acco midterm s
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Accounting
is a service activity to provide quantitative information, primarily financial in nature, about economic entities, that is intended to be useful in making economic decisions, in making reasoned choices among alternative courses of action
purpose of accounting
is to accumulate and report on financial information about an entity.
accounting records
This information is then used to reach decisions about how to manage the business, or invest in it, or lend money to it. This information is accumulated in ____
Middle East
Accounting traces its roots to the ______ region, where as early as 8500 BC, tradesmen use clay objects to represent commodities such as flocks of sheep, jars of spices and oil, bolts of clothing and other goods.
clay tablets
Some archeologists unearthed clay tablets marred with symbols and other writings and interpreted them to mean record of goods sold and other statistics at those times.
papyri
In later years, ____ were used as the medium for record keeping
1494
In ____, Friar Luca Pacioli, the Father of Modern Accounting and Bookkeeping, wrote a book which contains discussions on the double-entry bookkeeping system.
Friar Luca Pacioli
the Father of Modern Accounting and Bookkeeping
summa de Arithmetica, Geometria, Proportioni et Proportionalita
The book was entitled ________ (Everything about Arithmetic, Geometry, Proportions, and Proportionality). It summarizes the existing mathematical knowledge at that time. Friar Pacioli was considered the father of double-entry bookkeeping.
cost accounting
which deals with the assignment of costs to products, emerged during this period. Also, during this period, the corporate form of business organization was created to accommodate the need for the increasing large amounts of funds which was required to finance the expansion of business.
Financial Accounting
involves recording and clarifying business transactions along with preparation and presentation of general-purpose financial statements.
Managerial Accounting
works to improve the company's administration, enhance its profit, and provide management with financial reports that influence planning and budgets. This branch of accounting performs forecasting to advise management on the best business practices to meet goals and maintain profit. It includes conducting internal examinations through cost to volume profit (CVP) or break-even point (BEP) analysis, factors that affect decision making.
Cost Accounting
This branch considers all factors of manufacturing to accurately determine the cost of a project or venture.
Cost Accounting
analyzes manufacturing costs to prepare and present reports that inform decision-makers on how to reduce cost, or when to spend more. It monitors projects for waste and cost control. It regularly analyzes actual costs over budget to determine future monetary actions.
Auditing
examine and monitor a business for accurate reporting, compliance with tax laws and regulations, and financial integrity. This involves verification, inspection and other procedures to check the accuracy of reports.
Tax Accounting
follows state and federal tax rules during tax planning or in the preparation of tax returns. This branch reports on the effect of taxes on a business and may offer advisory services on minimizing taxes or the consequences of tax decisions
Tax Accountants
calculate income and other taxes depending on the structure of the business. Since taxes and income brackets vary from entity to entity, tax accounting is well-versed in tax laws surrounding sole proprietorships, corporations.
Government Accounting
oversees and records state and national fund allocation and disbursement. Government accounting tracks the movement of money through various agencies and ensures budget requirements are kept or met.
Government Accountants
work in state and national programs such as healthcare, housing, and education.
accounting entity
is a clearly defined economic unit for which a separate set of accounting records is maintained. The organization should engage in clearly identifiable economic activities, control economic resources, and be segregated from the personal transactions of its officers, owners, and employees
transactions
The accounting entity concept states that the ______ associated with a business must be separately recorded from those of its owners or other businesses.
separate accounting records
Doing so requires the use of ______ for the organization that completely exclude the assets and liabilities of any other entity or the owner.
Business
an organization in which basic resources are applied to the activities involved in the production and distribution of goods and services to customers or clients. The objective of most businesses is to maximize profits. Of course, some businesses would operate with a purpose other than to raise profits, like to provide benefits to society. Although some of these concepts and principles apply to not-for-profit businesses as well.
Processes of Accounting
a. Identifying and analyzing the business transactions
b. Recording or Bookkeeping
c. Classifying and Summarizing
d. Communicating or Reporting
Identifying and analyzing the business transactions
through accounting, economic activities are identified from the many events in a business. These activities which are of financial character are called business transactions and are measured in terms of money.
Recording or Bookkeeping
A systematic and chronological record of financial transactions is to be maintained. The recording of transactions can either be manually or electronically and according to the date of occurrence.
Classifying and summarizing
is the sorting or grouping of similar and interrelated transactions in their respective class. For instance, all transactions involving cash are grouped to report a single net cash figure.
Communicating or Reporting
business transactions in a given period are recorded, classified into groups and summarized. This process allows accountants to prepare reports called financial statements. In order to create useful reports, financial information must be maintained in an organized way
Internal users
reports like financial reports are used by those who direct the day-to-day operations of a business enterprise. These individuals are collectively referred to as “Management” and the related area of accounting is called management accounting.
External users
included in the firm's annual report, are used by individuals and organizations that have an economic interest in the business but are not part of its management.
Internal, external
Users of Accounting Reports
External Users
1. The Bank and other Lenders (for loan or borrowing concerns)
2. Potential Investors (with regards to earning capability of the entity)
3. Suppliers (for trading or contracting)
4. Customers (for long-term warranty, etc.)
5. Employees’ Unions (to determine the reasonableness of their
benefits)
6. Competitors (for marketing competitions)
7. Government Agencies (for compliance purposes)
8. The Media (for reporting to the public)
Internal Users
1. Owners or Stockholders
2. The Board of Directors or any policy decision making body
3. Chief Executive Officers, Treasurer, and other officials
4. Managers (Upper Level, Middle or Low level)
5. Other key employees
Single, Partnership, Corporation, Cooperative
Forms of Business Orgs.
Single
where the owner of the business is only one person and is called a proprietor. It is the easiest form of business to organize as it does not need to comply with many legal formalities and requires only a small amount of investment to start the business, but you do need to obtain any necessary licenses and permits to operate legally.
Partnership
where there are two or more investors who contributed money, property or industry to a common fund with the intention of dividing the profits among themselves; owners are called partners
Corporation
business owned by five or more persons where such business becomes an artificial being created by the operation of law, having the rights of succession, and the powers and attributes expressly authorized by law or incident to its existence. This means that the corporation itself not the shareholders is held liable for the actions and debts the business incurs
Cooperative
business organization owned by and operated for the benefit of those using its services
Service, Merchandising, Manufacturing
Types of Business Activities
Journal
is called the Book of Original Entry because it is where the transactions are first recorded. Transactions are recorded in the journal in chronological order, that is, according to the date of occurrence.
General Journal
a type of journal to record general class of transactions
Special Journal
type of journal to record specific class of transactions like cash receipts, cash disbursements, purchase and sales transactions.
Journalizing
the process of recording transactions in the journal
Journal Entry
is a an entry record in the journal for every transaction that has debit and credit line items.
Single Journal Entry
is an entry with only one debit and one credit line items.
Compound Journal Entry
is an entry with more than one debit or credit itemsm
Account
is a record of each asset, liability, capital, expense and revenue
Chart of Accounts
simply the list of all various specific accounts that are set and being used by the company to record business transactions. _____ have assigned code or number for every account listed.
Business Transaction
are events that have some effect on the resources of a firm or on the source of the firm’s assets. It is also an activity that has exchange of values. Normally, this involves a value received and a value parted with.
external transaction
When the transaction is between a business and an outsider, it is an _____ . An example of it is a purchase of office supplies from the supplier
internal transaction
transaction that happen within the business that do not involve outsiders are called ______ . An example of it is when the owner invests capital to the business.
source document
These are the document evidences that describe the essential facts of the transactions. Examples of source documents are receipts of cash paid or received, checks written or received, bills sent to customers for services performed or bills received from suppliers for items purchased, etc.
financial statement
is the end product of the accounting process. They are the means by which financial information about an economic entity is communicated to the various users of financial information.
Assets, Liabilities, Capital, Revenue, Expenses
Elements of Financial Statement
Assets
are defined as resources controlled by the enterprise as a result of past transaction and from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the enterprise. In layman’s term, ____ are properties owned by the company.
Liabilities
are defined as present obligations of an enterprise arising from past transactions or events, the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow of resources from the enterprise. In simple terms, ____ are the financial obligation or debts of the business.
Capital
represents the equity or ownership of the owner on the total assets of the business. It is the residual claims in the total assets after deducting all the liabilities
Withdrawal
are the amounts withdrawn by the owner from the business for personal use.
Revenues/Income
is the gross inflow of economic benefits during the period arising from the operation of the business, other than those investments of the owner/s. Its common examples are: Sales Revenue, Service Revenue, Rent Income, Interest Income, etc.
Expenses
is the gross outflow of economic benefits during the period from the operation of the business, other than those withdrawal of the owner/s.
Ledger
provides a summary of transactions per account for an accounting period and it is called the Book of Final Entry
General Ledger
Each account of the business has an individual record in the ______ wherein the effects of business transactions are summarized.
Posting
is the process of transferring the entries from the journal to the ledger. If an account is debited in the journal, it will also be posted on the debit side of the account in the ledger. Likewise, a credit entry in the journal is also posted on the credit side of the account in the ledger.
pencil footing
After posting the journal entries to the ledger, the amounts of the debit and credit columns of the accounts are totalled and the difference between the debit and credit totals is determined as the account ending balance. This process is called _____
T-Account
is a very useful tool that is used for illustrations, analyzing transactions and in problem solving. It is called T-account because it resembles big letter T. It appears as follows:
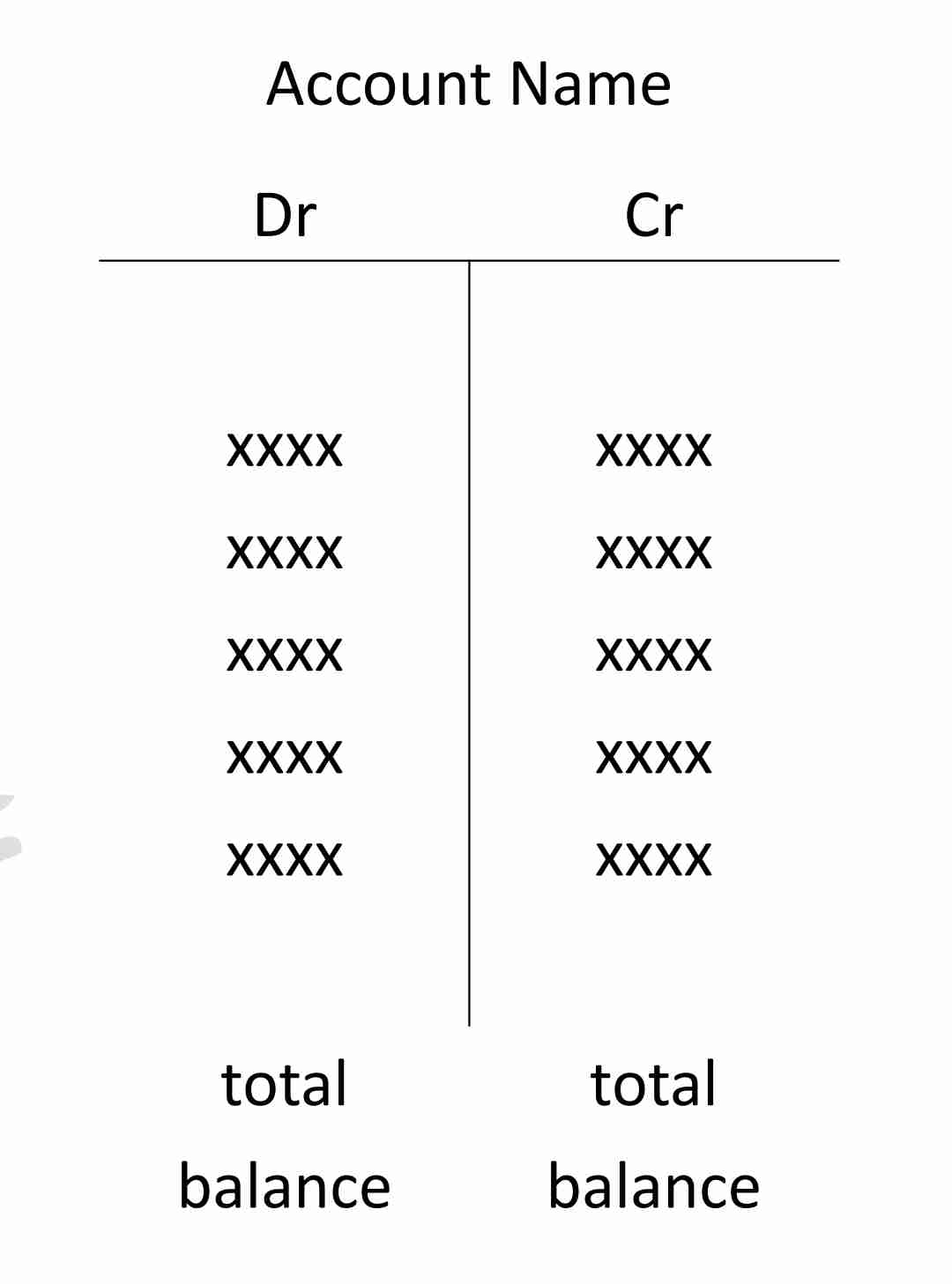
Trial Balance
is a summary listing of the account titles and the balance of each account. It is prepared to test the equality of the debit and credit balances of the accounts in the ledger
cash basis of accounting
revenue is recognized when cash is received and expenses is recognized when cash is paid.
accrual basis of accounting
revenue is recognized when sales are made or services are performed, regardless of when cash is received and expense is recognized as incurred, whether or not cash is paid out.
Matching Principle
relates to the expense recognition which requires that costs and expenses incurred in generating the revenue should be properly matched against the related revenue in determining the net income or net loss for the period.
Adjusting Entries
are entries prepared at the end of an accounting period to update or adjust the balances of accounts
Accrual
refer to the recognition of expense already incurred though not yet paid, and the recognition of revenue already earned though not yet received
Accrued Expenses
are expenses already incurred but not yet paid as at the end of the accounting period. These are also called Accrued Liabilities or Accrued Payable. Examples of this are as Taxes Payable, Interest Payable, Utilities Payable, Salaries Payable, Rent Payable, etc.
Accrued Revenues
are revenues already earned by the business but not yet collected as at the end of the accounting period. These are also called Accrued Assets or Accrued Receivable. Examples of this are as Interest Receivable, Rent Receivable,
Defferals
refers to the postponement of the recognition of revenue which the company has received or collected in advance and the postponement of the recognition of expense which has been paid in advance.
Prepaid Expenses
are expenses paid in advance. Since the economic benefits will be received in the future, prepaid expenses are treated as assets.
Unearned Revenue
are revenue collected in advance. Since these revenues are not yet earned by the business, these are treated as liabilities