Amides and Nitriles
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
How are amides formed?
React the acid with basic ammonia to give the ammonium carboxylate salt. Heat the salt; this results in water being lost and the amide is produced.
Heat the acid or its ammonium salt with urea at 120°C.
What reaction do amides undergo to form nitriles?
Amides undergo dehydration reactions to form nitriles.
P4O10 is used.
How else are nitriles formed?
From halogenoalkanes.
Reagents: Potassium cyanide (KCN) using an alcohol-water mixture as a solvent.
Conditions: Heated under reflux.
What type of reaction occurs when forming nitriles from halogenoalkanes?
Nucleophilic substitution.
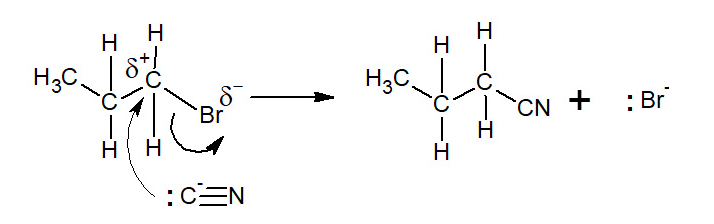
Do aromatic halogenolkanes react with cyanide ions?
No- the ring carbon atoms are not suspectible to nucleophilic attack.
How are hydroxynitriles formed?
By reacting aldehydes / ketones with hydrogen cyanide (HCN) in the presence of sodium or potassium cyanide.
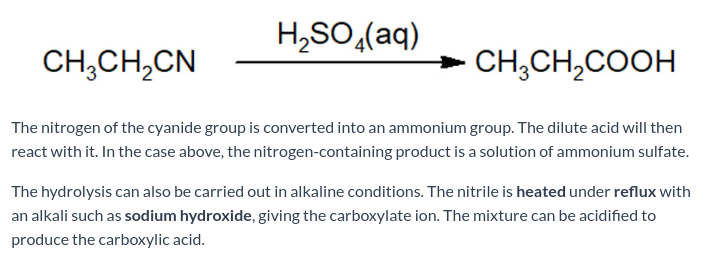
Nitriles are hydrolysed to form what?
Carboxylic acids.
State what reagents / conditions are needed to hydrolyse nitriles to carboxylic acids.
The reaction is heated under reflux with a dilute acid (H2SO4).
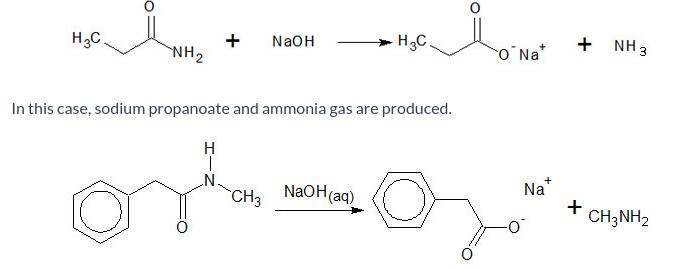
Describe what happens during hydrolysis of amides.
This reaction is carried out by heating the amide, under r-eflux, with aqueous sodium hydroxide.
The carbon-nitrogen bond is broken, giving the sodium carboxylate ion and a nitrogen containing compound. The nitrogen containing compound differs depending on whether the nitrogen was substituted or not.
Again, the carboxylic acid can be obtained by acidification (reprotonation) using a dilute acid.
Nitriles are converted to primary amines in what type of reaction?
Reduction reaction.
LiAlH4 dissolved in ethoxyethane is used.