chapter 6-Integumantary system
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
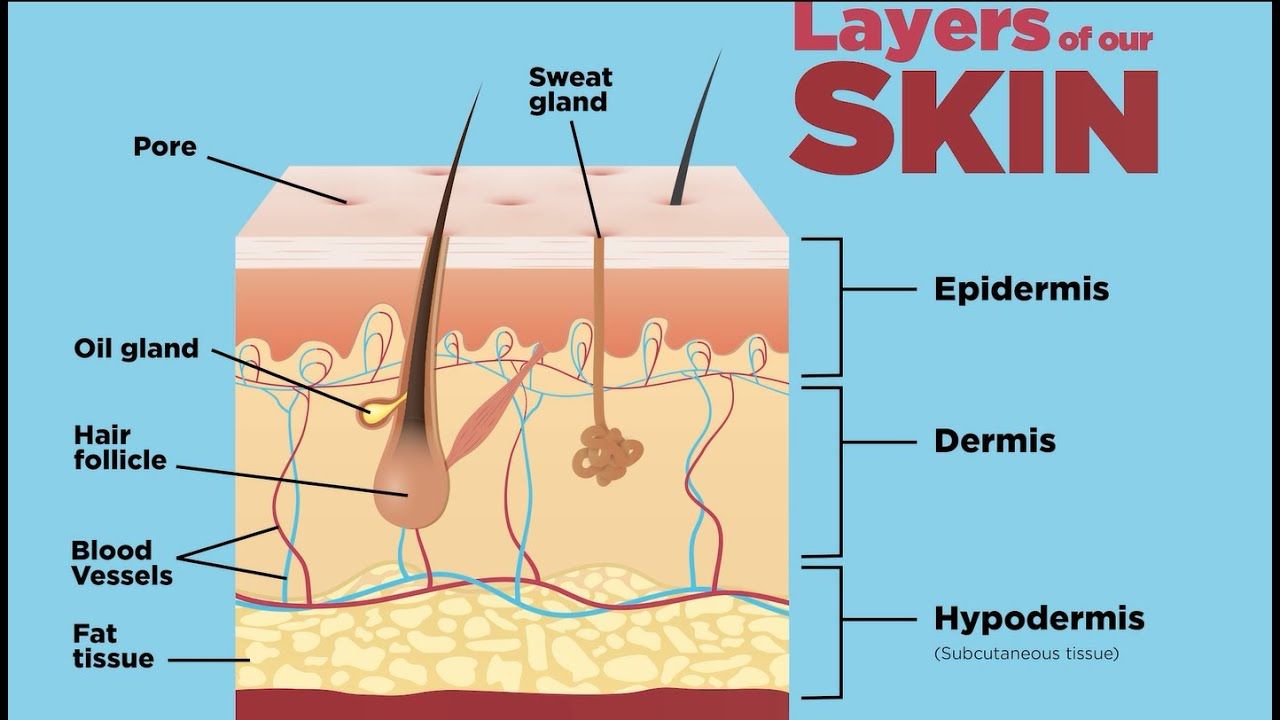
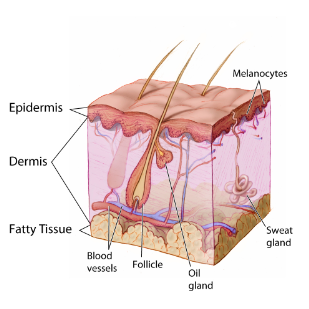
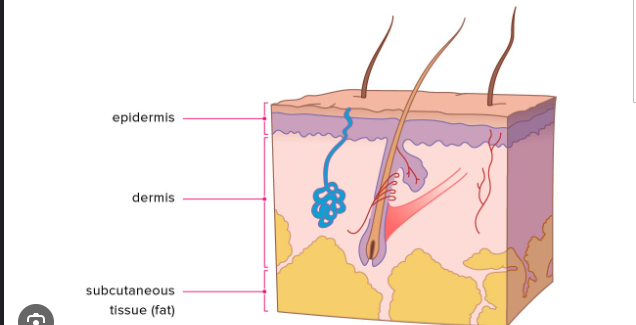
Layers of Skin
Epidermis
Dermis
Subcutaneous
Epidermis
stratified squamous epithelium
no direct blood supply
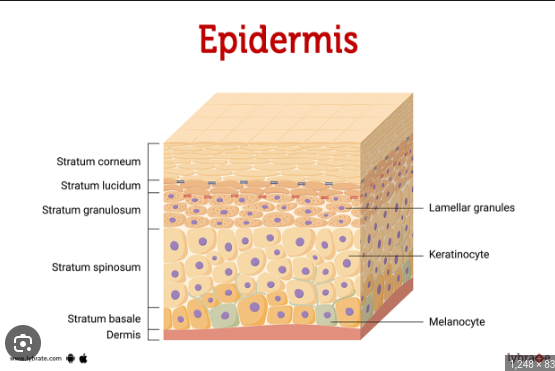
Stratum Basale
layer closest to the basement membrane
attachment of the epidermis to the dermis
nourished by underlying connective tissue
cells that travel upward and die and become keratinized (water proof)
Basal Cell Carcinoma
most common human cancer
found in sun exposed areas of the skin
Stratum Corneum
Outer most layer of dead cells
a barrier between the deeper layers of skin and the outside environment,
prevents toxins and bacteria from entering the body
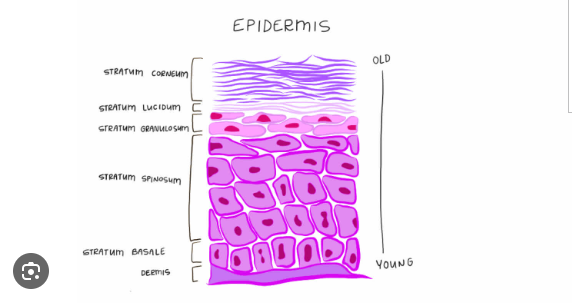
Melanocytes
cell release melanin(pigment) to color skin
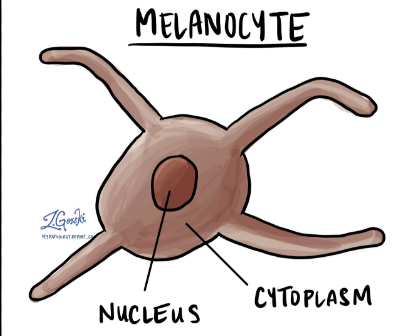
Eumelanin
brownish black pigment
Pheomelanin
reddish yellow pigment
Melanin
Protects the deeper tissues from ultraviolet light
Genetics & UV light affects skin color
Blood in dermis may affect skin color
Melanoma
most deadly skin cancer
watch for the ABCs
Asymmetry
Color
Diameter
Evolution
Dermis
Binds and supplies blood to epidermis
location of nerves (touch) hair folicles, Oil (sebaceous) glands, & sweat glands
fibrous connective tissue with collagen(strength) & elastin (elasticity)
Subcutaneous
loose connective and adipose(insulation& padding)
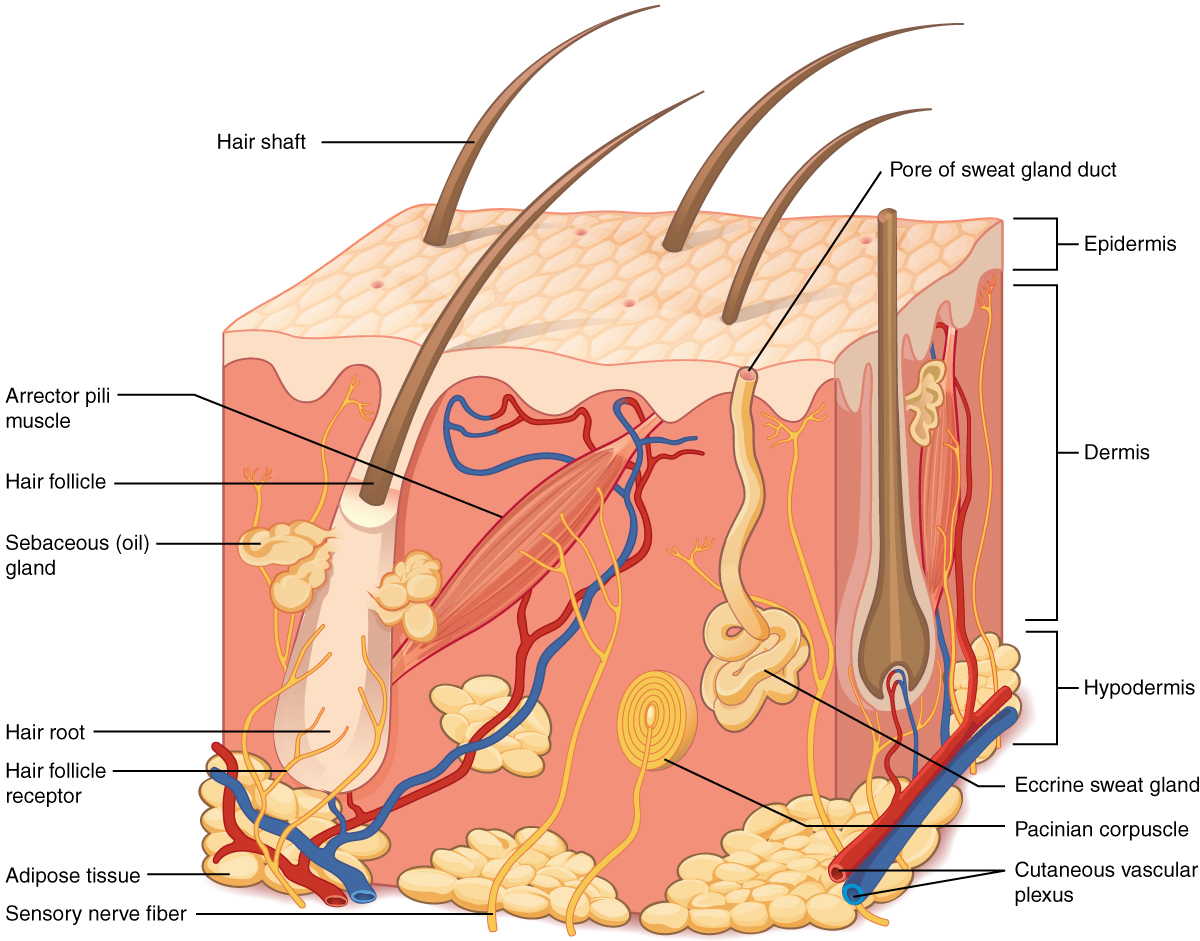
Hair
Found on all surfaces except palms,soles,lips,nipple & external genitalia
The root is at the bottom of an epidermal depression
Nourished by the blood vessels from the dermis
color from genetic- amount of melanin present
smooth muscle(involuntary) attached to each hair follicle
Muscle contracts, shortens & hair stands on end= goose bumps
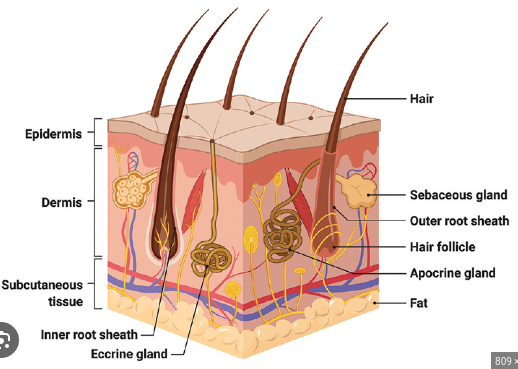
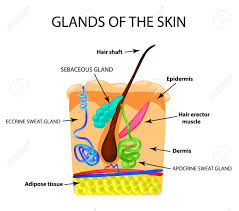
Sebaceous Glands
usually attached to hair follicle
holocrine gland secretes oily mixture keeps skin soft and water proof
acne is caused by overactive sebaceous glands
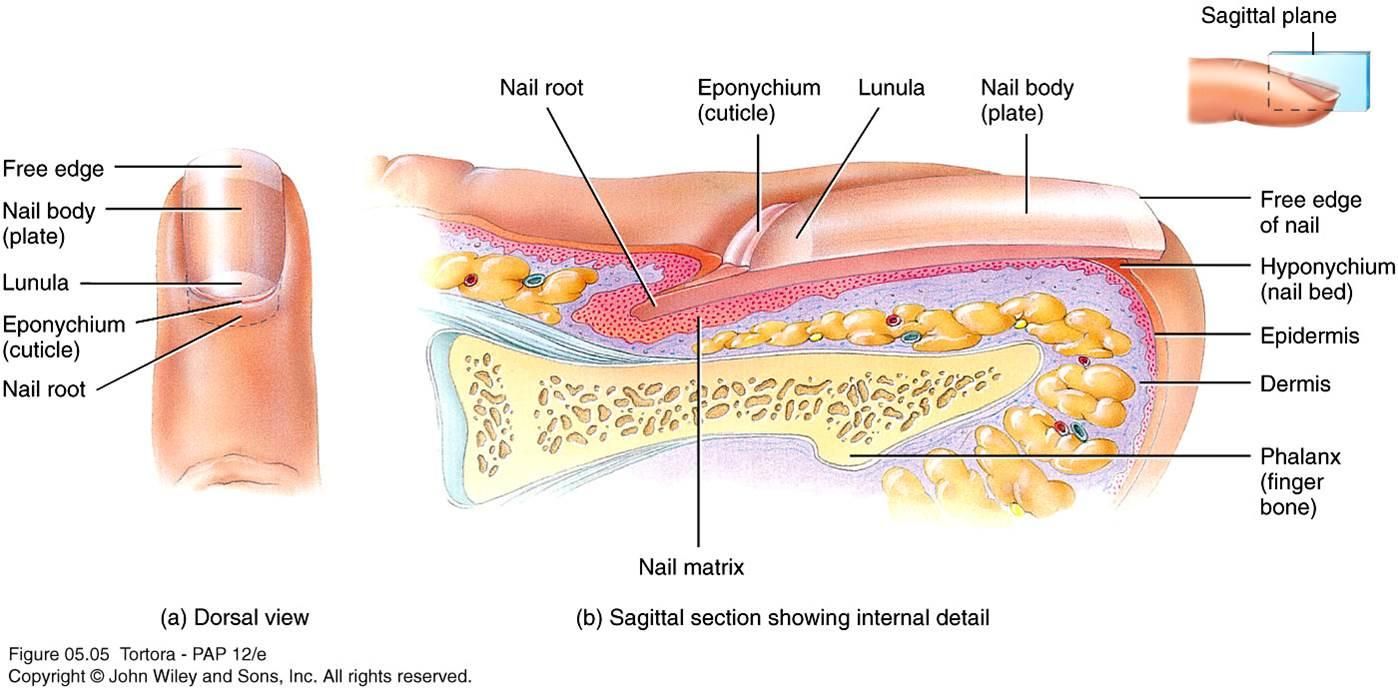
Nails
protection covers ends of fingers and toes
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium cells
nail root- location of cellular division
Lunula(white half moon shaped area) growing region
nail bed- nail attached too
Sweat Glands
Eccrine Glands- not associated with hair follicles
found in forehead,neck & back ( most abundant) in palms of hands & soles of feet
responds to rise of body temp
sweat is released onto surface of the skin via pore
Apocrine glands-associated with hair
found in armpits & groin(most abundant in pubic region)
begin functioning at puberty
ear wax formed by modified glands of this type
Burn Information
1.Common Symptoms-
*Redness
*swelling
*pain
*peeling of skin
*shock
*white or charrded skin
First Degree-(superficial Parcial-thickness)effect outerlayer[epidermis], notice redness very sensitive to touch, skin will appear blanched when light pressure is applied. involve minimal tissue damage Sunburn is a good example of a first-degree burn.
Second Degree-(deep partial thickness)affect both the outer layer(epidermis) & underlying layer (dermis)causing redness, pain, swelling and blisters. affect sweat glands, and hair follicles.If not properly treated, swelling and decreased blood flow in the tissue can result in the burn becoming a third-degree burn.
Third-degree- (full thickness)affect the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis, causing charring of skin or a translucent white color, with coagulated vessels visible just below the skin surface. Healing from third-degree burns is very slow due the skin tissue and structures being destroyed. Third-degree burns usually result in extensive scarring.
![<p>1.Common Symptoms-</p><p>*Redness</p><p>*swelling</p><p>*pain</p><p>*peeling of skin</p><p>*shock</p><p>*white or charrded skin</p><p><mark data-color="purple">First Degree</mark>-(superficial Parcial-thickness)effect outerlayer[epidermis], notice redness very sensitive to touch, skin will appear blanched when light pressure is applied. involve minimal tissue damage Sunburn is a good example of a first-degree burn.</p><p><mark data-color="purple">Second Degree</mark>-(deep partial thickness)affect both the outer layer(epidermis) & underlying layer (dermis)causing redness, pain, swelling and blisters. affect sweat glands, and hair follicles.If not properly treated, swelling and decreased blood flow in the tissue can result in the burn becoming a third-degree burn.</p><p><mark data-color="purple">Third-degree</mark>- (full thickness)affect the epidermis, dermis and hypodermis, causing charring of skin or a translucent white color, with coagulated vessels visible just below the skin surface. Healing from third-degree burns is very slow due the skin tissue and structures being destroyed. Third-degree burns usually result in extensive scarring.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9ec46eb7-d4c1-4e5d-8efe-40d912e12d87.jpeg)
Functions of the skin
Protection- from water loss, disease,& injury
sensory-temperature & touch
Vitamin D Production-makes its way to the skin with UV exposure
Regulation of body Temperature-
*Normal body temp is 98.6
*Increase of body temp = Hyperthermia-Body triggers the dermal blood vessels to relax [vasodilation:vas(o)-vessel] and the heat dissipates to the outside. Sweat glands release fluid onto the skin surface as fluid.
*Decrease of body temp = Hypothermia- Blood vessels contract which decreases blood flow to reduce heat loss. Sweat glands become inactive. Skeletal muscle contract to release heat(shiver)
Healing of Wounds-
1. Inflammation- Red swollen;caused by blood vessels dilating and forced fluids to leave the vessels this provides nutrients & oxygen to an area.
2.Shallow Break- epithelial cells fill in gap
3.Deep Break- [into dermis/subutaneous] scab forms, then fibroblast form new collagens;binds edges together, phagtonic cells remove dermis
4. New connective tissue may be seen (scar)
Sebum
produce thick oily substance to stay moisturizerized
Dermatitis
inflammation of the skin
arrector pili
smooth muscle cause goosebumps
pressure ulcer
usaaly found over joints
cause by low blood suply cells die
Serous Membrane
This membrane type lines body
cavities that lack openings to the
outside (parietal/visceral).
Mucous Membrane
This membrane type lines body
cavities that open to the outside.
Vitamin D
depends on the skin
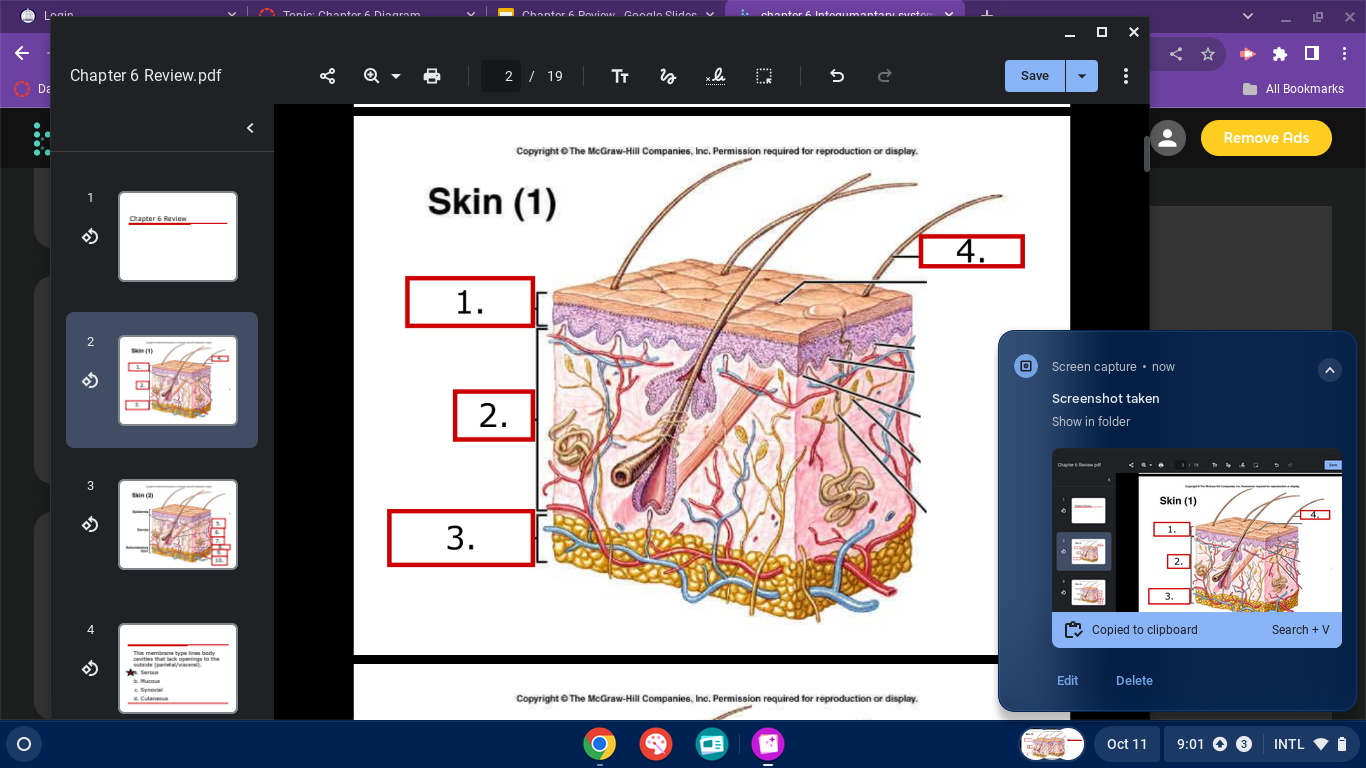
skin diagram
epidermis
dermis
subcutaneous layer/ hypodermis
hair shaft
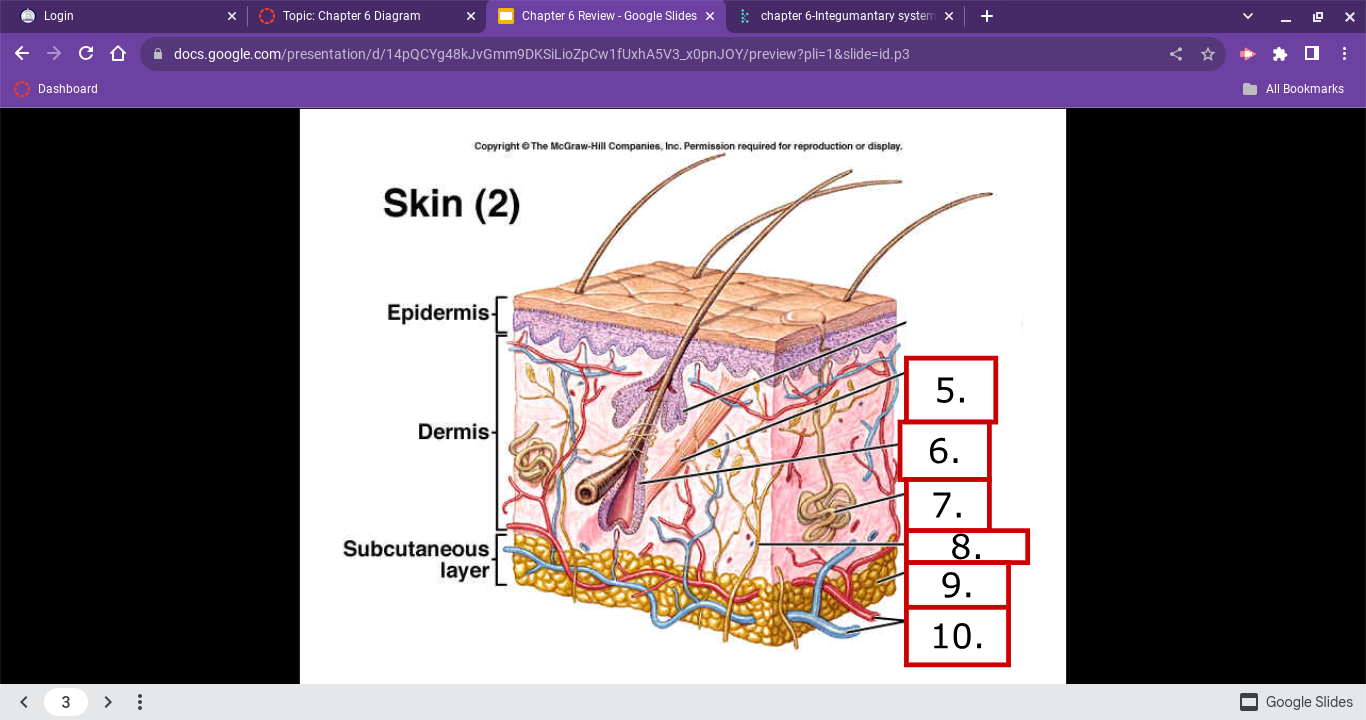
skin diagram
Arrector Pili
hair folicle
sweat glands
nerve fiber
adipose cells
blood vessels