Lesson 4- Lesson 4A- FLUID AND ELECTROLYTES, ADRENERGIC BLOCKERS, ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS and ANTICOAGULANTS and Lesson 4B- Lesson 4B- SHOCK, ADRENERGIC AGENTS, ANTICOAGULANTS, AND FLUID AND ELECTROLYTES
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What body system is regulated by sodium?
CNS
What body system is regulated by potassium?
cardiac
What body system is regulated by calcium?
neuro/nerves
What body system is regulated by magnesium?
neuro/nerves
What are 2 conditions change how adrenergic agents act in the body?
Hyperthyroidism- causes the receptors on the blood vessels and muscles to be more sensitive to epinephrine
Cocaine use- prevents catecholamines (epinephrine) from Reuptake into vesicles
what are some uses of epinephrine? (5)
Vasoconstriction (A1)
Delays absorption of anesthetics
Control superficial bleeding
Elevate blood pressure
Mydriasis- pupil dilation (A1)
Restore cardiac function during arrest/asystole (B1)
Bronchodilaiton in asthma (B2)
Anaphylactic shock (A&B)
what are some adverse reactions to epinephrine?
hypertensive crisis- excessive blood pressure
Dysrhythmias
Angina pectoris
Hyperglycemia
what does ephedrine do? What receptors does it activate?
pressor effect that lasts 10x longer than epinephrine
Functions:
Peripheral vasoconstrictor
increases cardiac output
Dilates bronchi
Adverse effects- hypertension
Activates alpha and beta receptors
what are some other adrenergic agents?
amphetamines
Isoproterenol
Dobutamine
Phenylephrine
Pseudoephedrine
what does dopamine do (@low dose, @moderate dose, @high dose)? What receptors does it activate?
low dose- increases renal perfusion- B1
Moderate dose- increases HR and BP in shock- A1
HR should not exceed much above 110bpm
High dose- maintain BP after a code- A1
how do we recognize bronchodilators/B2 agonists?
”-terol”
What drugs are used to treat shock? (4 typically, 4 if needed)
Blood/Colloids/Crystalloids
Oxygen
Vasopressors
Dopamine
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
Phenylephrine
Inotropic Agents
Digoxin
Dobutamine
Antibiotics (if needed)
Corticosteroids (if needed)
Antihistamines (if needed)
Bronchodilators (if needed)
what are some adverse reactions of alpha 1 adrenergic agonists?
sensitivity to light
Hypertension
Excessive vasoconstriction can cause tissue death
Bradycardia
what are some adverse reactions of alpha 2 adrenergic agonists?
headache
Dry mouth/nose
Altered taste
Conjunctivitis
Pruritus
what are some adverse reactions of beta 1 adrenergic agonists?
tachycardia
Chest pain
Dysrhythmias of the heart
what are some adverse reactions of beta 2 adrenergic agonists?
hyperglycemia
Tremors
what are some adverse reactions of beta 3 adrenergic agonists?
potential of releasing stored chemicals
What do alpha 1 blockers do?
Prevents dilation of the pupil
Dilates arterioles on skin, mucus membranes, and viscera
Dilates veins
Decrease peripheral resistance → decreases BP
Relax bladder neck and prostatic capsule
what are some adverse reactions to alpha 1 blockers?
Orthostatic hypotension
Some reflex tachycardia
Nasal congestion- distention of nasal veins
Impotence- inhibition of ejaculation
What are some adverse reactions of alpha 2 blockers?
Can increase reflex tachycardia
What are the drugs that are the non-selective alpha blockers?
phentolamine
Phenoxybenzamine
what are some uses of alpha blockers?
HTN
BPH
pheochromocytoma
Block catacholamine infiltration
Raynaud’s disease
What drugs are alpha 1 selective blockers? How are they identified?
“-zosin”
doxazosin
Prazosin
Terazosin
Tamsulosin
what are the indications for alpha 1 selective blockers? (2)
HTN
BPH
What are the therapeutic effects of beta 1 blockers? (3)
Cardioselective
decrease heart rate
Decrease contraction of heart AKA cardiac output
Blocks kidney from releasing renin
What are the therapeutic effects of beta 2 blockers? (3)
predominant effects on bronchials and vascular smooth muscle
Bronchoconstriction
Vasodilation
Decrease glycogenolysis and glucagon secretion (hypoglycemia without normal response of tachycardia)
what are the beta blockers indicated for?
HTN
Angina pectoris
Cardiac dysrhythmias
MI
HF
Hyperthyroidism
Migraine
Stage fright
Pheochromocytoma
Glaucoma
useful for ischemic conditions-
ischemia to blockade of artery
angina to myocardial infarction- narrowed coronary arteries
TIA- carotid/brain arteries narrowed
Raynaud’s disease
how are beta blockers recognized?
“-olol”
what are some adverse reactions to beta blockers?
bradycardia
AV heart block
HF
Rebound cardia excitation
Bronchoconstriction
Inhibition of glycogenolysis- use with caution in diabetes pts
Masks hypoglycemia
CNS effects- depression, insomnia, nightmares, hallucinations
What are some adverse reactions of centrally acting alpha 2 agonists?
drowsiness ← CNS depression
Xerostomia ← dry mouth ← decreases in about 4 weeks
Rebounding HTN
How do calcium channel blockers work?
Block the movement of calcium into vascular smooth muscle and the myocardium
how are calcium channel blockers identified?
”-dipine”
Ex. Amlodipine, nifedipine, nicardipine, AND verapamil
How does the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system work?
Renin secreted by kidney
Liver releases angiotensin I
Angiotensin I is converted to angiotensin II in the presence of ACE (angiotensin converting enzyme)
Aldosterone can be secreted from angiotensin II
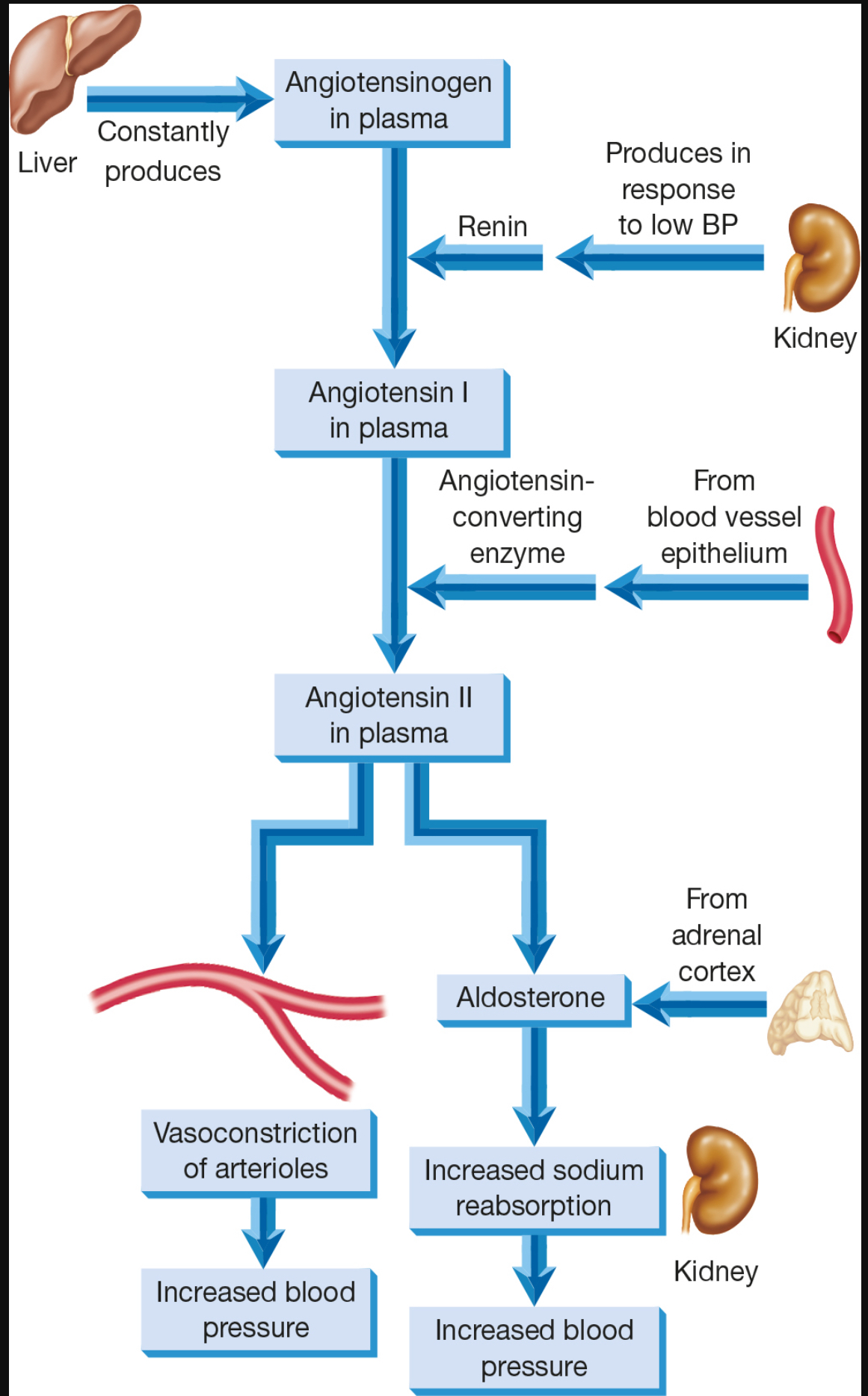
what does angiotensin II cause? (4)
Vasoconstriction
Release of aldosterone
Increases blood pressure
Increases blood volume
What does aldosterone cause?
sodium and water retention
What is the therapeutic action (3) and effects (2) of ACE inhibitors?
Angiotensin remains inactive if the converting enzyme can not work
Angiotensin II is not formed
Prevent breakdown of bradykinins and other prostaglandin vasodilators
Effects of ^^^:
Less vasoconstriction
Less aldosterone (less sodium and water retained by the body)
how are ACE inhibitors identified?
”-pril”
Ex.
Captopril (Capoten)
Short half-life
Lisinopril (Prinivil & Zestril)
Enalapril (Vasotec)
Available orally and IV
Short half-life
Benazepril (Lotensin)
Fosinopril (Monopril)
Moexiril (Univasc)
Perindopril (Aceon)
Quinapril (Accupril)
Ramipril (Altace)
Trandolapril (Mavik)
What do ACE inhibitors do? (3)
Lower BP/decrease after load
Lower blood volume/decrease preload
Less work on heart, so the heart tends to maintain its size and shape ← less remodeling
what are some adverse reactions to ACE inhibitors?
dry cough
Hyperkalemia- excreted in kidney so any kidney probs can lead to this as well
What is the action of angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs)?
blocks angiotensin II receptor sites on vascular smooth muscle and the adrenal gland (release of aldosterone)
what are ARBs indicated for? (2)
HTN
HF
how do ARBs differ from ACE inhibitors? Why are they sometimes preferred?
ARBs don’t produce a dry cough
Preferred to ACE inhibitors bc there are fewer adverse reactions, especially those that can become severe (ex. Hyperkalemia)
How are ARBs identified?
“-sartan”
Ex.
Losartin (Cozaar)
Eprosartan (Teveten)
Valsartan (Diovan)
Irbesartan (Avapro)
Candesartan (Atacand)
Olmesartan (Benicar)
Telmisartan (Micardis)
Azilsartan (Edarbi)
what is the method of action for vasodilators?
act directly on the arterials and/or venous smooth muscle
What are some examples of vasodilators?
minoxidil
Hydralazine
Diazoxide
Nitroprusside
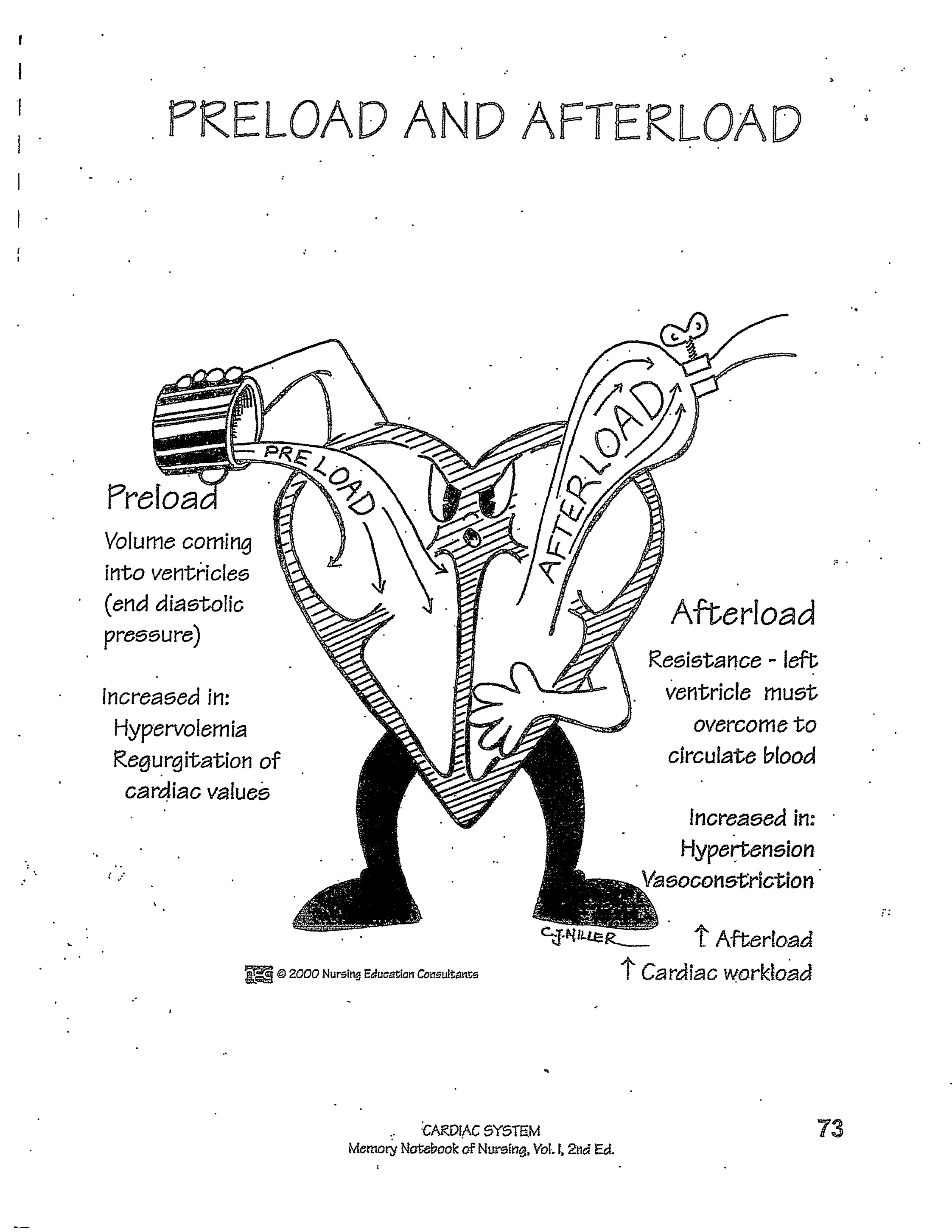
what is preload? When is it increased?
volume of blood coming INTO the ventricles AKA end diastolic pressure
Increased in: hypervolemia and regurgitation of cardiac values
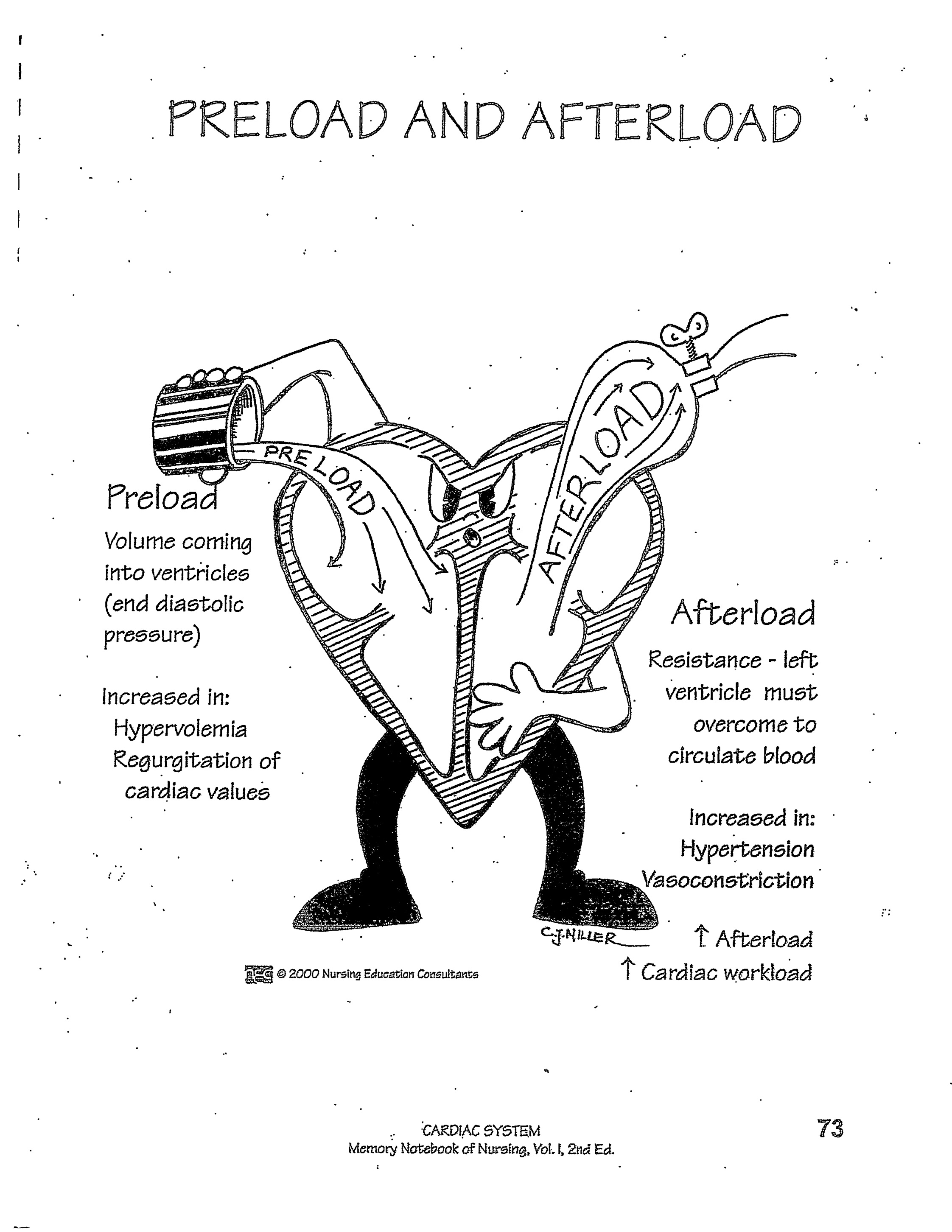
what is afterload? When is it increased?
resistance that the left ventricle must overcome to circulate blood
Increased in: HTN and vasoconstriction
Increased afterload = increased cardiac workload
What is the goal of treatment with antihypertensives?
Reduce blood volume- diuretics, low sodium diet
Reduce cardiac output- reduce HR and/or Contractility- beta blockers
Lower peripheral vascular resistance- vasodilators
what are the goals of treating pre-hypertension?
Exercise- 5000 steps or more
Lower cholesterol (LDL and triglycerides)- with statins and diet
Moderate sodium diet
Prevention of diabetes
what is the drug of choice for treating HTN in pregnant women?
methyldopa
What are the stages of blood clotting?
Platelet aggregation
Thromboplastin generated
Prothrombin is converted to thrombin
Fibrinogen is converted to fibrin
what is the coagulation cascade?
production of fibrin to reinforce platelet patch ← a clot is formed!
extrinsic pathway- stimulated by external injury (ex. Stab wound)
Intrinsic factor- started from injury inside the blood vessel
What is the role of vitamin K in blood clotting?
It is used by the liver to form prothrombin and various factors crucial in the clotting cascade
What is the goal of anticoagulant therapy? what is the therapy indicated for?
prevent clots in VEINS
inhibit the action or formation of one or more clotting factors and prevent clots from forming
Used to treat thromboembolic disorders
what are the types of anticoagulant drugs? (4)
Heparins
Warfarin (Coumadin)
Factor Xa inhibitors
Thrombin inhibitors
how does heparin work?
inactivates several clotting factors to prevent clots from growing which allows the body proper time to break down the clot before it grows out of control
How does warfarin work?
inhibits vitamin K dependent clotting factors which also inhibits prothrombin synthesis
How are factor Xa inhibitors indicated for?
Prevents DVTs and pulmonary embolism
BUT DOES NOT REMOVE IT!!
how do thrombin inhibitors work?
inhibit thrombin activity which prevents fibrin clots
What lab test is important to monitor while someone is on UNFRACTIONED heparin?
aPTT levels
what are the differences between unfractionated heparin and low molecular weight heparins?
unfractionated-
administered IV and subQ
aPTT should be monitored frequently
Low molecular weight-
administered ONLY subQ
No frequent aPTT monitoring needed
What are some indications from unfractionated heparin? (4). Can it be used during pregnancy?
Pulmonary embolism
Stroke
DVT
Atrial fibrillation
Note: can be used during pregnancy