MHS AP Psychology- Unit 0
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Experiment
A way of confirming the validity of psychological findings with consistent and repeatable results
Hypothesis
testable prediction, not yet confirmed or unconfirmed
Operational Definitions
a carefully worded statement of the exact procedures, helps with future replication
Theories
explanations that organize and predict
Experimental Group
the group being tested/exposed; recieves the IV
Control Group
the group NOT being tested/exposed; may receive the placebo; its results compared to experimental group
Independent Variable (IV)
manipulated factor
Dependent Variable (DV)
consistent factor
Random Selection (AKA Random Sample)
a random selection of a diverse population used to eliminate bias; leads to generalizability
Random Assignment
subjects placed in experimental/control groups at random to eliminate bias
Convience Sampling
technique where subjects are chosen based on proximity/accessibility (diminishes integrity)
Confounding Variables
factors that cause differences between the experimental group and the control group other than the IV (age, gender, home life, etc.). Only happens in experiments
Sampling Bias
when a sample is not representative of the population from which it is drawn
Experimenter Bias
when the experimenter (intentionally or unintentionally) influences the results to portray a certain outcome
Social Desirability Bias
the tendency of survey respondents to give socially approved answers to questions about oneself
Correlational Study
study that determines the relationship between 2 variables
Naturalistic Observations
unhindered observations in a natural environment (modern uses may include technology such as apple watches and internet/social media usage)
Case Study
study of one individual in great detail
Meta-Analysis
a procedure for statistically combining the results of many different research studies (nonexperimental method)
Scatterplots
a graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the values of two variables. The slope of the points suggests the direction of the relationship between the two variables, the amount of scatter suggests the strength of the correlation
Quantitative data/research
Data that is in numbers
Qualitative data/research
Data in the form of words
Correlation Coefficient
measures the relationship strength between 2 variables ranging from -1 to 1
Positive Correlation
A correlation where as one variable increases, the other also increases, or as one decreases so does the other. Both variables move in the same direction.
Negative Correlation
as one variable increases, the other decreases
Positive Skew
mean > median > mode
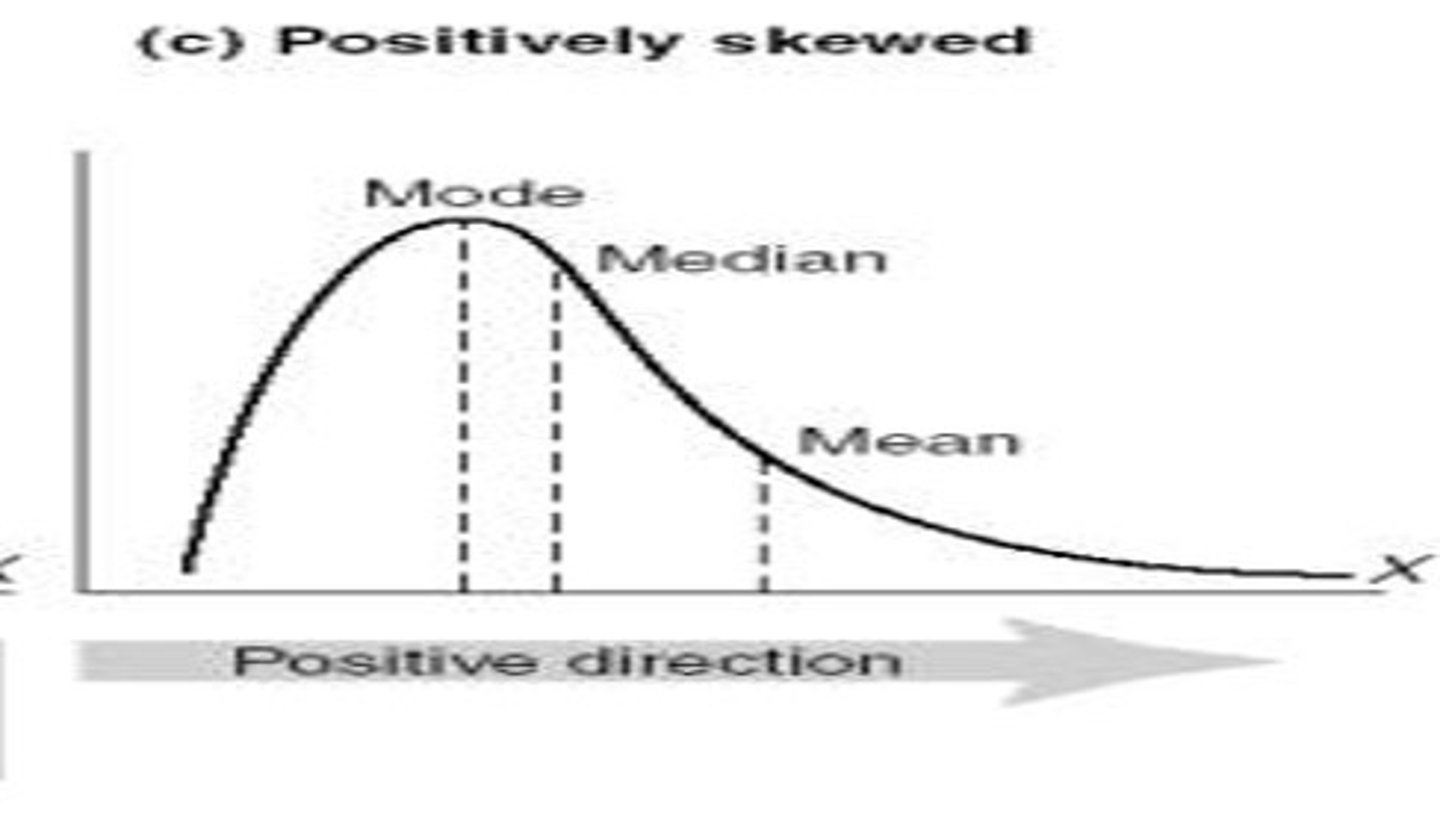
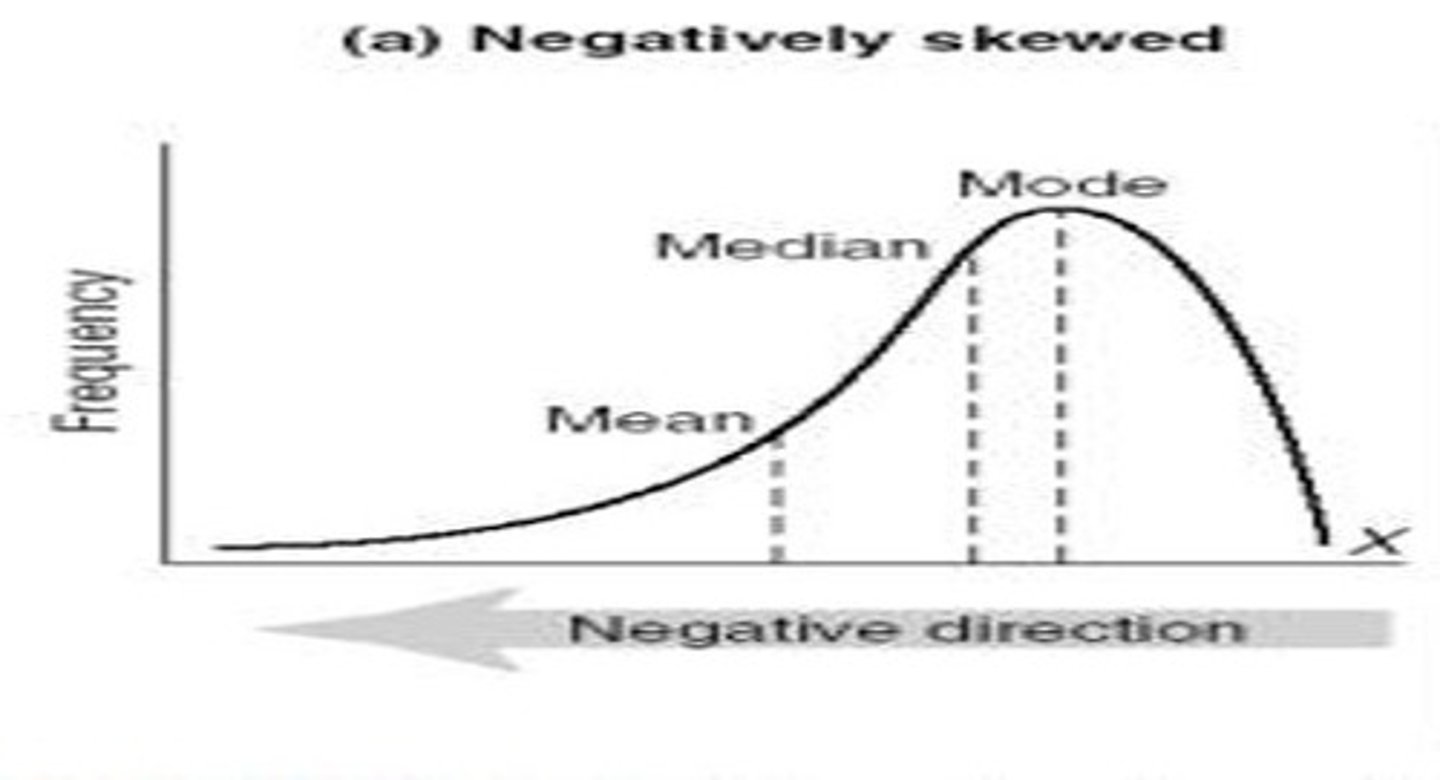
Negative Skew
mean < median < mode
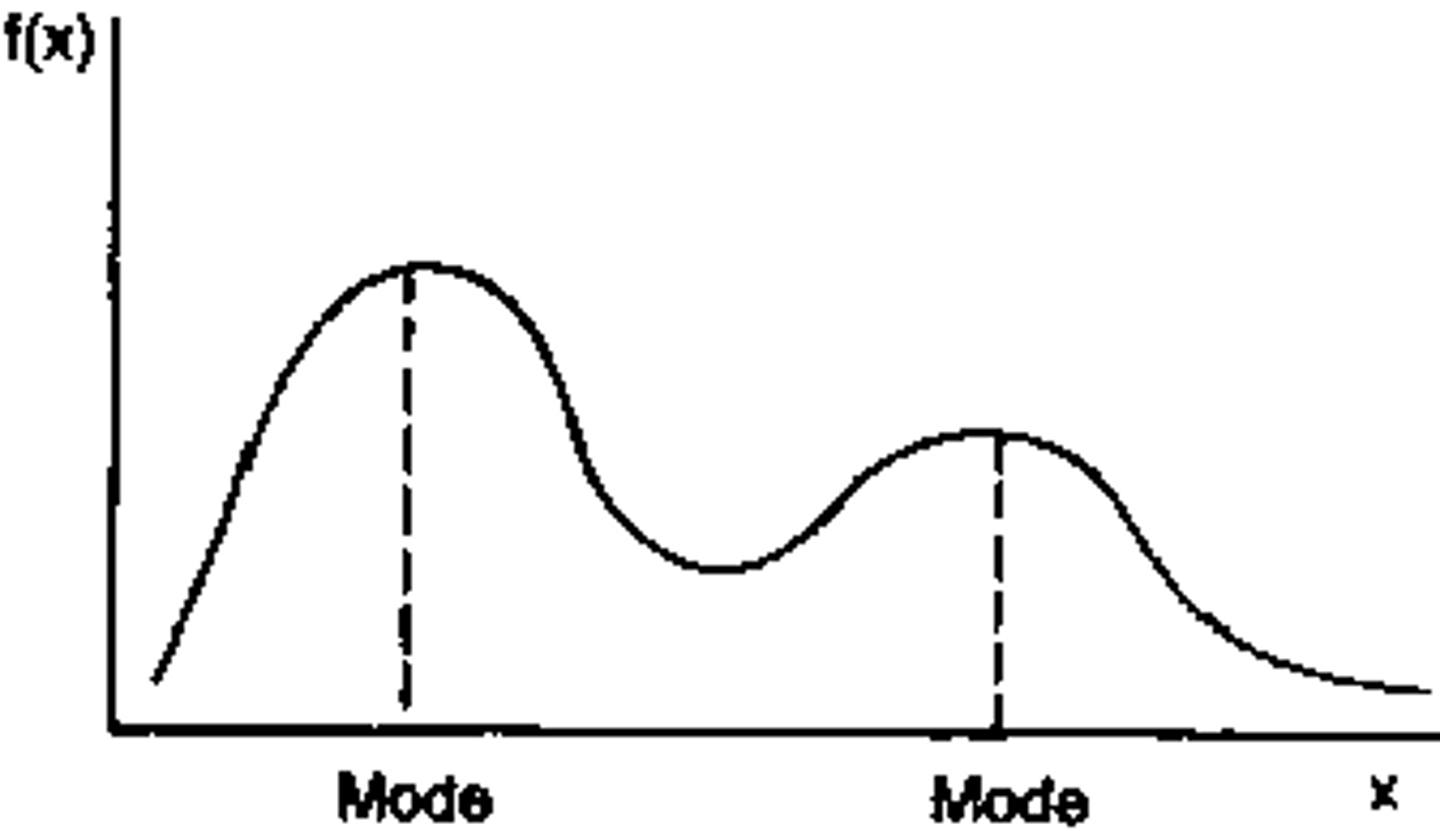
Bimodal
data set with two peaks
Measures of Central Tendency
the mean, median, and mode of a data set. these represent the typical or common characteristics of a data set
Mode
most frequently occurring score
Mean
average of data set
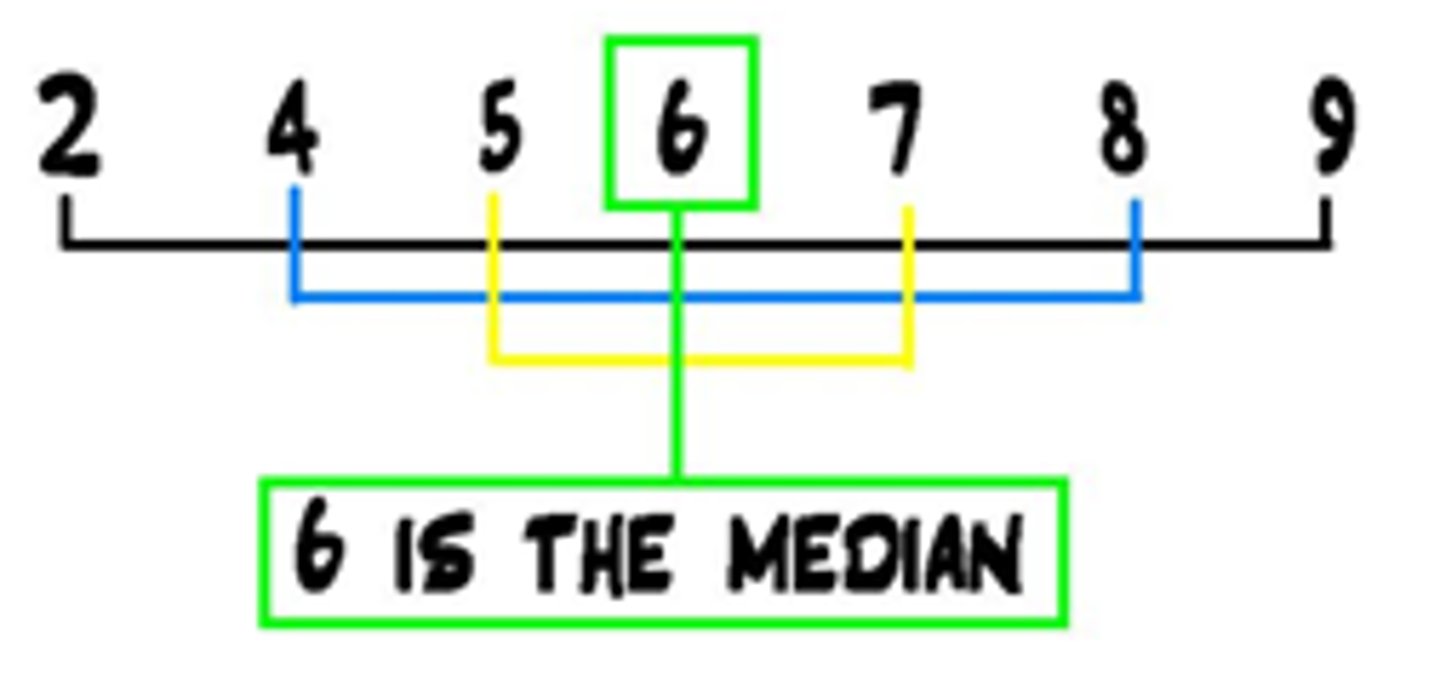
Median
the middle score in a distribution
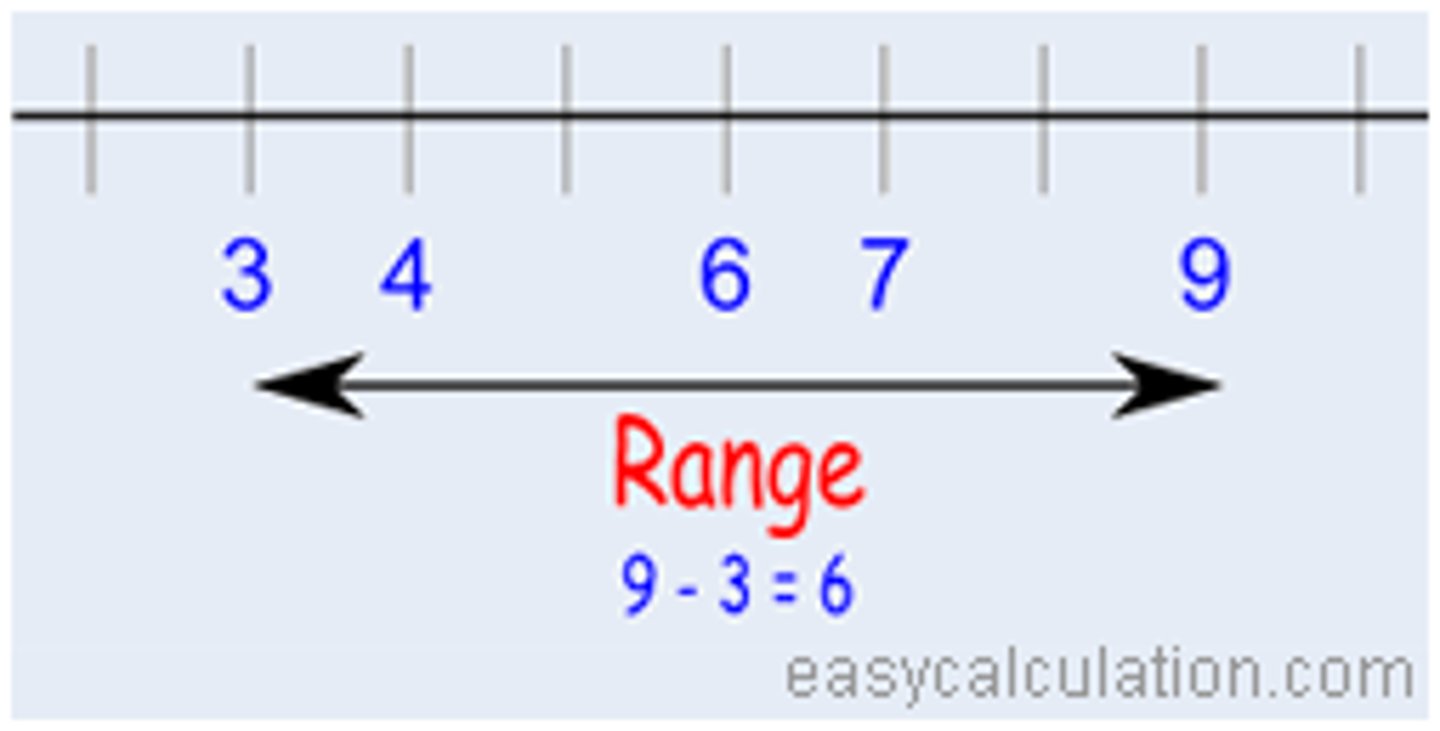
Range
the difference between the highest and lowest scores
percentile rank
percentage of scores that fall below a given score
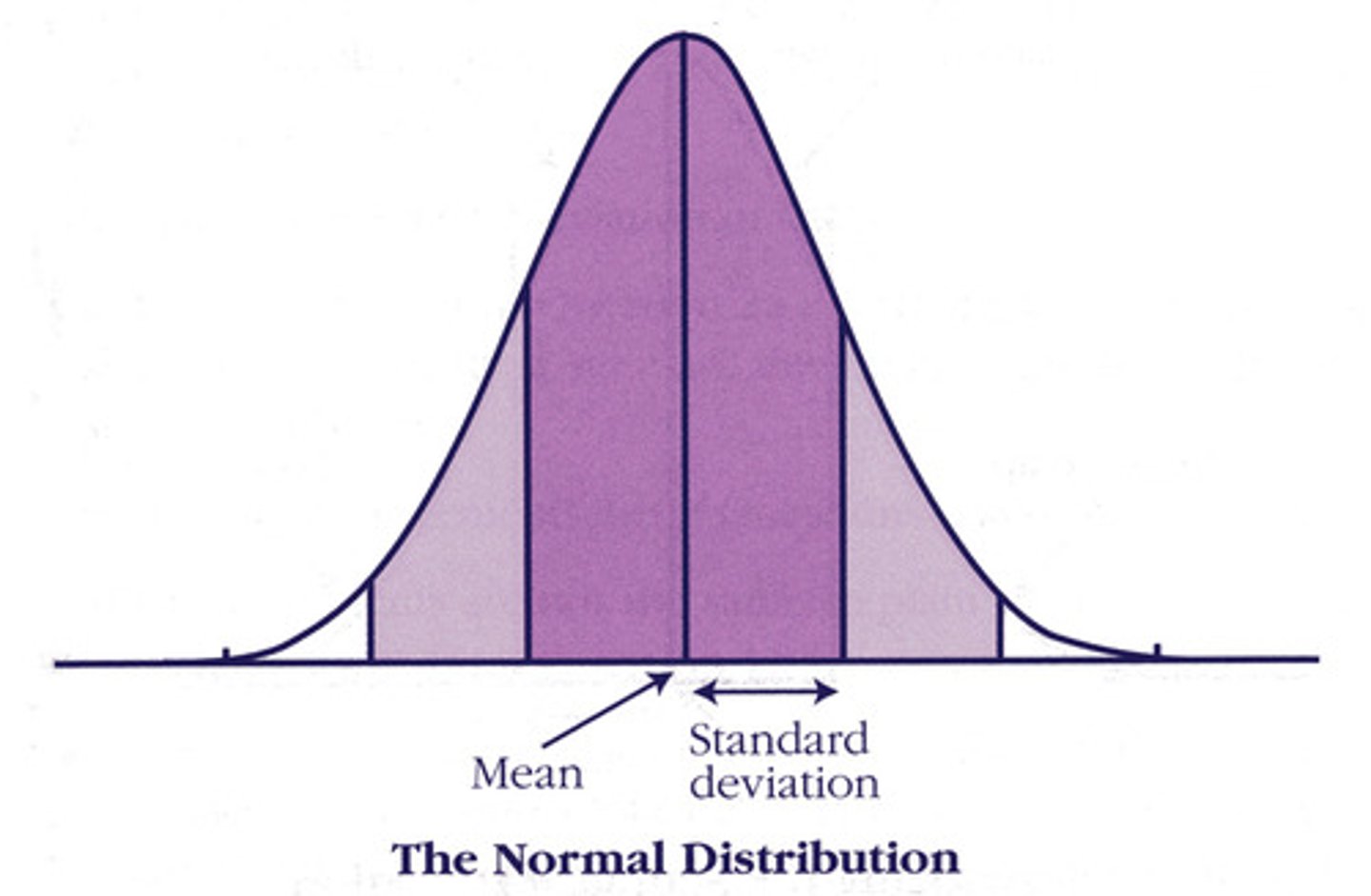
Standard Deviation (SD)
measures the average difference between each score and the mean of the data set
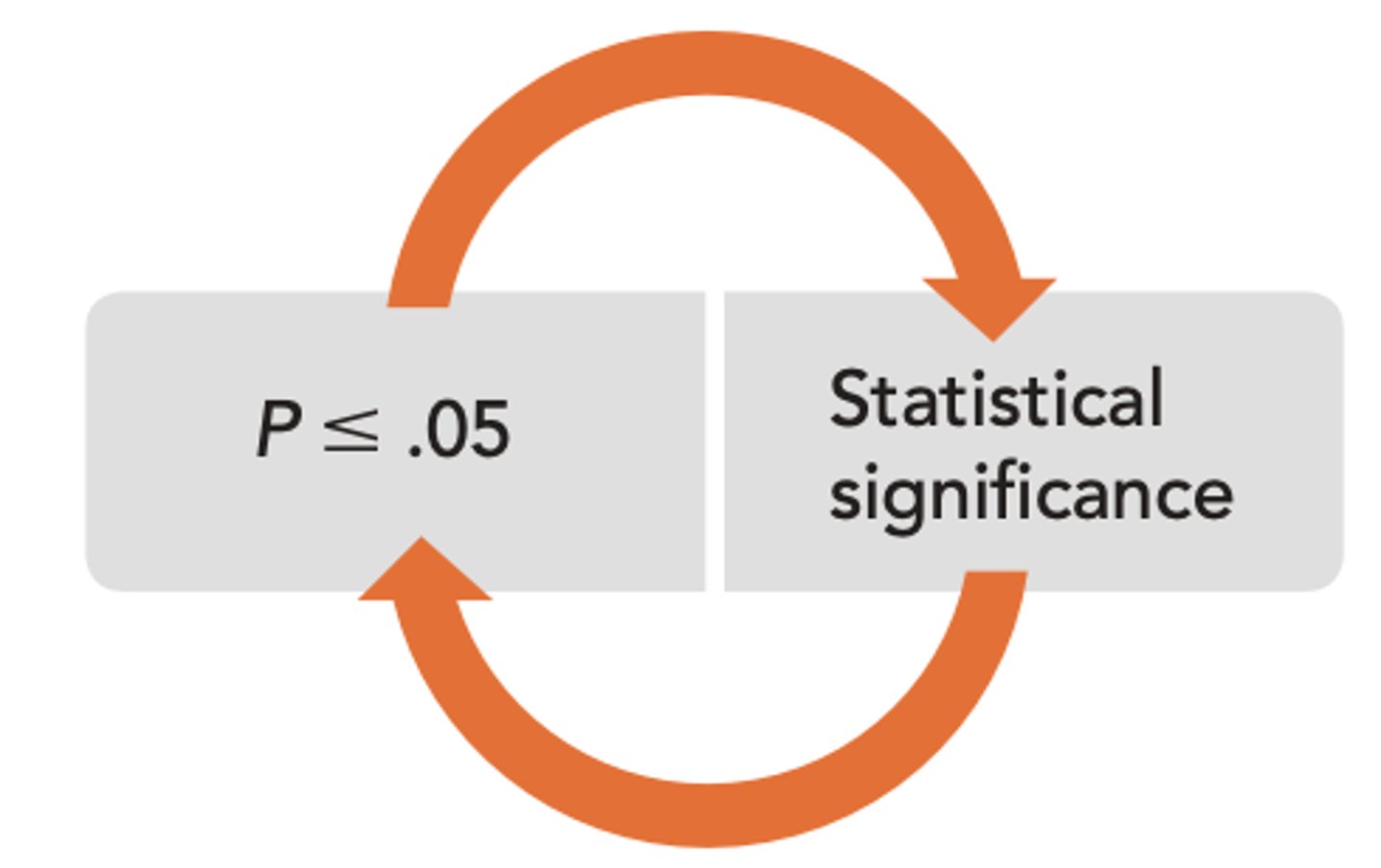
Statistical Significance
a statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance (goal is 95%)
Institutional Review Board (IRB)
A committee at each institution where research is conducted to review every experiment for ethics and methodology.
IACUC (Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee)
committee that approves or denies permission for studies involving animals
Experimental Prerequisites
1) Obtain informed consent of the subjects
2) Protection from physical harm or discomfort
3) Confidentiality regarding subject information
4) A full debrief of the results for subjects afterwards
Informed Assent
-case in which child is informed about what is going to be required and they have the opportunity to agree to or disagree to treatment
-children of different ages require different levels of confidentiality
Falsifiable
the possibility that a hypothesized relationship can be shown to be incorrect
Survey
non-experimental method for obtaining the self-reported attitudes or behaviors of a particular group, Wording effect and self reporting can be problematic.
Self-Report Bias
bias when people report their behavior inaccurately
Random Sampling
a sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion
Population
all those in a group being studied, from which samples may be drawn
Variable
anything that can vary and is feasible and ethical to measure
Illusory Correlation
perceiving a relationship where none exists, or perceiving a stronger-than-actual relationship
Regresson Toward the Mean
the tendency for extreme or unusual scores or events to fall back (regress) toward the average
Placebo Effect
the phenomenon in which the expectations of the participants in a study can influence their behavior
Informed Consent
giving potential participants enough information about a study to enable them to choose whether they wish to participate
Debriefing
the post-experimental explanation of a study, including its purpose and any deceptions, to its participants
Descriptive Statistics
numerical data used to measure and describe characteristics of groups. Includes measures of central tendency and measures of variation.
Inferential Statistics
numerical data that allow one to generalize- to infer from sample data the probability of something being true of a population
Effect Size
the strength of a relationship between two or more variables

Psychology
the scientific study of behavior and mental processes
Biopsychosocial Perspective
A perspective on psychopathology that emphasizes the biological, psychological, and social factors that contribute to mental illness.
Peer Review
A process by which the procedures and results of an experiment are evaluated by other scientists who are in the same field or who are conducting similar research.
Single-Blind Procedure
research design in which participants don't know whether they are in the experimental or control group
Double-Blind Procedure
an experimental procedure in which both the research participants and the research staff are ignorant (blind) about whether the research participants have received the treatment or a placebo. Commonly used in drug-evaluation studies.
Protection from Harm
the right of research participants to be protected from physical or psychological harm
Confidentiality
the act of holding information in confidence, not to be released to unauthorized individuals
Psychology as a science
uses systematic methods to observe human behavior and draw conclusions
American Psychological Association (APA)
World's largest association of psychologists with around 152,000 members including scientists, educators, clinicians, consultants and students
Experimental Psychologists
the study of behavior and thinking using the experimental method
industrial/organizational psychologist
a psychologist who uses psychological concepts to make the workplace a more satisfying environment for employees and managers
Clinical psychologists
Psychologists who specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of psychological disorders and everyday behavioral problems.
counseling psychologist
A psychologist who specializes in the treatment of milder emotional and behavioral disturbances.
Psychiatrist vs. Psychologist
- can prescribe vs. cannot prescribe
- M.D. vs. M.A, M.S.W, Ph.D, Psy.D, Ed.D
biopsychosocial approach
an integrated perspective that incorporates biological, psychological, and social-cultural levels of analysis to explain human behavior
Replication
repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding extends to other participants and circumstances
Validity
the extent to which a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to
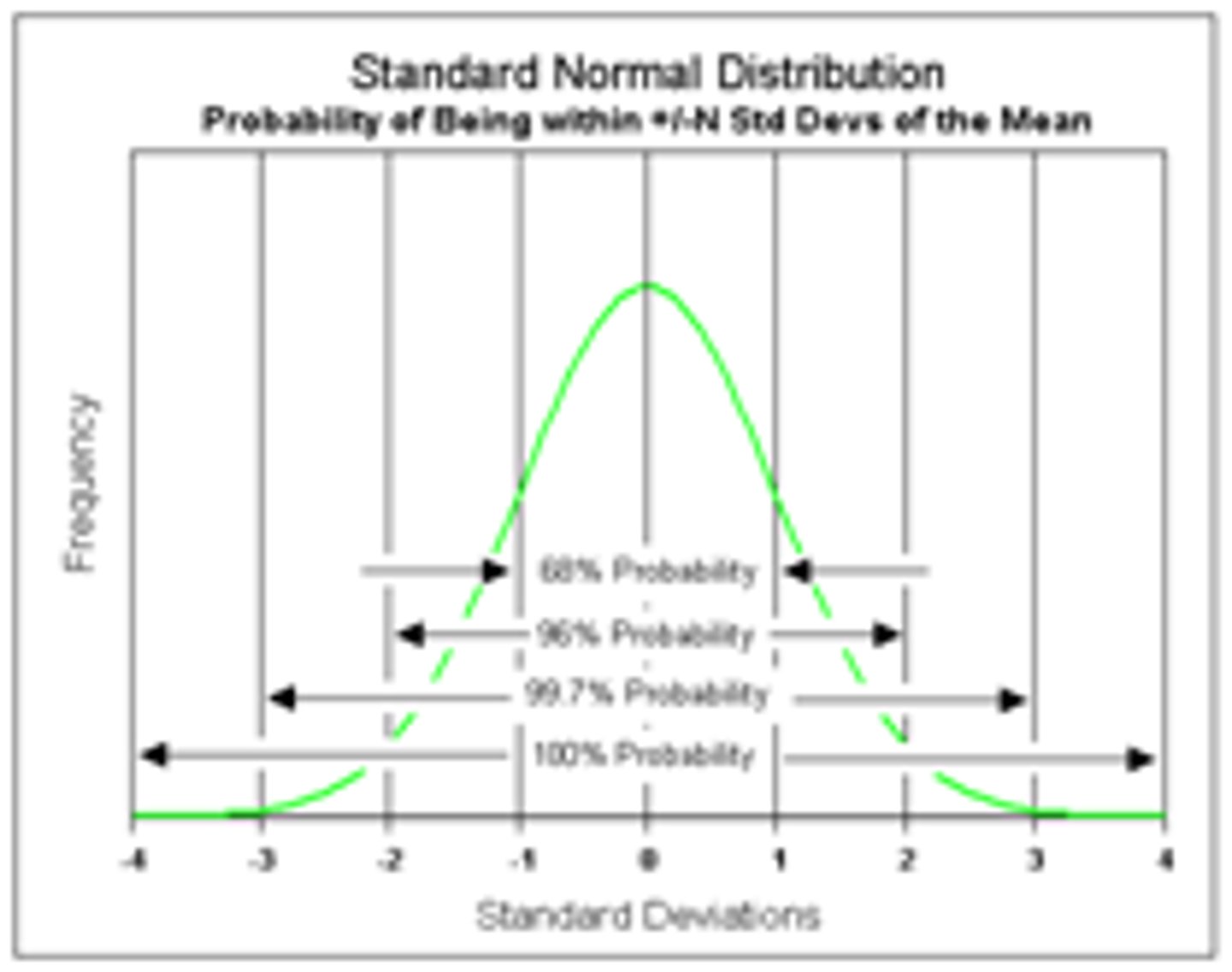
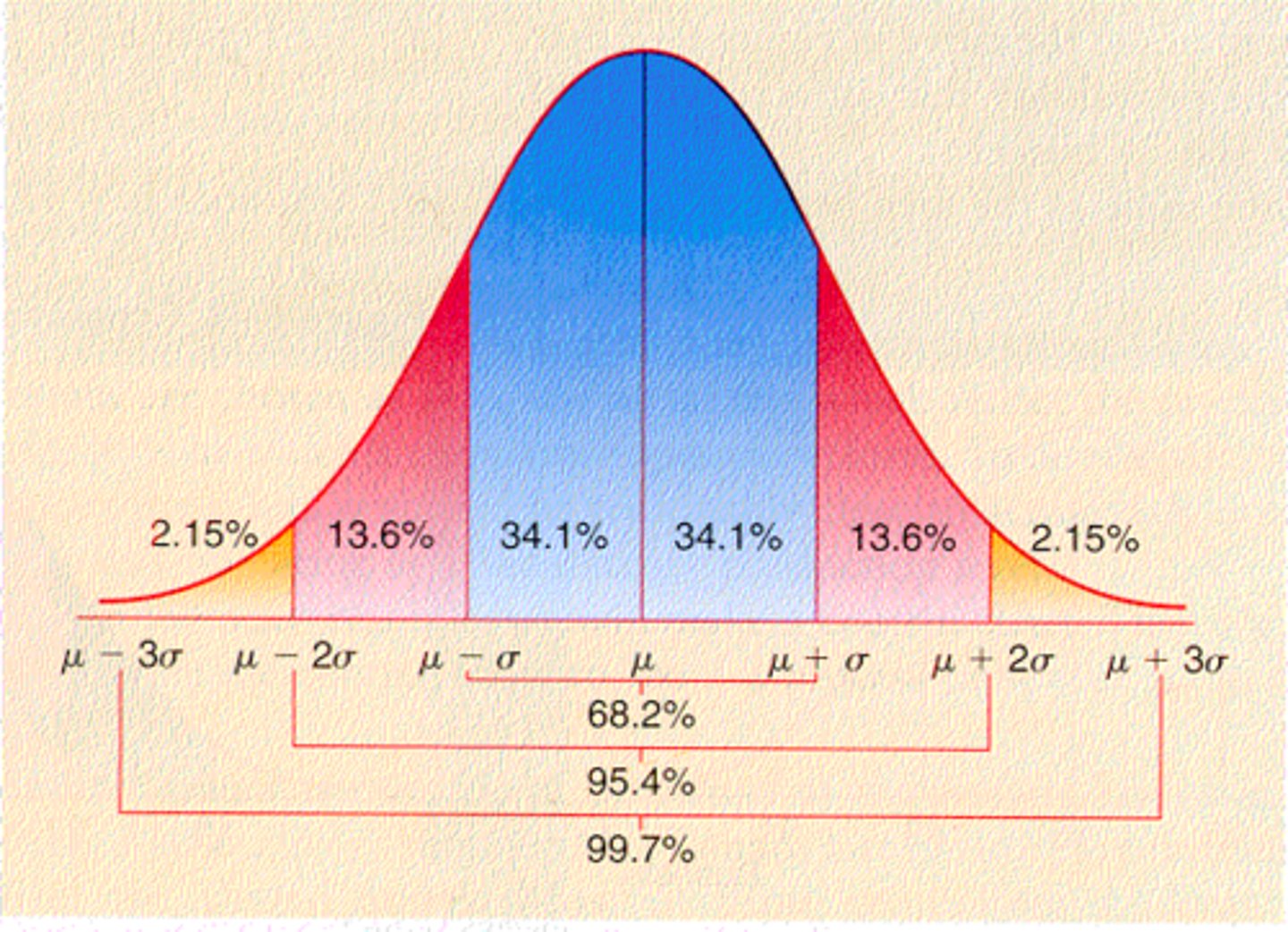
normal curve (normal distribution)
a symmetrical, bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many types of data; most scores fall near the mean (about 68 percent fall within one standard deviation of it) and fewer and fewer near the extremes. (68-95-99.7)
Scientific Method Steps
Theory, Hypothesis, Experiment, Data Collection, Conclusion, If necessary restart
non-experimental research methods
Case studies, surveys, correlational studies, meta-analysis, naturalistic observation
directionality problem
a problem encountered in correlational studies; the researchers find a relationship between two variables, but they cannot determine which variable may have caused changes in the other variable
third variable problem
the concept that a correlation between two variables may stem from both being influenced by some third variable (unknown)
correlation is not causation
just because two variables correlate strongly does not mean that one caused the other, only an experiment with manipulated variables cab determine causation
confederates (in research)
a person who secretly takes part in an experiment as an accomplice to the researcher, pretending to be a subject or participant
structured interview
a research procedure in which all participants are asked to answer the same questions; gathers qualitative data