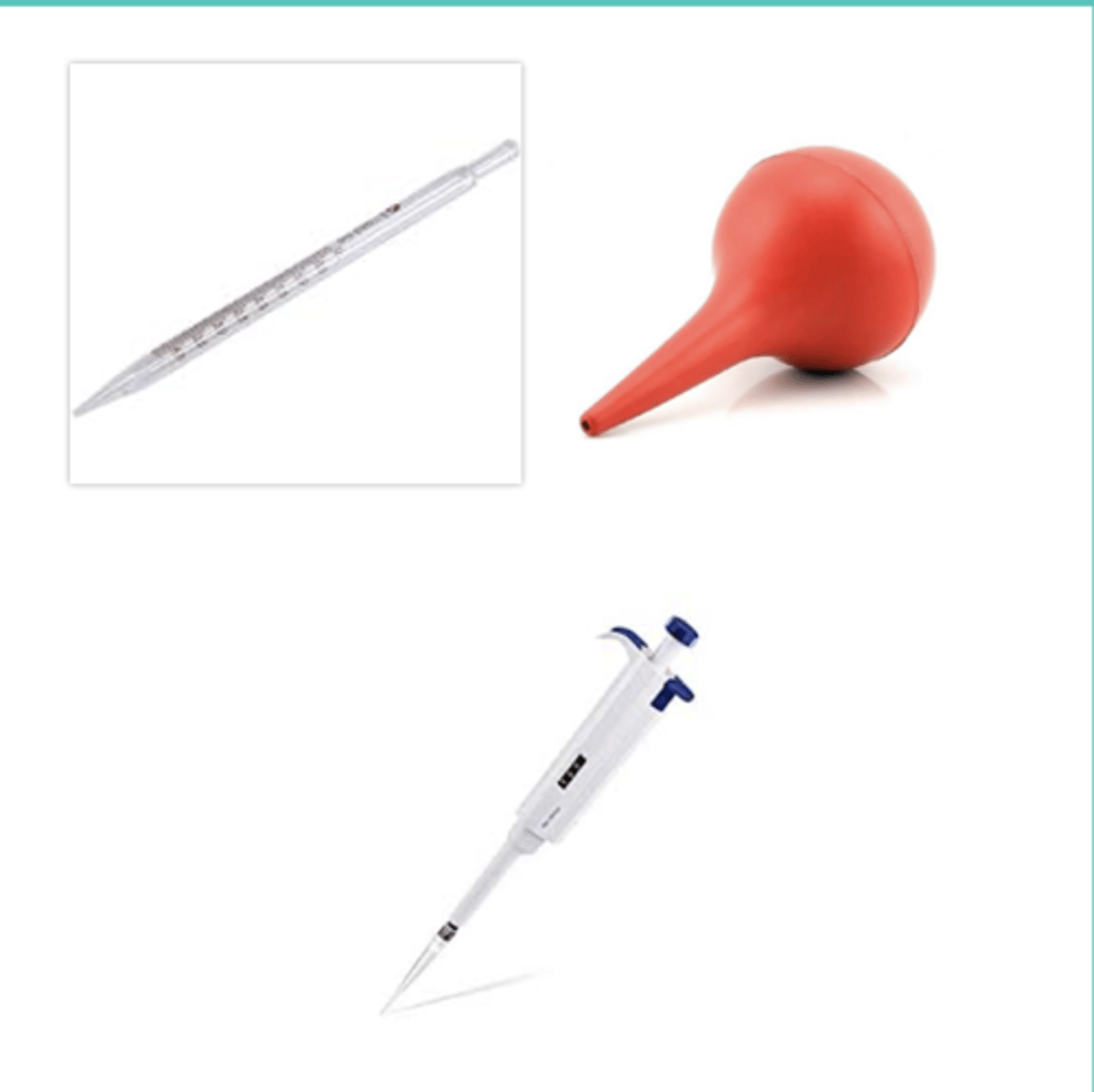

proper use of pipette
To clean one, draw distilled water into the pipette and tilt it, so that the water makes contact with the inside surface of the pipette.
Repeat this process twice, then rinse the entire pipette with distilled water to finish cleaning it.
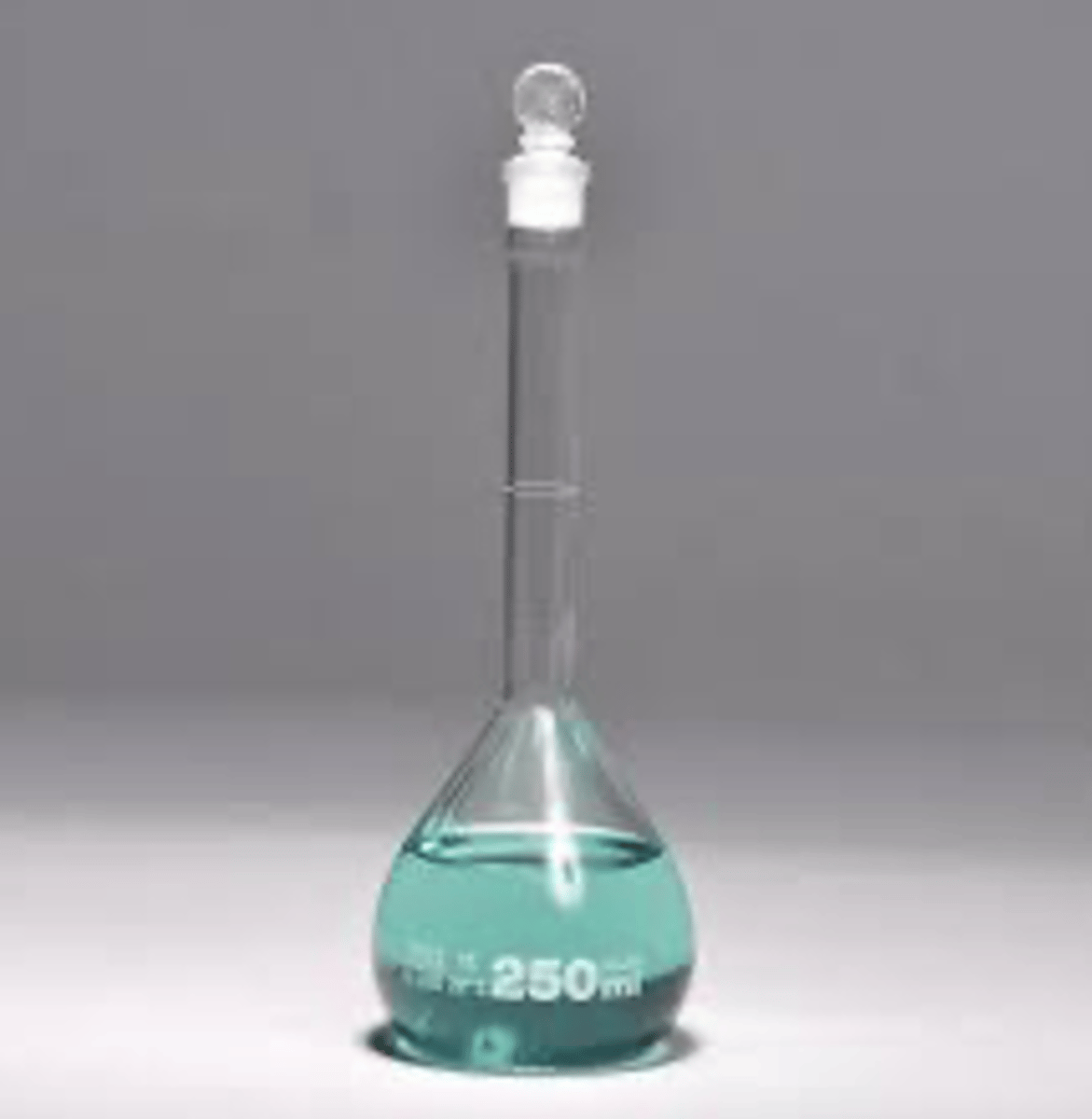
volumetric flask
oType of laboratory glassware used to prepare solutions
oFlat bottomed bulb with an elongated neck calibrated to hold a set volume at a mark on the neck (1st apparatus)

direct
directly prepare solution inside the flask (swirl in infinity sign = homogenous)
indirect
use separate container
proper use of volumetric flask
Should be clean prior to use. Do not use a brush when cleaning the inside walls of the flask.
Dissolve the desired mass of the reagent directly in the flask or dissolve first the chemical in a beaker then transfer it to the volumetric flask ensuring that every drop is transferred.
After each addition of the solvent, the flask should be swirled carefully to allow even distribution of the solute and the solvent to produce a homogenous solution.
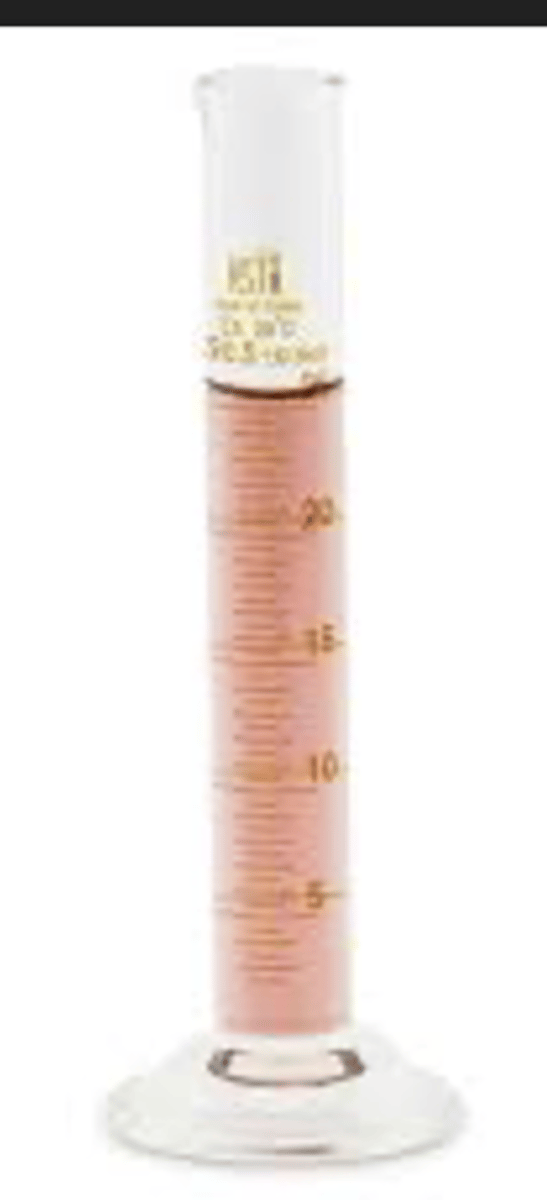
graduated cylinder
Narrow, cylindrical container marked with horizontal lines to represent units of measurement and used to precisely measure the volume of liquids

sources of error in use
1.Rinse water adhering to walls of apparatus. The apparatus may be dried, but it is more convenient and just as accurate to wash it out with small successive portions of the liquid to be used, discarding the washings.
2.Grease films and dirty apparatus cause irregularities in the delivery of liquid and distort the meniscus.
3.Parallax must be avoided to secure proper readings of the level of the meniscus.
4.Variations in temperature lead to changes in volume of vessels and liquids. All measurements therefore should be made at a temperature closely approximating that at which the apparatus was calibrated.
5. Air bubbles trapped beneath the liquid surface, especially below the stopcock in burettes, displace liquid.
6. Heat, such as supplied by hot solutions, causes calibrated volumetric apparatus to suffer a slight permanent change in volume.
7. Most salts when dissolved produce a change in temperature, with concomitant change in volume of the solution. (NaOH pellet + water = exothermic)
8. Failure to use apparatus in a manner approaching as nearly as possible that followed in calibration.
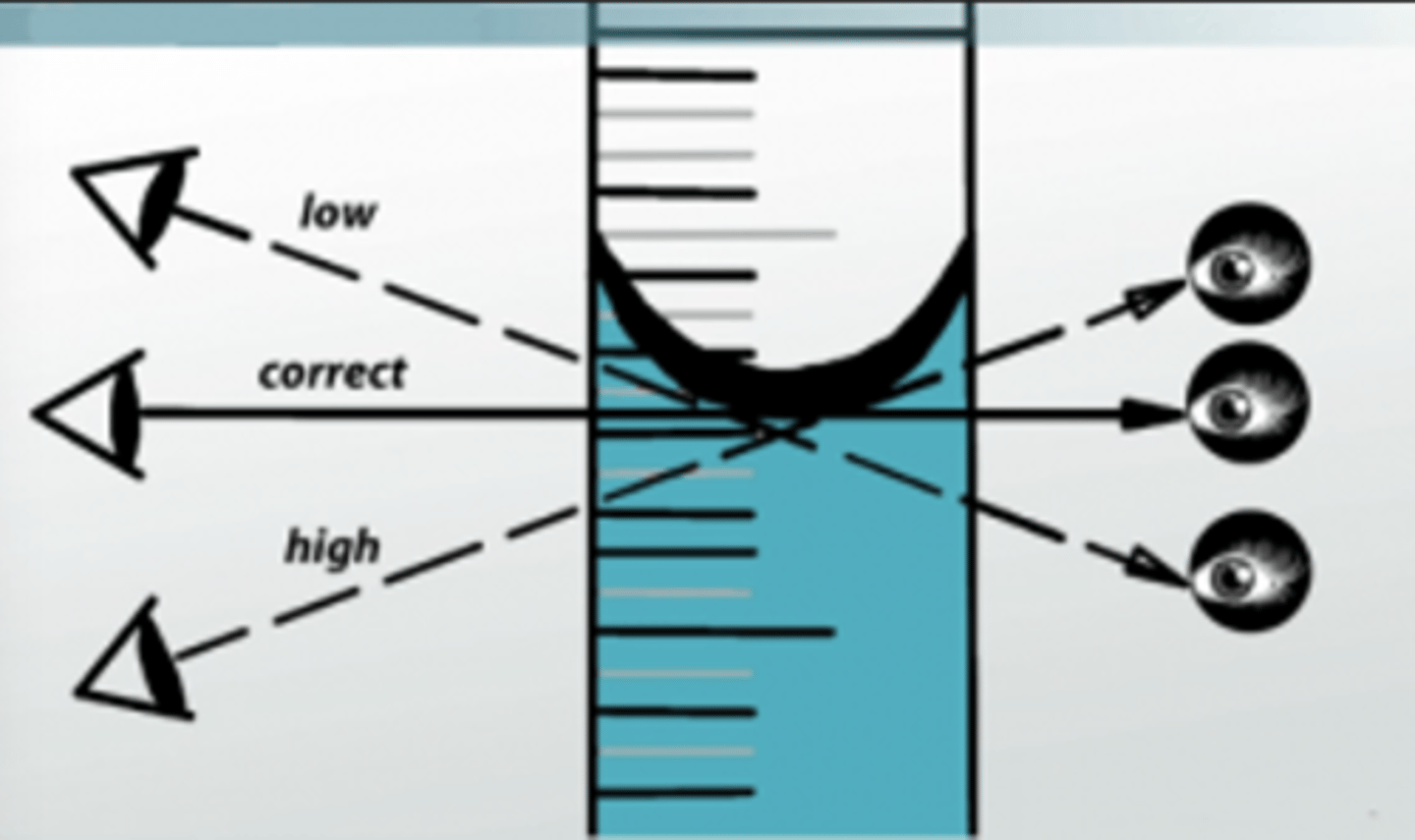
parallax
displacement of measurement due to observers POV
20 deg C
calibrated at this temperature to get accurate measurement
air bubbles
dislodge by opening burette