Bio 30 Unit B Reproductive systems
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Goal of human reproduction
To produce offspring
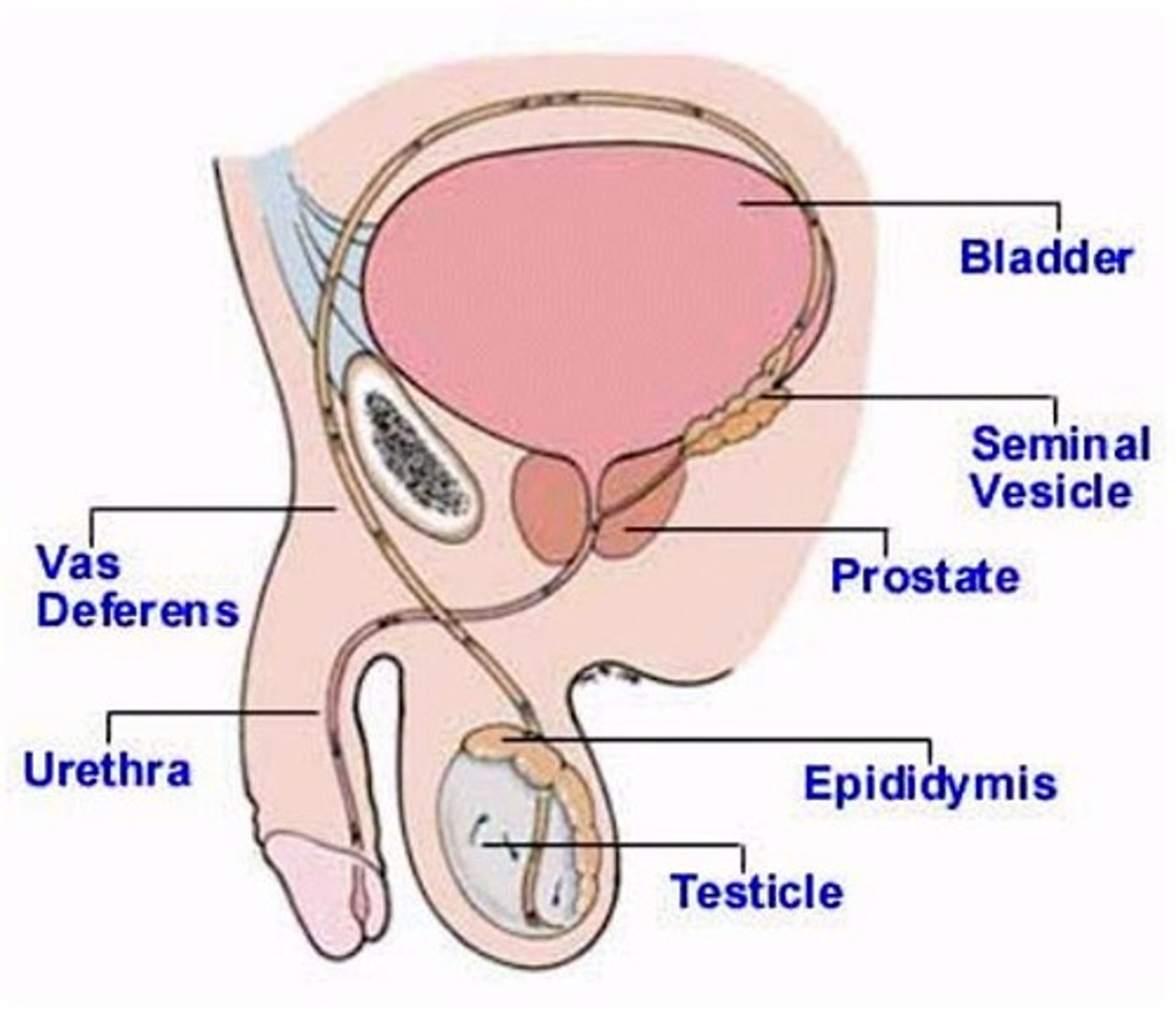
Labelled Male Reproductive System (frontal)
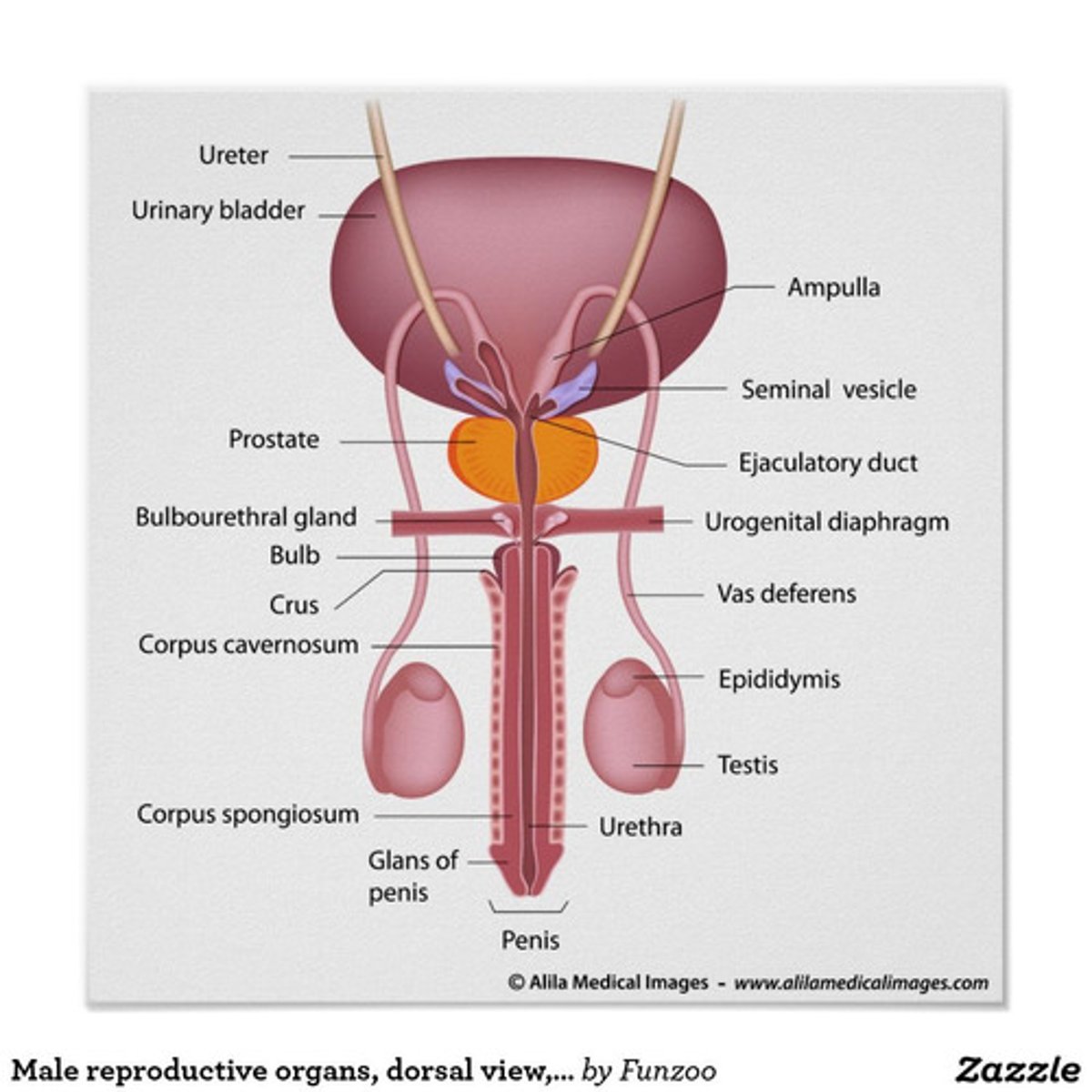
Labelled Male Reproductive System (side view)
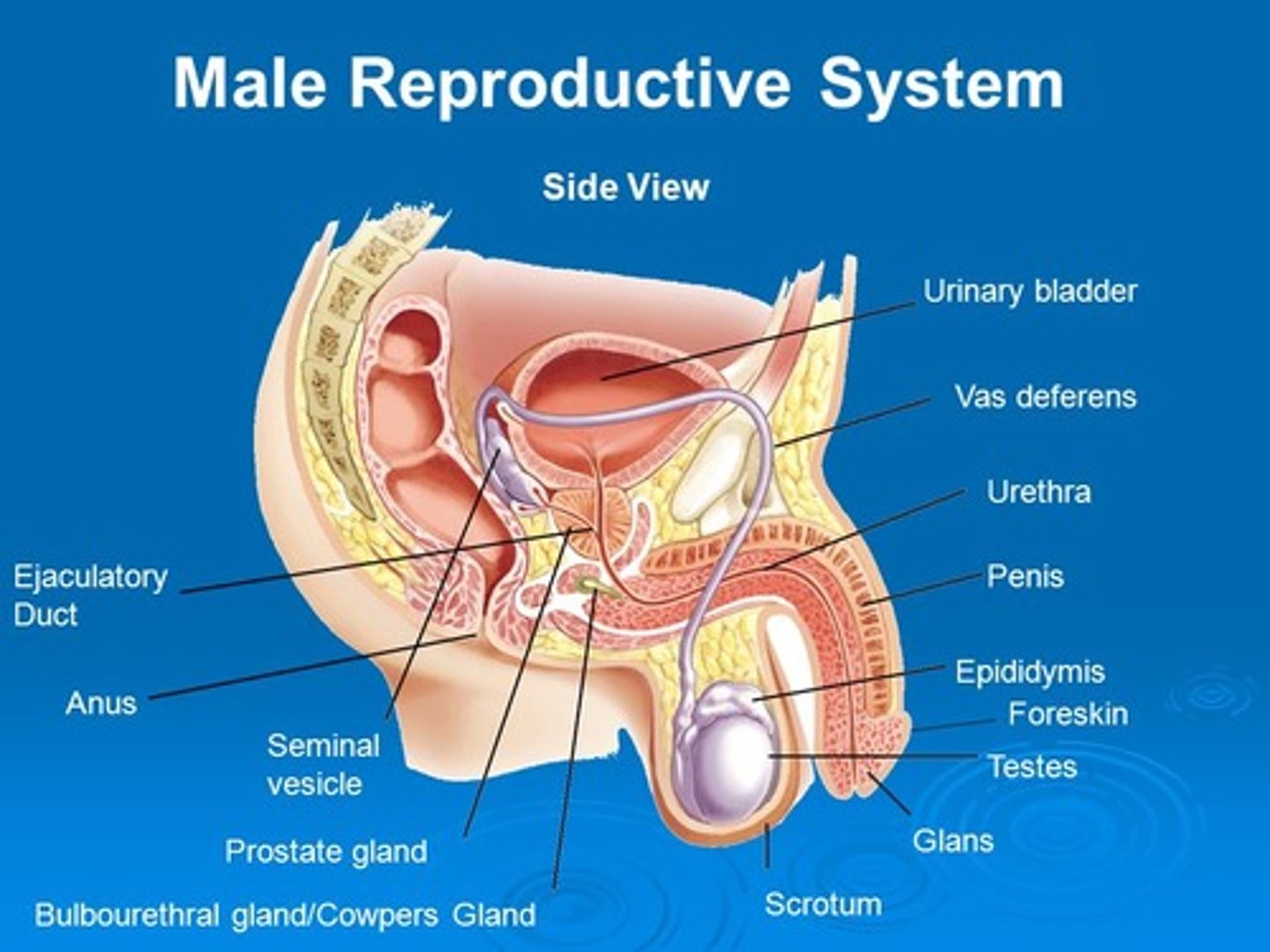
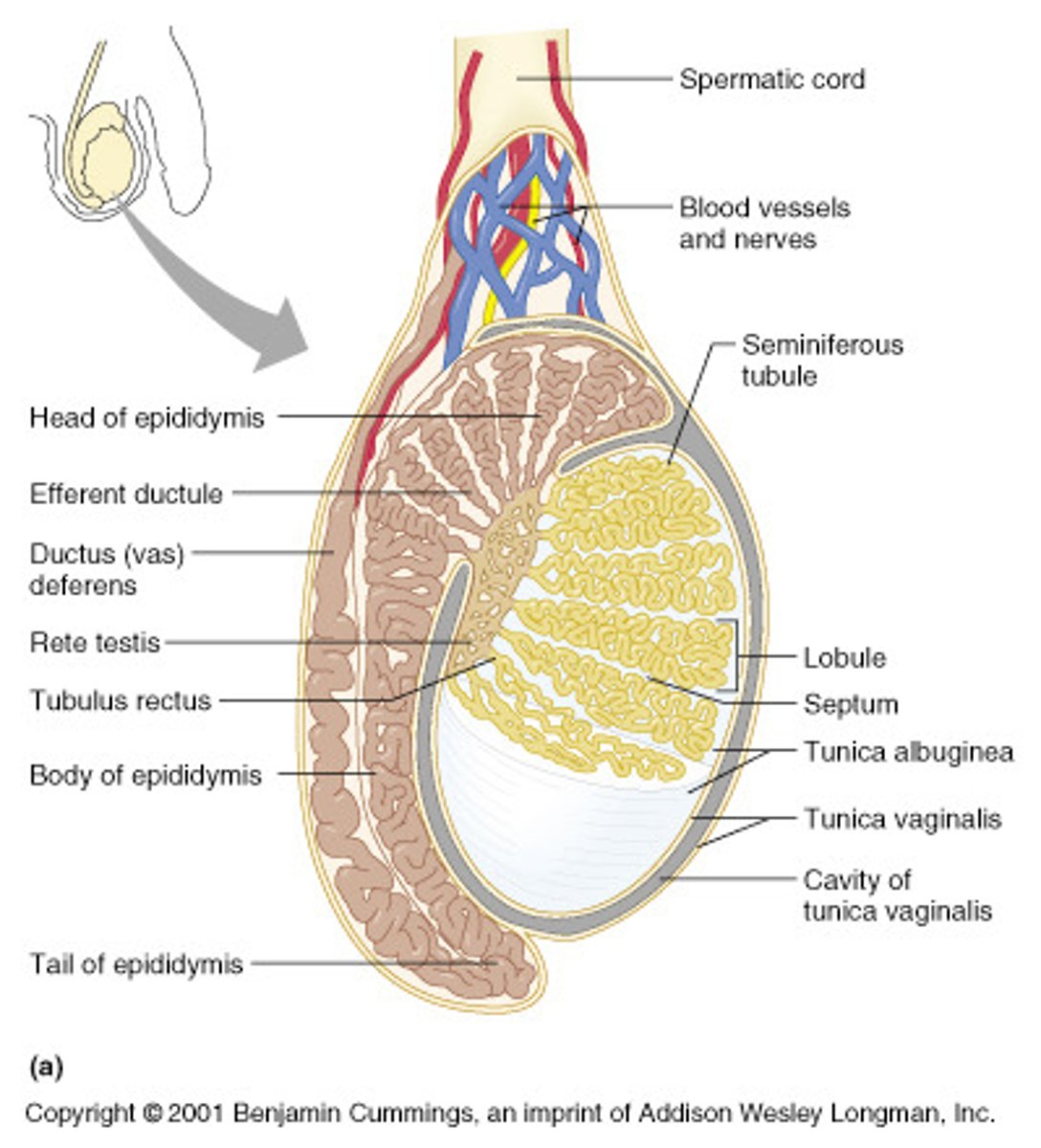
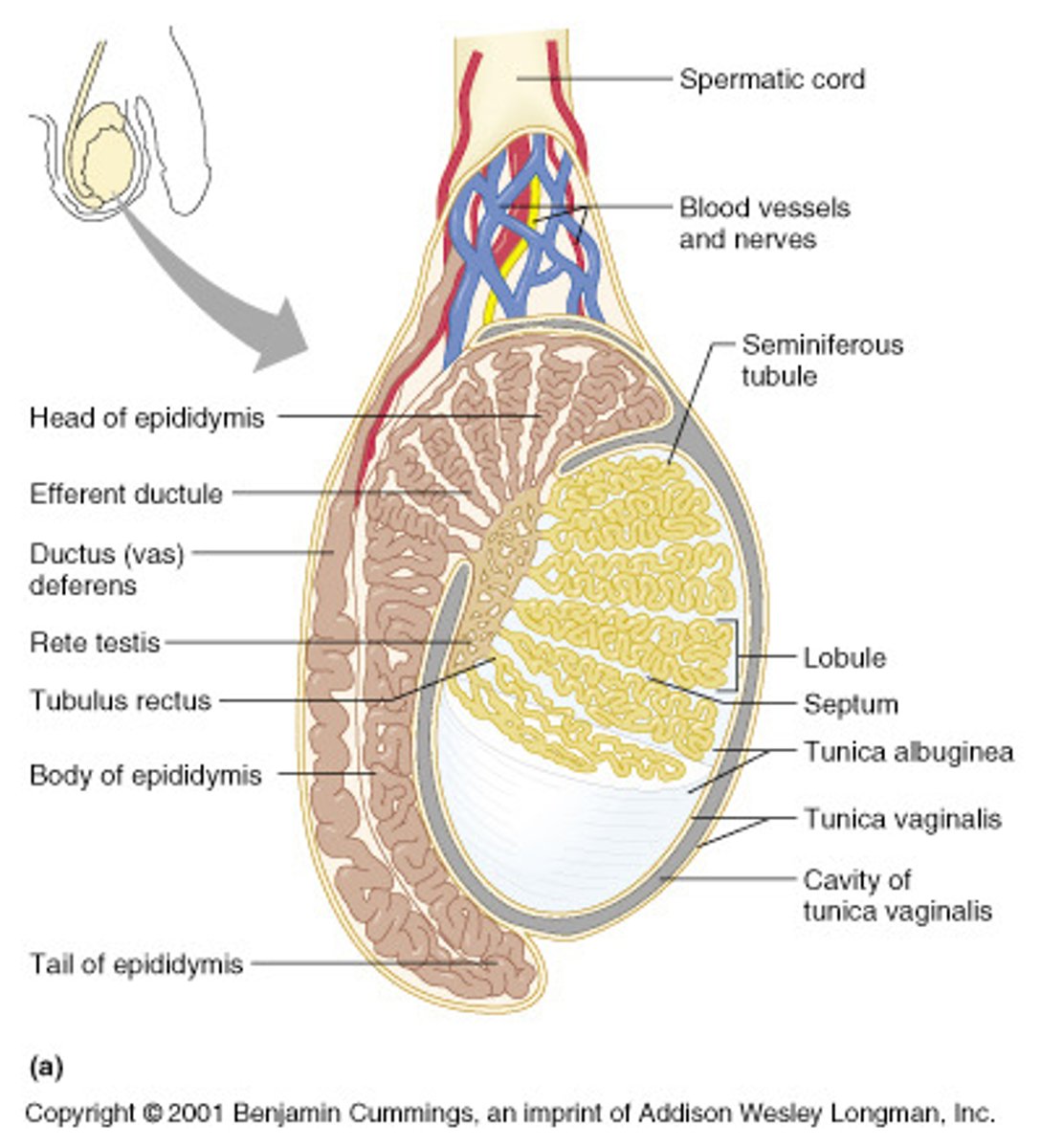
Testes
- Contained within the scrotum
- Produce sperm and sex hormones
- Contains interstitial cells and seminiferous tubules
Interstitial cells
- In the testes
- Produce testosterone
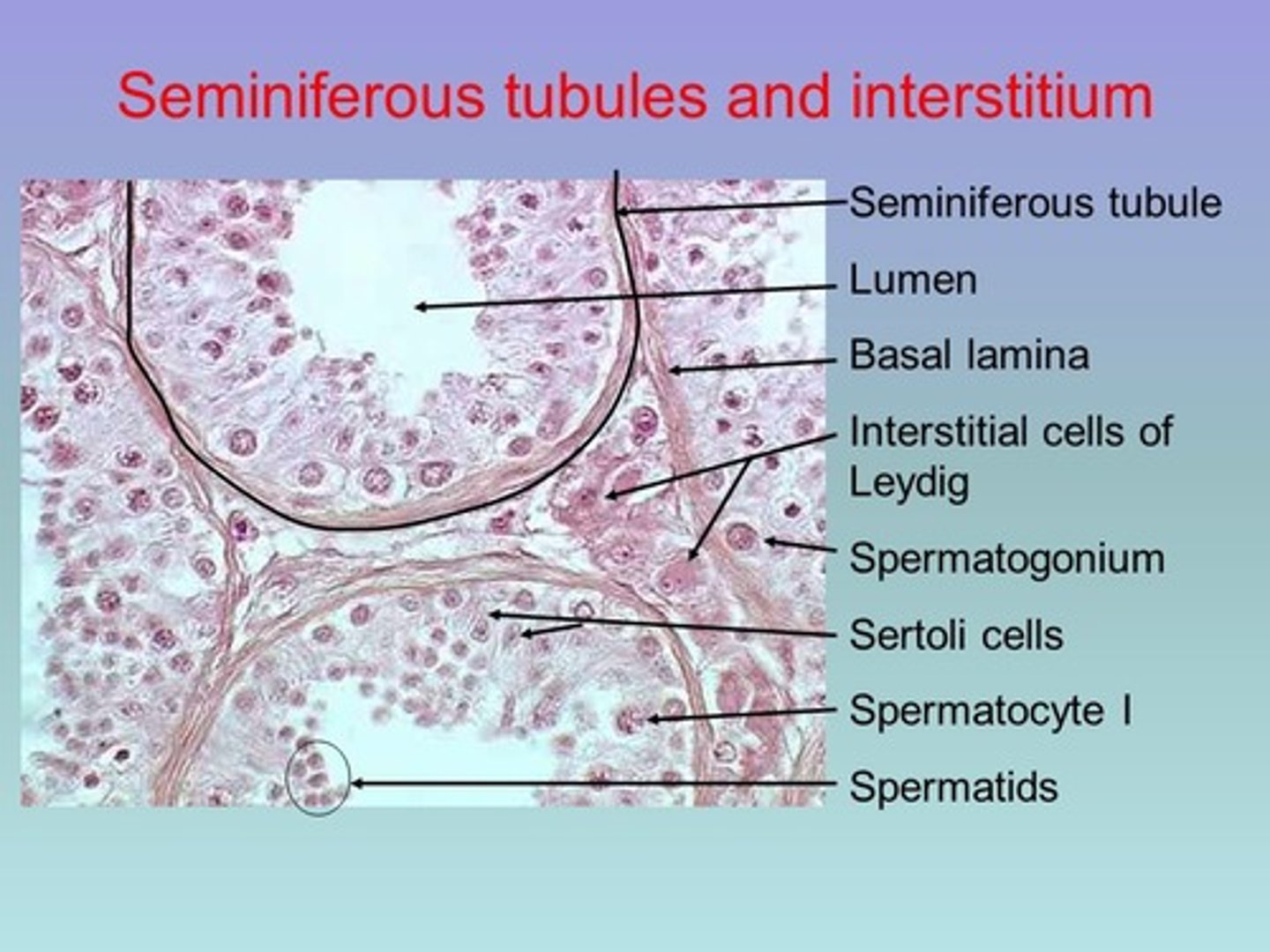
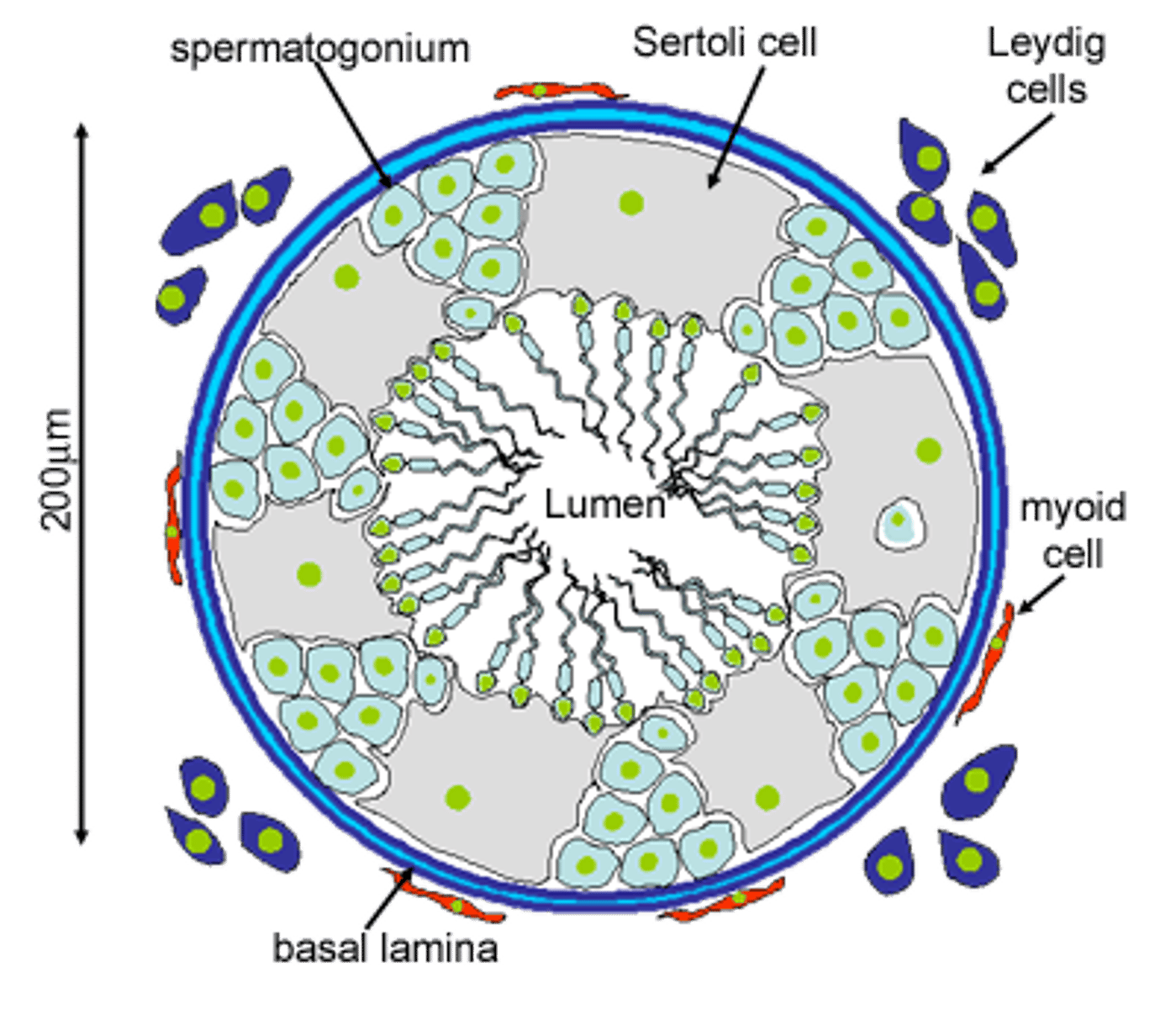
Seminiferous tubules
- In the testes
- Produce sperm

Sertoli cells
Somatic cells of the testis that are essential for testis formation and spermatogenesis. Facilitate the progression of germ cells to spermatozoa.
Epididymis
- A long, tightly coiled duct lying outside each testis.
- Site of sperm storage and final sperm maturation
Vas deferens
- Tube like structures that carry sperm from the epididymis to the urethra.
- Pass into the abdominal cavity, where they curve around the bladder and empty into the ejaculatory duct.
- Ends at ampulla
Ampulla

Urethra
- Located within the penis
- Transports both urine and semen out of the penis
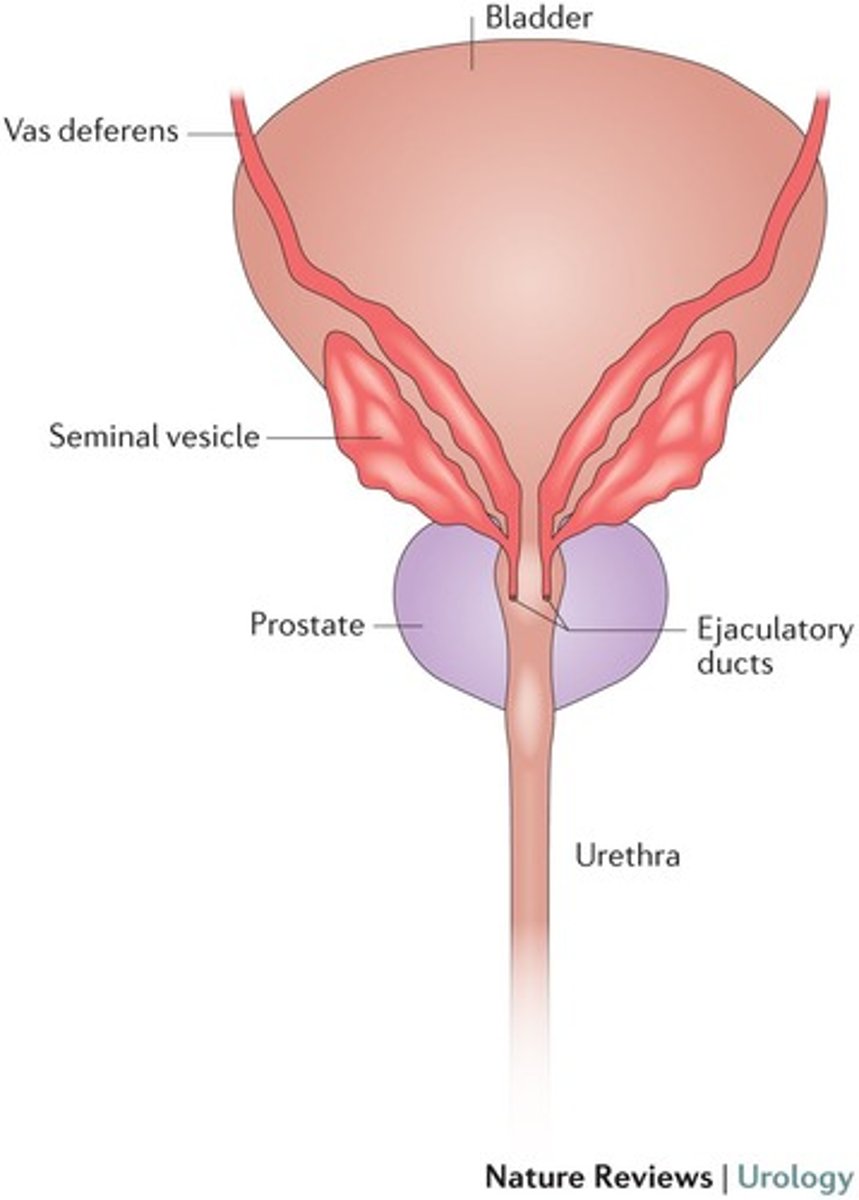
Ejaculatory duct
Ensures that urine and semen are not transported at the same time.
Penis
- Spongy, erectile tissue containing distensible blood spaces extends through the shaft of the penis.
- Transports sperm from the vas deferens to the vagina
What are the three supporting glands in the male reproductive system?
- Seminal vesicle
- Prostate gland
- Cowper's/Bulbourethral gland
Purpose of supporting glands
Sperm could not survive without the secretions provided by the three supporting glands
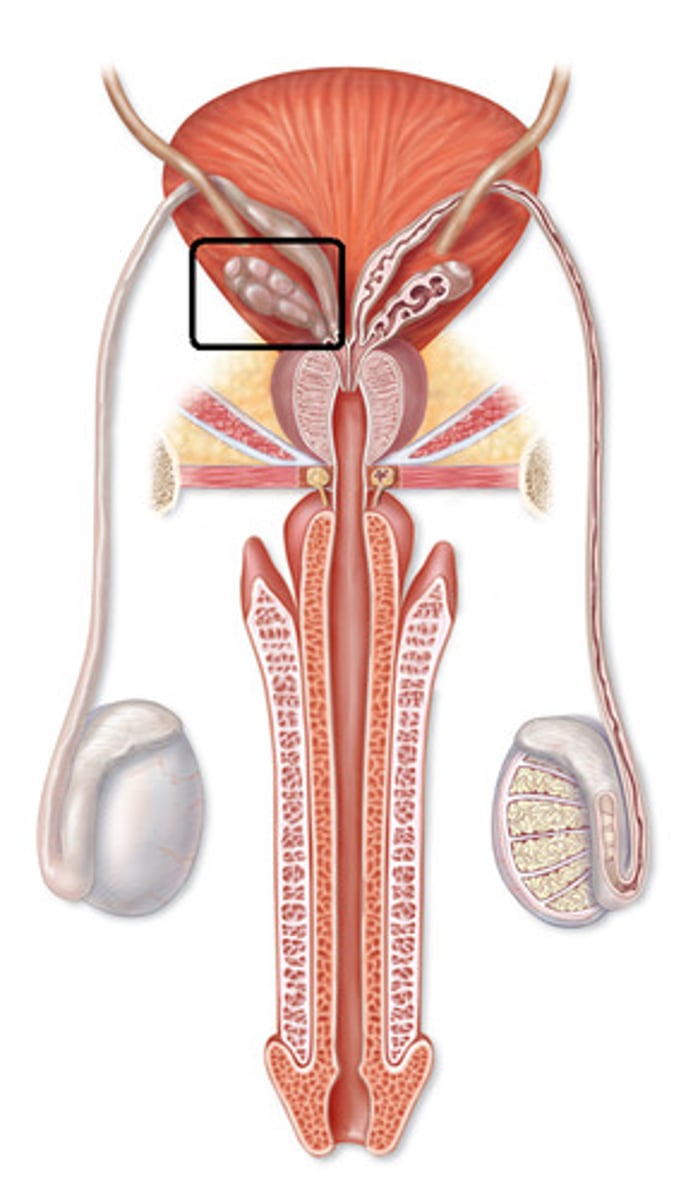
Seminal vesicle
- Attached to Vas Deferens, right before prostate and ejaculatory duct
- Contributes a secretion that contains fructose and Prostaglandins
Fructose purpose
Energy source for sperm cell
Prostaglandins purpose
Trigger rhythmic contractions of smooth muscle along female reproductive tract to assist in movement of sperm cells
Prostate gland
- A single, doughnut-shaped gland that surrounds the upper portion of the urethra just below the bladder.
- Contributes fluid to semen that protect sperm cells from the acidic environment of the VAGINA.
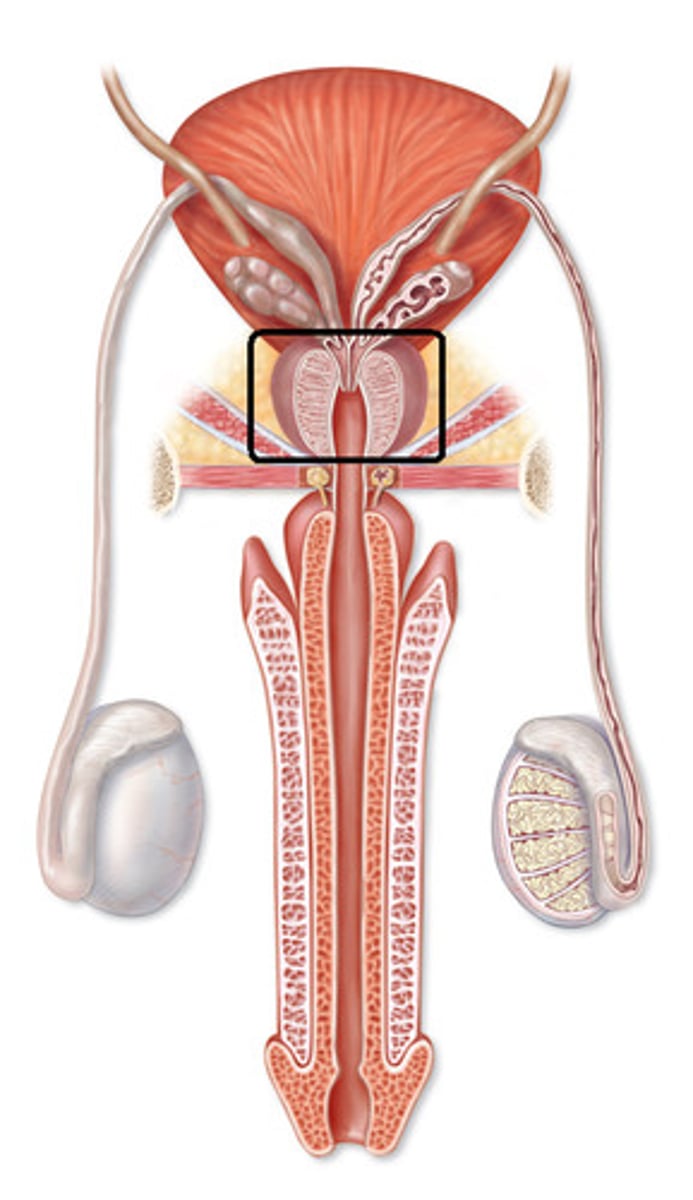
Cowper's/Bulbourethral gland
- Attached to urethra
- Contributes a mucus-rich fluid to buffer the seminal fluid through the urethra.

Sperm pathway
Seminiferous tubules, Epididymis, Vas Deferens, (seminal), Ejaculatory Duct, (prostate, cowpers), Urethra, Penis
Secondary male sex characteristics
Growth of facial and body hair
Enlargement of larynx
Increased muscle mass and strength
Shoulders widen
Larger hands and feet
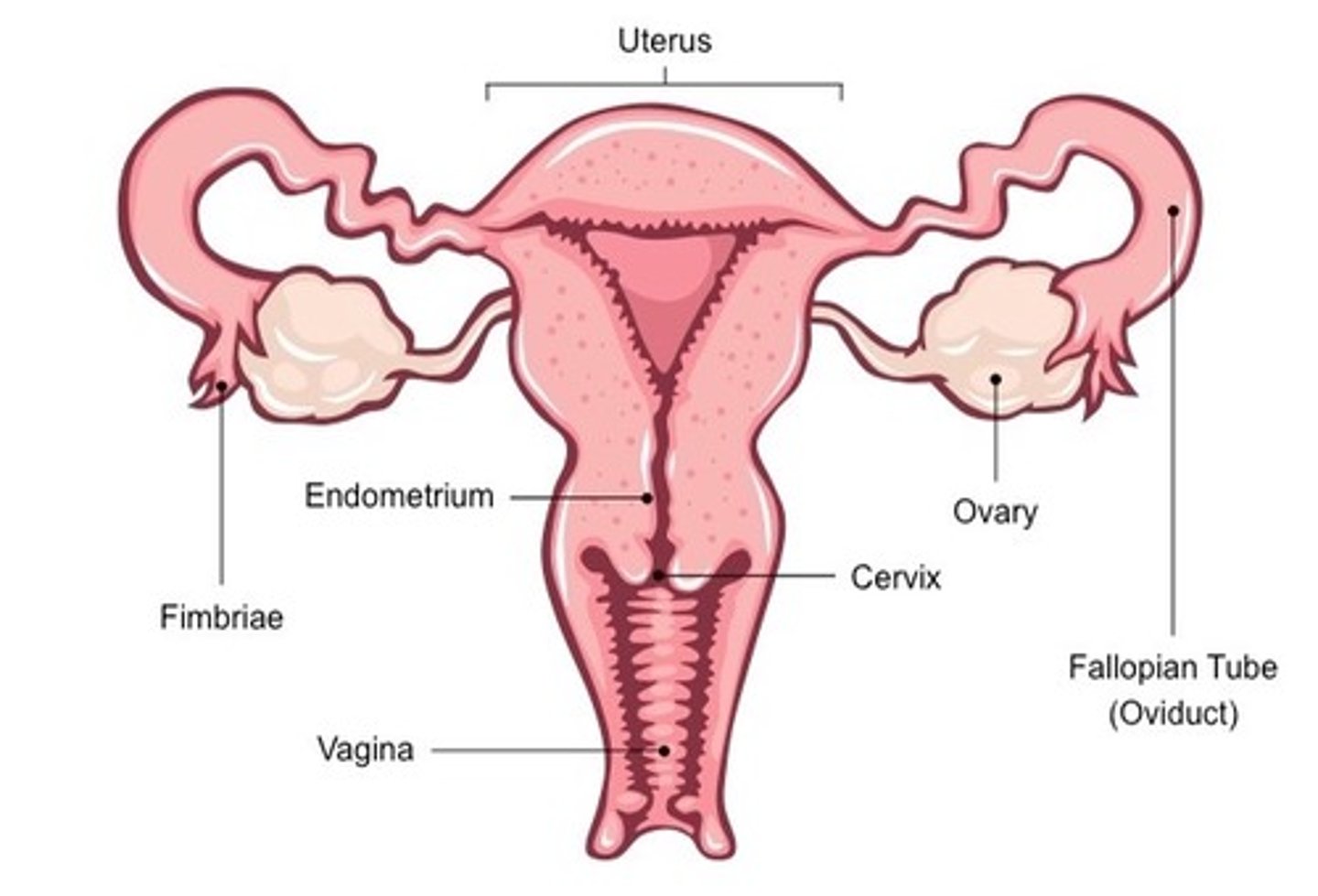
Labelled Female Reproductive System (frontal)
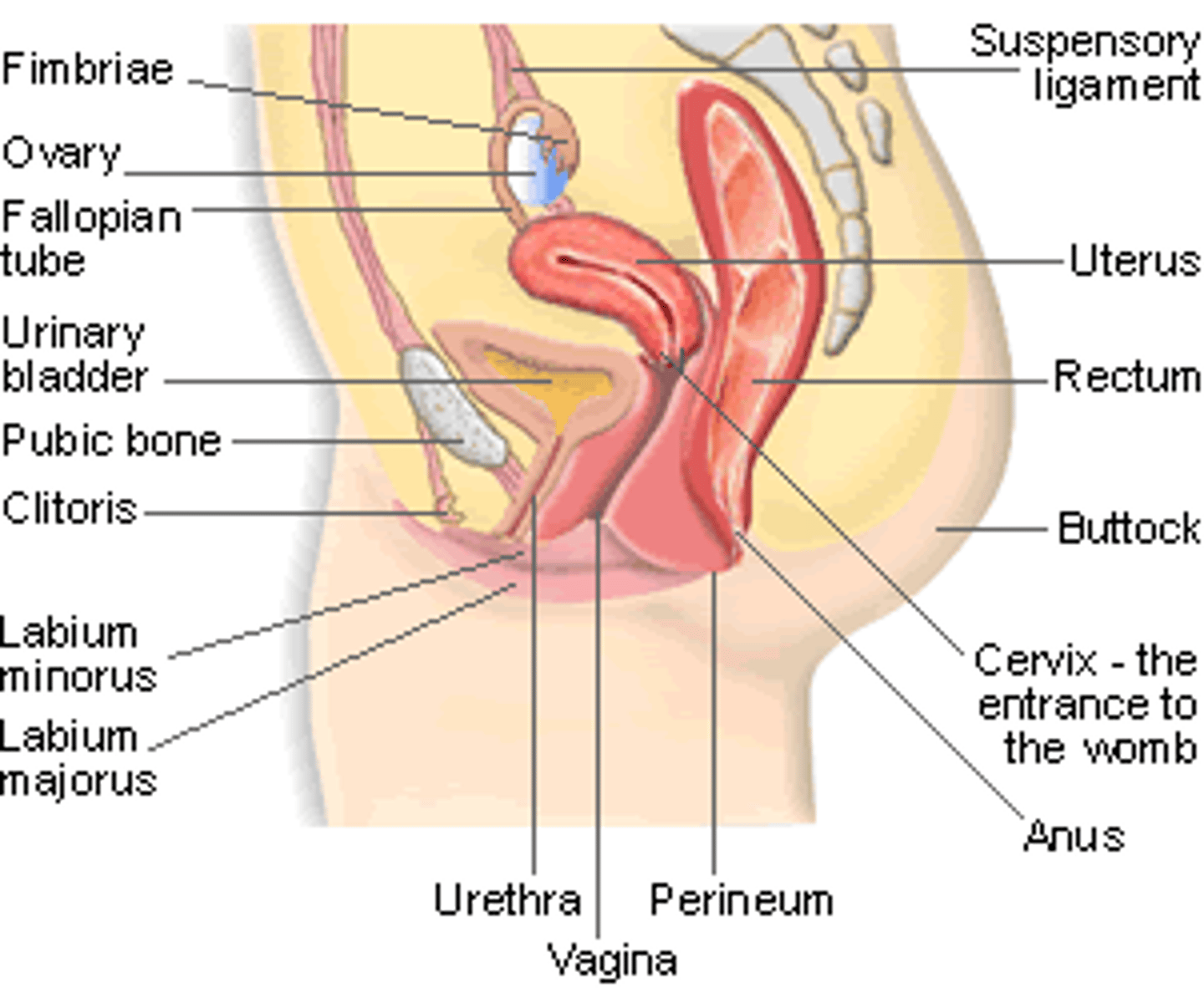
Labelled Female Reproductive System (side view)
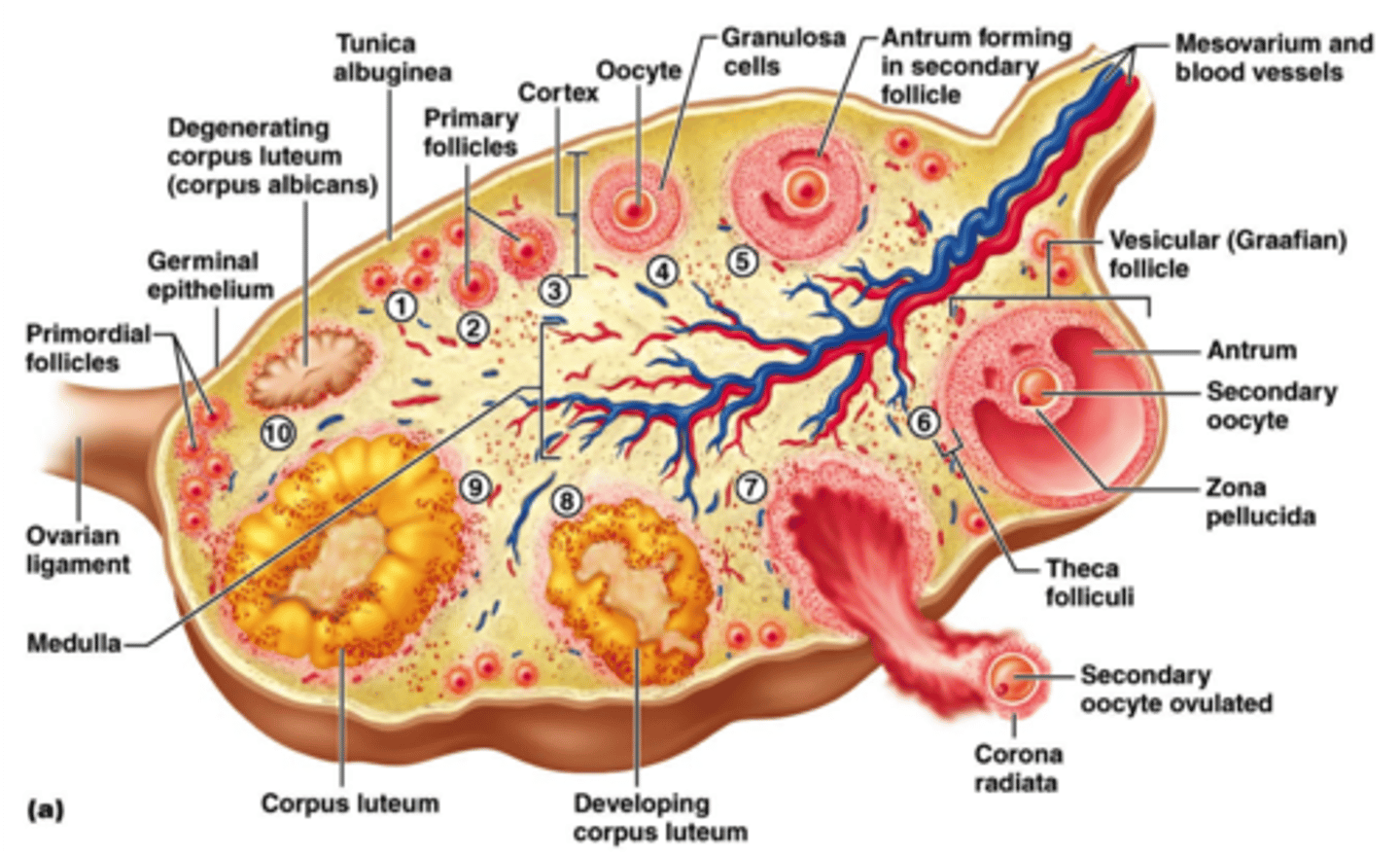
Ovaries
- Site of egg production and maturation.
- Produce female sex hormones (estrogen and progesterone).
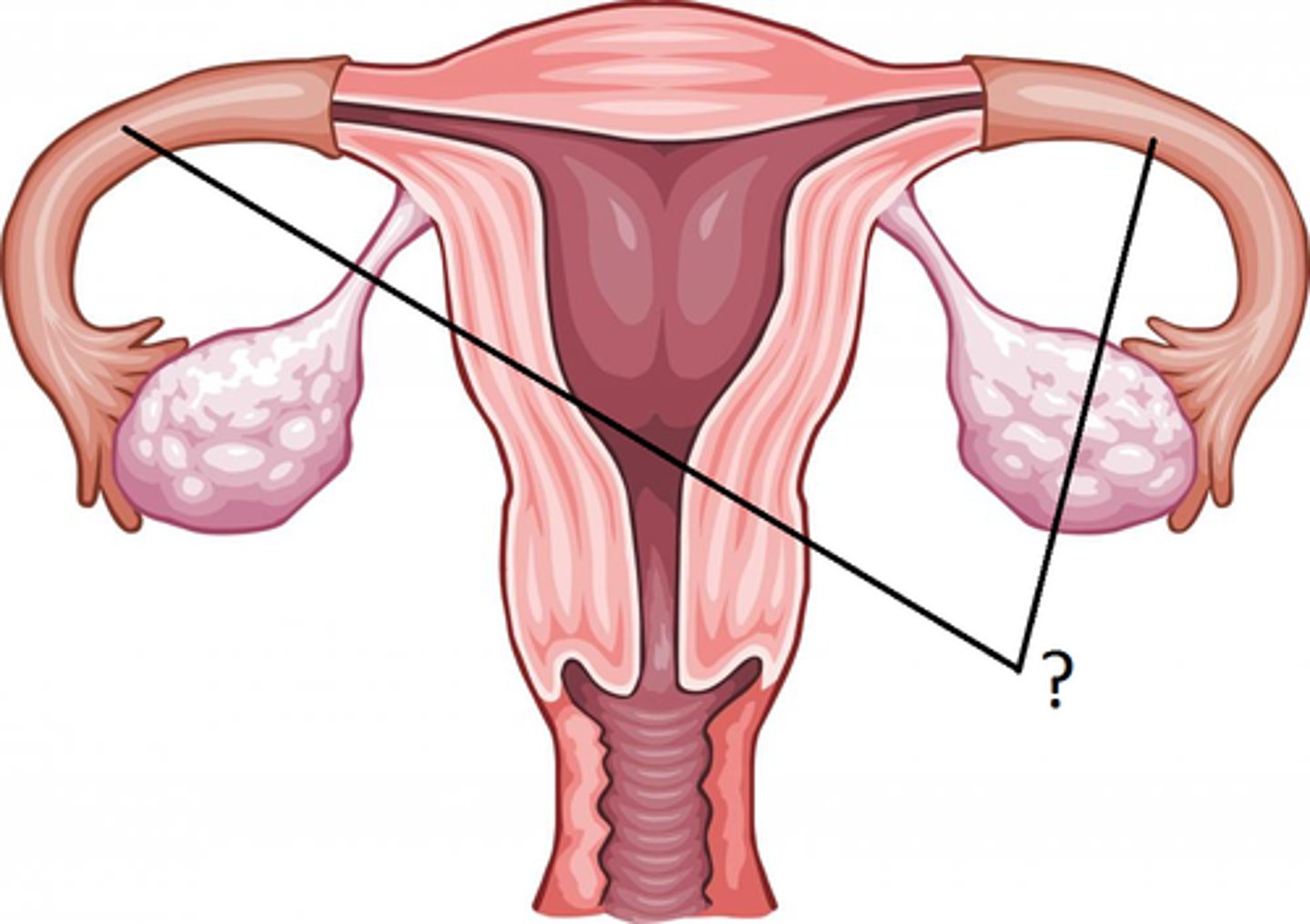
Fimbria
- Transports egg from ovary to fallopian tube.
- Fingerlike processes that wrap near to, but do not touch, the ovary.
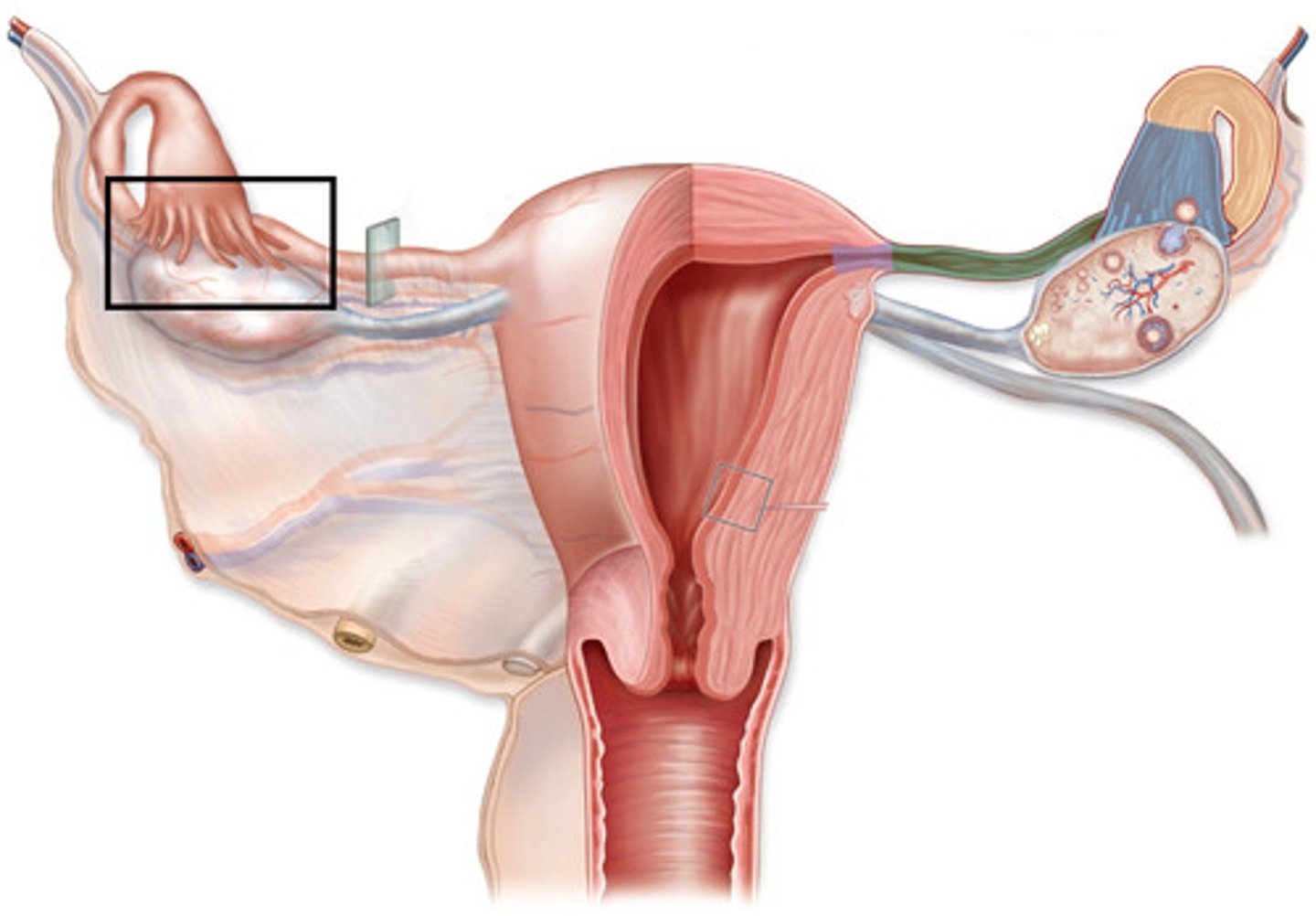
Oviduct (fallopian tube)
- Two tubes extending from each ovary.
- The site of final maturation of the egg and usually the site of fertilization.
- Carry the egg from the fimbria to the uterus.
-Contracts like the intestinal tract - peristalsis
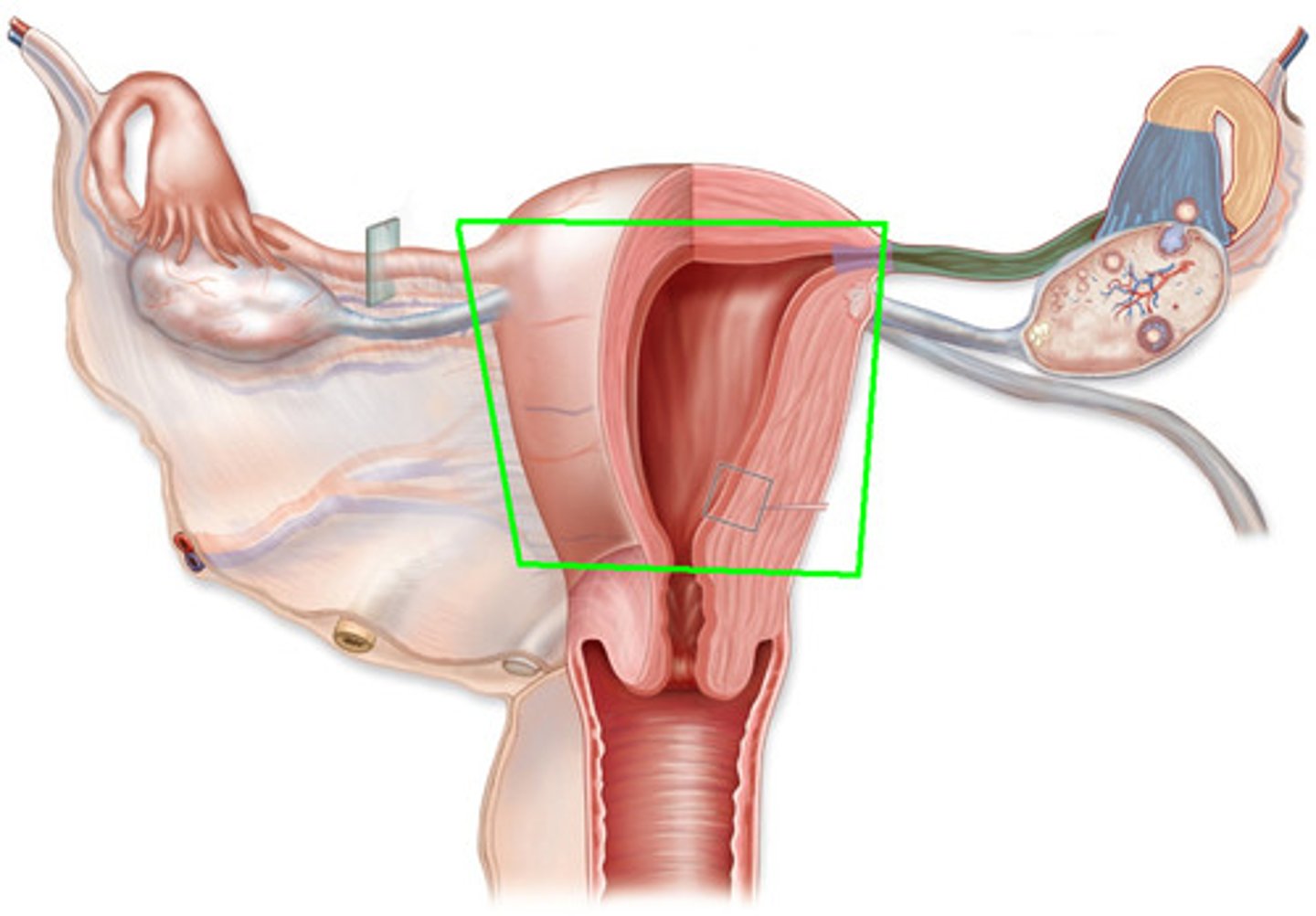
Uterus
- A muscular-walled, hollow, pear shaped organ.
- Site of fetal development.
- Inner lining = endometrium
Endometrium
- The endometrial lining is integral to successful implantation of the fertilized egg. It is built up each month in preparation for fertilized egg.
- If no fertilization, it sheds
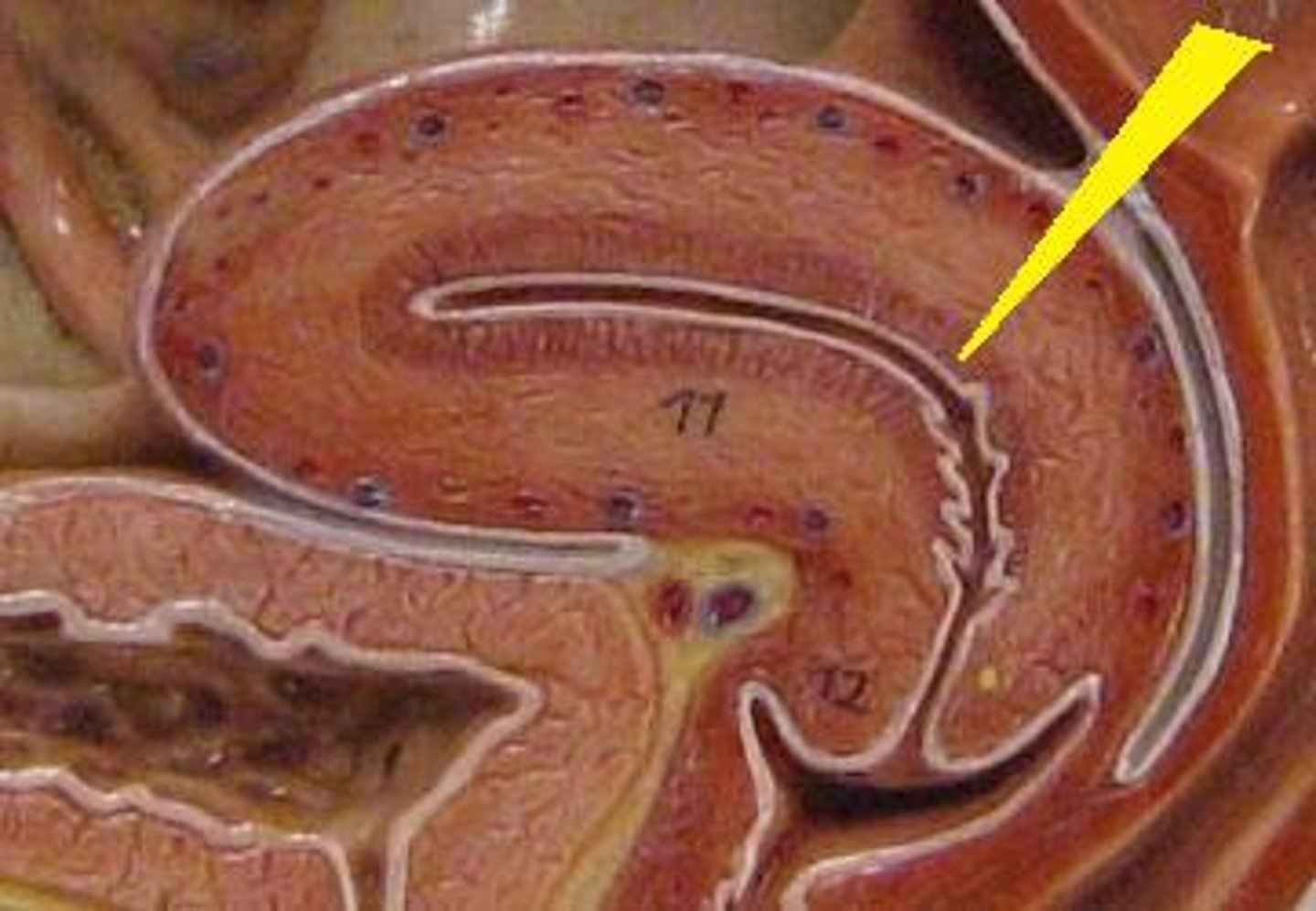
Cervix
- The opening from the uterus into the vagina.
- During pregnancy, muscle is tightened to
hold fetus in place
- Contains cervical glands that secrete a
mucus which blocks spread of bacteria.
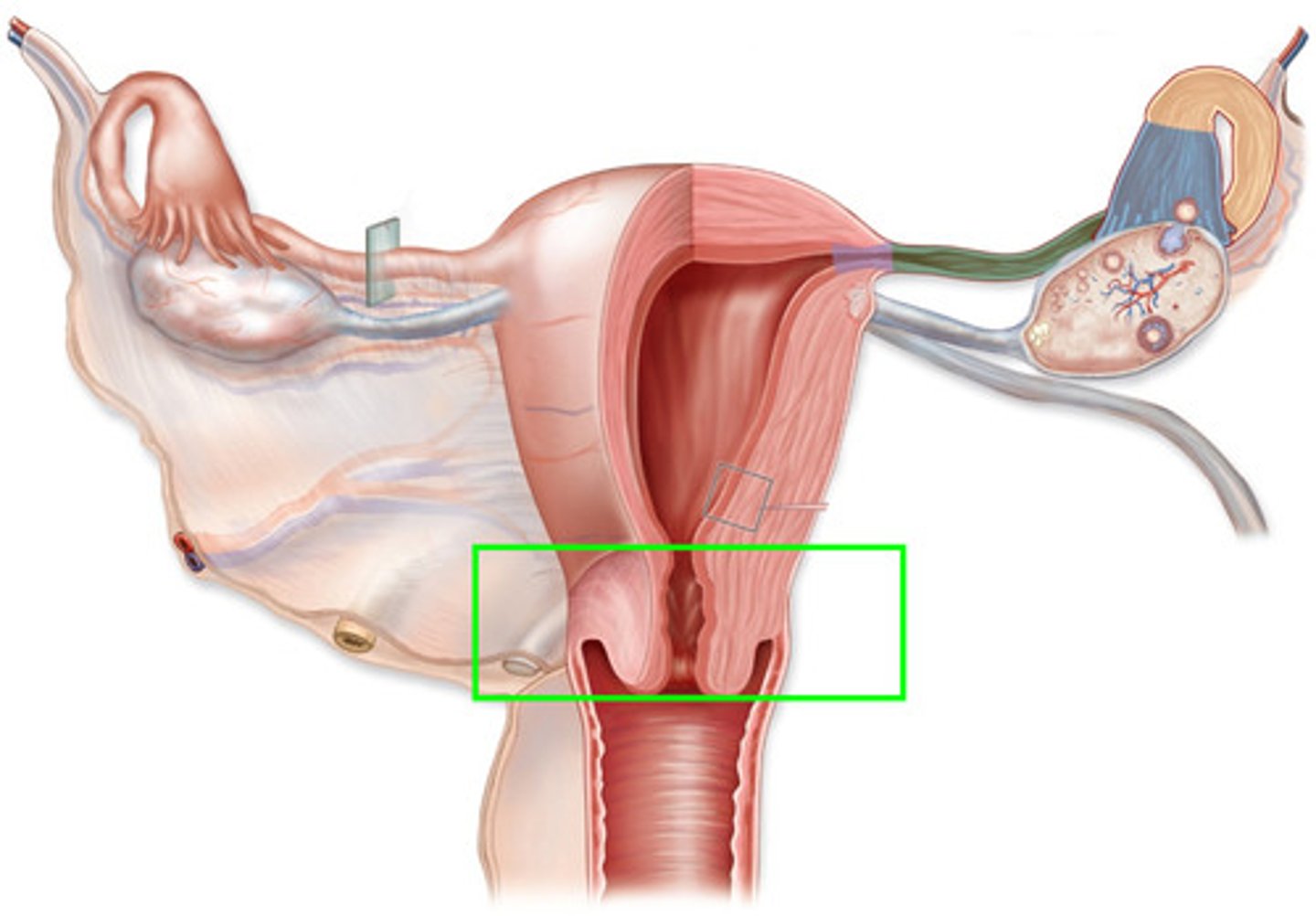
Vagina
- Thin-walled tube (8-10 cm long)
- Lies between the bladder and the rectum and extends from the cervix to the body exterior
- Provides a passageway for delivery of an infant and for menstrual flow.
- Receives the penis (and semen) during sexual intercourse (female organ of copulation).
- Lubricated by cervical glands
- Acidic pH for protection against infection
Secondary sex characteristics in females
• Enlarged breasts
• Less facial hair than men
• Hair growth in armpits and pubis
• Wider at the hips than at the shoulders
• Fat deposits around buttocks and hips
• More body fat than men
• Hands and feet usually smaller and narrower than males
• Angle from thigh to ankle is slightly bent
Oogenesis
-process where females gametes are produced
-occurs in ovaries in specialized cells (follicles)
Primary oocyte
-46 chromosomes, goes through meiosis
-produces 2 new cells each with 23 chromosomes
Secondary oocyte
-produced by primary oocyte
-has 23 chromosomes
-majority of cytoplasm and nutrients move here
Polar body
-produced by primary oocyte
-has 23 chromosomes
-receives little cytoplasm and dies
Fimbrae
draws ovum into fallopian tube
Corpus luteum
what the follicles which surrounded the released egg remain in the ovary turn into (releases progesterone)
Corpus albicans
scar left on the ovary if pregnancy does NOT occur (degeneration)
Meiosis II
-secondary oocyte beings this in the fallopian tube each month once puberty begins
-completed only if the egg is fertilized (releases Ca+ ions and prevents second sperm cell from fertilizing the egg)
Menstrual Cycle
-preparing uterus for implantation of blastocyst (early stage embryo)
-starts at puberty when pituitary secretes FSH
-lasts until menopause
-4 phases
Flow
-shedding of endometrium
-all hormone levels are low
-pituitary secretes some FSH to start developing a follicle in ovary
Follicular
-follicles are developing/swelling and releasing estrogen
-endometrium builds up again
-increased estrogen = negative feedback on FSH secretion, positive feedback on LH secretion (-FSH, +LH)
Ovulation
-occurs where the secondary oocyte is released from ovary
-egg and small amount of follicular fluid bursts from ovary
-caused by surge in LH from pituitary
Luteal
-remaining follicle turns into corpus luteum to secrete estrogen and progesterone (p. continues developing endometrium)
-prevents further ovulation and uterine contractions
-increased estrogen/progesterone levels = inhibits FSH and LH
-no FSH = no further development of follicles
-no LH = corpus luteum breaks down
-both lead to decrease in estrogen and progesterone
Fertilization
-ovum and sperm meet in fallopian tube to form a zygote 4-6 hours after intercourse
Path of sperm for fertilization
Vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes
Cleavage
zygote goes through mitosis going up in cells by 2 without increasing in size (smaller with each division, ex: 2 cells, 4 cells, 8, cells, etc)
Morula
mass of cells 4 days after fertilization
Blastocyst
-hollow ball of cells by the time it reaches the uterus
-digests the endometrium by releasing enzymes 8-9 days after ovulation
-early stage of embryo development
Outer sphere of cells
form the extraembryonic structures in blastocyst
Inner cell mass
-gives rise for the embryo to develop
-moves to the middle of the blastocyst and becomes 3-layered disk (embryo)
Embryonic disk
-supported by a short stalk that connects to the blastocyst with the endometrium
-becomes umbilical cord
Gastrulation
process of forming the 3-layered disk
Ectoderm
layer of skin, hair, nails, spinal cord, sense organs
Mesoderm
layer of bone, muscle, connective tissue, blood, circulatory and excretory systems
Endoderm
layer of digestive tract, lining of digestive/respiratory tract, liver, lungs, pancreas, and thyroid
Morphogenesis
differentiation of cells (cells with different jobs)
Extraembryonic structures (membranes)
-chorion
-amnion
-allantois
-yolk sac
Chorion
-produces hCG which acts like LH to maintain corpus luteum for first trimester and to maintain progesterone to help stop contractions
-helps form placenta
-hCG levels is identified through pregnancy tests
Amnion
-fluid filled sac that surrounds embryo and protects it from infection, dehydration, impact, and temperature change
Yolk sac
site of blood cell formation
Allantois
-grows outward
-provides umbilical vessels for placenta
For implantation
-endometrium must be maintained
-maintained estrogen/progesterone levels = negative feedback on LH and FSH
LH in fertilization
-needed to sustain corpus luteum
-maintains estrogen/progesterone levels
-prevent contractions and shedding of endometrium
Placenta
-disc shaped mass of spongy tissue formed by maternal endometrium and chorionic villi from chorion layer
-small gap that separates fetal blood from maternal blood (do not mix)
-allows exchanges of gases, wastes, nutrients, hormones, and antibodies
-secretes estrogen/progesterone the last 6 months of pregnancy
-secretes relaxin
Umbilical cord
attaches fetus to the placenta
First trimester
-embryonic tissues form
-most of major systems form and tiny toes and fingers are visible
-embryo referred to as a fetus by 9th week
Second trimester
-all organs formed but not fully developed
-development continues and fetus size increases
-bony parts of skeleton begin to form
Third trimester
-organs enlarge and finish development
-organ systems mature in preparation for breathing
Parturition/childbirth
-hormonal and physical changes in mothers body
-triggered by falling of estrogen/progesterone levels
-babys head shifts downward and contracts the cervix
-after delivery, umbilical cord is cut
-uterus contracts to dislodge placenta from uterine wall
Prostaglandins
-from glands in the uterine wall
-appears in mothers blood prior to labor
-trigger strong uterine contractions
Lactation
-estrogen/progesterone prepare breasts for milk production
-each lobe of glandular tissue has small duct that carries fluid toward the nipple (about 20 lobes total)
-prolactin (anterior pituitary) stimulates breast to produce fluid
-milk production in inhibited before birth as increased progesterone prevent action of prolactin
Prolactin in lactation
-at first, stimulates the production of colostrum—fluid like breast milk but lacks fat
-few days after birth, it stimulates the production of milk that contains fat
Amniocentesis
-insertion of hollow needle through abdominal wall into uterus
-small amounts of ____ fluid and live fetal cells are withdrawn from ____ sac
-from this, karotype can determine if the baby has defects like DS, cystic fibrosis, and hemophilia
-offered to women who has increased risk of having children with genetic abnormalities between 15 and 18 weeks
Chorionic villi sampling
small sample of tissue is removed from chorionic villi in early stages of pregnancy for karotype
Ultrasound
soundwaves used to determine babys position and size
In vitro fertilization (IVF)
-ovarian stimulation (purified forms of FSH)
-egg retrieval by laparoscopy (light suction) or ultrasound (needle withdrawing)
-fertilization by mixing semen with eggs and incubating them at an identical temperature to womans body
-embryo transfer by placing embryos in catheter to insert into vagina and cervix to transfer them to uterus
Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT)
ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, fertilization followed by transfer of zygote into the females fallopian tubes
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
-insertion of single sperm directly into cytoplasm of mature egg
-zygote is then inserted into the uterus or the fallopian tube
Intrauterine insemination
-ovulation stimulating meds to mature eggs
-24-36 hours after LH spikes, a sample of semen is washed to separate semen from seminal fluid
Artificial insemination
sperm injected into female repro. tract through catheter (cervix, uterus, or fallopian tube)
Fraternal twins
2 eggs, 2 sperm, different placenta, different DNA
Identical twins
1 egg, egg splits, can share same placenta, same DNA
Controversy
u choose embryo, its eye color, athletic ability, height, etc, sperm for sale
Prenatal surgery
abnormalities corrected in uterus