KIN223 Exam 2
1/204
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
205 Terms
The most abundant rid of the membrane consist of a head and two tails. This type of lipid is
glycoprotein
A steroid
Choleste
Glycolipid
A phospholipid
A phospholipid
which of the following choices describes three general functions of cells must perform
- Maintain shape, obtain, nutrients, and dispose of waste
- Take up oxygen, prevent water entry, undergo mitosis frequently
- Respond to all hormones, maintain a waterproof barrier, give rise to gametes
- Grow until dividing, store, complex, carbohydrates, generate antibodies
Maintain shape, obtain, nutrients, and dispose of waste
The shape of skeletal muscle cells is described as
Cylindrical
Irregular
Columnar
Bioconcave
Spherical
Cylindrical
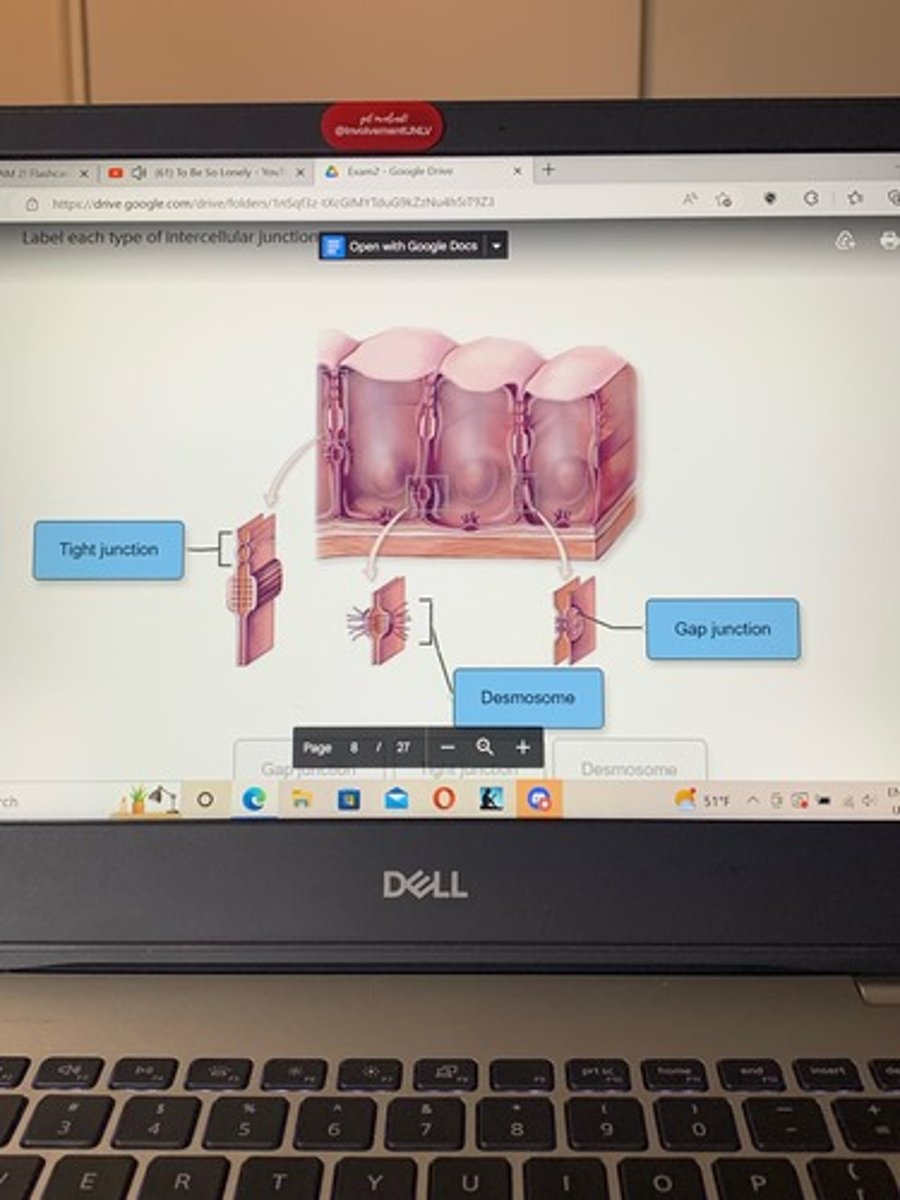
these junctions hold adjacent cells together, and provide resistance to mechanical stress
Synapses
Tight junctions
desmosomes
Gap junctions
desmosomes
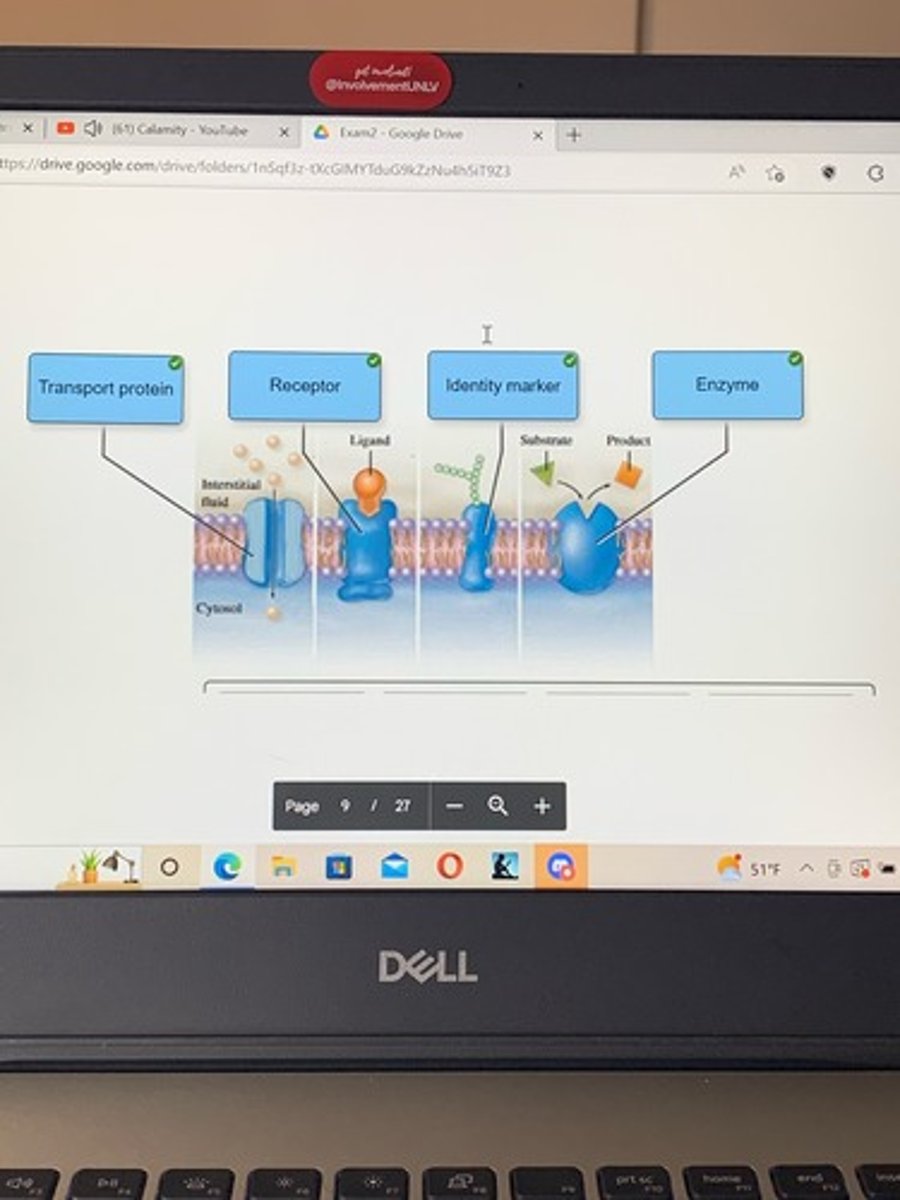
proteins that assist the movement of a substance across the membrane are called ___ proteins.
Catalytic
Identification
Cytoskeleton
Intercellular attachment
Transport
Transport
mucus is moved along the lining of the trachea by extensions from the cell membrane is known as
microvilli
stereovilli
cilia
flagella
cilia
which is a non-membrane bound organelle?
Mitochondrion
Golgi apparatus
Lysosome
Microtubule
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Microtubular
The term flagellum is appropriate for the structure. It represents because it means.
The center
An eyelid
A nut or kernel
A whip
A bunch
Whip
The lipid that stabilizes the membrane at extreme temperatures, and is found in the hydrophobic regions of the bilayer is
Glycolipid
glycocalyx
The polar head
Cholesterol
The nonpolar tails
Cholesterol
Label each type of intercellular junction.
junctions
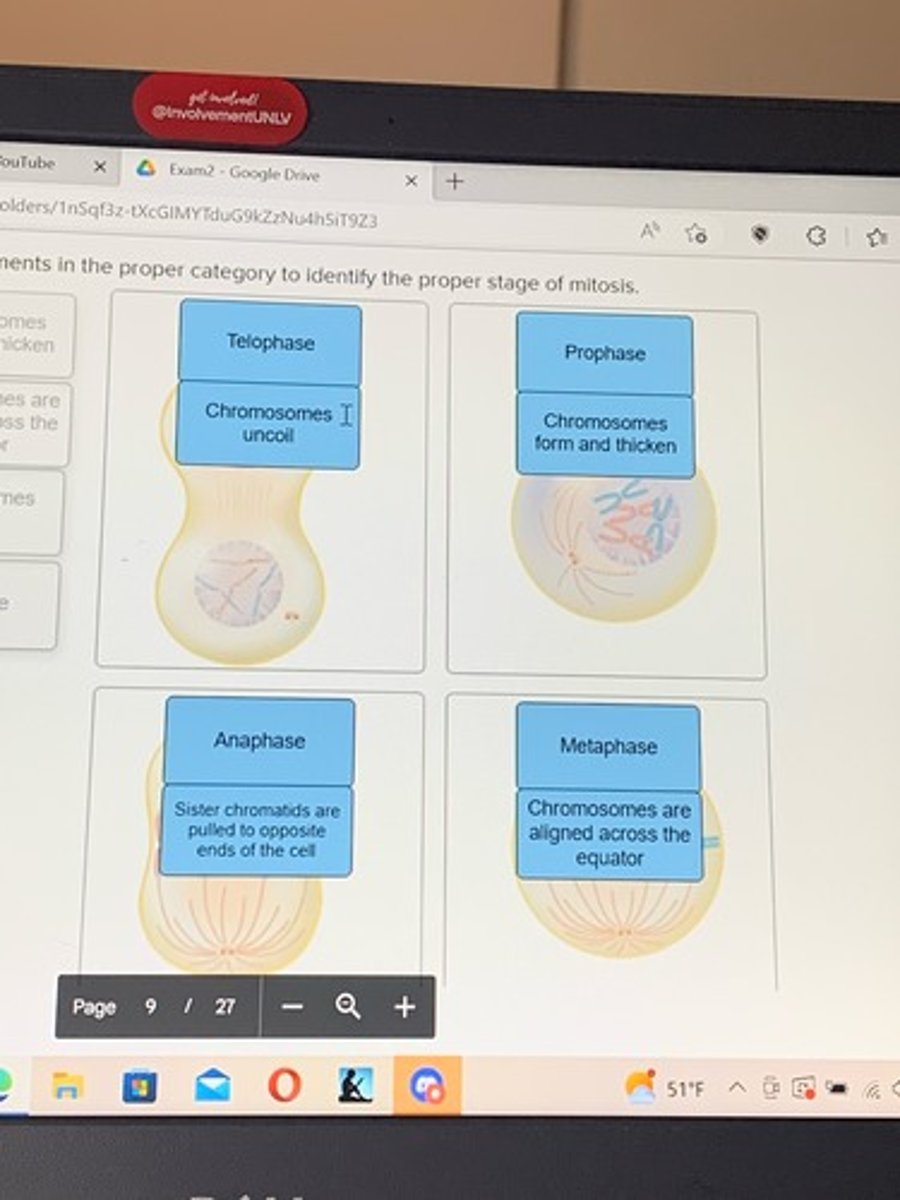
place each of the terms or statements in the proper category to identify the proper stage of mitosis
stages of mitosis
Identify the plasma, membrane proteins in the figure
Plasma membrane proteins
where in the body would you expect to find a perichondrium
inside of the brain
lining kidney tubules
Covering bones
Covering the heart
Covering cartilage
Covering cartilage
shrinkage of tissue by a decrease in either cell number or so size is termed
Metaplasia
Atrophy
hyper trophy
Fibrosis
Neoplasia
atrophy
The outer most layer of the pleural membrane is the
Intrapleural fluid
parietal pleura
Thoracic pleura
visceral pleura
pleura cavity
parietal pleura
The type of muscle that has elongated, multi nucleated cells and is under voluntary control is __ muscle
Smooth
Skeletal
Cardiac
Skeletal
Which of the primary tissue types is most widely distributed throughout the body?
connective
Nervous
Muscle
Epithelium
connective
this type of muscle lacks striations, and is found in the walls of most viscera, such as the stomach and blood vessels
Smooth
Cardiac
Skeletal
smooth
The largest of the body membranes, commonly called the skin, is the ___ membrane.
cutaneous
cartilaginous
Mucous
Synovial
Serous
cutaneous
which body membrane protects the body from water loss and home to internal organs?
cutaneous
Synovial
serous
mucous
cutaneous
which unit of bone consist of a central canal (containing blood vessels, nerves, and lymph vessels) surrounded by concentric rings of calcified matrix?
Osteocyte
lamella
canaliculus
Trabeculum
Osteon
Osteon
this type of membrane that lines many of the bodies joints is a ___ membrane.
cutaneous
mucous
Synovial
metastatic
serous
synovial
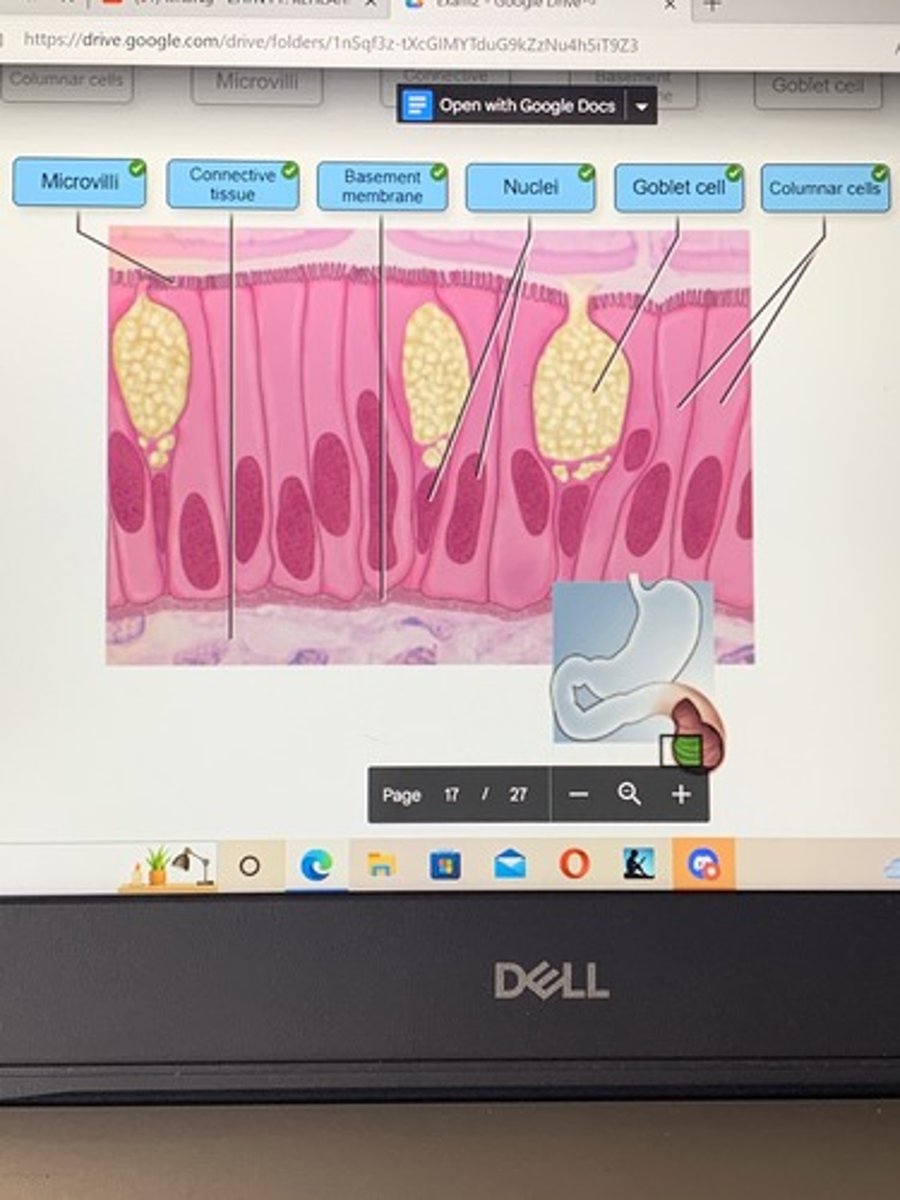
Correctly label the following areas on the slide of simple columnar epithelium
Simple, columnar, epithelium
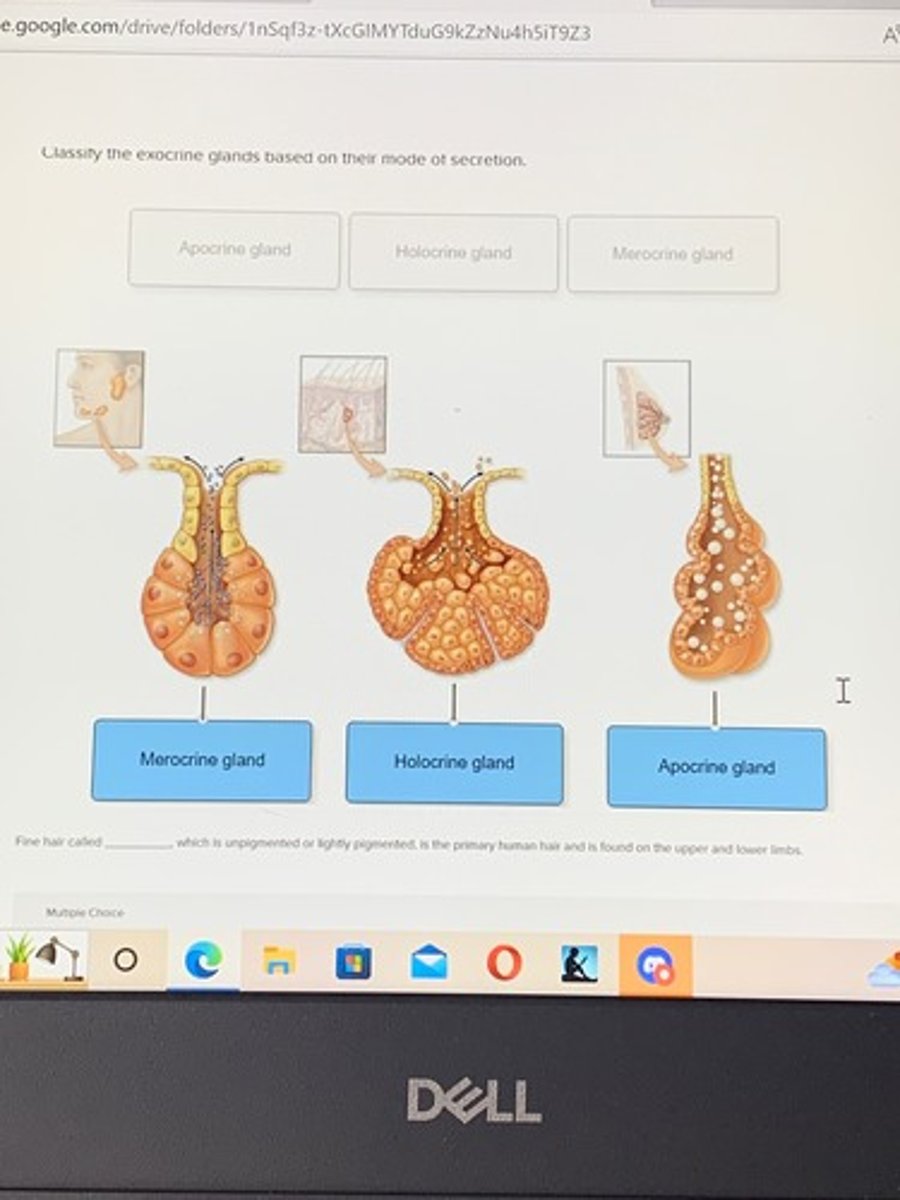
Classify the exocrine glands based on their mode of secretion
exocrine Glands
find hair called ____, which is unpigmented order, lightly pigmented, is the primary care and is found on the upper and lower limbs
Cuticle
lanugo
phalanx
vellus
Terminal
vellus
The type of gland, that secretes way into a hair follicle that is found on the axillary, anal, and genital regions is the ___ sweat glands.
merocrine
Sebaceous
ceruminous
Apocrine
Apocrine
which is the actively growing part of the nail
Nail root
Nail folds
Nail beds
Free edge
Nail matrix
Nail matrix
thick skin contains
- 7 epidermal strata and lacks sweat glands
- 4 epidermal strata and lack sebaceous glands
- 5 epidermal strata and lacks sebaceous glands
- 6 epidermal strata and lacks sweat glands
- 5 epiderm strata and lacks sweat glands
5 epidermal strata and lacks sebaceous glands
Tactile (Merkel) cells are sensitive to
Touch
Sound
Heat
Light
Cold
touch
Epidermal dendritic (Langerhans) cells function, as part of the___ response.
Immune
Sensory
Heating
Tanning
Sweating
immune
The deeper sub layer of the dermis is the ___ layer, and it is the ___ of the two.
papillary, thinner
reticular , thicker
Reticular, thinner
papillary, thicker
reticular , thicker
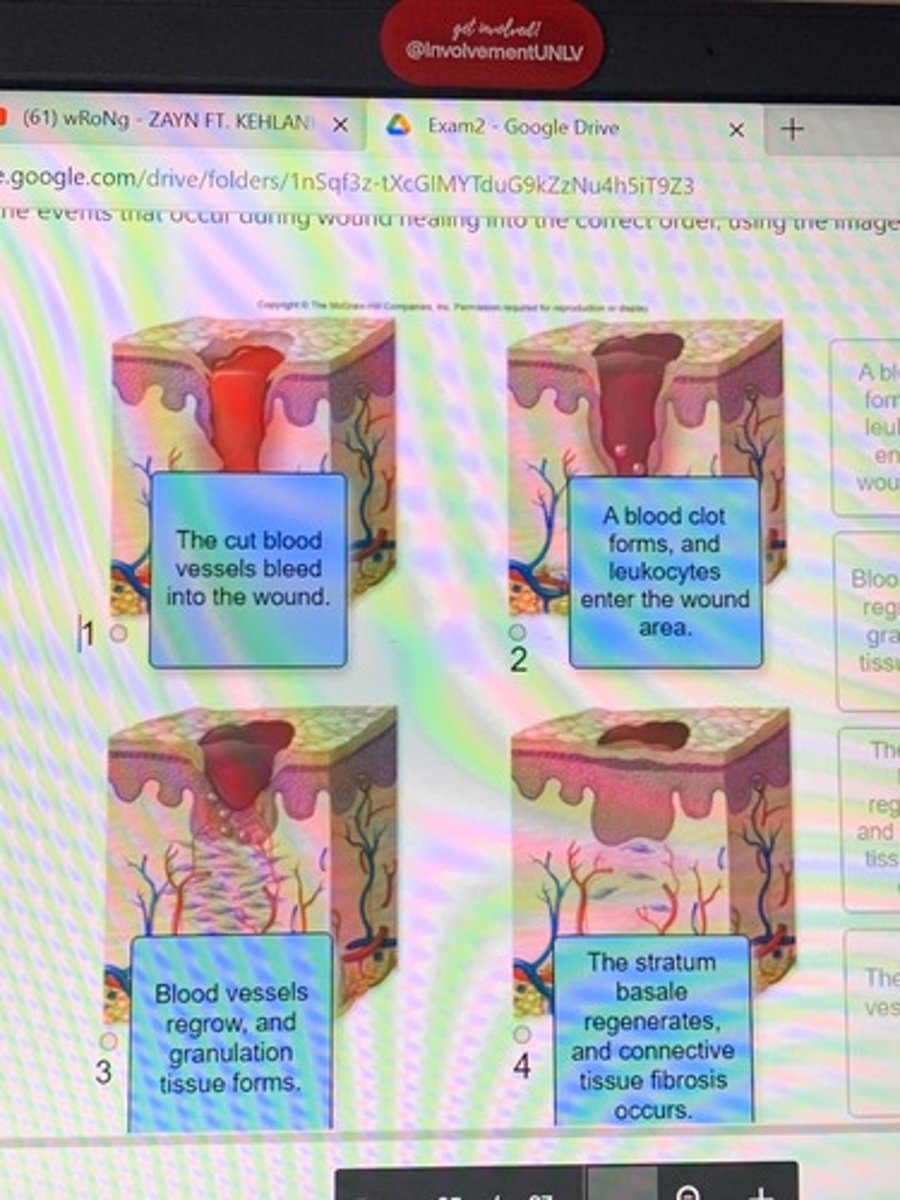
Placed events that occur during wound healing in the correct order, used images as a guide
Wound healing
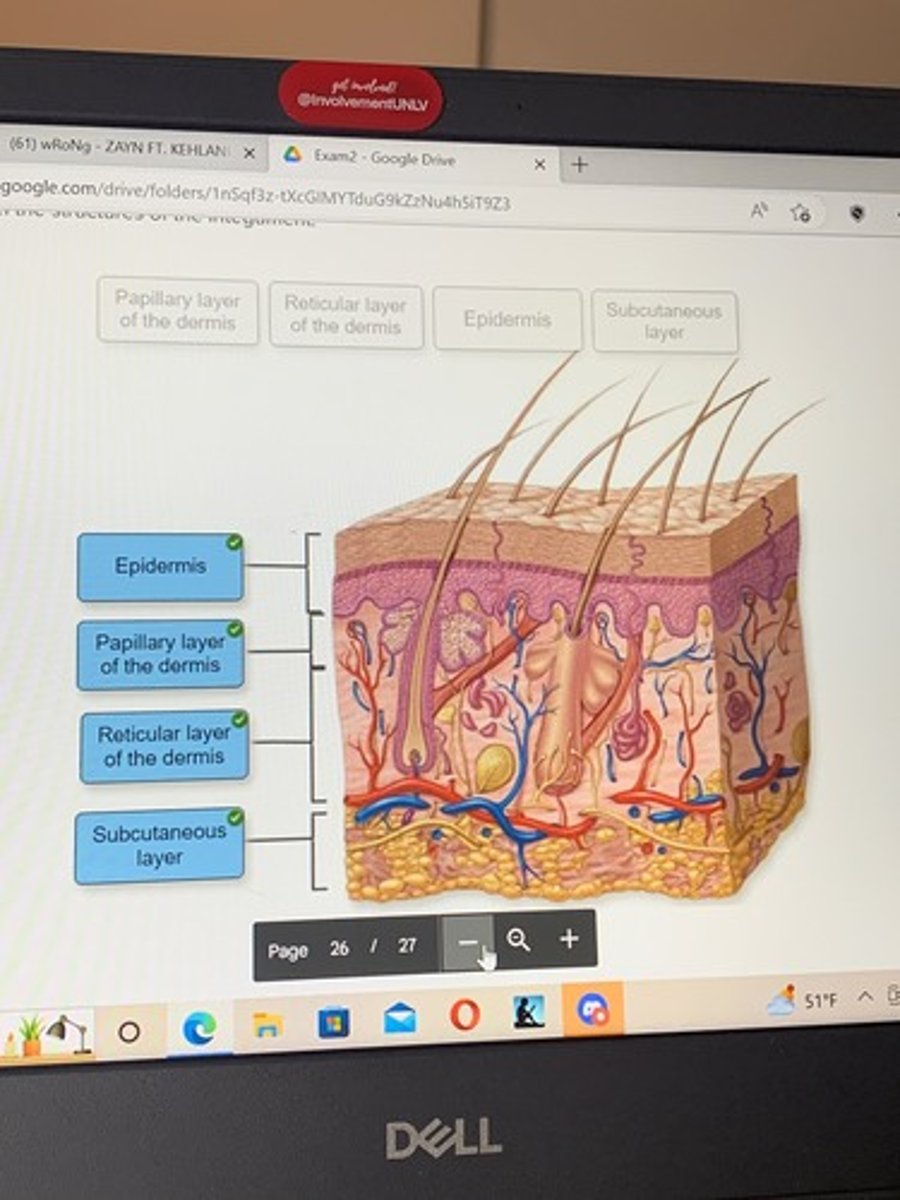
Label the structures of the integument
Structures of the integument
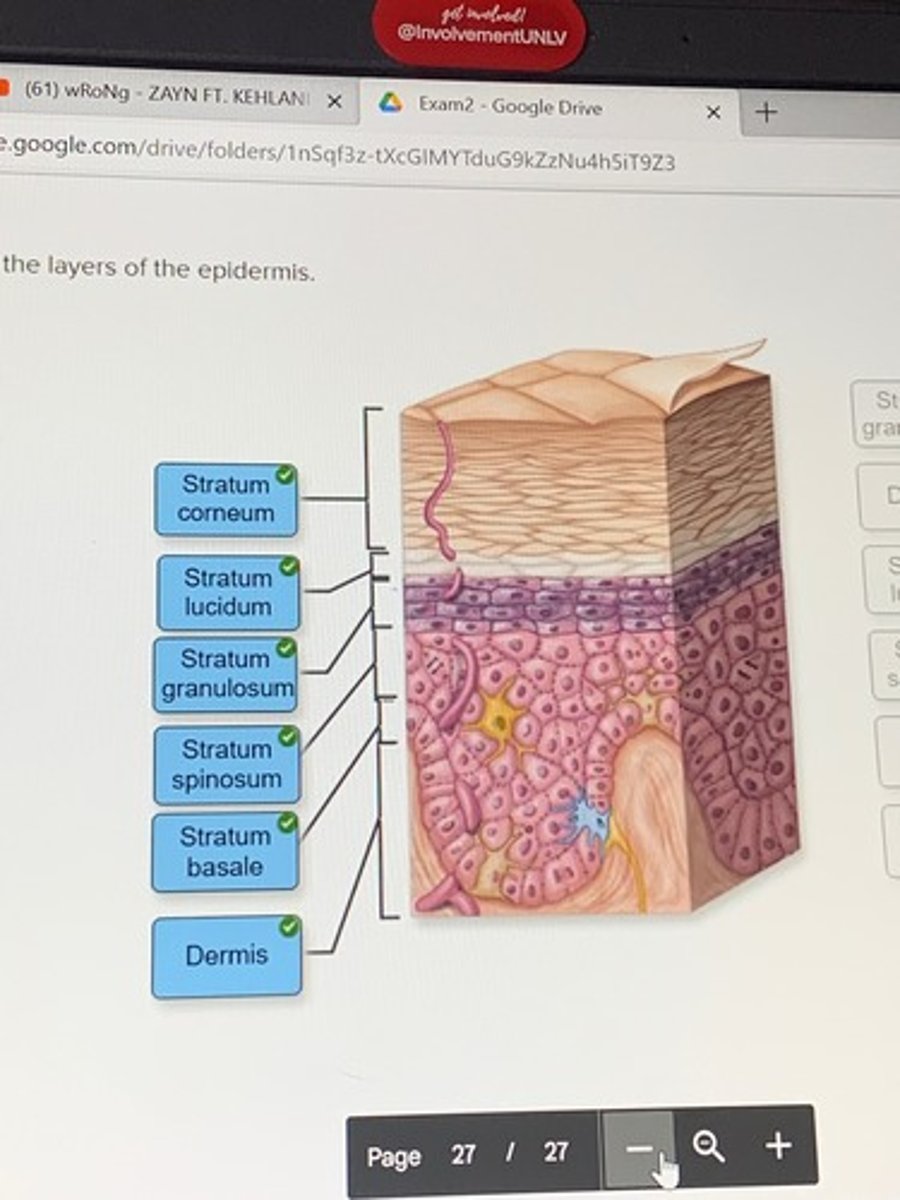
Label the layers of the epidermis
Layers of the epidermis
The folds of the internal membrane of the mitochondrion are called
Vacuoles
Vesicles
Cristae
cisternae
Matrix
cristae
Identify the organelle that provides enzymes for autolysis.
peroxisomes
Golgi apparatus
Smooth ER
Mitochondria
Lysosomes
lysosomes
during osmosis, water moves towards the solution with the_____ solute concentration
Lesser
Greater
Greater
if the nutrient glycogen is found stored inside a cell, it is considered a
pigment
Non-membrane bound organelle
Membrane bound, organelle
Inclusion
Inclusion
The uptake of material through the plasma, membrane by the formation of a vesicle is __, whereas the fusion of a vesicle with the plasma membrane is the release of its contents outside of the cell is called_____
Pinocytosis; endocytosis
Endocytosis; exocytosis
Exocytosis; pinocytosis
Endocytosis; pinocytosis
endocytosis; exocytosis
Correctly identify the parts of the endoplasmic reticulum
Endo plasmic reticulum
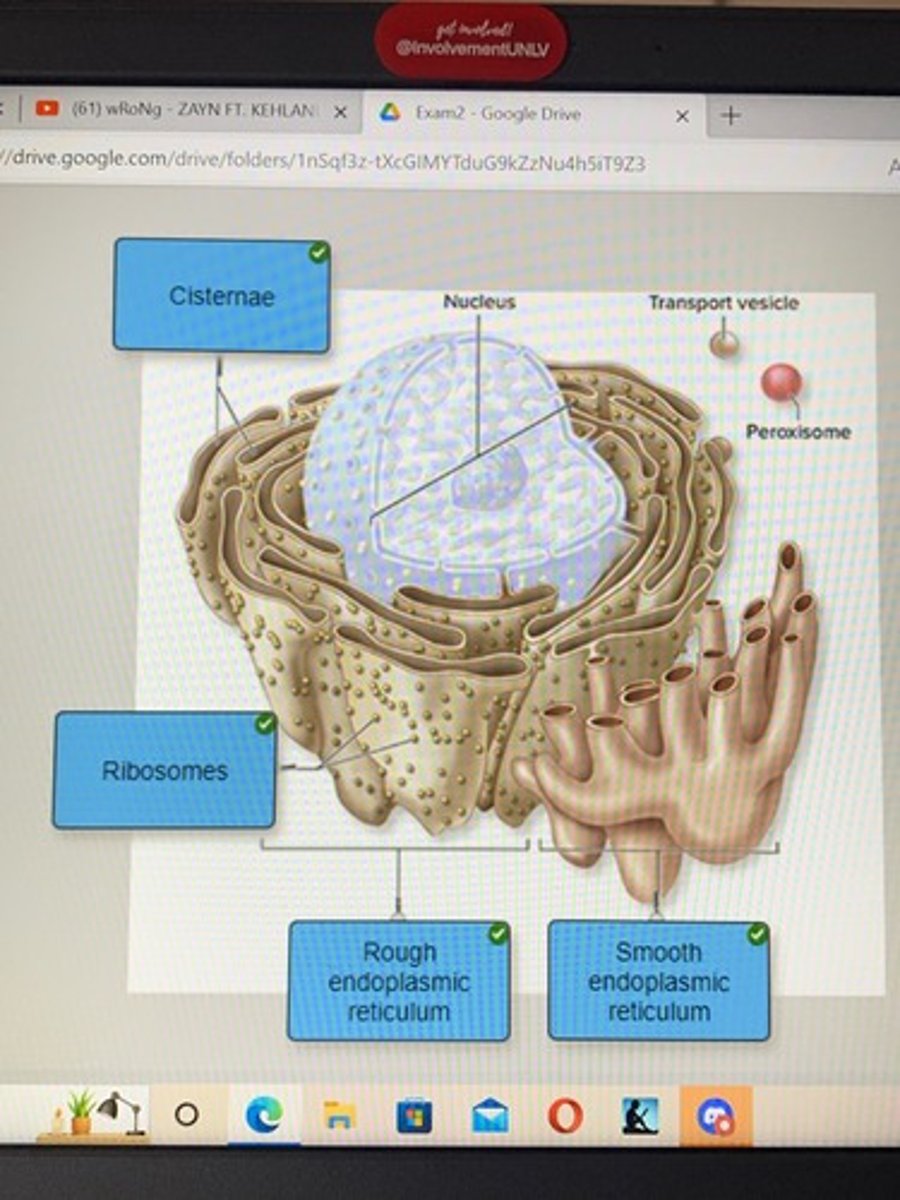
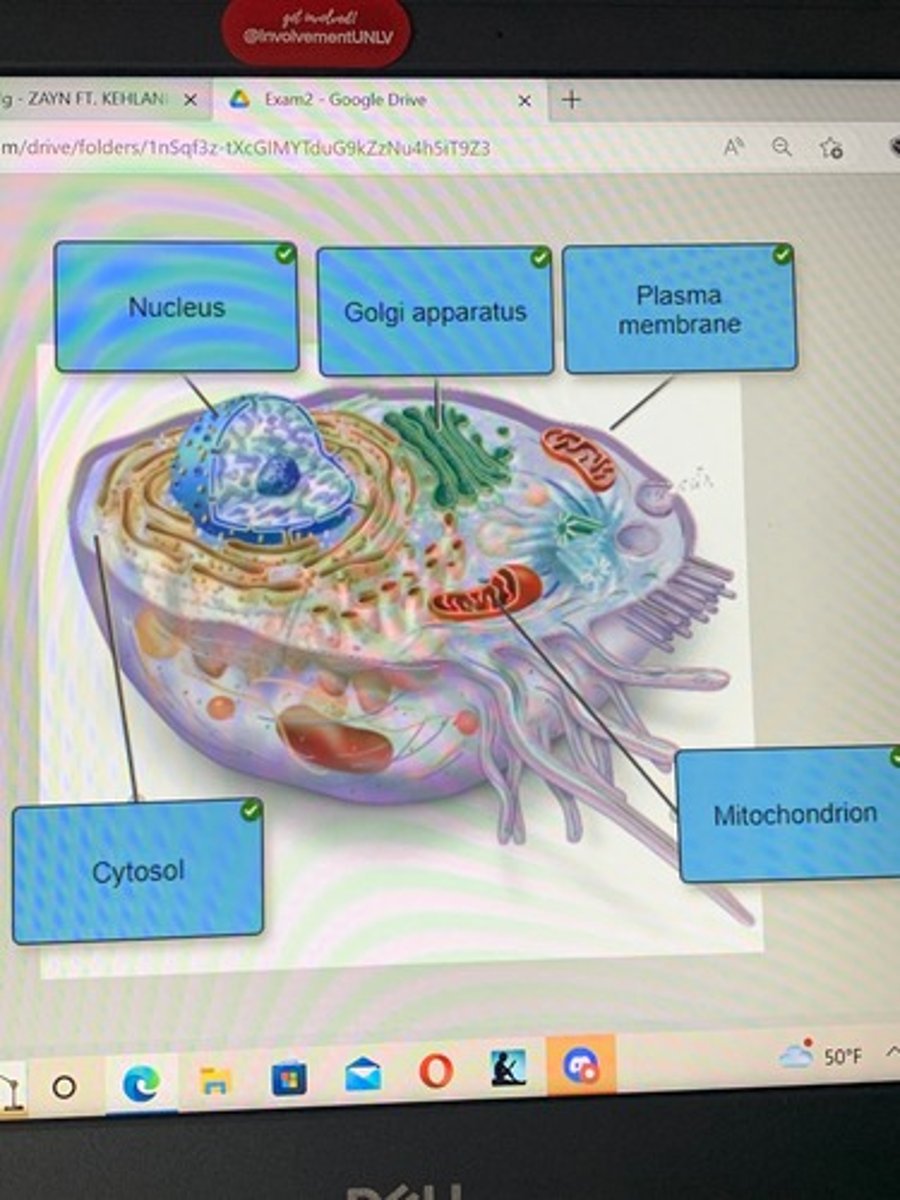
identify the structures of a prototypical human cell
prototypical human cell
which of the following is not a function of the epithelial tissue?
No exceptions; these are all functions of the epithelial tissue
Sensation
Selective permeability
Physical
Secretion
No exceptions; these are all functions of the epithelial tissue
dendrites
- Transmits signals away from the cell body
- Transmit signals towards the cell body
- Manufacture proteins to be used by neurons
- Use hormones to transmit information
- Release neurotransmitter
Transmit signals towards the cell body
if a person were unable to form saliva, what type of gland would be missing or malfunctioning?
Apocrine glands
holocrine glands
merocrine glands
merocrine glands
The most common type of cartilage, named for its glassy appearance, is
Fibrocartilage
Hyaline cartilage
Elastic cartilage
Reticular cartilage
Areolar cartilage
Hyaline cartilage
Label parts of the hypodermis
Hypodermis
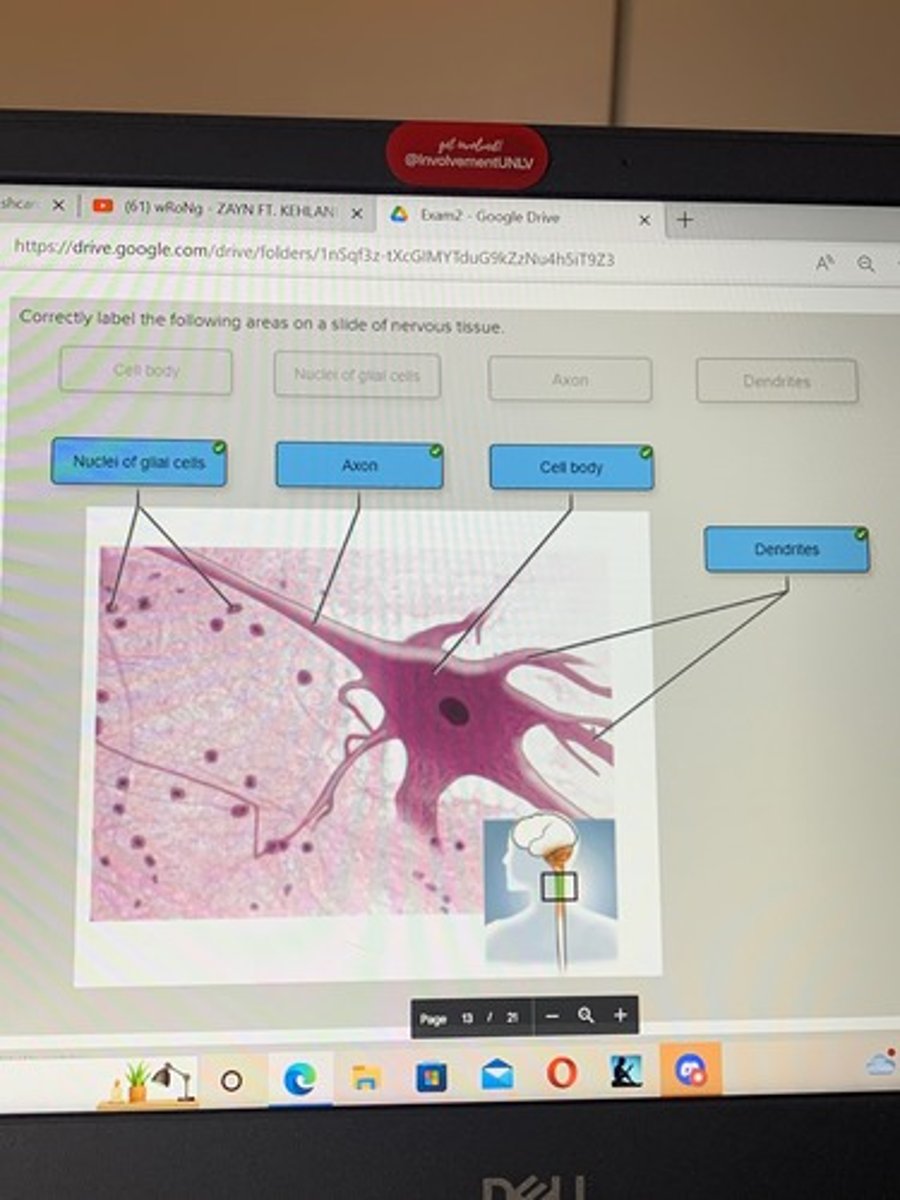
Correctly, label the following areas on the slide of nervous tissue
Nervous tissue
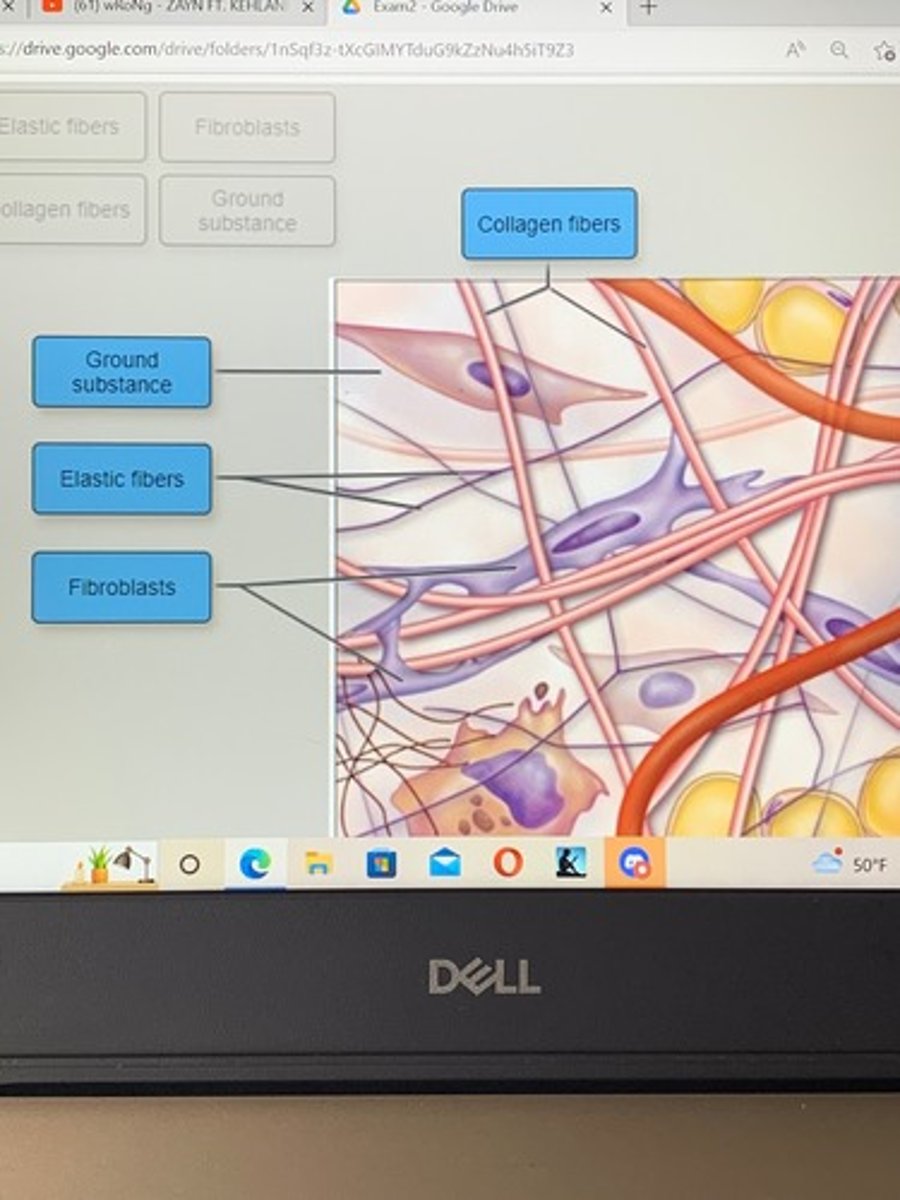
The reticular layer of the dermis consist primarily of
Reticular connective tissue
Elastic connective tissue
Adipose tissue
Nervous tissue
dense irregular connective tissue
dense irregular connective tissue
The delivery of drugs through the skin through the use of an adhesive patch is called ___ administration.
Intramuscular
Hypodermal
Subcutaneous
Transdermal
Transdermal
complete each sentence by dragging the proper word or phrase into the correct position. Not all terms will be used.
.
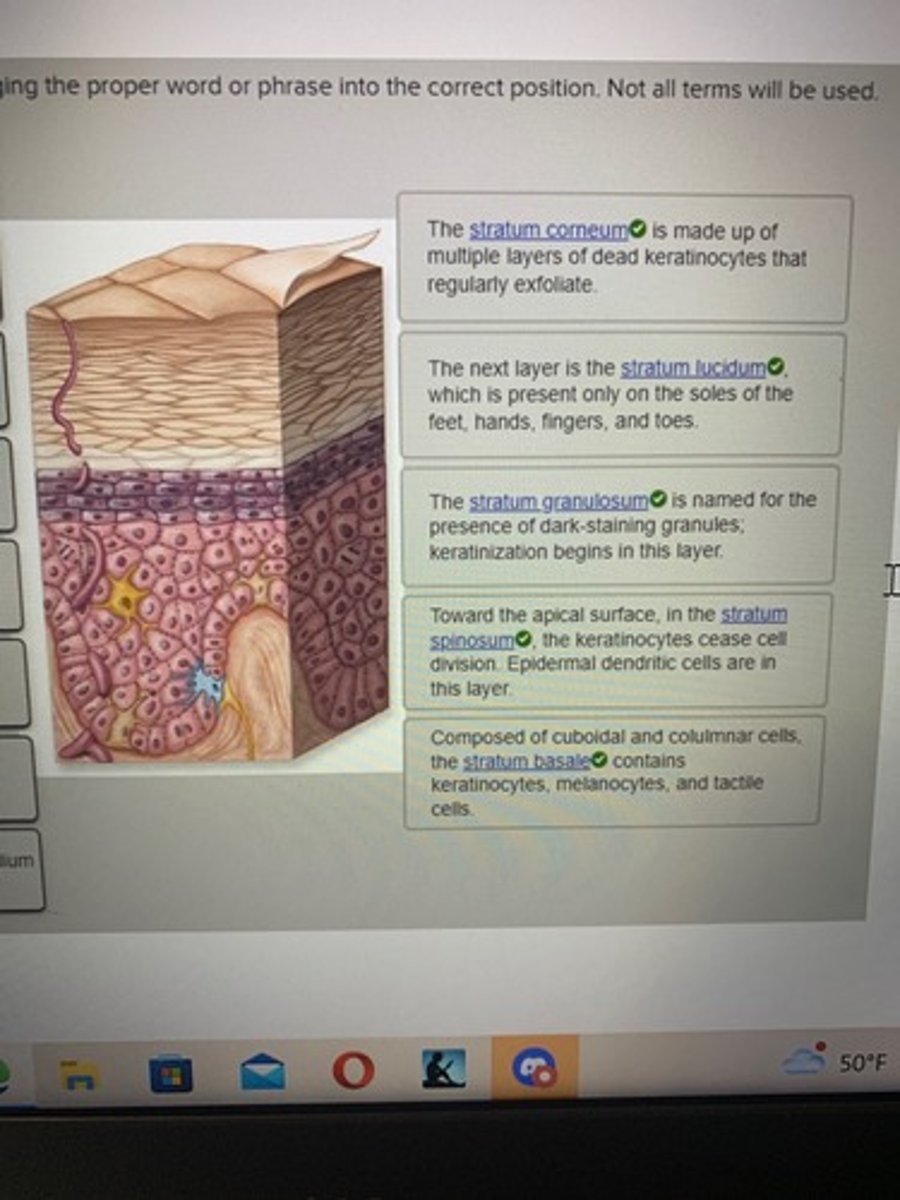
The phase of mitosis that begins as spindle fibers pulls sister chromatids apart at the centromere is
Anaphase
Prophase
Interphase
Telophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
diffusion rate is fastest when the concentration gradient is
Steepest and the temperature is at body temp.
Slightest and temp is at body temp
Steepest and temperature is highest
Slightest and temperature is highest
Slightest and temperature is lowest
steepest and temperature is highest
The release of Neuro transmitter from a neuron is an example of
- endocytosis and is a form of passive transport
- exocytosis and is a form of passive transport
- Receptor mediated endocytosis, and it requires expediture of ATP
- exocytosis, and it requires expenditure of ATP
- pinocytosis and it is a form of primary active transport
exocytosis, and it requires expenditure of ATP
in humans, the only sell that bears a flagellum is the ___ cell
Brain
Kidney
Red blood
Sperm
oocyte
sperm
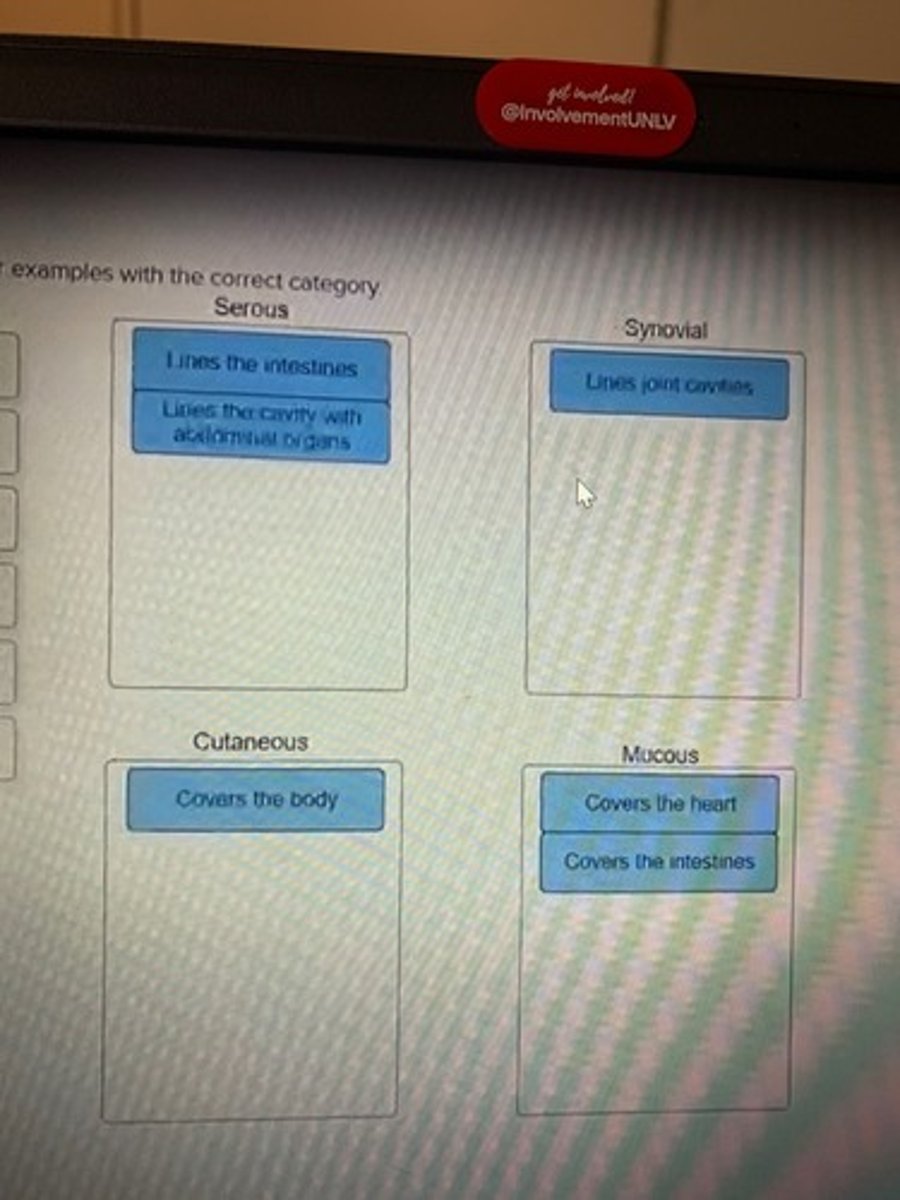
Place the following terms or examples with the correct category
Correct category
Lines of cleavage, or a result of
Wounds to the epidermidis such as hematomas
The alignment of dermal papillae
The alignment of epidermal ridges
The orientation of collagen fibers in the dermis
The orientation of collagen fibers in the dermis
which statement is true regarding the subcutaneous layer (hypodermis)?
it's responsible for the ridges known as fingerprints
It's the superficial region of the dermis
It stabilizes the position of the skin and binds it to the underlying structures
It is keratinized, squamous epithelium
It's stabilizes the position of the skin and bones it to underlying structures
exposure to the ultraviolet, light darken skin by stimulating synthesis of
Melatonin
Hemoglobin
Melanin
cyanin
carotene
melanin
what is the composition of the subcutaneous layer?
-Areolar connective tissue
-Areolar connective tissue and dense irregular connective tissue
-Adipose connective tissue
-Dense, irregular connective tissue
-Areolar connective tissue and adipose connective tissue
Areolar connective tissue and adipose connective tissue
During transcription
a protein is formed as a DNA sequence is read.
an RNA molecule is formed as a DNA sequence is read.
a protein is formed as a RNA sequence is read.
an amino acid is transferred to a ribosome as a DNA sequence is read.
a DNA sequence is formed as a RNA sequence is read.
an RNA molecule is formed as a DNA sequence is read.
Apoptosis is best described as
the process of immune cells recognizing an infected cell as "foreign".
the process of an aging cell becoming cancerous.
the destruction of a cell through mechanical damage.
a process where cells destroy themselves.
a process where cells destroy themselves.
The _______ is responsible for forming the outer, limiting barrier of a cell.
mitochondrion
ribosome
peroxisome
centrosome
plasma membrane
plasma membrane
The building blocks that form the DNA double helix are called
nitrogenous acids.
steroid bases.
nucleotides.
nucleoli.
nuclear pores.
nucleotides.
When a cell surrounds a large particle with pseudopodia and then engulfs it, the process is called
phagocytosis.
exocytosis.
secondary active transport.
pinocytosis.
receptor-mediated endopinocytosis.
phagocytosis.
Pinocytosis is the process in which the cell
internalizes ("eats") a large solid particle.
pumps small solutes against their concentration gradient and out of the cell.
internalizes ("drinks") a droplet of interstitial fluid.
splits ("pinches") off a small part of itself to secrete into the extracellular space.
internalizes ("drinks") a droplet of interstitial fluid.
!The function of the nucleolus is to make!
the secretions that will be packaged by the Golgi apparatus.
histones.
DNA molecules.
the deoxyribose sugar.
the subunits of ribosomes.
the subunits of ribosomes.
!When a cell is placed in a solution with a very low solute concentration, water diffuses into the cell. Such a solution is called a(n) _________ solution.!
isotonic
endergonic
hypertonic
hypotonic
hypotonic
Proteins that are embedded within, and extend across, the phospholipid bilayer are called _____ proteins.
catalytic
integral
peripheral
cytoskeleton
integral
The phase of mitosis that begins as spindle fibers pull sister chromatids apart at the centromere is
anaphase.
metaphase.
telophase.
prophase.
interphase.
anaphase.
Channel-mediated diffusion is a subtype of
simple diffusion.
facilitated diffusion.
active transport.
carrier-mediated diffusion.
endocytosis.
facilitated diffusion.
Which of the following is not a component of the cytoplasm?
Organelles
Chromatin
Cytosol
Inclusions
Chromatin
Movement of a substance from an area of higher concentration to one where it is less concentrated is known as
facilitation.
equilibrium.
active transport.
selective transport.
diffusion.
diffusion.
Which of the following serve to increase the surface area of a cell for absorption and secretion?
Cilia and microvilli
Cilia
Flagella
Cilia and flagella
Microvilli
Microvilli
Forms the outer barrier of the cell
cytoplasm
plasma membrane
nucleus
plasma membrane
Contains the cytosol, inclusions, and organelles
cytoplasm
plasma membrane
nucleus
cytoplasm
The cell's control center
cytoplasm
plasma membrane
nucleus
nucleus
Movement of fluids through a selectively permeable membrane caused by hydrostatic pressure is referred to as _____.
osmosis
hydrostatic pressure
filtration
carrier-mediated diffusion
concentration gradient
simple diffusion
filtration
The pressure exerted by a fluid on the inside wall of its container (or vessel, in the case of the human body), is called ____.
osmosis
hydrostatic pressure
filtration
carrier-mediated diffusion
concentration gradient
simple diffusion
hydrostatic pressure
The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration describes ___.
osmosis
hydrostatic pressure
filtration
carrier-mediated diffusion
concentration gradient
simple diffusion
simple diffusion
Movement away from high solvent concentration or towards high solute concentration describes
osmosis
hydrostatic pressure
filtration
carrier-mediated diffusion
concentration gradient
simple diffusion
osmosis
The movement of small, polar molecules across the plasma membrane by a carrier protein is called.
osmosis
hydrostatic pressure
filtration
carrier-mediated diffusion
concentration gradient
simple diffusion
carrier-mediated diffusion
Label each type of intercellular junction.

Which type of epithelium is composed of multiple layers, including an apical layer containing tall, slender cells?
Simple columnar
Stratified squamous
Pseudostratified squamous
Simple squamous
Stratified columnar
Stratified columnar
Endocrine glands
lack ducts and secrete their products into the bloodstream or into interstitial fluid.
lack ducts and secrete their products onto the skin surface.
possess short ducts and secrete their products directly onto the skin surface.
possess ducts to secrete their products into the bloodstream or into interstitial fluid.
secrete mucus directly into a body cavity.
lack ducts and secrete their products into the bloodstream or into interstitial fluid.
Ligaments are very strong but resistant to stretch. Which protein fiber probably predominates?
Collagen
Reticular
Adipose
Elastic
Collagen
Plasma is
platelets and a watery ground substance.
a dissolved ground matrix and a lining of epithelial cells.
a liquid ground substance containing dissolved proteins.
platelets, red blood cells, and white blood cells.
a liquefied ground substance that includes several dissolved cells.
a liquid ground substance containing dissolved proteins.
Which tissue type covers body surfaces and lines the inside of organs and body cavities?
Muscle
Connective
Epithelial
Nervous
None of the choices is correct.
Epithelial
The primary role of epithelial tissue in the stomach is
regulation of contraction.
housing blood vessels and nerves.
secretion of substances for chemical digestion.
mixing and propulsion of foodstuffs.
secretion of substances for chemical digestion.
Connective tissue proper is divided into two broad categories: loose connective tissue and dense connective tissue. This classification is based upon the
size of the cells present.
origin of the tissue type.
number of different cells types and their respective arrangement.
relative proportions of cells, fibers, and ground substance present.
location of the tissue.
relative proportions of cells, fibers, and ground substance present.
Suppose that you were involved in an automobile accident and suffered a back injury. When examined by your physician you are told that you have a slipped disc in the lower back. What type of tissue is involved?
Bone
Fibrocartilage
Elastic cartilage
Adipose tissue
Dense regular connective tissue
Fibrocartilage
Endocrine glands secrete
sweat.
hormones.
saliva.
digestive enzymes.
All of the choices are correct.
hormones.
The type of muscle that is found in blood vessel walls is __________ muscle.
cardiac
skeletal
smooth
smooth
Groups of similar cells and extracellular products that carry out a common function are called
organs.
organ systems.
matrices.
tissues.
tissues.
The type of epithelium that lines the urinary bladder and may include some binucleated cells is called ____________ epithelium.
simple squamous
stratified squamous nonkeratinized
stratified squamous keratinized
pseudostratified
transitional
transitional
The heart is confined within a double-walled serous membrane sac. The part of the membrane that is in contact with the heart is the _____ layer.
visceral
serous
synovial
parietal
mesothelial
visceral
The two types of cells that make up the nervous system are
neurons and mast cells.
neurons and chondrocytes.
macrophages and mast cells.
neurons and glial cells.
mast cells and fibrocytes.
neurons and glial cells.
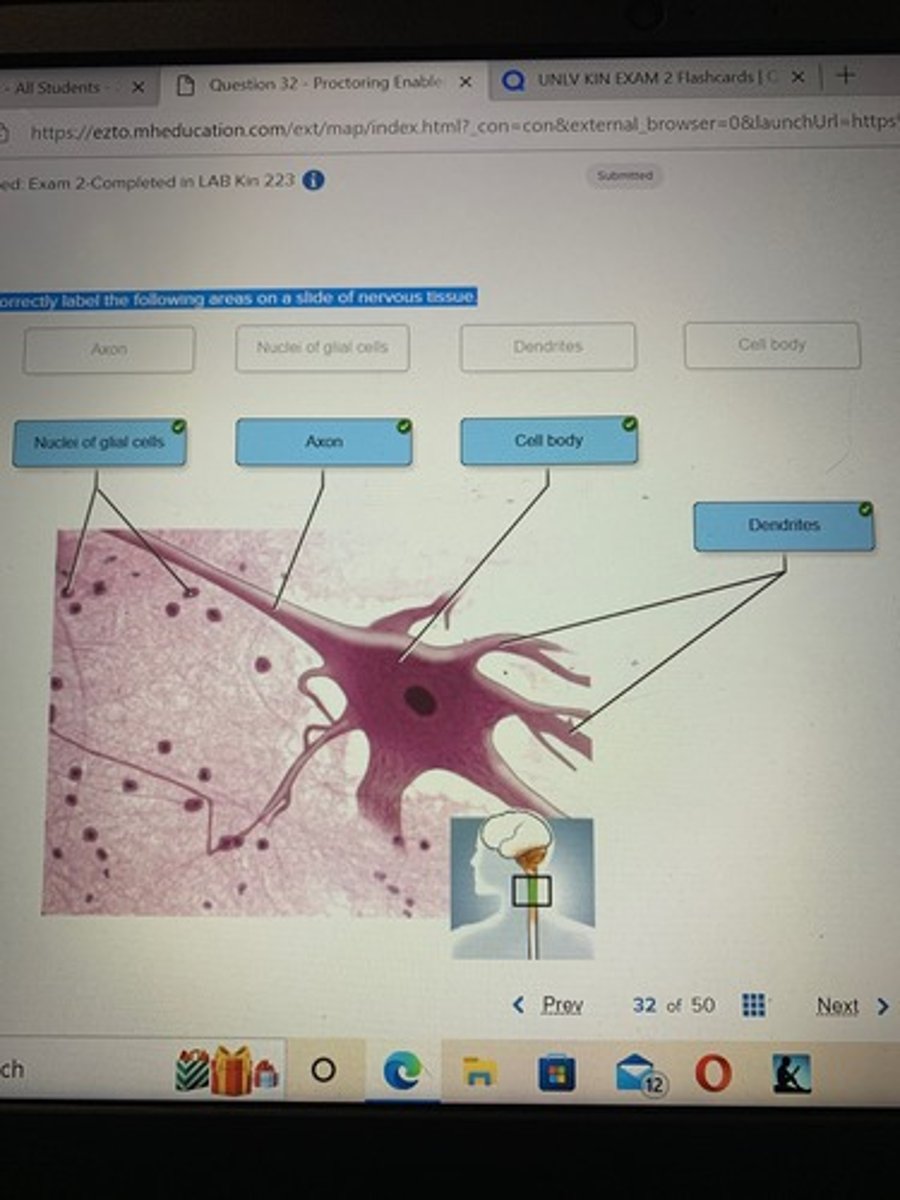
Correctly label the following areas on a slide of nervous tissue.
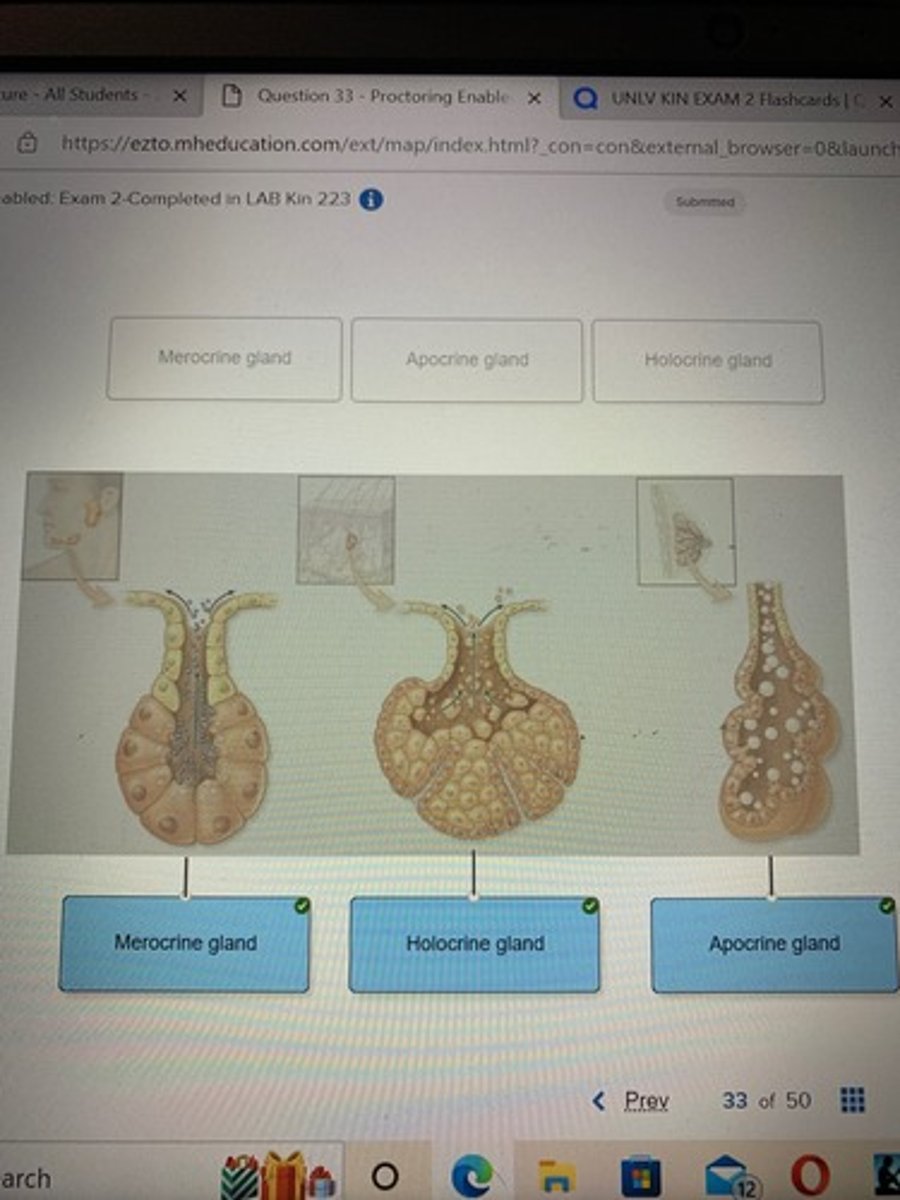
Classify the exocrine glands based on their mode of secretion.
The structure responsible for pulling on the follicle and causing "goose bumps" is the
epithelial root sheath.
internal root sheath.
papilla.
arrector pili muscle.
external root sheath.
arrector pili muscle.
Normally, skin color results from a combination of
a: melanin
b: hemoglobin
c: bilirubin
d: carotene
a, d
a, c, d
b, c, d
a, b, c
a, b, d