Unit 1 Atomic Structure and Properties
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Atomic mass unit (Amu)
1/12 the mass in carbon-12 used to express atomic and molecular weights. The mass of one mole of a substance (in grams) is numerically equal to its atomic or molecular mass (in amu).
Ex: 1 mol of copper is 63.55, g/mol is 63.55, amu is 63.55
How to calculate specific ions in a sample
Find moles of the whole subtance
Multiply by the amount of the ions we’re tryna find
multiply by avagadros number 6.022×10²³
ex: find Na ions in 10g of Na2SO4
2(22.99)+32.06+4(16) =142.04g/mol 10/142.05= 0.0704 mol Na2SO4
two Na+ so.. 0.0704×2 = 0.141 mol Na+ ions
0.141 × 6.022×10²³ = 8.48×10²² Na+ ions
How to find MASS of _ moles of an isotope
multiply number of moles by avagadro.
multiply by mass of the isotope in amu.
Ex: given isotope 1: mass 90 amu, relative abundance 51.34%. Find mass of 2 moles
2(6.022×10²³)=1.2044×1024
(1.2044×1024) × 90 = 1.083×1026
How many atoms in 1 mol of copper?
6.022×10²³
The atoms in 1 mole of EVERY element is avogadros #
Isotopes have different ____ but same ____
Different neutrons, same protons
Calculate average atomic mass from isotopes
(atomic mass amu x abundance %) + (atomic mass amu x abundance %)
elemental analysis
-Finds how many atoms of an element in a compound
-Determine purity of a compound in a mixture
(Useful to find formula unit of a compound)
Different samples of a chemical compound always have the same ..
Composition of elements
What it means is that it doesn’t matter where the compound comes from, it will have the same % or ratio of elements each time
(Discovered by Joseph Proust)
Atomic Theory
All events composed of atoms
Atoms cannot be created/destroyed in a chemical reaction
Atoms of one element are different from another elements atoms. All atoms of an element are identical.
All compounds have a fixed ratio of atoms of elements
Made by John Dalton 1803
What was proven wrong of the Atomic Theory?
It is found that all atoms of an element are NOT identical!!
Isotopes exist!
How to find empirical formula of compound from its % of elements
Turn the percents into grams
Divide them by the element gfm to find moles
Divide every mol by the smallest mol
Empirical formula
LOWEST ratio of elements, simplest form
How to find MOLECULAR formula
If molecular mass is given…
Add up molar mass (GFM) for the compound
Divide it by given molecular mass
Multiply the empirical mass by the answer
Ex: Empirical formula C4H5N2O has molecular mass 194 amu.
C4H5N2O = 97 amu… 194/97=2. Multiply C4H5N2O by 2! = C8H10N4O2
How to find purity of compound in mixture? (Elemental analysis)
Option 1
% of elements in the compound ONLY / 100
Option 2
100%- contaminating element %
Ex: NaCl sample contaminated w/sulfur. Sample has 25% Na, 39% Cl, 36% S
Option 1: 100-36 S= 64% pure
Option 2: (25 Na + 39 Cl) / 100 = 64% pure
A sample contains 2 different elements that are bonded. Is it a mixture or a pure substance?
PURE SUBSTANCE!
If the elements are bonded it forms one species. If its only one species in a substance its uniform/pure.
If elements are NOT bonded, they are different species so mixture.
How many orbitals in sublevel s, p, and d?
s=1 orbital (since it can hold 2 e-) 1s2
p=3 orbitals (since it can hold 6 e-) 2p6
d=5 orbitals (since it can hold 10 e-) 3d10
f=7 orbitals (since it can hold 14 e-) 4f14
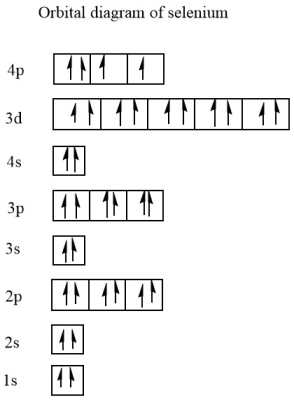
what is the e- config of Se?
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p4
or [Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p4
![<p>1s<sup>2</sup> 2s<sup>2</sup> 2p<sup>6</sup> 3s<sup>2</sup> 3p<sup>6</sup> 4s<sup>2</sup> 3d<sup>10</sup> 4p<sup>4</sup></p><p>or [Ar]<sup> </sup>4s<sup>2</sup> 3d<sup>10</sup> 4p<sup>4</sup></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7b216a78-7758-46f0-ba16-48d0f8012afc.png)
Does Se have unpaired e-? How many?
2 unpaired e-
fill out the orbital notation and look at 4p
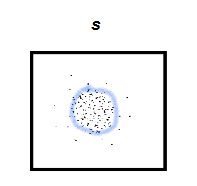
What does an s orbital look like?
looks like a circle
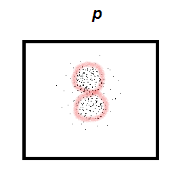
What does a p orbital look like?
looks like an 8
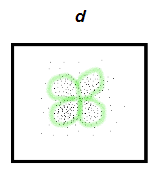
what does a d orbital look like?
looks like a 4 clover leaf or butterfly
Determine valence and core e- from… 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p4
6 valence e- , 28 core e-
whats the highest (outermost) number shell? n=4…. So 4s2 and 4p4 2+4=6
The rest is core e- so 28
Coulombs law equation
F= ke (q1q2/r2)
F direct to q (doubling any q will double F)
F decreases ALOT as distance increases
common sense bro
atomic radius ___ when the # of e- shells ___
increases, increases