Cell Communication
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
4 types of signaling
Paracrine
Endocrine
Autocrine
Direct Signaling
Paracrine signaling
Move by diffusion through extracellular matrix
Endocrine signaling
Signals are sent from distant cells, typically produce a slower response with a long lasting effect
Autocrine signaling
Signaling cells can bind to the ligand that they release, cell signals itself
Direct signaling
Small signaling molecules move across gap junctions between cells
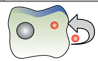
What kind of chemical signaling is this?
Autocrine signaling
What kind of chemical signaling is this?
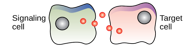
What kind of chemical signaling is this?
Direct signaling
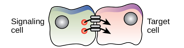
What kind of chemical signaling is this?
Paracrine signaling
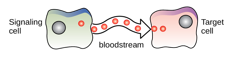
What kind of chemical signaling is this?
Endocrine signaling
What kind of cell signaling is a neurotransmitter?
Paracrine signaling
What can some enzymes do to neurotransmitters?
They can degrade some types and cause the signal to be terminated.
Sometimes we can inhibit these enzymes intentionally to speed up acetylcholine activity through the means of medication
Synaptic gap
distance between the presynaptic cell and the postsynaptic cell
What part of the neuron receives signals?
Dendrites
What parts of the neuron sends signals?
Terminal buttons
What is the body of the neuron called?
The soma
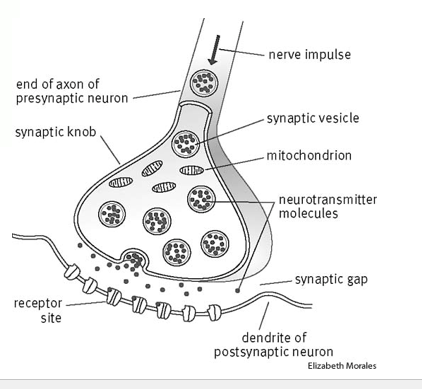
What’s going on here?
A nerve impulse travels down the axon and gets absorbed by the synaptic knob, forming a synaptic vesicle, which holds all of the content of the nerve impulse
The synaptic vesicle then travels down the knob and releases the signal at the synaptic gap.
Acetylcholine
Controls skeletal muscles and may function in the sleep-wake cycle, learning, memory, and mood
What is acetylcholine made out of?
Acetyl-CoA and choline.
Acetylcholine is broken down by…
Acitylcholinesterase
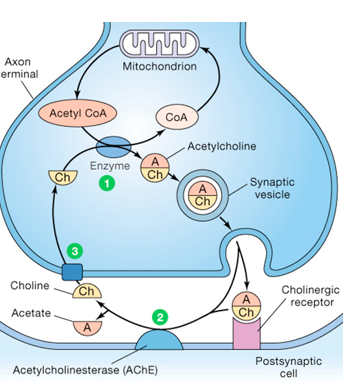
What’s going on here?
Acetylcholine is made out of acetyl-CoA and choline. The acetylcholine is put into a synaptic vessel and exits the cell, bound to a receptor. Acetylcholine is broken into acetate and choline by acetylcholinesterase.
Drugs
Any substance that alters body function when it is introduced from an external source
Agonist
Activates cell signaling (activates cell receptors), making it faster
Botulinus venom is an…
Antagonist, it prevents ACh release.
Black widow spider venom is an …
Agonist. It increase release of ACh
Organophosphorus Insecticides: how does it work?
Antagonist
OP blocks acetylcholinesterase → ACh is not being broken down → accumulation of ACh
Is nicotine an agonist or antagonist?
Both
Low doses → Agonist
High Doses → Antagonist
Antagonist
Slows down cell signaling by inhibiting receptors
Nicotine at low doses
activates receptors → acts as an agonist →increased heart rate and dopamine release
Nicotine at high doses
receptors are constantly activated → receptors are desensitized → receptors stop responding (or slowed permanently)
Histamine
Neurotransmitter responsible for allergy symptoms
Antihistamine function
Blocks histamine receptors
Receptor
A molecule which a hormone or a neurotransmitter reacts with to get a response from a target cell
What are the messenger molecules?
Hormones
Neurotransmitters
Hormones
Travel through the bloodstream to reach their target cell
Effects last longer, takes longer for effect to kick in
Secreted by the endocrine system\
ex. epinephrine
Neurotransmitter
Travel between neurons quickly
Effects are short-lived, kick in really fast (fraction of a second)
ex. acetylcholine
What does the endocrine system include?
All cells that secrete hormones into the blood stream
Do hormones carry out chemical reactions?
nope, they are just messengers
Who is the boss of the endocrine system?
The hypothalamus
How does the hypothalamus talk to other tissues?
Direct neural control
Direct release of hormones
Indirect control through release of regulatory hormones
Direct neural control
hypothalamus → adrenal gland → epinephrine
Hypothalamus send nerve signals directly to the adrenal gland
Direct release of hormones
hypothalamus → antidiuretic hormone
Hypothalamus produces hormones that get sent down into the bloodstream
Indirect control through release of regulatory hormones
hypothalamus → pituitary gland → thyrotropin → thyroid gland → thyroid hormones
Hypothalamus releases activating/inhibiting hormones which causes the pituitary to speed up/slow down the release of their hormones
3 main classes of hormones
Amino acid derivatives
Polypeptides
Steroids
Example of amino acid derivatives as hormones
Melatonin
Example of polypeptides as hormones
vasopressin
Example of steroids as hormones
estradiol
Which hormone class can actually go inside the cell?
Steroids
Why can steroids enter the cell directly?
They are hydrophobic and nonpolar
Once a steroid is inside the cell, what does it need to remain stable before activation?
A chaperone protein
Why can’t polypeptides and amino acid derivatives enter the cell?
They are water-soluble
How can non-steroid hormones send signals to cells?
They bind to a receptor molecule on the cell membrane. That cell membrane activates a G-protein, which activates an effector enzyme. This effector enzyme converts ATP to cAMP which will go on to activate other reactions.
What is the role of cAMP in non-steroid signal transduction
it is the second messenger
Second messenger
Carries the cell signal inside the cell when a hormone can’t enter
Thyroxine
Iodine-containing hormone produced by the thyroid gland
What causes goiters?
low iodine (more is needed) → more thyroxine is made → thyroid is enlarged to make more thyroxine
Epinephrine
Increase the availability of glucose as a source of energy
Released from adrenal glands when we need an instant response to danger
Takes a few seconds to kick in
Epinephrine is an amino acid derivative. How does it do signal transduction?
Via second messenger cAMP
How does epinephrine increase glucose availability?
breaks down more glycogen into glucose-6-phosphate, then converts to glucose through glycolysis.
glucose released into the bloodstream for energy
What is the largest class of hormones?
Polypeptides
Average size for polypeptide hormones
~100 - 150 amino acids, there are outliers on both sides tho
Propagation of the signal methods
Signal transduction
Dimerization
Signaling Pathway
Signal integration
Signal transduction
Ligand binds to a receptor and the signal gets transmitted through the cell membrane into the cytoplasm
Dimerization
two receptors bind to each other to form a stable complex
Signaling pathway
chain of events that occur after a ligand binds to a receptor; think second messengers, enzymes, activated proteins
Signal integration
Signals from 2+ receptors can merge and activate the same response in a cell
Difference between dimerization and signal integration
dimerization → receptors link to activate
signal integration → different signals merge in the cell to control the response
Response to the signal: Gene Expression
The signal outside the cell changes what genes are active inside the cell.
Apoptosis
Self induced cell death