sociology learning objectives - miterm 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
1
New cards
Human cognitive bias
Confirmation bias: our tendency to ignore evidence/observations that contradict our beliefs (ex: climate change)
Attribution error: our tendency to attribute people's behavior/life outcomes to innate character or personality traits rather than to external.situational factors (ex:homeless people/external - dont value working/situational - mental health)
Implicit bias: subconscious biases toward outside groups (and subconscious preferences towards one's own group)
Attribution error: our tendency to attribute people's behavior/life outcomes to innate character or personality traits rather than to external.situational factors (ex:homeless people/external - dont value working/situational - mental health)
Implicit bias: subconscious biases toward outside groups (and subconscious preferences towards one's own group)
2
New cards
The sociological perspective
We live in a very individualists society
However our individual lives are deeply entangled with and shaped by our social environments
Our social environments greatly influence our identities, beliefs, values and behavior
Our social environments also greatly influence our experiences, opportunities and life outcomes
However our individual lives are deeply entangled with and shaped by our social environments
Our social environments greatly influence our identities, beliefs, values and behavior
Our social environments also greatly influence our experiences, opportunities and life outcomes
3
New cards
The sociological perspective - 2 levels
Structural level of society (macro)
EX: our culture, health care systems, uw madison, legal system
Symbolic level of society (micro)
Ex: Individual interactions, thoughts. Perceptions, etc
EX: our culture, health care systems, uw madison, legal system
Symbolic level of society (micro)
Ex: Individual interactions, thoughts. Perceptions, etc
4
New cards
The social and cultural construction of reality (missing cultural)
Social structure: a system of organized activity, durable relationships, and routine practices (ex: economic, educational, legal, family, media, religion etc)
5
New cards
race/ethnicity as a structural phenomenon
- There is an organized, durable race/ethnic hierarchy in our society
- race/ethnic groups at the top of the hierarchy (on average) have greater access to values resources than those at the bottom
- race/ethnic groups at the top of the hierarchy (on average) have greater access to values resources than those at the bottom
---Ex: Schools often put such students on the academic or AP “track”; blacks and hispanics more likely to be put on a lower vocational “track” (structural practice)
---Ex: This contributes to the achievement gap (structural outcome)
- race/ethnic groups at the top of the hierarchy (on average) have greater access to values resources than those at the bottom
- race/ethnic groups at the top of the hierarchy (on average) have greater access to values resources than those at the bottom
---Ex: Schools often put such students on the academic or AP “track”; blacks and hispanics more likely to be put on a lower vocational “track” (structural practice)
---Ex: This contributes to the achievement gap (structural outcome)
6
New cards
race/ethnicity as a symbolic phenomenon
- racial groups are typically defined according to arbitrary physical (external) traits (why did we choose to differentiate among racial groups? Why skin color? Why not eyes, height, feet? It was a social decision)
---Ex: Common stereotype: white and asian-american students are more academically skilled (symbolic)
---Ex: Reinforced and reproduced the stereotype (symbolic)
---Ex: Common stereotype: white and asian-american students are more academically skilled (symbolic)
---Ex: Reinforced and reproduced the stereotype (symbolic)
7
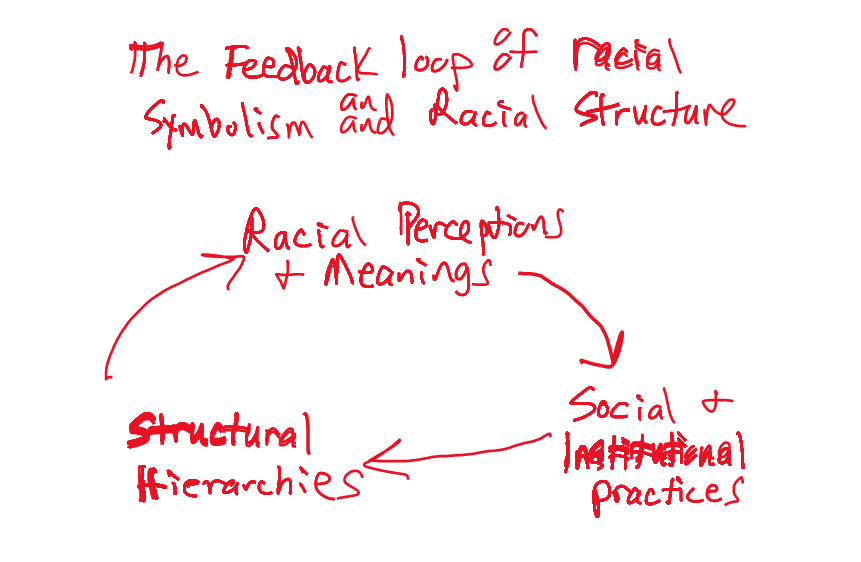
New cards
How the structural and the symbolic dimension are closely connected to and reinforce one another
Ex: standardized testing, charter/private schools chose who attends to school, biases in tests, AP/non AP
8
New cards
Why race is not a meaningful biological category (why it is a social construct)
- here is no biological reality to racial groupings
---Genetically, all human being are 99.9% identical to each other
---There is as much genetic diversity WITHIN race/ethinic groups as ACROSS race/ethinc groups
---There can be meaningful genetic differences between some geographic populations (ex: basketball and football mostly black but its not from a genetic advantage) (runners from western africa dominating a certain race)
---Populations are often (mistakenly) equated with racial groups
- So race is not a biological category of people (not objectively real or “natural”)
---Genetically, all human being are 99.9% identical to each other
---There is as much genetic diversity WITHIN race/ethinic groups as ACROSS race/ethinc groups
---There can be meaningful genetic differences between some geographic populations (ex: basketball and football mostly black but its not from a genetic advantage) (runners from western africa dominating a certain race)
---Populations are often (mistakenly) equated with racial groups
- So race is not a biological category of people (not objectively real or “natural”)
9
New cards
How the definition of ethnicity formally differs from the definition of race
- Race: a socially constructed category of people who share arbitrarily selected physical traits
- Ethnicity: a socially constructed category of people who share a common identity based on culture, language, and (typically) nationality (Ex: irish: Kenyan; Vietnamese; brazilian; seminole; etc)
- Ethnicity: a socially constructed category of people who share a common identity based on culture, language, and (typically) nationality (Ex: irish: Kenyan; Vietnamese; brazilian; seminole; etc)
10
New cards
The concept of “pan” ethnicity and some examples
Definition: Some racial/ethinic categories encompass numerous distinct ethnic groups/nationalities
examples:
Latin americans (geography) and hispanic (language): Mexico; cuba; puerto rico; honduras; panama; guatemala; venezuela; argentina; chile, etc
Asian american and pacific islander: China; india; korea; philippines; syria; iraq; indonesia; vietnam; japan; hmong; samoan; etc
Native americans: Encompasses many distinct tribes/nations
examples:
Latin americans (geography) and hispanic (language): Mexico; cuba; puerto rico; honduras; panama; guatemala; venezuela; argentina; chile, etc
Asian american and pacific islander: China; india; korea; philippines; syria; iraq; indonesia; vietnam; japan; hmong; samoan; etc
Native americans: Encompasses many distinct tribes/nations
11
New cards
The current and projected race/ethnic makeup of the U.S.
census?

12
New cards
Racial formation and racialization
Definition of
Racial formation: the historical processes by which social, economic, and political forces determine the content and meaning of racial [and ethnic] categories
Racialization: process by which a group is assigned a racial identity and place within a social hierarchy
Racial formation: the historical processes by which social, economic, and political forces determine the content and meaning of racial [and ethnic] categories
Racialization: process by which a group is assigned a racial identity and place within a social hierarchy
13
New cards
Early formation/racialization in the U.S. (what historical and social focus was it built upon?)
Slavery
war/conquest
Demand for cheap labor
war/conquest
Demand for cheap labor
14
New cards
Racial projects - discussed in class
Scientific racism (early 1900s): Darwin's theory of evolution used to “prove” that some racial groups were genetically superior
Salvery and the invention of “white” and “black”
U.S. conquest of native americans and mexico
Chinese immigration and demand for cheap labor
Salvery and the invention of “white” and “black”
U.S. conquest of native americans and mexico
Chinese immigration and demand for cheap labor
15
New cards
Conceptualizing racism as a continuum (See figures presented in lecture)
...

16
New cards
Minority groups
A race/ethnic group that receives (on average) significantly less of society's values resources and outcomes
17
New cards
Prejudice (including two specific hypotheses about prejudice)
definition: Negative feelings/attitudes towards other groups
Examples
Group threat hypothesis of prejudice: prejudice derives from the relative position of different racial groups in society (dominant groups feel entitled to social advantage and fear losing that advantage to “outsiders”) {ex: group prejudice toward immigrants - taking our jobs}
Contact hypothesis: more proximity between race/ethnic groups reduces prejudice (key argument of cultural diversity)
Examples
Group threat hypothesis of prejudice: prejudice derives from the relative position of different racial groups in society (dominant groups feel entitled to social advantage and fear losing that advantage to “outsiders”) {ex: group prejudice toward immigrants - taking our jobs}
Contact hypothesis: more proximity between race/ethnic groups reduces prejudice (key argument of cultural diversity)
18
New cards
Stereotypes
Cultural and behavioral generalizations (positive or negative, but typically incorrect) about an entire group of people
Minority groups are likely to be perceived according to negative generalizations
Prejudice and stereotypes align with the symbolic dimension of race/ethnicity
Minority groups are likely to be perceived according to negative generalizations
Prejudice and stereotypes align with the symbolic dimension of race/ethnicity
19
New cards
Discrimination (two types of discrimination presented in class)
Definition: Unequal treatment of an individual or group because of race/ethnicity
Discriminatory INTENT
Discrimination occurs when an individual or institution PURPOSELY treat members of one group different from those of another
Discriminatory OUTCOMES or CONSEQUENCES
Discrimination is defines not by its motivation but by the RESULTS of normal routine social practices (republican doesnt mean racsit reading)
Formally neutral (or “color-blind”) practices can reinforce stable patterns of race/ethnic inequality (Ex: property taxes to fund schools)
Discriminatory INTENT
Discrimination occurs when an individual or institution PURPOSELY treat members of one group different from those of another
Discriminatory OUTCOMES or CONSEQUENCES
Discrimination is defines not by its motivation but by the RESULTS of normal routine social practices (republican doesnt mean racsit reading)
Formally neutral (or “color-blind”) practices can reinforce stable patterns of race/ethnic inequality (Ex: property taxes to fund schools)
20
New cards
Definition of racism as a social system of advantage and disadvantage
An organized social system of practices, relationships, and ideas in which some groups are systematically advantages or disadvantages on account of race/ethnic characteristics (Has both STRUCTURAL and SYMBOLIC components )
21
New cards
Two racial social system in U.S. history
traditional/hard racism
color blind/soft racism
color blind/soft racism
22
New cards
traditional/hard racism
Ex:
Dislike, hate, prejudice towards another group
White supremacy (kkk)
racial/ethnic violence/hate crimes; racial/ethnic slurs
Slavery; segregation; lynchings
Employer refusing to hire; landlord refusing to rent
Store employee calling security; police harassment
Things in common: 1. Racism is overt, intentional 2. Racism is rooted in “bad” or mean beliefs/attitudes 3. Bad beliefs/ attitudes lead to bad/discriminatory behavior
Dislike, hate, prejudice towards another group
White supremacy (kkk)
racial/ethnic violence/hate crimes; racial/ethnic slurs
Slavery; segregation; lynchings
Employer refusing to hire; landlord refusing to rent
Store employee calling security; police harassment
Things in common: 1. Racism is overt, intentional 2. Racism is rooted in “bad” or mean beliefs/attitudes 3. Bad beliefs/ attitudes lead to bad/discriminatory behavior
23
New cards
Color blind/soft racism
Color blindness is the dominant racial project of the past 50 years
Racial preferences for any group is wrong and should be prohibited
We should just stop talking about race
Racial preferences for any group is wrong and should be prohibited
We should just stop talking about race
24
New cards
White privilege
The UNEARNED and UNACKNOWLEDGED advantages that came from being a member of the dominant racial/ethnic group (colorblind ideology)
25
New cards
False equivalencies
Reverse racism
Answer: the equivalency of power, hierarchy and inequality
Minority groups are structurally located at lower positions in the race/ethnic hierarchy
These practices do not systematically oppress/disadvateg whites (sociologically speaking)
Answer: the equivalency of power, hierarchy and inequality
Minority groups are structurally located at lower positions in the race/ethnic hierarchy
These practices do not systematically oppress/disadvateg whites (sociologically speaking)
26
New cards
The several conditions that contributed to emergence of the Civil rights movement
Economic restructuring and demographic changes
Political changes
Legal reforms
Cold war politics (non shooting war with soviet union)
THE CIVIL RIGHTS MOVEMENT
Political changes
Legal reforms
Cold war politics (non shooting war with soviet union)
THE CIVIL RIGHTS MOVEMENT
27
New cards
The civil rights movement
non violent direct action as the main tactic
NAACP; SNCC;SCLC
American Indian activism
Key protest events (several discussed in lecture; rely on textbook for further details)
Montgomery bus boycott (1955)
Student sit ins (1960)
Freedom rights (1961)
Burgingham campaign (1963)
March on washington (1964)
March on selma for voting rights (1965)
NAACP; SNCC;SCLC
American Indian activism
Key protest events (several discussed in lecture; rely on textbook for further details)
Montgomery bus boycott (1955)
Student sit ins (1960)
Freedom rights (1961)
Burgingham campaign (1963)
March on washington (1964)
March on selma for voting rights (1965)
28
New cards
Civil rights legislation (3)
civil rights act of 1964
voting rights act of 1965
fair housing act of 1968
voting rights act of 1965
fair housing act of 1968
29
New cards
Civil rights act of 1964 - what did the new laws do?
Illegal to discriminate in public accommodations (title 2)
Federal fund cut off for discrimination (title VI)
Illegal to discriminate in employment (title VII)
Federal fund cut off for discrimination (title VI)
Illegal to discriminate in employment (title VII)
30
New cards
Voting rights act of 1965 - what did the new laws do?)
Eliminated barriers to black registration and voting
No more poll taxes; literacy tests, etc
No more poll taxes; literacy tests, etc
31
New cards
Fair housing act of 1968 - what did the new laws do?
Illegal to discriminate in the sale or rental of housing
32
New cards
Black power movement - How did it differ from the civil rights movement?
Coincided with the civil rights movement
Far less popular (particularly among whites) then the civil rights movement (Malcolm X vs MLK Jr)
Seen as threatening to white society
--Emphasis on racial difference: black pride and culture
--Militancy vs. conciliation
--Willingness to use violence in self defense
--Rhetoric of separation rather than integration
Far less popular (particularly among whites) then the civil rights movement (Malcolm X vs MLK Jr)
Seen as threatening to white society
--Emphasis on racial difference: black pride and culture
--Militancy vs. conciliation
--Willingness to use violence in self defense
--Rhetoric of separation rather than integration
33
New cards
The american indian movement (AIM-video documentary)
Grievances, tactics, objectives (Notes from video that I took - might need to add more)
What were some of the tactics/forms of activism that AIM used?
Press release
Taking over national monument
“Sue indian power” on george washington's head
Taking over bureau
Protests
What were some of their major grievances?
Someone mudered and tortured by red necks
Gov didn't take them seriously
Man not charged for murder
Getting hunted
What were some of their demands?
Strive to correct and change
to control their own community and contribute to city planning
Hire people of indian descent
20 point program (established within the law based on treaties and agreements
What were some of the tactics/forms of activism that AIM used?
Press release
Taking over national monument
“Sue indian power” on george washington's head
Taking over bureau
Protests
What were some of their major grievances?
Someone mudered and tortured by red necks
Gov didn't take them seriously
Man not charged for murder
Getting hunted
What were some of their demands?
Strive to correct and change
to control their own community and contribute to city planning
Hire people of indian descent
20 point program (established within the law based on treaties and agreements
34
New cards
Racial projects
Black slavery
War and conquer (manifest destiny)
Exploration of cheap labor
Melting pot
But can also be positive (civil rights movement, Asian American and American Indian separatist movements)
War and conquer (manifest destiny)
Exploration of cheap labor
Melting pot
But can also be positive (civil rights movement, Asian American and American Indian separatist movements)
35
New cards
Several foundational principles
○ Several foundational principles:
■ Racism is built into race/ethnic hierarchies
■ Racism plays out at the individual and institutional levels
■ Racism can exist even in the absence of hatred and intentional acts of discrimination (exists along a continuum)
■ The ideology of “color blindness” is NOT racially neutral
● Absence of overt discrimination but still not racially
neutral
■ Racism is built into race/ethnic hierarchies
■ Racism plays out at the individual and institutional levels
■ Racism can exist even in the absence of hatred and intentional acts of discrimination (exists along a continuum)
■ The ideology of “color blindness” is NOT racially neutral
● Absence of overt discrimination but still not racially
neutral
36
New cards
Sociological perspective vs. biological determinism
….
37
New cards
Current US census race/ethnic categories
White, Black or African American, American Indian or Alaska Native, Asian, Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander