Lumbopelvic Competency
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
5-7 cm
what is the normal range for lumbar flexion using a tape measure?
1-3 cm
what is the normal range for lumbar extension using a tape measure?
18-38
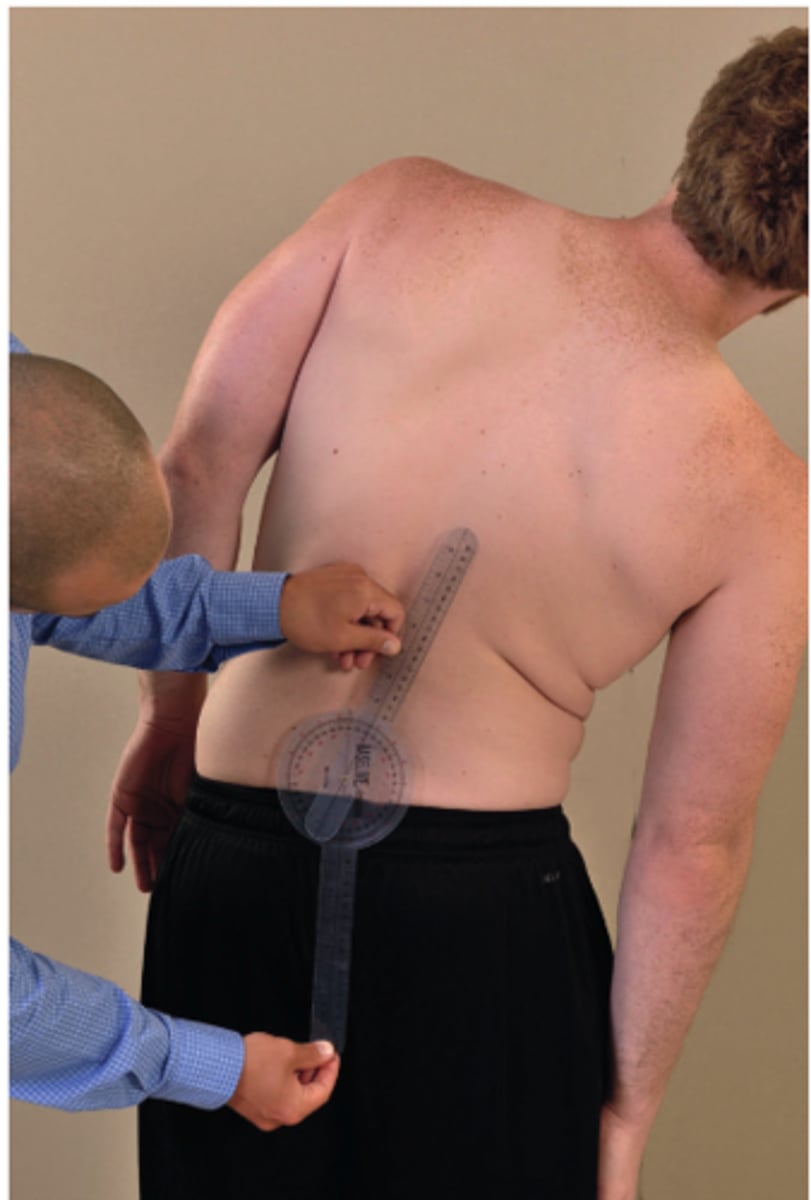
what is the normal range for thoracolumbar sidebending?
lumbar flexion
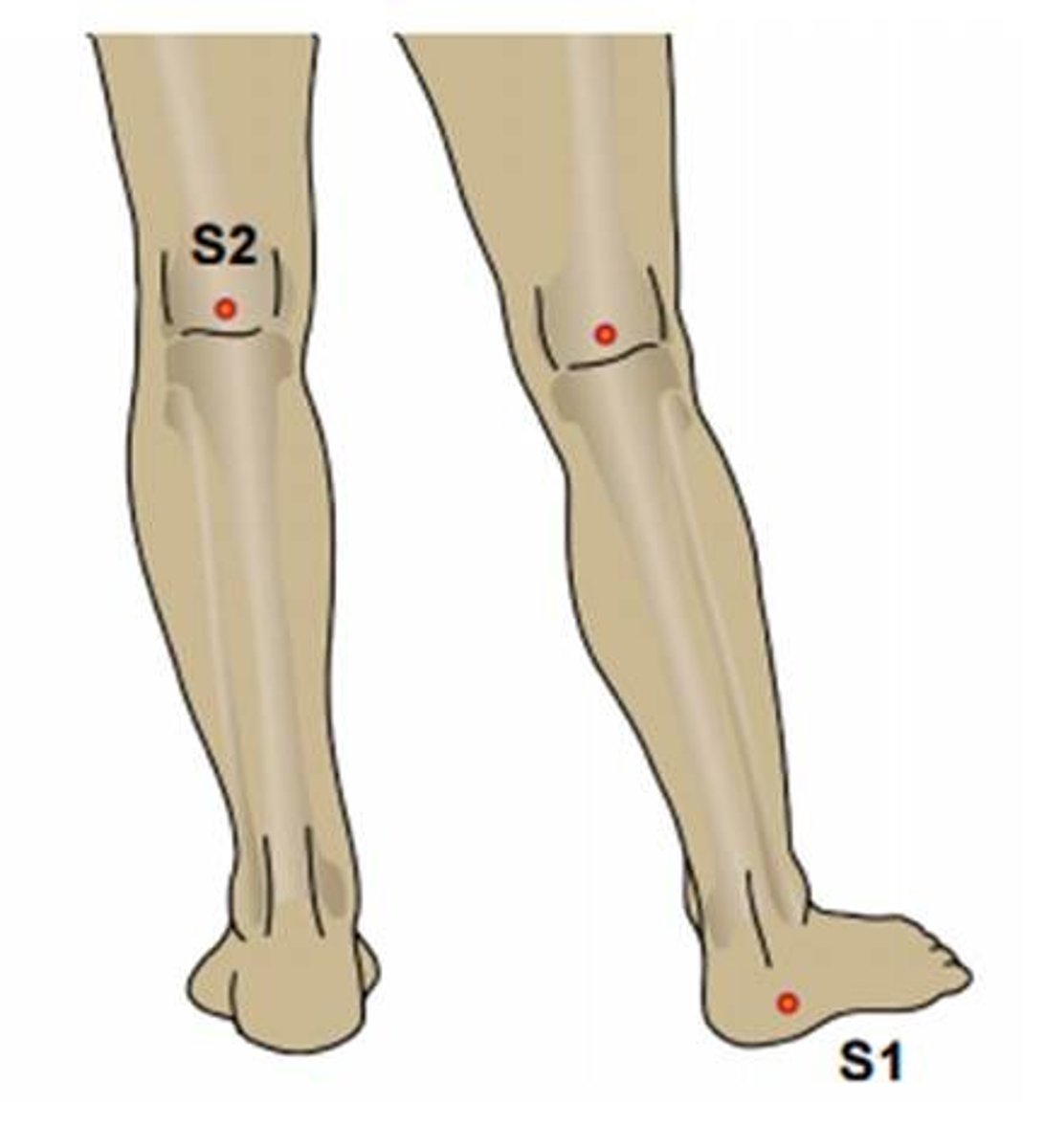
15 cm above S2
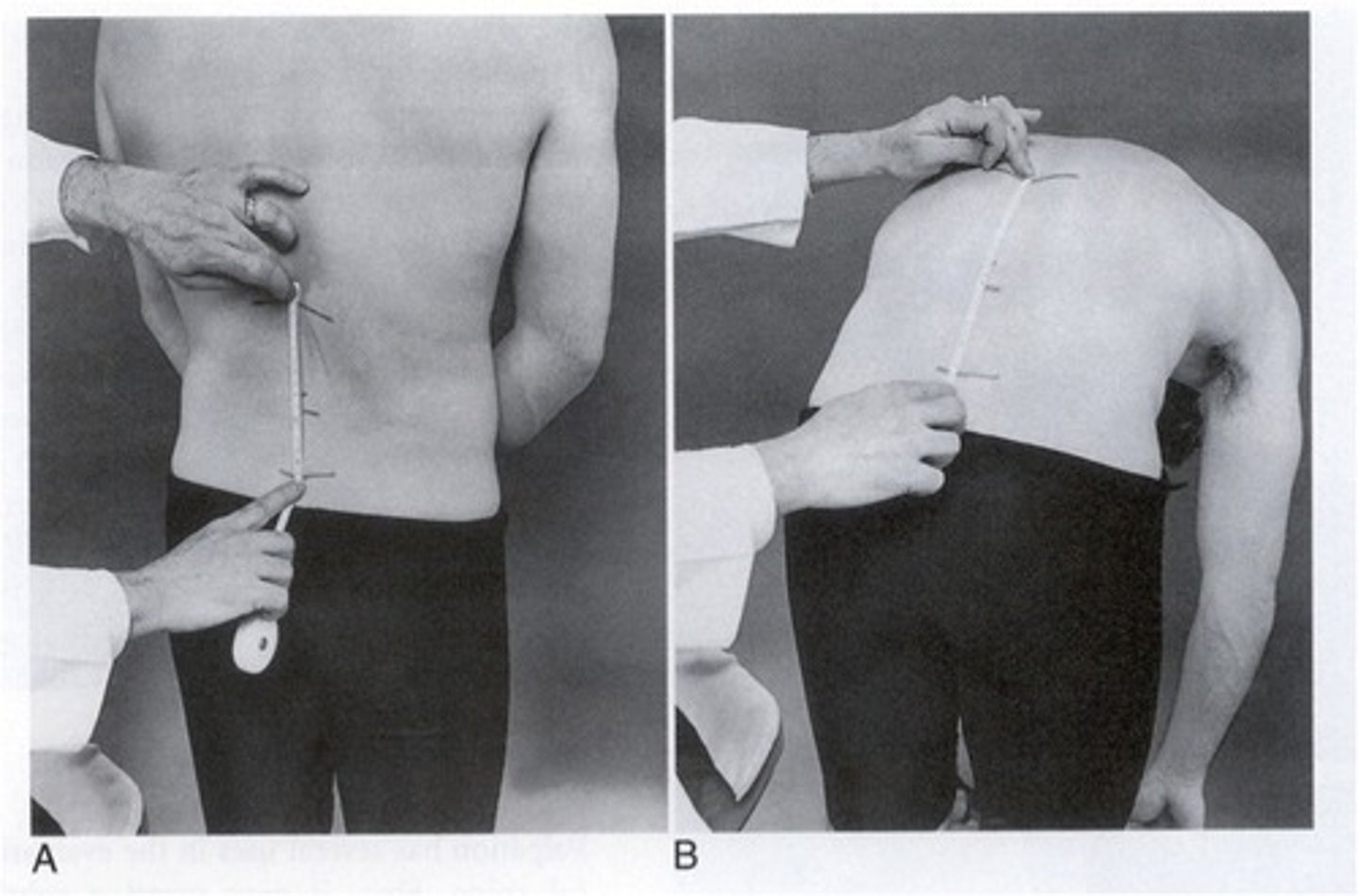
lumbar extension
15 cm above S2
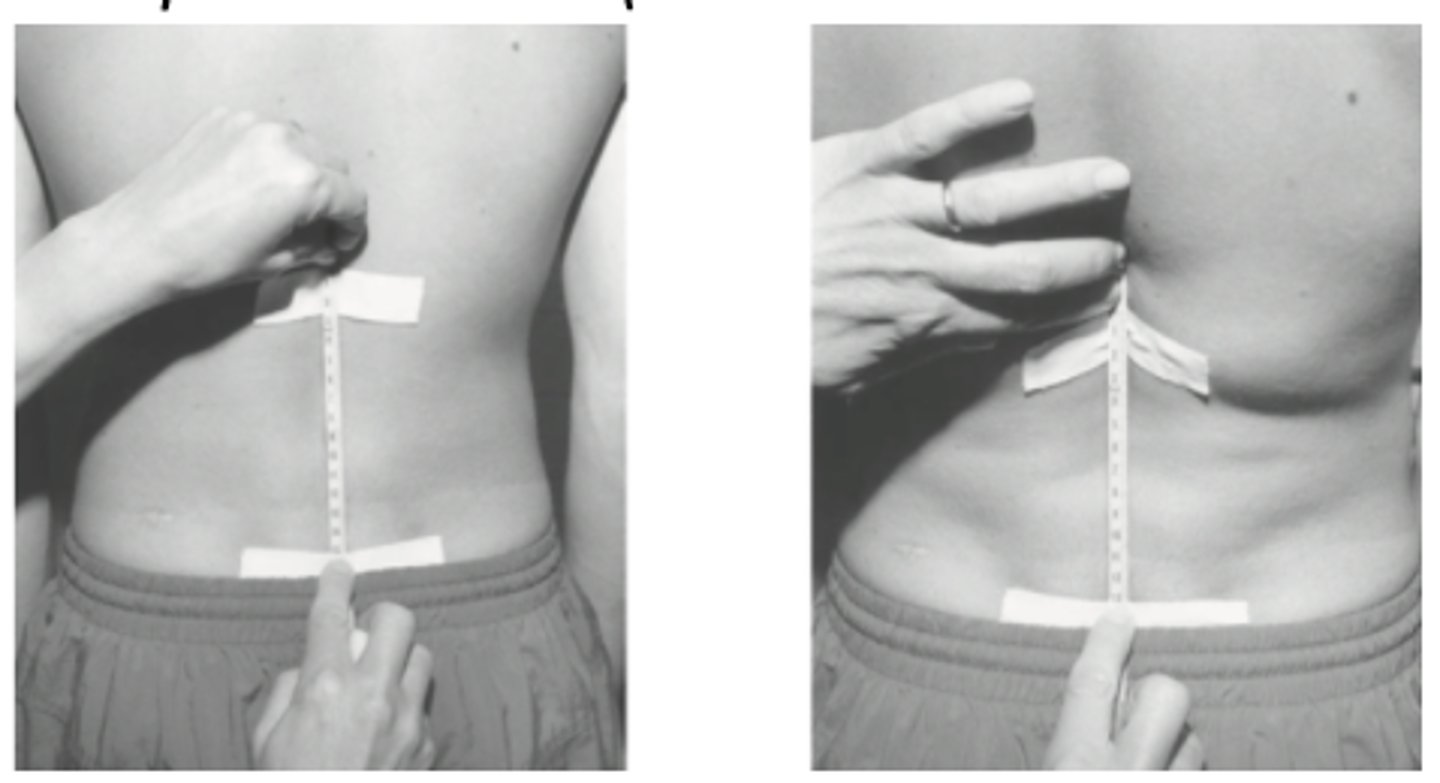
thoracolumbar SB
S2 and inline with C7
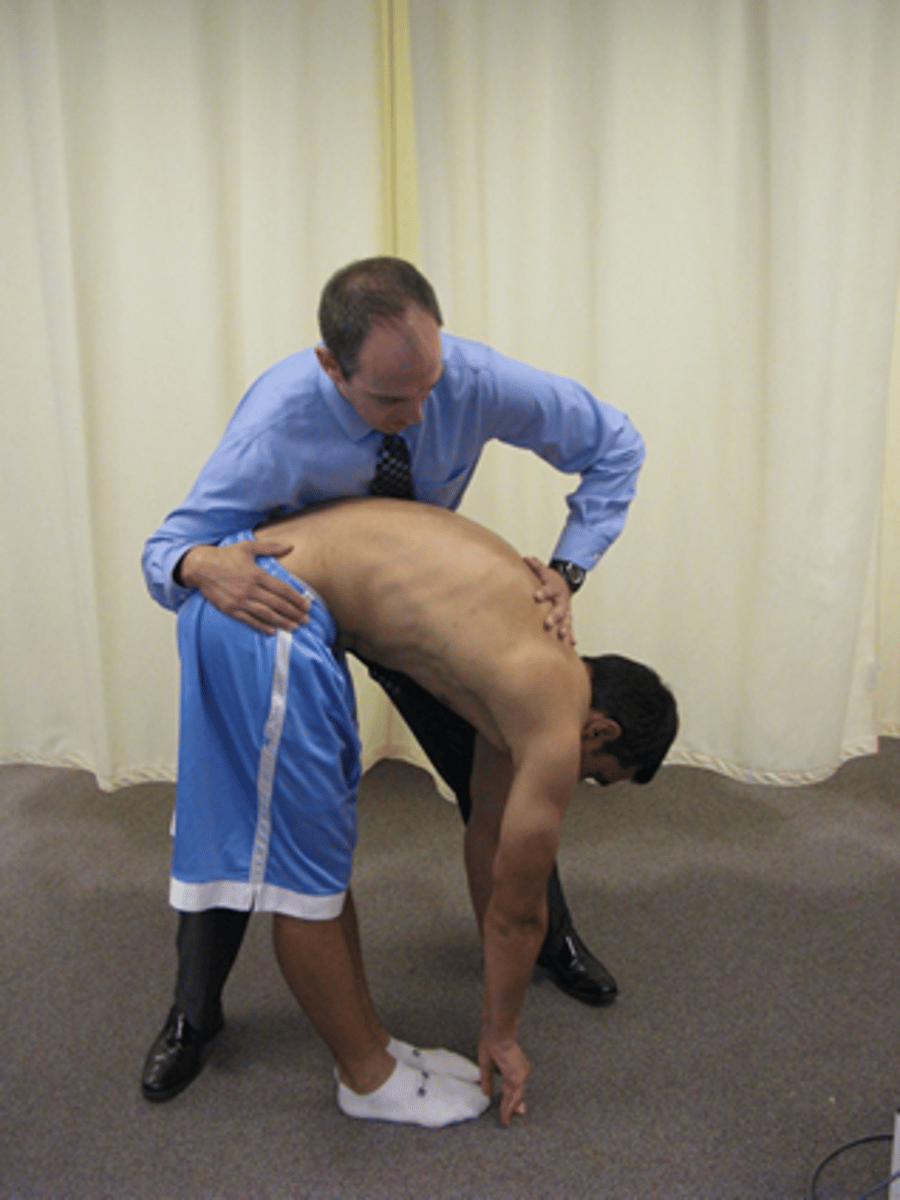
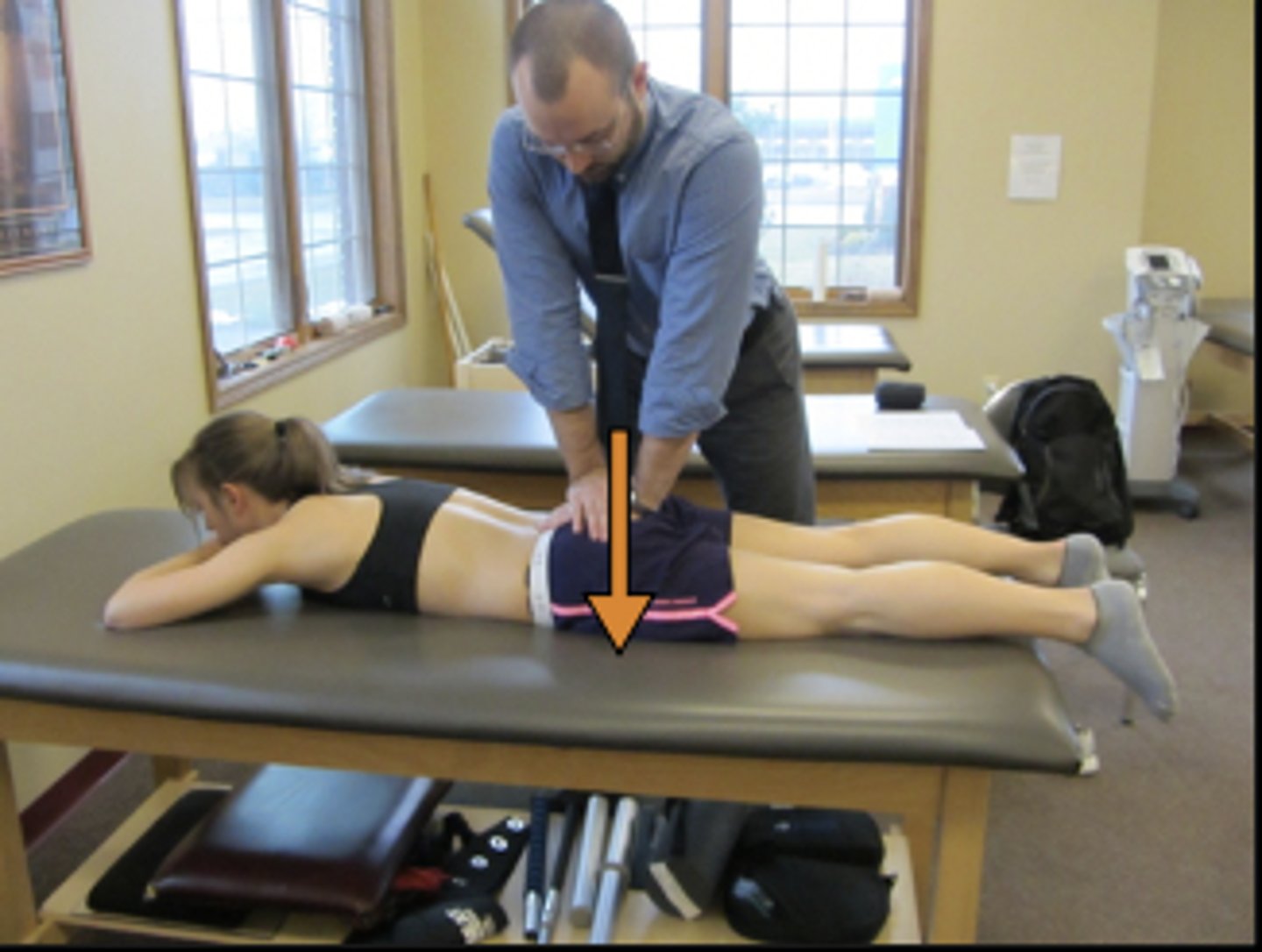
lumbar flexion overpressure
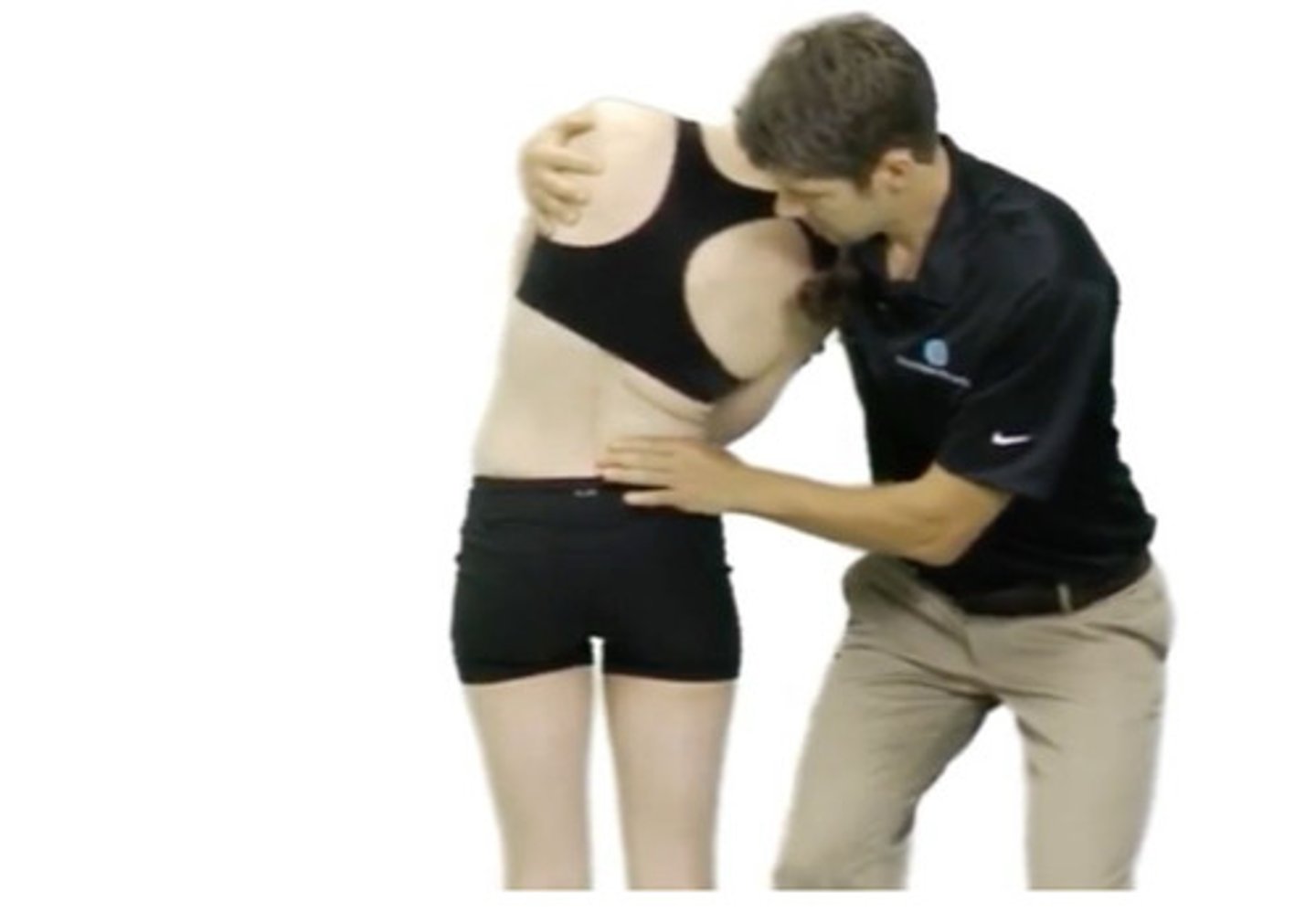
lumbar extension overpressure
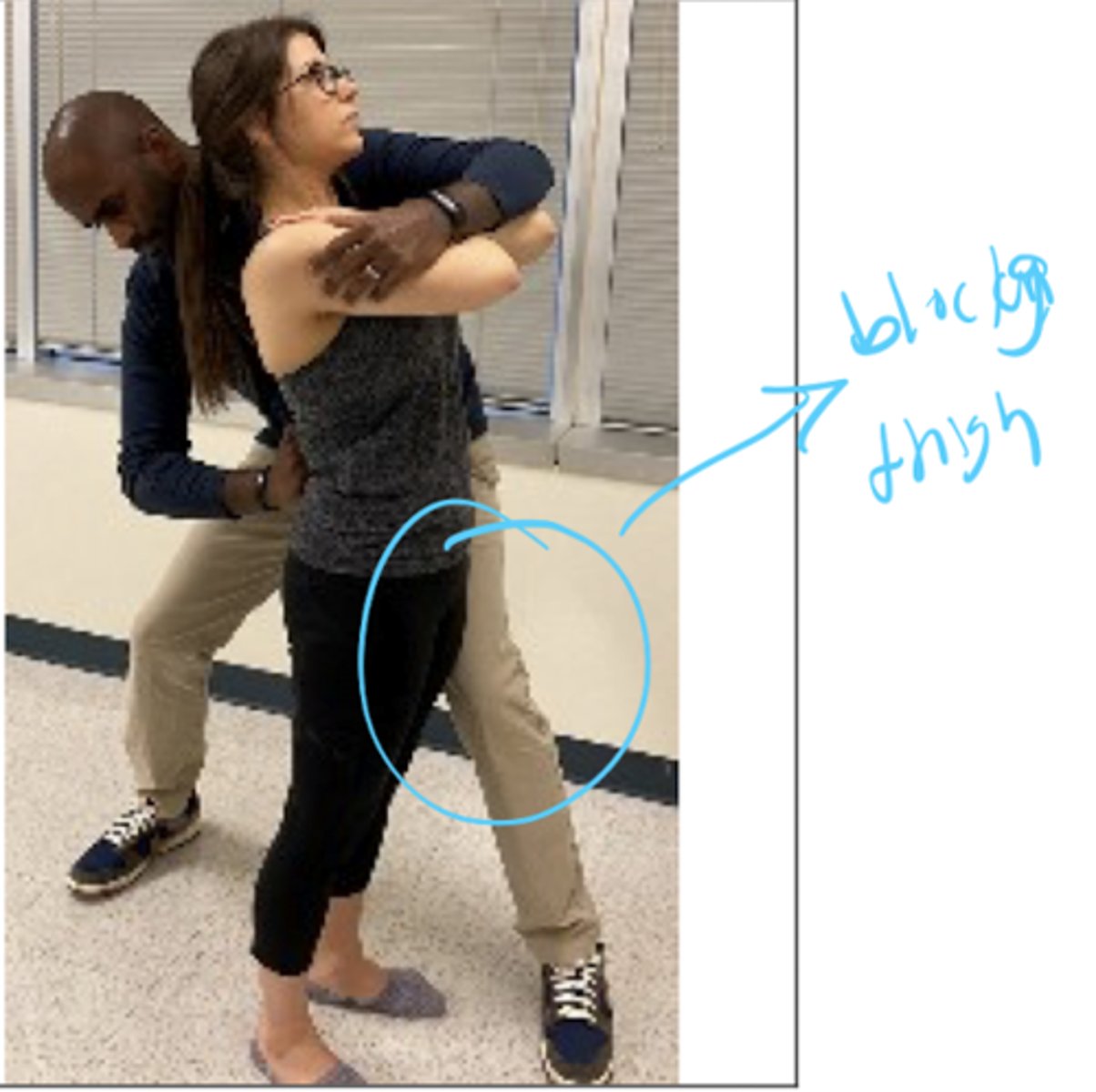
lateral flexion overpressure
mckenzie lateral shift correction
pull pelvis towards you and hold 10-15 seconds
+ if increased symptoms on affected side
if pt has a lateral shift deformity, an opposite side glide will help determine if it is correctable
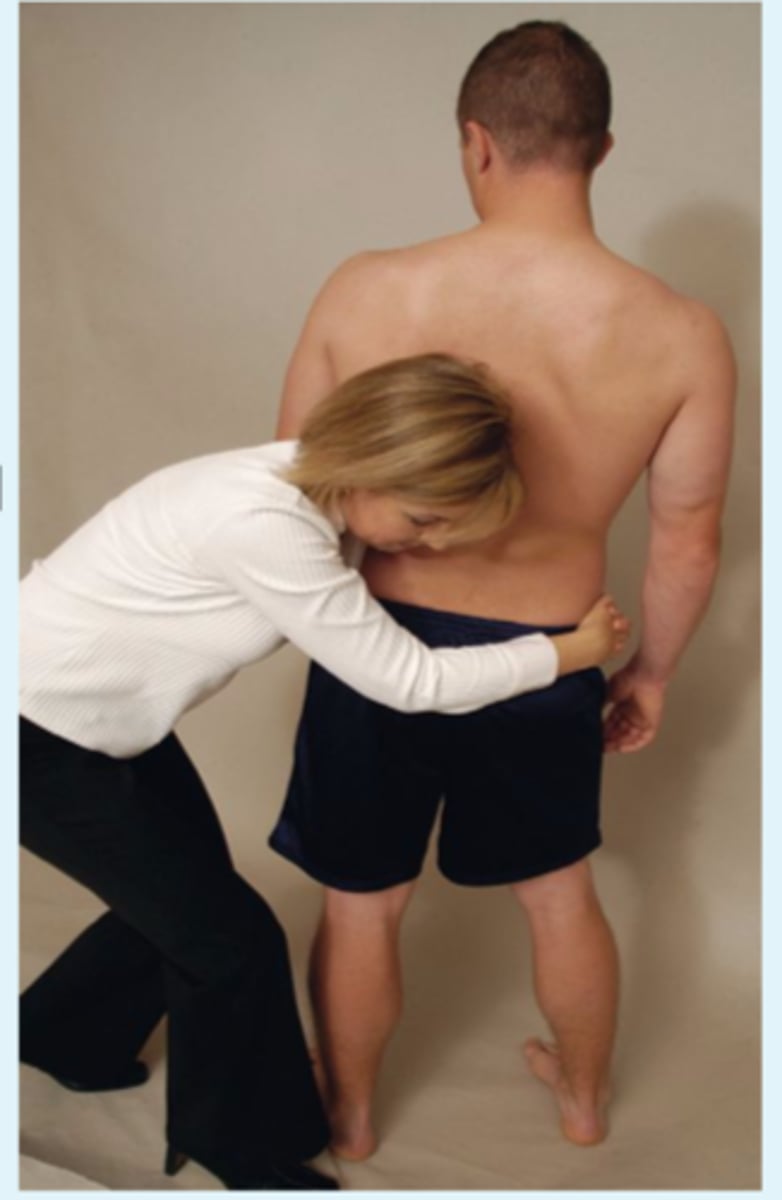
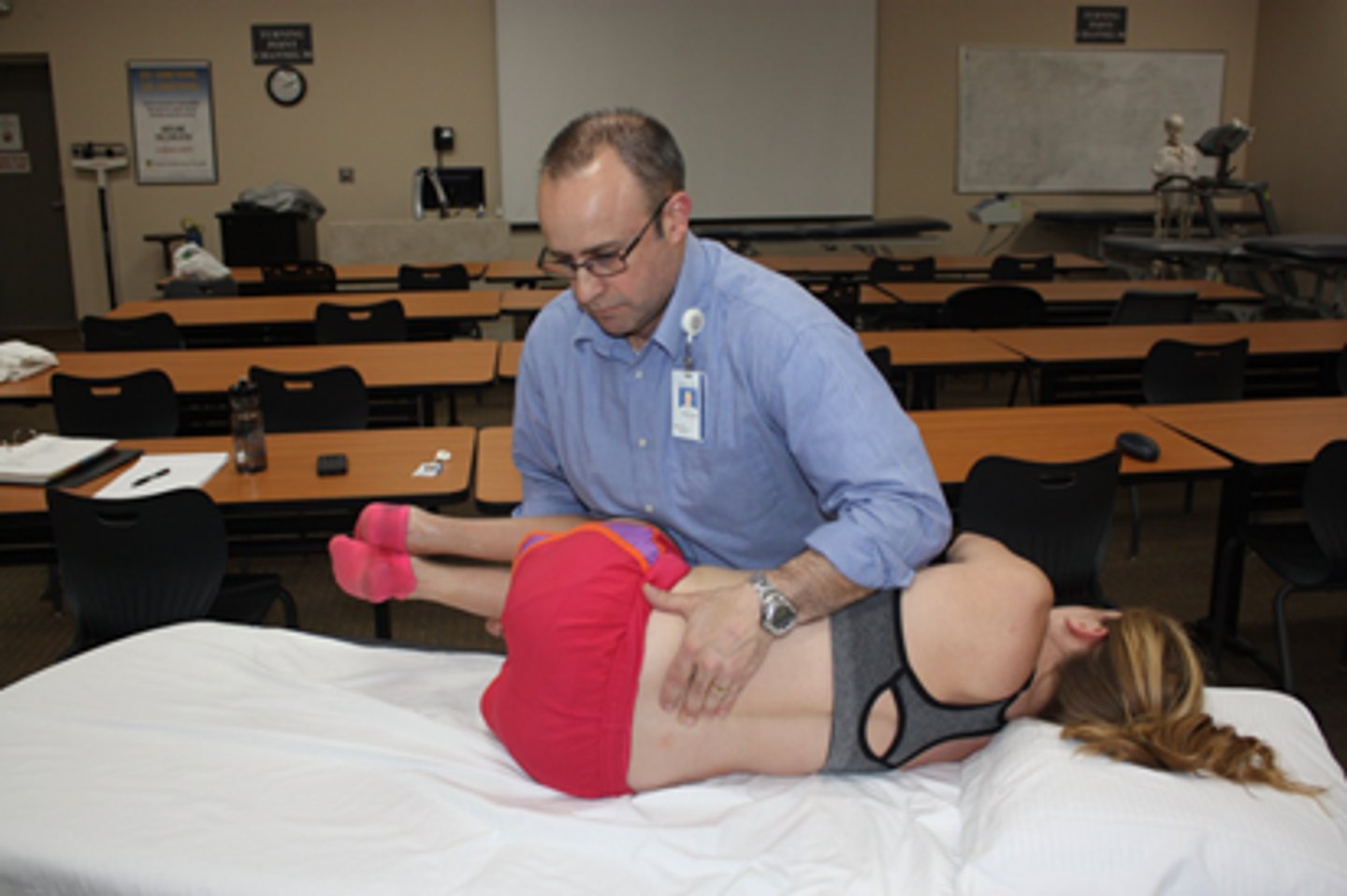
flexion PPIVM
SP should gap with flexion
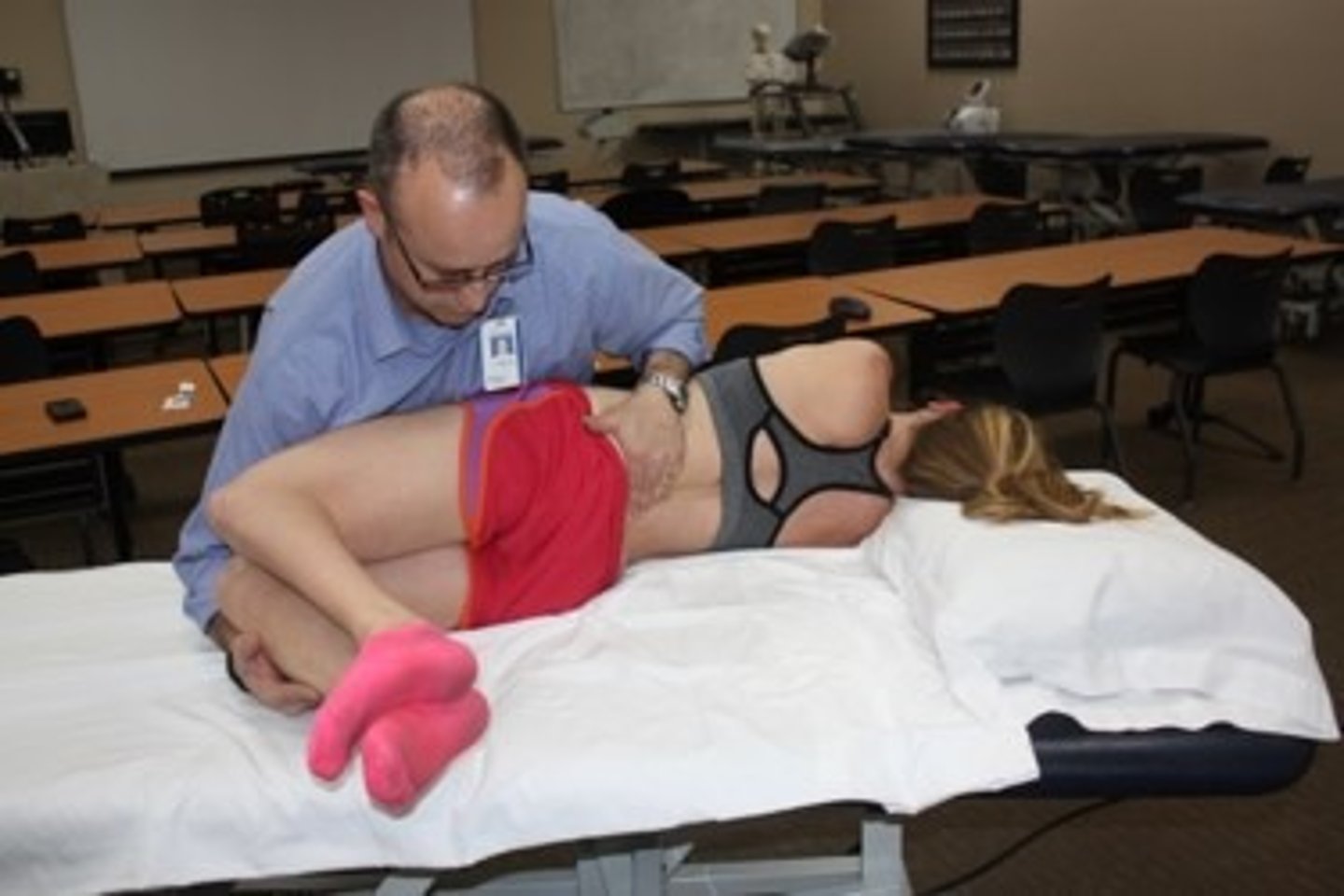
extension PPIVM
SPs should compress with extension
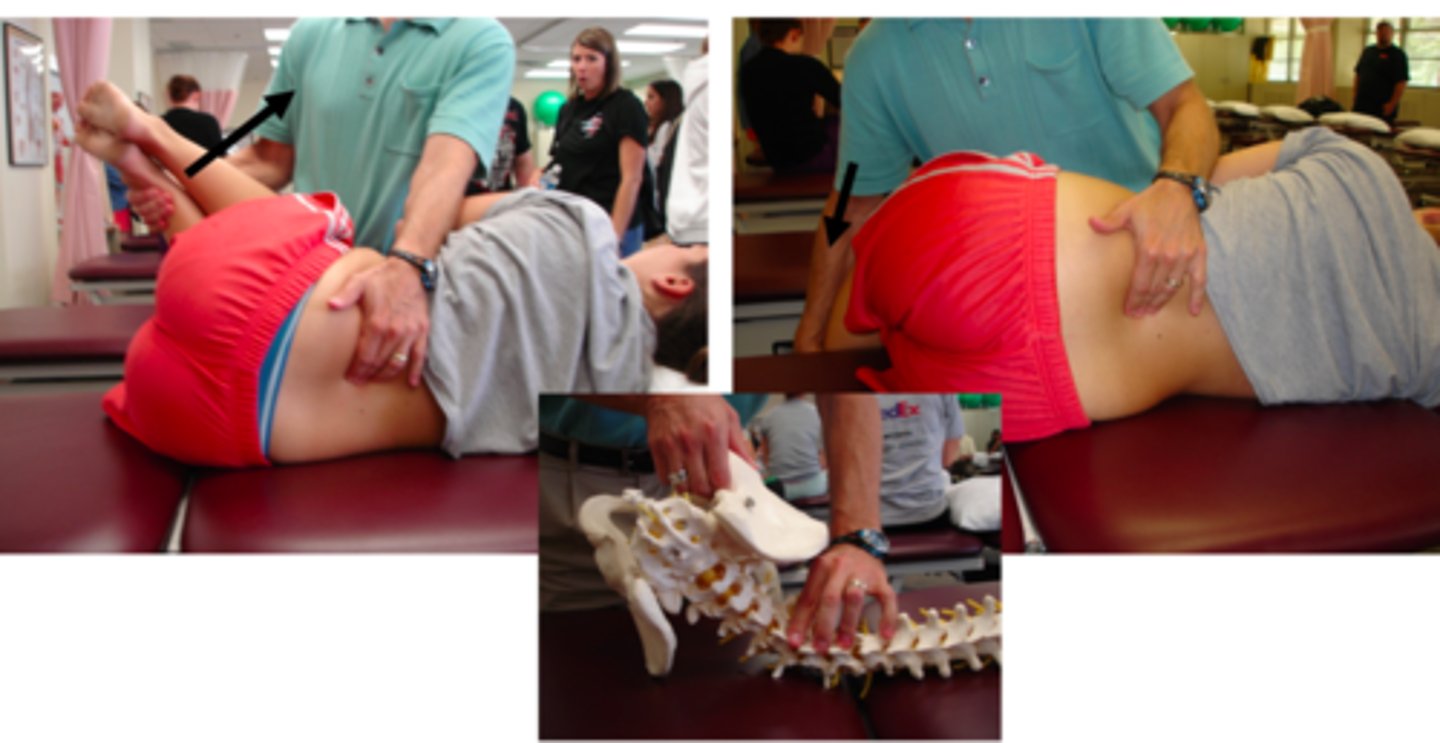
sidebending PPIVM
R sidelying: SP should gap on the R and compress on the L
L sidelying: SP should gap on the L and compress on the R
L2 dermatome
anterior mid-thigh
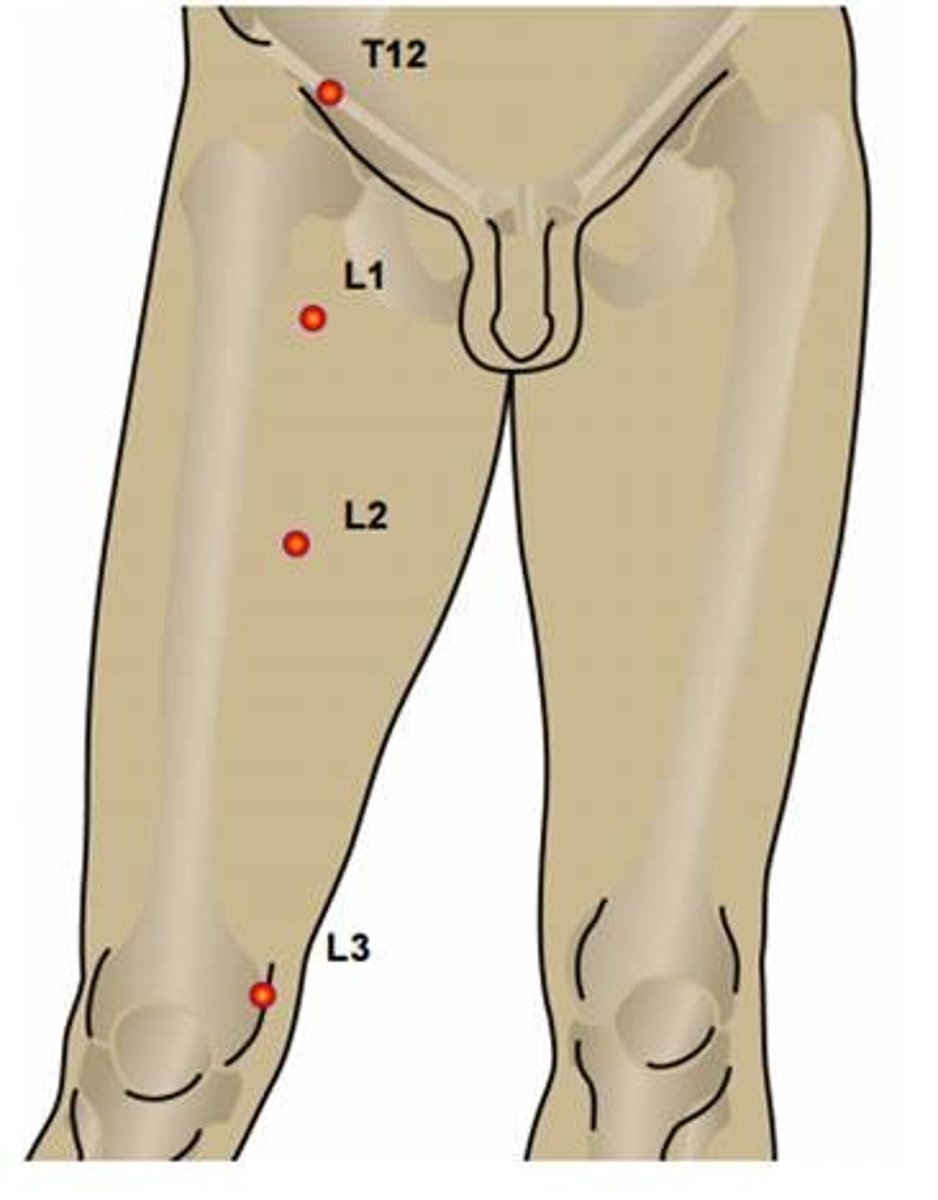
L3 dermatome
medial side of the knee joint
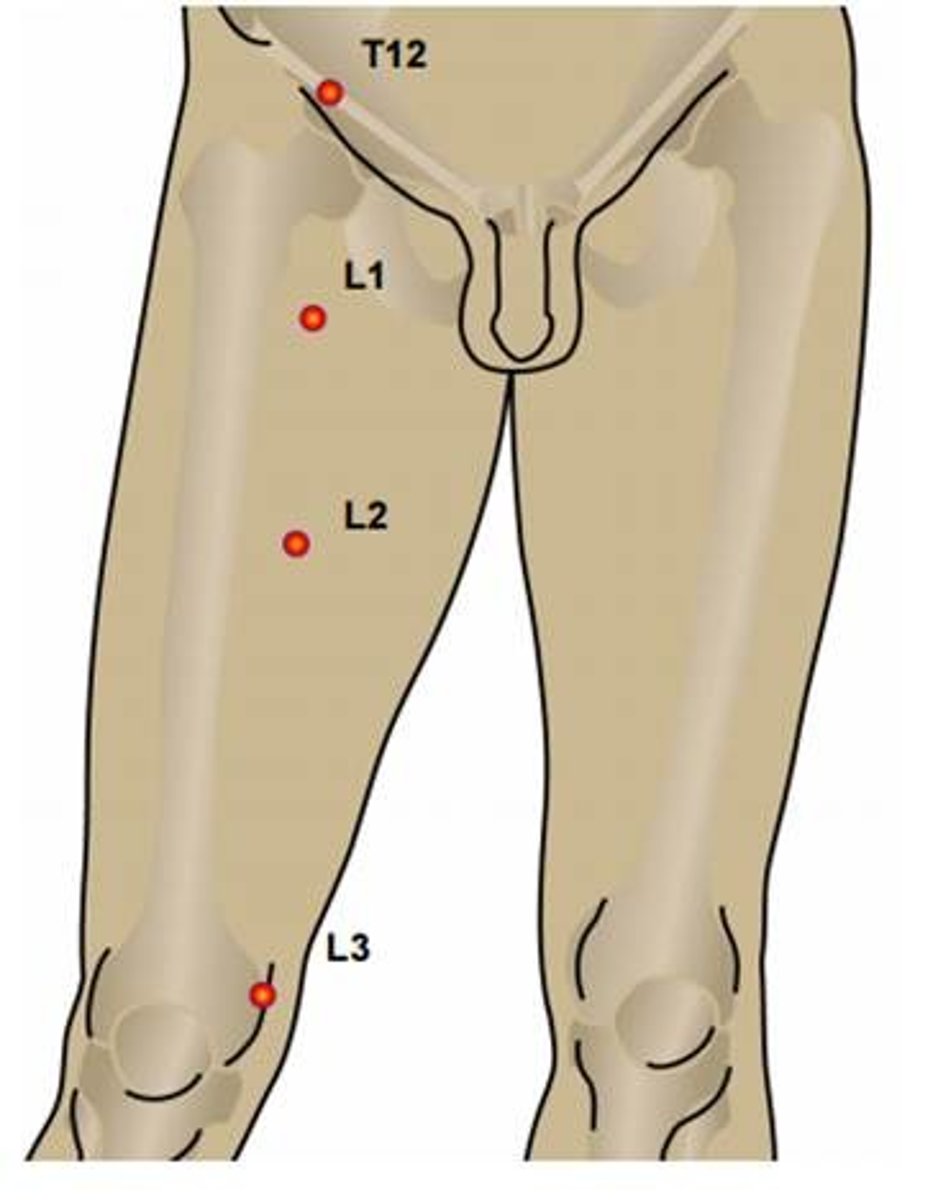
L4 dermatome
medial lower leg and foot
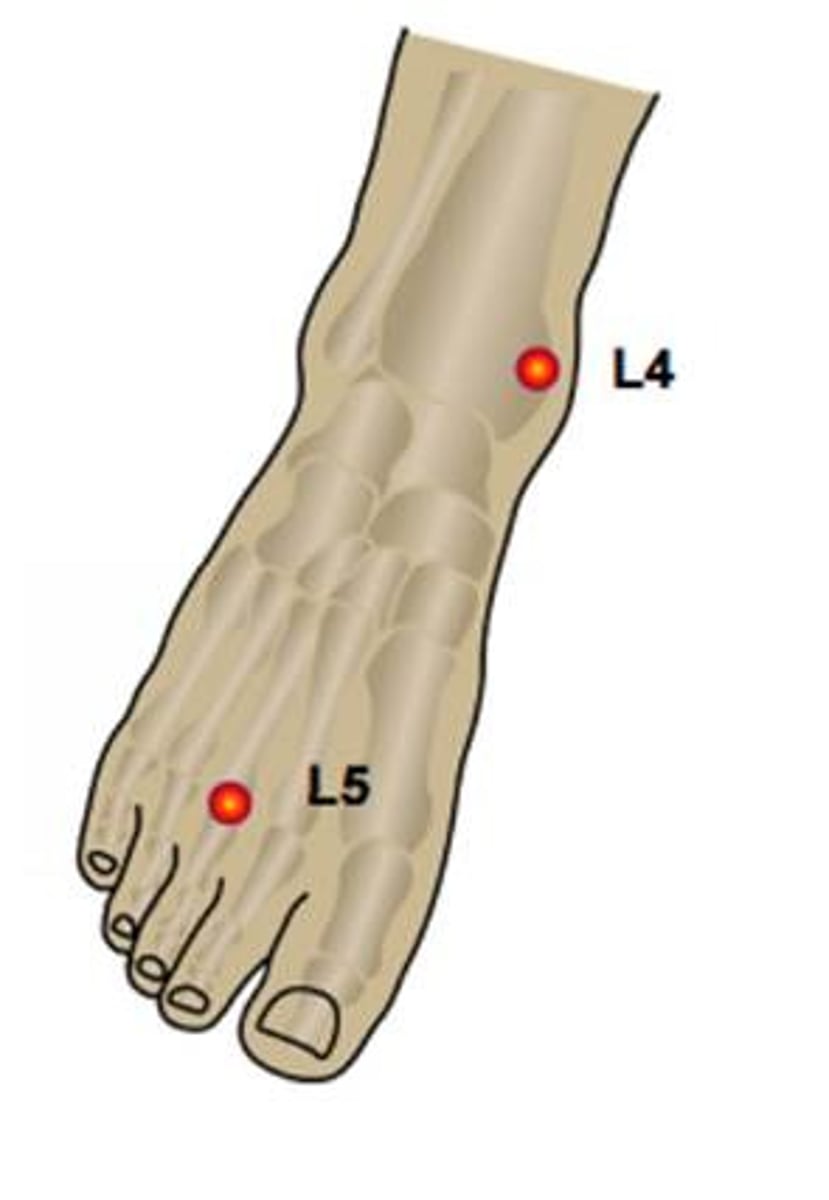
L5 dermatome
anterolateral leg to the dorsum of the foot
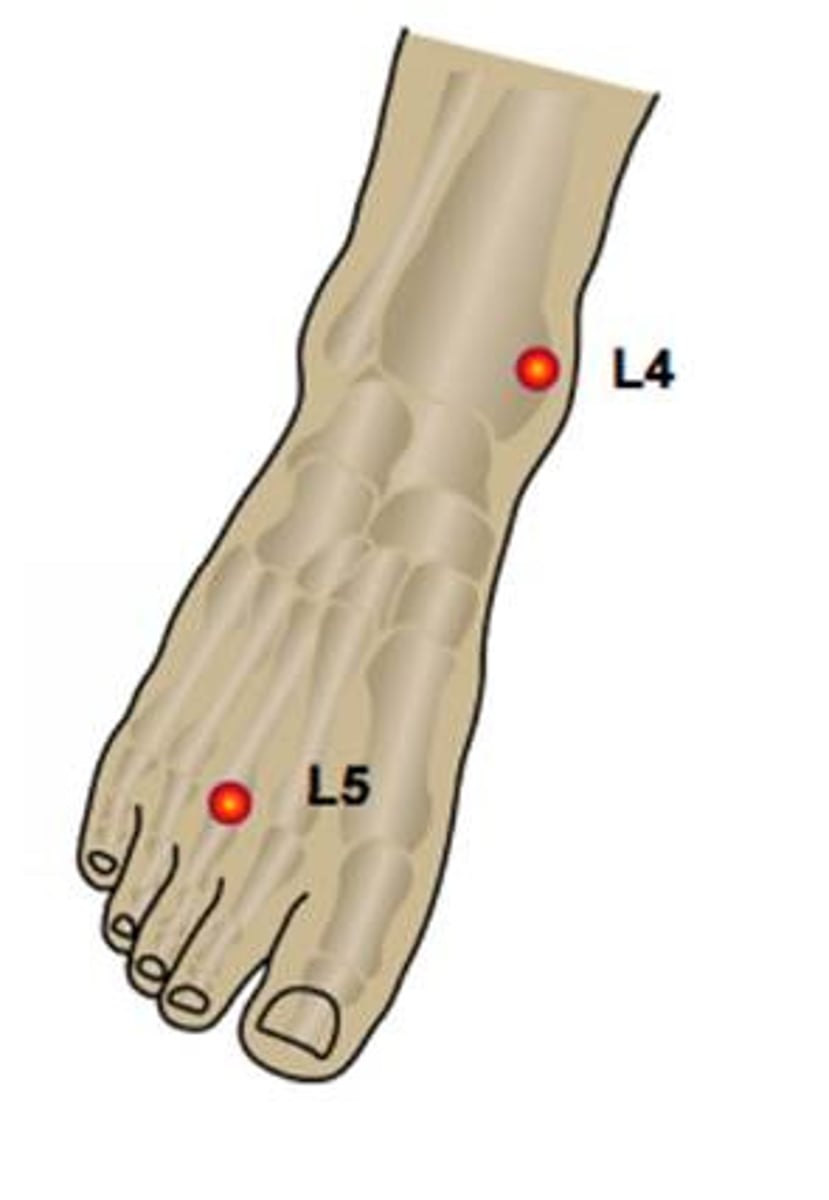
S1 dermatome
lateral side of the foot
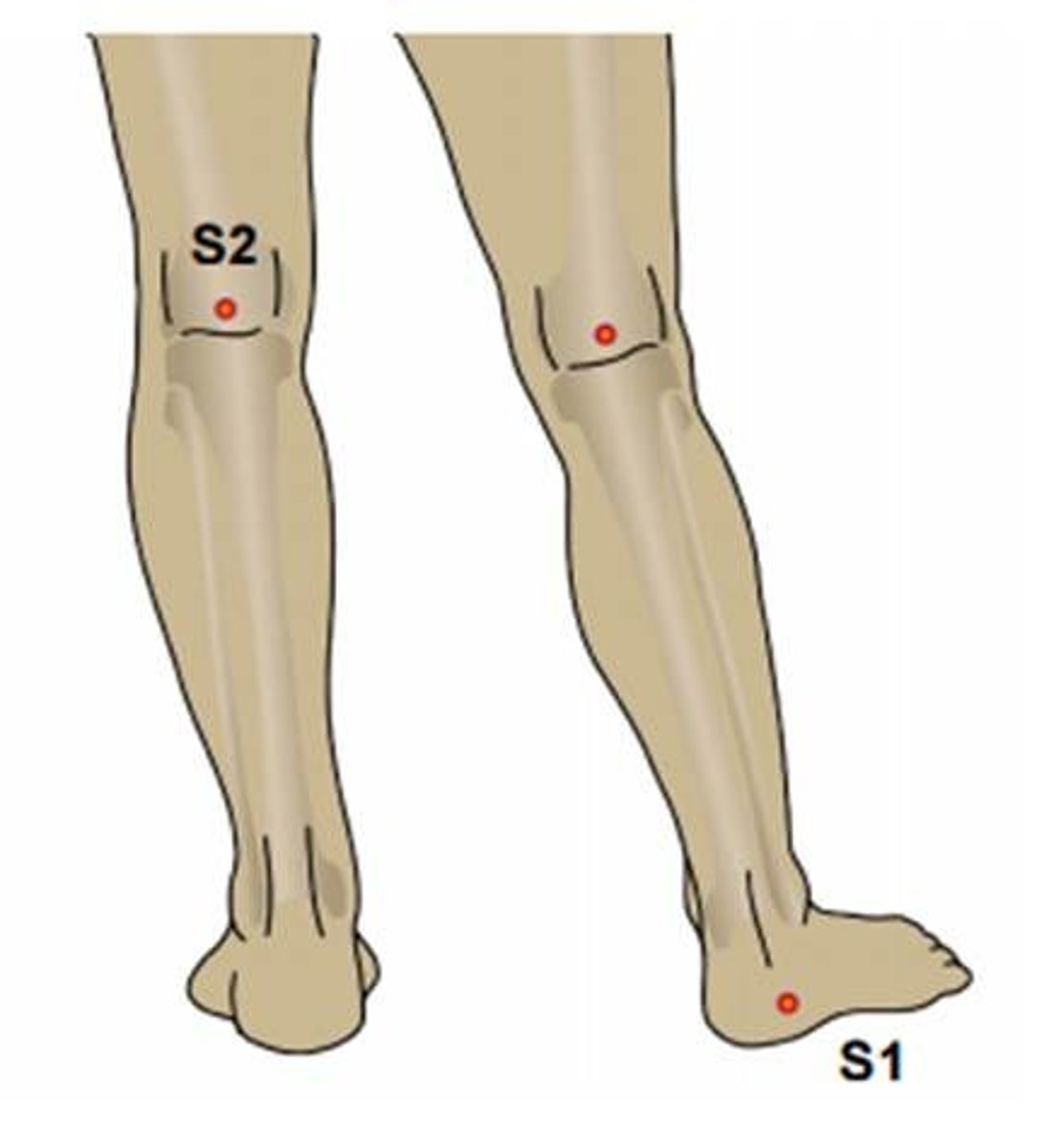
S2 dermatome
mid posterior thigh and calf and plantar surface of the foot
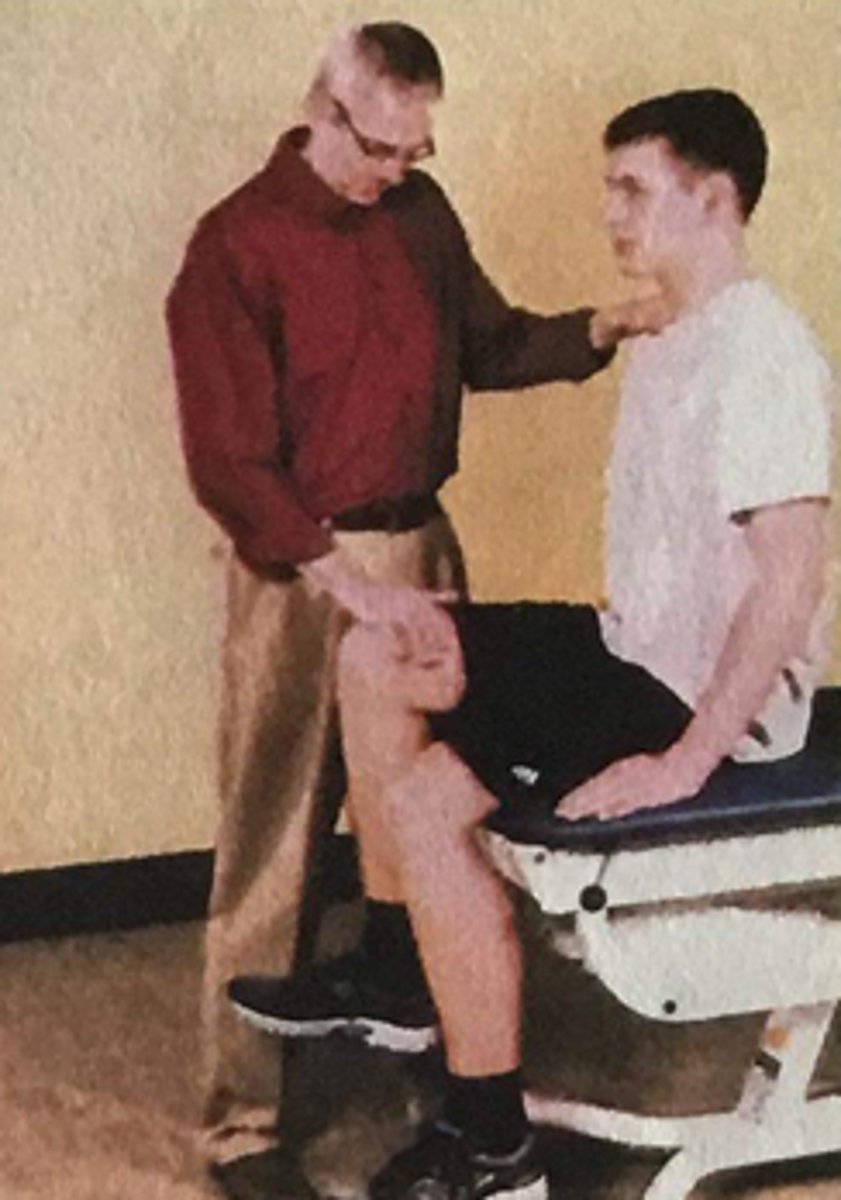
L2 myotome
resisted hip flexion
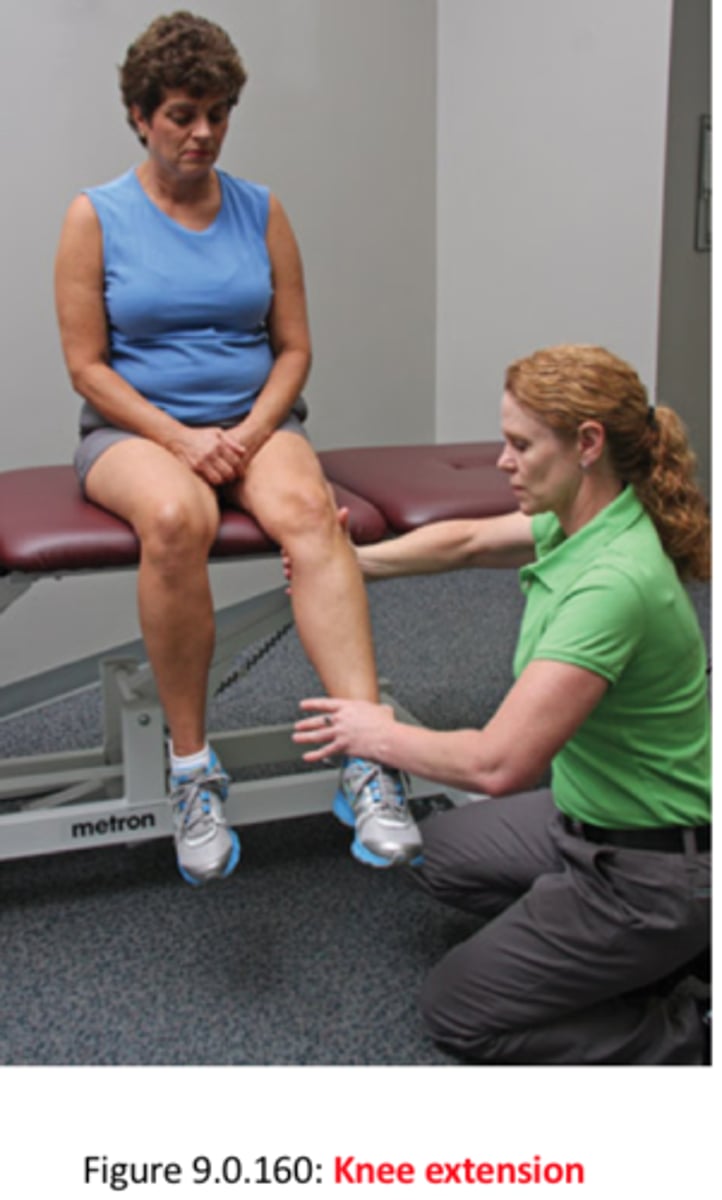
L3 myotome
resisted knee extension
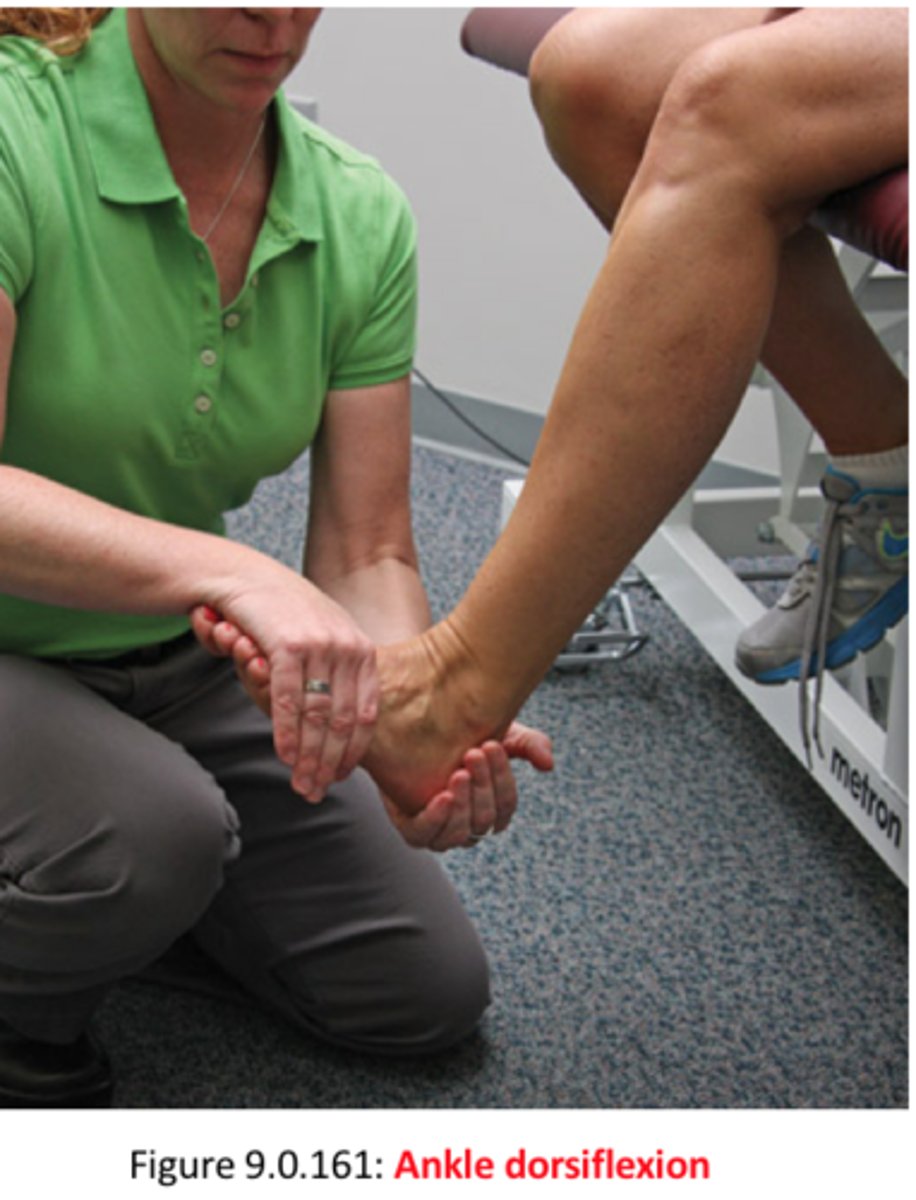
L4 myotome
resisted DF and inversion
L5 myotome
resisted great toe extension
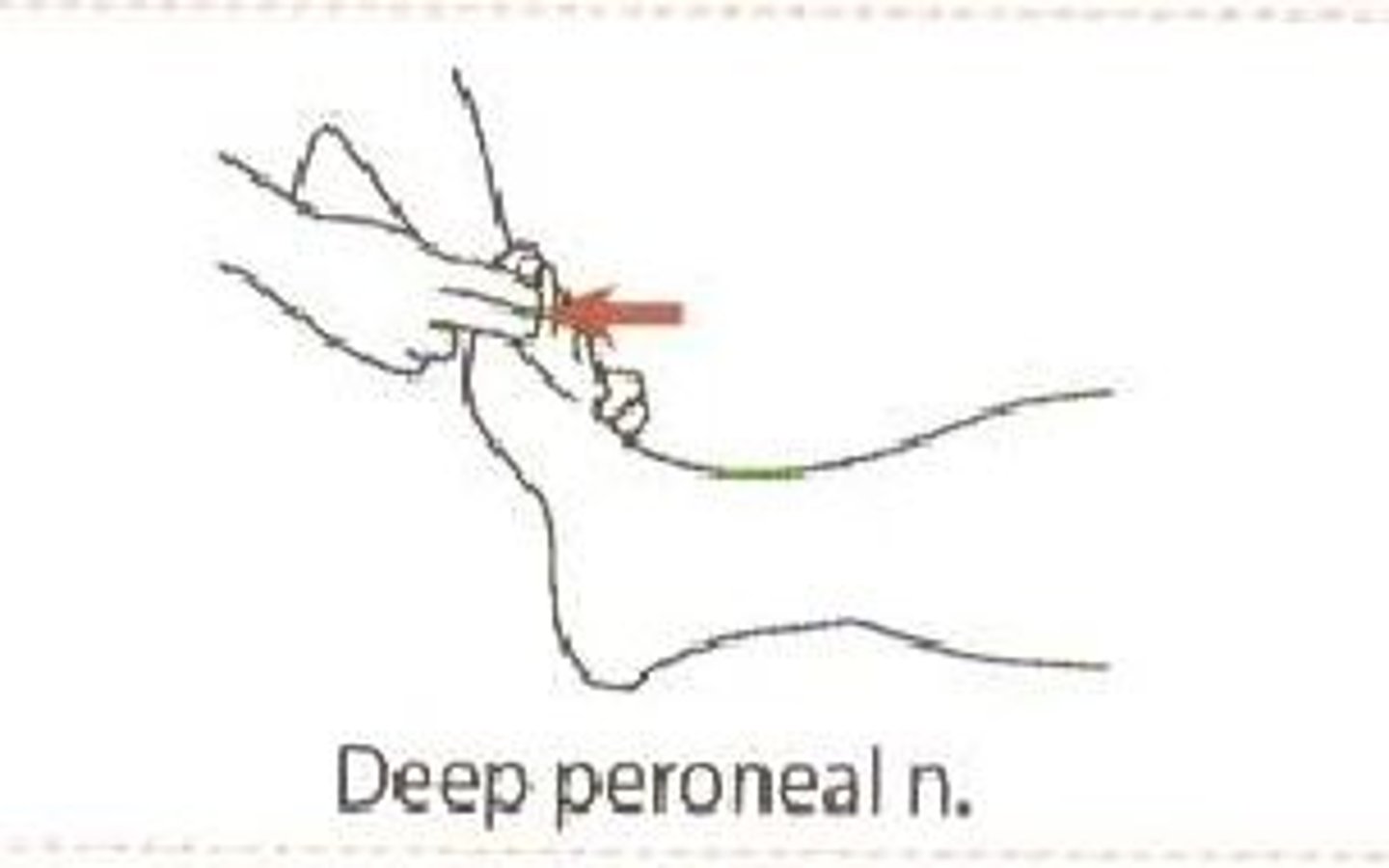
S1 myotome
resisted ankle PF and eversion
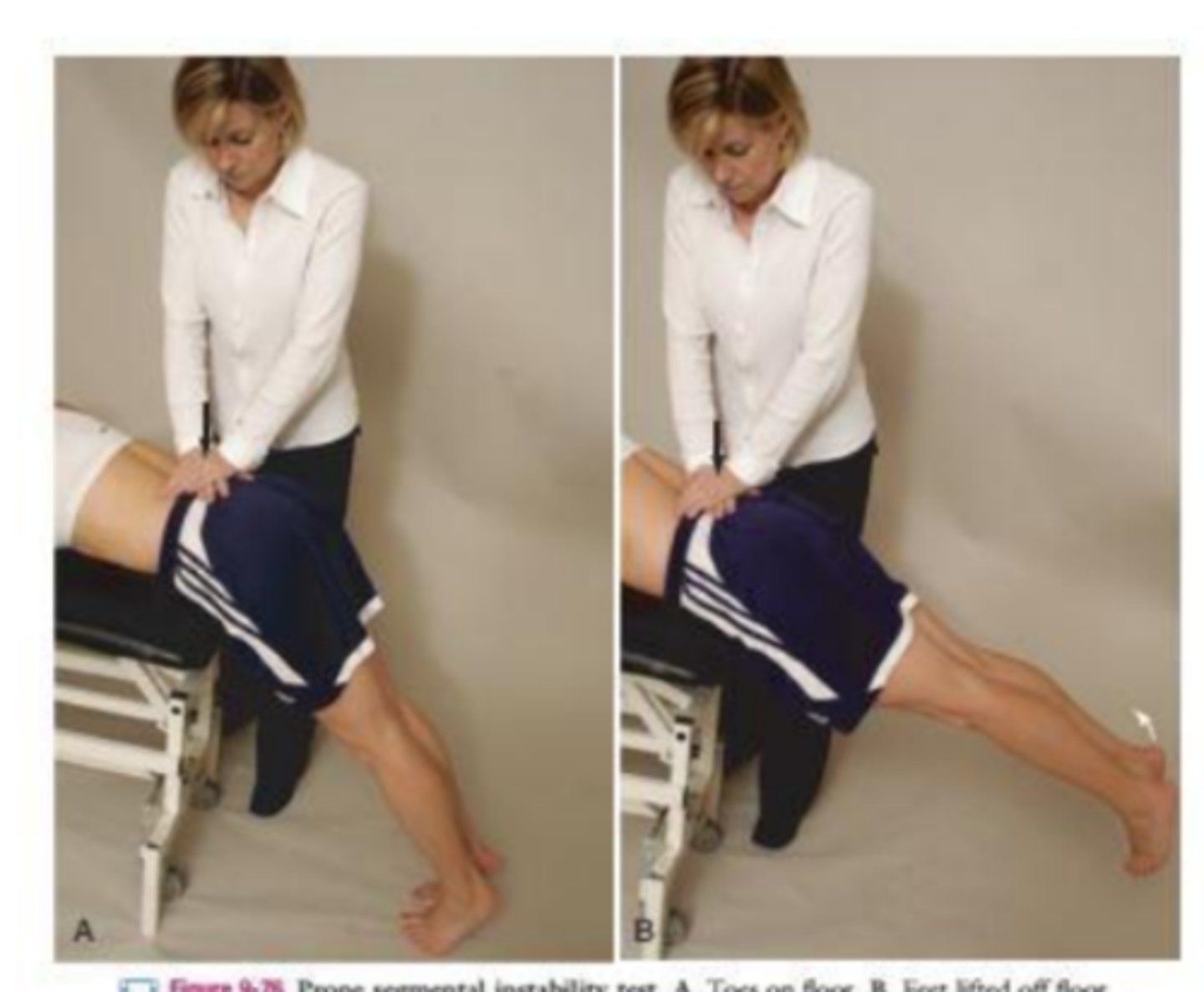
prone instability test
+ test if pain is present in first part, but subsides in second part
part of CPR for lumbar instability
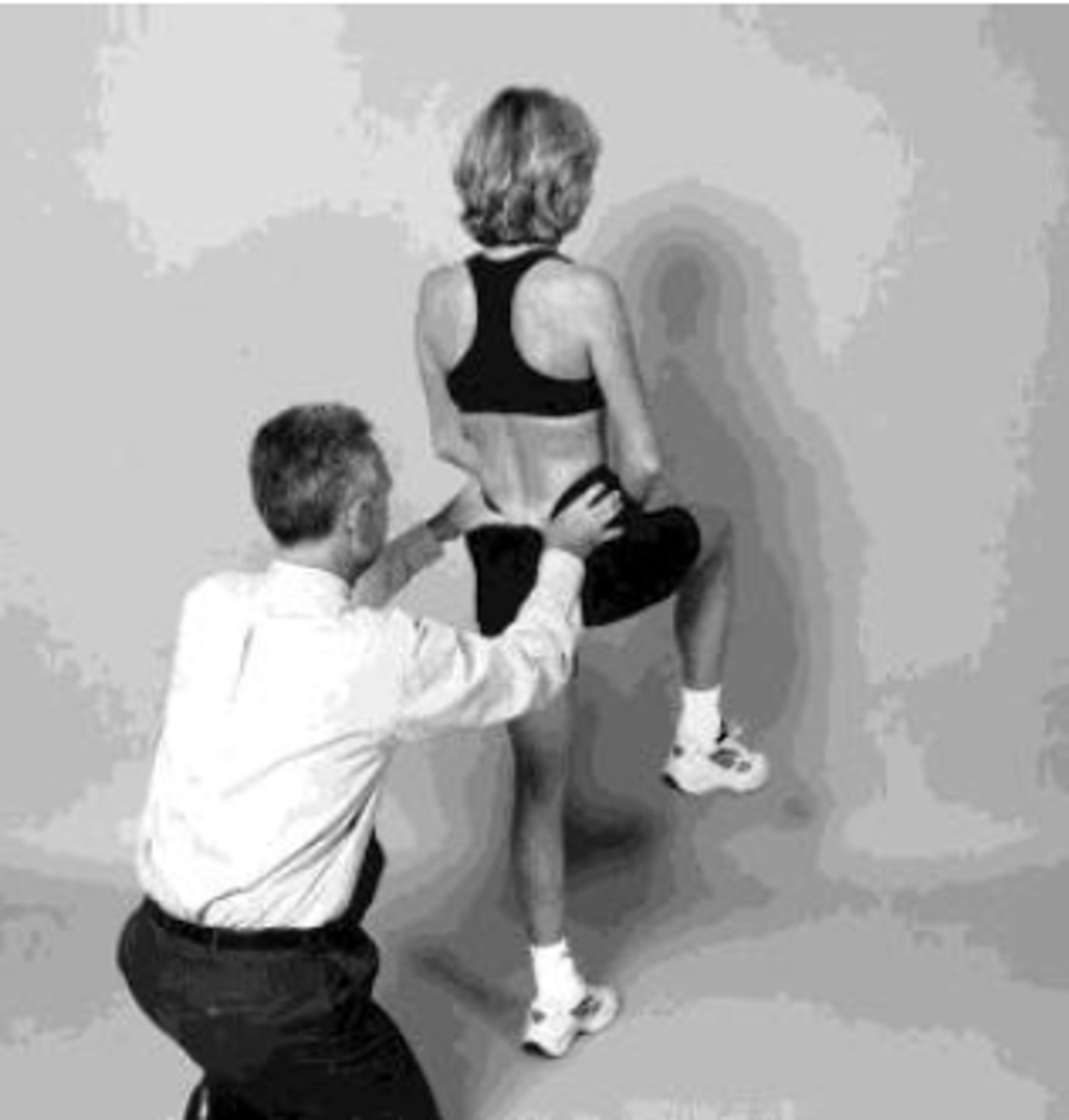
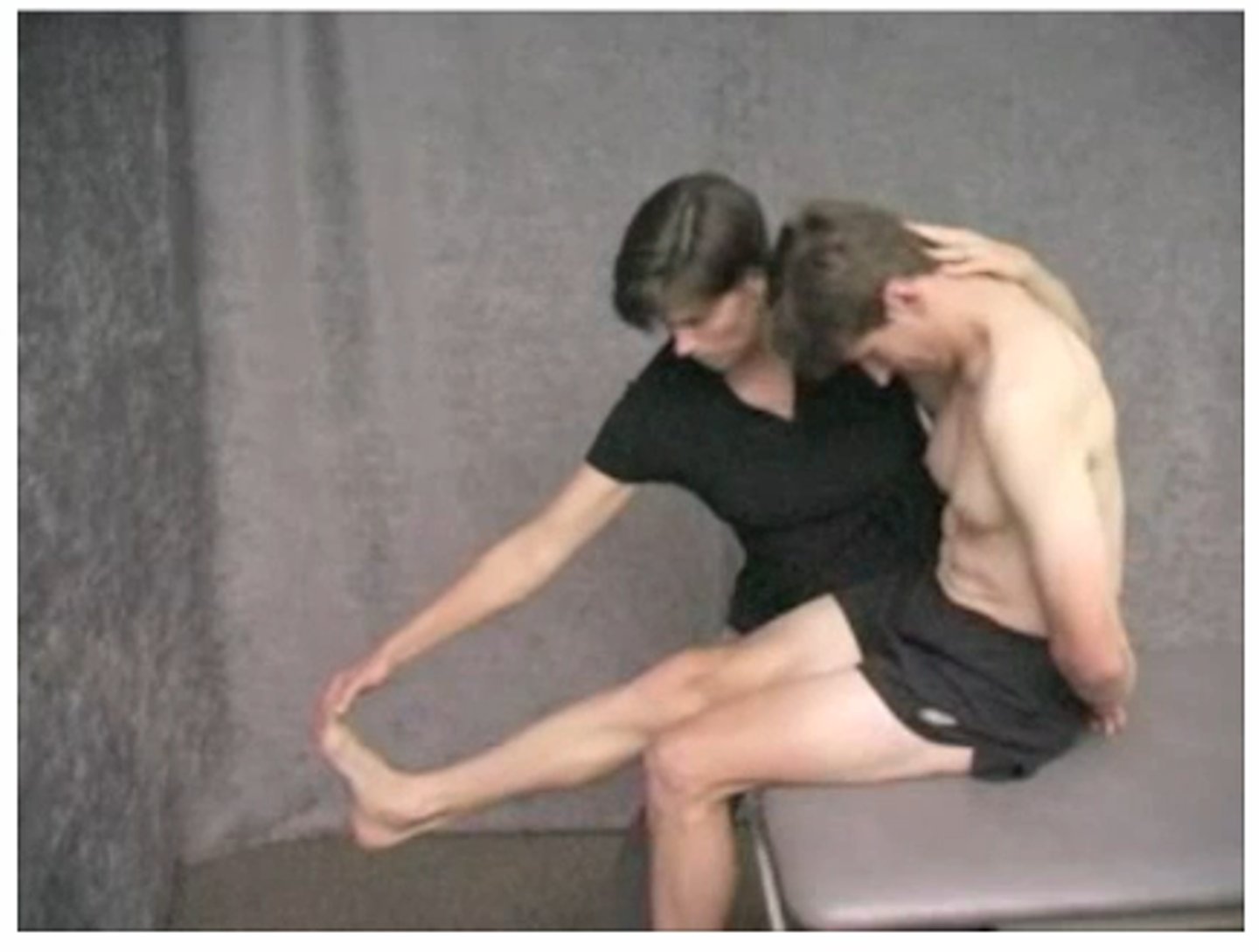
stork standing test
(+) for pars interarticularis defect on loaded side
palpate both PSIS

slump test
identifies dysfunction of neurological structures supplying the lower limb
+ if symptoms earlier in motion and asymmetrical
sacral thrust test
6 vigorous downward thrusts at S2-S3
+ if concordant sign is produced
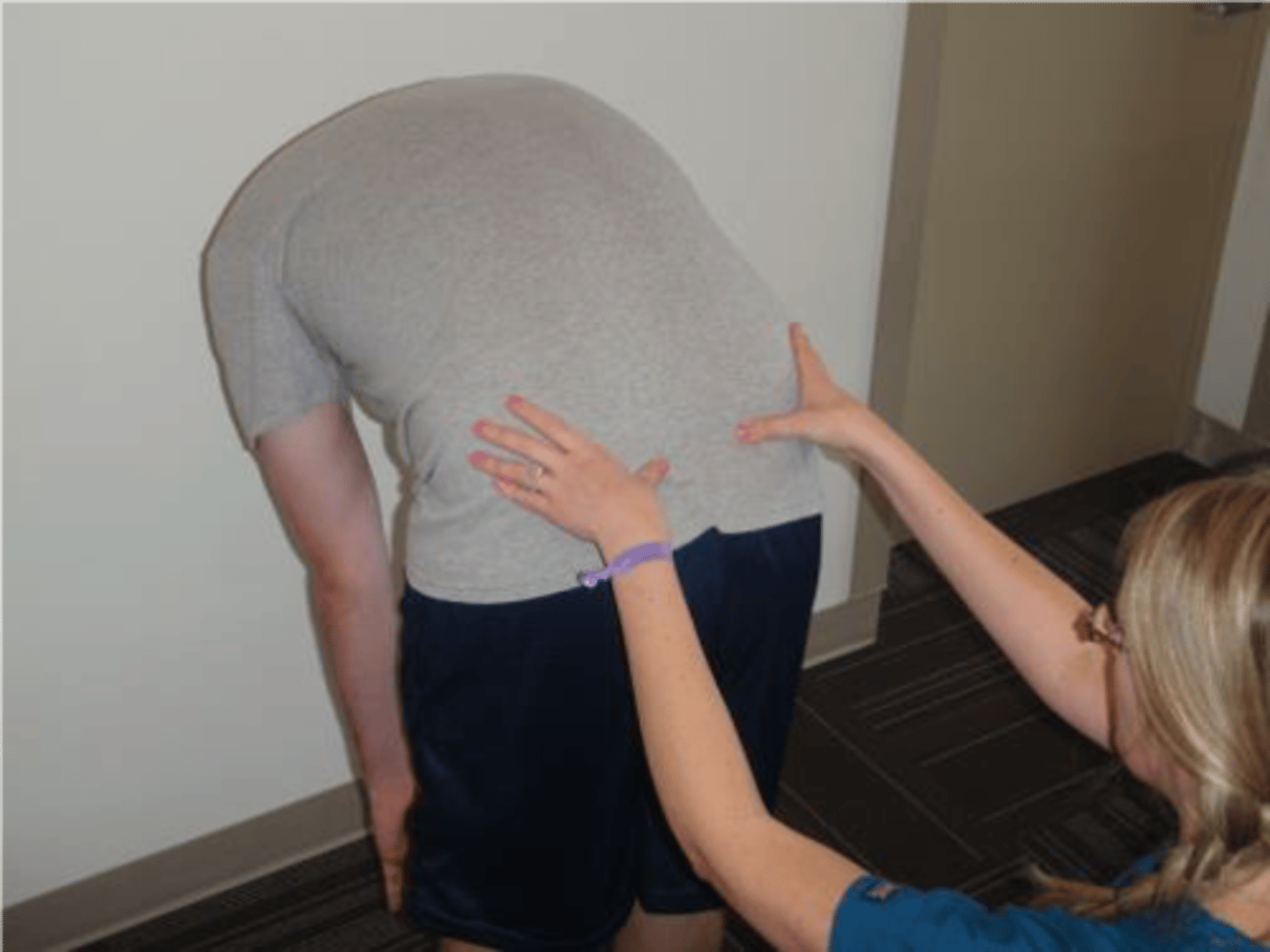
flexion in standing test
palpate both PSIS
+ test if asymmetry of motion of one PSIS relative to the other
testing for motion restriction
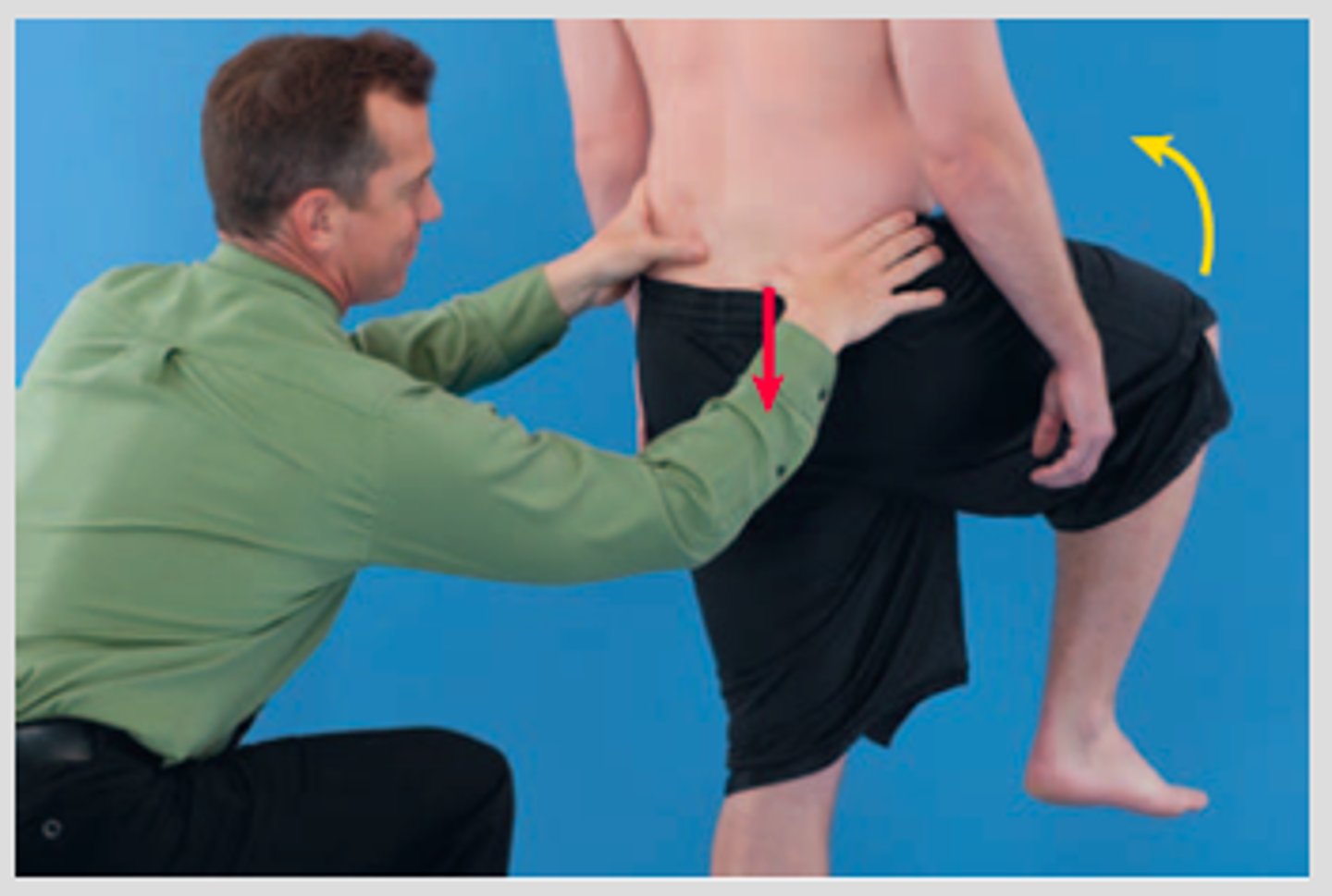
gillet's test
palpate both PSIS or PSIS and S2
should have inferior and lateral movement of tested PSIS relative to the sacrum
+ test if no inferior movement or PSIS moves anterior of thumb on PSIS
alternate gillet test
patient standing with equal weight through each leg
- therapist palpates the innominate bone, PSIS, and sacrum by placing the R thumb directly on R PSIS with the rest of the R hand contacting the R innominate bone
- palpate S2 with L thumb
- patient actively flexes the CL hip into 90 degrees of flexion and 90 knee flexion
- + test if R PSIS moves upward
- (-) test if unchanged
supine to long sit test
therapist passively flexes both legs and then extends them
- compare positions of the malleoli in supine and then compare when patient comes into sitting
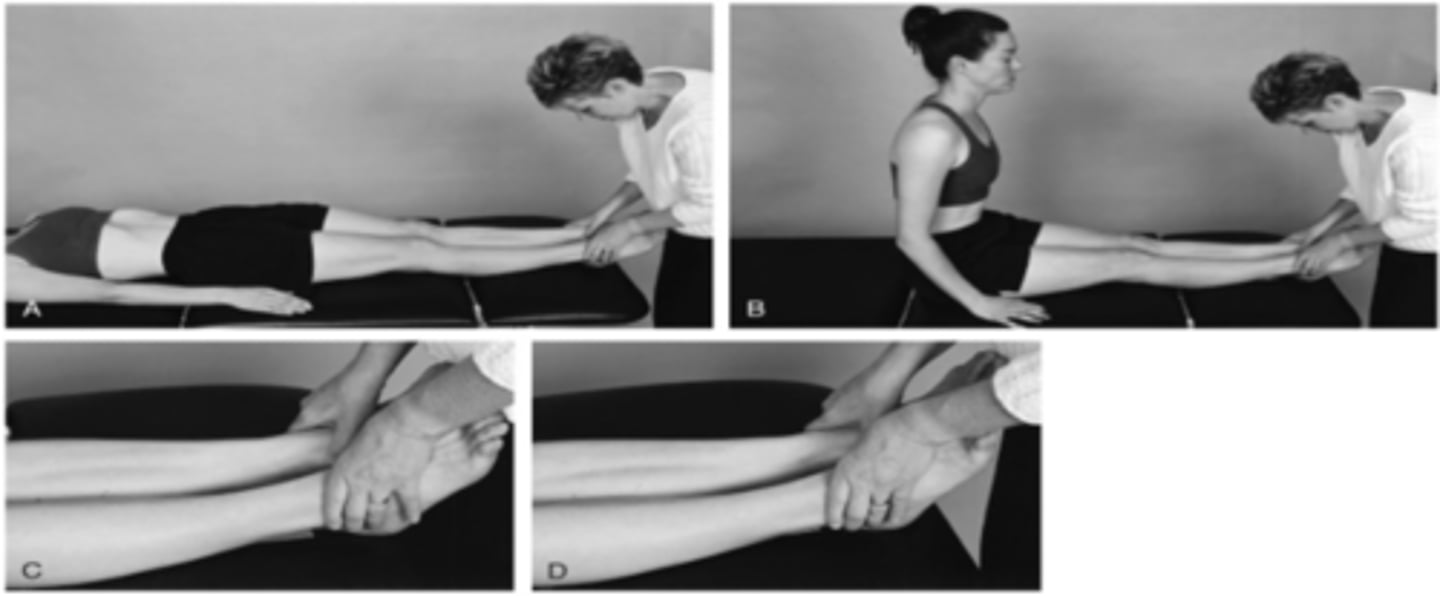
anterior
if a patient's leg moves from long to short the innominate is _____
posterior
if a patient's leg moves from short to long the innominate is _____
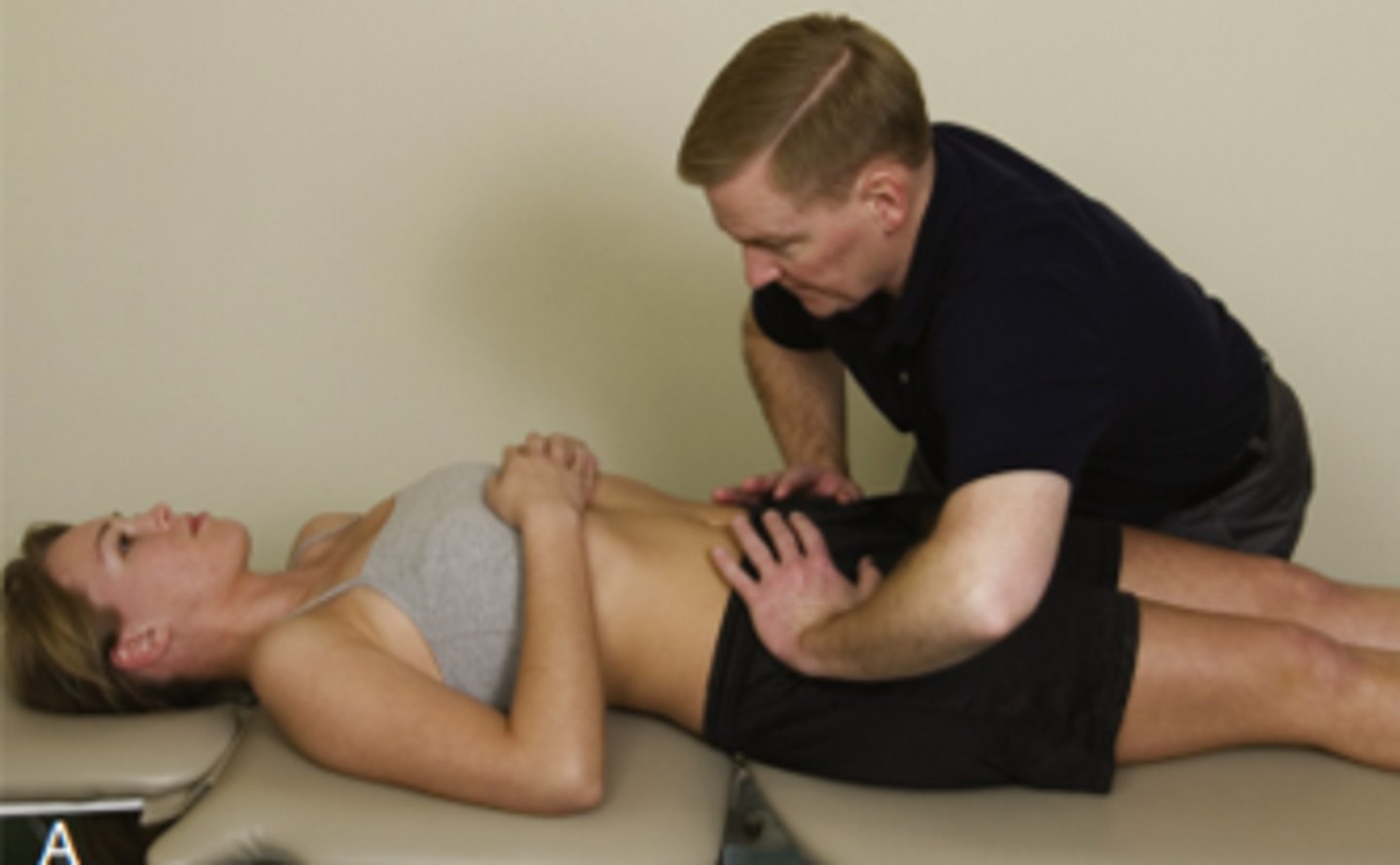
SIJ compression
compresses posteriorly and distracts anteriorly
+ if concordant pain is reproduced
SIJ distraction
compresses anteriorly and gaps posteriorly
+ if concordant pain is reproduced
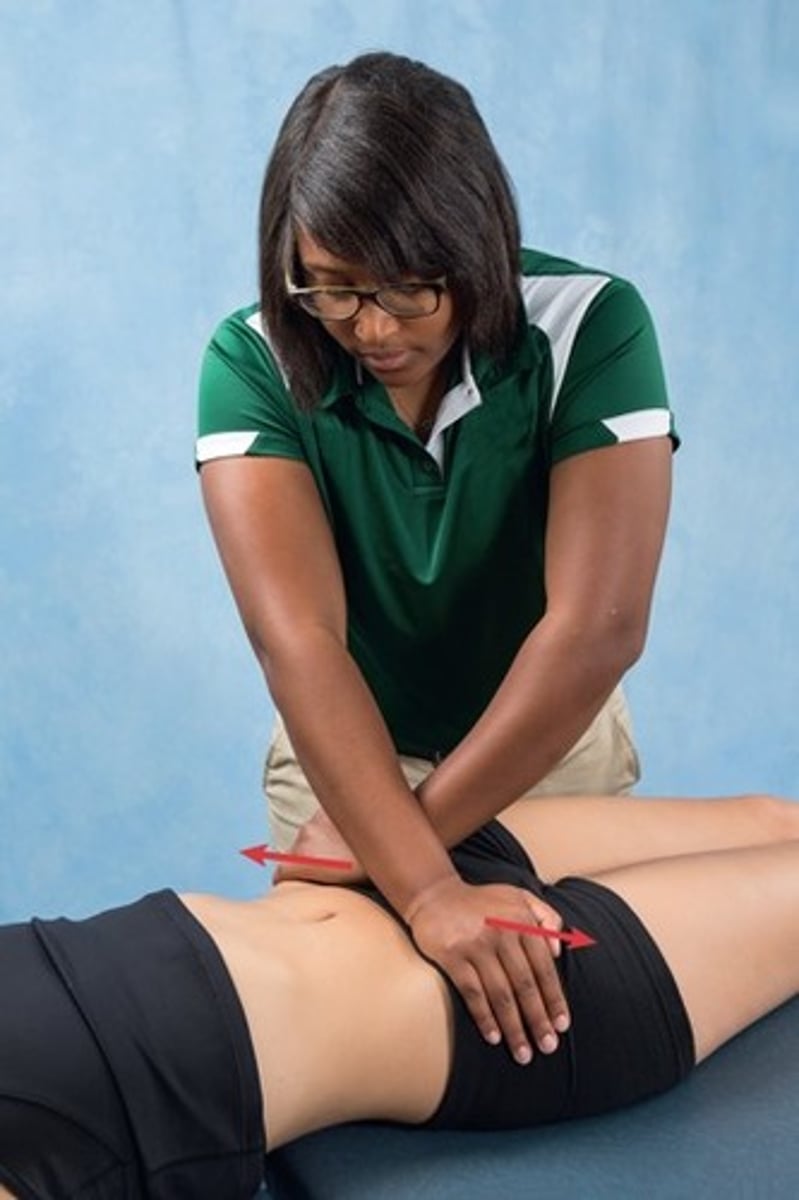
active SLR
+ test: when the patient is able to lift the leg higher and/or has
decreased symptoms with the leg lift when PT compresses SIJ
POSH test
hand under sacrum and push posteriorly through the femur at varying angles of abd/add
+ if buttock pain is reproduced
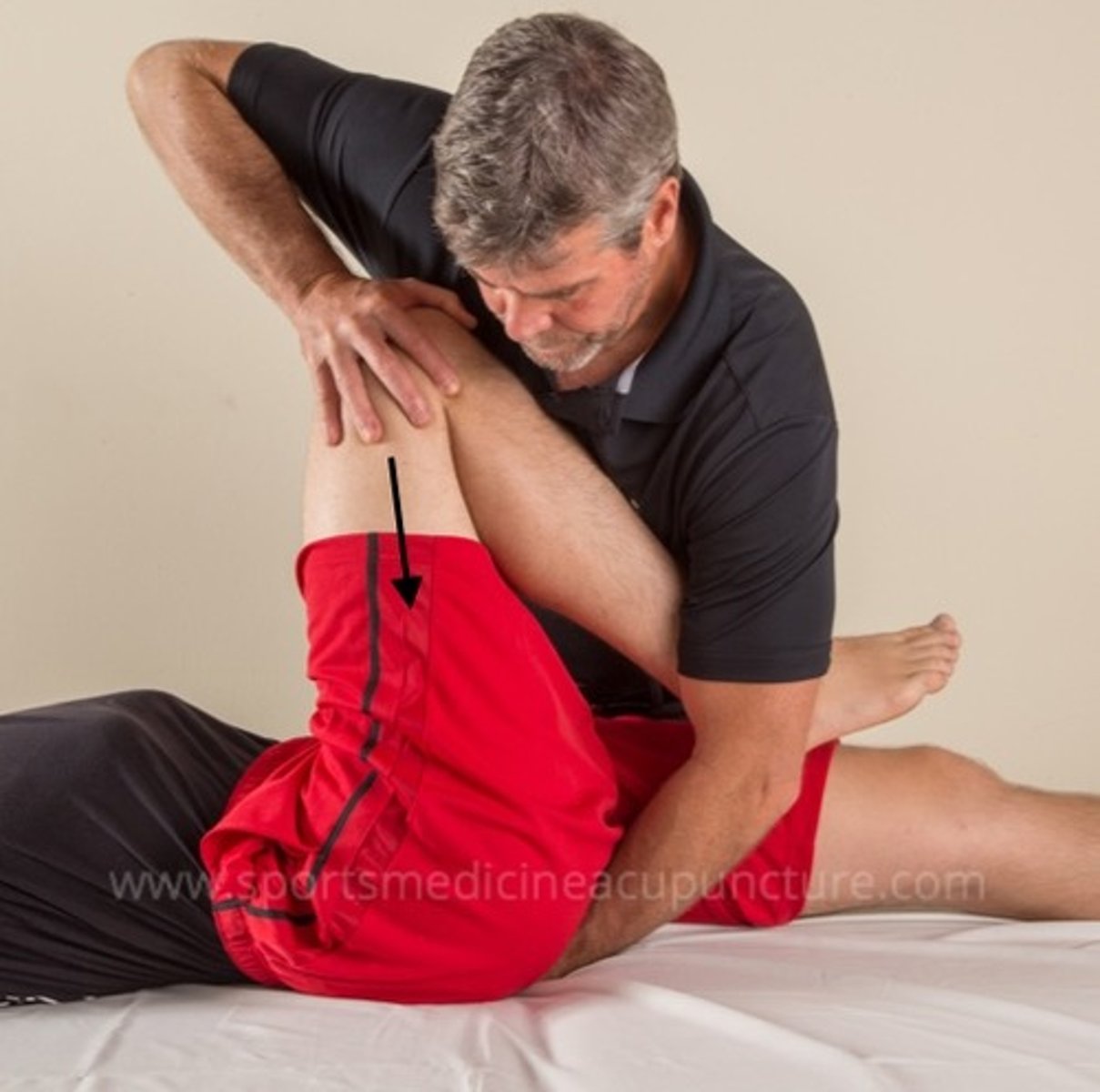
thomas test
tests muscle length of iliopsoas/rectus femoris
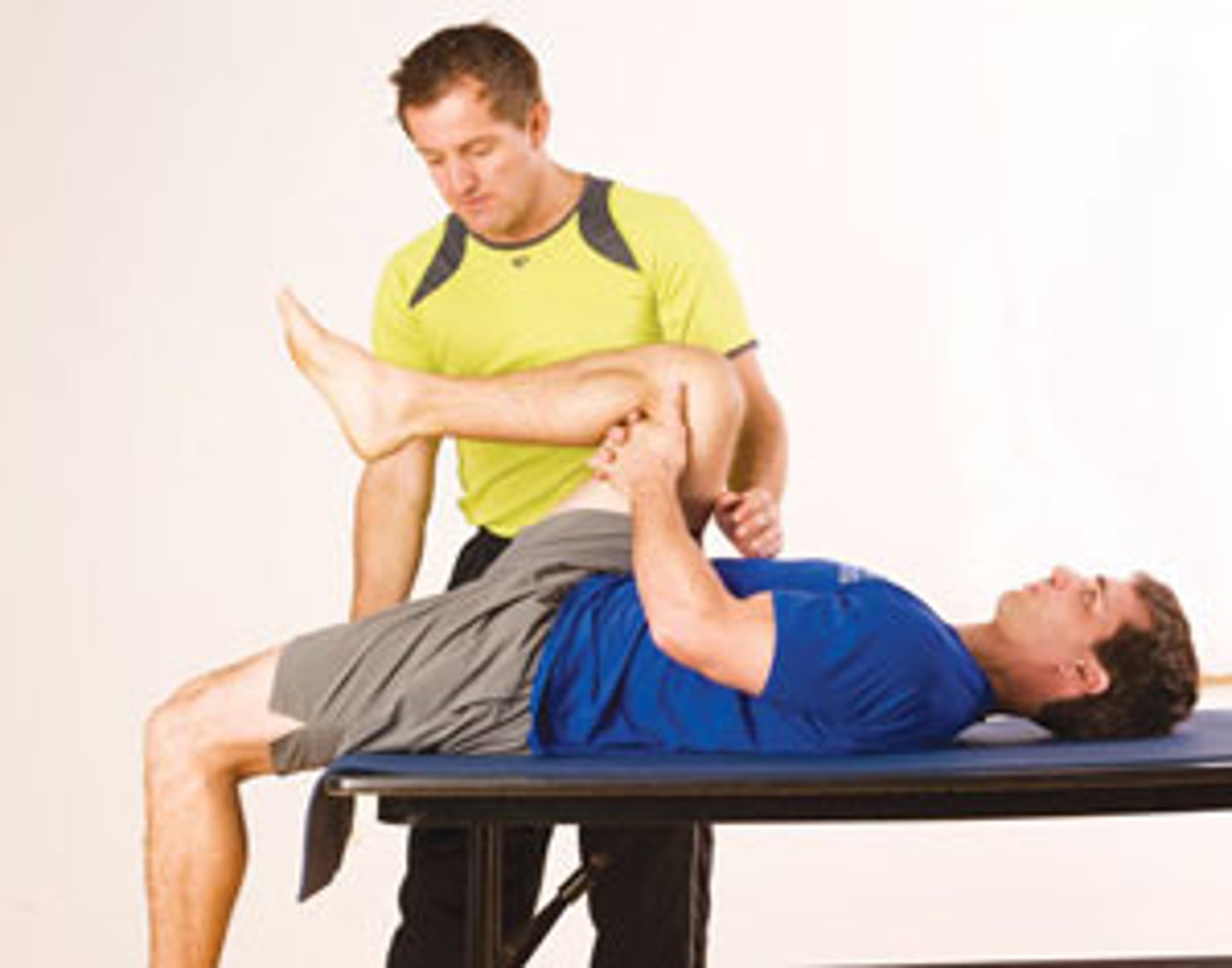

hip rotation in prone test
test IR and ER
assess for symmetry
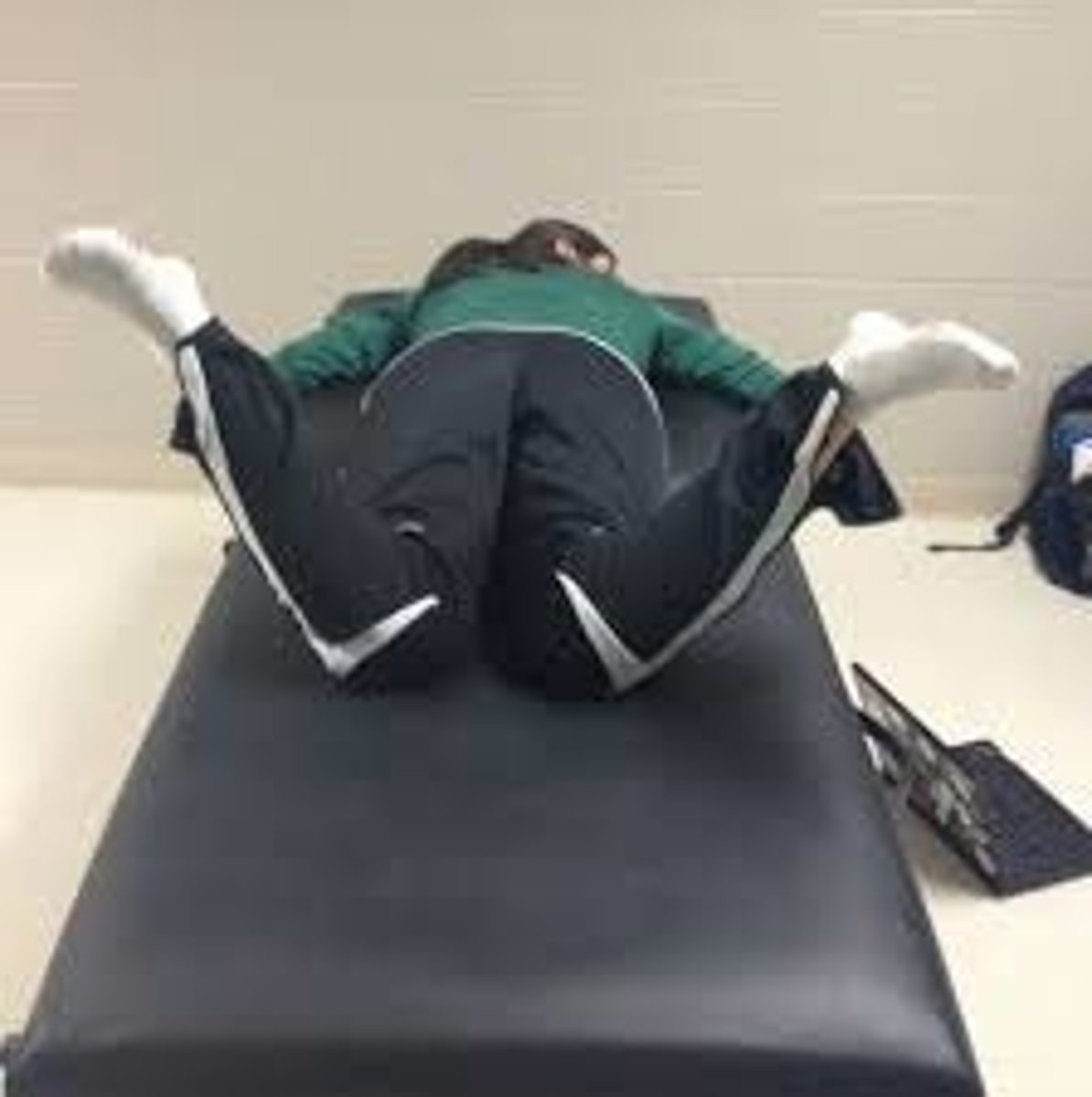
sorensen test
tests the endurance of back extensors
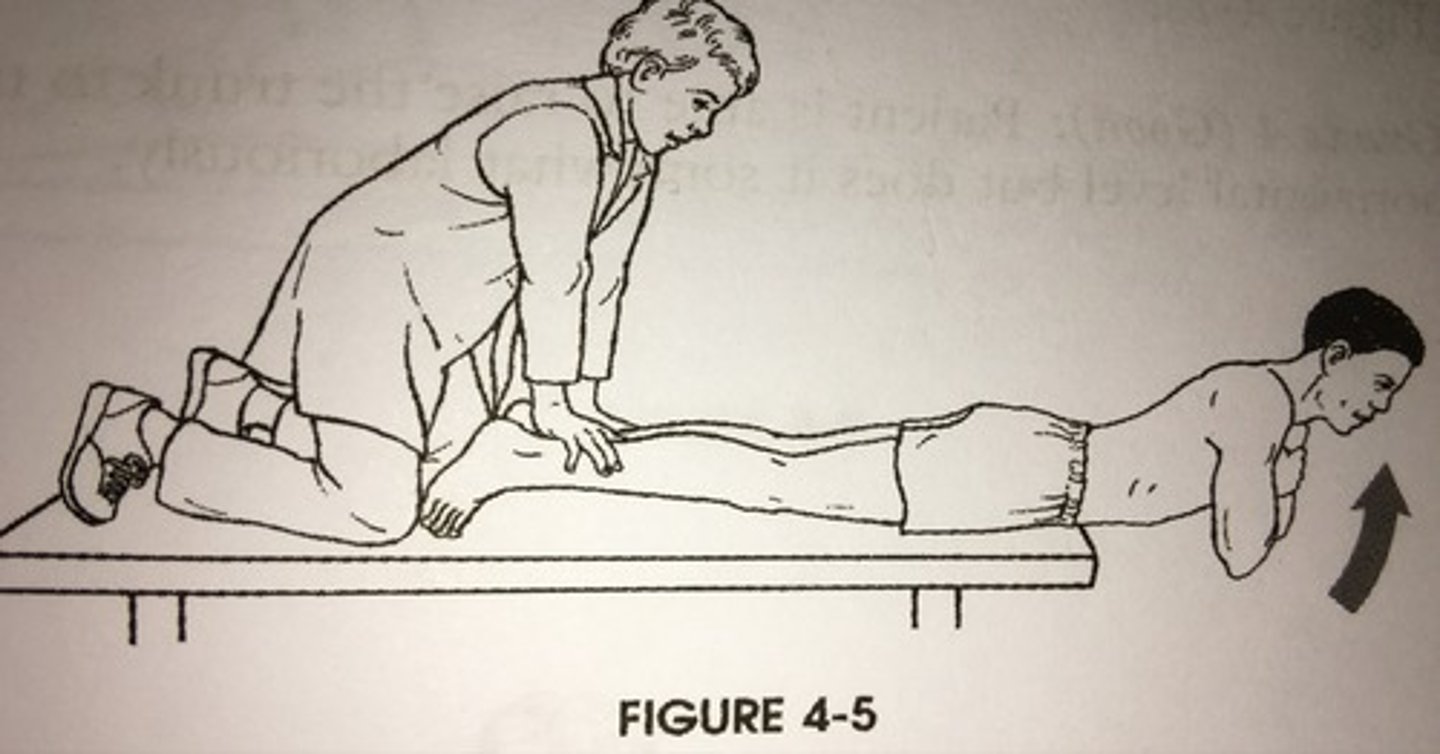
> 28 seconds
what is the norm for men for the sorensen test?
> 29 seconds
what is the norm for women for the Sorensen test?
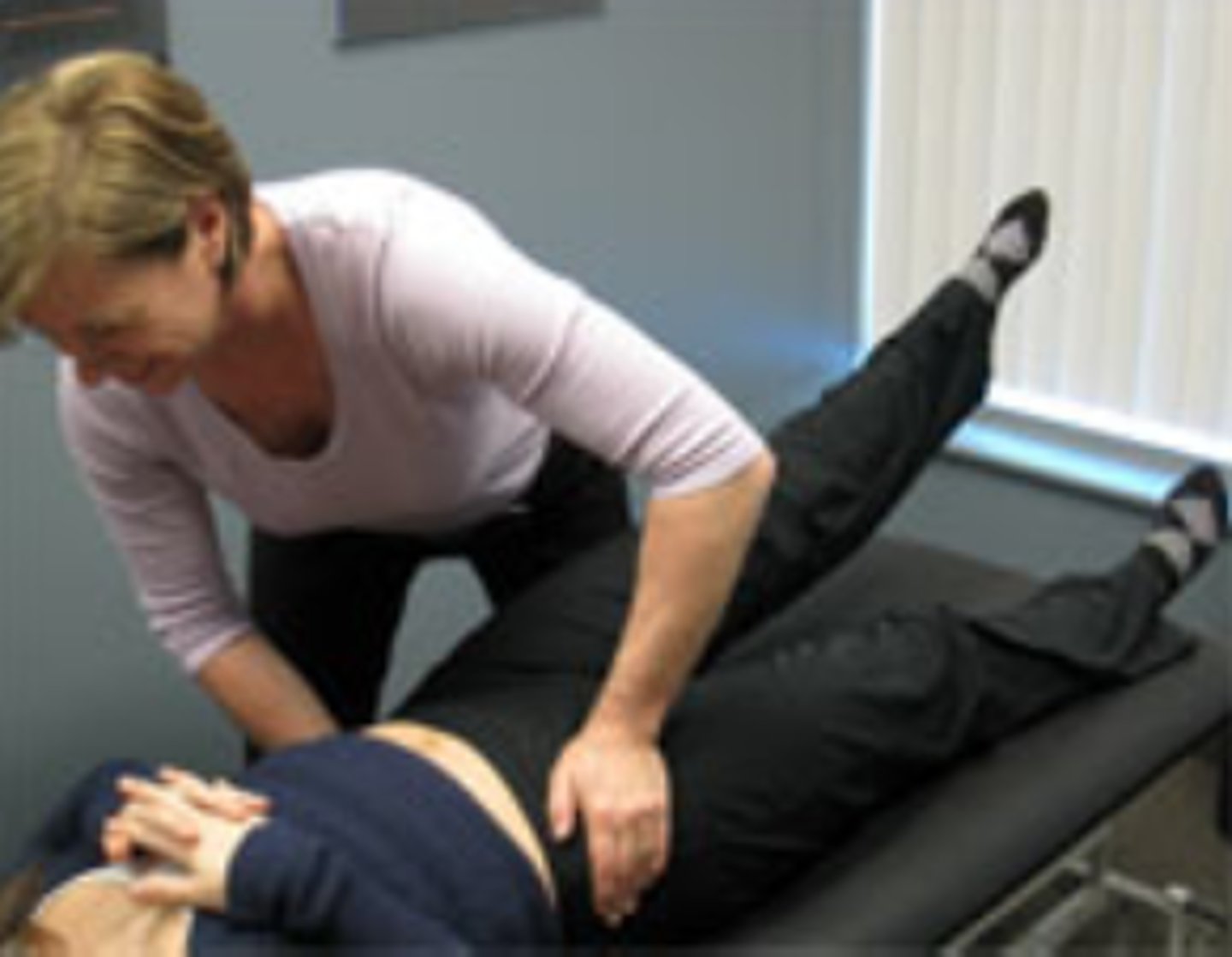
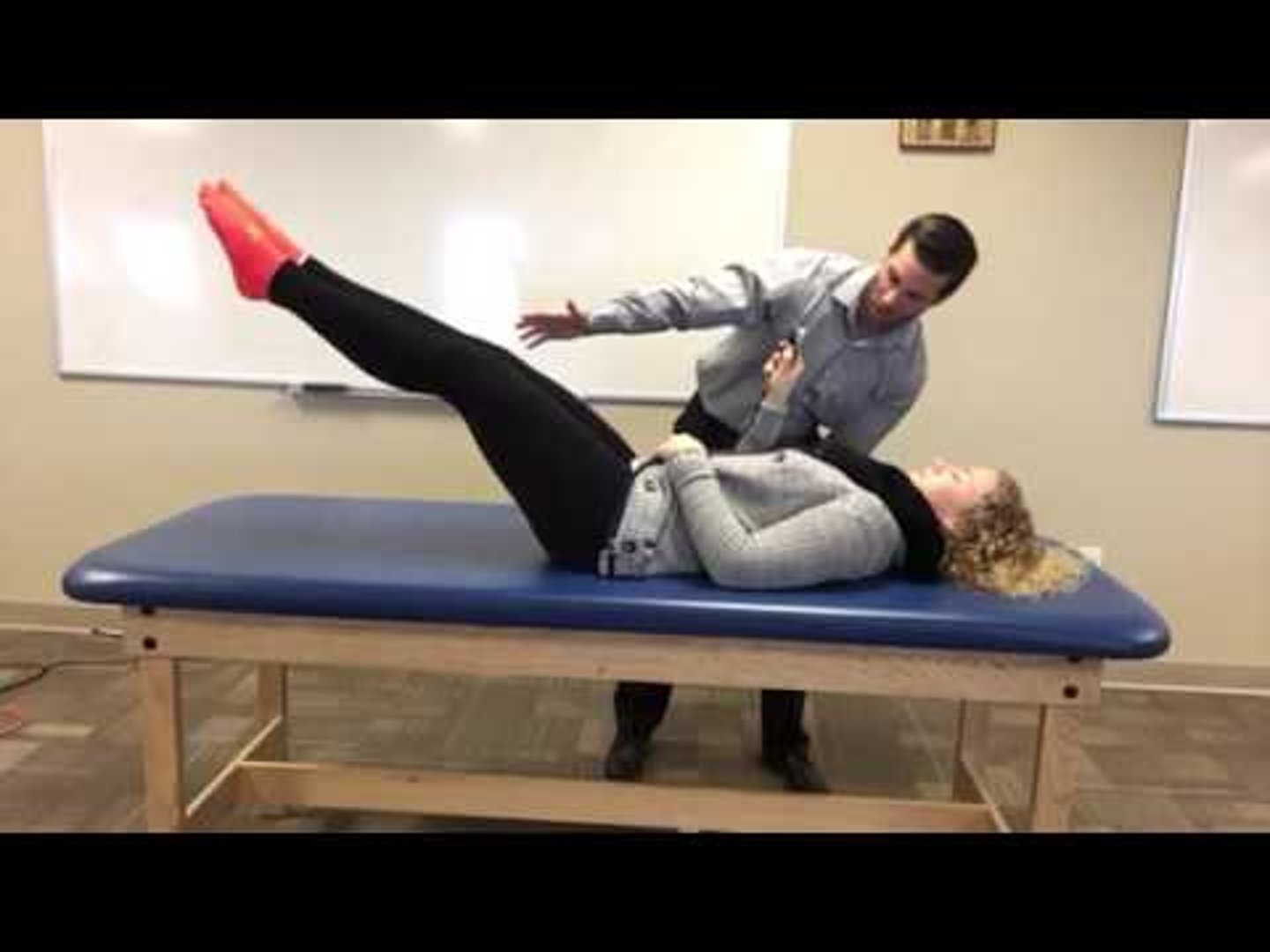
double leg lowering test
measures core stability and strength

0-15 degrees
5 for double leg lowering?
15-45 degrees
4 for double leg lowering
45-75 degrees
3 for double leg lowering
75-90 degrees
2 for double leg lowering
unable to hold pelvis in neutral
1 for double leg lowering
spine rotators and multifidi test
1. single straight arm hold
2. single straight leg hold
3. CL straight arm and leg hold
assesses ability of the spinal rotators and multifidus to stabilize the trunk during dynamic extremity movements
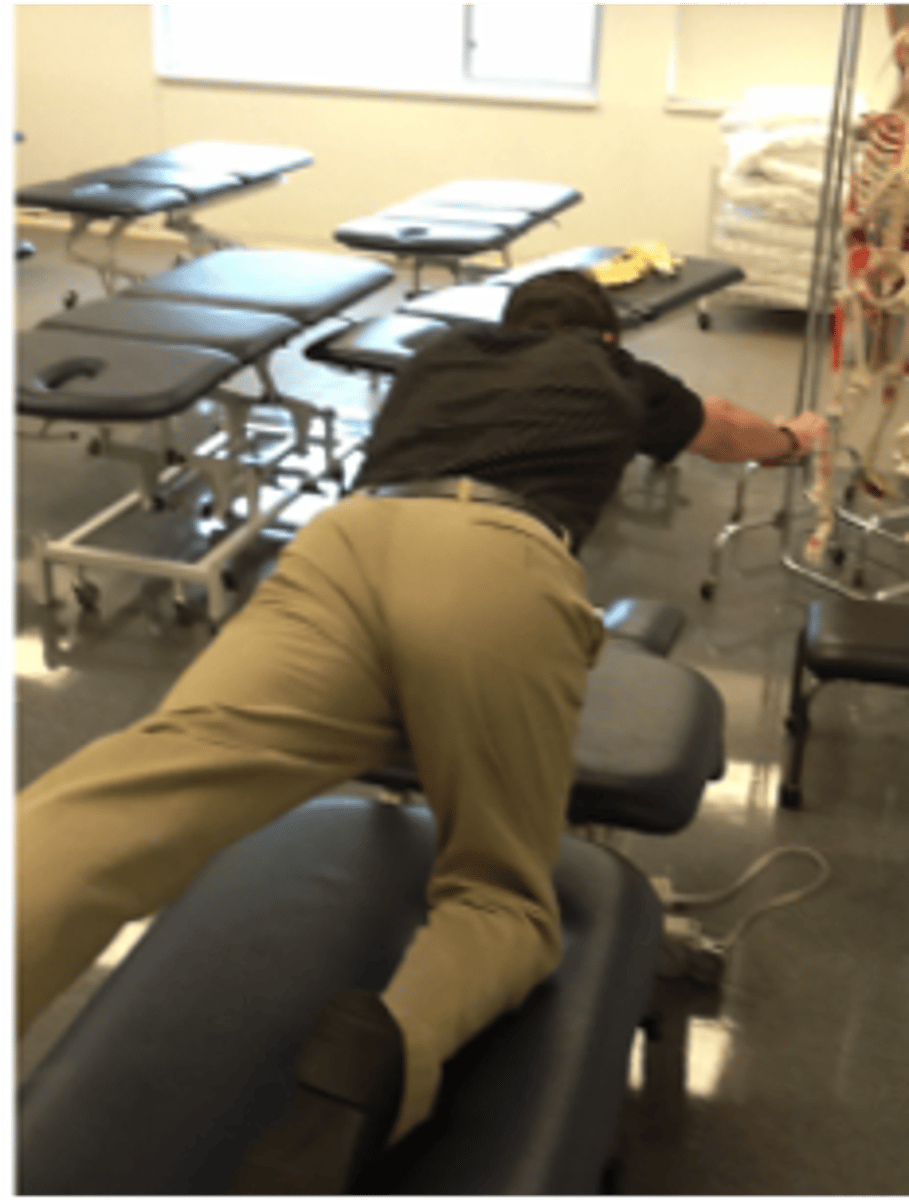
CL arm and leg lift 20-30s
grade 5 for spine rotators/multifidus
single leg lift 15-20s
grade 4 for spine rotators/multifidus
single arm lift 15-20s
grade 3 for spine rotators/multifidus
unable to hold during staight arm raise
grade 2 for spine rotators/multifidus
unable to raise arm or leg
grade 1 for spine rotators/multifidus
supine isometric chest raise test
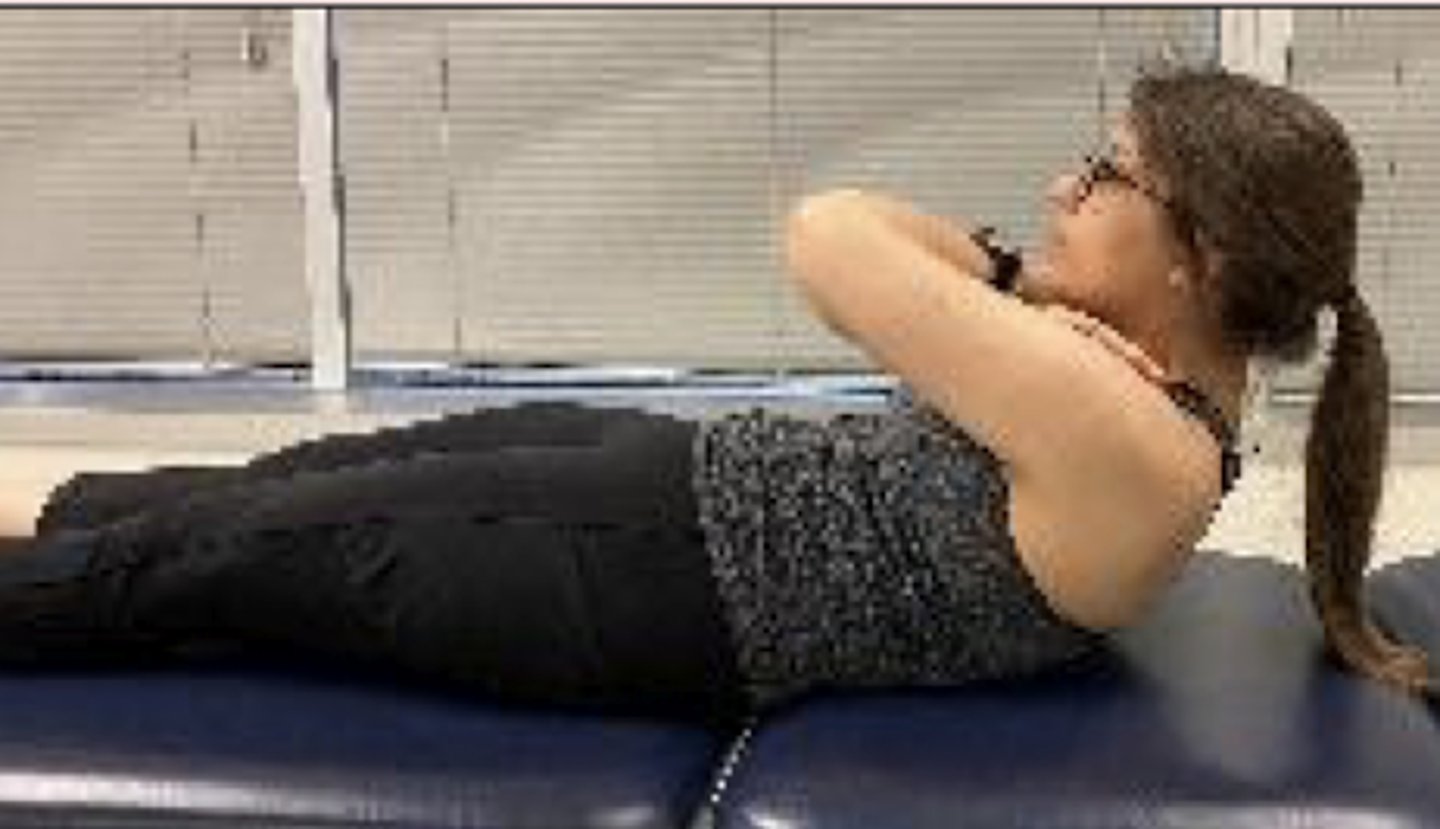
34 seconds
what is the norm for men for the supine isometric chest raise test?
24 seconds
what is the norm for women for the isometric chest raise test?
sacral sulci palpation
assess for depth, tenderness, and swelling
look for one side deeper and one side more shallow
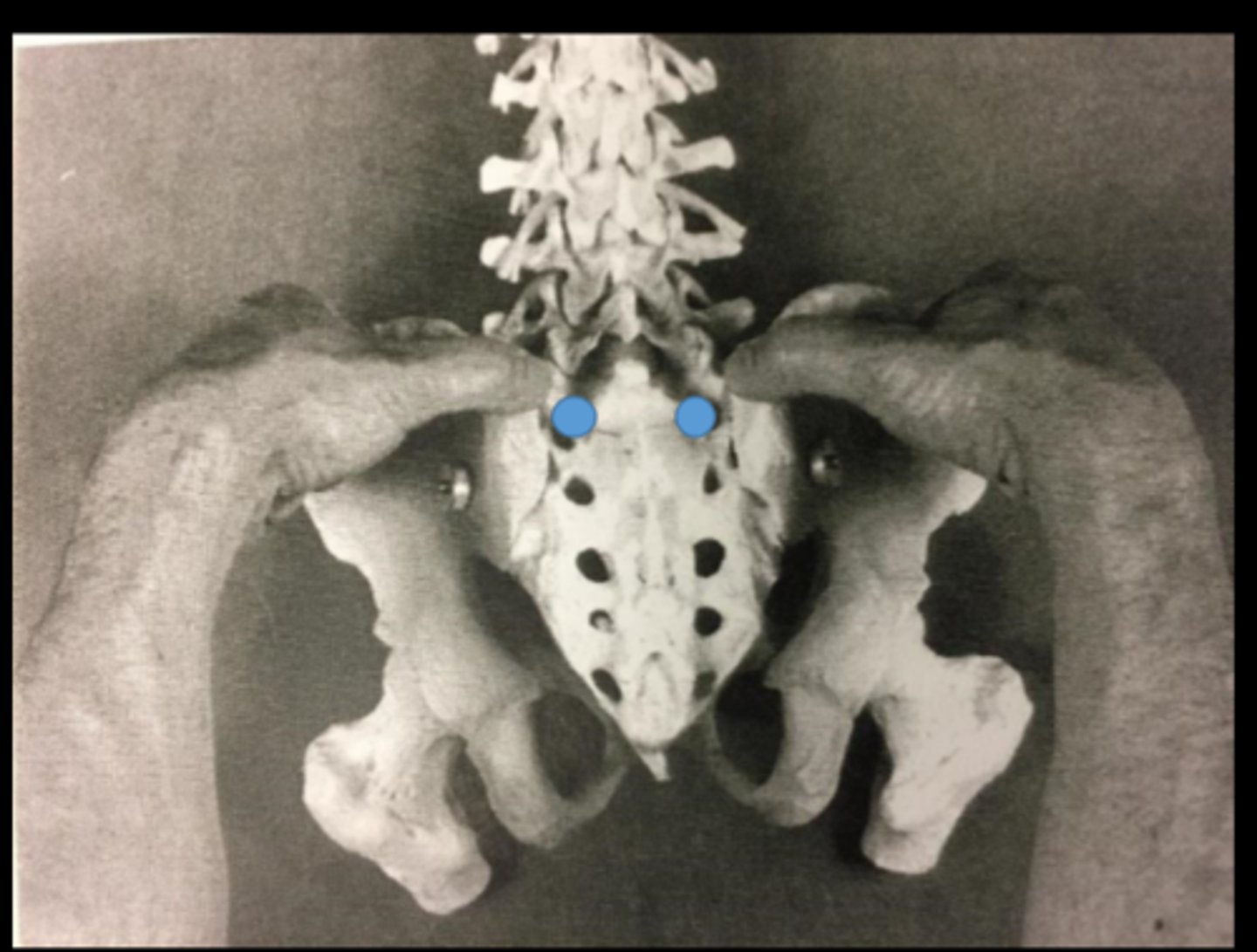
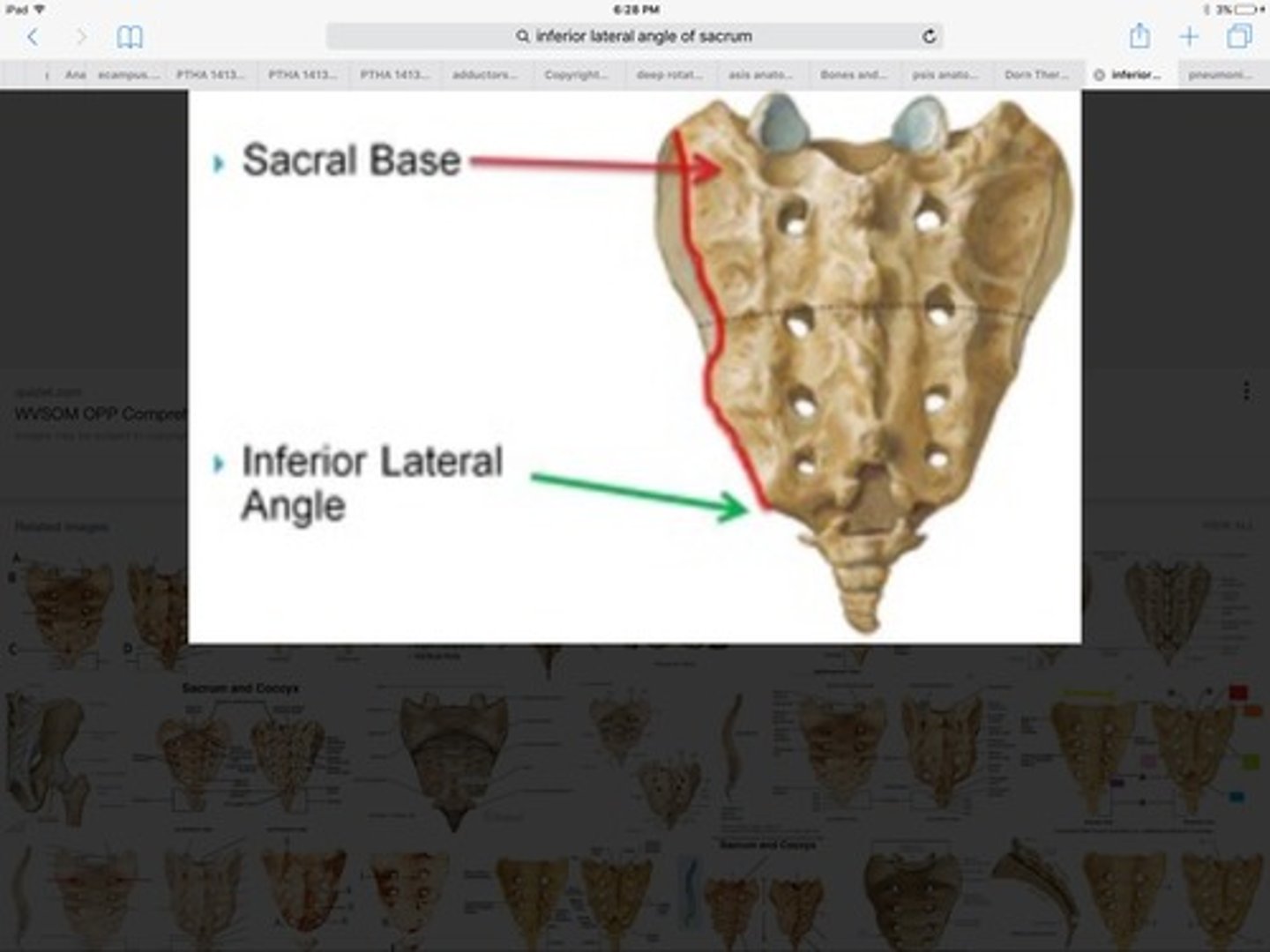
ILA palpation
-Sacral Sulci
-Thumbs walk down until you fall off sacrum
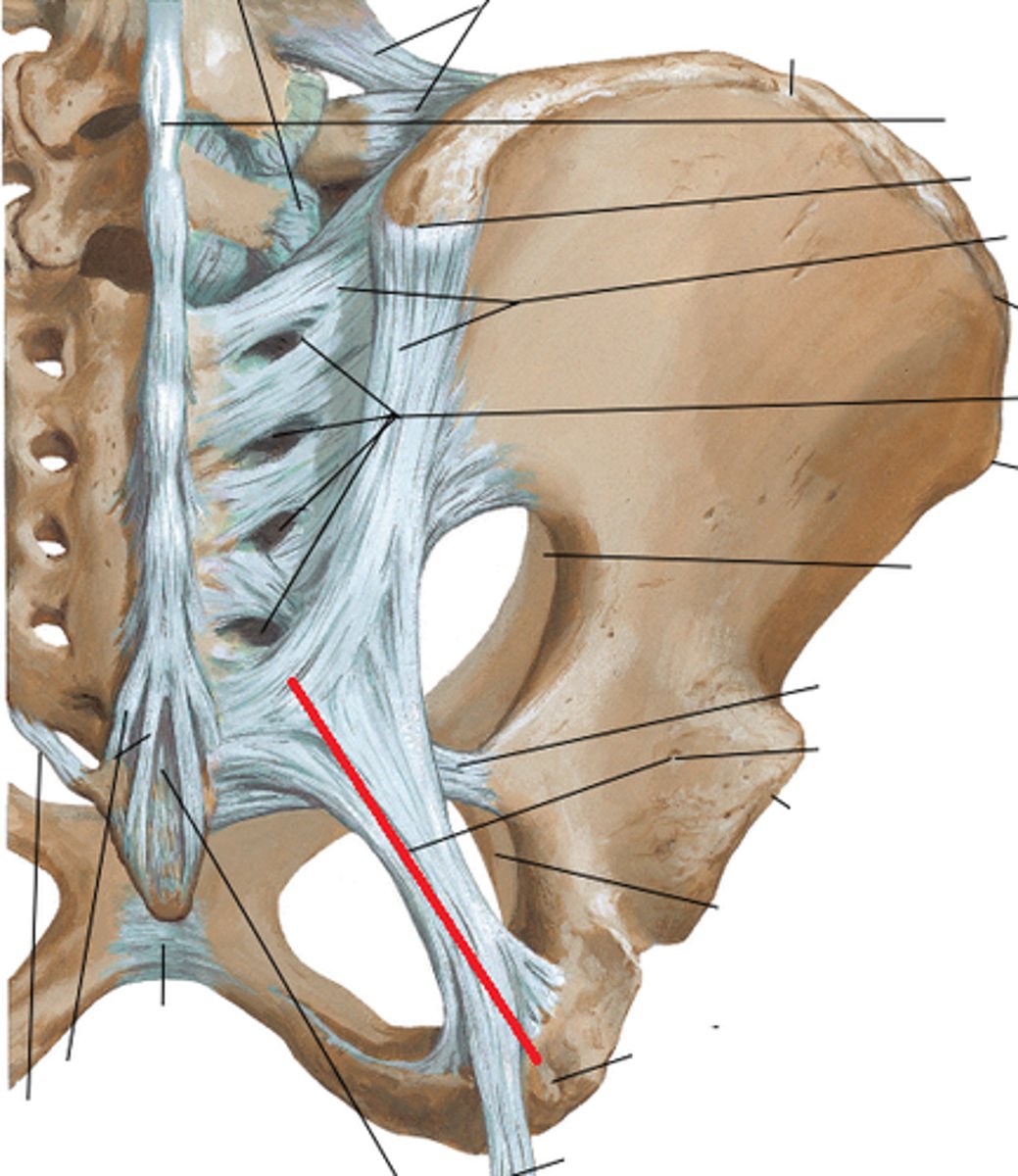
sacrotuberous ligament palpation
runs from the ischial tuberosity to the sacrum. So you will find the distal aspect of the sacrum and the ischial tuberosity and the line formed between both these points will be the ligament. You can run your finger perpendicular to confirm the structure.
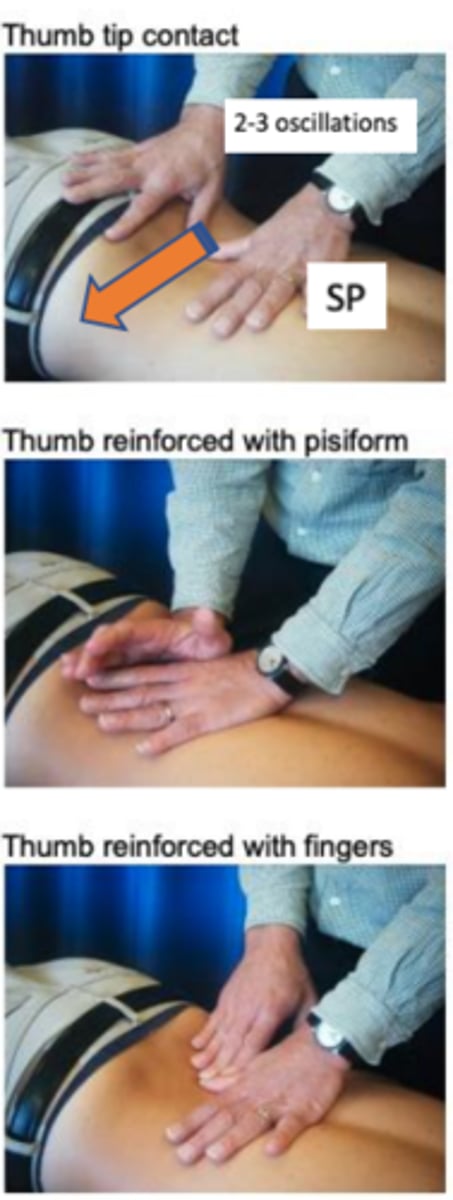
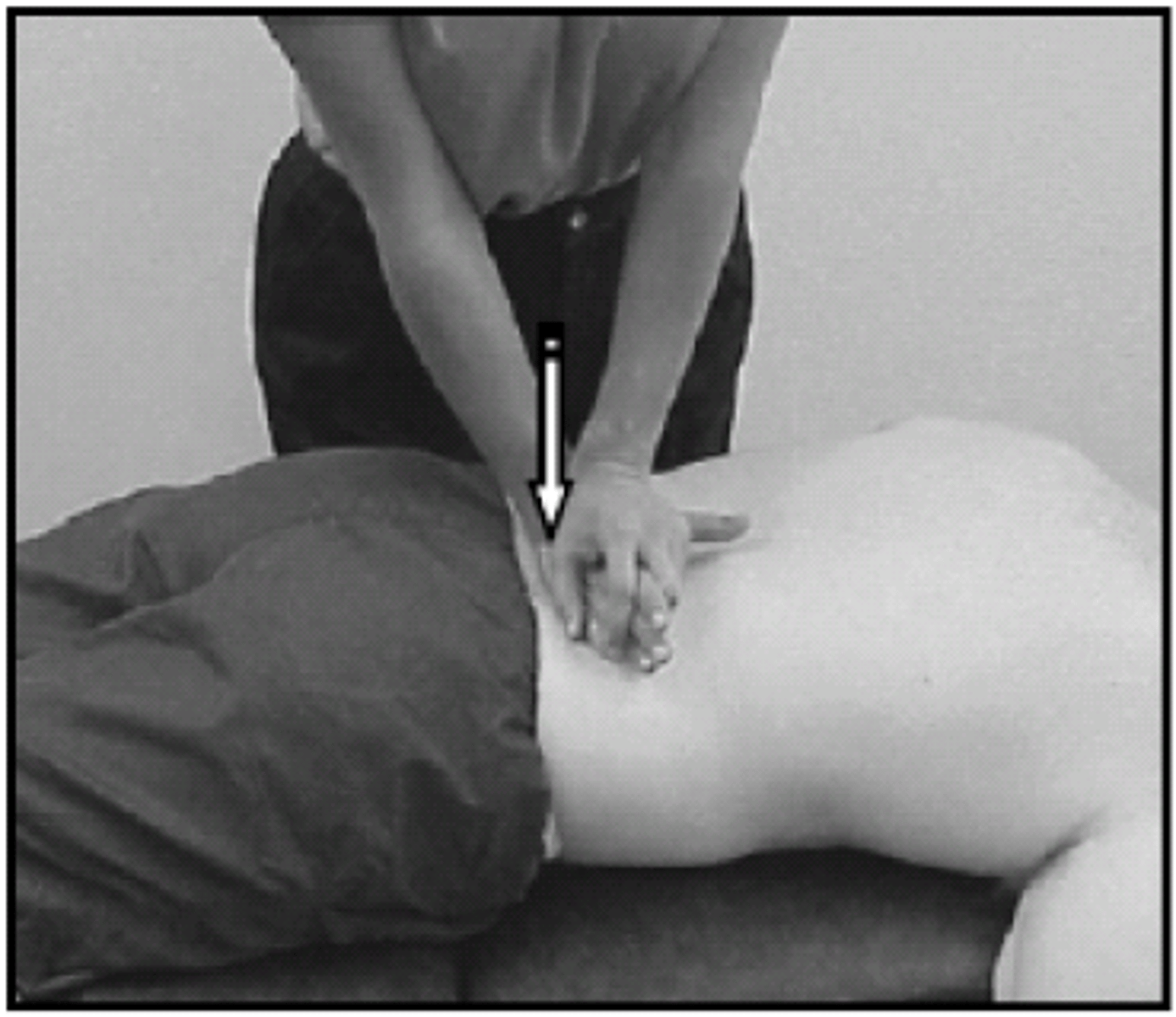
lumbar central PA
1. Stand over pt with long lever arm (vertical, arm over palm), stand in a straddle & hinge at hips; Extend wrist to tension/lock pisiform
3. Palpate spinous process with pisiform & assess for resistance/symmetry/pain/asymmetry
lumbar unilateral PA
Palpate transverse process with pisiform or thumb; TP is almost directly across from SP
- Causes contralateral rotation: Compression of superior contralateral side, distraction of superior ipsilateral side; Opposite occurs at the inferior facets
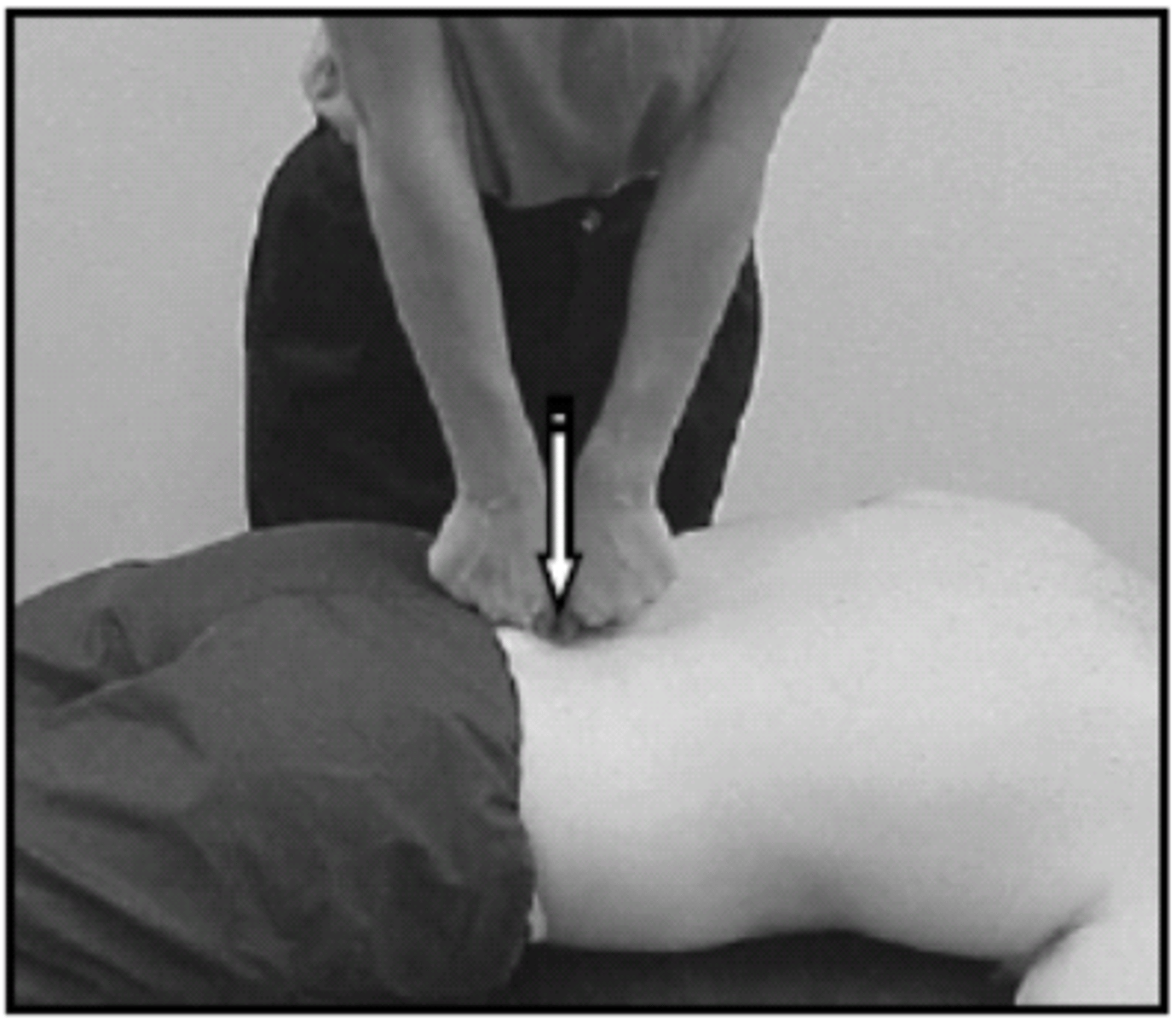
lumbar transverse PAIVM