PSYC 325 MIDTERM
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:56 AM on 6/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
1
New cards
Socialization
the process by which we learn the behaviours, values, skills, beliefs & norms of our society
* significant impact on youth
* significant impact on youth
2
New cards
Media
the intermediary to transmit info.
* means for communicating a message
* means for communicating a message
3
New cards
Mass media
sharing of messages facilitated by technology to large amounts of people
4
New cards
Correlational design
examining the relationship between 2 variables
5
New cards
Experimental design
can examine cause & effect
* includes random assignment
* measures IV & DV
* includes random assignment
* measures IV & DV
6
New cards
Longitudinal design
same participants are repeatedly tested over time
* most commonly used with correlational designs
* most commonly used with correlational designs
7
New cards
Content analysis
analyzing the content of media to identify patterns, themes & concepts in recorded communication
* you systematically collect data from a set of texts, which can be written, oral, or visual: Books, newspapers and magazines. Speeches and interviews
* you systematically collect data from a set of texts, which can be written, oral, or visual: Books, newspapers and magazines. Speeches and interviews
8
New cards
Natural experiments
where naturally occurring circumstances randomly create differences between indv’s
* ex: studying COVID-19 babies (researchers had no control)
* ex: studying COVID-19 babies (researchers had no control)
9
New cards
Meta-analysis
relies on studies that have already been created & draws further conclusions
10
New cards
Media use trends
* TV remains most common form of media entertainment
* hard to study as people may lie or not know
* huge increase of screen time over last 8 years
→ larger jump for boys, low SES, communities of colour
* hard to study as people may lie or not know
* huge increase of screen time over last 8 years
→ larger jump for boys, low SES, communities of colour
11
New cards
Infant (0-3) media preference
* bright colours, striking perceptual features
* educational content
* cartoons
* parentese speaking
* ex: teletubbies
* educational content
* cartoons
* parentese speaking
* ex: teletubbies
12
New cards
Child (3-12) media preference
* more complex content (story / narrative that fits into their level of knowledge)
* comedy
* gender-stereotyped content
* NOT interested in educational content (spinach effect)
* comedy
* gender-stereotyped content
* NOT interested in educational content (spinach effect)
13
New cards
Adolescent media preference
* speed & variety
* social media
* reality & realistic content
* ex: tiktok
* social media
* reality & realistic content
* ex: tiktok
14
New cards
Video deficit
until around 3, infants are less likely to learn from a screen than from a live interaction
* babies can imitate actions when watching live but not from a tv screen (same for word learning)
* its possible to learn from screens but only simple things
* babies can imitate actions when watching live but not from a tv screen (same for word learning)
* its possible to learn from screens but only simple things
15
New cards
Symbolic representation
under the age of 3 children don’t understand the TV screen means something else
* its not the actual TV they struggle with but the symbol linkage
* have more success when TV looks like a window (real world)
* its not the actual TV they struggle with but the symbol linkage
* have more success when TV looks like a window (real world)
16
New cards
When might an infant/ toddler learn better from screen media?
* socially contingent (video chat)
* an adult is also watching & engaging with them
* socially meaningful characters & cues are used
* they are watching familiar people / characters
* an adult is also watching & engaging with them
* socially meaningful characters & cues are used
* they are watching familiar people / characters
17
New cards
Perceptual processing
how things physically look/sound
* younger children can only focus on this
* occurs in media too (focus on appearance not actions)
* younger children can only focus on this
* occurs in media too (focus on appearance not actions)

18
New cards
Conceptual processing
making deeper connections to information
19
New cards
Piaget’s centration
displayed that young children can only focus on perceptually salient features
* believe that the volume of liquid changes when poured in new jar
* until about age 6-7
* believe that the volume of liquid changes when poured in new jar
* until about age 6-7
20
New cards
Understanding the message
* young children often fixate on action, not underlying motives or messages
* inference doesn’t seem to develop until 6-8+
* inference doesn’t seem to develop until 6-8+
21
New cards
Reality vs. Fantasy
children 3 & under struggle to understand the relationship between media & reality
22
New cards
Identity & Media
* searching for an identity is an important hallmark of adolescence
* use of social media helps create identity?
* 50% of 9-18yr olds have pretended to be someone else on the internet
* heavily focused on peers & fitting in
* use of social media helps create identity?
* 50% of 9-18yr olds have pretended to be someone else on the internet
* heavily focused on peers & fitting in
23
New cards
Imaginary audience
the belief that others are always paying attention to you
24
New cards
Personal fable
the belief that you & your experiences are unique
25
New cards
Brain development in adolescence
* limbic system (reward system) more developed than prefrontal cortex
* increased risky behaviour & media use
* increased risky behaviour & media use
26
New cards
Sexuality in adolescence
* increased interest in sexual content
* teens using media to understand / explore their sexuality
* teens using media to understand / explore their sexuality
27
New cards
Hypodermic needle theory
believes that everyone is impacted by media in the exact same way
* idea that media “injects” us & changes our beliefs
* original theory of media effects that arose from propaganda
* idea that media “injects” us & changes our beliefs
* original theory of media effects that arose from propaganda
28
New cards
Cultivation theory
media gradually cultivates certain views in the audience **over time**
* drip, drip theory
* constant exposure starts to cultivate similar views in those who consume the same media
* different impacts based on amount of use
* drip, drip theory
* constant exposure starts to cultivate similar views in those who consume the same media
* different impacts based on amount of use
29
New cards
Resonance
the similarity between media and an indv’s circumstances
* how relatable it is
* how relatable it is
30
New cards
Mainstreaming
the idea that heavy users of the same media will tend to homogenize in their views / beliefs
31
New cards
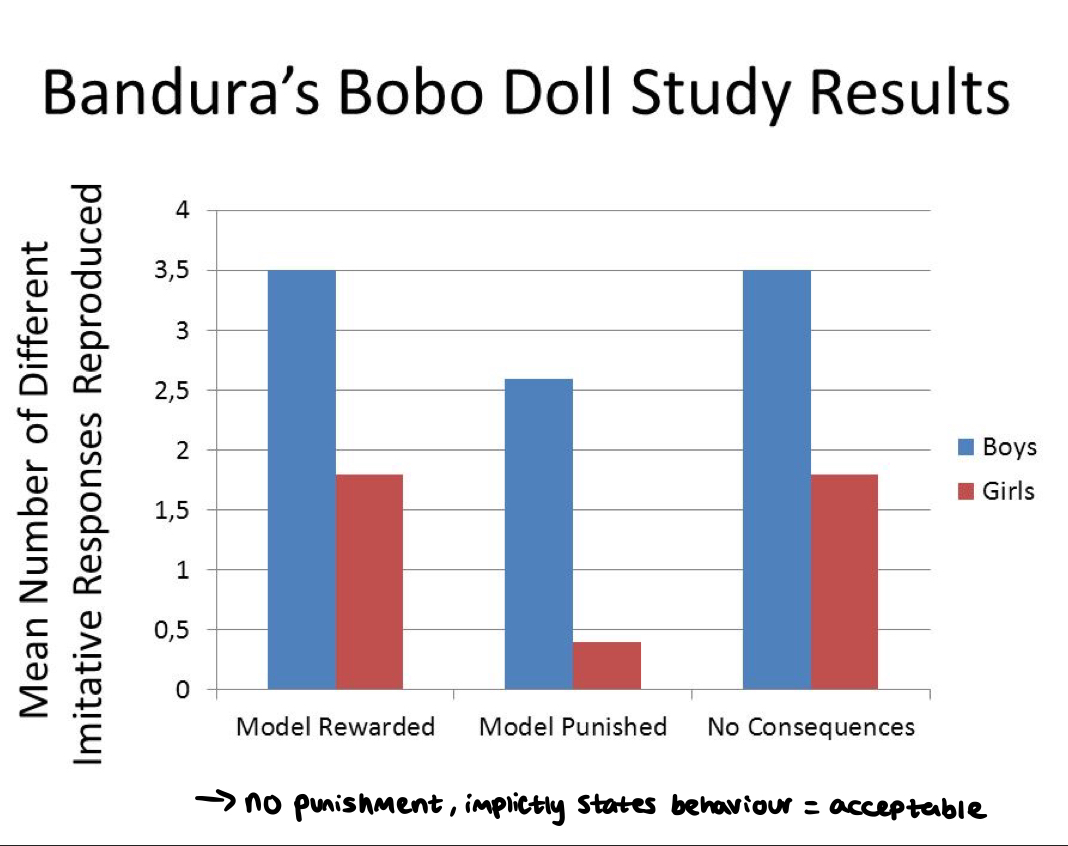
Social learning / social cognition theory
we learn behaviour through observing the behaviour of others
* Bandura’s bobo doll experiment
* Bandura’s bobo doll experiment
32
New cards
Uses & gratifications theory
Indv’s are driven to media for various reasons & those reasons matter
* media effects us differently depending on our motivations for consumption
* could be habit, escape, companionship, learning, relaxation, sensation etc.
* media effects us differently depending on our motivations for consumption
* could be habit, escape, companionship, learning, relaxation, sensation etc.
33
New cards
“The medium is the message”
Marshall Mcluhan statement
* meaning the medium of media itself has an impact
* the creation of new technology is changing humans the most
* meaning the medium of media itself has an impact
* the creation of new technology is changing humans the most
34
New cards
Reduction Hypothesis
consuming high amounts of screen media leads to poor academic achievement
* a general correlation does exist but not very strong
* media use correlated with academic performance, test scores, poorer educational content
* a general correlation does exist but not very strong
* media use correlated with academic performance, test scores, poorer educational content
35
New cards
What are some theories to why the reduction hypothesis occurs?
* time displacement
* mental effort
* attention & impulsivity
* mental effort
* attention & impulsivity
36
New cards
Time displacement
media takes away from intellectually beneficial activities (takes up your time)
* but many studies suggest that media use generally displaces other media use
* exception: screen media displacing reading in young children which impacts reading acquisition
* but many studies suggest that media use generally displaces other media use
* exception: screen media displacing reading in young children which impacts reading acquisition
37
New cards
Mental effort
media use is passive and causes passive thinking to become the norm
* idea that media “trains you”
* very little evidence (young kids are often quite engaged)
* idea that media “trains you”
* very little evidence (young kids are often quite engaged)
38
New cards
Attention & impulsivity
media use shortens attention spans and increases impulse behaviour
* very inconclusive results
* very inconclusive results
39
New cards
Possible 3rd variables to the reduction hypothesis?
* parental monitoring
* SES of family
* SES of family
40
New cards
Goldilocks / curvilinear pattern
some studies have suggested a moderate use of media is positively correlated with achievement but heavy use has a negative correlation
41
New cards
Content matters patterns with children
children saw better educational achievement when watching educational content (tested at 2-3 & then 5-7 yr olds)
* no correlation with non educational children content
* negative correlation when watching tv meant for general audience
\
longitudinal study:
* tested at 5 & 15
* informative content positive correlation with grades in boys
* “violent” cartoons negative correlation with grades in girls
* no correlation with non educational children content
* negative correlation when watching tv meant for general audience
\
longitudinal study:
* tested at 5 & 15
* informative content positive correlation with grades in boys
* “violent” cartoons negative correlation with grades in girls
42
New cards
Why was sesame street created?
to foster intellectual & cultural development in preschoolers
* focus on children from low income & marginalized backgrounds
* use of research on child development to create content
* many studies link watching it to academic skills
* focus on children from low income & marginalized backgrounds
* use of research on child development to create content
* many studies link watching it to academic skills
43
New cards
Educational media success
most success shown when the media has specific goals
* many teach children vocab, spelling, literacy & prosocial skills
* struggle to teach more complex skills (grammar)
* many teach children vocab, spelling, literacy & prosocial skills
* struggle to teach more complex skills (grammar)
44
New cards
Features of good educational media
* moderate discrepancy: differs slightly from what they know so they can build of previous knowledge but be slightly challenged
* repetition to repeat goals & ideas
* participatory cues
* repetition to repeat goals & ideas
* participatory cues
45
New cards
Age of prime educational media
children aged 3-5 benefit best
* younger struggle to learn due to video deficit
* older: lose interest? not as good content?
* younger struggle to learn due to video deficit
* older: lose interest? not as good content?
46
New cards
Capacity model
we have limited cognitive resources in our working memory which makes it hard to focus on too many concepts at a time
* narrative & educational content compete for resources
* narrative always wins
* narrative & educational content compete for resources
* narrative always wins
47
New cards
What do we learn from gaming?
* problem solving
* persistence
* creativity
* possible improvement in aspects of visual attention / cognitive processing
* persistence
* creativity
* possible improvement in aspects of visual attention / cognitive processing
48
New cards
Violence
any act or threat of force against the self or others
49
New cards
Media violence
media that portrays some form of harm
50
New cards
Aggression
any action intended to cause harm
* physical & verbal both direct
* relational can be direct / indirect (harming someone’s social relations / status)
* physical & verbal both direct
* relational can be direct / indirect (harming someone’s social relations / status)
51
New cards
Factors that impact that impact the likelihood of acting aggressively
* aggressive emotions
* aggressive traits
* physiological factors
* aggressive thoughts
* aggressive traits
* physiological factors
* aggressive thoughts
52
New cards
Catharsis
a historical theory that believed violent impulses could be ‘purged’ through consuming violent media
53
New cards
Social cognition theory & violence
argued against catharsis & supported observational learning
* impacted by reinforcements & punishments
* influenced by personal factors / cognitions
* impacted by reinforcements & punishments
* influenced by personal factors / cognitions
54
New cards
Scripts
personal “screenplays” that give us an idea of what is expected to occur during interactions (guides our behaviour)
* based on experiences & observational learning
* violent media may create expectations that conflict is solved through violence
\
* based on experiences & observational learning
* violent media may create expectations that conflict is solved through violence
\
55
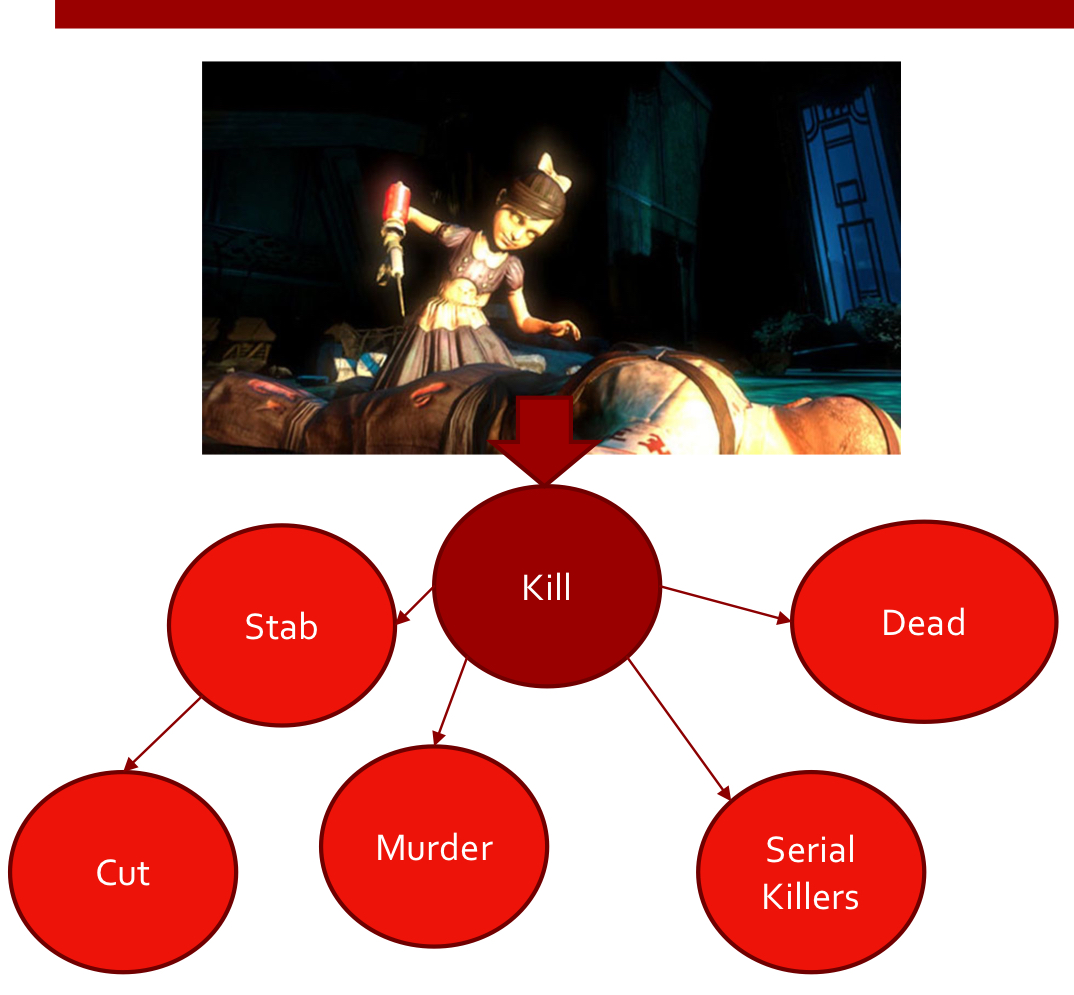
New cards
Priming
violent stimuli activates aggressive thoughts which can then “prime” other related thoughts
* constant violent stimuli can affect future reactions by activating violent thoughts
* constant violent stimuli can affect future reactions by activating violent thoughts
56
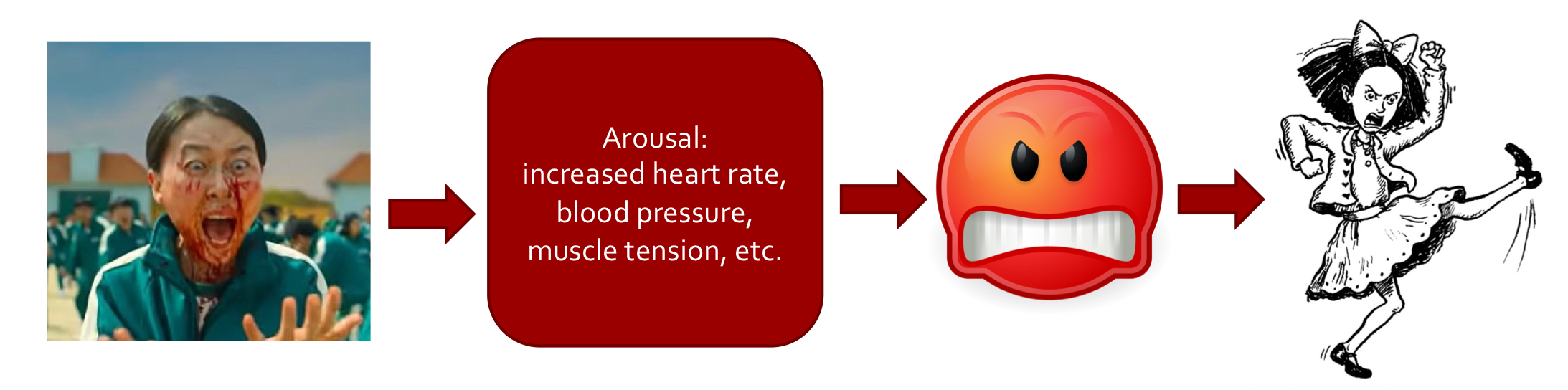
New cards
Excitation Transfer
consuming violent media leads to arousal which we accidentally interpret as anger
* become more likely to act aggressively
* (short term)
* become more likely to act aggressively
* (short term)
57
New cards
Desensitization
repeated exposure to media violence leads to lessened emotional reaction (normalized)
* long term
* long term
58
New cards
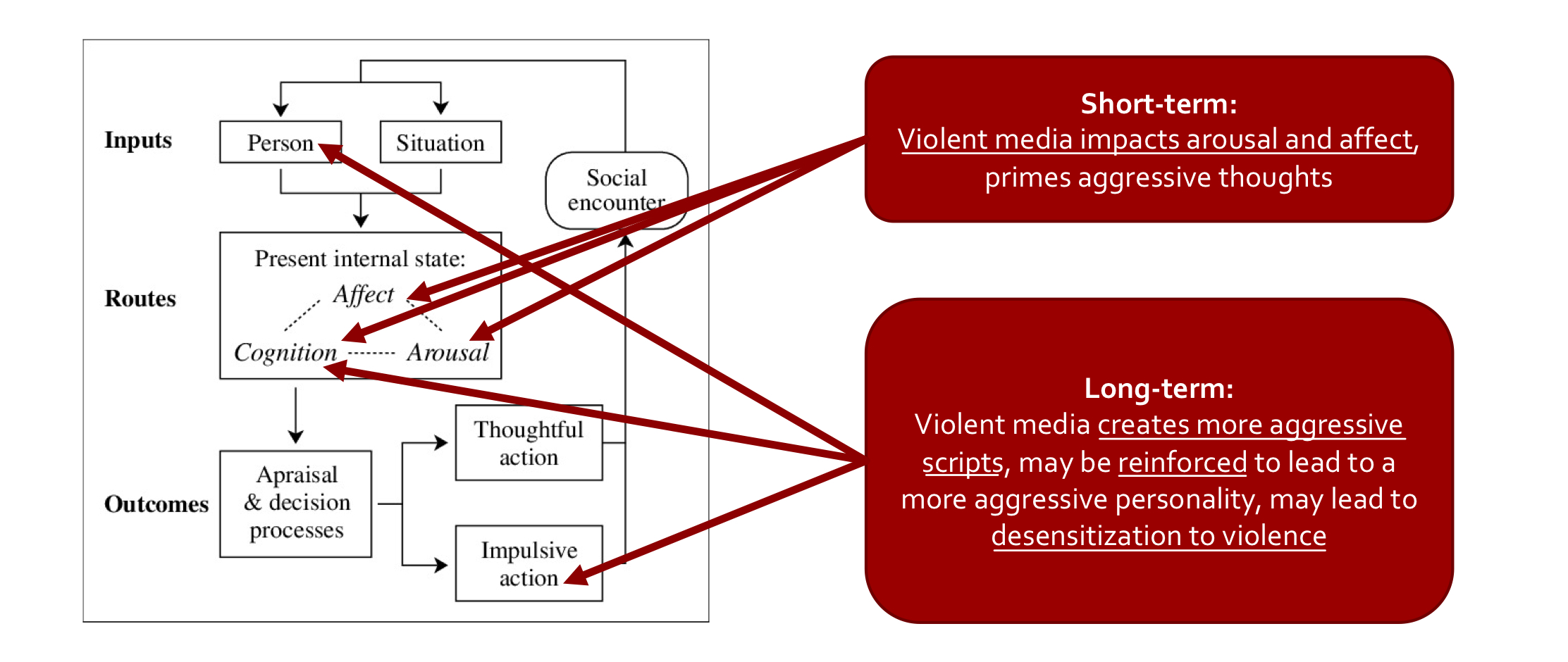
General aggression model
an attempt to integrate multiple theories to explain the impacts of violent media
**input variables:** determine an indv’s likelihood to act aggressively (personality, genetics etc.)
→ impact **routes** to aggressive behaviour by influencing the internal state
→ a given situation is then appraised, creating the **outcome** of whether to act aggressively or not (evaluate situation & choose response)
\
**input variables:** determine an indv’s likelihood to act aggressively (personality, genetics etc.)
→ impact **routes** to aggressive behaviour by influencing the internal state
→ a given situation is then appraised, creating the **outcome** of whether to act aggressively or not (evaluate situation & choose response)
\
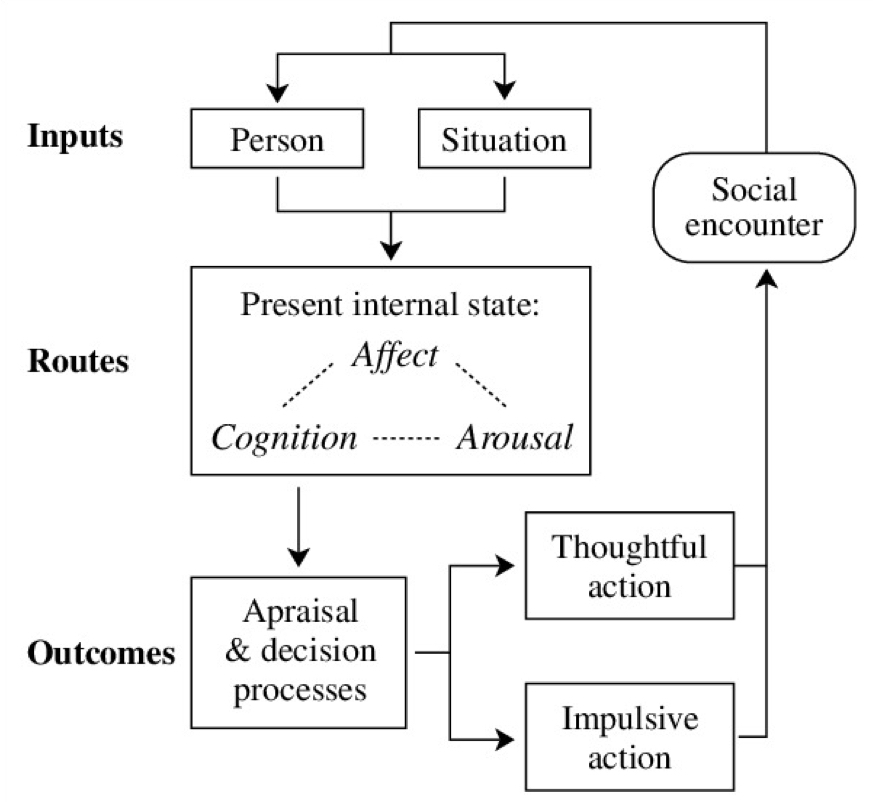
59
New cards
General aggression model short & long term impacts
short-term: violent media impacts arousal & affect, it also primes aggressive thoughts
long-term: violent media creates more aggressive scripts which may be reinforced & lead to a more aggressive personality and/or desensitization to violence
long-term: violent media creates more aggressive scripts which may be reinforced & lead to a more aggressive personality and/or desensitization to violence
60
New cards
TV violence correlation
most studies show a positive correlation between TV consumption & aggressive cognitions / behaviour
* exposure to TV violence correlated with kids willingness to use violence & the perceived effectiveness of violence
* more consistently seen with boys
* exposure to TV violence correlated with kids willingness to use violence & the perceived effectiveness of violence
* more consistently seen with boys
61
New cards
Video game violence correlation
most studies show positive correlation
* violent video game play correlated to lower empathy & positive attitudes towards violence
* violent video game play correlated to lower empathy & positive attitudes towards violence
62
New cards
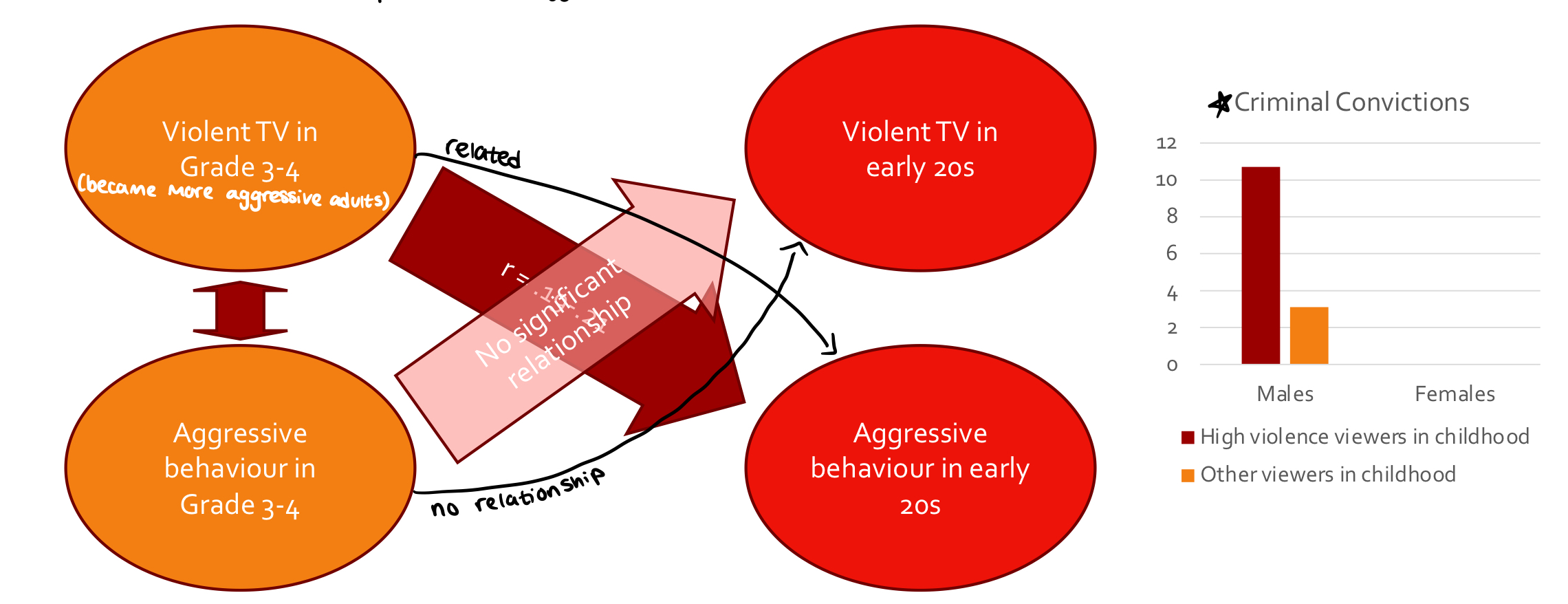
Longitudinal designs with violent media
most studies suggest that consumption of media violence can predict aggressive behaviour in future
* violent TV consumption in grade 3-4 related to aggressive behaviour in early 20s
* aggressive behaviour in grade 3-4 not related to violent TV consumption in early 20s
* violent TV consumption in grade 3-4 related to aggressive behaviour in early 20s
* aggressive behaviour in grade 3-4 not related to violent TV consumption in early 20s
63
New cards
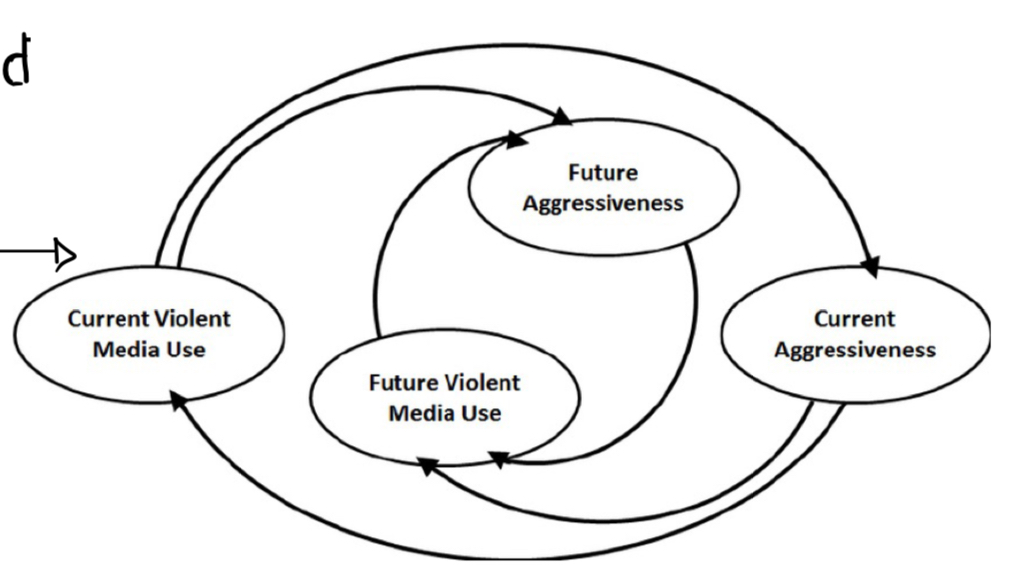
Downward spiral model
a consistent spiral relationship between aggressiveness and violent media use
* hard to predict beginning
* hard to predict beginning
64
New cards
TV / video games violence & experimental research
Those who watch TV violence / play violent video games are more likely to demonstrate aggressive behaviours/cognitions
(majority of studies NOT ALL)
* small to moderate effect
(majority of studies NOT ALL)
* small to moderate effect
65
New cards
Who is most likely to consumer violent media?
* boys
* highly aggressive individuals
* younger children
* highly aggressive individuals
* younger children
66
New cards
When are people most likely to immitate violence?
* children imitating children
* men imitating men
* playing with personalized avatars
* men imitating men
* playing with personalized avatars
67
New cards
Wishful identification
wanting to be like certain characters
* wishful identification linked to impact of violent media (more aggressive)
* wishful identification linked to impact of violent media (more aggressive)
68
New cards
What features of media may lead to more aggression?
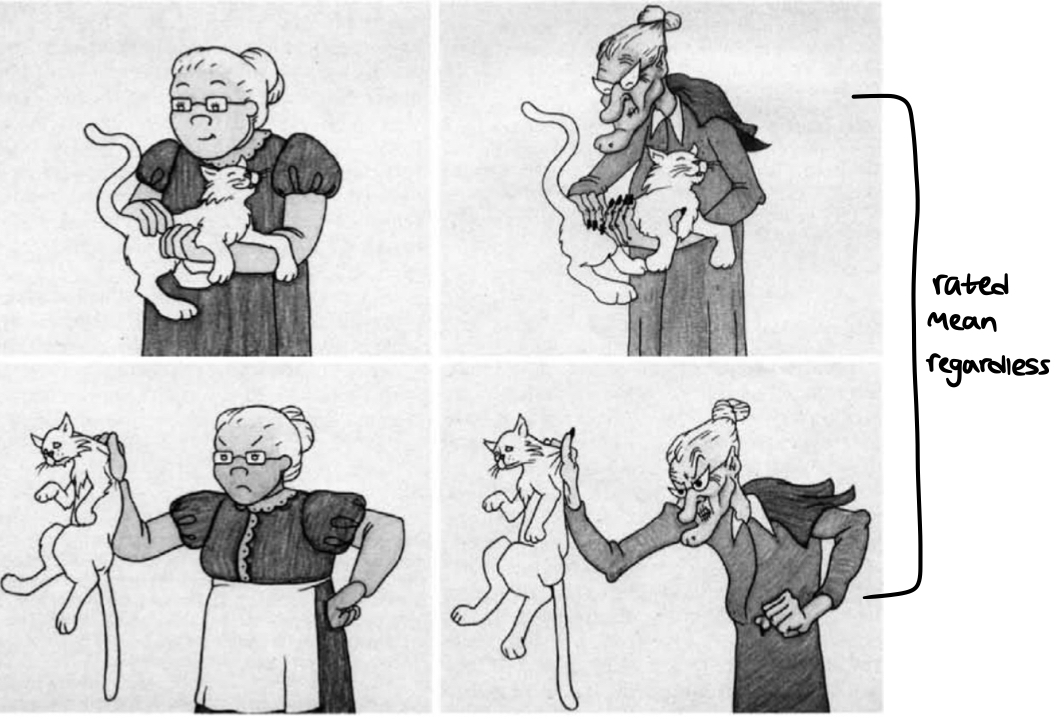
* perpetrators are appealing
* violence is rewarded or unpunished
* no consequences to victim
* violence is for a purpose (jusitified)
* violence is realistic
* violence is rewarded or unpunished
* no consequences to victim
* violence is for a purpose (jusitified)
* violence is realistic
69
New cards
Prosocial behaviour & violent video games
prosocial behaviour was more common after cooperative video game play (especially violent ones)
* it meets psychological needs of satisfaction
* collaborative play linked more to feelings of competence, relatedness, enjoyment
* it meets psychological needs of satisfaction
* collaborative play linked more to feelings of competence, relatedness, enjoyment
70
New cards
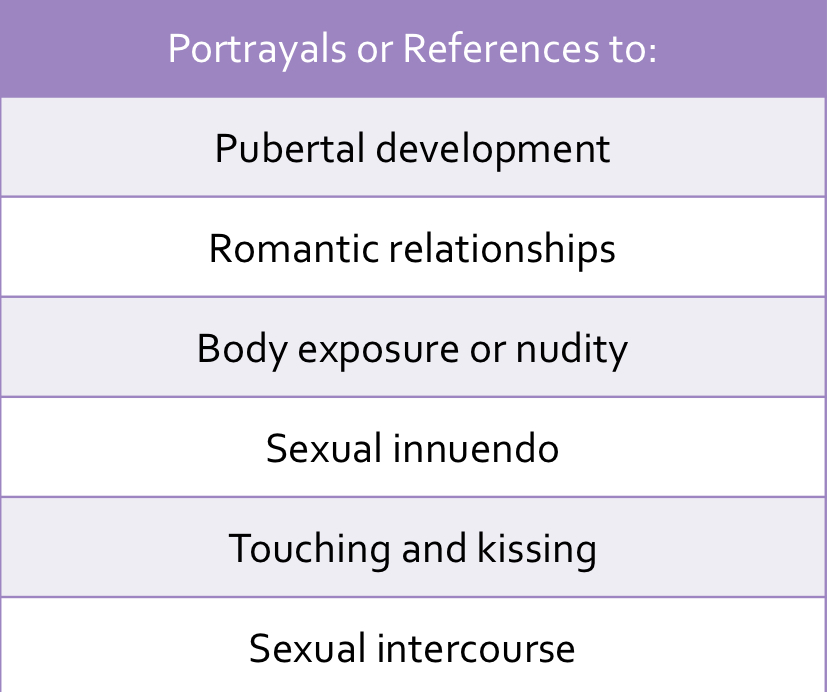
Sexual media
any representation of sex or sexual themes
* sexual behaviour (broadly defined even kissing)
* suggestions of sexual behaviour
* sexual talk (much more common)
* sexual behaviour (broadly defined even kissing)
* suggestions of sexual behaviour
* sexual talk (much more common)
71
New cards
Sexual media messages
* youth oriented media often does not include messages about the risks & responsibility
* most common consequences portrayed are emotional
* more negative consequences for females and straight characters in comparison to male & LGBTQ+
* most common consequences portrayed are emotional
* more negative consequences for females and straight characters in comparison to male & LGBTQ+
72
New cards
Heterosexual script
most sexual encounters are depicted through a heterosexual lens
* gendered behaviour (men pursue women are pursued)
* gendered behaviour (men pursue women are pursued)
73
New cards
Sexual socialization
how we learn to think about sex
* our sexual knowledge, values, attitudes & behaviours develop
* influenced by biology, parents, peers, culture, media
* our sexual knowledge, values, attitudes & behaviours develop
* influenced by biology, parents, peers, culture, media
74
New cards
Third person effect
teens often think that media impacts sexual development for others but not necessarily for themselves
75
New cards
Sexualization
to make something sexual
* connecting value to the trait of being sexy
* sexuality being inappropriately imposed on someone
* connecting value to the trait of being sexy
* sexuality being inappropriately imposed on someone
76
New cards
Sexual objectification
turning a person into a thing or object for the sexual use of others
77
New cards
Social cognition theory & sexual media
the idea that media consumers will observe & model sexual behaviour
* more likely to model indv’s similar to self / those with positive traits
* more likely to model indv’s similar to self / those with positive traits
78
New cards
Cultivation theory & sexual media
long term repeated consumption of sexual themes will shape attitudes & beliefs
* repeatedly being shown the same messages
* repeatedly being shown the same messages
79
New cards
Sexual scripts theory
sexuality & sexual behaviour determined by stereotyped patterns of sexual expectations
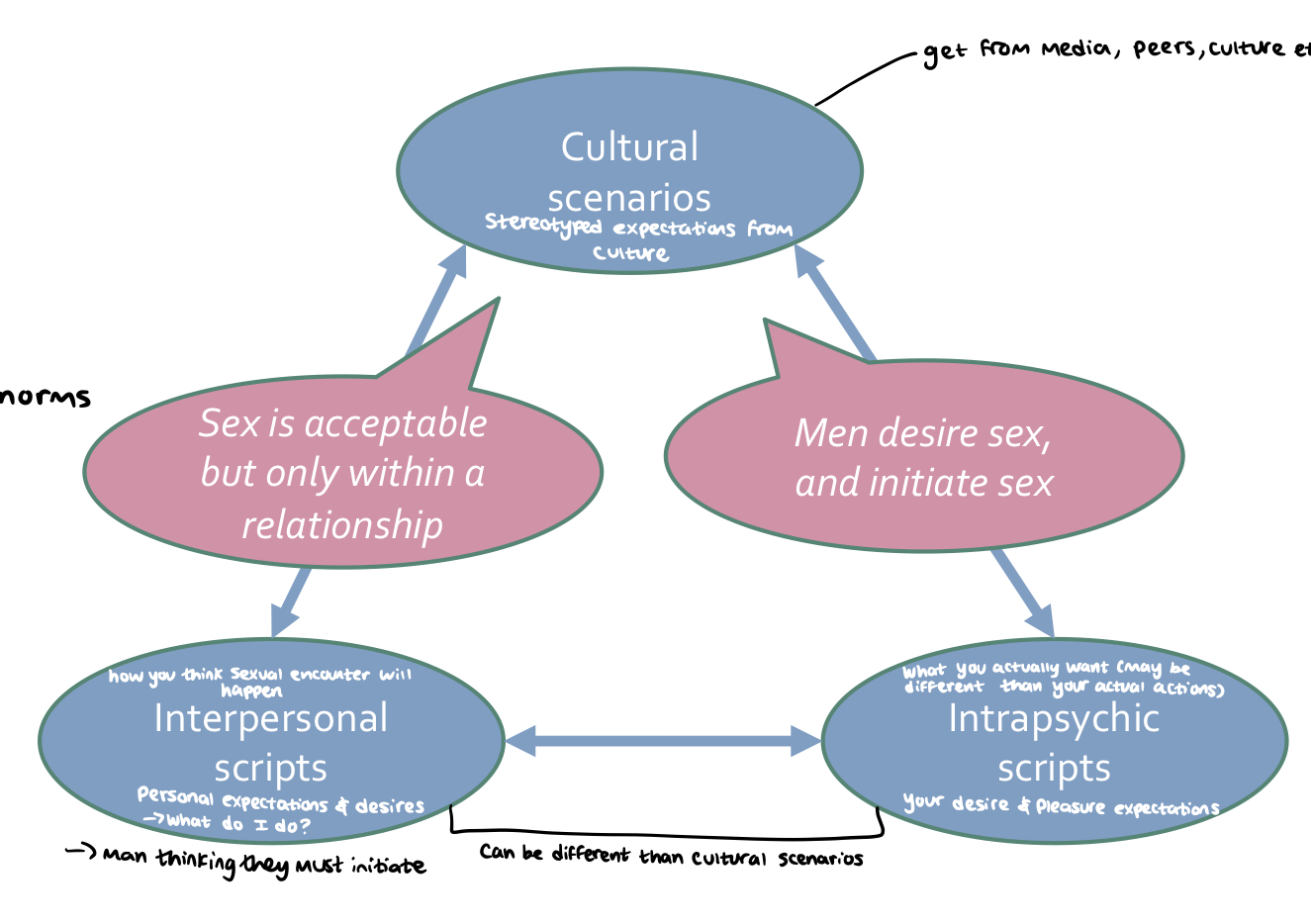
80
New cards
Media practice model
media use is active and individual, we choose what to consumer & how it impacts us
* our identity plays a major role in the interaction
* our identity plays a major role in the interaction
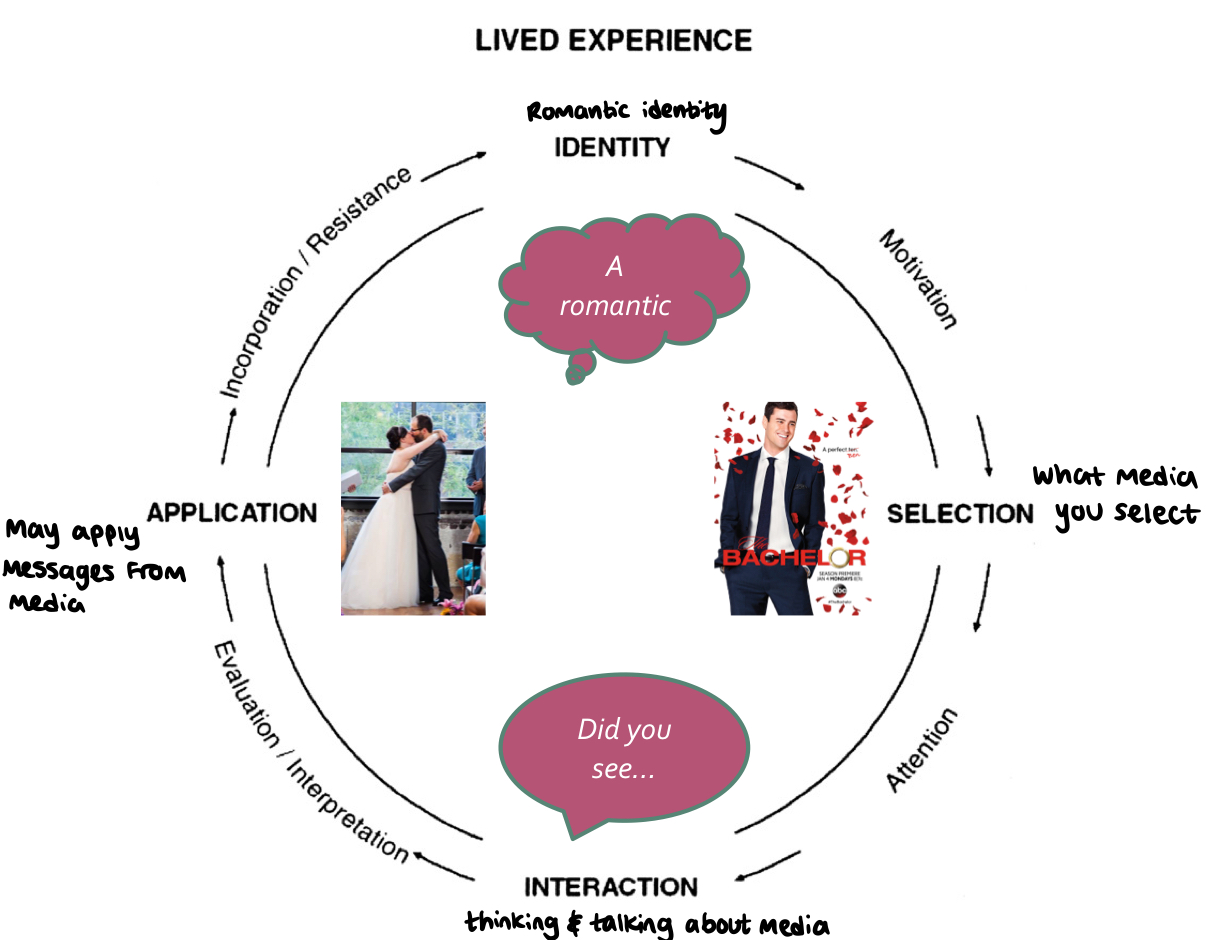
81
New cards
Sexual cognition research
consuming greater amounts of sexual media associated with…
* more accepting of sex, especially towards sex outside of a committed relationship
* belief that more friends are engaging in sexual behaviour (only about 50% of teens)
* expectations of fewer negative consequences associated with sex
* beliefs of women as sex objects
* more accepting of sex, especially towards sex outside of a committed relationship
* belief that more friends are engaging in sexual behaviour (only about 50% of teens)
* expectations of fewer negative consequences associated with sex
* beliefs of women as sex objects
82
New cards
Sexual media as educational tool
* media can have a positive impact on sexual knowledge
83
New cards
Sexual media & sexual behaviour
greater amounts of sexual media correlated with
* greater likelihood of having engaged in sexual behaviour
* more sexual partners
* having started sexual behaviour at earlier ages
* greater likelihood of having engaged in sexual behaviour
* more sexual partners
* having started sexual behaviour at earlier ages
84
New cards
Sexual media exposure race differences
* white youth who watched more sexual media predicted them having sex at an earlier age
* black youth not impacted by media (but still having sex at younger ages)
* ex: a white 13 year old would be most affected by sexual media
* black youth not impacted by media (but still having sex at younger ages)
* ex: a white 13 year old would be most affected by sexual media
85
New cards
Sexual media exposure age differences
early adolescence is impacted more compared to late / adulthood
86
New cards
Limitations of sexual media & sexual behaviour correlations
* accuracy of survey response
* sample demographics (biased)
* correlation not causation
* lack of generalizability
* focus only on sexual risks not sexual satisfaction
* sample demographics (biased)
* correlation not causation
* lack of generalizability
* focus only on sexual risks not sexual satisfaction
87
New cards
Queer representation in media
TV: historically very little representation but increasing
* LGBTQ+ indv’s often portrayed as sexless or hypersexualized
* stereotyped one dimensional portrayals (funny gay best friend or only defined by their sexuality)
* linked to more accepting views on straight consumers
* LGBTQ+ indv’s often portrayed as sexless or hypersexualized
* stereotyped one dimensional portrayals (funny gay best friend or only defined by their sexuality)
* linked to more accepting views on straight consumers
88
New cards
Queer consumers
* often report getting info. about sex & sexuality from media
* cane be validating or demeaning portrayals
* cane be validating or demeaning portrayals
89
New cards
Intergroup contact theory
stereotyping & discrimination can be reduced when indv’s from different social groups have contact
90
New cards
Parasocial contact hypothesis
media consumers can form relationships with media characters which may reduce stereotyping & discrimination
91
New cards
Sexually explicit media
direct depictions of sexual activities with the intention to arouse
* genitals shown
* penetration visinle
* genitals shown
* penetration visinle
92
New cards
Sexually explicit media & youth
sizeable proportion of youth are exposed to pornography
* huge range between 7-98%
* unintentional exposure more common 19-84%
* intentional: 7-59%
* huge range between 7-98%
* unintentional exposure more common 19-84%
* intentional: 7-59%
93
New cards
Whio is more likely to access sexually explicit media?
* men/ boys
* pubertally more advanced
* indv’s high in sensation seeking
* weak or troubled family relationships
* pubertally more advanced
* indv’s high in sensation seeking
* weak or troubled family relationships
94
New cards
Negative impacts of porn
* more permissive views about sex
* greater likelihood of sexual behaviour / casual sex
* gender stereotyped beliefs
* sexual agression linked to violent porn?
* possibly believe sex has no risks / consequences
* greater likelihood of sexual behaviour / casual sex
* gender stereotyped beliefs
* sexual agression linked to violent porn?
* possibly believe sex has no risks / consequences
95
New cards
Positive impacts of porn
* source of info. about sex
* knowledge about human body
* recognizing / confirming sexual identity
* sexual satisfaction
* knowledge about human body
* recognizing / confirming sexual identity
* sexual satisfaction
96
New cards
Global time estimates (GTE)
a participant answers a series of questions regarding the amount of time spent engaging in a particular media-related activity
* imprecise data
* prone to social desirability
* imprecise data
* prone to social desirability
97
New cards
Social desirability
when people provide answers they deem are more socially acceptable
98
New cards
Time use diaries (TUD)
respondents record all of their activities over a 24 hour period (including non-media related activities)
* relays an indv’s day is it unfolds
* don’t provide any info regarding the content of media consumed
* relays an indv’s day is it unfolds
* don’t provide any info regarding the content of media consumed
99
New cards
Media diaries
TUD’s that spotlight media use
* participants easily record their media consumption by circling an answer on a guide
* parents fill out for children under 8
* participants easily record their media consumption by circling an answer on a guide
* parents fill out for children under 8
100
New cards
Electronic monitoring (EMSs)
collect media data automatically by connecting a meter to a tv set or having the indv carry around a small portable meter
* record the type of content & use of media
* but a failure to login or log out can produce erroneous data
* primarily used for commercial assessments of radio & tv use
* record the type of content & use of media
* but a failure to login or log out can produce erroneous data
* primarily used for commercial assessments of radio & tv use