Unit 3 Bio (Cells)
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
3 Pillars of Cell Theory
1) all living things are made of cells;
2) cells are the basic units of structure and function;
3) all cells come from existing cells
Cell
the smallest unit of life (has all the properties of life)
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
S:V ratio gets smaller the more size a cell has
1) volume of object = increases with cube of diameter; surface area = increases with square of diameter
2) Cell volume = size of cell; cell surface area = size of membrane
3) B/C Volume is getting larger quicker than the S, the S:V ratio gets smaller and smaller until the V eventually catches the S
4) Cells want much larger S compared to V because this allows them to exchange things like waste and nutrients with environment quicker (Think a concert hall with more exits compared to the people vs one with just one exit for a ton of people)
5) So: larger the volume, the worse the S:V ratio is, so the worse the exchange rates
Prokaryotic
Cells that do not have a nucleus.
Features:
1) have non-membrane-bound organelles
2) no nucleus; instead have nucleoid region
3) _ <10 µm (micrometers)
Include:
1) bacteria
2) archea
Eukaryotic
Cells that have an enclosed nucleus
Features:
1) have many membrane bound organelles
2) have a nucleus
3) 10-100 µm (micrometers)
4) plants, animals, fungi, protists
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Features
1) cell membrane that surrounds them
2) cytoplasm
3) DNA
Cytoplasm
Gel like substance in a cell
organelle
a structure within a cell with a specialized function
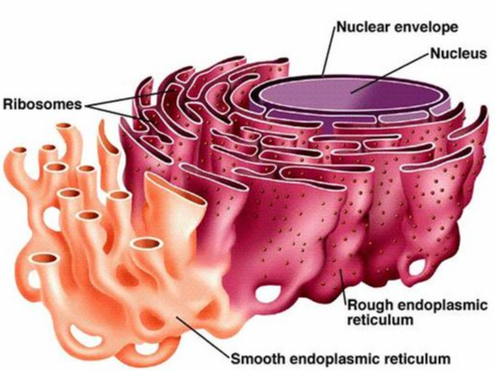
nucleus
organelle with two membranes that holds DNA. Includes (nuclear envelope, nucleolus, and nucleoplasm.)
1) tells proteins what to do
2) makes ribosomes (assembled in nucleolus)
Nucleoid Region
General area where DNA hangs out
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
The place where soon-to-be exported proteins are made by ribosomes (contains ribosomes)
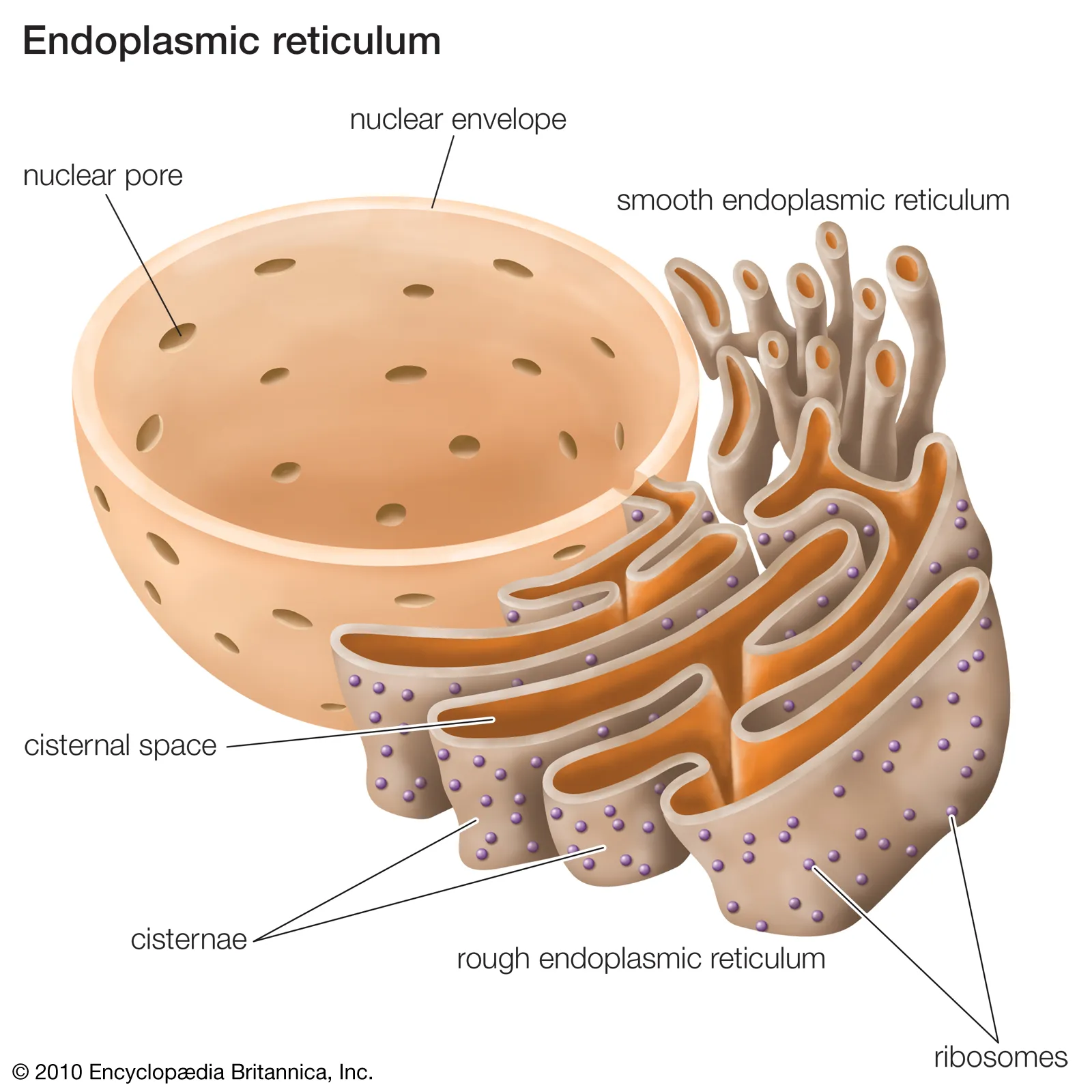
Ribosomes
workers that assemble proteins
1) build primary structure of proteins
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Coral reef-like structure
1) synthesize lipids like steroids and membranes
2) detoxify substances
3) store calcium
Protein Transportation Steps (REALLY IMPORTANT)
Ribosomes make proteins in RER
Folding and structural modifications
Vesicle transports proteins to the Golgi
Golgi modifies packages further and sorts proteins
Proteins are packaged into vesicles again
Leave the cell destined for secretion
*
*
*
Rasheer Flemming’s Valley Girlfriend Plays Lacrosse
Golgi
Distribution center
1) marks proteins
2) modifies proteins
3) sorts proteins
4) ships proteins
Endosymbiotic Theory
organelles with DNA and bacteria-like features are a product of an ancestor being absorbed by ancient eukaryote and domesticated to an organelle
Cytoskeleton (and 5 functions)
made of proteins (in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes) (Different sizes)
1) structure/support of cell
2) internal movement/transport
3) transport of entire cell
4) chromosome movement
5) cell splitting during cell divison
Cell Movement with Cytoskeleton
1) internal movement = organelles use cytoskeleton to move from 1 part of cell to another
2) external movement = cilia and flagella (microtubes wrapped in plasma membrane that use energy to create movement) and cytoplasmic streaming
Organelles Unique to Animal Cells vs Plant Cells
1) Animals = flagellum, lysosomes, centriole
2) Plants = central vacuole, chloroplast, + cell wall
Central Vcuole
Storage locker
1) stores water for plants
Contractile Vacuoles
pump to remove water (ex: paramecium using to pump out excess water and keep size)
Mitochandria
does cellular respiration
1) cellular respiration = breaks down food into carbon dioxide to release energy and create ATP
Chloroplast
Green bacteria-like organelle with DNA and ribosomes that does photosynthesis (found in plant cells)
1) photosynthesis = absorbs light and converts it to chemical bond energy by forming glucose
lysosomes
Digestive organelles
1) creates and uses digestive enzymes
2) produced by golgi
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from high to low concentration (down the concentration gradient.)
Concentration Gradient
Natural inclination of molecules to move from places of high concentration to areas with low concentration.
Diffusion of 1 solute
Molecules move across the membrane at random moments, eventually creating equilibrium
equilibrium
balance
Diffusion of 2 solutes
same thing but until same ratio/# of both on both sides (equilibrium)
Selective Permeability
only certain molecules can pass through
1) cell membranes have selective permeability
Permeable molecules
Molecules allowed to pass through the cell membrane (allowed to pass through because phospholipids have nonpolar insides that polar cannot stick to to slide past.)
1) nonpolar molecules (easy, somewhat hard if they're big though)
2) small polar molecules (polar but small enough to sneak past w/ difficulty. ex: H20.)
Impermeable
Molecules that are not allowed to pass through the cell membrane (phospholipid insides are nonpolar, so some molecules won't rock w/ it)
1) large polar molecules (too big to even sneak through)
2) ions (charged and very polar.)
(Im)permeable Molecules Explanation
Phospholipids are amphipathic (polar head and nonpolar tails). B/C of the way they form, nonpolar insides form inside of the cell membrane, so polar can't adhere or sneak through unless really small.)
Osmosis
The difficusion of water molecules from high to low water concentration across a semi-permeable membrane
1) occurs when the solute cannot cross the membrane. Water moves to match the ratios
Toncity
Ability of a solution to make water move in and out of a cell through osmosis
Hypotonic Solutions
Outside water concentration is higher, causing water to move inside cell
1) animal cell = lysed (inflated)
2) plant cell = turgid (inflated; optimal state b/c liking having a lot of water to keep their cell membrane puffed out and strong)
isotonic Solutions
Balanced water concentration so no net flow of water
1) animal cell = normal
2) plant cell = flaccid ("normal" size but bad because they need the inflow of H20 to be stretched out)
Hypertonic
Outside water concentration is lower so water leaves the cell
1) animal cell = shriveled
2) plant cell = plasmolyzed (shriveled)
Passive Transport
Diffusion following the natural concentration gradient
Facilitated Diffusion
Diffusion that occurs with the help of a protein in the cell membrane
1) a type of passive transport
2) solute binds to protein and protein changes shape to move it across (then returns back)
Active Diffusion
Movement against the concentration gradient that requires energy in order to occur (ATP = way a cell used energy)
1) membrane protein using energy to change shape to move molecules across the membrane
2) from low to high
3) using ATP to create a gradient
phosphorylation
when a phosphate is added to a transport protein using ATP hydrolysis
1) changes shape of protein and moves ion across membrane
2) produces phosphate and ADP
Transport/Carrier Protein
Protein in the cell membrane that carries an impermeable protein through the membrane
Passive vs Acrtive
1) Active requires ATP to change the shape of the protein
2) Active moves against the concentration gradient (low to high)
1st Law of Thermodynamics (Law of Conservation of Energy)
energy cannot be created or destroyed; can only converted from one form to another
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
the entropy (disorder) in the universe always increases
1) creating order costs energy while creating disorder does not cost energy
Diffiusion & the 2nd Law of Thermodynamics
1) higher concentration = more ordered than when particles are spread out
2) mols move from high to low to occupy more possible locations, increasing the randomness/entropy
Net diffusion
overall directional movement of mols from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
energy
ability to cause something to change
entropy
randomness
kinetic energy
movement of molecules
potential energy
stored energy
reactants
what is needed for a reaction
products
what is produced by a reaction
Chemical Covalent Bonds
represent stored/potential energy
endergonic reaction
stores energy
1) makes chemical bonds
exergonic reaction
releases energy
2) breaks chemical bonds
activation
energy
energy required for a chemical reaction
1) needed by stable molecules to break bonds
Enzymes
proteins (usually) that lower activation energy
1) bio catalysts = speed up reactions by lowering activation rate
2) not consumed in reaction (reusable)
3) usually proteins
4) selective with reactions; shape determines specificity b/c only specific substrates fit into activation sites*
5) reactants could try to reach AE on their own with heat, but need to maintain homeostasis.
substrate
the specific reactant an enzyme reacts on
active site
region of enzyme where substrate fits into
Glycoprotein
attached to cell membrane
1) cell to cell signaling
Cell to Cell Signaling
when cells communicate by sending signals to one another
Competitive Inhibitors
blocks substrates from enzyme's activation site
Noncompetitive Inhibitors
misshapes the enzyme without blocking out the activation site
Endocytosis
Vesicle entering the cell w/ something in it
Exocytosis
Vesicle leaving the cell carrying something