Midterm C11
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Define Disruptive Innovation
Innovations that create new markets or radically change existing ones by offering simpler, more affordable, or more convenient alternatives. These innovations initially serve niche or lower-end markets but eventually evolve to meet the needs of the mainstream.
Elements of Disruptive Innovation Theory
Market disruption
Lower price or increased accessibility
Simpler technology or business model
Gradual Market penetration
Value Network Change
Incumbent Response
Transformative Impact
Element of Disruptive Innovation Theory: Market Disruption
Disruptive innovation introduces a product or service that initially targets a small, often overlooked segment of the market, but eventually disrupts established market leaders.
Elements of Disruptive Innovation Theory: Lower price or Increased Accessibility
These innovations often start as cheaper more accesible alternatives to existing products or services, appealing to customers who are ignored by the mainstream market.
Elements of Disruptive Innovation Theory: Simpler Technology or Business Model
The innovation is usually simpler than existing solutions, utilizing new technology or a novel business model to deliver value in a different way.
Elements of Disruptive Innovation Theory: Gradual Market Penetration
Initially, these innovations may underperform compared to traditional offerings in mainstream markets, but they gradually improve and become attractive to a larger customer base
Elements of Disruptive Innovation Theory: Value Network Change
Disruptive innovations often require or create new value networks including new supply chains, distribution channels, and customer relationships, which are distinct from those of established companies.
Elements of Disruptive Innovation Theory: Incumbent Response
Established companies may struggle to response effectively to disruptive innovations due to their existing commitments, structures and value networks, which are geared towards their traditional offerings.
Elements of Disruptive Innovation Theory: Transformative Impact
Over time, disruptive innovations can radically transform industries, leading to the decline of established firms and the rise of new leaders, often reshaping the industry landscape entirely.
What are the stages to the Founders Journey
1. I'm a Founder
2. Wearing Off of Novelty
3. Trough of Sorrow
4. Releases of Improvement
5. Crash of Ineptitude
6. Wiggles of False Hope
7. The Promised Land!
8. Acquisition or Liquidity Event
9. Upside of Disruption
What is Creative Destruction?
Creative destruction is a process of dismantling old practices to make way for innovation. It's a driving force in capitalism. It involves breaking down entire systems to pave the way for new ideas.
Principles of Creative Descruction:
Innovation drives change
Competition forces business to improve
Entrepreneurs are agents of change who oversee innovation and educate stakeholders
Capital risk is essential for innovation
What is Moore's Law
The number of transistors on a microchip doubles approximately every two years, while the cost of computing is halved. This principle has accurately predicted the exponential growth of computing power over the past few decades. It implies that computers become faster and more powerful over time while also becoming cheaper to produce.
What is the Law of Accelerating Returns
Technology's relentless, predictable, and exponential growth will bring humans into the era that Kurzweil is most closely associated with, the singularity
What are Exponential Technologies
1) Rapidly accelerating following Law of Accelerating Returns and Moore's Law
2) Shaping major industries
Examples of Exponential Technologies
Artificial Intelligence
Solar and Fusion
Augmented and Virtual Reality
Data Science
Nanotech
Biotch
Why Exponential Technologies Matter: Abundance
Exponential technologies have the potential to create an abundance of resources and opportunities, making them widely accessible and reducing scarcity.
Why Exponential Technologies Matter: Abundance- Healthcare
AI, biotechnology, and nanotechnology enable personalized and accessible healthcare.
Why Exponential Technologies Matter: Abundance- Food Production
Precision farming and lab-grown meat boost sustainable food sources.
Why Exponential Technologies Matter: Abundance- Education
AI and VR/AR provide personalized, immersive education worldwide.
Why Exponential Technologies Matter: Abundance- Energy
Advances in renewable energy and battery storage promise abundant clean energy.
Why Exponential Technologies Matter: Abundance- Manufacturing
3D printing and AI-driven design reduce costs and waste.
Why Exponential Technologies Matter: Abundance- Water
Innovations like graphene filters and AI leak detection ensure clean water availability.
Why Exponential Technologies Matter: Abundance- Transportation
Autonomous vehicles and new tech make travel cheaper and safer.
Why Exponential Technologies Matter: Abundance- Housing
3D printing and smart materials lower housing costs and improve quality.
Why Exponential Technologies Matter: Abundance- Digital Assets
Blockchain creates opportunities across finance and industries.
Why Exponential Technologies Matter: Abundance- Space Exploration
Advanced tech supports abundant opportunities for exploration and resource use.
What are the 6Ds of Exponential Technologies?
Digitized
Deceptive
Disruptive
Dematerialized
Demonetized
Democratized
What are the 6Ds of Exponential Technologies: Digitized
Once a technology is digitized it becomes an information science, and so we can use computers to manage it.
What are the 6Ds of Exponential Technologies: Deceptive
Exponential growth is hard to spot. At the beginning of most exponentially advancing environments, the early stages of development are almost imperceptible. The technology seems like a toy.
What are the 6Ds of Exponential Technologies: Disruptive
After the initial deceptive growth, the development of an exponentially advancing technology can make the previous paradigm effectively obsolete, out-performing it in both effectiveness and cost.
What are the 6Ds of Exponential Technologies: Dematerialized
Items that were once large and unwieldy can now fit easily into our pockets. The miniaturization of sensors paired with digitization allows for the elimination of dedicated single-use physical devices.
What are the 6Ds of Exponential Technologies: Demonetized
Technologies like GPS and cameras, once costly, are now affordable and widely accessible due to integration into smartphones and the reduced costs of software and sensors.
What are the 6Ds of Exponential Technologies: Democratized
Technologies and information, once exclusive to the wealthy or specialized institutions, are now accessible to a large global population, providing equal opportunities through affordable internet-connected devices.
Define Lateral Thinking with Withered Technology
A concept that involves using older, often outdated or less advanced technologies (referred to as "withered technology") in innovative ways to solve problems or create new opportunities.
What are Porters Five Forces used for?
Analyzing the competitive forces that shape every industry, helping determine its strengths and weaknesses.
What are Porters Five Forces?
Threat of New Entrants, Determinants of Supplier Power, Rivalry Among Existing Firms, Determinants of Buyer Power, Threat of Substitute Products
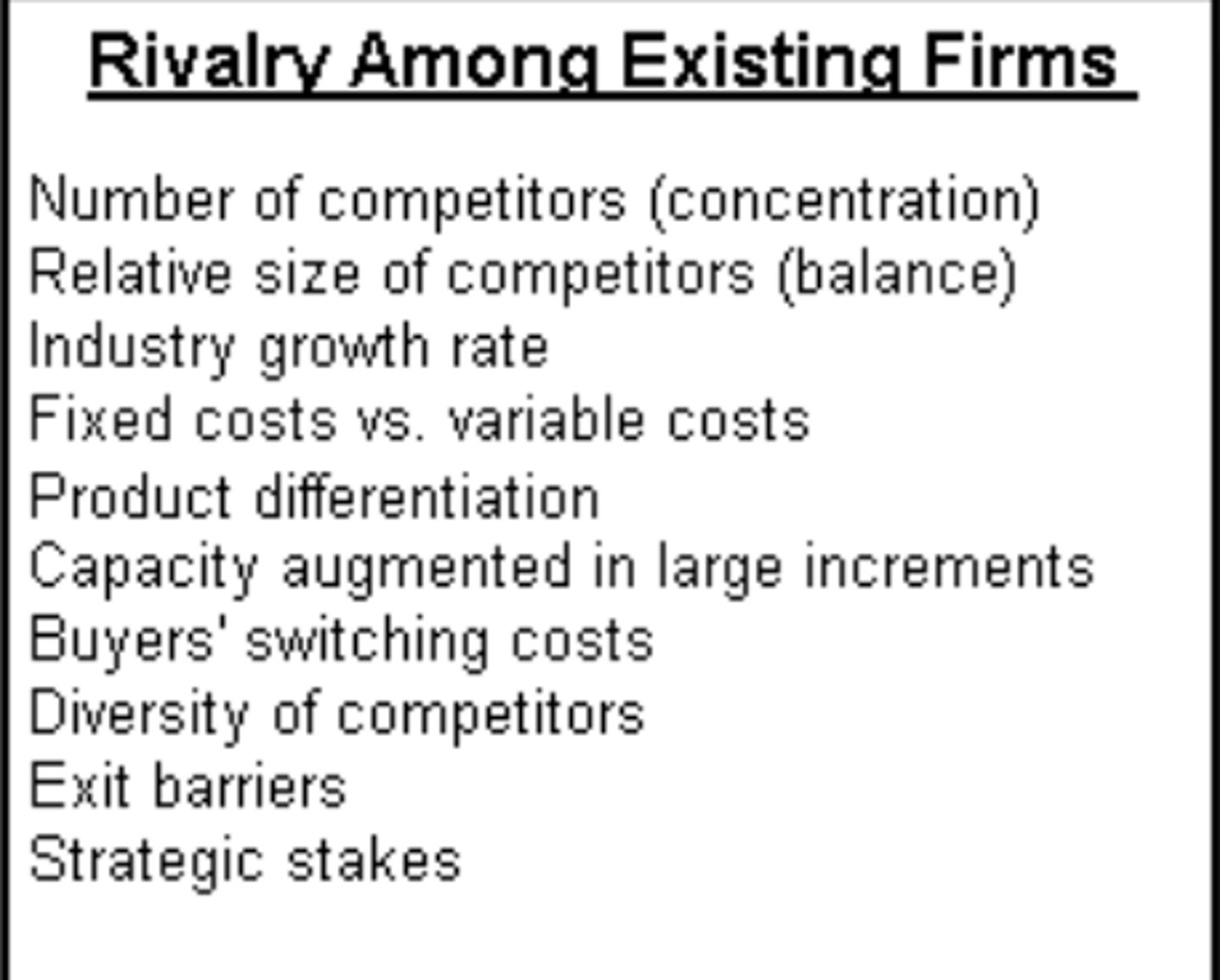
Threat of New Entrants
The ease or difficulty with which new competitors can enter the market.
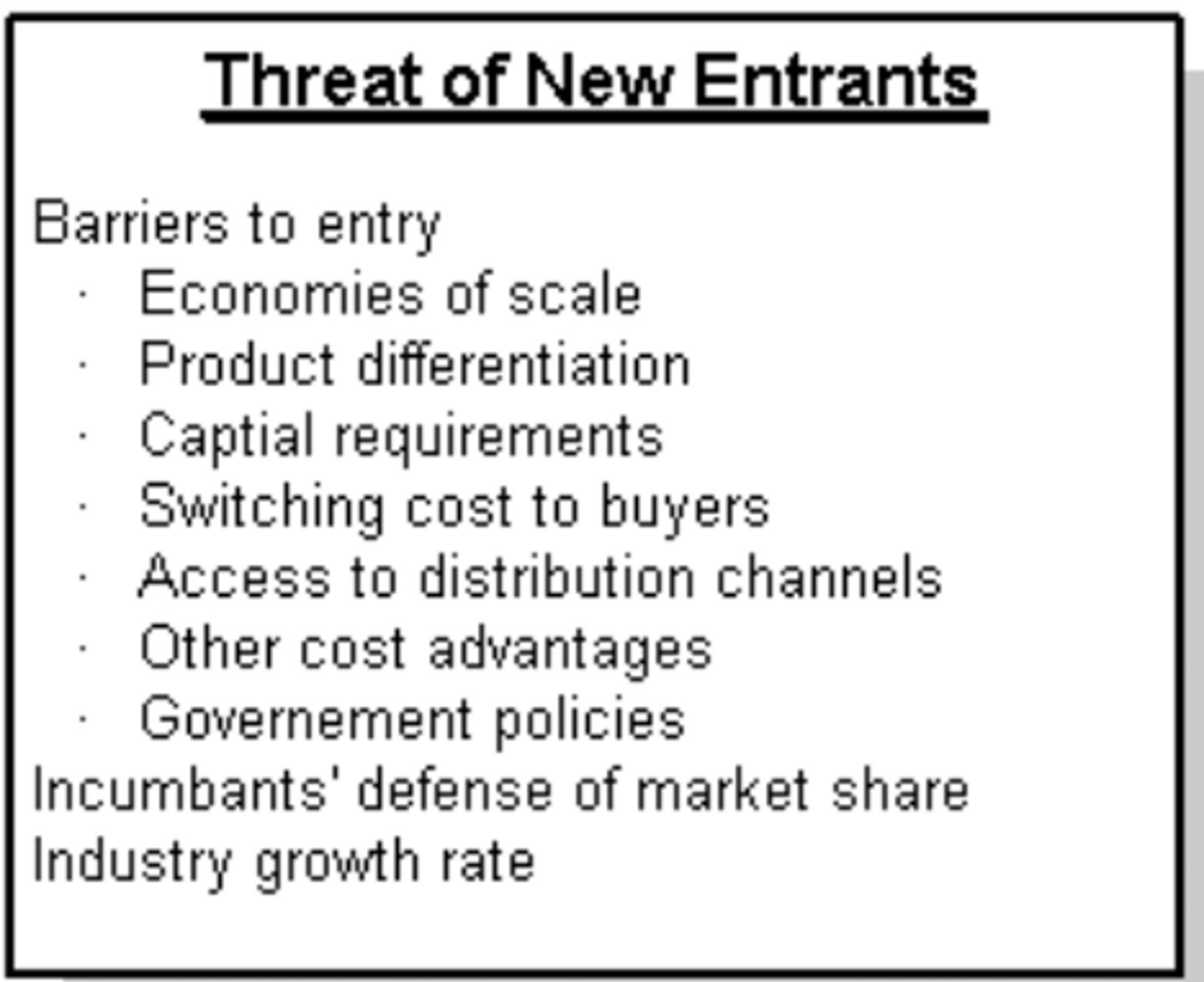
Determinants of Supplier Power
The power suppliers have to drive up the prices of inputs.
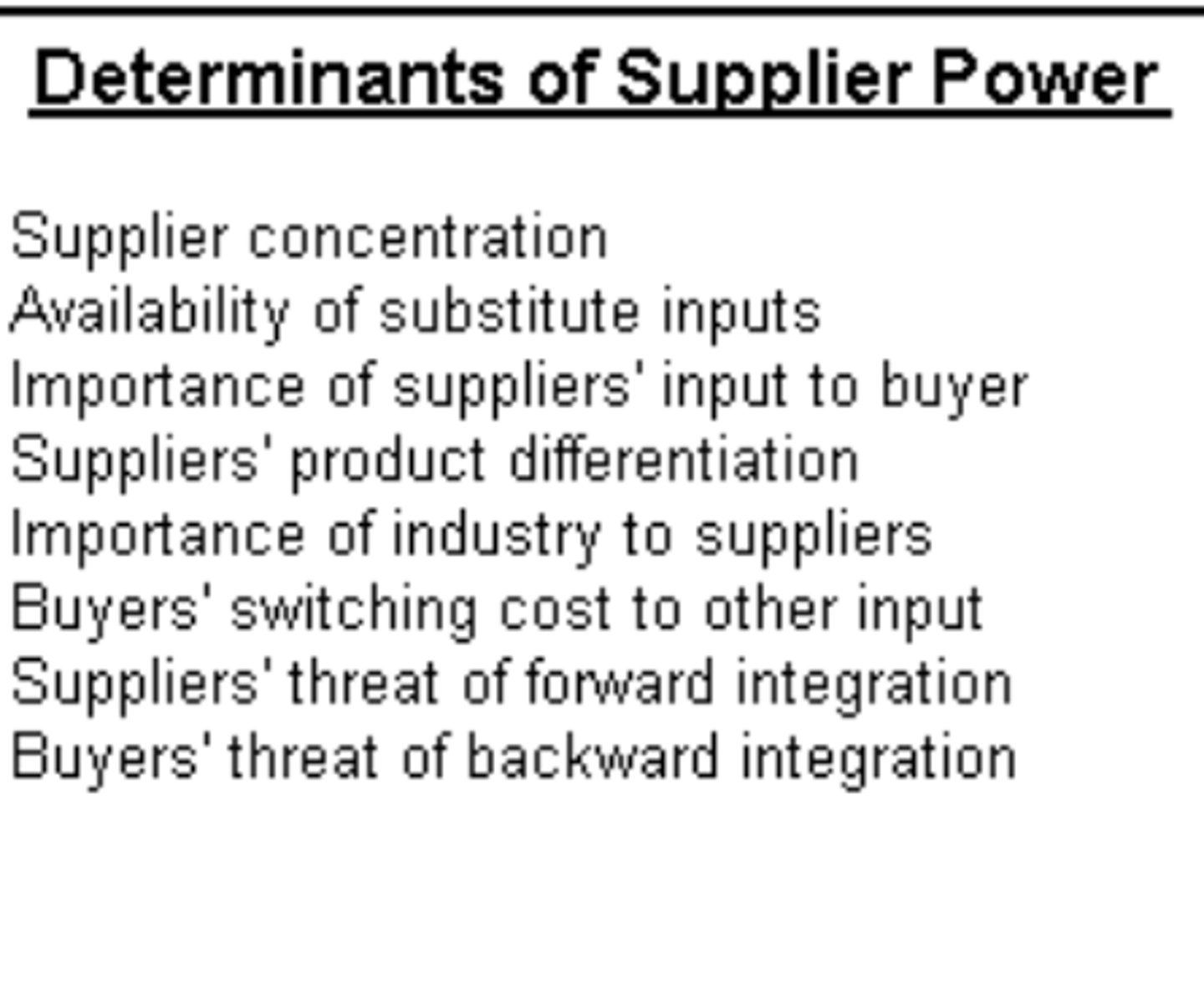
Rivalry Among Existing Firms
The intensity of competition among existing firms in the industry.
Determinants of Buyer Power
The power customers have to drive down prices or demand higher quality

Threat of Substitute Products
The likelihood of customer finding alternative products or services.

Where good ideas come from: Elightment
The idea of an "Enlightenment" or sudden "Eureka" moment for good ideas is unrealistic.
Instead, ideas come from networks—environments full of innovators and creators exchanging and building upon each other's thoughts.
Where good ideas come from: Liquid Network
A "Liquid Network" is an environment where diverse people, ideas, and backgrounds come together, fostering innovation.
Important breakthroughs often happen in collaborative spaces, like at lab meetings where researchers share findings and ideas.
Red Ocean strategy
Compete in existing markets, with focus on outperforming rivals and capturing a greater share of current demand.
Blue Ocean strategy
Create new market spaces free from competition, focusing on differentiation and low cost simultaneously (e.g. Cirque du Soleil)
Market Creating Strategy Traps
Customer Orientated Approach
Niche v.s. Market-Creation
Technology v.s. Value Innovation
Creative Destruction Misunderstanding
Market Creating Strategy Traps: Customer-Orientated Approach
Focusing on existing customers instead of exploring non-customers can limit new market creation.
Market Creating Strategy Traps: Niche vs. Market-Creation
Uncovering a niche is not the same as finding a new market space.
Market Creating Strategy Traps: Technology vs. Value Innovation
Market creation is driven by value innovation, not solely technological advancements.
Market Creating Strategy Traps: Creative Destruction Misunderstanding
Market creation can occur without displacing existing products.
Three Propositions for Blue Ocean Strategy
Value Proposition: What attracts buyers by providing value.
Profit Proposition: The business model that ensures profitability.
People Proposition: Motivation and alignment of those executing the strategy, including employees and stakeholders.
What does it mean to "Think in Bets"
Think in probabilities ot absolutes
Use data when making critical decisions
Gather feedback from stakeholders
Be comfortable changing your mind
What is a Signal?
A specific example of the future in the present. A Clue that things might soon become4 different.
What are examples of Signals
New technology
Scientific breakthrough
New business Model
Government Project
Change in demographics
Weird behavior
What is a Driver
A big change that is already underway
One can describe a Driver as going "from X to Y"
Signals appear because of underlying Drivers
What is the difference between Signals and Drivers
A signal is a specific example. A driver is a bigger force behind that example.
How do you find Drivers?
Look at patterns int he signals you are collecting
What are commonalities among the signals?
What's the bigger force behind the signals?
Signals>Drivers>Forecasts
This means that future thinkers who track signals and drivers can use that information to generate plausible forecasts for what will happen in the future.
What is Inflection Theory
Refers to the concept of critical turning points, or "inflection points," in business or technology that fundamentally alter the trajectory of an industry or organization.
What is an Inflection Point
an event that creates an opportunity for radical changes in behavior, thinking and technology. e.g. Telegraph, Smartphone, AI
When developing a product ask..
Why now? Because the wave is here right now. Paddle too early or too late and we miss the wave. Timing matters.
Inflection Theory: Insight
An Insight is a non obvious truth about how to harness one or more inflections to change human capacities or behaviors in a radical way.
What is a problem space
A stakeholder problem, need or benefit that the product should address. A product requirement
What is a solution space
A specific implementation to address the perceived need or product requirement.
What is the benefit of this distinction
When confronted with a problem - everyone’s natural impulse it to think of a solution
However, as soon as you start thinking of a solution you begin shutting off possibilities for getting a deeper understanding of the problem and therefore finding a truly meaningful solution
Better to start in the “problem space” - typically by talking to people and doing research - and stay until you have created a 360 Degree view of the problem
What is the Mom Test
It provides guidelines for asking effective questions during customer interviews to validate a business idea. The name comes from the idea that even your mom, who wants to support you, should give you honest feedback if you ask the right questions.
What is applicable about the Mom test?
Ask about real experiences to get actionable feedback (Chapter 1).
Seek disconfirming evidence to identify weaknesses early (Chapter 2).
Inquire about specific past actions for reliable insights (Chapter 3).
What is the benefit of a Data Dashboard?
Provides a foundation for data-based decision making as a team
Elements of a great dashboard?
Clarity and Simplicity
Focus on Key Metrics
User-Friendly Design
Clear Visual Hierarchy
Use equations, reference data, have conditional formatting
What does HPPO stand for
Highest Paid Person's Opinion
How do you Defeat the HPPO?
With Data
What is a Competitive Analysis
The process of evaluating your competitors to understand their strengths, weaknesses, products, and market position, in order to identify opportunities and develop a competitive advantage.
How to conduct a Competitive Analysis
Step 1: Define Scope
industry vertical? specific company?
Step 2: Gather Data
- Tools: Competitive analysis tools, web scraping
- Secondary Sources: Company reports, news articles, industry journals, market research reports.
- Primary Sources: Surveys, interviews, product testing, mystery shopping.
Optional Step: Porter’s Five Forces
- Threat of New Entrants
- Bargaining Power of Buyers
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- Threat of Substitute Products
- Competitive Rivalry
How to Communicate Opportunity
Competitive Landscape, Comparison Chart
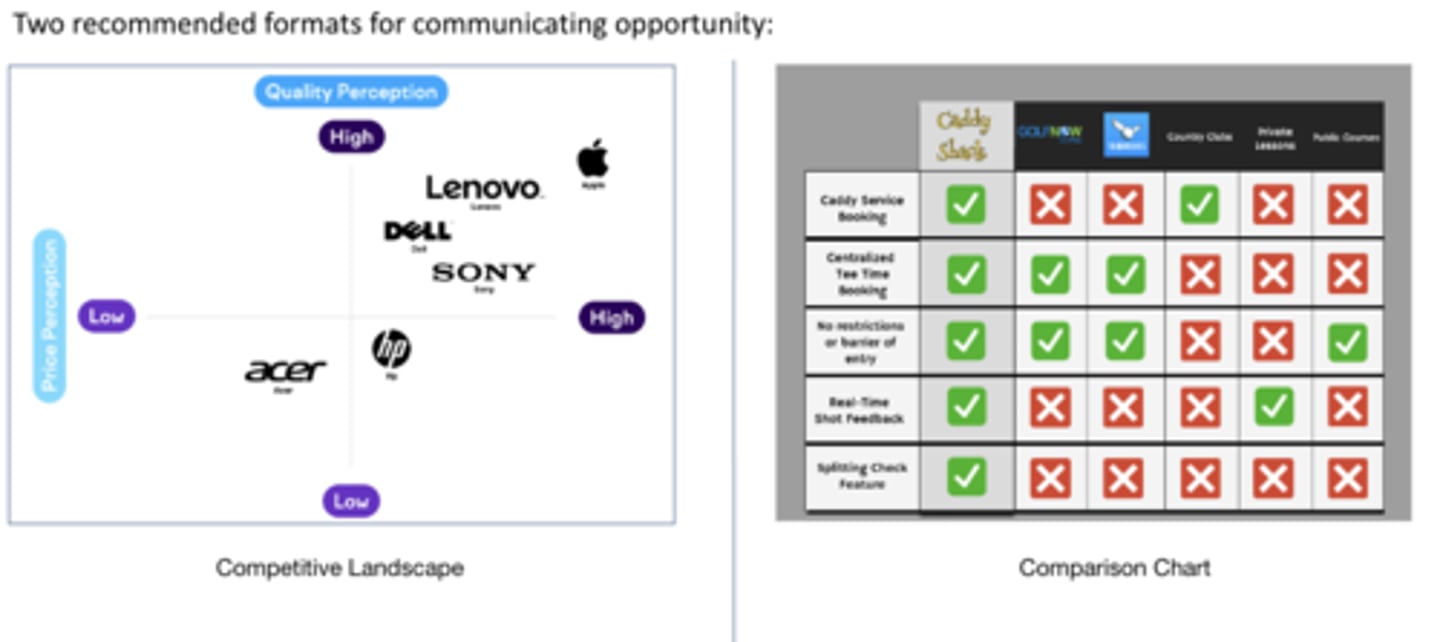
What is a Competitive Landscape (AKA Product Perception Map)
Storytelling device- communicates a story of opportunity with your startup
Key message emerges from the X and Y axis (which you define)
What is a Comparison Chart
Storytelling device - communicates a story of opportunity with your startup
Key message emerges from the rows of features that differentiate you from the competition. You define the rows!
What does it mean when an invest asks "How High is Up?"
They are trying to gauge
Market size and growth potential
Startups Capacity for Scaling
Competitive Landscape
Innovation and Disruption Potential
How do you communicate a Market Opportunity
TAM SAM SOM
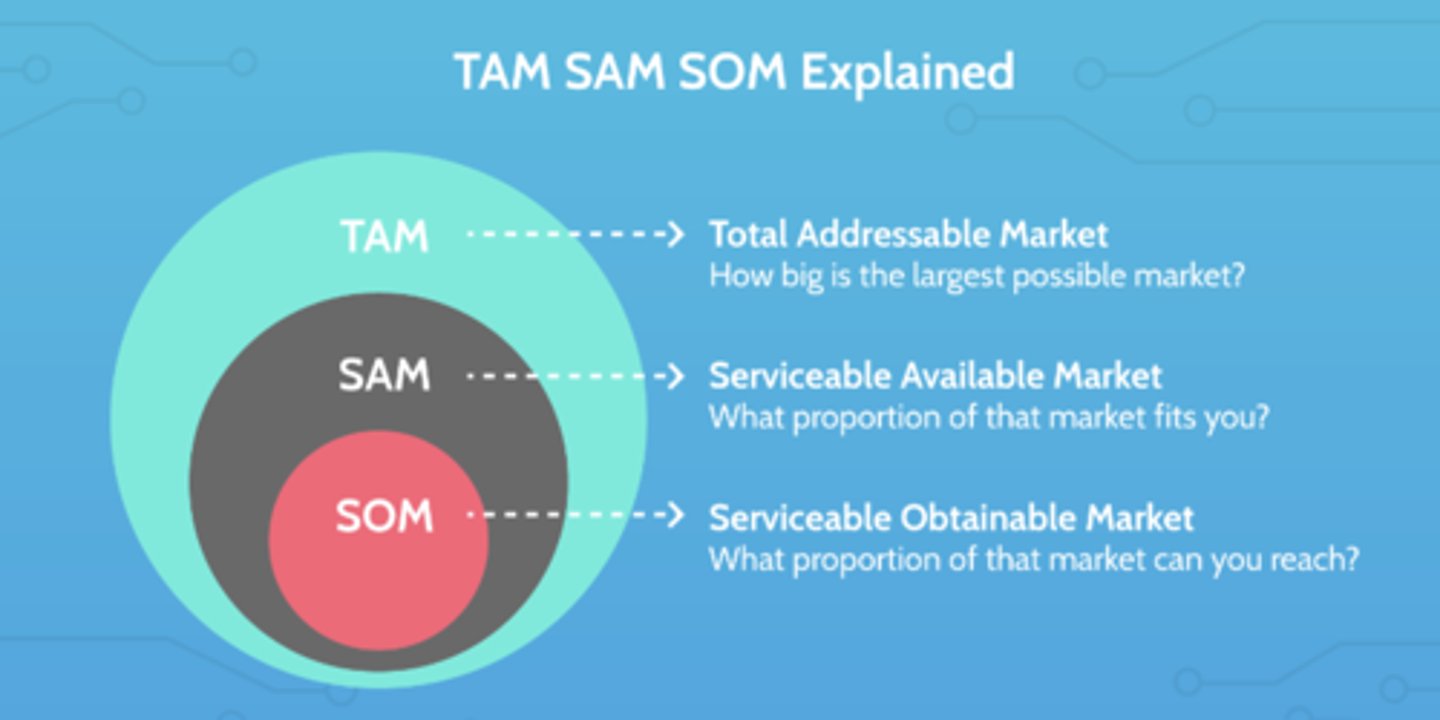
What is TAM
Total Addressable Market- How big is the largest possible market?
What is SAM
Serviceable Available Market- What proportion of that market fits you?
What is SOM
Serviceable Obtainable Market- What proportion of that market can you reach?
What are secondary sources to find market sizing?
Company Data
Web-based research sites
Public data and reports
Investment Banking Reports
