VTNE Review: Small Animal Intestinal Parasites
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
how are nematodes diagnosed?
via fecal floatation with zinc centrifugation
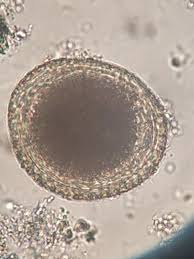
nematode
roundworm
most common in dogs and cats is Toxocara canis
causes the zoonotic disease ocular larva migrans
treated with piperazine, pyrantel, or fenbendazole
fecal-oral, transplacental infection most common
live in the small intestine
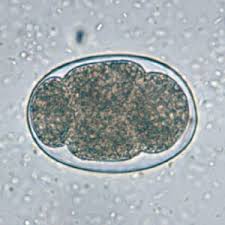
nematode
hookworm
most common species are Ancylostoma caninum and Uncinaria stenocephala
causes the zoonotic disease cutaneous larva migrans, which occurs via skin penetration
in percutaneous infection, the larvae migrate through the skin to the lung, where they molt and are swallowed and passed into the small intestine
treated with fenbendazole, pyrantel
can cause HGE and severe anemia
fecal-oral, transmammary (common in puppies), percutaneous infections
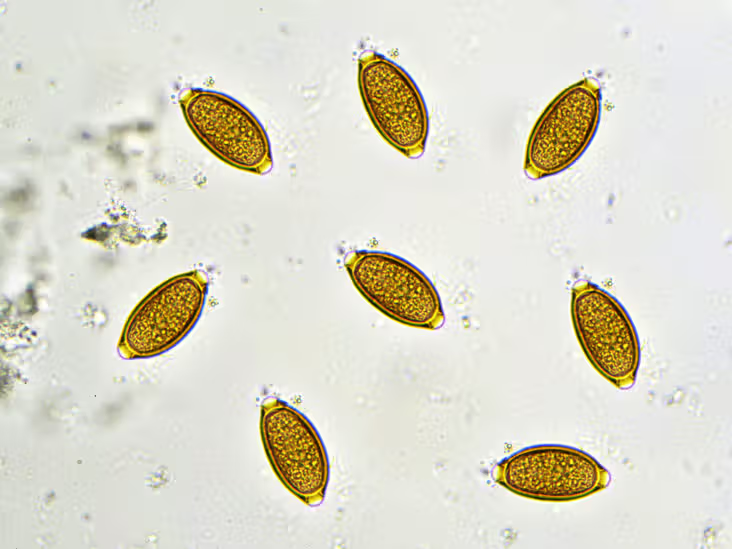
nematode
whipworms
Trichuris vulgaris
fecal-oral transmission
severe infection may lead to hyperkalemia and hyponatremia (pseudo-Addison’s)
large intestinal parasite
eggs have bipolar plugs on the ends
treated with fenbendazole, may be prevented with milbemycin (Interceptor)
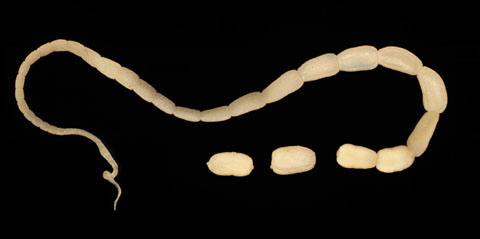
cestode
tapeworm
Dipylidium caninum is most common in dogs and cats and requires a flea as the intermediate host; flea is usually inadvertently swallowed due to grooming
Echinococcus granulosus and Taenia spp. are transmitted by ingestion of infective hydatid cysts during perdation of rabbits, rodents, birds, etc
flat and segmented; the eggs contained within the segments; segments are referred to as proglottids
proglottid pieces are released from the end of the worm and shed in the feces; resemble a grain of rice
praziquantel is the treatment of choice
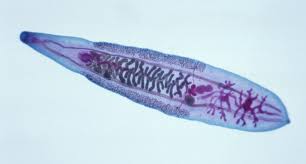
trematode
fluke
fasciola hepatica is the most well known and is known as the common liver fluke
adults can be found in the hepatic bile ducts
seen most commonly in cattle or sheep that have been grazing in endemic areas
requires a snail as an intermediate host and the parasite is most common in areas of high rainfall or moist environments
treated most commonly with albendazole
trematode
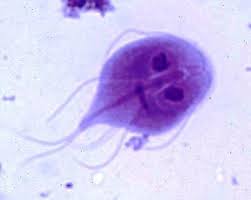
giardia
life cycle of flagellated protozoan (trophozoites) and infective resistant cysts
fecal-oral transmission, often through contaminated water sources
often causes a watery diarrhea
potentially zoonotic
treated most often with fenbendazole (Panacur) or metronidazole (Flagyl)
cysts may be seen on a fecal floatation but Giardia ELISA is the most sensitive test
the trophozoites may be seen on a direct smear of a fresh fecal sample
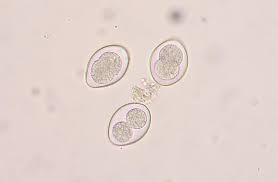
coccidia
single celled intestinal microscopic parasites
Isospora is most common in dogs and cats
Eimeria is most commonly seen in poultry/birds, rabbits
species specific
treated with sulfadimethoxine (Albon)
Eimeria stiedai causes hepatic coccidiosis in lagomorphs (rabbits)
seen on a fecal float or sometimes a direct smear