Genetics: Advanced Biology
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Gregor Mendel
1822-1884
Father of Genetics
Mendel Model
Used peas
Many dichotomous traits
Mendelian Cross
Bread “truebreeding” plants based on different traits
Truebreeding
Parents with certain traits always produce offspring with same traits
Reginald Punnett
1907
First punnet square
Punnett Square
Diagram used to predict genotypes of offspring of particular breeding experiment
Mendel’s Law of Dominance
Indicates a dominant and recessive allele
Law of Segregation
Heredity is particular
Alleles separated during gamete formation
Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment
Genes for a trait are inherited independently from other traits
Violations of independent assortment
Linkage: genes that are physically close together in chromosomes
Crossover: close genes are recombined together
Incomplete Dominance
Expression of two contrasting alleles such that the individual displays an intermediate phenotype
Codominance
Complete and simultaneous expression of both alleles for the same characteristic
Sex Linked Traits
Traits from genes on X & Y chromosomes
Female - XX
Male- XY
Lethal Alleles
A gene that shortens life expectancy
Hugo DeVries
Discovered Gene & Mutation
Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
Chromosomes carry the unit of heredity-genes
T.H. Morgan
Discovered XY chromosomes, eye color directly linked to sex, =>violates Mendel’s law of independent independent assortment
Alfred Sturtivant
Student of T.H. Morgan
Created first genetic map of genes
Karyotype
Individual’s chromosome number and appearance
Trisomy 21
Extra 21st chromosome
Non-disjunction => sister chromatids fail to separate in meiosis
Trait
Variation in the physical appearance of a heritable characteristic
Phenotype
Observable traits expressed by an organism
Allele
Gene variation that arise by mutation and exist at the same relative locations on homologous chromosomes
Dominant Allele
Trait that is expressed over another allele
Recessive Allele
Trait that is not expressed when paired with a dominant allele
Genotype
Underlying genetic makeup, consisting of both physically visible and non-expressed alleles
Heterozygote
Individual having two different alleles of a particular gene
Zygote
Single cell formed when a sperm cell fuses with an egg cell
Locus
Position of a gene on a chromosome
Wildtype allele
Most common allele of a gene in a natural population
Mutant Allele
Gene variant that differs from the standard or wildtype allele
Genetic Crossing Over
Exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids resulting in chromosomes that incorporate genes from both parents
Mutation
Variation in the nucleotide sequence (DNA) of a genome
Karyokinesis
Division of a cell nucleus during mitosis
Non-disjunction
When sister chromatids fail to separate in meiosis
Rosalind Franklin
Used x-ray diffraction through x-ray crystallography
Created photo 51
Photo 51
The missing link for discovery of actual genetic structure
James Watson & Francis Crick
Discovered the double helix structure of DNA
Central Dogma of Biology
DNA to RNA to Proteins
Process of Central Dogma
Transcription to mRNA processing to Translation
Transcription
The production of a RNA strand from a DNA template
Transcription: Initiation
Promoters of DNA sequences allow RNA Polymerase, Transcription Factors, and TATA Binding Protein bind to the DNA chain to initiate transcription.
Enhancers
Increase transcription
Silencers
Decrease transcription
Transcription: Elongation
RNA polymerase synthesizes mRNA by adding complimentary RNA nucleotides (A,U,G,C) into a chain in a 5’ to 3’ direction
Transcription: Termination
Cuts of the mRNA strand by either a cleavage cut or hair pin formation
mRNA Processing Qualities
5’ cap
PolyATail
Intron Splicing
PolyATail Qualities
Long chain of A nucleotides added to 3’ end of the mRNA strand
Stabilizes RNA
Prevents degradation of mRNA
5’ cap (Methylation Cap)
Added to 5’ end
Mediates splicing
Allows mRNA to be exported to the cytoplasm
Meselson & Stahl Experiment
Discovered DNA replication is semi conservative
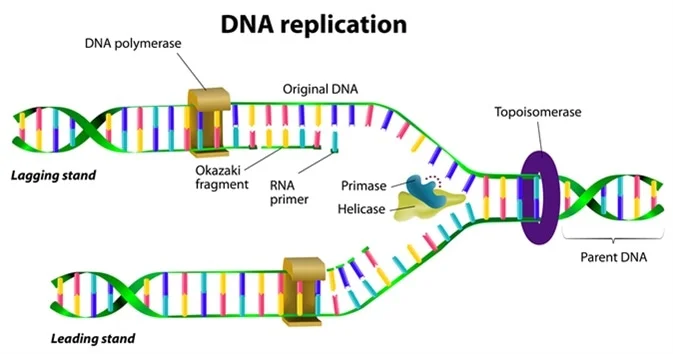
Proteins of DNA Replication
Helicase
Topoisomerase
Single Strand Binding Protein
Primase
DNA Polymerase
DNA Ligase
Helicase
Separates DNA strand
Topoisomerase
Prevents overwinding of DNA
Single Strand Binding Protein
Prevents helix form reforming
Primase
Synthesizes RNA primer
DNA Polymerase
Synthesizes new daughter DNA
DNA Ligase
Seals gaps between Okazaki Fragments
Okazaki Fragments
Formed from the lagging strands of DNA replication going 3’ to 5’
DNA Replication Picture
Type of Mutations
Point Mutations
Frameshift Mutations
Chromosomal Mutations
Point Mutations
Silent- non change in amino acid sequence
Missense- amino acid is substituted
Nonsense- a stop codon is subsitituted
Frameshift Mutations
results in a shift of a reading frame which causes wrong insertions or deletions
Chromosomal Mutations
Translocation- section of 1 chromosome ends on a different chromosome
Inversion- flipping of sections of chromosomes
Fusions- blending
Duplication- too many copies
Chromosomal Crossover
Nondisjunction- too many in a cell
Deletion- partial deletion of a chromosome
Intron Splicing
Noncoding introns are cut out the mRNA leaving only the coding positions
Translation (Protein Synthesis)
Decodes mRNA to produce polypeptides where ribosomes catalyze the reaction
Translation: Initiation
mRNA attaches to a small ribosomal subunit and a start codon with the appropriate anticodon attaches, a large ribosomal subunit will then attach
Translation: Elongation
tRNA brings amino acids matching each coding pair, an amino acid chain grows using peptidyl transferase
Translation: Termination
A stop codon is sensed and the process stops, the amino acid chain is sent to the Endoplasmic Reticulum for processing