Managerial Accounting Exam 1 (McGraw Hill ch.1-4)
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Financial Accounting
~Reports to those outside the organization: Owners, Creditors, Regulators, & Tax authorities.
~ financial consequences of past activities.
~ objectivity and verifiability.
~ precision.
~ Companywide reports
~Must follow GAAP/FRS
~Mandatory for external reports
Managerial Accounting
~concerned with providing information to managers within an organization so that they can formulate plans, control operations, and make decisions.
~Decisions affecting the future.
~relevance
~timeliness
~segment reports
~does NOT need to follow GAAP/FRS
~Not Mandatory
Segment
is a part or activity of an organization about which managers would like cost, revenue, or profit data. ex. departments, plants, or divisions
Planning
~involves establishing goals and specifying how to achieve them
~normally accompanied by a budget
Controlling
involves gathering feedback to ensure that the plan is being properly executed or modified as circumstances change
Decision Making
~involves selecting a course of action from competing alternatives
~basic managerial skill to make intelligent, data driven decisions
~What should we be selling?
Who should we be serving?
How should we execute?
A budget
is a detailed plan for the future that is usually expressed in formal quantitative terms
Performance report
compares budgeted data to actual data in an effort to identify and learn from excellent performance and to identify and eliminate sources of unsatisfactory performance.
Data Analytics
the process of analyzing data with the aid of specialized systems and software to draw conclusions about the information they contain
5 types of cost classifications
1) assigning costs to cost objects
2) manufacturing companies
3) preparing financial statements
4) predicting cost behavior
5) making decisions
Assigning costs to cost objects
~direct cost (can be easily traced)
~indirect cost (cannot be easily traced)
Accounting for cost in manufacturing companies
~Manufacturing Cost
~Nonmanufacturing Cost
Manufacturing Costs
~Direct Material (DM)
~Direct Labor (DL)
~Manufacturing Overhead (MOH)
nonmanufacturing costs
~selling costs ~administrative costs
Preparing Financial Statements
~Product costs (inventoriable)
~Period costs (expensed)
Predicting cost behavior in response to changes in activity
~Variable Cost (proportional to activity)
~Fixed Costs (constant in total)
~Mixed Costs (has variable & fixed elements)
cost object
anything for which cost data are desired: product, customers, plants, office locations, & departments
(assigning cost to cost objects can be either direct or indirect)
Direct Costs
~a cost that can be easily and conveniently traced to a specified cost object
~
indirect costs
~a cost that cannot be easily and conveniently traced to a specified cost object
~
Common Cost
~a cost that is incurred to support a number of cost objects but that cannot be traced to them individually
~common cost is a type of indirect cost
Manufacturing cost categories
1. Direct Materials
2. Direct Labor
3. Manufacturing Overhead (indirect cost)
Direct Materials (raw materials)
~raw materials that become an integral part of the product and that can be conveniently traced directly to it
~raw materials refer to any materials that are used in the final product (the finished product of one company can become the raw materials of another company)
Direct Labor
~consists of labor costs that can be easily traced to individual units of product
~sometimes called touch labor because they are typically touching the products being made
Prime Cost
the sum of direct materials cost and direct labor cost
(both direct manufacturing cost categories
Manufacturing Overhead
~includes all manufacturing costs except direct materials and direct labor
~MOH costs are indirect because they cannot be easily traced to specific products
_indirect materials
_indirect labor
_indirect cost
(also called indirect manufacturing overhead, factory overhead, &factory burden)
Indirect Materials
~raw materials whose costs cannot be easily or conveniently traced to finished products
Indirect Labor
The labor costs of janitors, supervisors, materials handlers, and other factory workers that cannot be conveniently traced to particular products.
Other Indirect Manufacturing Costs
~depreciation
~utility cost
~property taxes
~insurance premiums
~only those indirect cost associated with operating the factory are included in manufacturing overhead
Conversion Cost
~Direct Labor + Manufacturing Overhead
(the term conversion cost is used because these costs are incurred to convert direct materials into finished products)
nonmanufacturing costs
selling costs and administrative costs
(nonmanufacturing costs are also called selling, general, and administrative costs or just selling and admin costs)
selling costs
All costs that are incurred to secure customers orders and get the finished product to the customer.
~also called order-getting & order-filling costs
~include: advertising, shipping, sales travel, sales commissions, sales salaries, and cost of finished goods warehouse.
~can be either direct or indirect
administrative cost
include all costs associated with the general management of an organization rather than with manufacturing or selling
~include: executive compensation, general accounting, legal counsel, secretarial, public relations, and similar cost involved in the overall general admin.
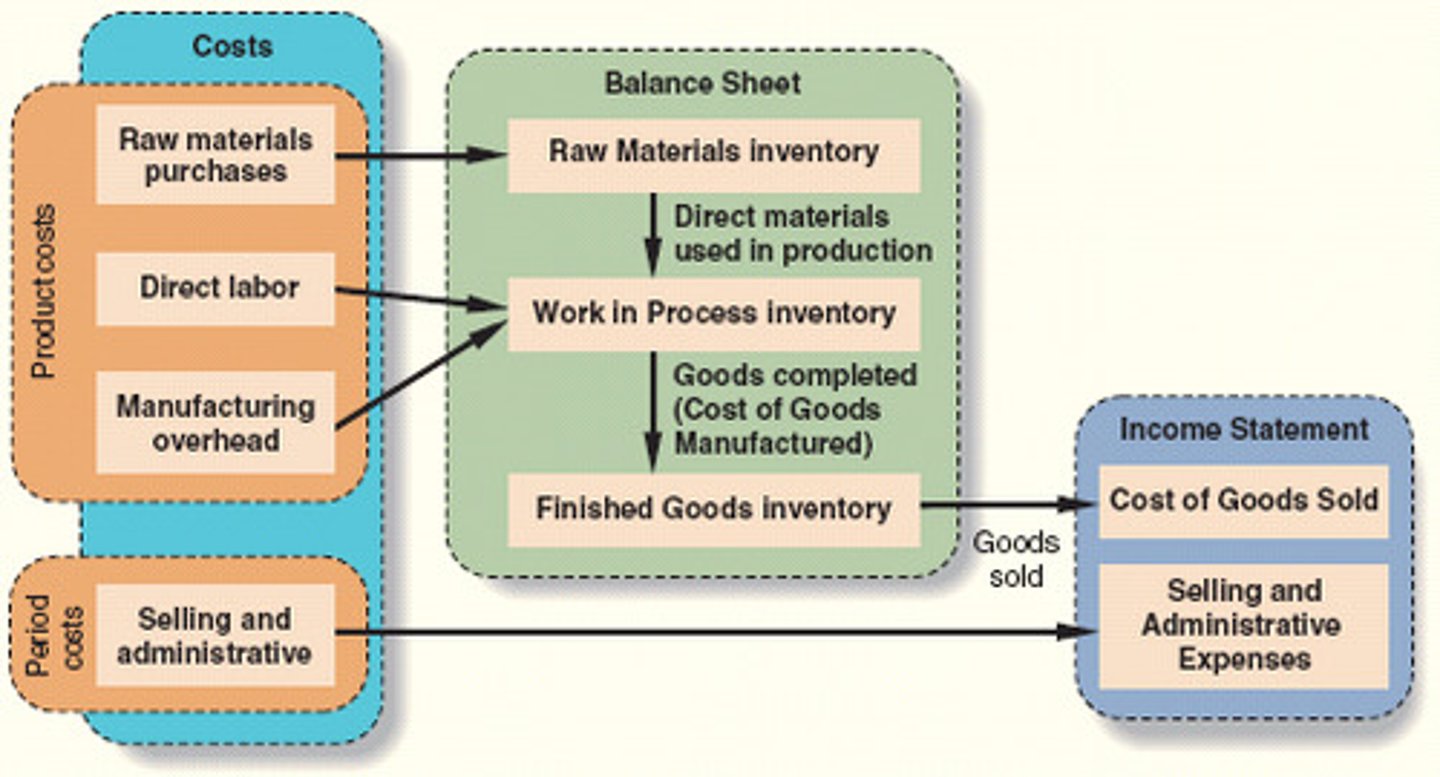
product costs (inventoriable costs)
~all costs involved in acquiring or making a product
~product cost "attach" to a unit of product
~include: DM, DL, & MOH
~Flows through three inventory accounts: Raw Materials, WIP, & Finished Goods before being transferred to COGS
~DM+DL+MOH
Work In Process
consists of units of production that are only partially complete and will require further work before they are ready for sale to customers
Finished Goods
consist of completed units of product that have not been sold to customers
Period Costs
~all costs that are not product costs
~all selling and admin. expenses are treated as period costs.
~period cost are not included as part of the cost purchased or manufactured goods, but are expensed in the income statement
~Selling+Admin.
cost flow diagram
variable costs
~costs that vary directly with the level of production
~ex. COGS, DM, DL, variable elements of selling and admin.
~cost are variable with respect to something like an activity base
~VariableManu.Cost=DM+DL+VaraibleMOH
activity base (cost driver)
~a measure of whatever causes the incurrence of a variable cost
~ex. Direct Labor-hrs, Machine-hrs(MH), units produced, & units sold
Fixed Costs
a cost that remains constant, in total, regardless of changes in the level of activity.
~includes depreciation, insurance, property tax, rent, & supervisory salaries. and Selling & admin.
~not affected by changes in activity
~can either be Committed or discretionary
~TotalFixedCosts = FixedMOH+Fixed Selling+FixedAdmin.
Committed Fixed Costs
represent organizational investments with a multiyear planning horizon that can't be significantly reduced even for short periods of time without making fundamental changes
Discretionary fixed costs
Those fixed costs that arise from annual decisions by management to spend on certain fixed cost items, such as advertising and research.
Relevant Range
the range of activity within which the assumption that cost behavior is strictly linear is reasonably valid
Mixed costs (semi variable costs)
contains both variable and fixed cost elements
Mixed Costs equation
Y=a+bx
Y= total mixed costs
a=the total fixed costs
b= the variable cost per unit
x= the level of activity.
Traditional Income Statement
Sales Revenue
- Cost of Goods Sold
= Gross Margin
- Selling & General and Administrative Expenses
= Net Income from Operations
Contribution Format Income Statement
sales revenue
- variable expenses
= contribution margin
- fixed expenses
= net operating income
Cost Of Goods Sold
beginning inventory
+ purchases
- ending inventory
=COGS
Contribution Approach to Income Statement
provides managers with an income statement that clearly distinguishes between fixed and variable costs and aids in planning, controlling, and decision making
contribution margin
~the variable portion of the contribution format income statement
~is the amount remaining from sales revenue after all variable expenses have been deducted
~ Sales-Variable =contribution margin
Job Order Costing
used in situations where many different products, each with individual and unique features, are produced each period
Job Cost sheet
records the materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead costs charged to that job
allocation base
a measure such as direct labor hours or machine hours that is used to assign overhead costs to products and services
Predetermined Overhead Rate
computed by dividing the total estimated manufacturing overhead cost for the period by the estimated total amount of the allocation base
overhead applied to a particular job
POHR x Amount of the allocation base incurred by the job
normal cost system
applies overhead costs to jobs by multiplying a predetermined overhead rate by the actual amount of the allocation base incurred by the jobs
plantwide overhead rate
a single predetermined overhead rate that is used throughout a plant to allocate all manufacturing OH costs to job based usage of DL-hrs
Multiple predetermined overhead rates
uses more than one overhead rate to apply overhead costs to jobs
Cost-plus pricing (markup pricing)
a pricing method in which a predetermined markup is applied to a cost based to determine the target selling price
schedule of cost of goods manufactured
A schedule that contains three elements of product costs—direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead—and that summarizes the portions of those costs that remain in ending Work in Process inventory and that are transferred out of Work in Process into Finished Goods.
schedule of cost of goods sold
A schedule that contains three elements of product costs—direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead—and that summarizes the portions of those costs that remain in ending Finished Goods inventory and that are transferred out of Finished Goods into Cost of Goods Sold.
Weighted Average Method
A process costing method that calculates unit costs by combining costs and outputs from the current and prior periods.
FIFO method
a process costing method in which calculates unit costs based solely on the costs and outputs from the current period
Equivalent Units
The product of the number of partially completed units and their percentage of completion with respect to a particular cost. Equivalent units are the number of complete whole units that could be obtained from the materials and effort contained in partially completed units.
~Equiv.Units=#of partially completed units X %completion
Weighted Average Method Steps
1. Compute the equivalent units of production
2. Compute the cost per equivalent unit
3. Assign costs to units
4. Prepare a cost reconciliation report
equivalent units of production
The units transferred to the next department (or to finished goods) during the period plus the equivalent units in the department's ending work in process inventory.
~Equiv.UnitsOfProduction = UnitsTransferredToNextDept.orFinishedGoods + Equiv.UnitsInEndingWIP
(Units in Beg. WIP) + (Units started into production or transferred in) =
= (Units in ending WIP inventory) + (Units completed & transferred out)
cost per equivalent unit formula
(Cost of beginning WIP inventory + Cost added during period) / Equivalent units of production
Cost to be accounted for
Cost of Beginning WIP
+ Cost added during period
Costs accounted for
Costs of Units Transferred Out + Ending WIP
operation costing
a costing system that uses job-order costing to assign materials costs and process costing to assign conversion costs.