Chemistry Paper 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/185
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:44 AM on 11/11/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
186 Terms
1
New cards
hydrogen ions
What are acids in solution a source of?
2
New cards
hydroxide
What are alkalis in solution a source of?
3
New cards
7
What is the pH of a neutral solution?
4
New cards
low (less than 7)
Do acidic solutions have high or low pH values?
5
New cards
high (greater than 7)
Do alkaline solutions have high or low pH values?
6
New cards
alkaline
Is this solution acidic or alkaline?

7
New cards
acidic
Is this solution acidic or alkaline?

8
New cards
red
Give the colour of methyl orange indicator when it is put into an acidic solution
9
New cards
yellow
Give the colour of methyl orange indicator when it is put into an neutral solution
10
New cards
yellow
Give the colour of methyl orange indicator when it is put into an alkaline solution
11
New cards
colourless
Give the colour of phenolphthalein indicator when it is put into an acidic solution
12
New cards
colourless
Give the colour of phenolphthalein indicator when it is put into an neutral solution
13
New cards
pink
Give the colour of phenolphthalein indicator when it is put into an alkaline solution
14
New cards
it decreases
What happens to pH when hydrogen ion concentration increases?
15
New cards
it increases
What happens to pH when hydrogen ion concentration decreases?
16
New cards
it decreases by 1
What happens to pH as hydrogen ion concentration in a solution increases by a factor of 10?
17
New cards
a concentrated solution has a higher amount of substance dissolved in the solution
What is the difference between a concentrated and dilute solution?
18
New cards
one that only partially dissociates into ions
What is a weak acid?
19
New cards
one that fully dissociates into ions
What is a strong acid?
20
New cards
any substance that reacts with an acid to form a salt and water only
What is a base?
21
New cards
soluble bases
What are alkalis?
22
New cards
salt + hydrogen
Complete this equation: acid + metal -->
23
New cards
salt + water
Complete this equation: acid + metal oxide -->
24
New cards
salt + water
Complete this equation: acid + metal hydroxide -->
25
New cards
salt + carbon dioxide + water
Complete this equation: acid + metal carbonate -->
26
New cards
a lit splint causes a 'pop'
What is the test for hydrogen?
27
New cards
lime water
What is needed to test for carbon dioxide?
28
New cards
lime water turns cloudy
What is the test for carbon dioxide?
29
New cards
a reaction between an acid and a base
What is a neutralisation reaction?
30
New cards
H+ + OH- → H2O
Write a general equation for a neutralisation reaction
31
New cards
titration
What technique needs to be used if soluble salts are prepared from an acid and a soluble reactant?
32
New cards
burette
Name this piece of apparatus
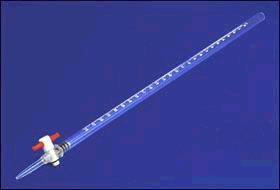
33
New cards
pipette
Name this piece of apparatus
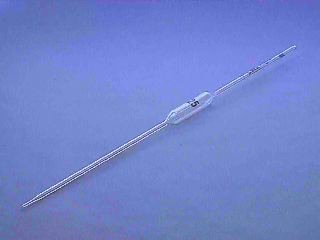
34
New cards
they are all soluble
What is true about common sodium, potassium and ammonium salts?
35
New cards
true
True or false: all nitrates are soluble
36
New cards
false: common chlorides are soluble except those of silver and lead
True or false: all chlorides are soluble
37
New cards
silver and lead
Give 2 examples of metals that form insoluble chlorides
38
New cards
false: common sulfates are soluble except those of lead, barium and calcium
True or false: all sulfates are soluble
39
New cards
lead, barium and calcium
Give 3 examples of metals that form insoluble sulfates
40
New cards
false: common carbonates and hydroxides are insoluble except those of sodium, potassium and ammonium
True or false: all carbonates are soluble
41
New cards
sodium, potassium and ammonium
Give 3 examples of cations that form soluble carbonates
42
New cards
ionic compounds in the molten state or dissolved in water
What are electrolytes?
43
New cards
a process in which electrical energy, from a direct current supply, decomposes electrolytes
What is electrolysis?
44
New cards
a positively charged ion
What is a cation?
45
New cards
a negatively charged ion
What is a anion?
46
New cards
a negatively charged electrode
What is a cathode?
47
New cards
a positively charged electrode
What is a anode?
48
New cards
the negatively charged cathode
Where do cations move to in electrolysis?
49
New cards
the positively charged anode
Where do anions move to in electrolysis?
50
New cards
copper and oxygen
What are the products of the electrolysis of copper chloride solution?
51
New cards
hydrogen and chlorine
What are the products of the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution?
52
New cards
hydrogen and oxygen
What are the products of the electrolysis of sodium sulfate solution?
53
New cards
oxygen and hydrogen
What are the products of the electrolysis of water acidified with sulfuric acid?
54
New cards
lead and bromine
What are the products of the electrolysis of molten lead bromide?
55
New cards
loss of electrons
What is oxidation?
56
New cards
gain of electrons
What is reduction?
57
New cards
at the cathode
Where does reduction occur during electrolysis?
58
New cards
at the anode
Where does oxidation occur during electrolysis?
59
New cards
oxygen and copper
What are the products of the electrolysis of copper sulfate solution?
60
New cards
pH meter
Give the term being defined: Electronic device used to measure the pH of a solution.
61
New cards
potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium, aluminium, (carbon), zinc, iron, (hydrogen), copper, silver, gold
Give the reactivity series (from most to least reactive)
62
New cards
the Earth's crust
Where are most metals are extracted from ores found?
63
New cards
in the Earth's crust as the uncombined elements
Where and how are unreactive metals found?
64
New cards
the gain of oxygen
What is oxidation?
65
New cards
the loss of oxygen
What is reduction?
66
New cards
they are reduced
What happens to ores when metals are extracted from them?
67
New cards
heating with carbon and electrolysis
Give 2 methods of extracting metals from their ores
68
New cards
the position of the metal in the reactivity series and the cost of the extraction process
Which 2 factors affect which method is chosen to extract a metal?
69
New cards
bacterial and phytoextraction
Name 2 biological methods of metal extraction
70
New cards
economic implications, preservation of both the
environment and the supply of valuable raw materials
environment and the supply of valuable raw materials
Give three advantages of recycling metals
71
New cards
consideration of the effect on the environment of obtaining the raw materials, manufacturing the product, using the product and disposing of the product when it is no longer useful
What are the four stages that are considered when doing a life time assessment for a product?
72
New cards
the reaction is reversible
What does this symbol tell you?
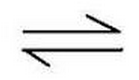
73
New cards
by changing the reaction conditions
How can the direction of some reversible reactions be altered?
74
New cards
temperature 450 °C
pressure 200 atmospheres
iron catalyst
pressure 200 atmospheres
iron catalyst
What are the conditions for the Haber process?
75
New cards
ammonia
What is made in the Haber process?
76
New cards
nitrogen and hydrogen
What reacts to form ammonia?
77
New cards
natural gas
What is hydrogen obtained from?
78
New cards
the air
What is nitrogen extracted from?
79
New cards
temperature, pressure, concentration
Give three factors that can be changed to affect the position of a dynamic equilibrium
80
New cards
gas
Which state of matter does this diagram represent?
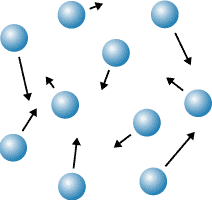
81
New cards
liquid
Which state of matter does this diagram represent?
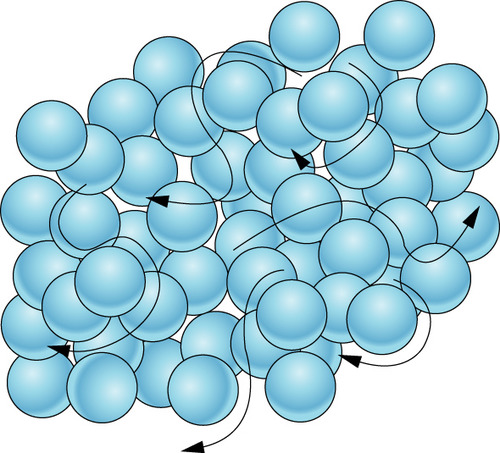
82
New cards
solid
Which state of matter does this diagram represent?
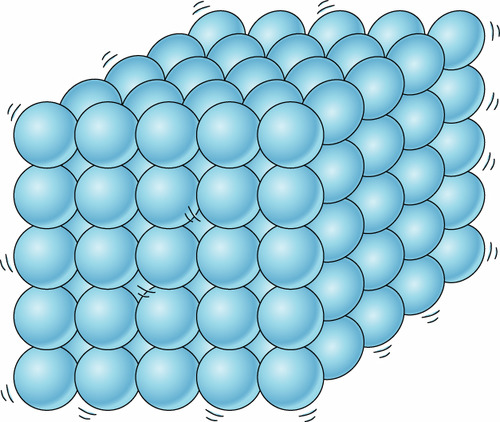
83
New cards
solid, liquid, gas
Sort the three states of matter into order of increasing energy
84
New cards
gas, liquid, solid
Sort the three states of matter into order of decreasing energy
85
New cards
physical changes
What term can be used to describe interconversions between states of matter?
86
New cards
melting
What is the name for the physical change when a solid turns into a liquid?
87
New cards
freezing
What is the name for the physical change when a liquid turns into a solid?
88
New cards
boiling / evaporating
What is the name for the physical change when a liquid turns into a gas?
89
New cards
condensing
What is the name for the physical change when a gas turns into a liquid?
90
New cards
something that is made up of only one element or compound
What is a pure substance?
91
New cards
when there are two or more elements or compounds not chemically bonded
What is a mixture?
92
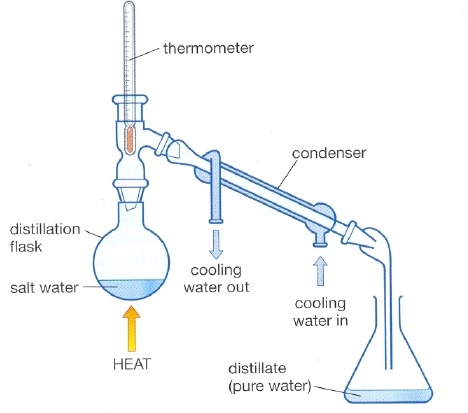
New cards
distillation
What process is this a diagram of?
93
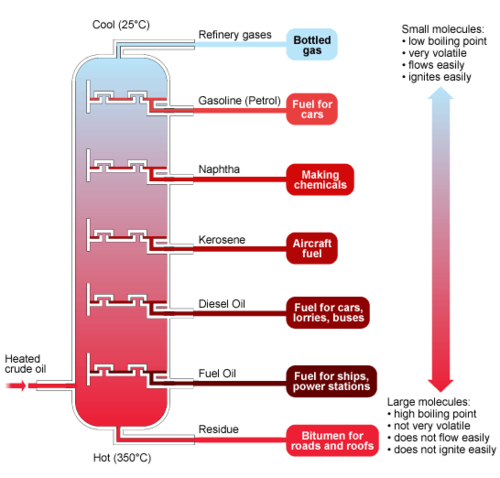
New cards
fractional distillation
What process is this a diagram of?
94
New cards
filtration
What process is this a diagram of?
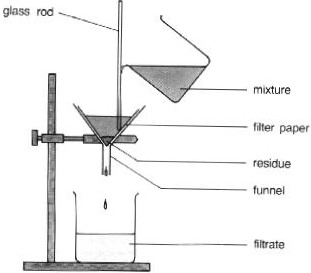
95
New cards
crystallisation
What process would you use this piece of equipment for?

96
New cards
paper chromatography
What is this a diagram of?
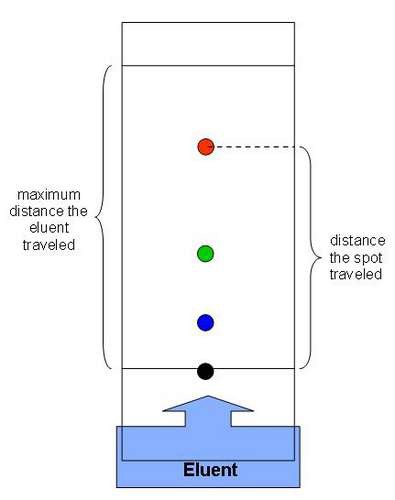
97
New cards
the solvent
What is the mobile phase in paper chromatography?
98
New cards
the paper
What is the stationary phase in paper chromatography?
99
New cards
there would only be one spot
How would you know if something was a pure substance when using paper chromatography?
100
New cards
Compare the Rf value with known values
How can you identify a substance using paper chromatography?