aetiology and management of gingival recession and sensitivity
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
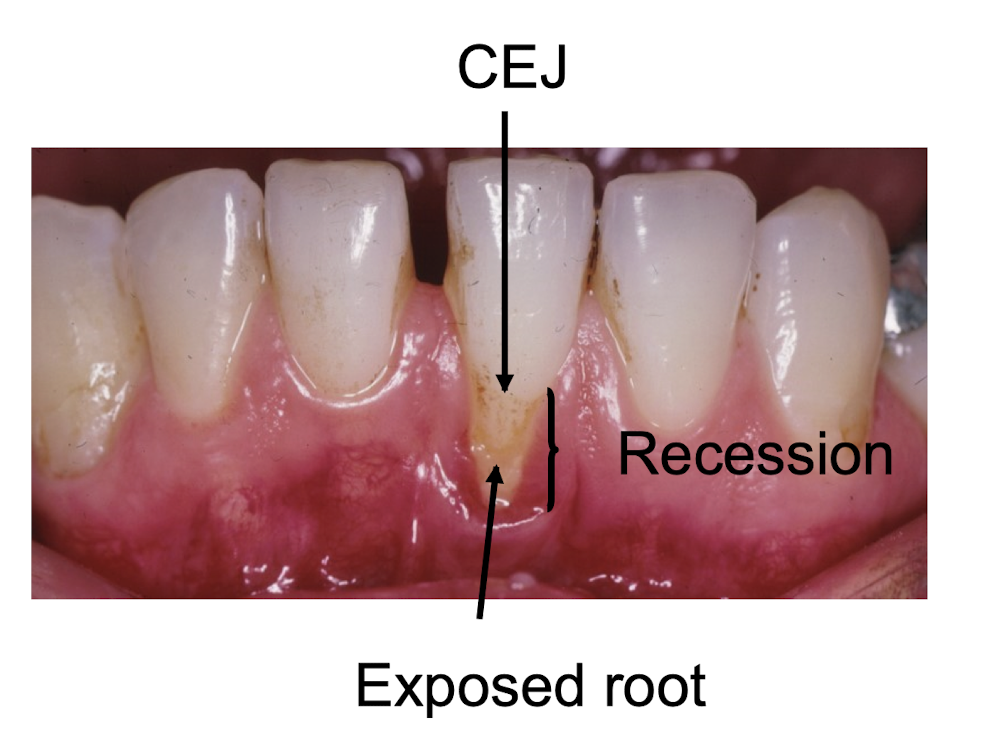
definition of recession
location of the gingival margin apical to the cemento-enamel junction resulting in exposure of the root surface
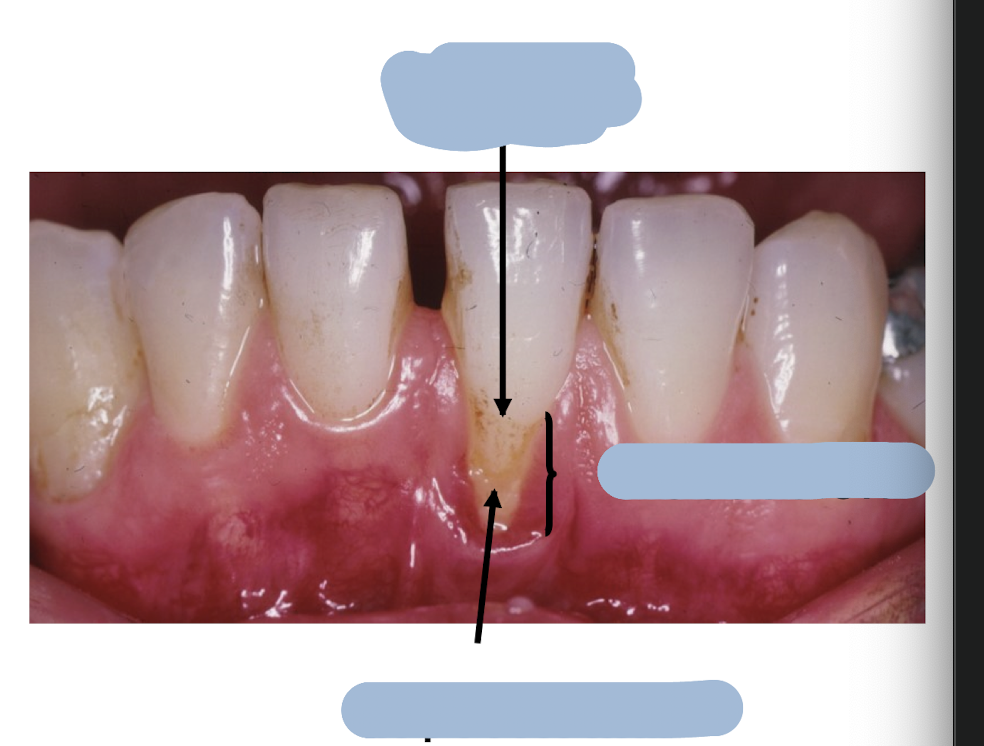
label the diagram
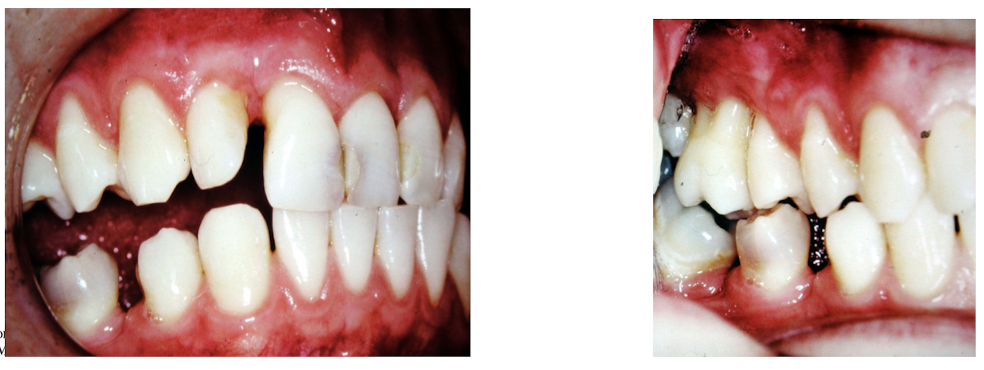
what is the incidence of recession
canines and premolars are most commonly affected
labial and buccal surface most commonly affected
what classification of recession is used
Miller 1985
what is class 1 recession
marginal tissue recession not extending to the mucogingival junction
no loss of interdental bone or soft tissue
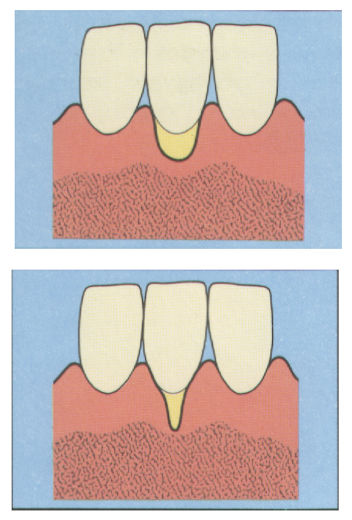
what is class 2 recession
marginal tissue recession extends to or beyond the mucogingival junction
no loss of interdental bone or soft tissue
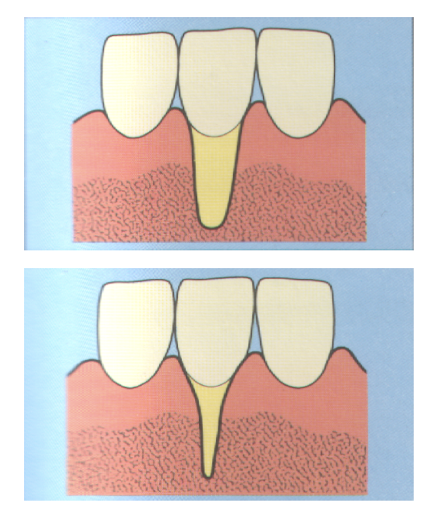
class 3 recession
marginal tissue recession extends to or beyond the mucogingival junction
loss of interdental bone or soft tissue is apical to the CEJ but coronal to the apical extent of the marginal tissue recession
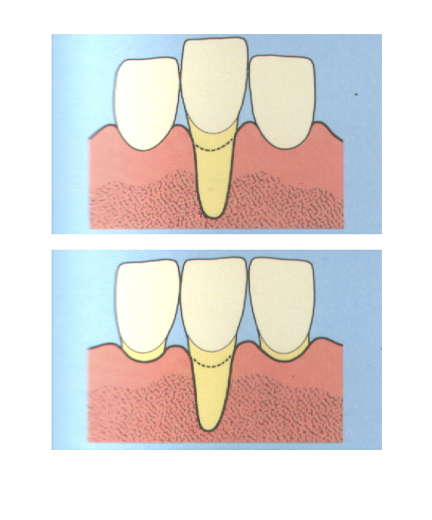
class 4 recession
marginal tissue recession extends to or beyond the mucogingival junction
loss of interdental bone extends to a level apical to the extent of the marginal tissue recession
what is the pathogenesis of recession
1 - plaque induced inflammation of the connective tissues
2 - trauma induced inflammation of the connective tissues
3 - connective tissue destruction
4 - proliferation of the epithelium from both sides
5 - interconnecting cord of epithelium is formed between oral and pocket epithelium
6 - subsidence of the epithelium surface
what 3 factors contribute to pathological bone disease
periodontal disease
periodontal treatment - pt will initially present with not alot of recession with non surgical tx then recession and sensitivity
smoking
calculus and smoking
smoking is a main cause of periodontal disease as well as unstable diabetes
smoking modifies recession
« darker gingivae so can tell sub calculus
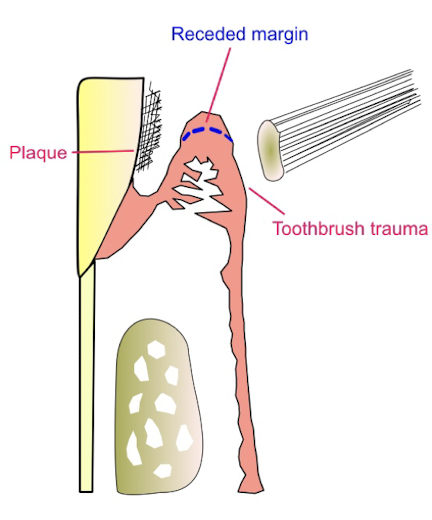
what can cause trauma to the gingivae
tooth brushing
fictitious injury e..g fingernail picking
malocclusion e.g. class 2 div 2 with a traumatic overbite
poorly designed partial denture
chemical trauma e.g. cocaine
lip/tongue stud
what are some local plaque retentive factors
calculus
subgingival restorative margins
high muscle attachments
frenal pulls - frenulum close to teeth so hard for pt to brush
overhanging restorations
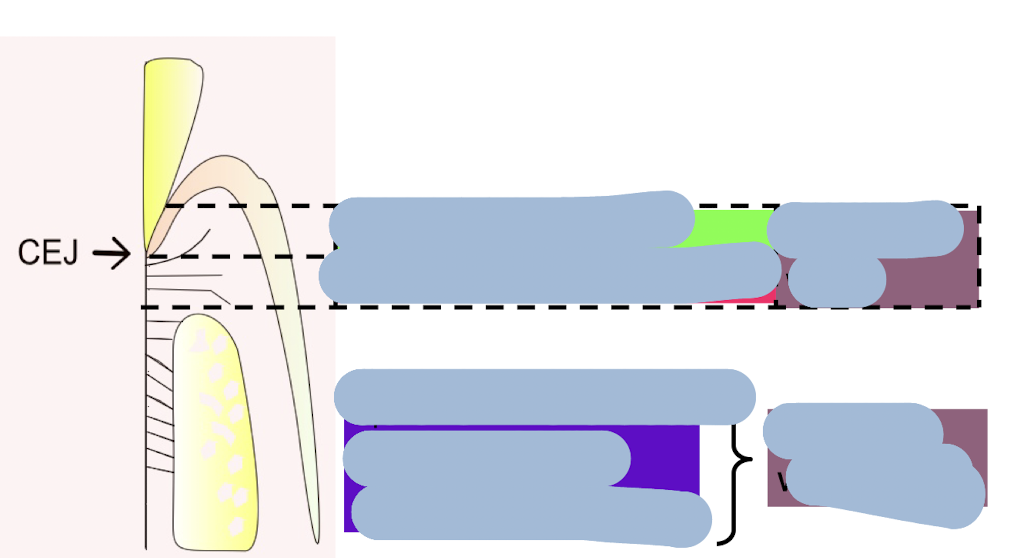
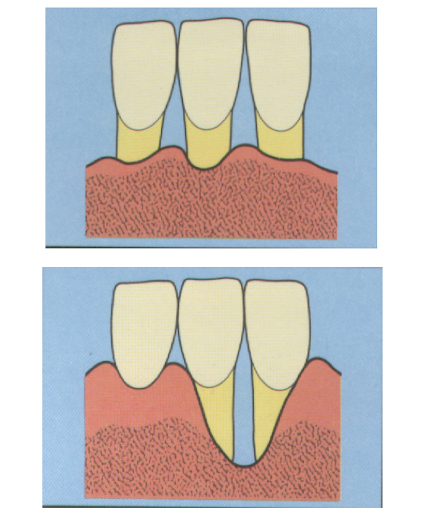
label this diagram
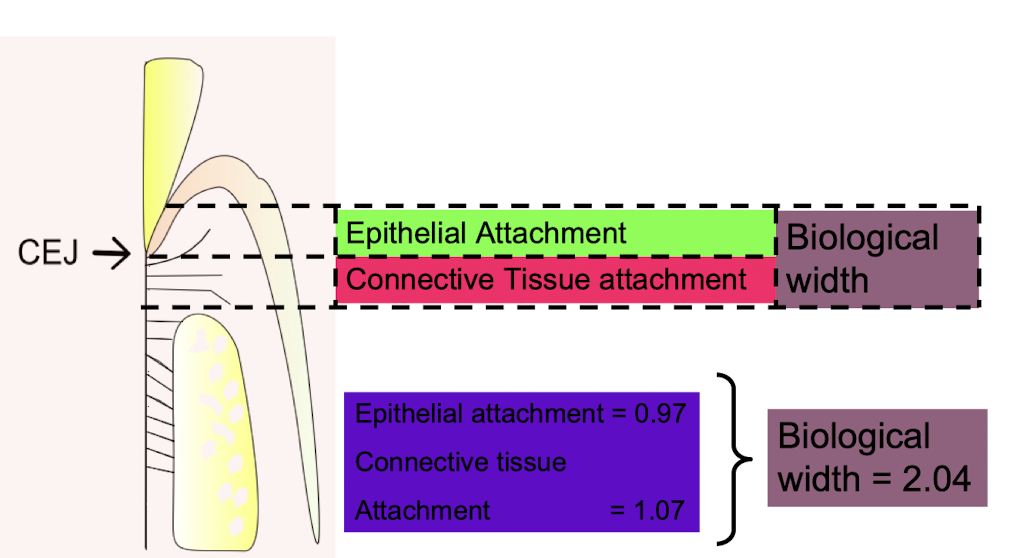
what is the link between restorations and the biological width
restorations invading the biological width can cause gingival recession (initially causes gingival inflammation then long term is recession
if restoration margin invades biological width, it will cause chronic inflammation, gingivitis, periodontitis, and subsequently recession (only place in necessary)
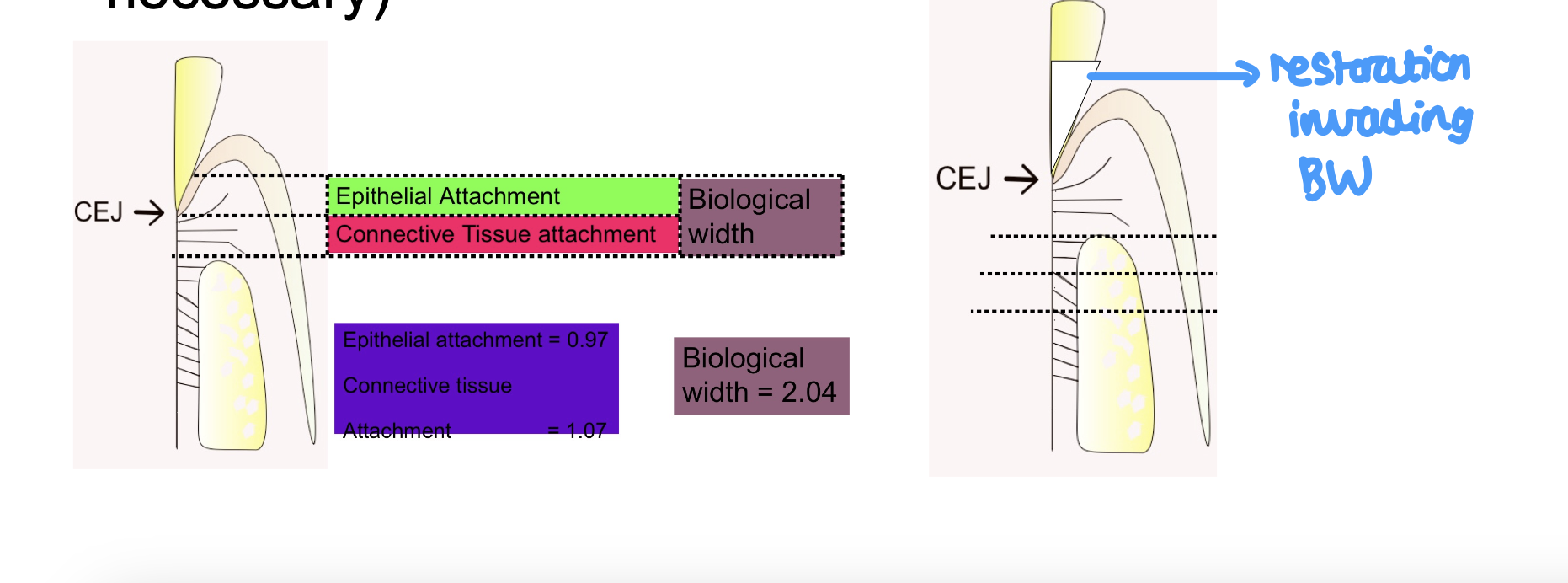
describe orthodontic tooth movement
excessive proclination especially when fixed appliances have or are being used - can cause recession
name some anatomical features that can also cause recession
thin gingival tissue
bone dehiscence
fenestration
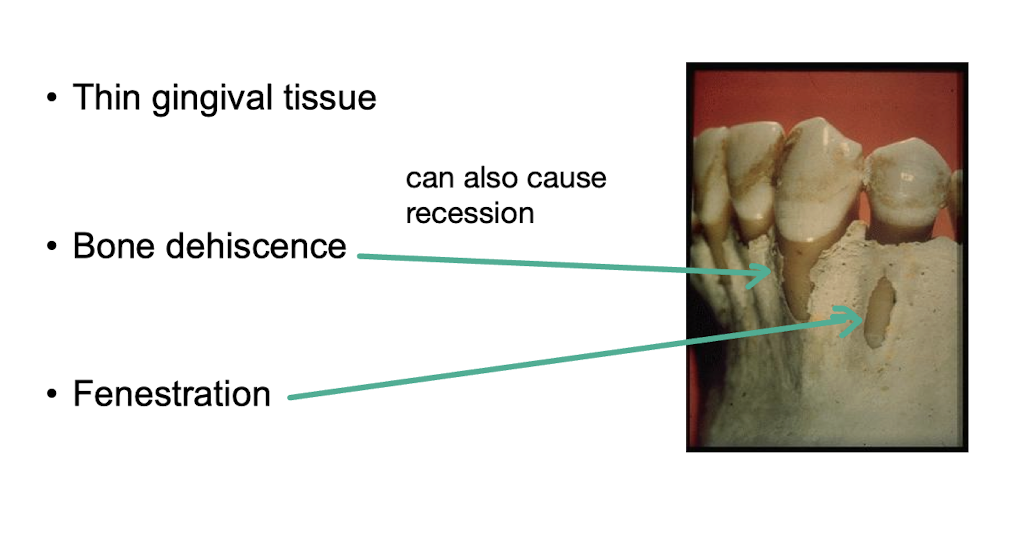
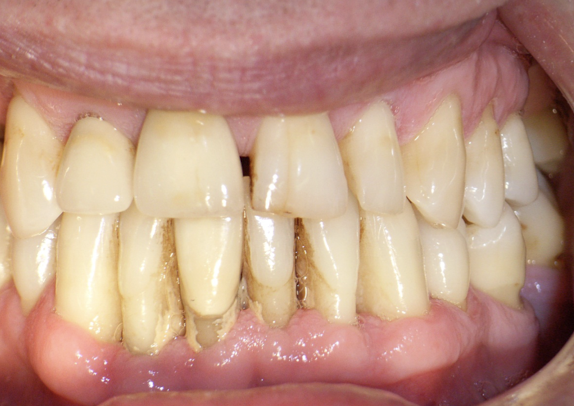
what are the complications of gingival recession
pain from exposed dentine - sensitivity
root caries
tooth abrasion
plaque retention and gingival inflammation
aesthetic concerns
what is the management of recession
monitor, measure, photograph, models
management of the aetiological factors
management of the consequences
first…
prescription from the dentist should be obtained
history and examination to identify the aetiological factors
what can be used to monitor
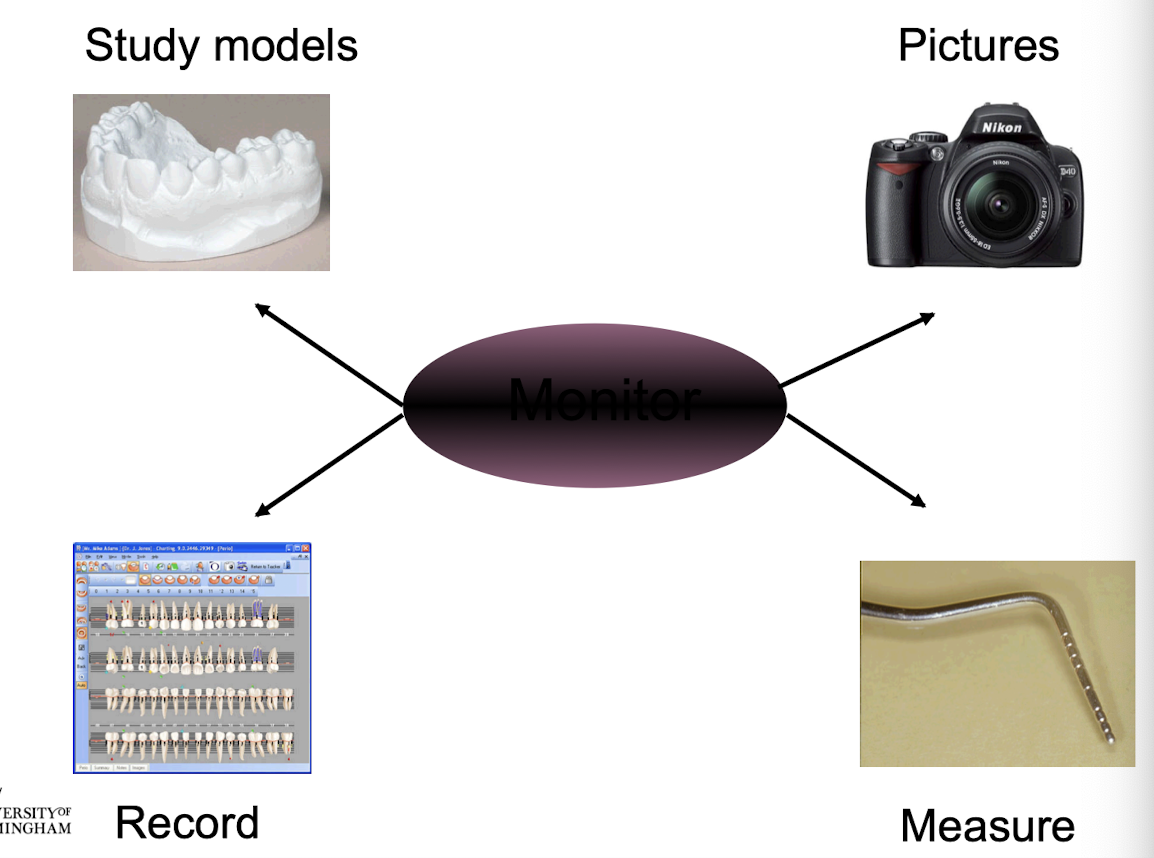
what is involved in the management of aetiological factors
advise on an atraumatic brushing technique
advice relating to traumatic habits
advice on smoking cessation
plaque control and OHI
remove all local factors e.g. scaling, overhang removal
dentist needs to correct deficient partial denture design
margins of restorations need to be placed supragingival where possible
what are the consequences that need to be managed
dentine hypersensitivity
root caries
aesthetics
mucogingival surgery
how can dentine hypersensitivity be managed
give dietery advice e.g. control of acid in the diet
antisensitivity dentrifices
fluoride mouthwash
professionally applied products - fluoride varnish, dentine bonding agents
restorations e.g. GIC, etched composite
what are the ideal agents of a desensitising agent
easily applied
non irritant to the pulp
painless on application
consistently effective
rapid in action
effective for a long period
non staining
what agents can we use
fluoride
potassium salts
strontium
colgate sensitive pro relief desensitising paste
dentine bonding agents
fluoride
fluoride occludes the dentinal tubules
duraphat, 22,600 ppm F
Gel Kam, 0.4% stannous fluoride and 1000ppm fluoride
mouthwash, fluoriguard 2,500ppm
potassium salts
potassium has a direct desensitising effect on the pulpal nerve fibres
sensodyne F, potassium nitrate 5.0%
colgate sensitive, potassium citrate 5.5%
strontium
strontium blocks or occludes dentinal tubules
sensodyne mint, strontium acetate 8.0%
colgate sensitive pro-relief desensitising paste
tubules occluded by a calcium rich layer created by the interaction of arginine and calcium carbonate
based on the amino acid arginine and calcium carbonate
available as a toothpaste and polishing paste used by the professional
dentine bonding agents
block or occlude dentinal tubules
seal and protect
routine restorative bonding agents
placing resin which physically blocks the tubules and stops movement of fluid in dentine tubules
how can we manage root caries
diet advice
fluoride application
restoration
what could the dentist consider for aesthetics
gingival veneers to cover exposed root surfaces and hide the spaces interdentally
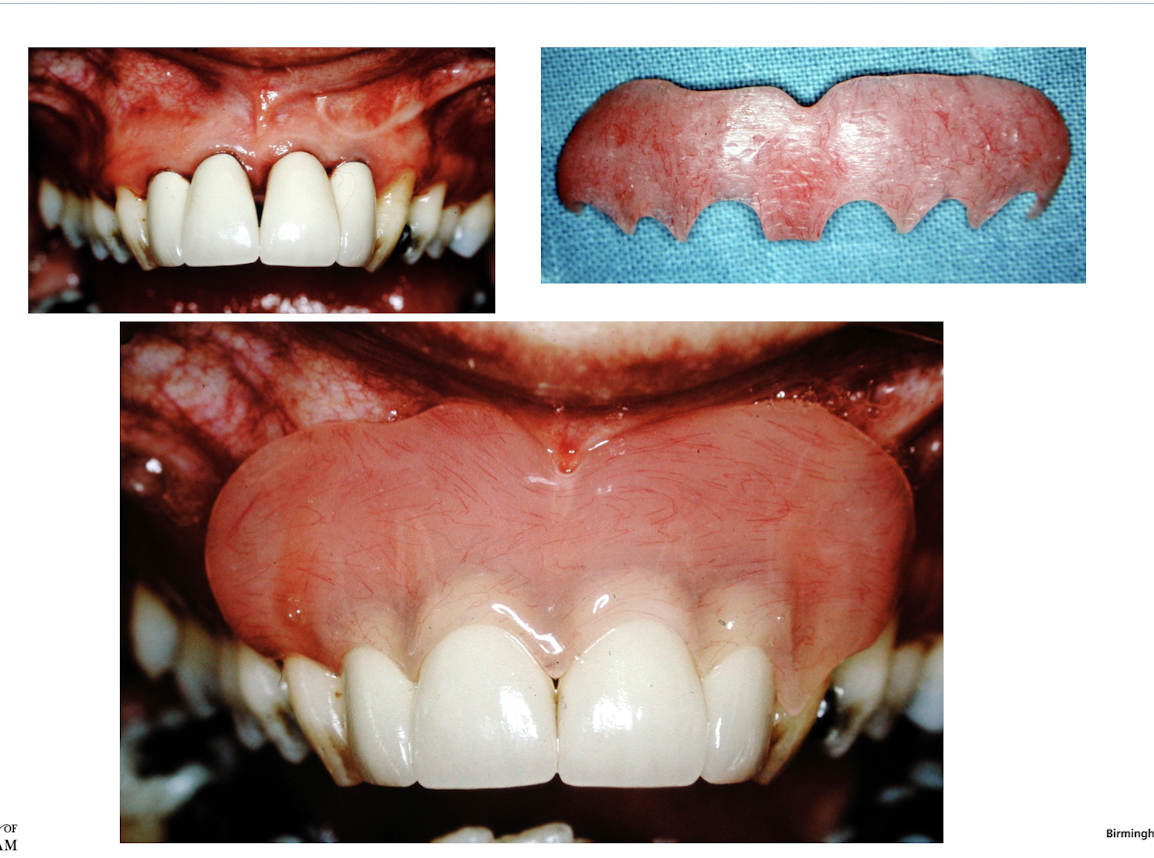
what is mucogingival surgery
root coverage using pedicle grafts
free grafts
guided tissue regeneration
pedicle graft
maintain their connection with the donor site after placement at the recipient site
lateral or coronary repositioned
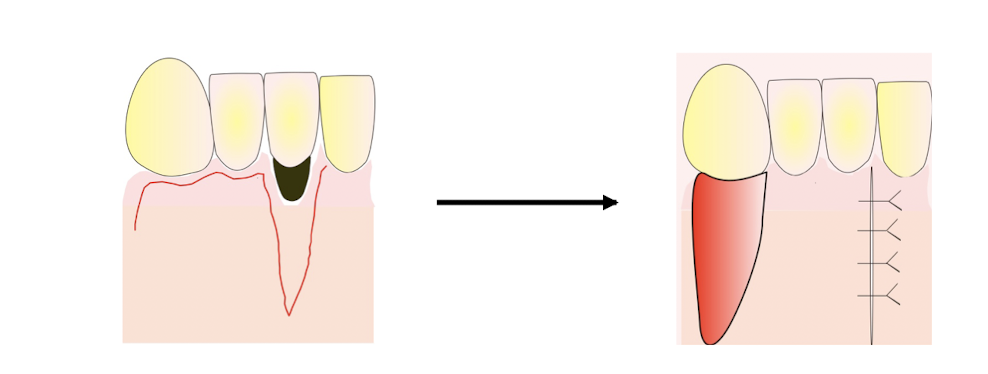
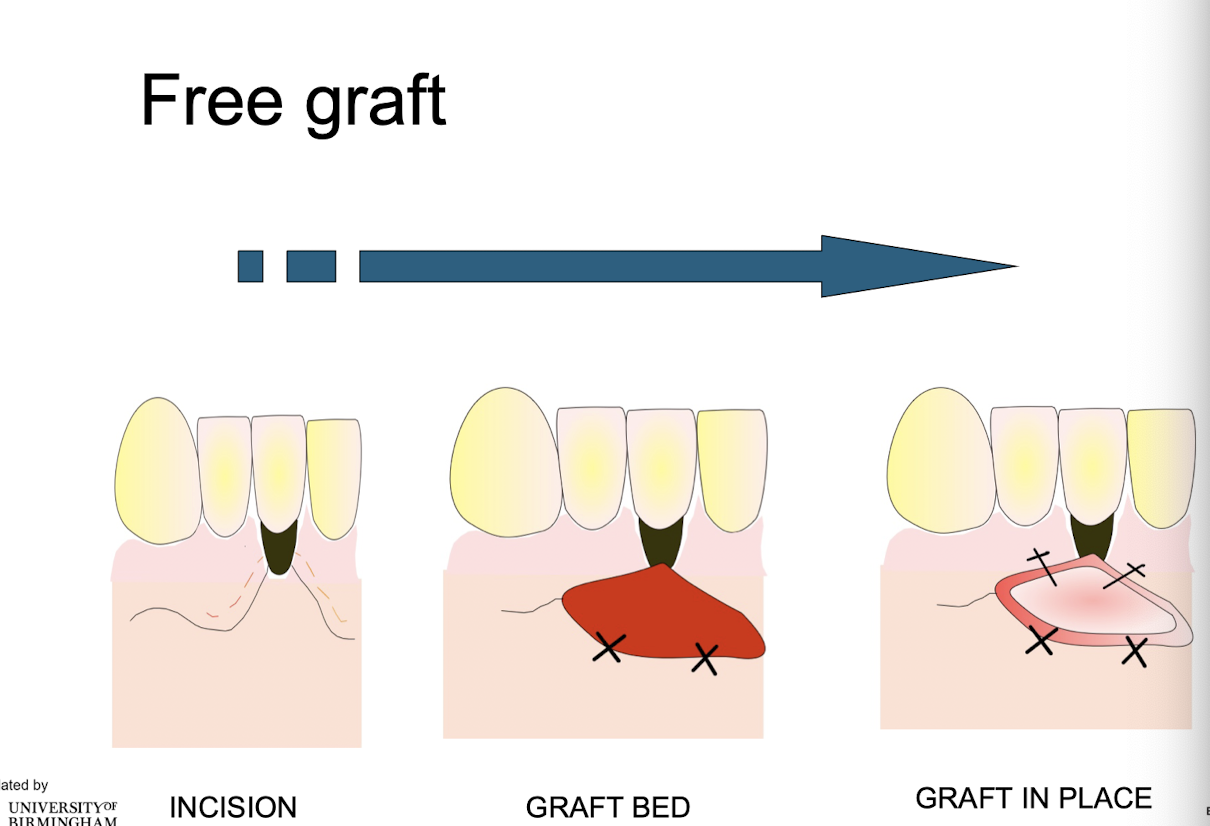
free graft
completely deprived of their connection with the donor area
e.g. dissected from palate and used elsewhere