Interventions Exam 1
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
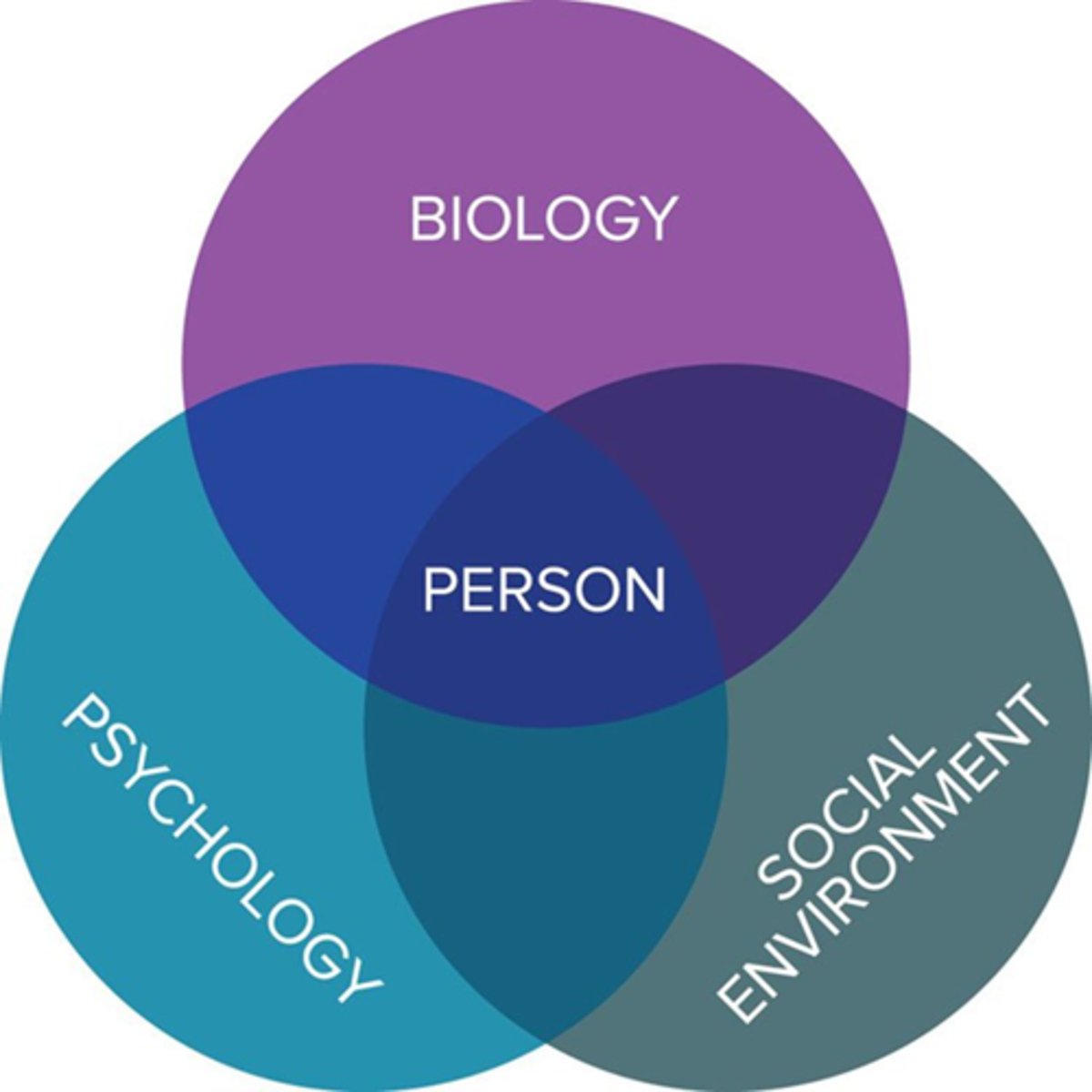
Biopsychosocial construct
Categories of intervention
education
respiratory
adaptive assistance
biophysical
functional training
integumentary repair and protection
manual therapy
motor function and movement training
therapeutic exercise
Evidence informed practice

What Influences Patient-Therapist Interactions in Musculoskeletal Physical Therapy?
PT interpersonal and communication skills
PT practical skills
individualized patient centered care
organizational and environmental factors
Managing conflict
use active listening skills, incorporate clear and calm communication, take time to think and avoid emotional response
Main goal of proper positioning
support, stabilize, and provide proper alignment of the axial and appendicular skeletal segments in a position that promotes the efficient function of the body systems
when is short term positioning used
specific exercise, therapy, able to change positions when treatment is complete
when is long term positioning used
when they must remain in one position for a long time, mobility limitations
contracture
a permanent shortening producing deformity or distortion
bony prominences associated with supine positioning
occipital tuberosity
spine and inferior angle of scapula
spinous processes of the vertebrae
posterior iliac crest
sacrum
posterior calcaneus
bony prominences associated with side-lying position
lateral ribs
lateral ear
lateral acromion process
epicondyles of humorous and femur
condyles of femur
malleolus
bony prominences associated with prone postion
forehead
ear
acromion
humerus head
sternum
ASIS
patella
tibial crest
dorsum of foot
bony prominences associated with sitting position
ischial tuberosity
posterior area of the thigh
sacrum
spinous process of the vertebrae
medial epicondyle of humerus
Contracture sites for supine position
shoulder internal rotators, extensors, adductors
hip and knee flexors
hip external rotators
ankle plantarflexors
contracture sites for prone position
neck rotators
shoulder internal and external rotators, extensors and adductors
ankle plantarflexors
contracture sites for side-lying and sitting positions
shoulder adductors and internal rotators
hip adductors, internal rotators
hip and knee flexors
body mechanics
allows maximal efficiency of the musculoskeletal system without causing undue fatigue
neutral position
anatomical midpoint between end ranges of joint motion
What are the 3 C
keep the curves, keep it close, and compensate
care of the extremities
neutral anatomical positioning of joints, avoid prolonged postures or repetitive motions, utilize adaptive equipment when needed, avoid working at end ROM, exercise and take breaks frequently
components of bed mobility
hooklying and bridging, supine scooting, rolling, supine to and from sit
types of rolling over
flexion strategy, extension strategy, log rolling strategy
ways to go from supine to/from sit
synchronous, through sidelying, log rolling, through long sitting, dependent
Dependent
requires full assistance, the patient is unable to help
max assistance
PT is able to help slightly (25-49%)
moderate assistance
pt is able to do part of the task without help but requires help with at least half (50-74%)
minimal assistance
pt is able to do the majority of the work (75-99%)
Contact guard
you only need to hold onto the gait belt during the task, otherwise the patient is able to complete without help
Stand by assist
only stand next to the patient while they complete the task, likely provide cues
supervision
pt requires someone within arms reach as a precaution; low probability of pt having a problem requiring assistance
independent
patient is able to independently complete task without supervision, would be safe for going home alone
modified independence
no assistance is needed however the patient requires used of equipment, takes increased time, requires maximal vocal cues, or completes the task in a modified way
different types of canes
standard single end cane, quad cane, bariatric, hurry cane
Who would use a single end cane
mild balance problems
slight LE weakness
unilateral LE pain
positives of single endpoint canes
can be stored and transported more easily than crutches or a walker
more functional on stairs and in narrow confined areas
inexpensive
different designs
adjustable (maybe)
limiting factors of single end point canes
provides very limited support because of its small BOS
cannot be used with WB restrictions
who would benefit from quad canes
unilateral LE pain
slight LE weakness
mild balance problems
slightly more than SEC
positives of Quad cane
can be stored and transported easier then a walker
more stable during ambulation than a SEC
can stand up on its own
relatively inexpensive
adjustable
limiting factors of a quad cane
may not fit on a standard stair unless turned sideways
slightly more cumbersome than a SEC
cannot be used with WB restrictions
how to fit axillary crutches
elbow angle 20-25 degrees
pad=2 inches below armpit
hand grip at wrist crease
who would use axillary crutches
NWB
weakness
requires ROM and upper body strength
need trunk support
contraindications to axillary crutches
shoulder strength
bilateral LE weakness
trunk weakness
axillary crutches positives
provides moderate degree of stability and balance improvement
permits wide range of gait patterns and ambulation speeds
can be used in individuals with weightbearing precautions/restrictions
easily adjustable for proper fit
easily stored and transported
can be used on stairs
relatively inexpensive
limiting factor for axillary crutches
more challenging
less stable
requires balance
may lead to axillary injuries
contraindications for loftstrand crutches
trunk weakness
who uses loftstrand crutches
weakness in LE
need to reduce WB in LE
mild balance impairment
good trunk stability
good UE strength and coordination
someone who needs them for a longer period of time
advantages of loftstrand crutches
less cumbersome
more maneuverable
provide more stability than SEC or quad cane
eliminate danger of axillary damage
more functional in small areas
can use hands
shorter, sleeker, lighter
disadvantages of loftstrand crutches
less lateral support
can be difficult to remove
requires functional standing balance and upper body strength
benefits of parallel bars
most stable
limits ambulation distance, location
safe starting point for patients with significant functional impairments
types of walkers
hemiwalker, 2WW, 4WW, platform walkers
limiting factors of a hemi walker
unsafe to use on stairs
cumbersome
cannot be used with weightbearing restrictions
positives for hemi walkers
more stable than SEC or quad cane
only requires use of unilateral UE/LE
can stand up on its own, adjustable
who would use a hemiwalker
unilateral LE weakness
mild to moderate balance problems
commonly after a CVA resulting in hemiparesis
positives of wheeled walkers
stability for upright standing through AD
may have seat for patient to rest
can have complete offloading with 2WW
limiting factors for wheeled walkers
must be able to navigate break systems
does have wheels
does allow some instability
taller the walker the tippier it is
transportation
contraindications for a wheeled walker
UE offloading as you need bilateral UE strength to navigate standard 2WW or 4WW
who would use a wheeled walker
requiring moderate to max stability in standing or offloading capabilities
moderate balance impairments
acute LE injury or amputations
platform walker uses (0WW)
beneficial for individuals unable to grasp with hands or weightbearing through fingers
encourages upright posture and more stable trunk position
what gait pattern is NWB with a 2WW
3 point
what gait pattern is pwb with a 2ww
modified 3 point
how to prevent falles
remove small rugs and mats
avoid waxed or wet floors
use secure stair handrails
remove clutter and loose objects (36 inches wide)
benefits of a gait belt
increases safety for you and your patient
prevents falls
decreases risk
reduces risk of liability
therapist guarding technique
physical therapist stands posteriolateral to pt weaker side
maintain a wide BOS
moves lead LE with device
one hand on gait belt
other hand near shoulder of patient
AD training instructional sequence
verbal instructions
ask if there is questions
provide manual contacts and verbal cuing
feedback to patient and review as needed