PDC-pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
how it works
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
the PDC is composed of…
3 enzyme subunits and 5 different cofactors
it covnertws pyruvate to acetyl CoA
occurs in the mitochondrial matrix
the co factors and their roles
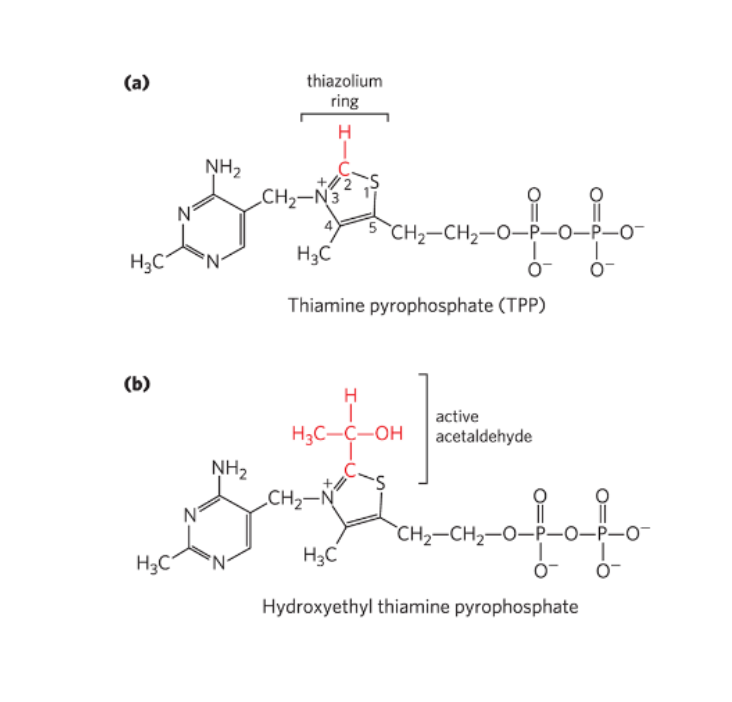
Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TPP)— bound to E1, derived from Vitamin B1, forms a reactive carbanion easily, carries aldehydes, promotes decarboxylation
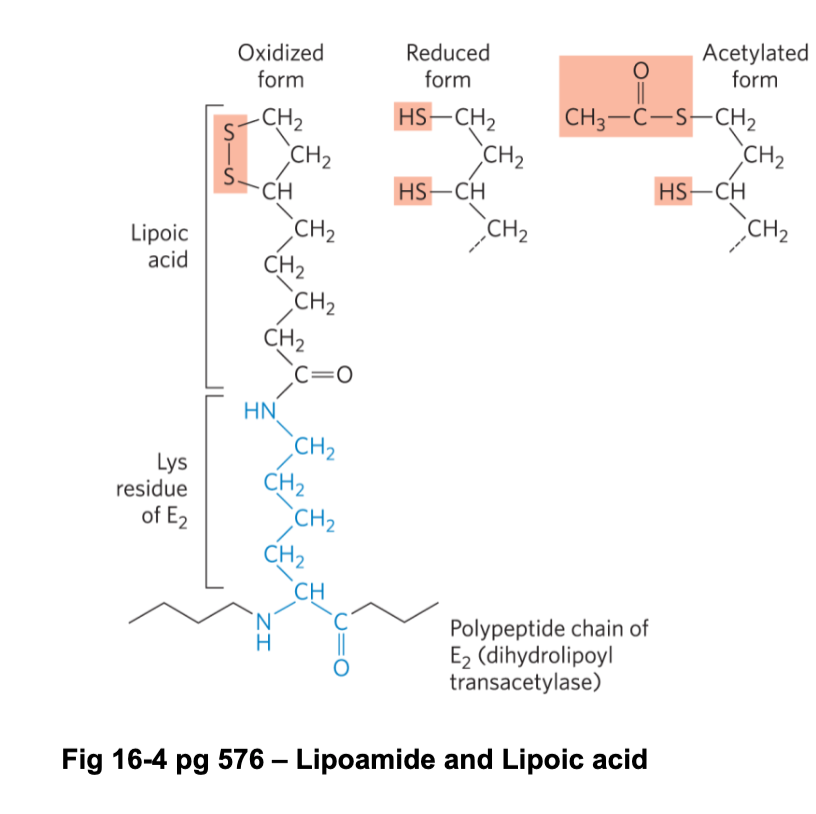
Lipoamide—bound to E2, lipoic acid can be attached to a Lys on E2 forming lipoamide, lipoamide oxidizes aldehydes to acyl groups resulting in the acyl group being bound to the disulfide group, acts a “robotic arm”
NAD+— free floating
FAD+—bound to E3
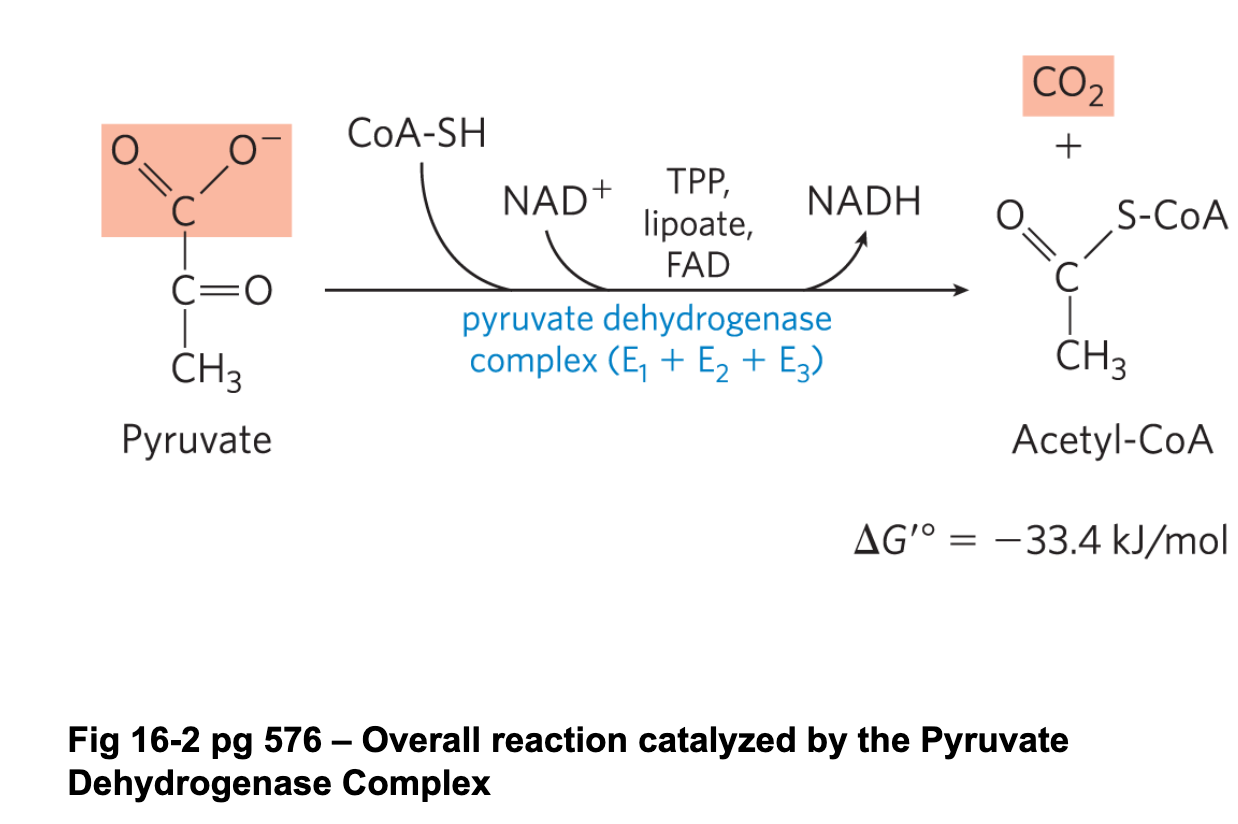
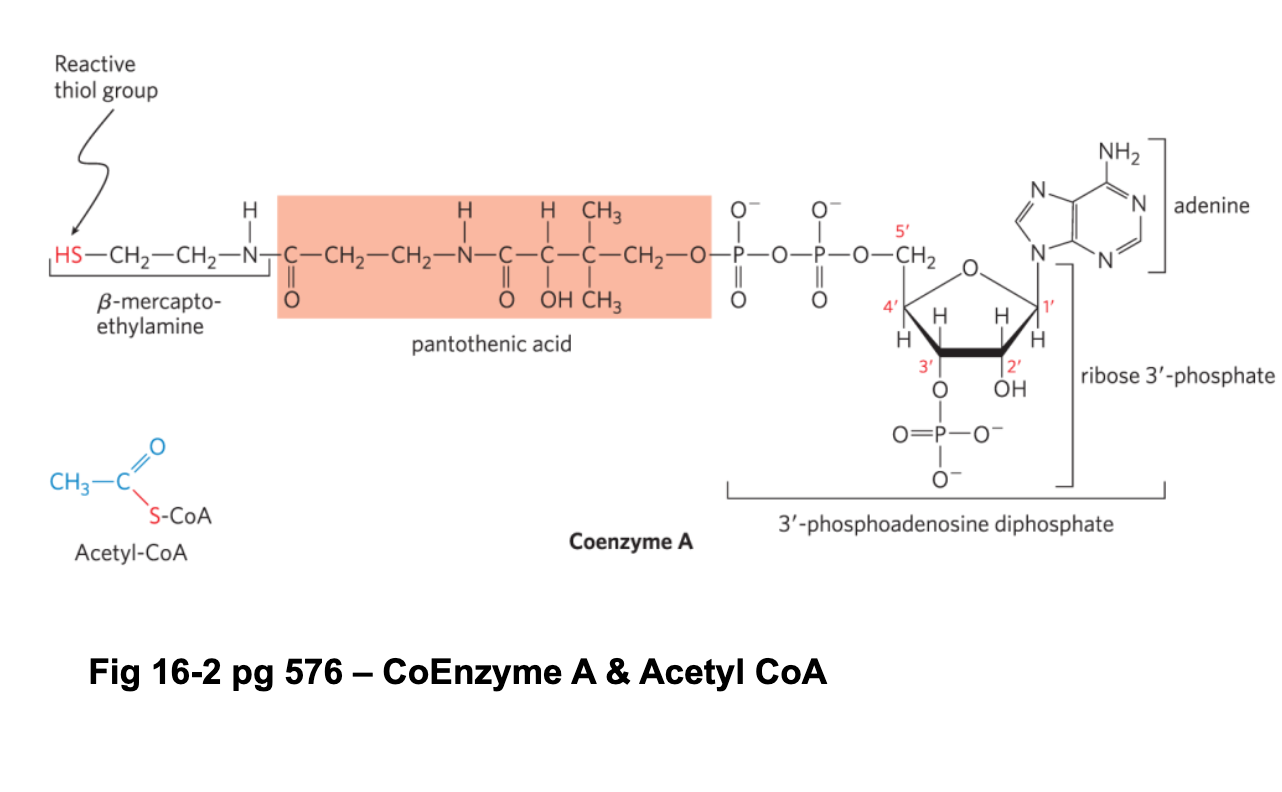
CoASH—free floating, composed of ADP and pantothenate (vitamin B5) and beta-mercaptor ethylamine, carrier of acyl groups, forms high energy thioester bonds
Mechanism of the PDC
Pyruvate enters E1, binds to TPP and is decarboxylated (forming Co2) to form the intermediate hydroxyethyl-TPP
Lipoamide arm (oxidized) enters E1
The hydroxyethyl group is oxidized to a acetyl group and is bound to the now reduced lipoamide arm (which we now call a dihydrolipoyl group)
The reduced arm carrying the acetyl unit moves into E2 and the acetyl group is transferred to CoA forming acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA leaves the enzyme
The reduced dihydrolipoyl lipoamide arm moves into E3 where it is oxidized by FAD. FAD is reduced to FADH2
NAD+ enters E3 and reoxidizes FADH2 back to FAD. NAD+ is reduced to NADH, which leaves E3. Now back at step 1
Regulation of the PDC
Increase of [acetyl CoA] allostreically inhibit E2
Increase of [NADH] allosterically inhibit E3
But the main control is on E1, where phosphorylation of a serine by a kinase leads to the inhibition of E1 and thus the entire complex.
This kinase is called the PDC associated kinase (always hanging around the PDC)
Acetyl CoA, NADH, and ATP all stimulate the kinase, causing the PDC to slow
Pyruvate, NAD+ and ADP all inhibit the kinase resulting in the PDC gradually becoming active again
General phosphatases will gradually (ie. slowly) dephosphorylate E1, resulting in it becoming more active again.
Cell signalling such as an increase in [Ca2+] and insulin activates the PDC associated phosphatase (PDCAP) which rapidly dephosphorylates E1, leading to a rapid increase in activity.
overall reaction of the PDC
Pyruvate + NAD+ + CoASH —> Acetyl CoA + CO2 + NADH + H+
involves a decarboxylation/oxidation of pyruvate to acetate in the form of a thioester, followed by the formation of acetyl coA
the 3 enzymes of the PDC
E1=pyruvate dehydrogenase
E2=dihydrolipoyl transacetylase
E3=dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
Co Enzyme A aka coA, CoASH structure
TPP structure
Lipoamide and Lipoic Acid