evolution pt. 2 (#9) (copy)
1/36
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
species
Latin word for “kind” or “apperance”
biological species concept
4 KINDS OF SPECIES CONCEPT:
group of populations whose members have the geographic area potential to interbreed in nature and produce viable, fertile offspring—but do not produce viable, fertile offspring with members of other such groups
ecological species concept
4 KINDS OF SPECIES CONCEPT:
defines a species in terms of its ecological niche, the sum of how members of the species interact with the nonliving and living parts of their environment;
niche: functional role
functional role
what is the niche in the ecological species concept?
morphological species concept
4 KINDS OF SPECIES CONCEPT:
distinguishes a species by body shape & other structural features
lineage species concept
4 KINDS OF SPECIES CONCEPT:
defines species as group of organisms that share a common ancestry & form a single branch on the tree of life;
addresses some limitations of the biological species concept by being applicable to asexual species and those lacking detailed reproductive data
speciation
how a new kind of plant or animal species is created;
occurs when a group within a species separates from other members of its species and develops its own unique characteristics;
process that caused many species that are similar split into many
allopatric (other country), sympatric speciation
2 types of speciation
True
TRUE OR FALSE:
Only species can perform interbreeding.
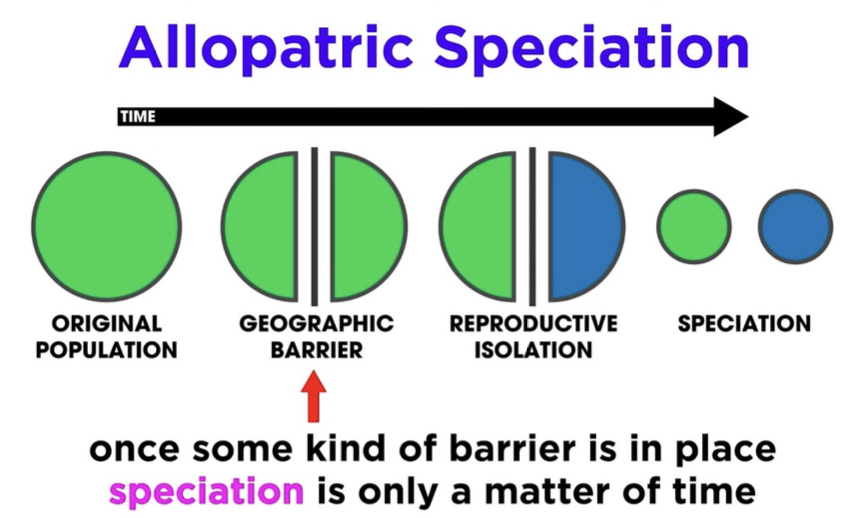
allopatric speciation
2 TYPES OF SPECIATION:
occurs when a population is divided into geographically isolated subpopulations, interrupting gene flow;
happens due to physical barrier;
can also occur without geological changes, like when individuals colonize a remote area
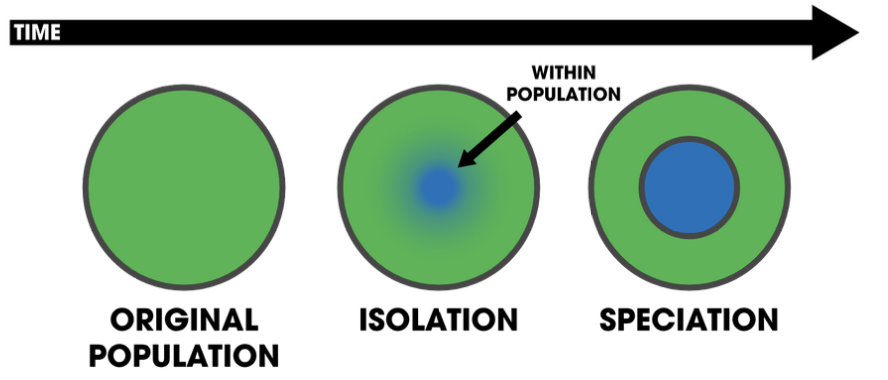
sympatric speciation
2 TYPES OF SPECIATION:
occurs when new species form within populations that live in the same area;
therefore: speciation can take place with or w/o geographic separation
reproductive isolation
separation leads to inability to produce offspring with each other
habitat/geographic, temporal, behavioral, mechanical, gametic isolation
5 prezygotic barriers
prezygotic barriers
prevent members of different species from mating to produce a zygote or fertilize
habitat/geographic isolation
5 PREZYGOTIC BARRIERS:
they occupy different habitats/places; mating is prevented because of the separation of species resulting from the difference in their habitat
temporal isolation
5 PREZYGOTIC BARRIERS:
they breed at different times
behavioral isolation
5 PREZYGOTIC BARRIERS:
different courtship & mating rituals
gametic isolation
5 PREZYGOTIC BARRIERS:
biochemical mechanisms may prevent gametes from fusing or the reproductive tract in the female may be an unfavorable environment for sperm
postzygotic barriers
keep hybrid zygotes—one-celled embryos with parents of two different species—from developing into healthy, fertile adults;
barriers that occur after zygote formation such as organisms that die as embryos or those that are born sterile
reduced hybrid viability, hybrid breakdown, reduced hybrid fertility
3 postzygotic barriers
reduced hybrid viability/hybrid inviability
3 POSTZYGOTIC BARRIERS:
hybrids do not complete development & fail to develop properly or die at an early age
ex. in some species of frogs, there are those who are able to interbreed with closely related species, but the hybrid offspring have lower fitness & potential to survive
hybrid breakdown
3 POSTZYGOTIC BARRIERS:
first-gen hybrids are viable & fertile, but their offspring aren’t
ex. sterile mule coming from horse & donkey; tigon from lion & tiger
results in mating of 2 F1 fertile offspring resulting in sterile F2 generation offspring
results in loss of fecundity & makes them unfit for establishing population
reduced hybrid fertility/hybrid sterility
3 POSTZYGOTIC BARRIERS:
hybrid offspring is viable but sterile;
occurs when the zygote is able to develop into healthy offspring, but they are unable to produce offspring and, thus unable to pass on their genetic material
ex. mule
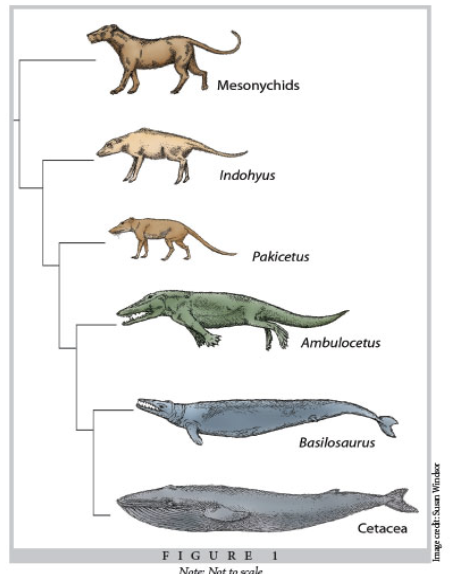
macroevolution
genetic change that occurs over long time scales, resulting in large changes in heritable traits in a population;
changes large enough that we consider this population a unique taxonomic group, or species
ex. evolution of whales from land-dwelling mammals to becoming fully aquatic
microevolution
genetic change over small timescales results in small changes in heritable traits;
ex. dev’t of antibiotic resistance in bacteria
when exposed to antibiotics, some bacteria with mutations that confer resistance survive & reproduce. over time the bacterial popu. becomes resistant to antibiotic, showing microevolution
phylogenetic tree
a hypothesis about the evolutionary relationships between species;
helps us visualize how different species are connected through common ancestors;
the closer 2 species are on the tree, the more recent their common ancestor
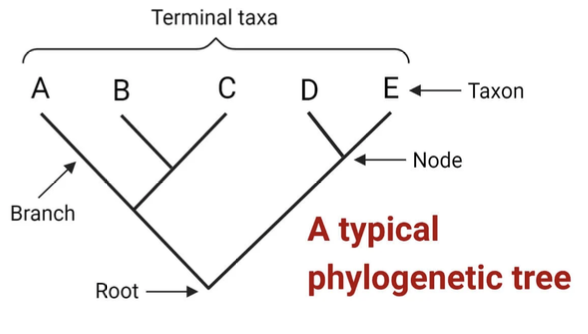
taxon
PARTS OF PHYLOGENETIC TREE:
endpoints of the branches represent present day species or sequences & are referred to as taxa
node
PARTS OF PHYLOGENETIC TREE:
connecting point where 2 branches come together
root
PARTS OF PHYLOGENETIC TREE:
common ancestor
unrooted & rooted
2 types of phylogenetic tree
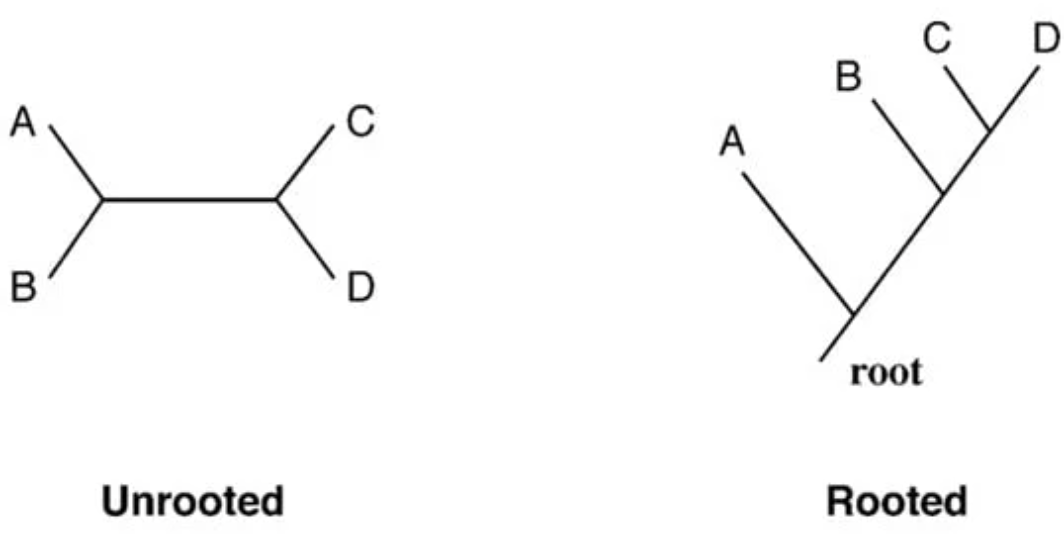
cladogram
displays only the branching pattern of evolutionary relationships among organisms
clade
taxon or group consisting of a single species and all its descendants
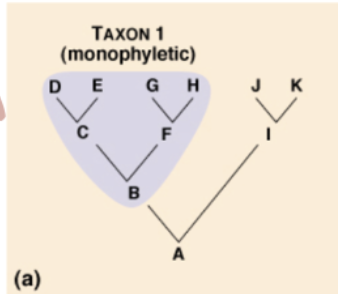
monophyletic group
3 TYPES OF CLADES:
includes all organisms that descended from a single ancestor
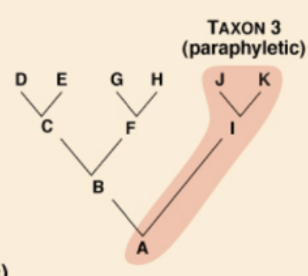
paraphyletic group
3 TYPES OF CLADES:
includes the most recent common ancestor, but not all of its descendants
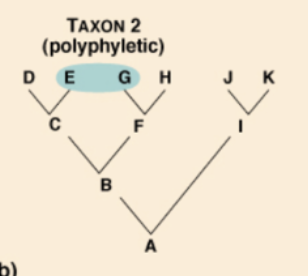
polyphyletic group
3 TYPES OF CLADES:
includes unrelated organisms descended from more than one ancestor
ecological
SPECIES CONCEPT?:
bald eagle - thrives in open water in North America & feeds on fishes
Ph eagle - inhabits tropical rainforests & eats small mammals
morphological
SPECIES CONCEPT?:
Rafflesia amoldii - largest flower
Rafflesia panechoana - smallest flower among all Rafflesia species