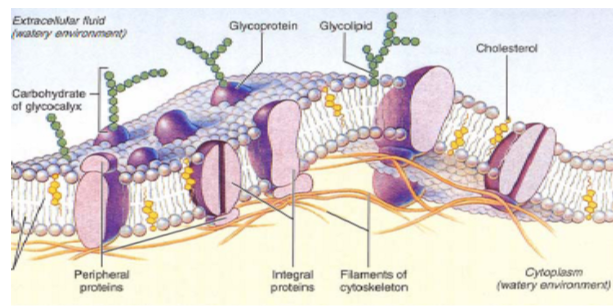
biological membrane structure
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
membrane components
lipid bilayer: structural backbone
phospholipids (most abundant
glycolipids
cholesterol
proteins are:
transporters
enzymes
signal transductors
carbohydrates attached to proteins and lipids
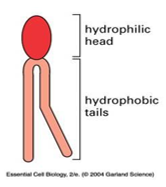
lipid bilayer
polar head group of phospholipids has an affinity for water
their hydrocarbon tails avoid water, favored structure is a biomolecular sheet
formation is a self assembly
hydrophobic interactions are the major driving forces
electrostatic and hydrogen bonding between polar head and water
self sealing
lipids in a membrane
majority are phospholipids
they are amphipathic - hydrophilic and hydrophobic components
these lipids spontaneously form bilayers in aqueous solution:
vesicles
micelles
have cholesterol
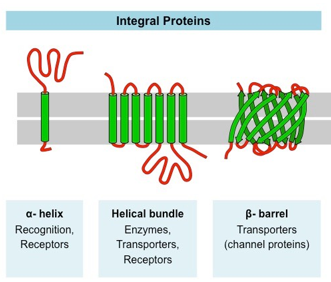
integral proteins in the cell membrane
span the cell membrane, sometimes once, others more
either terminus may be inside or outside the cell
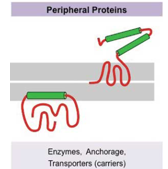
peripheral membrane proteins
these proteins adhere sometimes temporarily to the biological membrane
they do not enter into the hydrophobic space within the cell membrane but can push into the peripheral regions of the lipid bilayer
they attach to integral membrane proteins
membrane carbohydrates
components of complex molecules on the cell membrane
glycoproteins
glycolipids
proteoglycans
carbohydrates forms a layer around the cell on the outside of the membrane only called the glycocalyx
this layer functions as a barrier between a cell and its surrounding, also a mediator for cell-cell interactions. It protects a cell membrane from the direct action of physical forces and stresses allowing the membrane to maintain its integrity
functions of the cell (plasma) membrane
it is a sheet like structure that forms closed boundaries
physical isolation, acts as a barrier
holds molecules inside the cell
allows the regulation of exchange into and out of the membrane
fluid mosaic model
structure of cell membranes as a dynamic and flexible arrangement of various components
small amounts of lipids interact specifically with particular membrane proteins
proteins can diffuse laterally but are not free to rotate
passive diffusion
unaided spontaneous movement of solute molecules down their concentration gradient, from high to low, until solutes equilibrate across the bilayer
entropically driven
maximum entropy at equilibrium
facilitated diffusion
carrier mediated diffusion (uses an integral protein)
occurs down concentration gradient
dependent on integral proteins
does not used energy
active transport
movement against a concentration gradient
does not use energy
2 forms: primary active transport, secondary active transport
primary active transport
removes 3 Na+ ions from the cell cycle in exchange from 2 K+ ions.
movement of Na is against the concentration gradient. this means the process needs energy
The ATPase binds to ATP and 3 Na ions. ATP phosphorylates the ATPase and induces conformational change. The Na ions are released into the ECF. 2 K ions bind from the ECF and the ATPase is dephosphorylated and reverts to its previous conformation. K ions are release into the cell
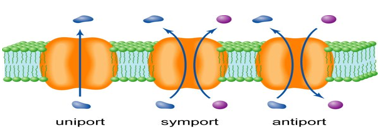
secondary active transport
carrier protein that moves a specific substance against its concentration gradient
carrier protein can also move another substance at the same time
the concentration gradient for one substance provides the driving force for the carrier protein
second substance gets a free ride
endocytosis and exocytosis
brings proteins/solid particles into and out of the cell
phagocytosis (cell eating)
pinocytosis (cell drinking)
receptor mediated endocytosis