The Basic X-ray Circuit (Ch 6 Part 2)
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
The power for x-ray generation comes from the incoming line current or main power, which comes in the form of what two things?
Single-Phase power
Three-phase power (multiphase power)
What is the incoming line current in the U.S for alternating current?
60 Hz
How many volts does the incoming line of current carry?
200-240 volts
What does nearly all x-ray equipment operate on?
210-220 volts
Single-phase power could be presented as:
Incoming line: alternating current (AC) or negative side
Incoming line: direct current (DC) or full-wave rectified
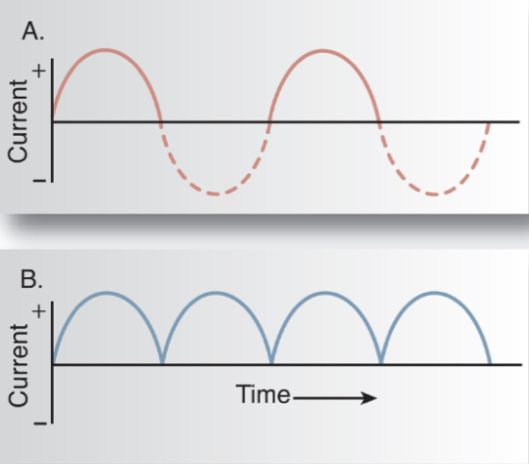
What is this image showing?
How single phase-power could be presented
During single-phase, the tube will drop to zero how many times a second using an incoming line of 60 Hz?
120 times
_____ x-rays are produced when the tube drops to zero
No
Three-phase power (multiphase) could be presented as:
Three-phase incoming line: alternating current (AC)
Three-phase incoming line: direct current (DC) or full-wave rectified
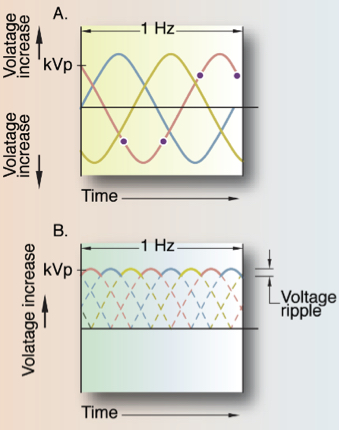
What is this image showing?
Three-phase power
What phase is the machines preferred power?
Three phase
Every time the machines power begins to drop it is boosted back up by what?
The next incoming wave of power
During three phase the voltage _____ reaches 0, however voltage ripple occurs
Never
What are the two circuits in an x-ray unit?
Main, tube, or high voltage circuit
Filament or low voltage circuit
What is the main purpose of the main, tube, or high voltage circuit?
To provide the tube with potential difference (kVp) and produce x-rays
The main, tube, or high voltage circuit modifies the incoming power so that the radiographer can control what three things?
Voltage (kVp)
Amperage (mA)
Exposure time (seconds)
What all makes up the main, tube, or high voltage circuit?
Main switch
Circuit breakers
Exposure switch
Main switch
Turns the power on and off
Circuit breakers
Prevents overload (fire)
Exposure switch
A remote controlled device to allow the flow of electrons through the circuit (begins exposure)
The exposure switch activates the rotating of the ______
Anode
What are the two steps to the exposure switch?
Pressing the exposure switch halfway starts the anode rotating
Pressing the exposure switch all the way takes the exposure
What is the purpose of the filament or low voltage circuit?
It provides the filament with modified power in order for thermionic emission to occur. Basically the purpose is to heat up the filament
The filament or low voltage circuit modified the incoming line power to produce __________ from the filament wire
Thermionic emission
The filament or low voltage circuits incoming voltage is stepped down from?
6 to 12 volts
The filament or low voltage circuits amperage (current) is modified to?
3 to 5 amperes
The filament or low voltage circuit’s amperage will provide enough current to _____ electrons at the filament to produce the milliamperes necessary across the tube
Boil off
The filament or low voltage circuit supply is draw directly from the _____ supply
Main circuits
When you set the mA station (100,200,400 etc) you are actually adjusting the number of _______ flowing through the filament or low voltage circuit
Amps
What is the amperage in the filament or low voltage circuit adjusted with?
A variable resistor known as a rheostat
What is the rheostat referred to as?
The mA selector
Once the technique is set and the exposure begins with the filament or low voltage circuit, the current is sent to the ______ to be modified before it reaches the filament
Step down transformer
When designing an x-ray room, the control console must be placed in a manner that is impossible for the operator to be?
Exposed
An exception to the rule above is in mobile radiography where the cord must be ______long minimally
6 feet
A radiographer will stand on the ______ side of the main circuit
Primary, low-voltage
What are the 3 types of exposure timers?
Electronic timer
mAs timer
Automatic Exposure Control (AEC)
The electronic timer is the most complicated and expensive, but the most ______ timer
Accurate
The electronic timer operates by charging a ________ which then terminates the exposure
Silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR)
The electronic timer is accurate to ________ millisecond
1 (0.001 second)
What is the most common timer used under modern radiographic/x-ray equipment
Electronic timer
The mAs timer is used in ________ units
Capacitor discharge
The mAs timer monitors the product of mA and time to give the _____ desired
mAs
When using the _______ timer, the tech sets the mAs and it decides what mA and time to use
mAs
What is automatic exposure control (AEC) also known as?
Automatically exposure devices (AED)
What are automatic exposure controls programmed to do?
Automatically terminate the exposure when a predetermined exposure has been reached
AEC’s only control the ______ while the mA and kVp still must
be set by the radiographer though
Exposure time
What are the two types of AEC’s?
Phototimer or photomultiplier
Ionization chamber
The phototimer is an older device that used a ______ to
regulate the exposure
Thyratron
The phototimer is placed _____________ meaning that x-rays will pass through the patient, tabletop, and cassette to strike a photo (light) emitting
screen
Under the patient and the cassette
The phototimer’s light energy is changed into electrons by a _______
Photomultiplier tube
When the phototimer’s number of electrons reaches a preset value, the exposure is _______; however this is problem because the photomultiplier is located behind the cassette, making these readings inaccurate
Terminated
The phototimer or photomultiplier is _____ used today
Rarely
Where are ionization chambers placed?
Between the patient and the cassette
When using an ionization chamber, the x-rays ionize the ______in the chamber and the liberate electrons which will cause a current (electrical charge) that travels along a wire to a timer in the circuit
Gas/air
Ionization chambers must be thin (5 mm) and _______
Radiolucent
Where are ionization chambers located?
In front of the cassette
When the ionization chambers predetermined amount of current is produced, the exposure is _______
Terminated
What makes up the vast majority of AEC’s today?
Ionization chambers which are commonly used due to their efficiency and accuracy in measuring exposure
The ________ of an AEC is the length of time necessary
for the AEC to respond to the radiation and for the generator to terminate
the exposure
Minimum reaction time
Phototimers have a minimum reaction time of _________
0.05 seconds (1/20th of a second)
Ionization chambers have a minimum reaction time of _________
0.001 seconds (1 millisecond)
The AEC’s _______ will terminate the exposure at a specific time
even if the AEC does not read the predetermined exposure
Backup time
Who sets the AEC’s backup time?
Technologist
The AEC’s backup time should _______ be set when using an AEC
Always
The AEC’s backup time _________ exceed the tube limit
Cannot
The AEC’s backup time should be set to ______% of the anticipated manual
mAs
150%
What would you set the back-up mAs at if your anticipated technique was 75 kVp @ 50 mAs?
You figure this out by doing 50 × 1.5 = 75 mAs
TH U.S Public Law 90-602 states that generators must terminate the exposure at _______ mAs for above 50 kVp
600 mAs
The U.S Public Law 90-602 sates the generators must terminate the exposure at ______ mAs for exposure below 50 kVp
2000 mAs
What is the falling load generator is specifically designed for what?
Three phase or high frequency generators
A falling load generator’s exposure begins with a _____ amperage and then will fall
during the exposure
High
What are the two disadvantages of using the falling load generator?
1) The operator will not know what mA the machine will select and must rely on the mAs timer to terminate the exposure
2) They shorten tube life due to a higher mA setting being used, so the filament will wear out quicker
Where are all of the technologist-operated controls located?
On the low voltage side of the main circuit to minimize hazard of electrical shock
The main/tube/high voltage circuit and filament/low voltage circuit combine at
the ________ to complete the basic x-ray circuit
Control console
What does the control console consist of?
Line monitor = monitors electricity coming in
Line compensator = keeps constant source of power
Rotor/Exposure Switch
mA Selector (Rheostat)
Time Selector
kVp Selector (Autotransformer)
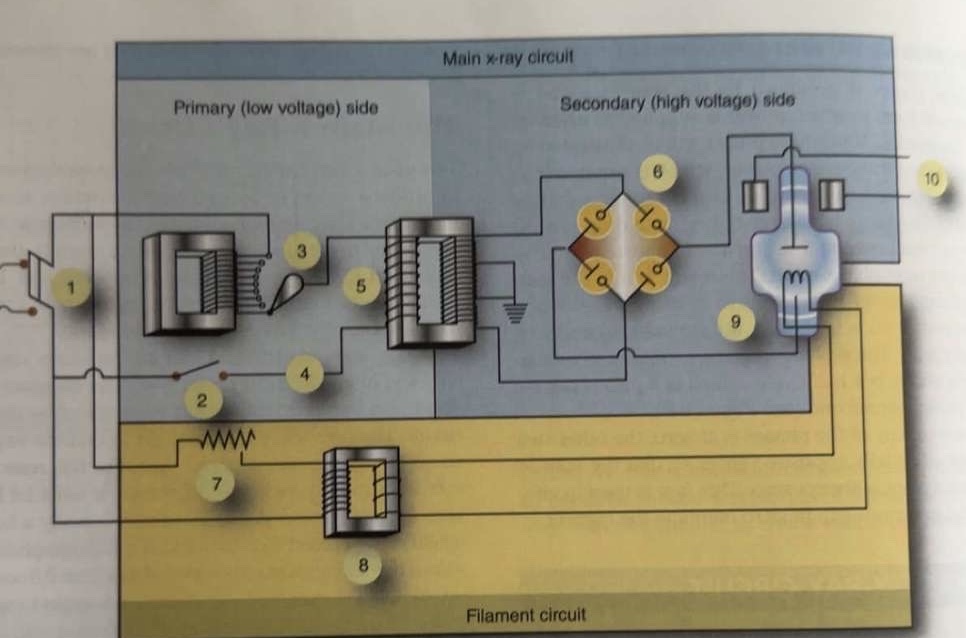
What is 1 pointing to?
Main breaker
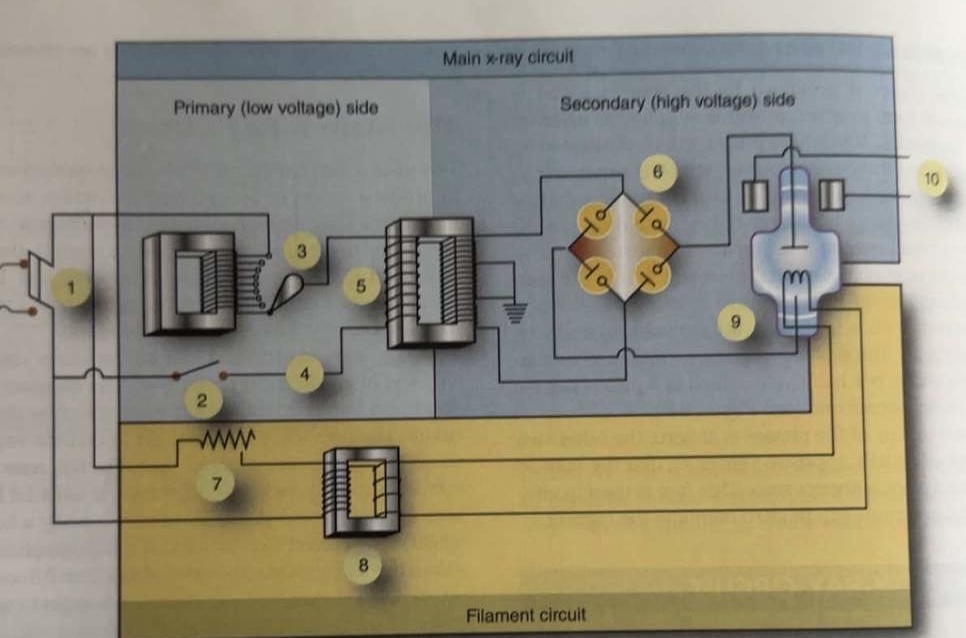
What is 2 pointing to?
Exposure switch
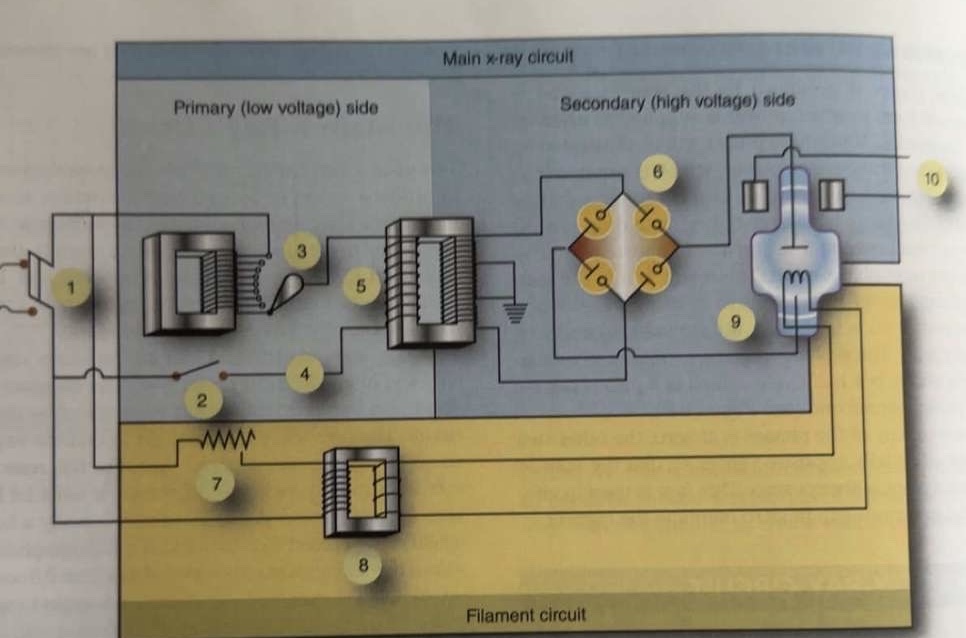
What is 3 pointing to?
Autotransformer
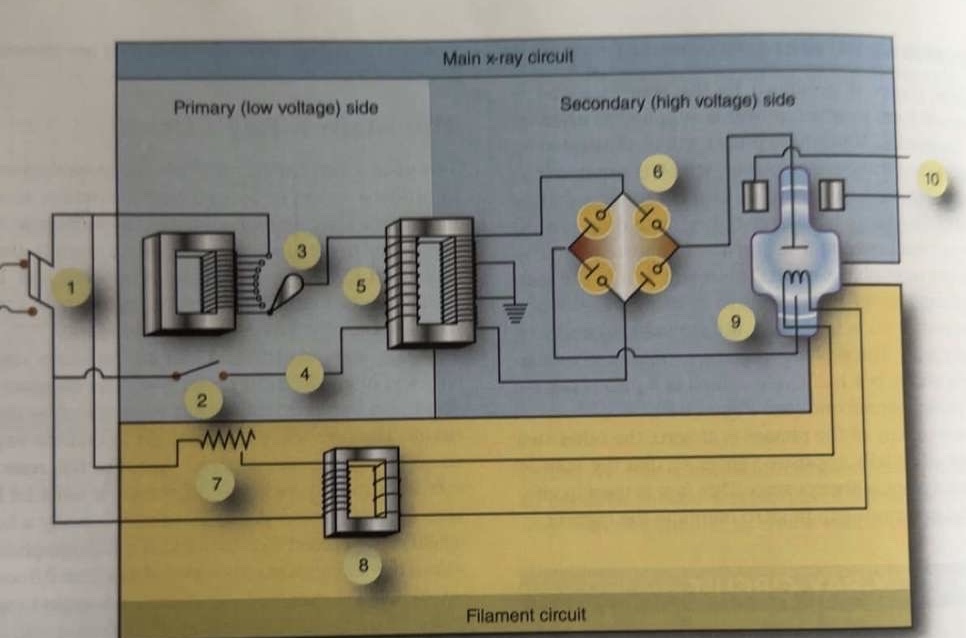
What is 4 pointing to?
Timer circuit
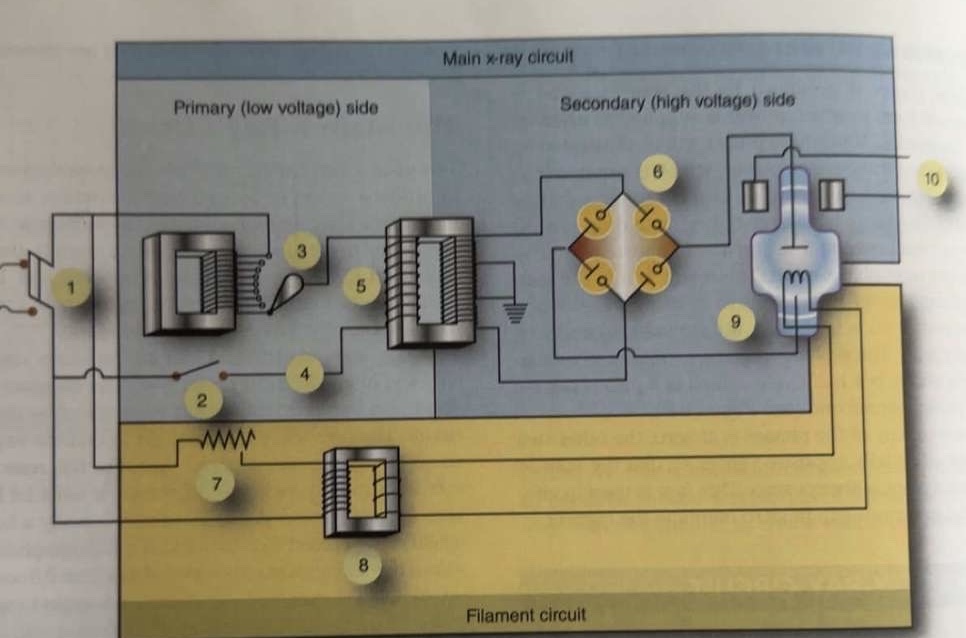
What is 5 pointing to?
High-voltage step-up transformer
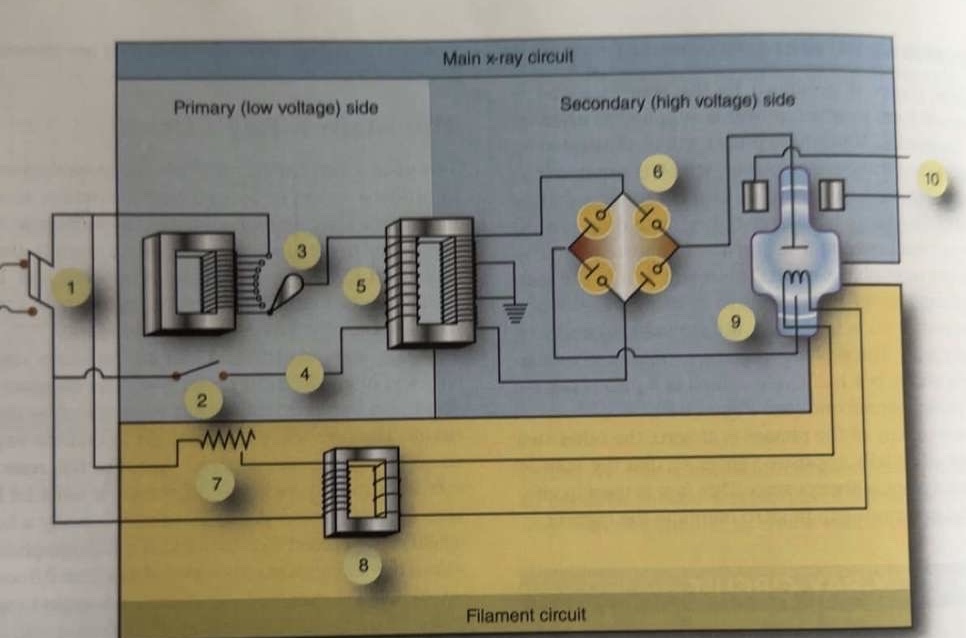
What is 6 pointing to?
Four-diode rectification circuit
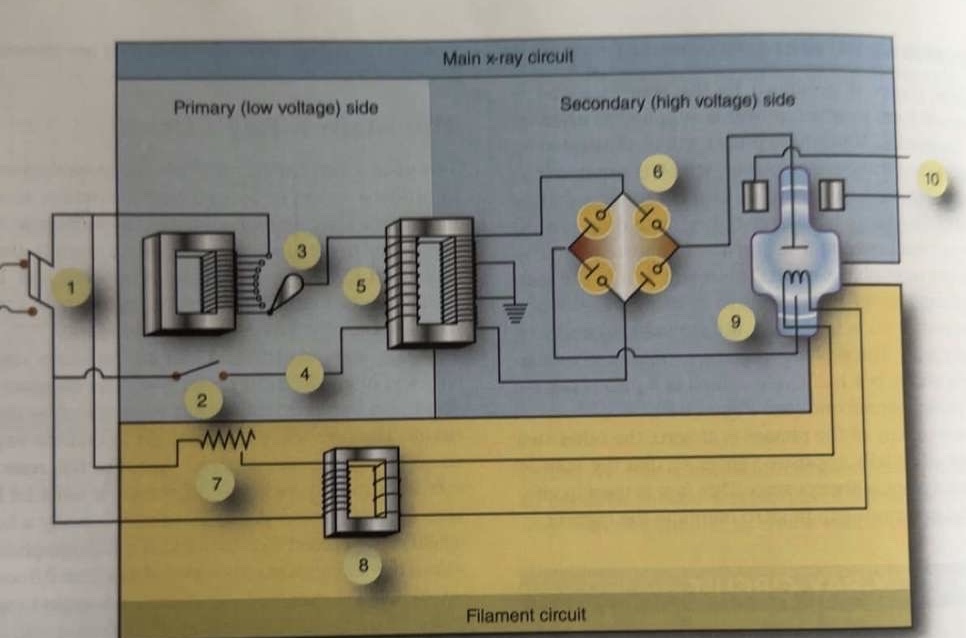
What is 7 pointing to?
Filament circuit variable resistance
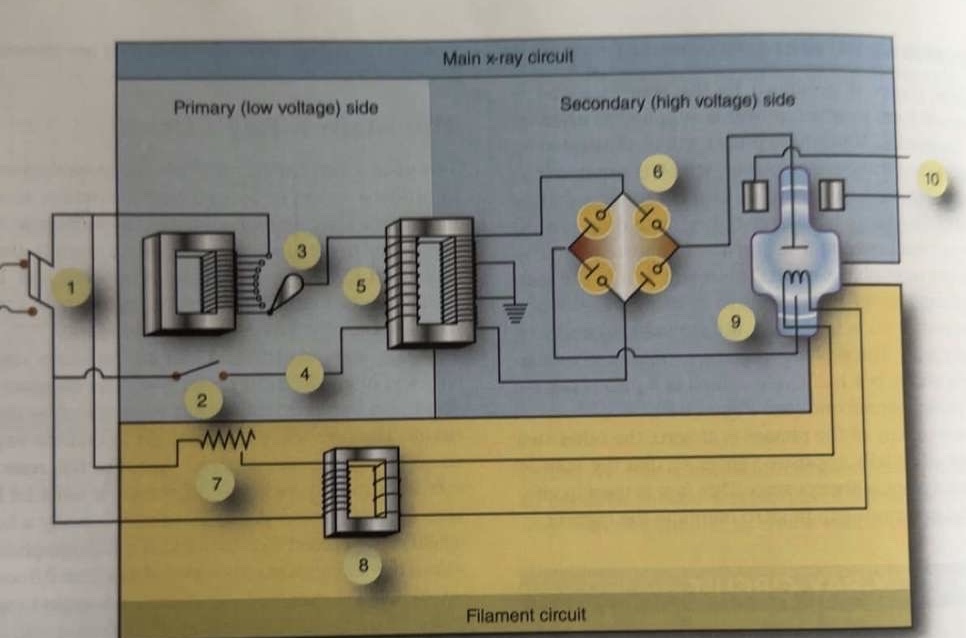
What is 8 pointing to?
Filament step-down transformer
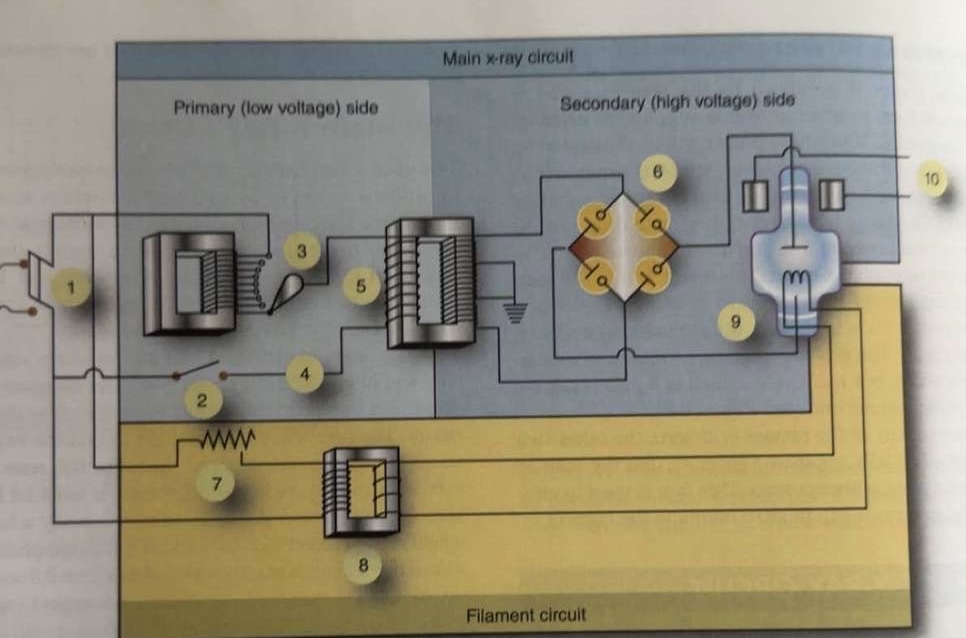
What is 9 pointing to?
X-ray tube
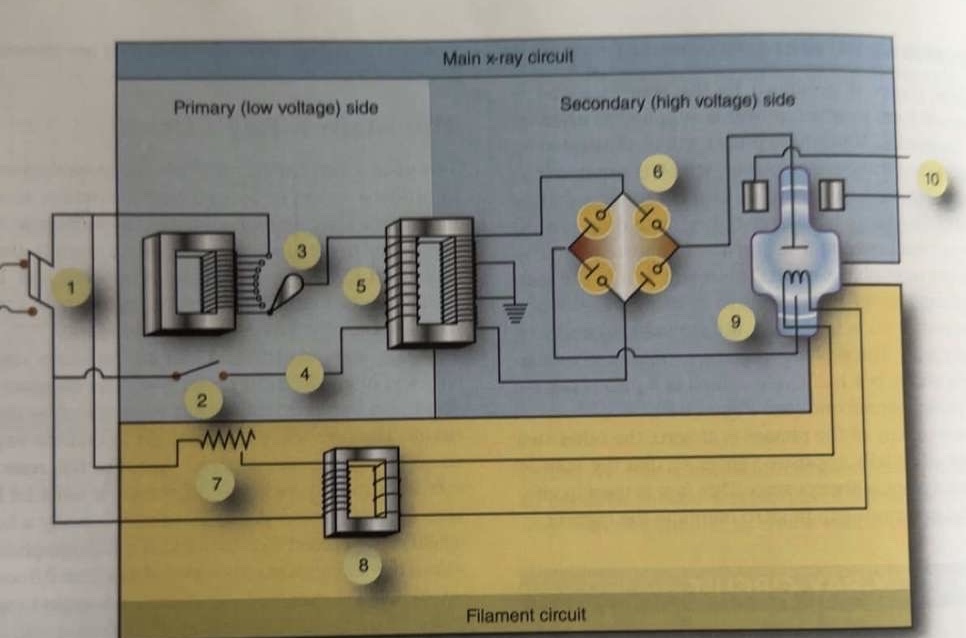
What is 10 pointing to?
Rotor stator
Where is the autotransformer located in the circuit?
Between incoming line and exposure switch
Where is the variable resistor located in the circuit?
In the filament circuit between incoming line and step-down transformer
Where is the timer circuit located in the circuit?
Between exposure switch and step-up transformer
Where is the stator located in the circuit?
Separate circuit from stator of anode motor
Where is the switch located in the circuit?
Between autotransformer and timer circuit
Step-up transformer
Used to increase kVp level for x-ray production
Ground
Helps prevent you from being electrocuted
mA meter
Measures current
Rectification bridge
Changes AC to DC
Step-down transformer
Used in filament circuit to increase current flow to the cathode
Focal spot selector
Large or small focal spot determines which wire will be heated
What are the 4 types of generators?
Single Phase (A)
three-Phase, Six-Pulse (3ø, 6P)
Three-Phase, Twelve- Pulse (3ø, 12P)
High frequency (HF)
A single phase generator has a full-wave rectified current that produces 2 pulses per cycle or _____ pulses per second
120
The voltage drops to ______ twice per cycle for a single phase generator
Zero
A single phase generator has a _____% voltage ripple
100