1.7 - Collision Theory and Factors Affecting Rates
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
requirements for an effective collision
The orientation of the reactants (the collision geometry) must be favourable
The collision must occur with sufficient energy
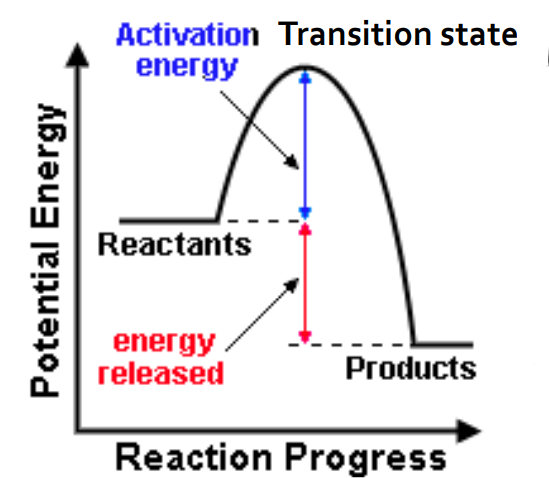
exothermic reaction potential energy diagram
endothermic reaction potential energy diagram
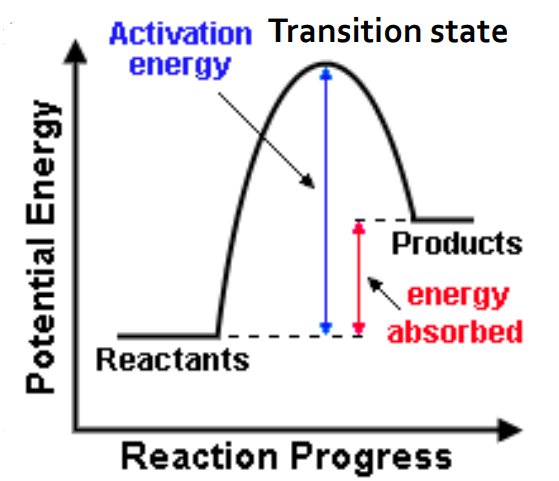
activation energy (Ea)
minimum kinetic energy required between reactants for a reaction to proceed
no way to predict activation energy from enthalpy change
in general, reactions with lower activation energy tend to proceed quickly at room temperature (regardless of endo or exo)
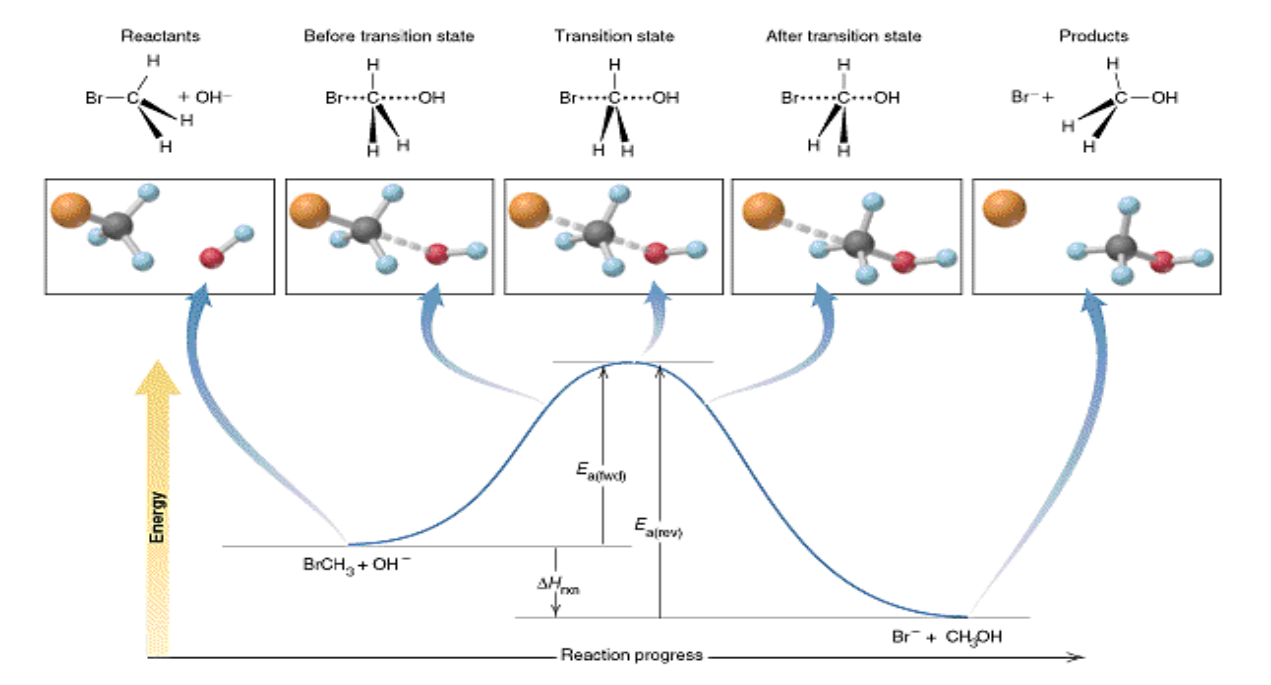
activated complex
a chemical species temporarily formed by the colliding reactant molecules before the final product is formed
contains partially formed bonds representing the maximum potential energy point in the change
aka transition state
factors affecting reaction rates
Concentration of a solution
Surface area of the particles of a solid reactant
Temperature
State/Phase
Presence of a catalyst
Nature of the reactants
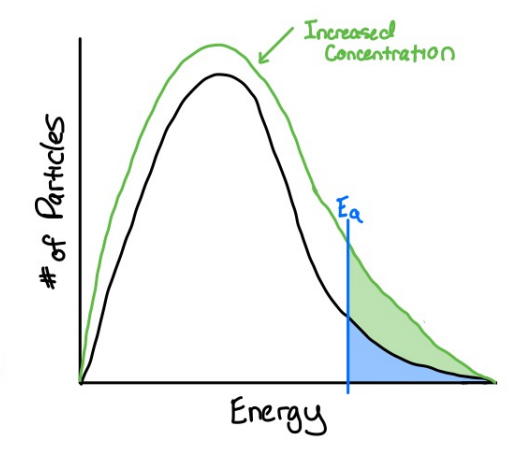
how does concentration affect reaction rate
increasing the concentration of reactants leads to a greater number of collisions per unit time, therefore a greater number of effective collisions are likely to occur
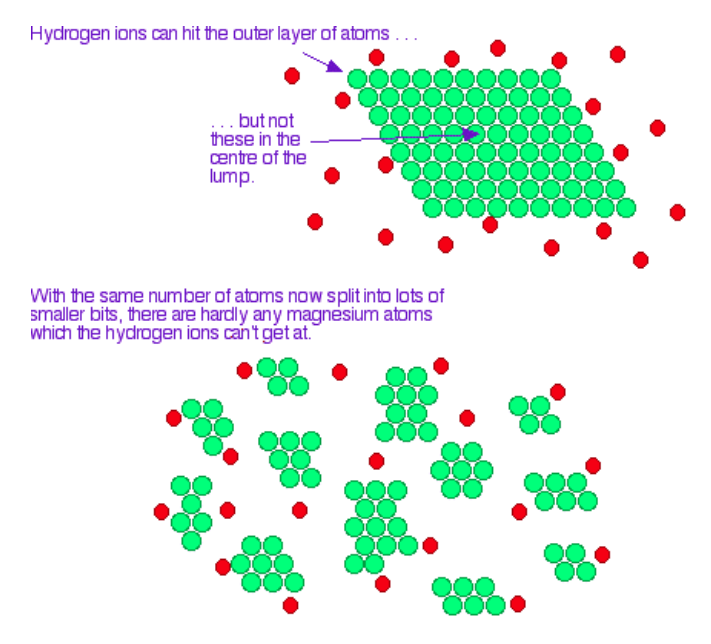
how does surface area affect reaction rate
increasing the surface area of a solid increases the number of surfaces where a collision can take place, increasing the number of collisions and effective collisions, which increases the reaction rate
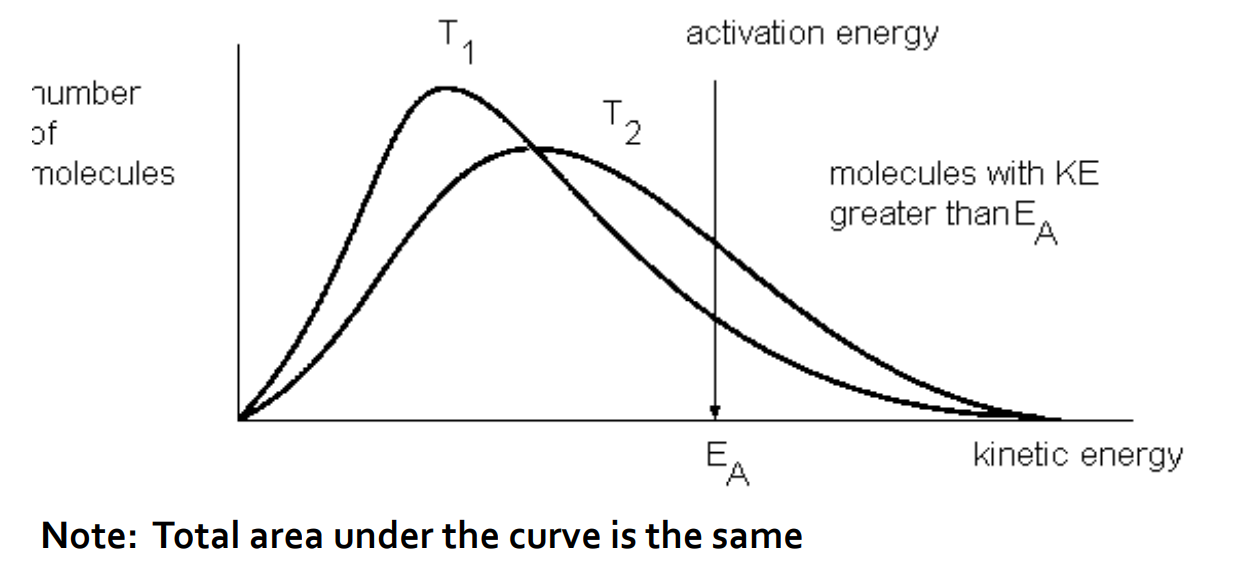
how does temperature affect reaction rate
increasing temperature causes:
Greater amount of kinetic energy in each collision
More frequent collisions, increasing the number of effective collisions
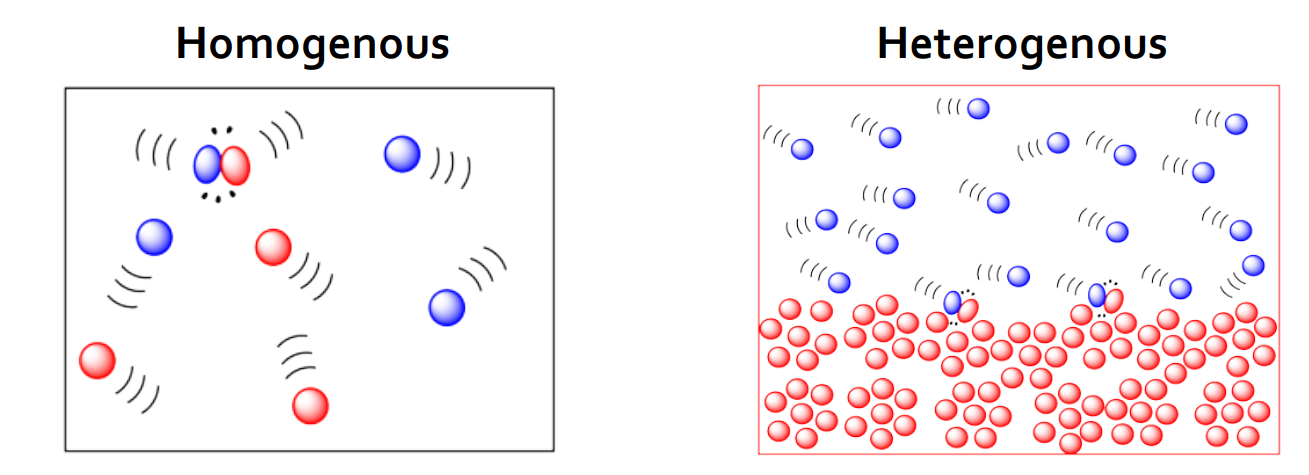
how does the state/phase of reactants affect reaction rate
reactions where all reactants are in the same state (homogeneous) will occur at a faster rate than when reactants are in different states (heterogeneous)
solids (slow), liquids (fast), gases (fastest)
stirring increases the rate of reaction
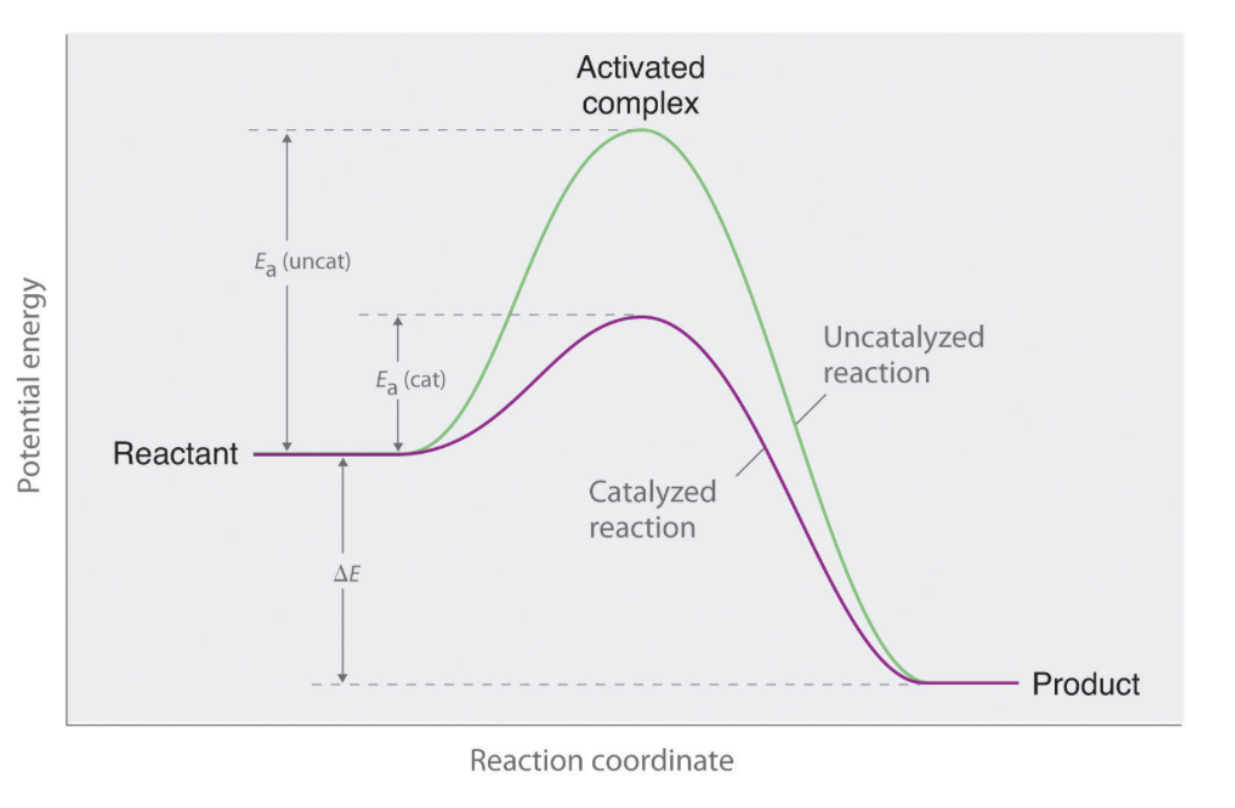
how does the presence of a catalyst affect reaction rate
speeds up the rate of reaction by introducing an alternate reaction mechanism to the products lowers the activation energy requirement, speeding up both forward and reverse rates of reaction
Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution for catalyst
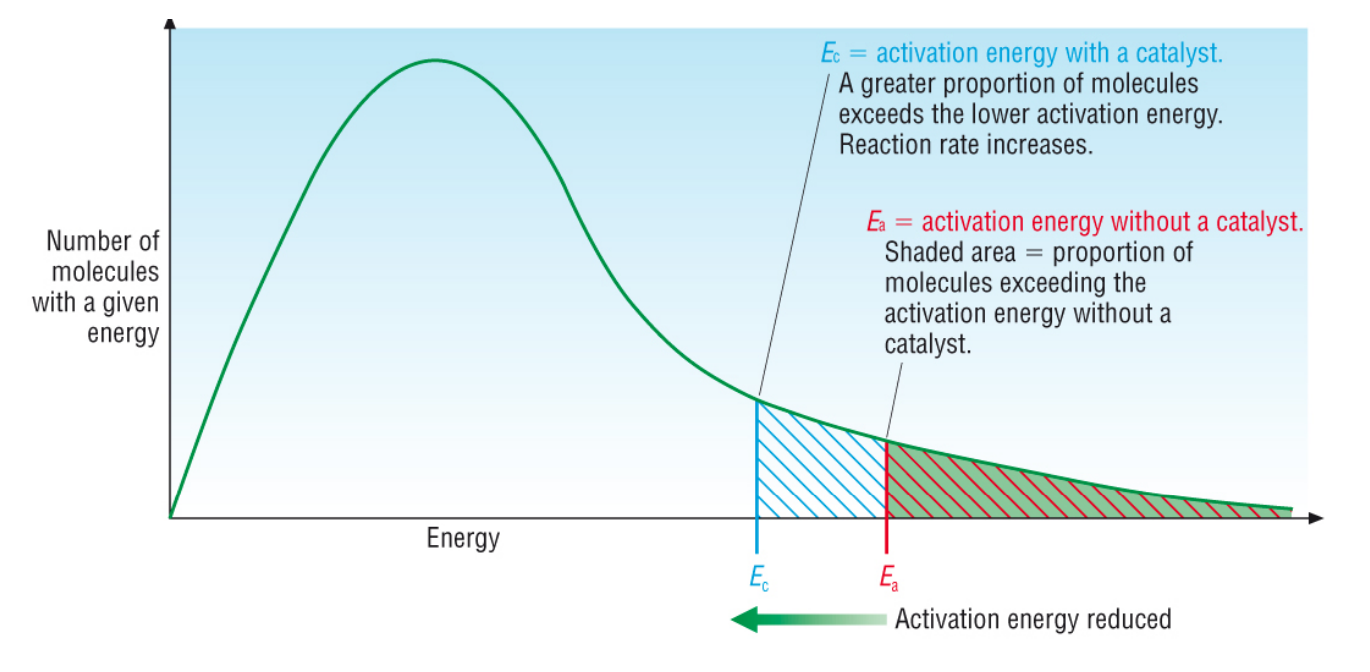
theoretical effect of catalyst
bend or stretch bonds to make them easier to break / react
bring two reactants close together
provide a microenvironment for reactions
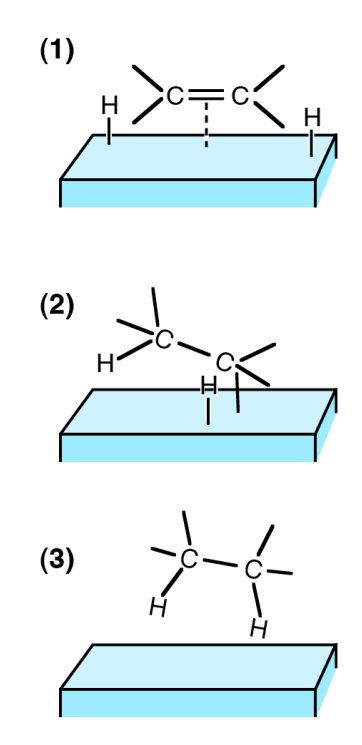
types of catalyst
Homogenous catalysts – the catalyst exists in the same phase as the reactants
Heterogenous catalysts – the catalyst exists in a phase that is different from the phase of the reaction it catalyzes
inhibitor
decreases the rate of a reaction, interferes with a catalyst to slow down reaction, increases activation energy
how does the nature of reactant affect reaction rate
state of matter (gases tend to react faster than solids, aq solutions tend to react faster than species in other states)
reactions between ions (transfer of electrons) are faster than reactions between molecules (involves breaking bonds)
weaker bonds broken faster than stronger bonds, eg. C-C vs C=C
reactions that break fewer bonds occur faster than reactions that break more bonds