Lecture 14: Autonomic Nervous System & Somatic Nervous System
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Nerves
Groups of axons in PNS
Tracts
Groups of axons in CNS
Nuclei
Groups of cell bodies in CNS
Ganglia
Groups of cell bodies in PNS
Autonomic system
Controls involuntary functions, maintains homeostasis, has afferent and efferent neurons, and efferent neurons innervate visceral organs
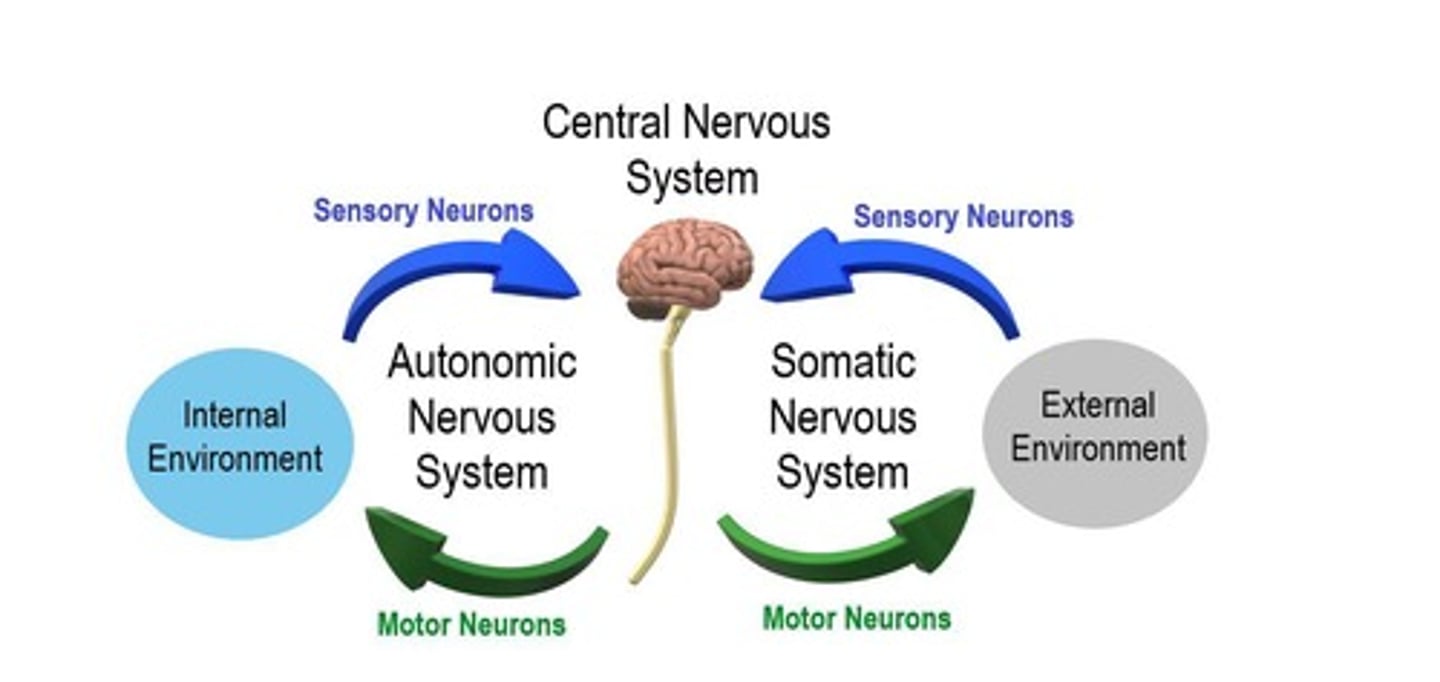
Somatic system
Controls voluntary functions, has afferent and efferent neurons, and efferent neurons innervate skeletal muscles
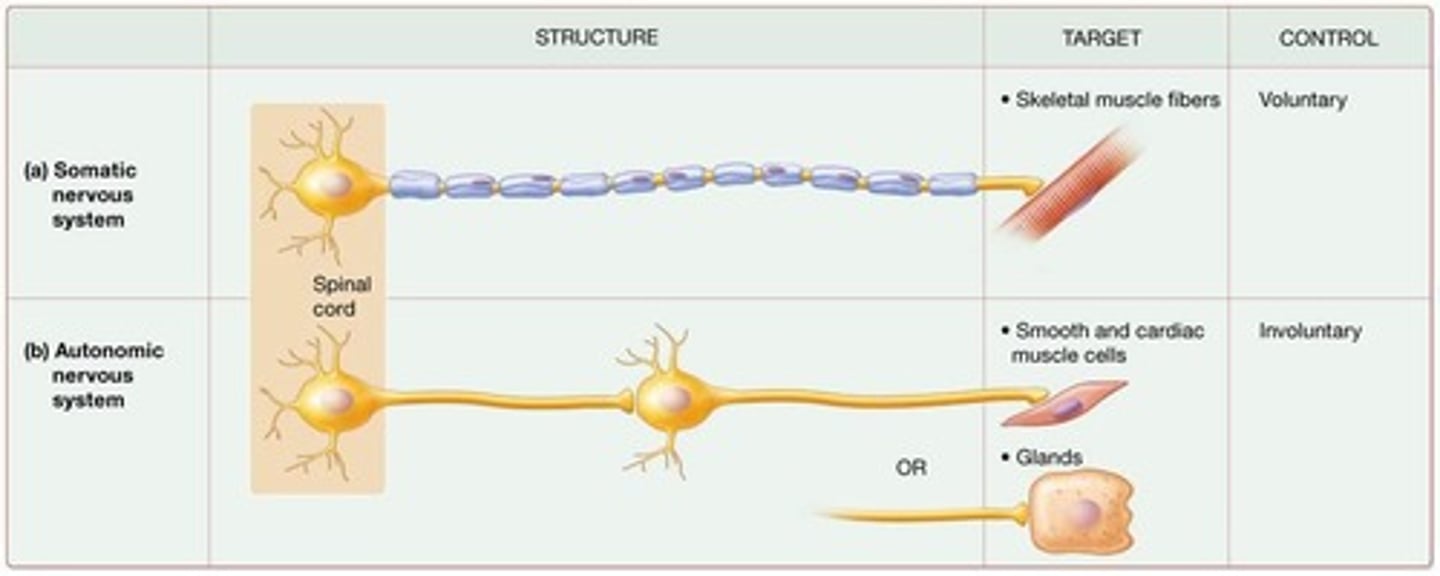
Somatic Motor Division
Neurons innervate skeletal muscles and lead to voluntary muscle contractions initiated consciously
Autonomic Motor Division
Neurons innervate smooth muscle cells, cardiac muscle cells, and glands, leading to involuntary actions initiated not consciously
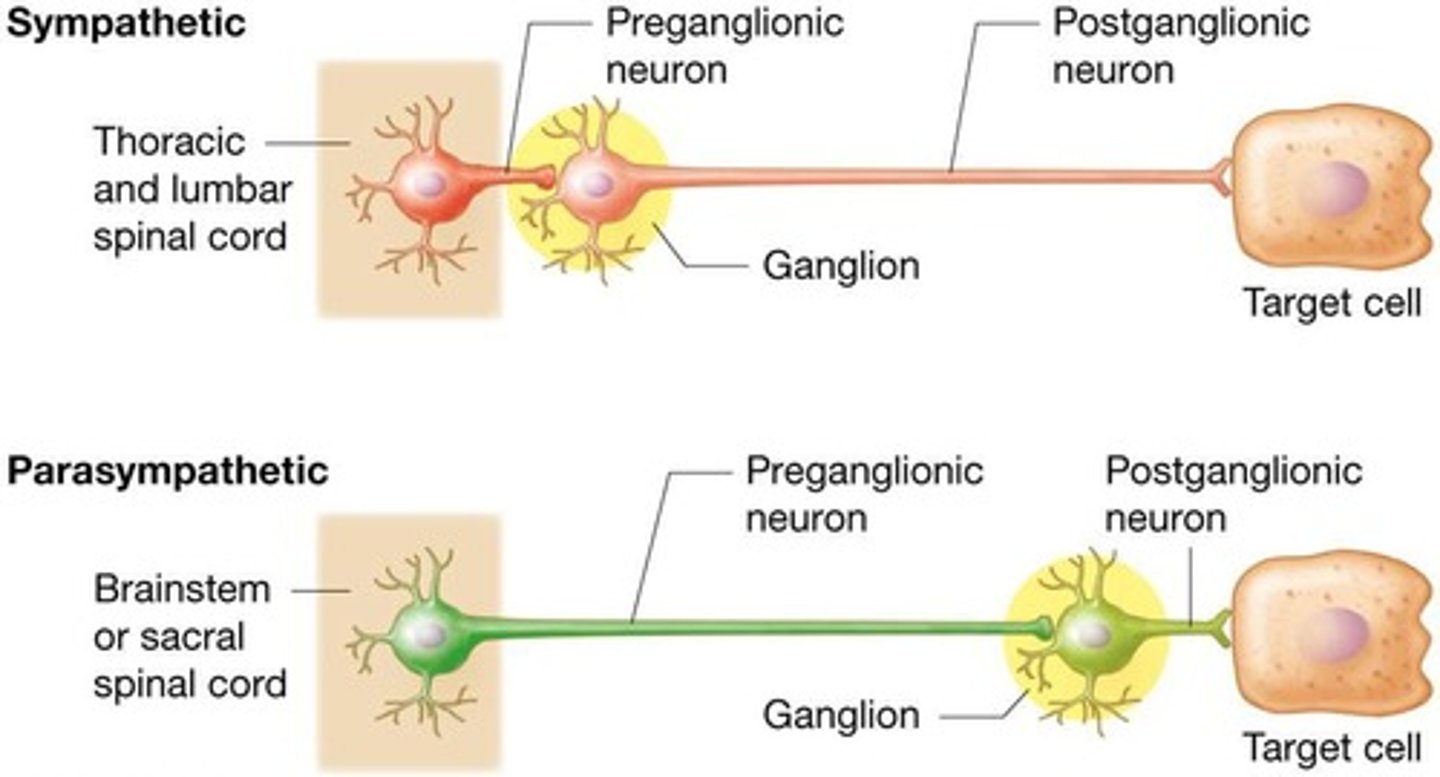
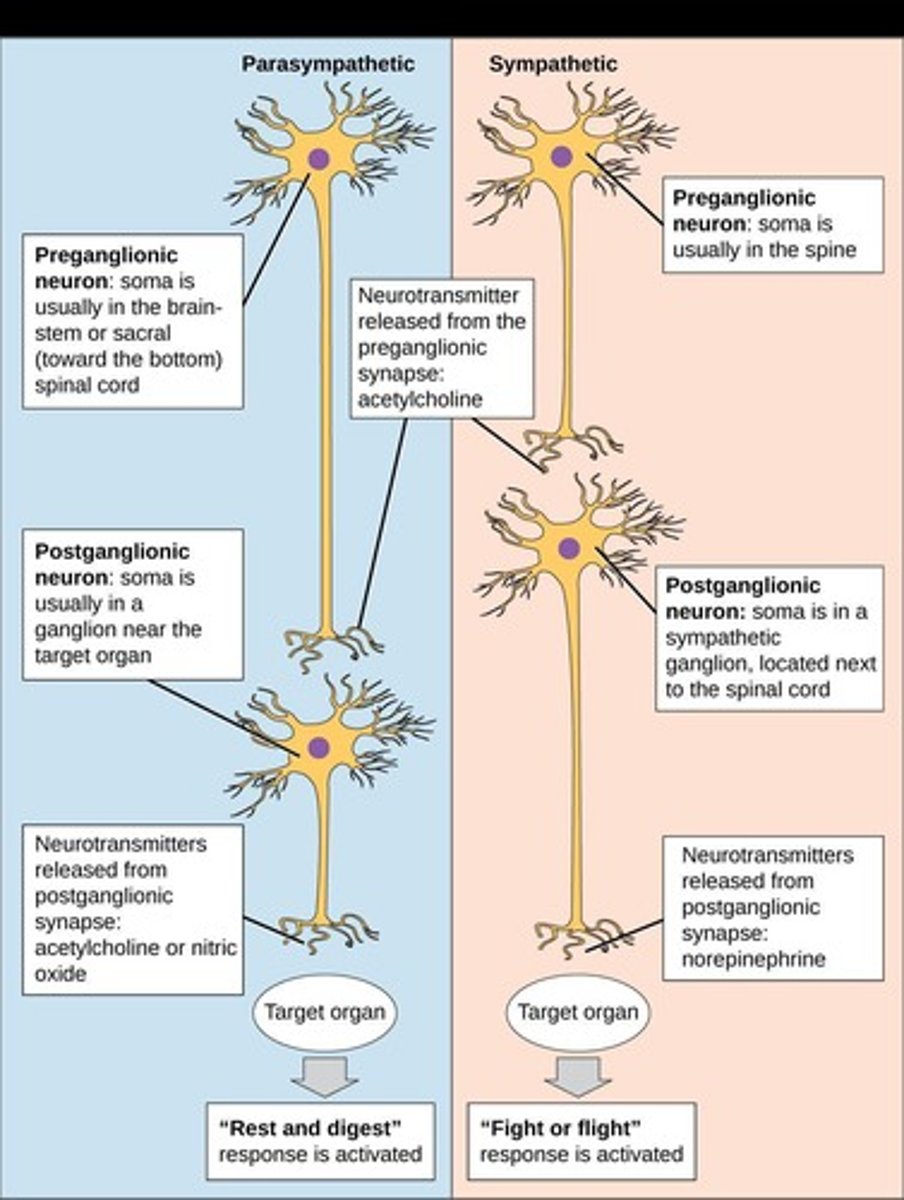
Preganglionic neuron
Initial efferent neuron with cell body residing within CNS, all axon terminals release ACh
Postganglionic neuron
Cell body resides in autonomic ganglion in PNS, axons travel to target cells, release either ACh or norepinephrine, and trigger specific changes
Visceral reflex
A reflex specific to the autonomic division to which it belongs
Central nervous system
Coordinates and contributes to autonomic functions
General senses
Senses that include touch, pain, temperature, and proprioception
Special senses
Senses that include sight, hearing, taste, smell, and equilibrium
Sensory neurons
Neurons related to general senses and special senses
Motor neurons
Neurons that innervate skeletal muscles
Involuntary actions
Actions produced by the autonomic motor division
Voluntary muscle contractions
Contractions produced by the somatic motor division
Afferent neurons
Neurons that carry sensory information to the central nervous system
Efferent neurons
Neurons that carry motor commands from the central nervous system to effectors
Homeostasis
The maintenance of stable internal conditions by the autonomic system
Enteric division
Part of the autonomic nervous system that controls digestion
Target effector
The organ or tissue that responds to autonomic input
Somatic Nervous System
The axon of a single, myelinated somatic motor neuron extends from the CNS to the skeletal muscle fiber it innervates.
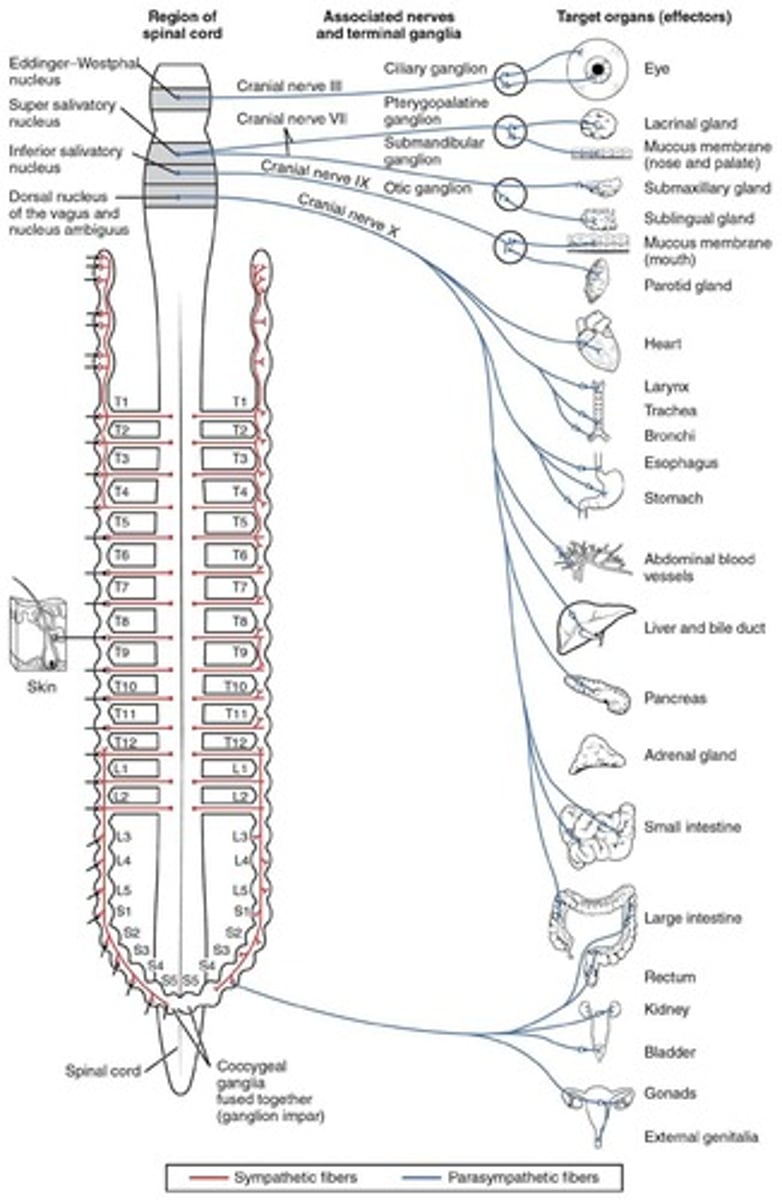
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Craniosacral division; most active during resting conditions; 'rest and digest' response.
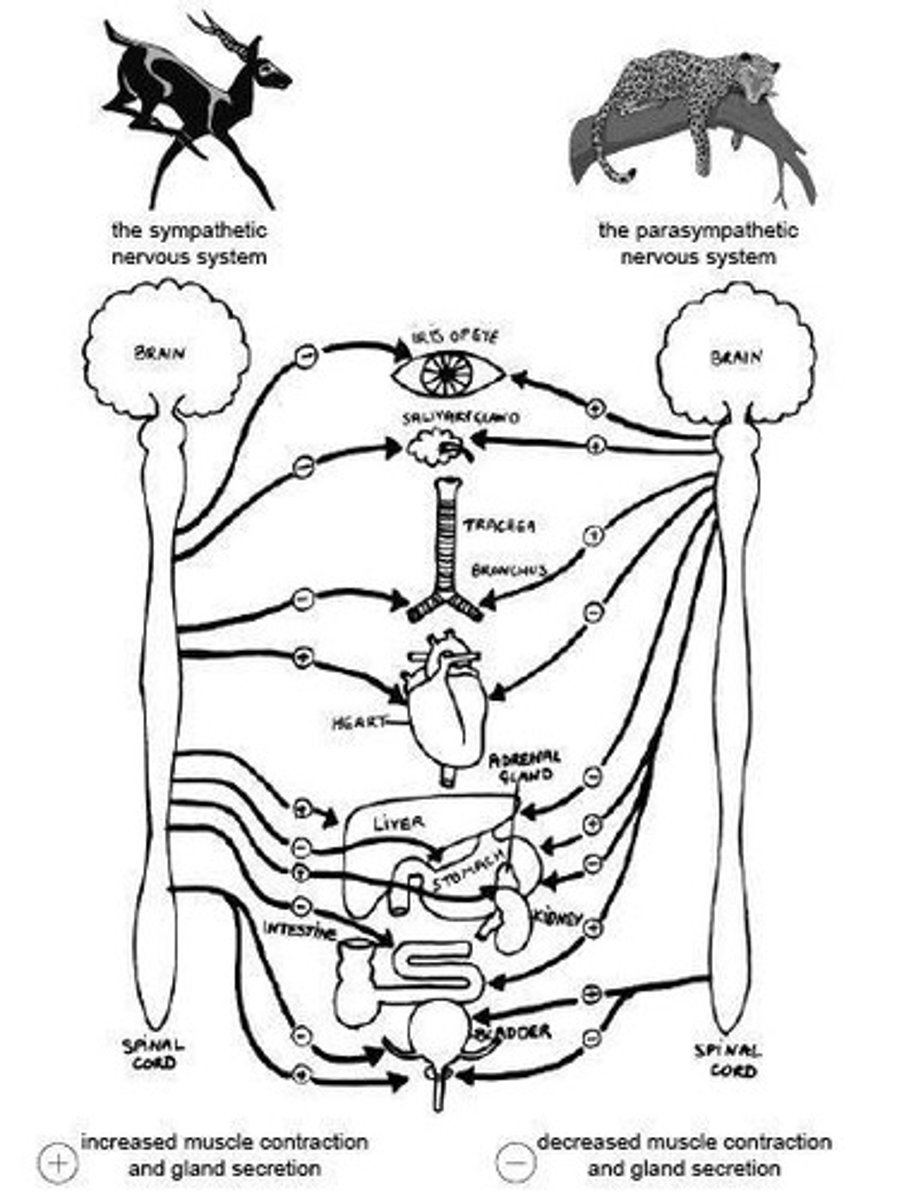
Sympathetic Nervous System
Thoracolumbar division; most active during times of stress/exertion; 'fight or flight or freeze or fawn' response.
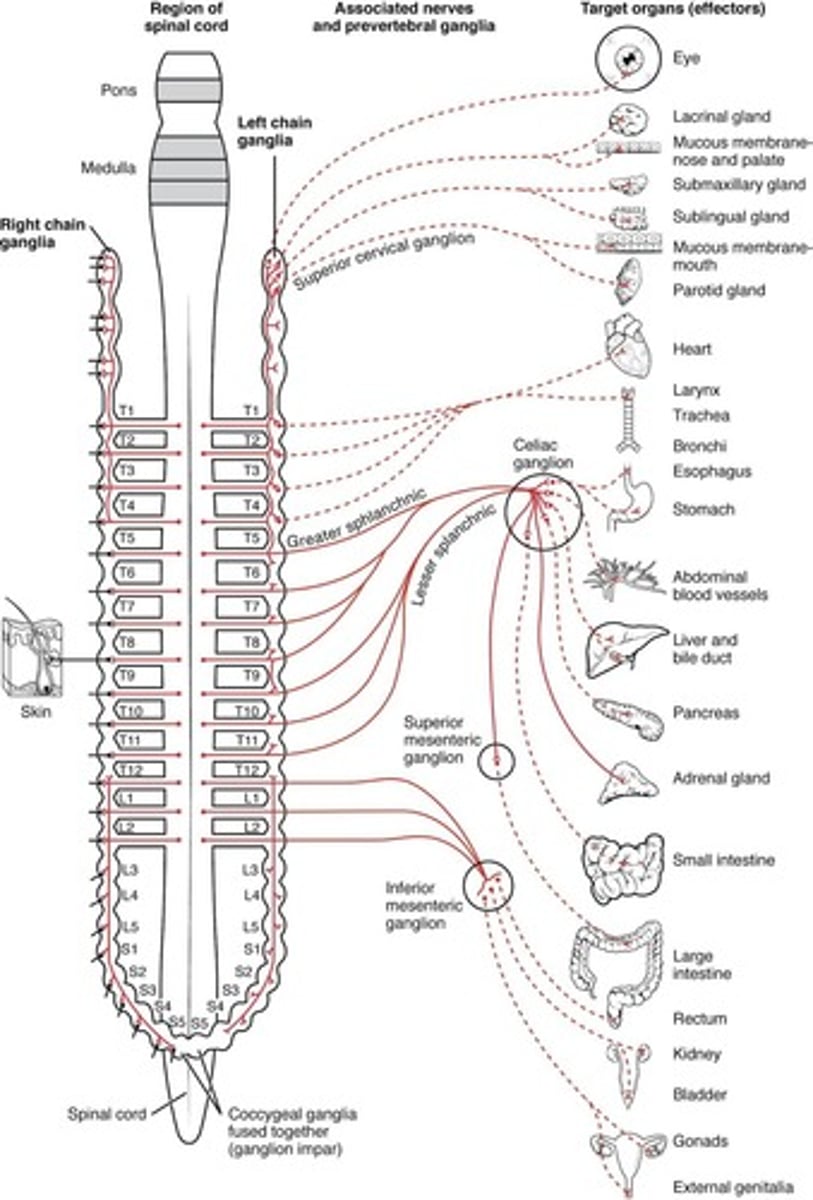
Sympathetic NS Effects
Prepares body for increased activity levels; dilates pupils, increases heart rate, increases breathing rate, decreases digestive activity.
Parasympathetic NS Effects
Conserves energy during relaxation; constricts pupils, decreases heart rate, decreases breathing rate, increases digestive activity.
ANS Motor Pathways
Most autonomic motor pathways consist of two motor neurons in series: a preganglionic neuron and a postganglionic neuron.
Sympathetic Division
Stimulation leads to increased alertness and metabolism to be ready for an emergency.
Parasympathetic Division
Stimulation slows down most body activities.
Sympathetic Preganglionic Axons
Short; secretes ACh.
Sympathetic Postganglionic Axons
Long; secretes NorE. or ACh.
Parasympathetic Preganglionic Axons
Long; secretes ACh.
Parasympathetic Postganglionic Axons
Short; secretes ACh.
Sympathetic Ganglia
Cell bodies of the sympathetic preganglionic neurons are part of the lateral gray horns of all thoracic segments and of the first two lumbar segments of the spinal cord.
Sympathetic Trunk Ganglia
Lie in a vertical row on either side of the vertebral column.
Prevertebral Ganglia
Lie anterior to the vertebral column and close to the large abdominal arteries.
Sympathetic Outflow
Cell bodies of preganglionic neurons are in the lateral horns of the gray matter in the 12 thoracic and first 2 or 3 lumbar segments.
Parasympathetic Outflow
Cell bodies of the preganglionic neurons are in the nuclei of four cranial nerves (III, VII, IX, and X) in the brain stem and in the lateral gray matter of sacral segments 2-4 of the spinal cord.
Autonomic Plexuses
The abdomen and pelvis contain major autonomic plexuses which are often named after the artery along which they are distributed.
Celiac Plexus
One of the major autonomic plexuses in the abdomen.
Superior Mesenteric Plexus
One of the major autonomic plexuses in the abdomen.
Inferior Mesenteric Plexus
One of the major autonomic plexuses in the abdomen.
Renal Plexus
One of the major autonomic plexuses in the abdomen.
Hypogastric Plexus
One of the major autonomic plexuses in the abdomen.
Cholinergic Neurons
Release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
Cholinergic Receptors
Include nicotinic receptors and muscarinic receptors.
Adrenergic neurons
Release norepinephrine (noradrenalin)
Sympathetic
Part of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for stressful or emergency situations.
Parasympathetic
Part of the autonomic nervous system that conserves energy and restores the body to a state of calm.
Preganglionic
Neurons that release acetylcholine to nicotinic receptors.
Postganglionic
Neurons that release acetylcholine to muscarinic receptors.
Norepinephrine
A neurotransmitter that binds to α- or β-adrenergic receptors.
Sympathetic Receptor Classes
Two types: Adrenergic receptors and Cholinergic receptors.
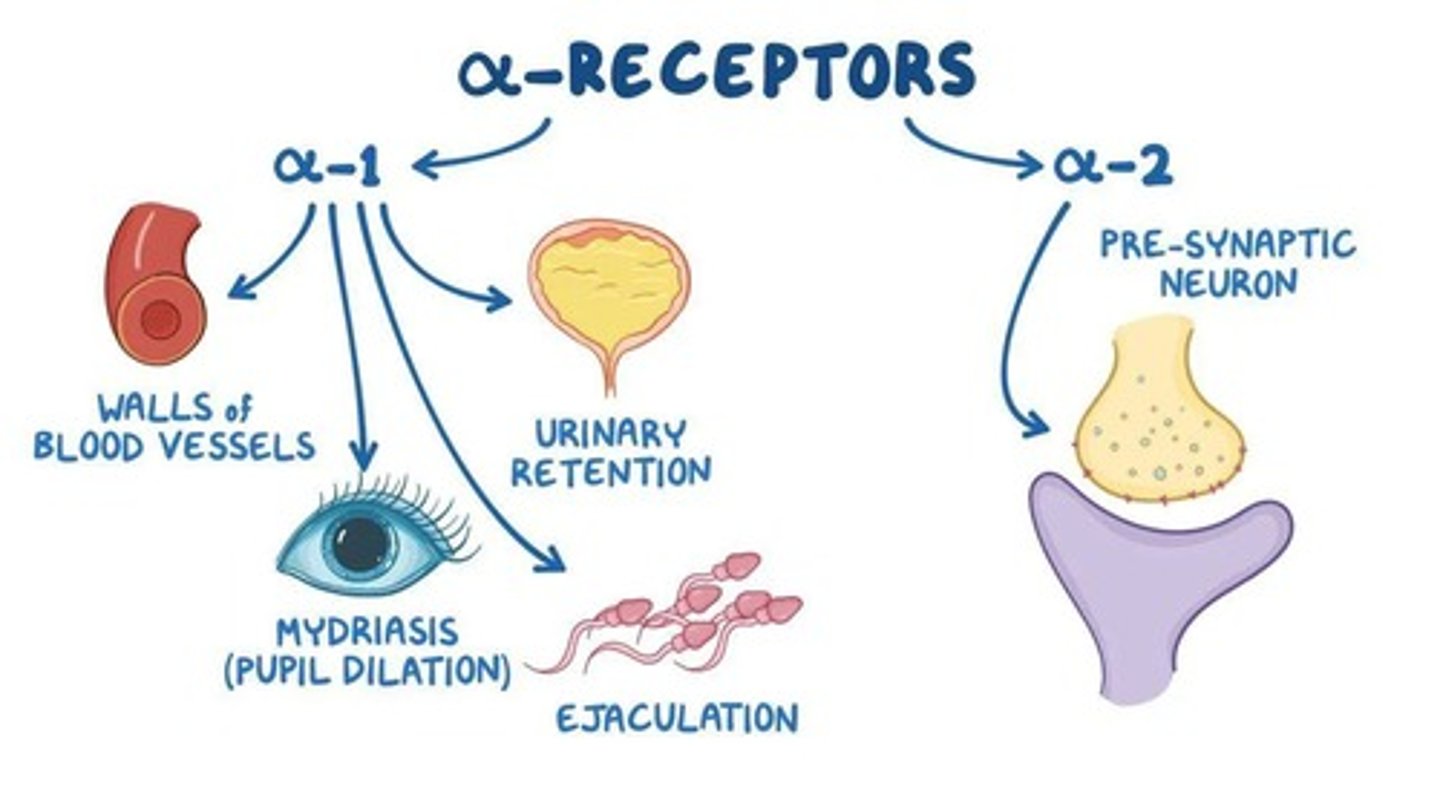
Adrenergic receptors
Bind to epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Alpha adrenergic
A major type of adrenergic receptor.
Beta adrenergic
A major type of adrenergic receptor with subtypes: Beta-1, Beta-2, and Beta-3.
Beta-1 receptors
Located in the plasma membrane of cardiac muscle cells, certain kidney cells, and adipose cells.
Beta-2 receptors
Located in the plasma membrane of smooth muscle cells lining airways of the respiratory tract and in the wall of the urinary bladder.
Beta-3 receptors
Primarily found in adipose cells and smooth muscle cells in walls of the digestive tract.
Muscarinic receptors
Type of cholinergic receptor found on sweat glands in skin.
Nicotinic receptors
Type of cholinergic receptor located in the plasma membrane of all postganglionic neurons.
Cholinergic vs. Adrenergic
Cholinergic neurons release acetylcholine while adrenergic neurons release norepinephrine.
Sensation
Conscious and subconscious awareness of changes in the external or internal environment.
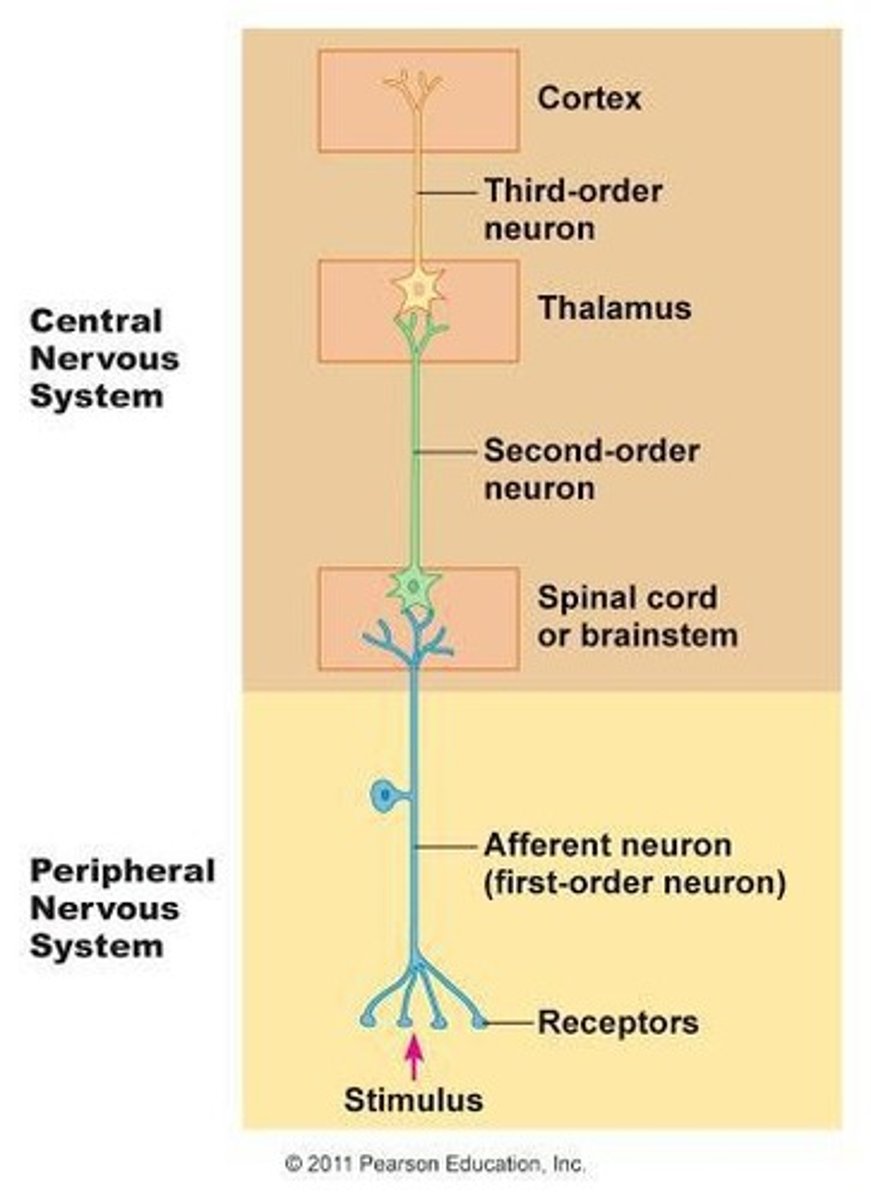
Components of sensation
Stimulation of the sensory receptor → transduction of the stimulus → generation of nerve impulses → integration of sensory input.
Classification of Sensory Receptors
Divided into general senses (somatic and visceral) and special senses (smell, taste, vision, hearing, and equilibrium).
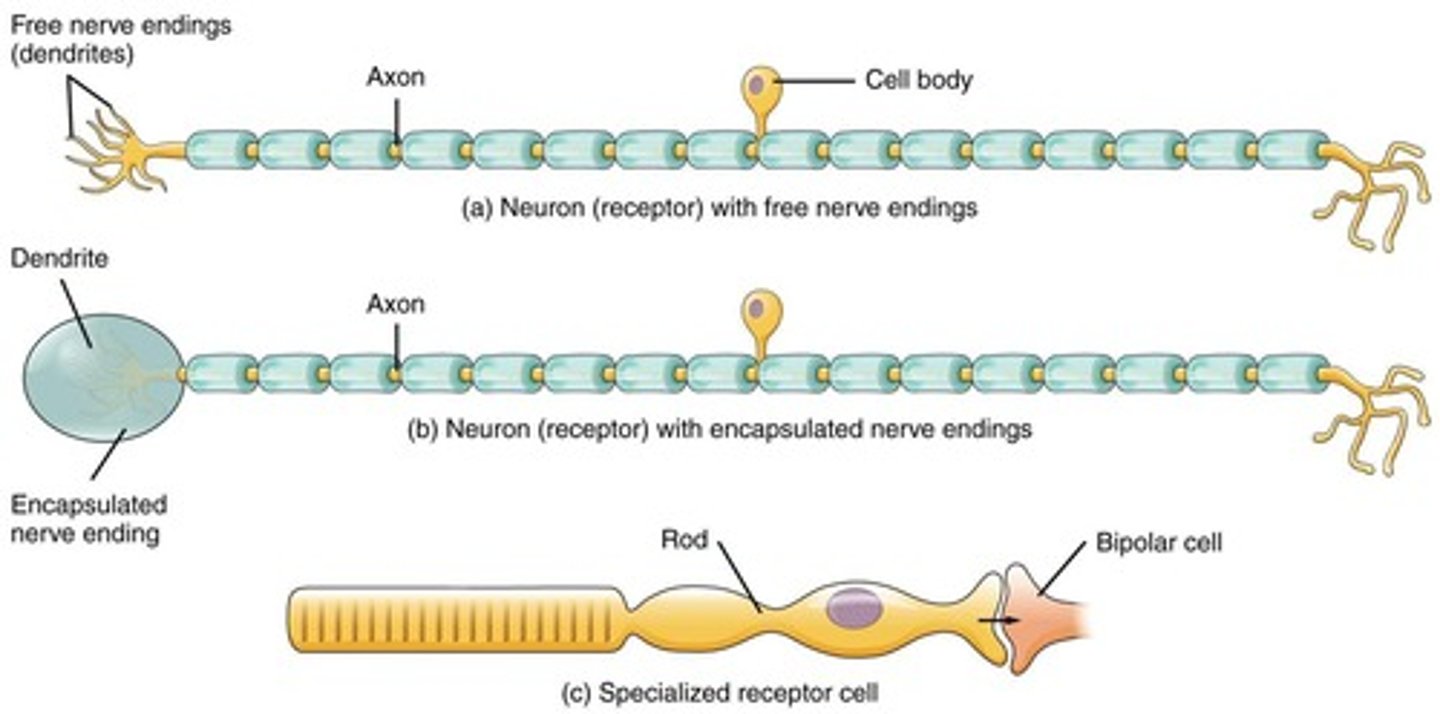
Types of Sensory Receptors
Includes free nerve endings (pain and thermoreceptors) and encapsulated nerve endings (like pacinian and Meissner's corpuscles).
Exteroceptors
Sensory receptors located at or near the body surface.
Interoceptors
Sensory receptors located inside the body, including blood vessels, viscera, and the nervous system.
Proprioceptors
Sensory receptors located in muscles, tendons, joints, and the inner ear.
Mechanoreceptors
Sensory receptors that respond to touch and pressure.
Thermoreceptors
Sensory receptors that respond to temperature changes.
Nociceptors
Sensory receptors that detect pain.
Photoreceptors
Sensory receptors that are specific to the retina.
Chemoreceptors
Sensory receptors that respond to smell, taste, O2, and CO2.
Osmoreceptors
A type of chemoreceptor that responds to osmotic pressure.
Baroreceptors
A type of mechanoreceptor that responds to pressure.
Sensory Receptor Adaptation
The decrease in potentials during a maintained, constant stimulus.
Rapidly adapting receptors
Receptors that detect pressure, touch, and smell.
Slowly adapting receptors
Receptors that detect pain, body position, and chemical composition of the blood.
Somatic Sensations
Sensory perceptions from receptors in the skin, muscles, tendons, and joints.
Tactile Sensations
Sensations that include touch, pressure, vibration, itch, and tickle.
Referred Pain
Pain felt in or just deep to the skin that overlies the stimulated organ or in a surface area far from the stimulated organ.
Proprioceptive Sensations
Sensations detected by proprioceptors, which include weight discrimination.
Somatic Sensory Pathways
Pathways that carry information from somatic sensory receptors to the primary somatosensory area in the cerebral cortex and to the cerebellum.
First-order neurons
Neurons that carry impulses from somatic receptors to the brainstem or spinal cord.
Second-order neurons
Neurons that carry impulses from the brainstem and spinal cord to the thalamus.
Third-order neurons
Neurons that carry impulses from the thalamus to the primary somatosensory area of the cortex on the same side.
Primary Somatosensory Area
The postcentral gyri located on both parietal lobes of the brain that receive sensory input from different parts of the body.
Lower motor neurons (LMNs)
Nerves that extend out of the brainstem and spinal cord, innervating skeletal muscles.
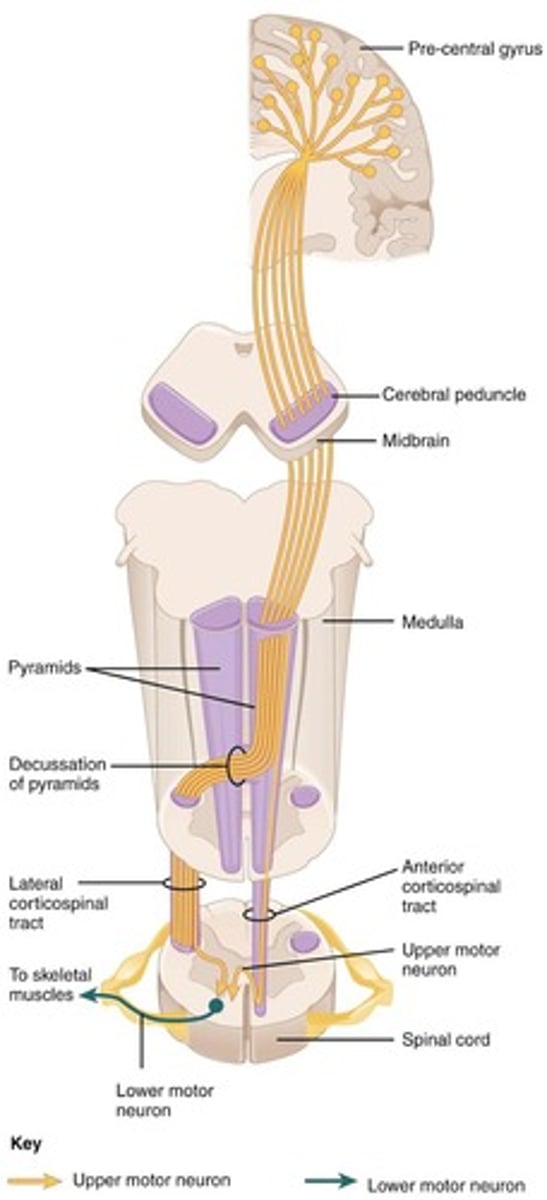
Somatic Motor Pathways
Pathways that provide input into lower motor neurons and are divided into distinct circuits.
Direct motor pathways
Pathways that deliver signals to LMNs from the cerebral cortex.
Indirect motor pathways
Pathways that deliver signals to LMNs from motor centers in the basal nuclei, cerebellum, and cerebral cortex.
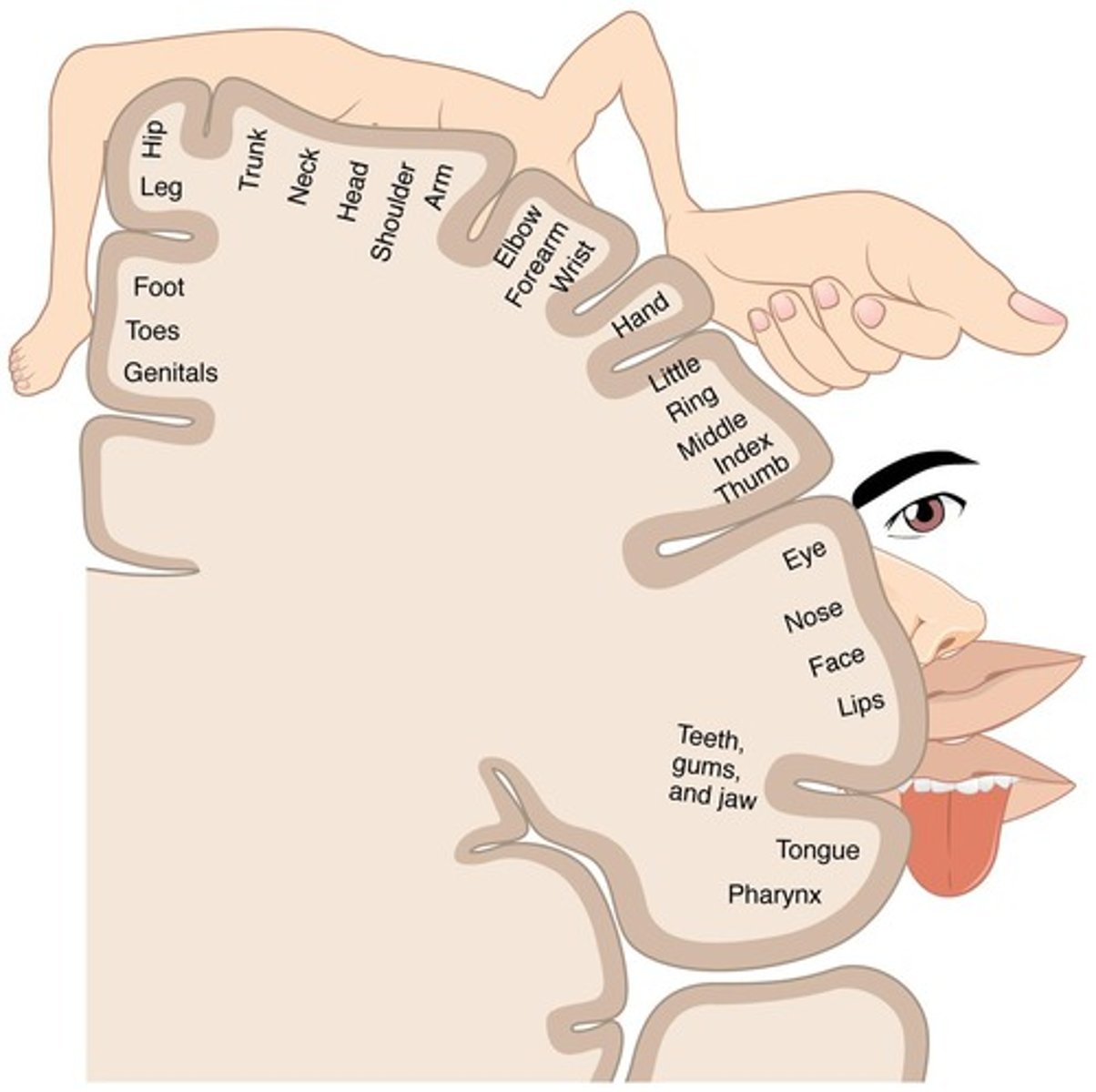
Primary Motor Area
The area of the brain where each point of the body maps to a specific region.

Autonomic Nervous System
A part of the nervous system that controls involuntary bodily functions.
Target Effector Response
The reaction of a target organ or tissue to autonomic input based on the released signaling molecule.
Central Nervous System Contribution
The role of the brain and spinal cord in coordinating and regulating autonomic functions.
Stimulus-Response Motor Pathway
The pathway through which sensory stimuli are processed and lead to motor responses.
Sympathetic Preganglionic Neurons
Neurons that originate in the spinal cord and synapse in the sympathetic trunk ganglia.