KNES 337 - Unit 12 Sugars, Starches, and Fibers
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
enriched vs. whole grain
On the ingredient label
“Enriched wheat flour” - by law means that vitamins were put back into white flour
“Whole grain whole wheat flour including the germ”
simple carbs
sugary, sweet, e.g. cereals, white bread, french fries, cookies, chocolates
complex carbs
starchy, e.g. bread, yam, broccoli, bananas, oats
oligosaccharides
3-60 monosaccharides, short chains of monosaccharides joined by bonds that cannot be broken by human enzymes (fiber sources)
fructans and galacto-oligosaccharides
type of oligosaccharides, found in inulin, garlic, onions
also wheat, artichokes, beans
polysaccharides
up to 1000s of monosaccharides, long chains joined by bonds, some are digestible (glycogen, starch) and some are not digestible (cellulose)
Found in potato, rice, pasta, bread, apple peel, seeds, nuts (very starchy foods)
polysaccharides found in
potato, rice, pasta, bread, apple peel, seeds, nuts
monosaccharides
most basic unit, e.g. glucose, fructose, galactose
Most abundant and nutritionally relevant is glucose
Only monosaccharides are absorbed into bloodstream
disaccharides
two monosaccharides joined by a covalent bond
sucrose
cane sugar, beet sugar, most widely used natural sweetener
= glucose + fructose
maltose
formed from the partial breakdown of starch and is often used in malt beverages (e.g. beer), bacteria ferment the maltose and make alcohol as a byproduct
= glucose + glucose
lactose
milk sugar, one of the only animal sugars besides glucose
= glucose + galactose
simple sugars
refers to monosaccharides and/or disaccharides
***Health Risk - rapidly absorbed into blood stream, increased insulin and inflammation
fiber
important because of what happens to it in the colon
the preferred fuel for gut microbiota
colon
bacterial enzymes can break down fiber to form short chain fatty acids and gas as a byproduct
Fiber is the preferred fuel for gut microbiota
Short chain fatty acids - very important messenger
Gas - flatulence
diet and gut microbiota
High fiber, whole natural foods → microbiota symbiosis → healthy gut microbiota
Processed foods, low fiber → microbiota dysbiosis → chronic disease
processed vs. ultraprocessed foods
If in a box, not necessarily highly processed
E.g. catelli pasta - “whole grain durum what semolina” - great choice!
E.g. chocolate lucky charms - “whole grain corn” (sounds good), but also “sugar, modified corn starch, corn syrup, dextrose…artifical flavour…cocoa processed with alkali, colour added” - not great
Significantly changed from its original state, with salt, sugar, fat, additives, preservatives, and/or artificial colours added
whole grain foods
in a grain of wheat, the outer bran layer is a rich source of dietary fiber
Germ: contains protein, unsaturated fats, thamin, niacin, riboflavin, iron, and other nutrients
Bran and germ are removed in the refining (i.e. making white flour)
Endosperm primarily contains starch, the storage form of glucose in plants = white flour
germ
contains protein, unsaturated fats, thamin, niacin, riboflavin, iron, and other nutrients
removed in refining
soluble fiber
food because it benefits health in several ways
Slows down glucose absorption, lowering peak blood levels of glucose
Reduces fat and cholesterol absorption
Found in oats, barley, psyllium, fruit pulp, peas, beans, citrus fruits, strawberries
psyllium
best place to get it is bran buds (Kellogg's All-Bran buds), reduces cholesterol absorption/lowers cholesterol (health claim)
oats
beta-glucan, oatmeal, oat flour
insoluble fiber
also benefits health in several ways
Moves bulk through the gut, controls gut pH, removes toxic waste, prevents constipation
Found in vegetables, wheat bran, whole grains, flax seed, popcorn, corn bran, seeds, nuts, apple peel
how body manages glucose
Blood glucose rises when you eat
High blood glucose stimulates pancreas to release insulin
Insulin - stimulates uptake of glucose into cells and storage as glycogen in liver and muscle, also helps convert excess glucose into fat stores
As body cells use glucose, blood levels decline
Low blood glucose stimulates pancreas to release glucagon
Glucagon - stimulates liver cells to break down glycogen and release glucose into blood
Blood glucose begins to rise
high blood glucose
stimulates pancreas to release insulin
insulin
stimulates uptake of glucose into cells and storage as glycogen in liver and muscle, also helps convert excess glucose into fat stores
low blood glucose
stimulates pancreas to release glucagon
glucagon
stimulates liver cells to break down glycogen and release glucose into blood
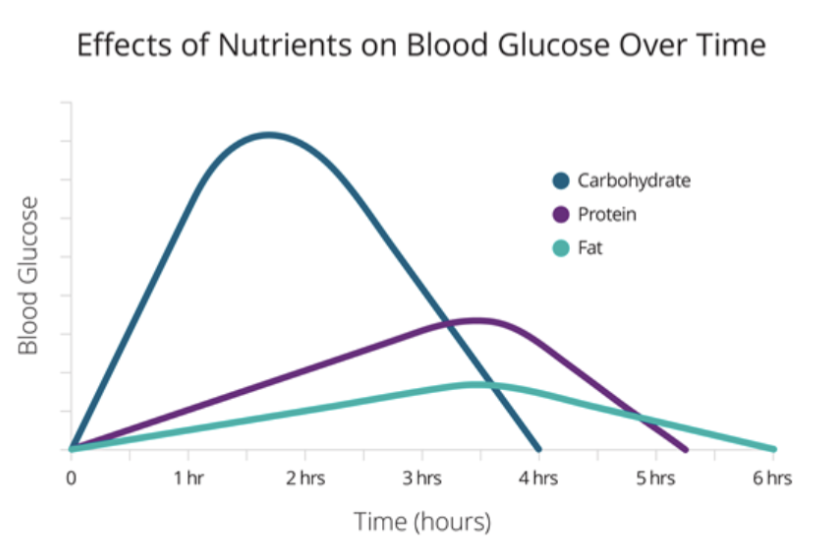
effects of nutrients on blood glucose over time
Carbohydrate is most responsive and most exposure to glucose - short term
Protein and fat - delayed response
Fat affects blood glucose the least
Ketogenic diet is based on this - 70% of all calories coming from fat to reduce blood glucose and reduce insulin usage
added sugars
Major sources of simple sugars in most diets are added during processing of food
Labels contain information on total sugars per serving but do not distinguish between naturally occurring and added sugars
Added sugars add calories without adding nutrients
All sugars now required to be included together on the ingredient lists (can’t spread them all out)
e.g. brown sugar, corn syrup, malt syrup, honey
e.g. milk is 13% of daily value of sugar, chocolate milk is 26%
bad side of sugar
Tooth decay
Empty calories (calories without nutrients
Often mixed with fats
Limit sweet and sticky foods, replace them with vegetables and fruits
Overall quality of diet decreases when sugar intake decreases
non-nutritive sweeteners
includes artificial and non-artificial zero-calorie sweeteners
Zero-calorie or low-calorie sweeteners - either artificially synthesized or naturally derived
E.g. aspartame, sucralose, acesulfame K, saccharin, advantame, neotame, stevioside
Use a very small amount to get a very sweet taste, e.g. advantame - 20x sweeter than sucrose
Reduce sugar content, but still get sweet taste
In pop, gum, yogurts, brownie mix, protein bars, protein powders
In anything that says “zero sugar”
Aspartame is in 6000 products - even in toothpaste, antibiotics
All approved, and in the marketplace, so not toxic - but not healthy either
sugar intake recommendations
No more than 6 teaspoons (24 grams) for women
No more than 9 teaspoons (36 grams) for men
Less than 6 teaspoons per day for children - and sugary beverages should be limited to no more than 8 oz a week
BUT for 1 can of soft drink = 10 teaspoons of sugar - exceeds all daily amounts
aspartame
very common artificial sweetener, a dipeptide (2 amino acids = aspartic acid + phenylalanine)
Digested by us - releases methanol, aspartic acid, and phenylalanine
Methanol converted to formaldehyde and then formic acid (most concerning), not good for our body, rapid conversion (formaldehyde converted to formic acid right away)
200x sweeter than sucrose
PKU (phenylketonuria) - products need to label “contains phenylalanine"
People with PKU unable to metabolize phenylalanine and will accumulate in their brain
Blue packets - Nutrasweet, Equal have aspartame, and many sodas
Acceptable daily intake is 40 mg/kg BW
Not compatible with high temperatures (> 30 degrees C)
Aspartame will start to degrade
Never cook or bake with aspartame
sucralose
made from sugar, chlorinated sugar, 600x sweeter than sugar, safe when heated, used for baking, yellow packets - splenda
acesulfame K
often used in combination with other artificial sweeteners, stable at high temperature
saccharin
discovered in 1879 by accident by chemist working on coal tar derivatives (he licked it and it was intensely sweet), 300x sweeter than sucrose
Banned in Canada in 1977 due to bladder cancer fears (it caused it in rats), but then brought it back because it was discovered that the mechanism by which it caused cancer in rats is not present in humans
sugar alternatives
do contribute calories, includes alcohol sugars, stevia
alcohol sugars
~2.6 kcal/g, e.g. xylitol, mannitol, sorbitol, erythritol
Used in chewing gum and other candies and foods
Can be used to mask the unpleasant aftertaste of some artificial sweeteners
Are not well absorbed in the gut, large amounts can cause diarrhea
stevia
herbal alternative, GRAS-status
initial studies with crude whole leaf extracts of stevia = reproductive, renal and cardiovascular toxicity, not initially approved
Purified stevioside preparations show no toxic effects
In 2012, Health Canada approved its use in foods
evidence in rodents
One of the first studies to revisit artificial sweeteners
So they don’t cause cancer, but are they affecting us in other ways?
Tested saccharin, sucralose, aspartame
Control mice, and NAS (non-nutritive sweeteners) mice
NAS had altered microbiota - increased glucose response (prediabetic state)
Used antibiotics to knock down microbiota - glucose tolerance back to normal - good but antibiotics have other bad effects
Also put altered microbiota into germ free mice - glucose intolerance increased as well
Looked at adult humans too - Some are responsive and some are non-responsive
Responders - blood glucose elevated, altering microbiota, glucose intolerance increases
Non-responders - microbiota doesn’t change, normal glucose tolerance
Not great conclusions
evidence in humans
For 2 weeks, 120 healthy adults consumed saccharin, sucralose, aspartame, stevia packets - does lower than acceptable daily intake
Compared with controls receiving packets containing the vehicle (glucose) or no supplement
Fecal transplant into mice - people into mice → every sweetener increase blood glucose in the mice
None of these are good for us if we are responders
Bottom responders - most are good, but saccharin can still cause a bad glucose response
Worst of all of these is saccharin - bad for both top and bottom responders - microbiota being messed up
erythritol
alcohol sugar, a zero-calorie sugar substitute found in Truvia, keto foods, might raise risk of stroke, death
Cleveland Clinic researcher found that erythritol was found in the blood of people who turned out to be at the highest risk for a bad cardiac outcome
High erythritol blood levels seemed to lower the threshold for triggering a clot
Erythritol promotes blood clots
Erythritol found in monk fruit sweeteners (white sugar replacement), not pure monk fruit extract, Splenda (ingredients: erythritol, stevia leaf extract)
Found in a protein bar by Dr. Reimer
Now she’s handing them out
maternal health with aspartame and stevia
Mother rats consumed aspartame or stevia during pregnancy and lactation
Offspring had more fat mass
FMT to germ free mice
Higher body fat % after 14 days
Worse glucose intolerance
Maternal consumption detrimental for offspring
Offspring didn’t have to consume it themselves to be obese
WHO and non-sugar sweeteners
WHO suggests non-sugar sweeteners not be used as a means of achieving weight control or reducing the risk of noncommunicable diseases (conditional recommendation)
Cut them out
Recommendation relevant for everyone
Not a homogenous class of compounds, each has a unique chemical structure
sugar and tooth decay
Sugar is sole food for bacteria → produce acid → bacteria form sticky white plaque → acid produced by bacteria for 20 min after sugar is eaten
Promoters of tooth decay:
Increased frequency of sticky food
Acidic beverages - coffee, tea
Excessive cleaning/polishing of teeth - whitening
Nursing bottle syndrome - don’t send kids to sleep with milk or juice in bottle
protective foods
Cheese - decreases acidity, increases pH of plaque
Protein - with calcium, strengthens enamel
fluoride
Remineralizes eroded enamel
In water, toothpaste, dental rinses
fluorosis
due to excess fluoride, mottled enamel during tooth development, too much fluoride, cosmetic condition that can only form in children < or = 8 years when permanent teeth are developing