ANFS240 Exam 4- reproductive & neuro
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
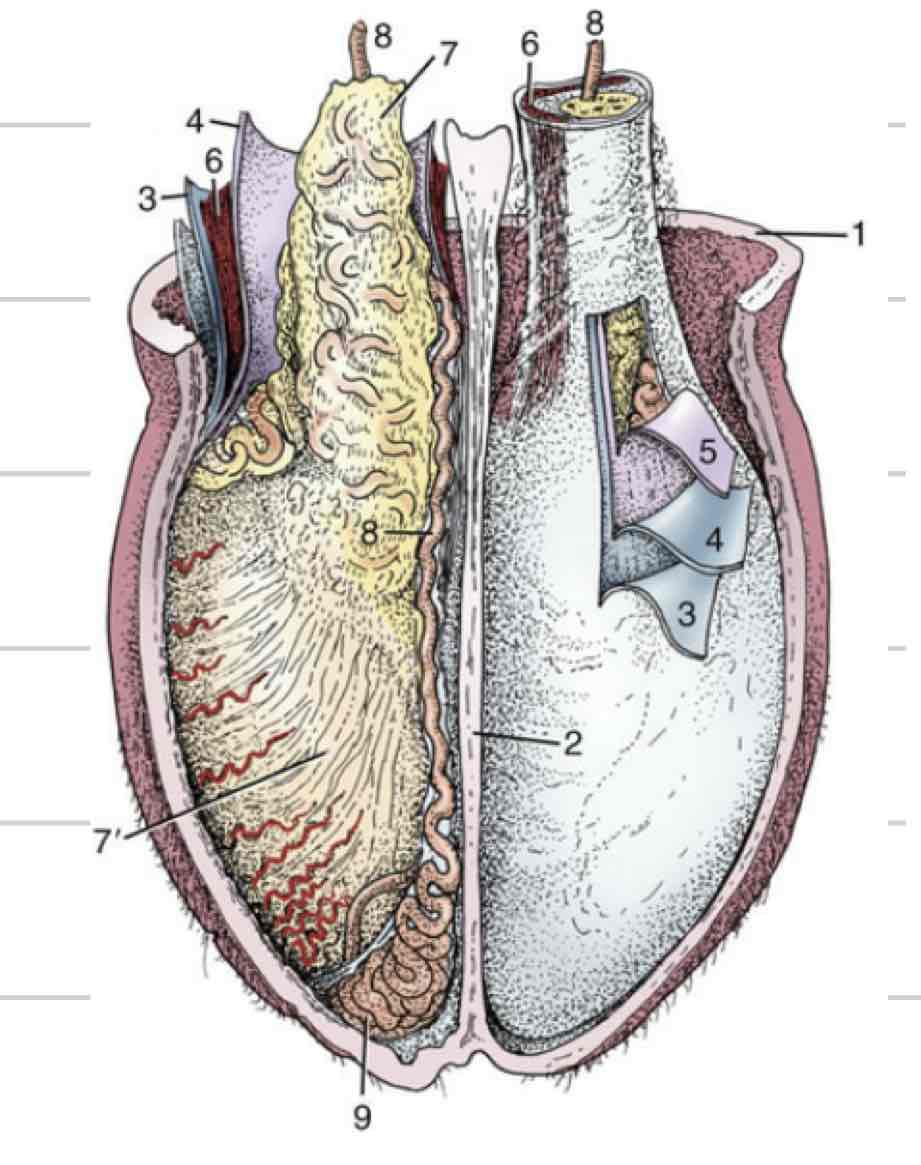
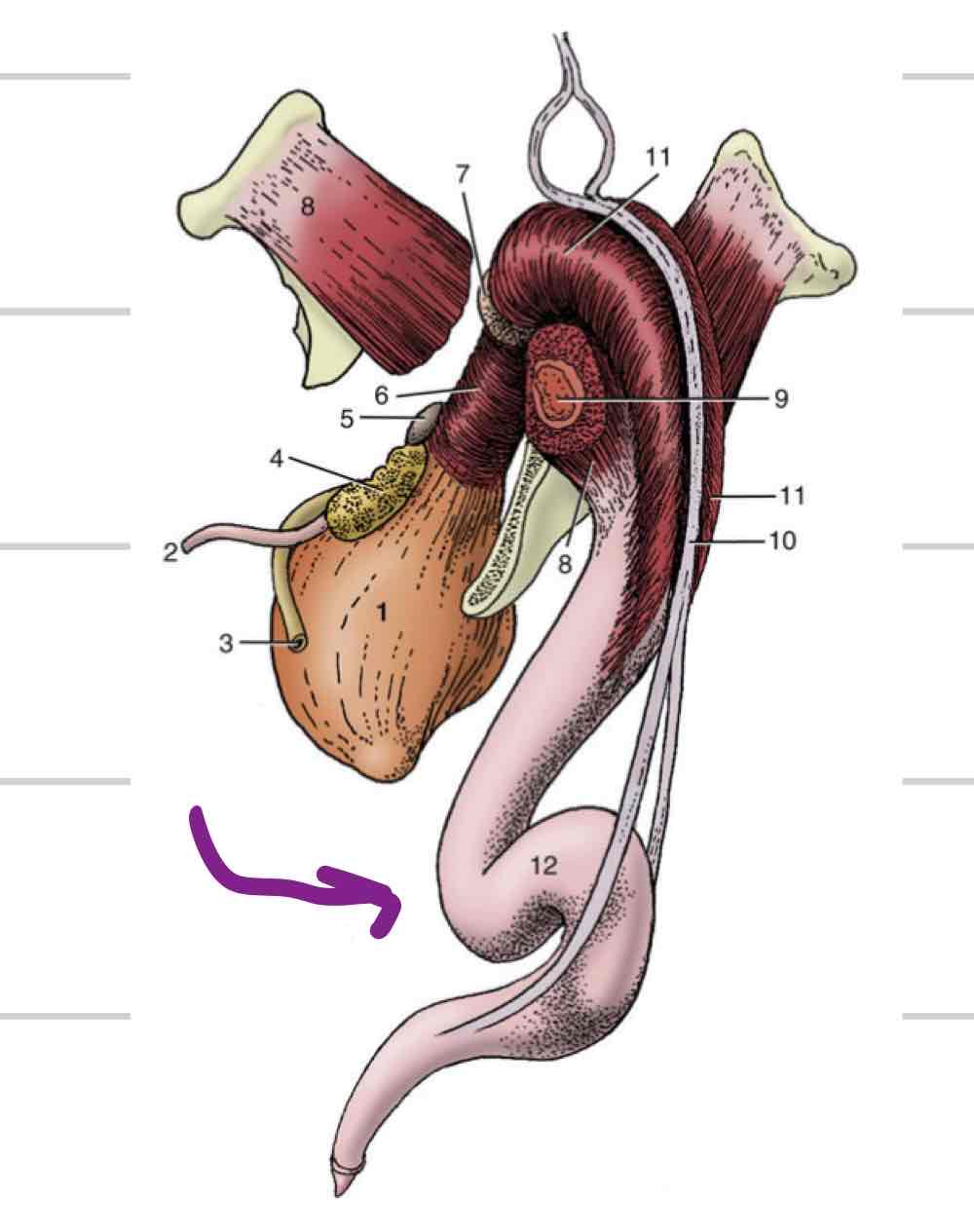
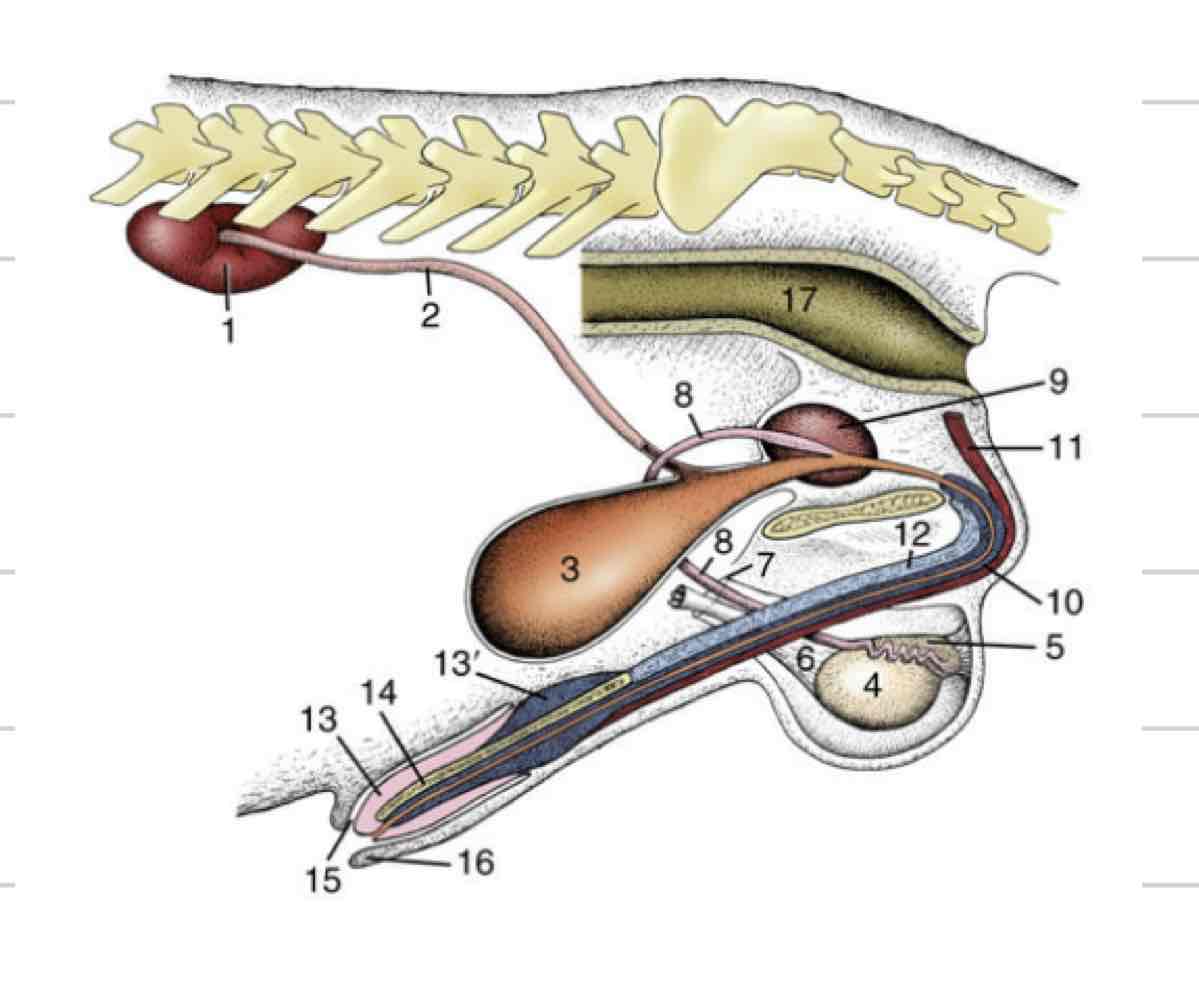
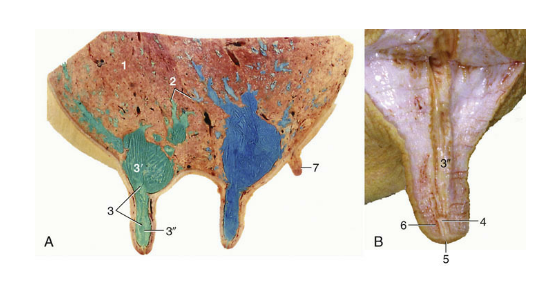
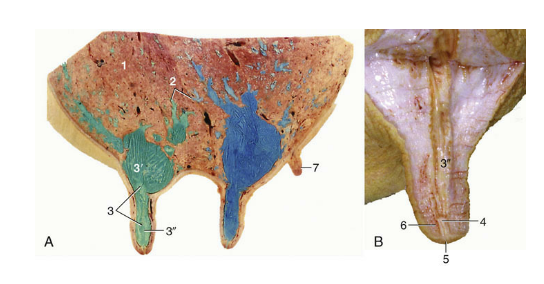
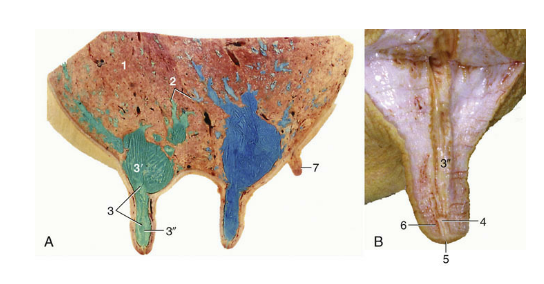
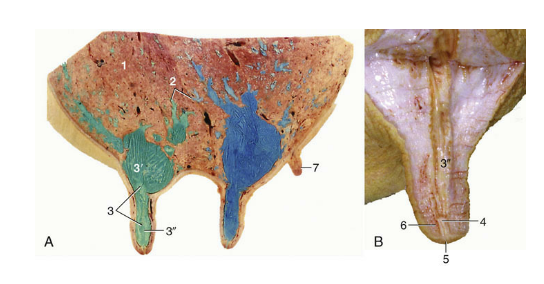
Testicle
site of spermatogenesis where sperm are created from stem cells
Endocrine function, create and release hormones like testosterone
Ovoid/ellipsoidal shape
Smooth outer surface with a firm parenchyma
Orientation and size varies based on species
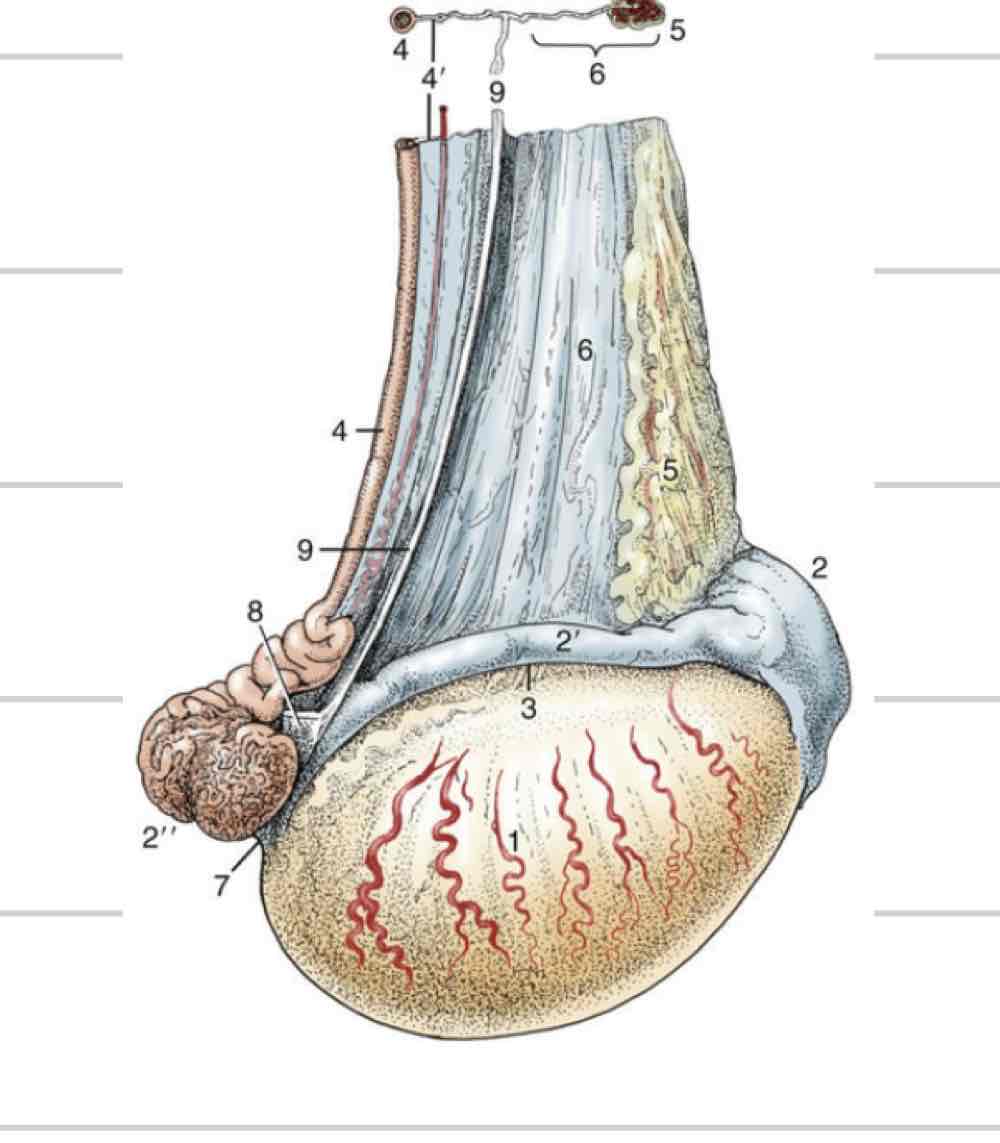
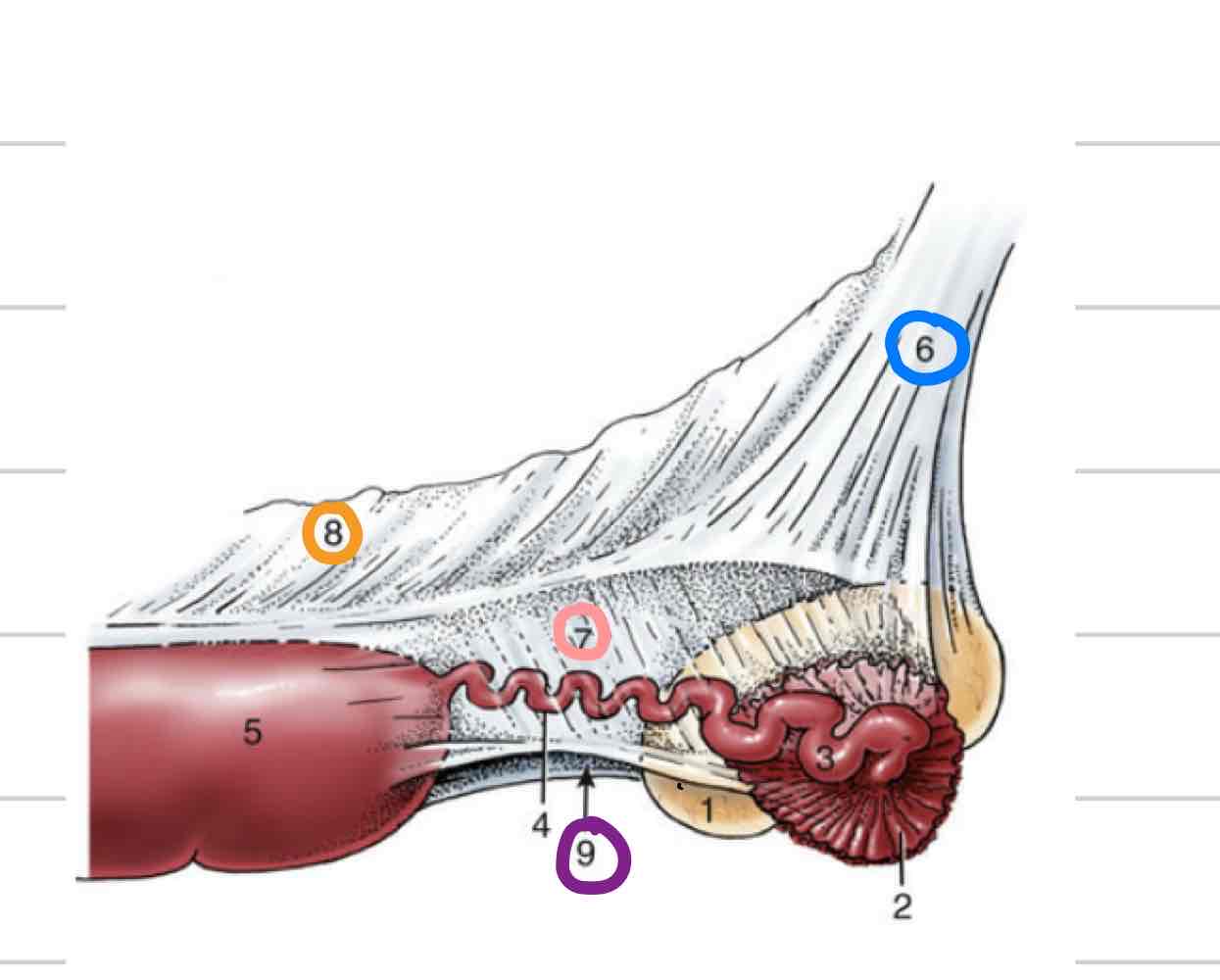
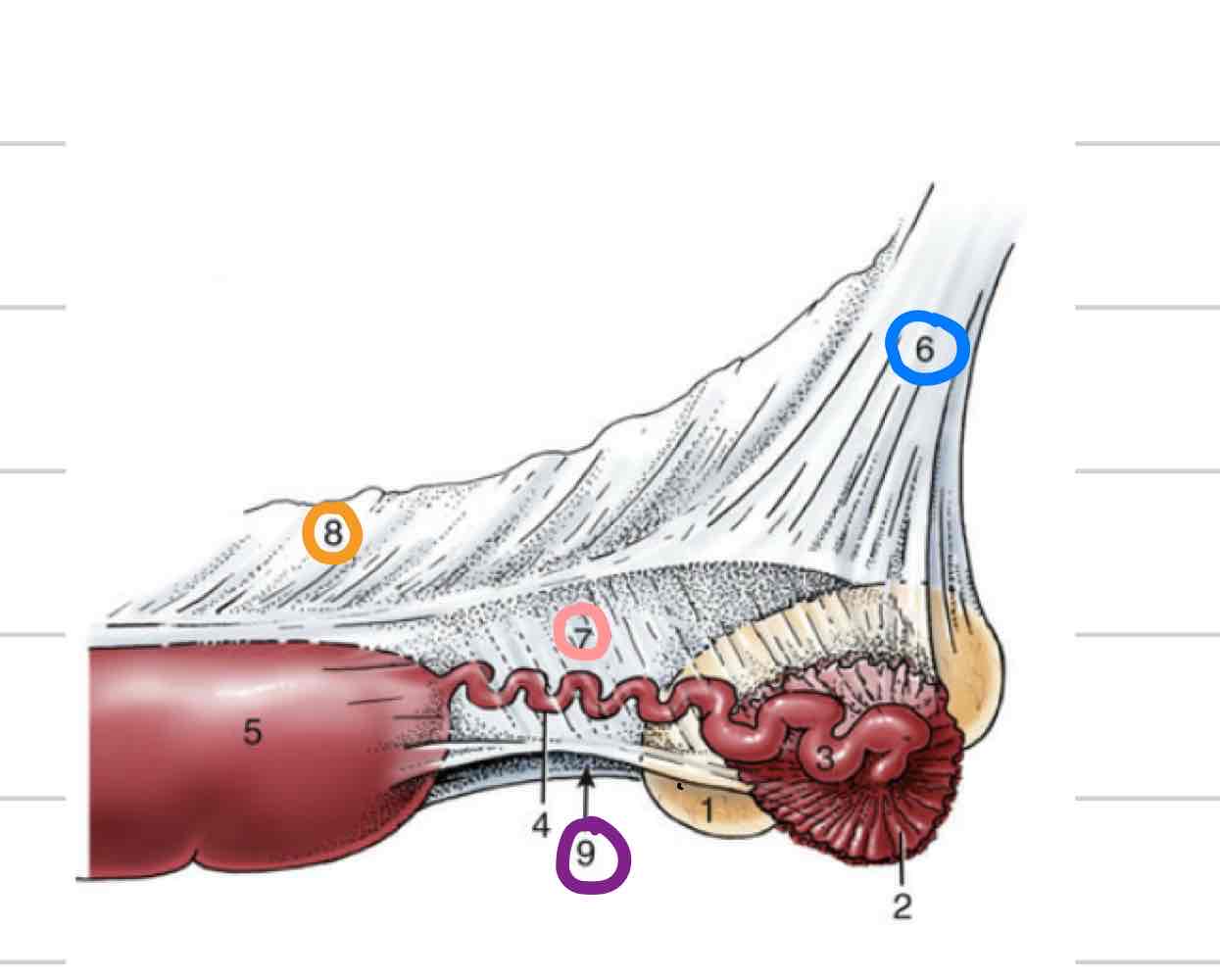
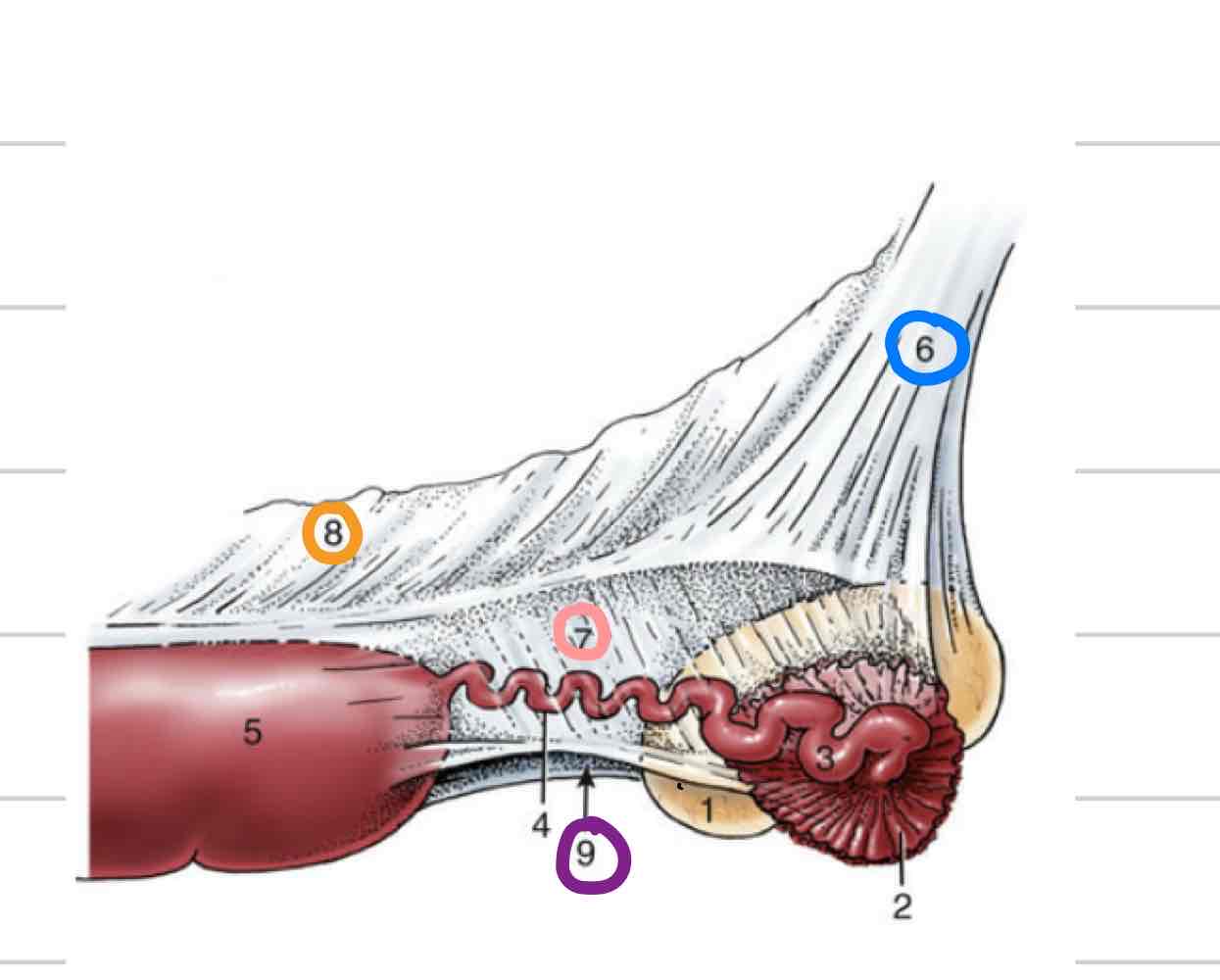
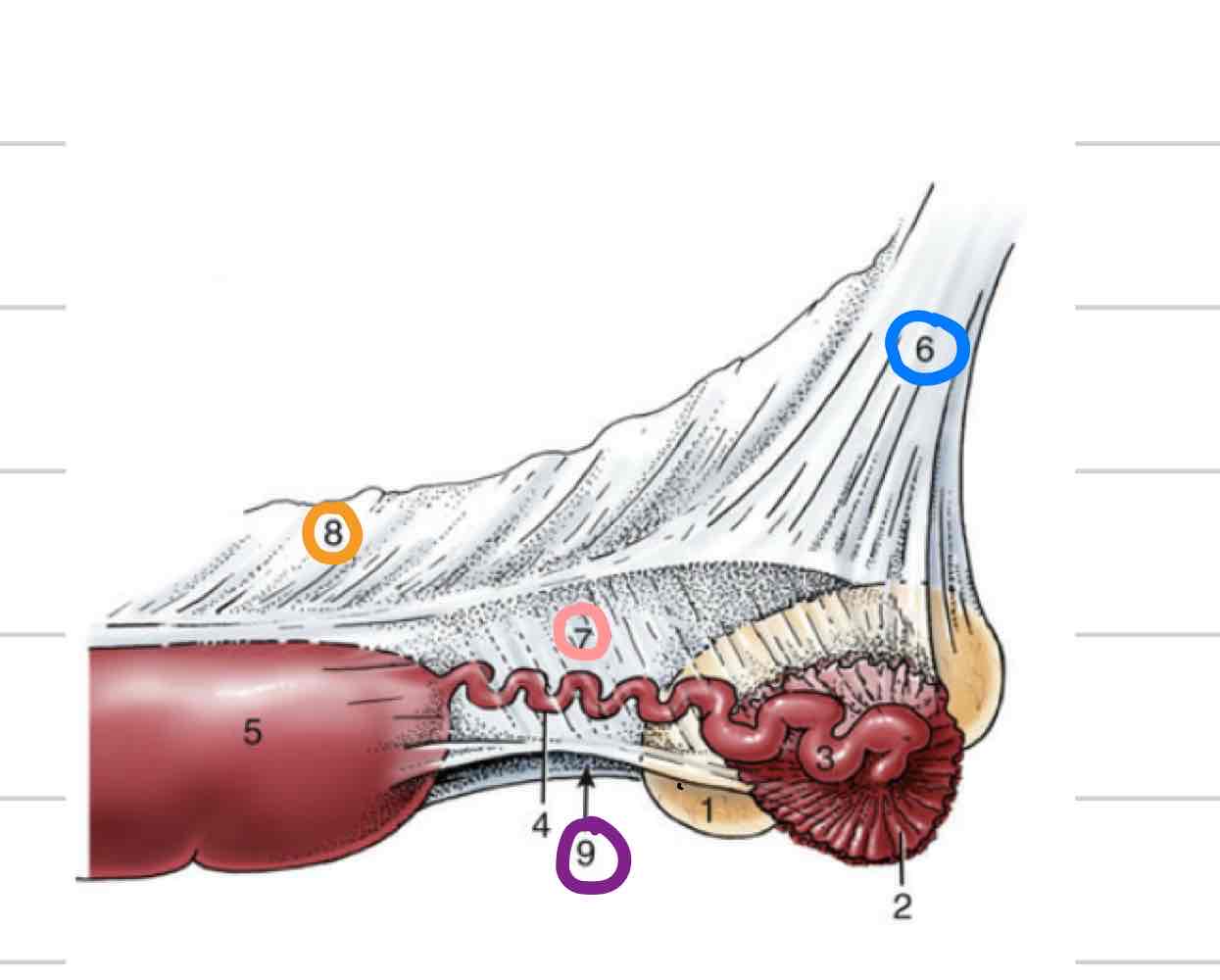
Epididymis
Adjacent to testicle
Where maturation of sperm occurs
3 parts
Head- (blue) where sperm enter from testicle
Body (orange)
Tail- (pink) sperm exit here matured
Deferent Duct
(Red) Continuous with tail of epididymis
Long, thin tube that extends to urethra
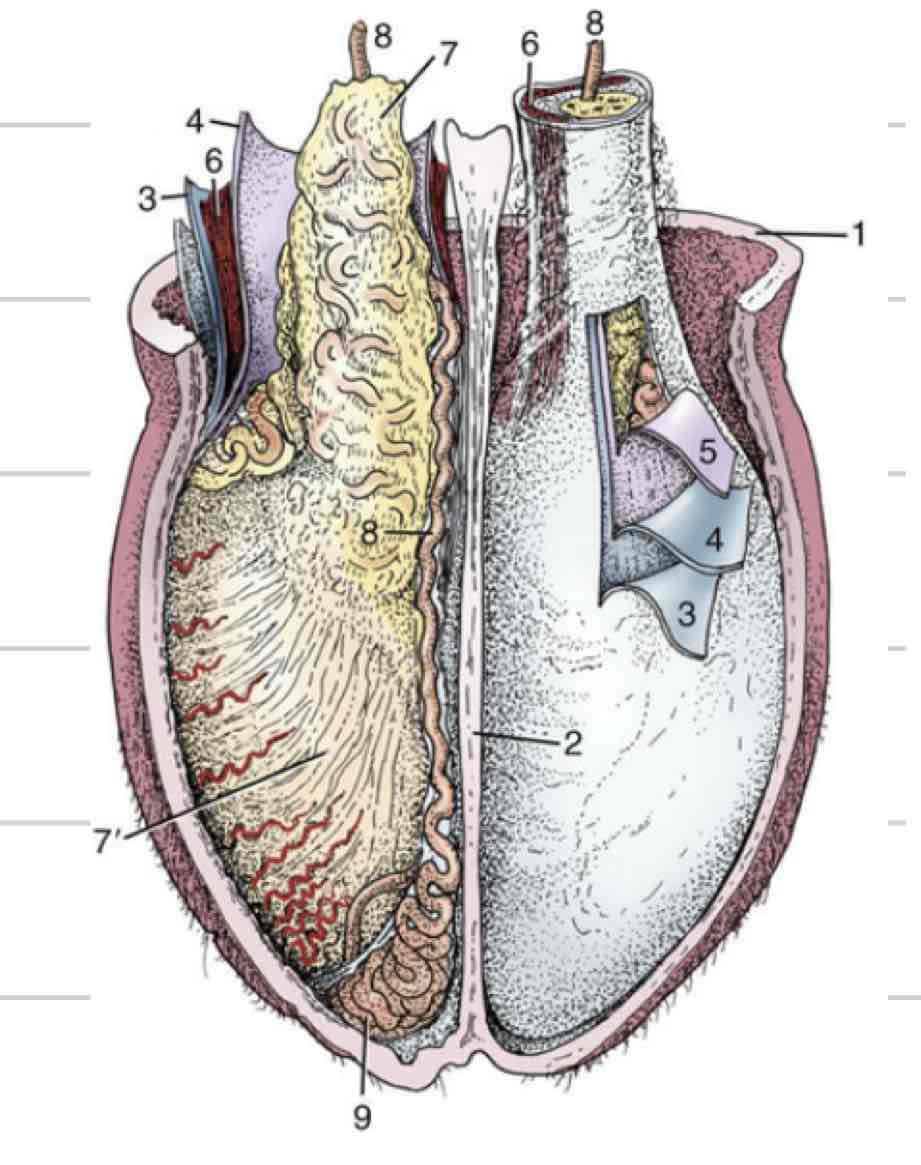
Tunica vaginalis
Membrane surrounding and enclosing testes
Invagination and extension of peritoneum
Both parietal and visceral layers
Visceral layer- tightly adhered to surface of testicle and epididymis
Space continuous with peritoneal cavity
Descend through vaginal ring-(blue) can cause inguinal hernia
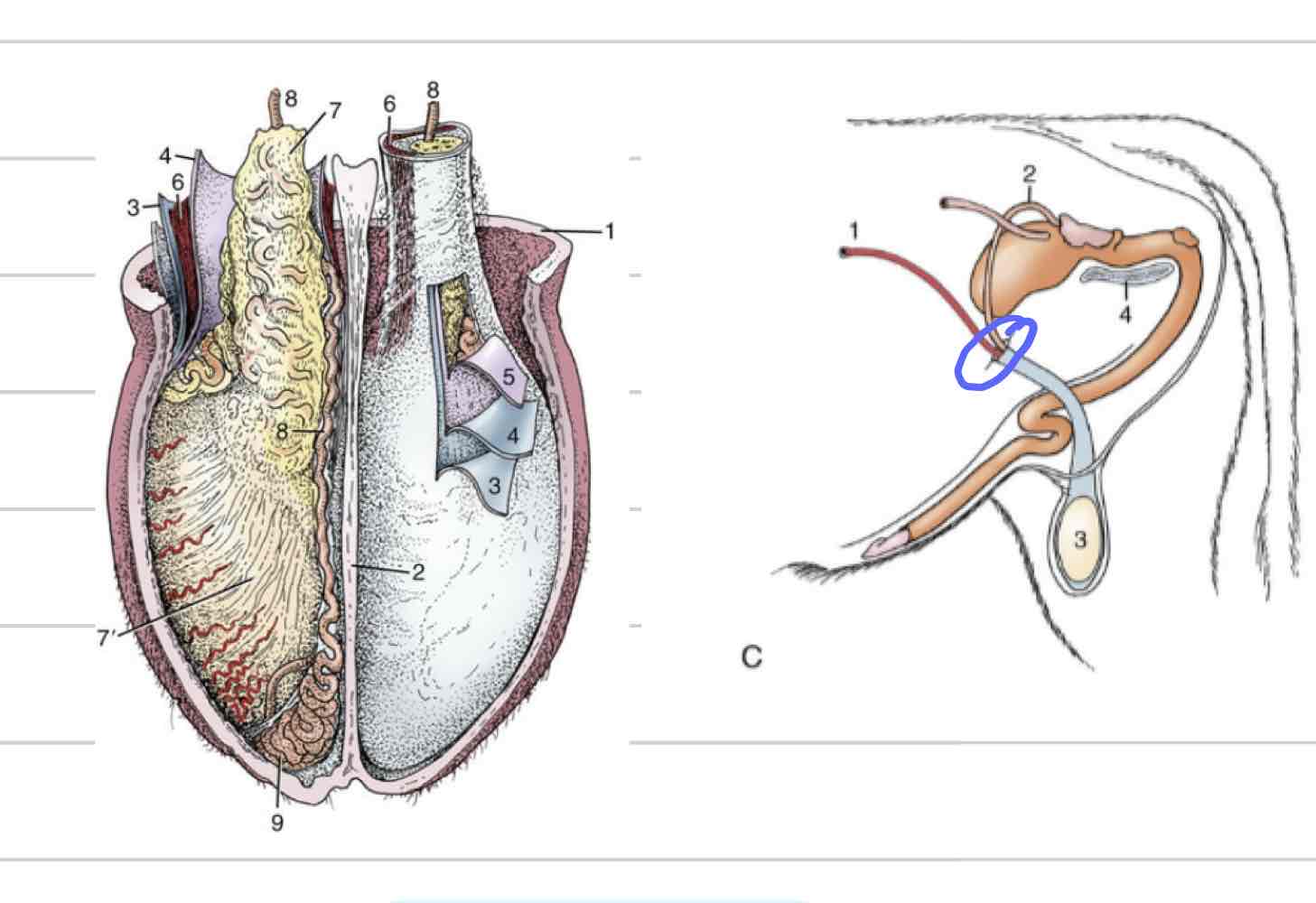
Tunica albuginea (testicle)
White covering that surrounds testicle, not epididymis
Mediastinum- projection that extends into testicle and divides into halves
Spermatic cord
varies in shape and length based on orientation of testes
Includes
Pampiniform plexus
Spermatic vein
Spermatic artery
Deferent duct
Cremaster muscle
Cremaster muscle
Muscle within spermatic cord that brings testes closer to body (retracting testicles)
Contracts due to pain, temperature, fear
Scrotum
Houses testicles, epididymis, spermatic cord
Adhered to tough musculofibrous layer- tunica dartos
External median groove called septum which divides left and right compartments
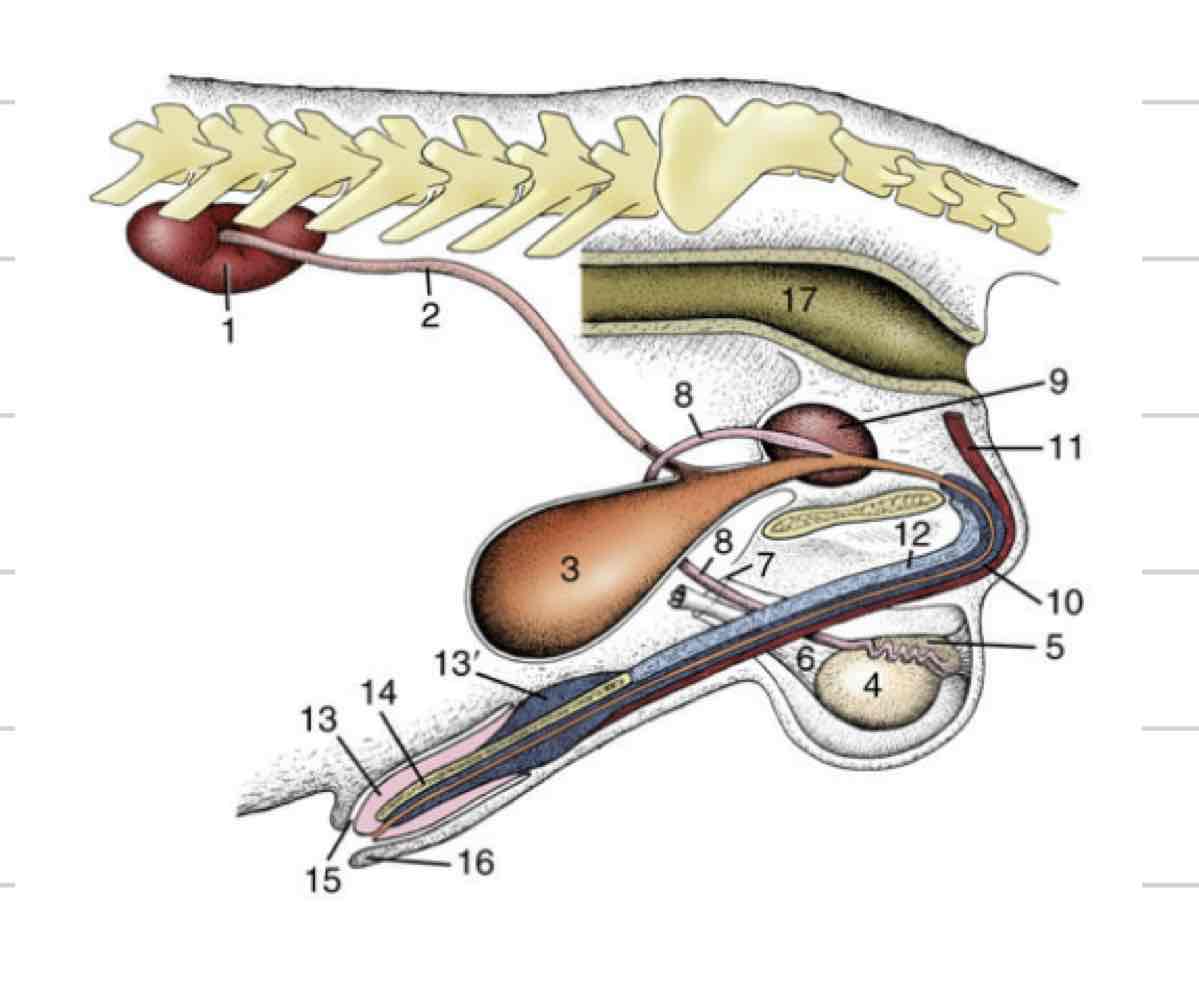
Male Urethra
extends from bladder to most distal end of penis
Carry both sperm and urine
Can be divided into spongy (external) and pelvic (internal)
Pelvic is where deferent ducts join
Spongy exists within the penis and is surrounded by vasculature
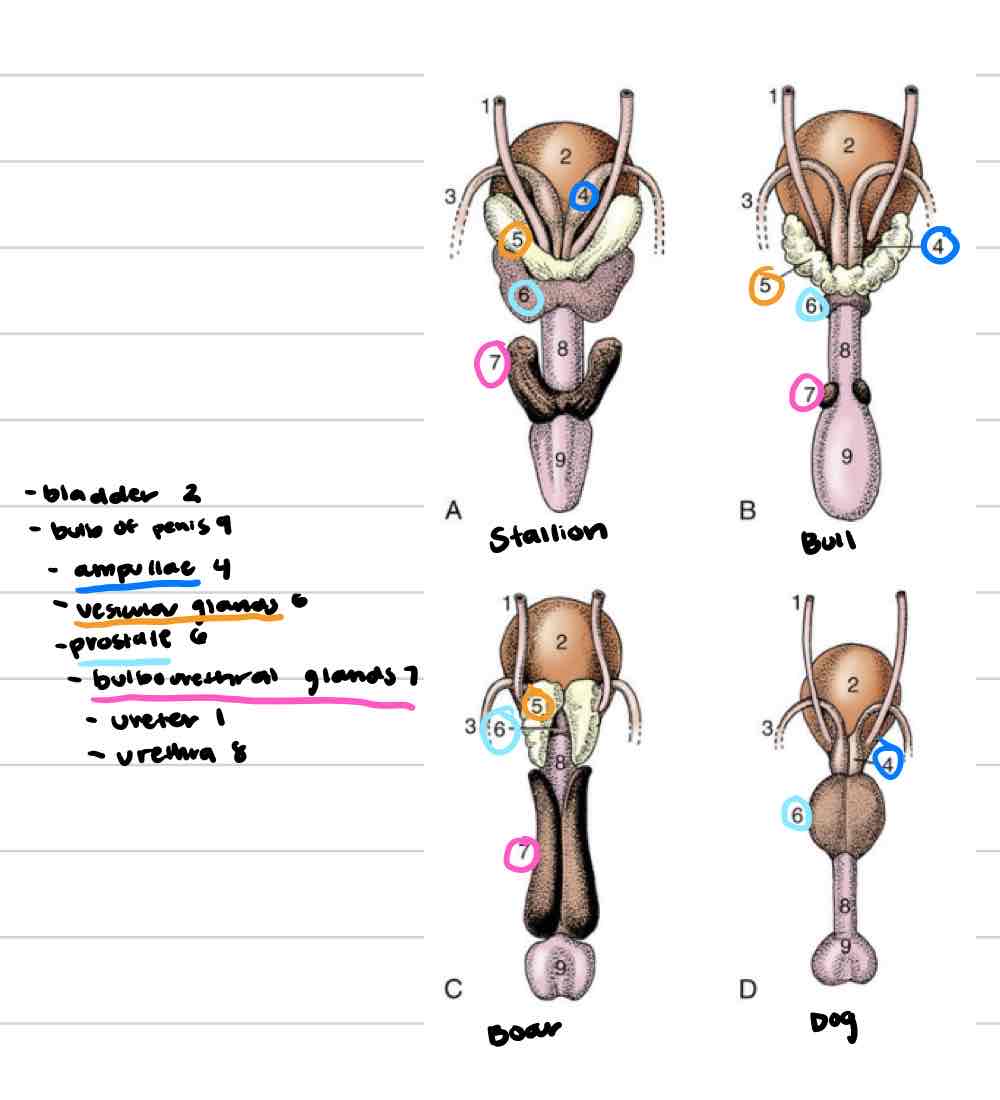
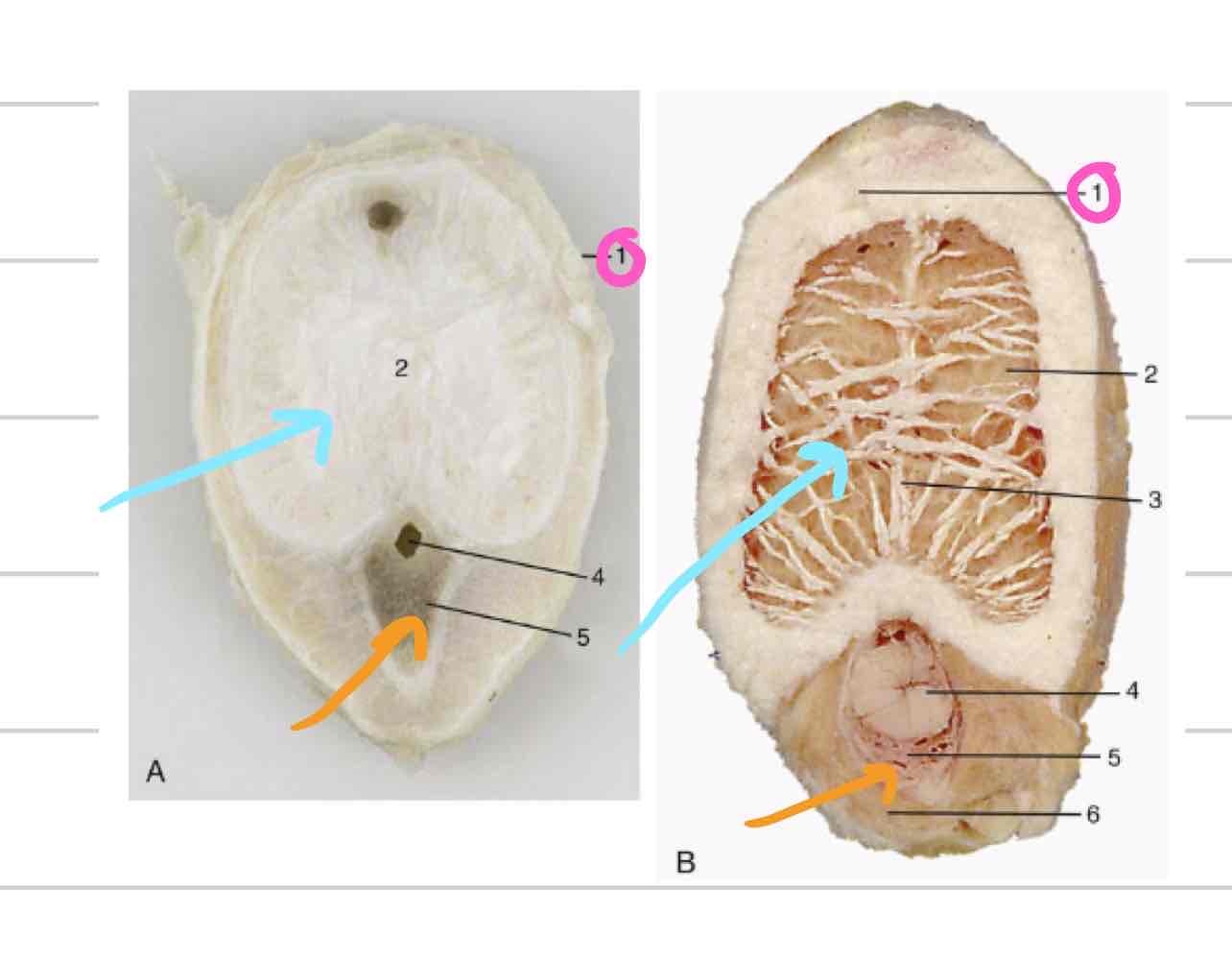
Accessory reproductive glands
Create and secrete fluid that sperm exists in during ejaculation
Feeds and keeps sperm alive
Increases amount of area sperm can be dispersed
4
Ampullae
Vesicular glands
Prostate
Bulbourethral glands
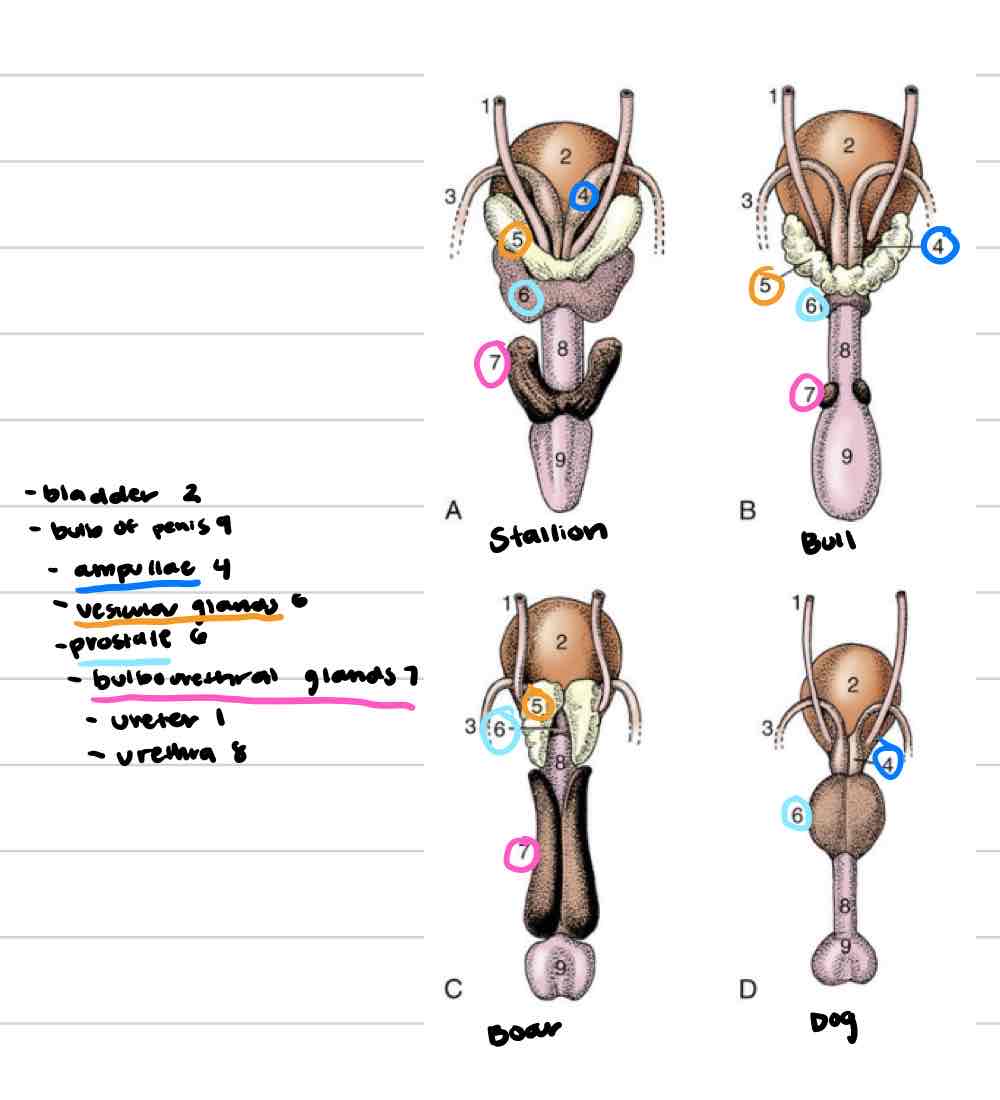
Ampullary glands
(Blue) Enlarged portion of deferent duct
Near or on top of bladder
Shares duct with vesicular gland that allows both glands to secrete fluid into deferent duct
Not found in boars or tomcats
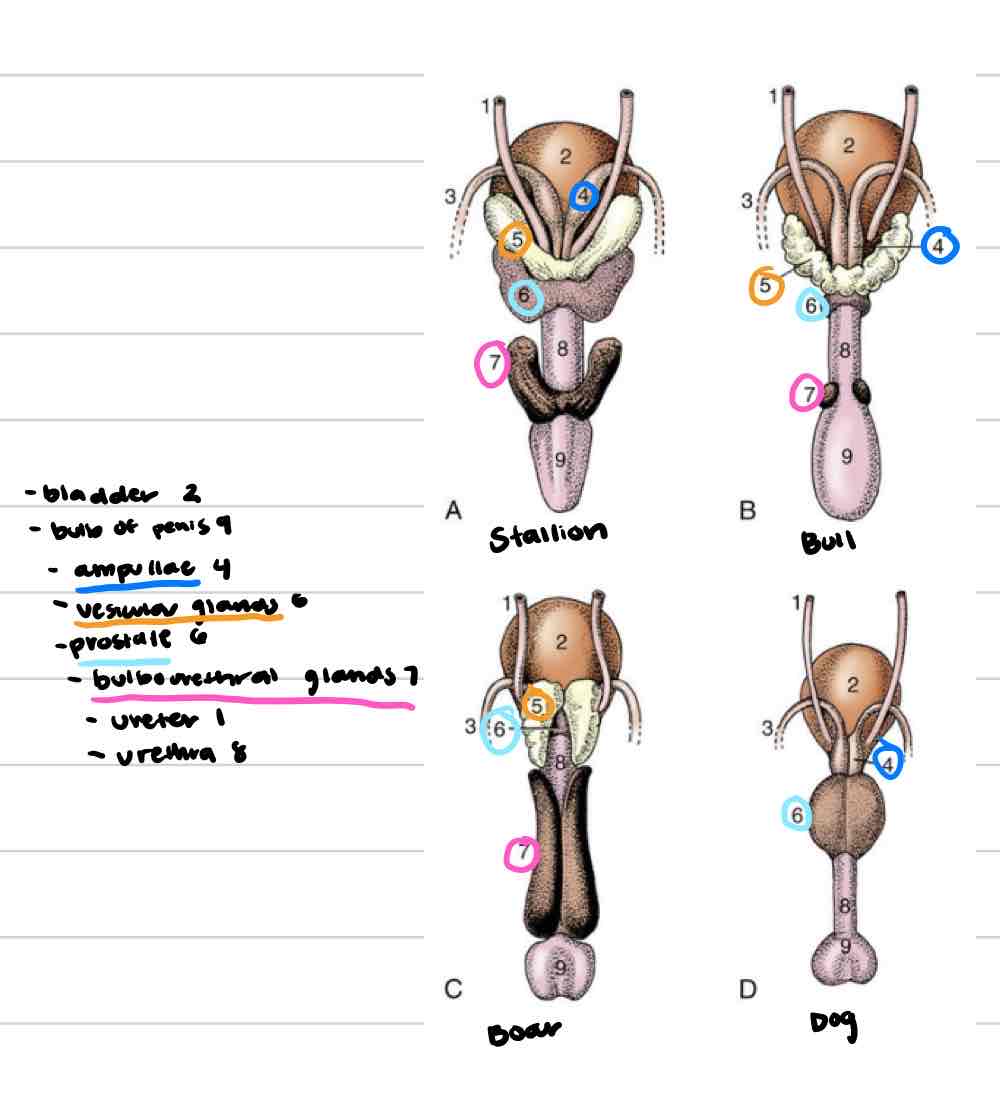
Vesicular glands
(Orange) Lateral to deferent ducts, shares duct with ampullae
Vary in appearance based on species
Horses: large, smooth, bladder-like
Other domestics: bumpy, thick walled
Not present in dog or cat
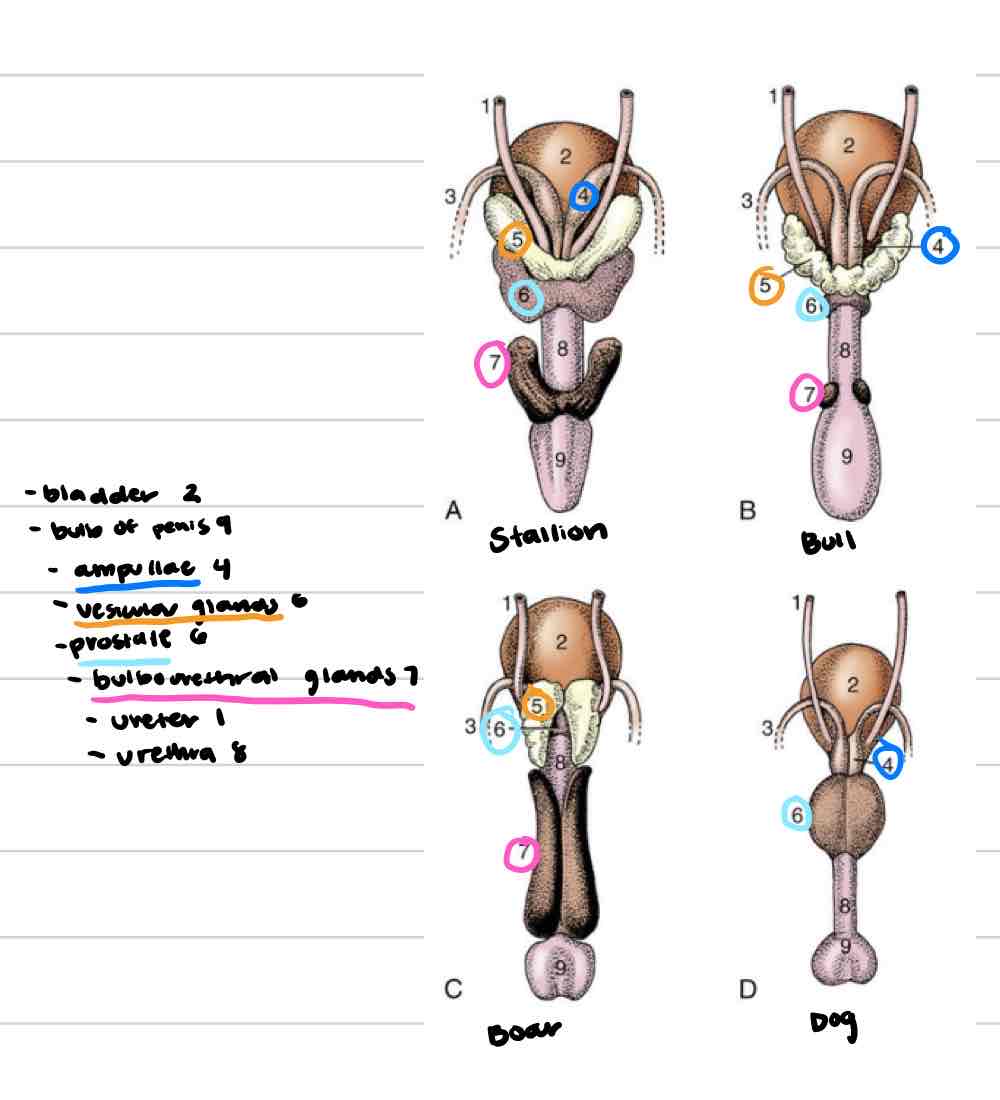
Prostate gland
(Light blue) 1 gland with 2 parts
One part is spread through a portion of urethra wall
Second part is external to urethra, surrounds from outside
Some species have both parts (dog/cat) and some only have one
Very well developed in dog and cat
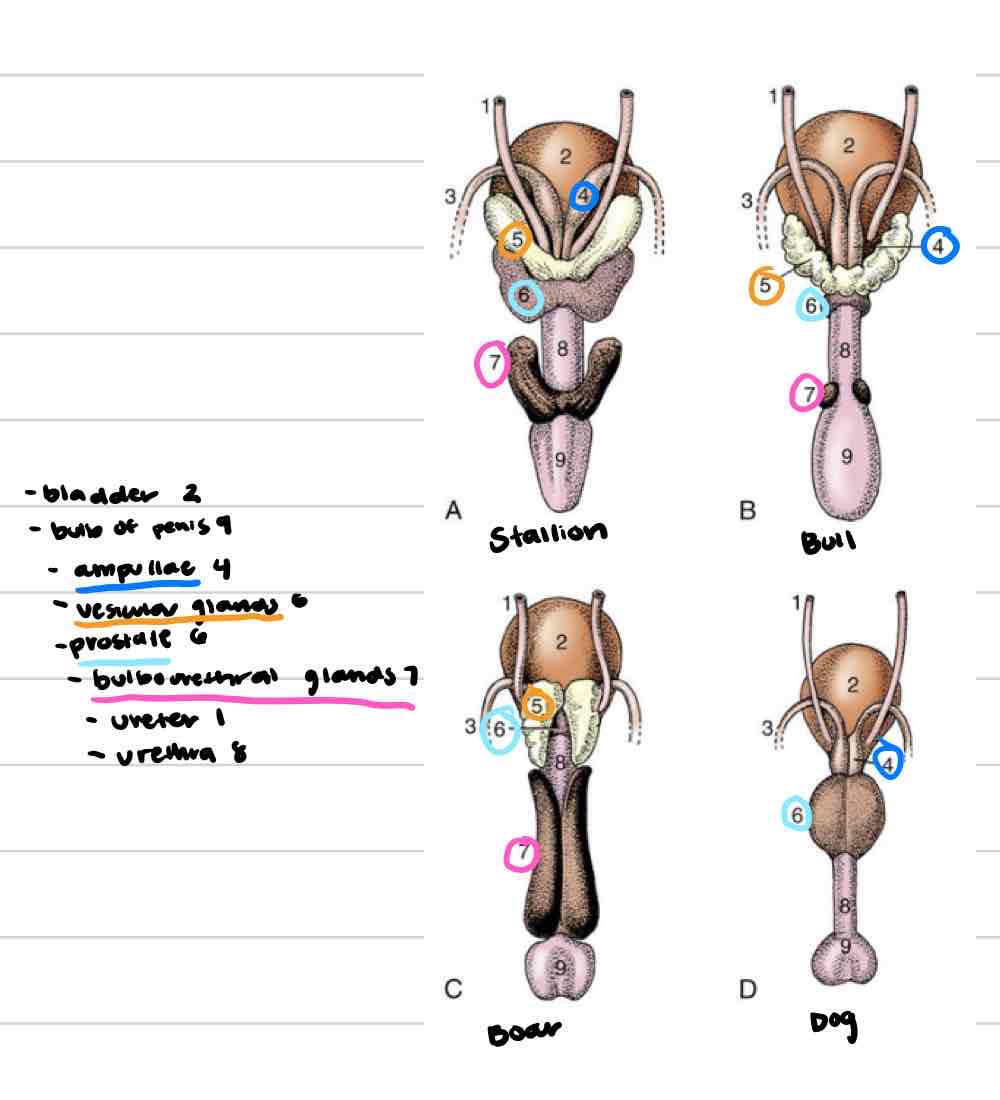
Bulbourethral glands
(Pink) Paired, dorsal to urethra
Most distal of accessory repro glands
Not present in dog, very small in cat
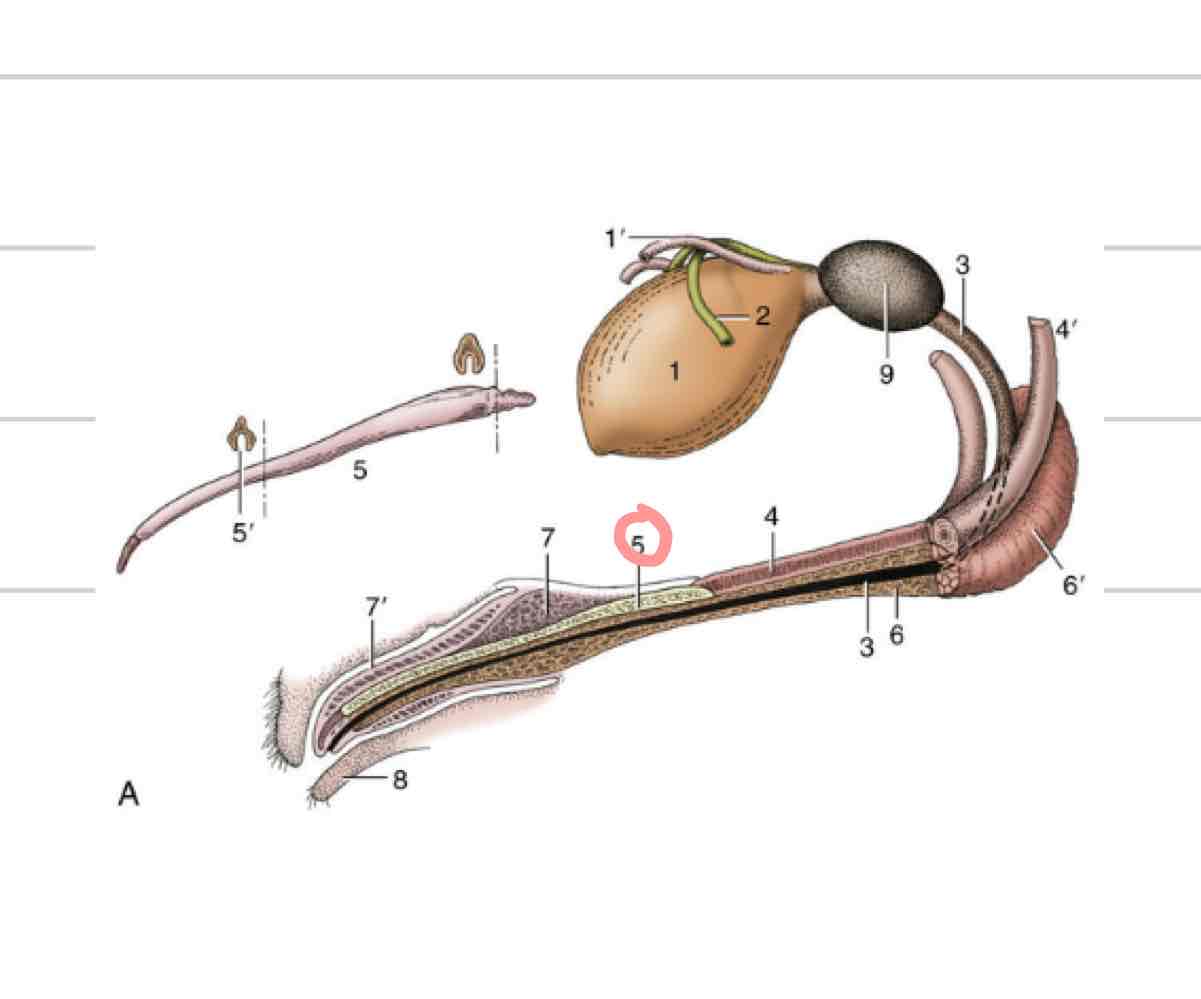
Penis/Prepuce
Suspended below trunk in all species except cat (circle is os penis)
Prepuce/sheath covers free end of penis when not sexually aroused
2 layers of prepuce
External(lamina externa): continuous with external integument
Internal(lamina interna): faces free end of penis, reflects back on itself in preputial cavity
Musculocavernous penis
erection occurs secondary to engorgement of erectile tissue with blood
Diameter and length increase with erection
Much less connective tissue to allow for blood

Fibroelastic penis
tough fibroelastic tissue, less open space
penis is firm when not erect
Does not increase much in diameter
Lengthening of penis via sigmoid flexure
Os penis
bone disconnected from skeleton
feline and canine penis
dorsal to urethra, within penile tissue for additional support and rigidity
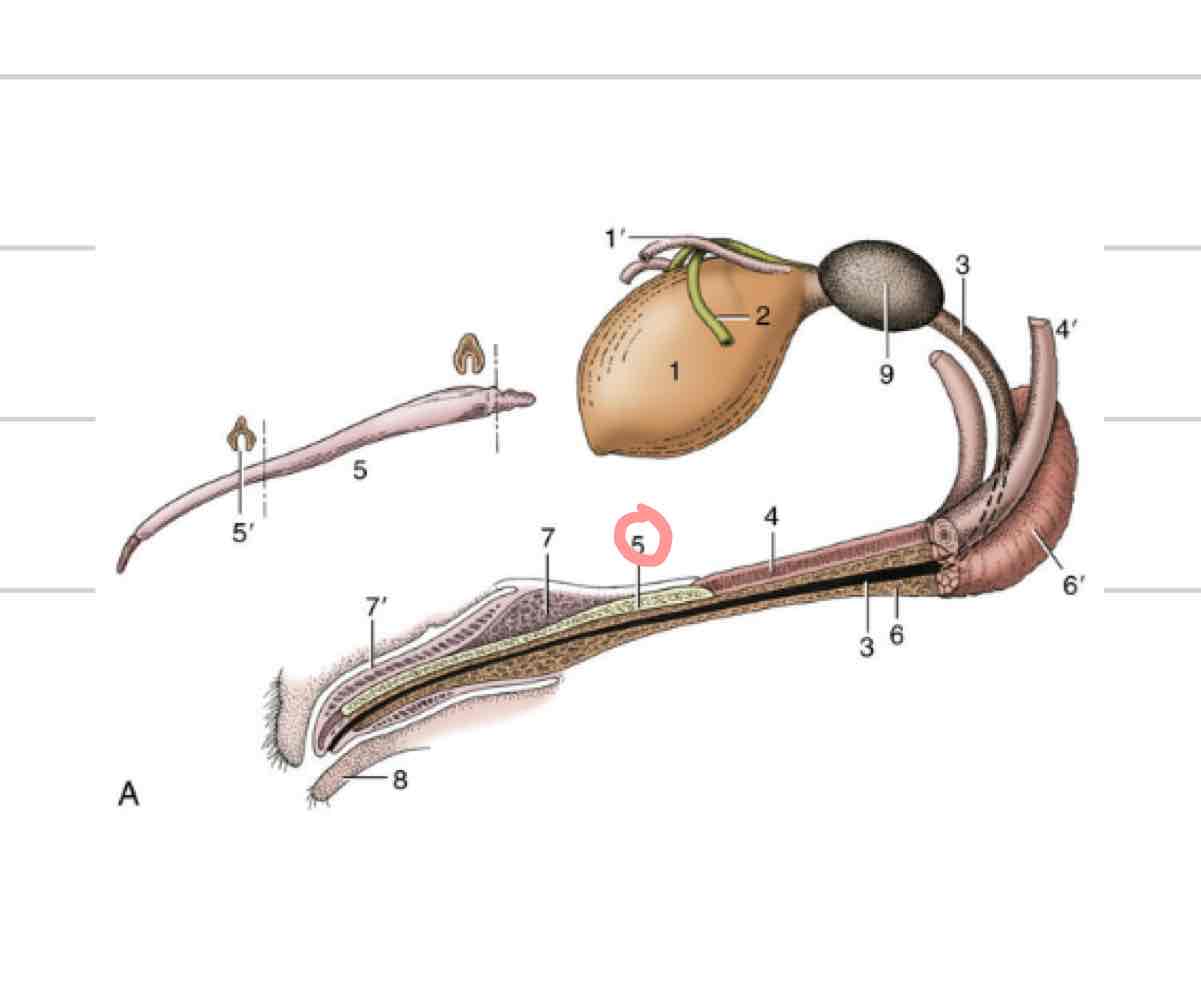
Parts of penis
Root- area of attachment, proximal
Body- main part of penis
Glans- distal part of penis

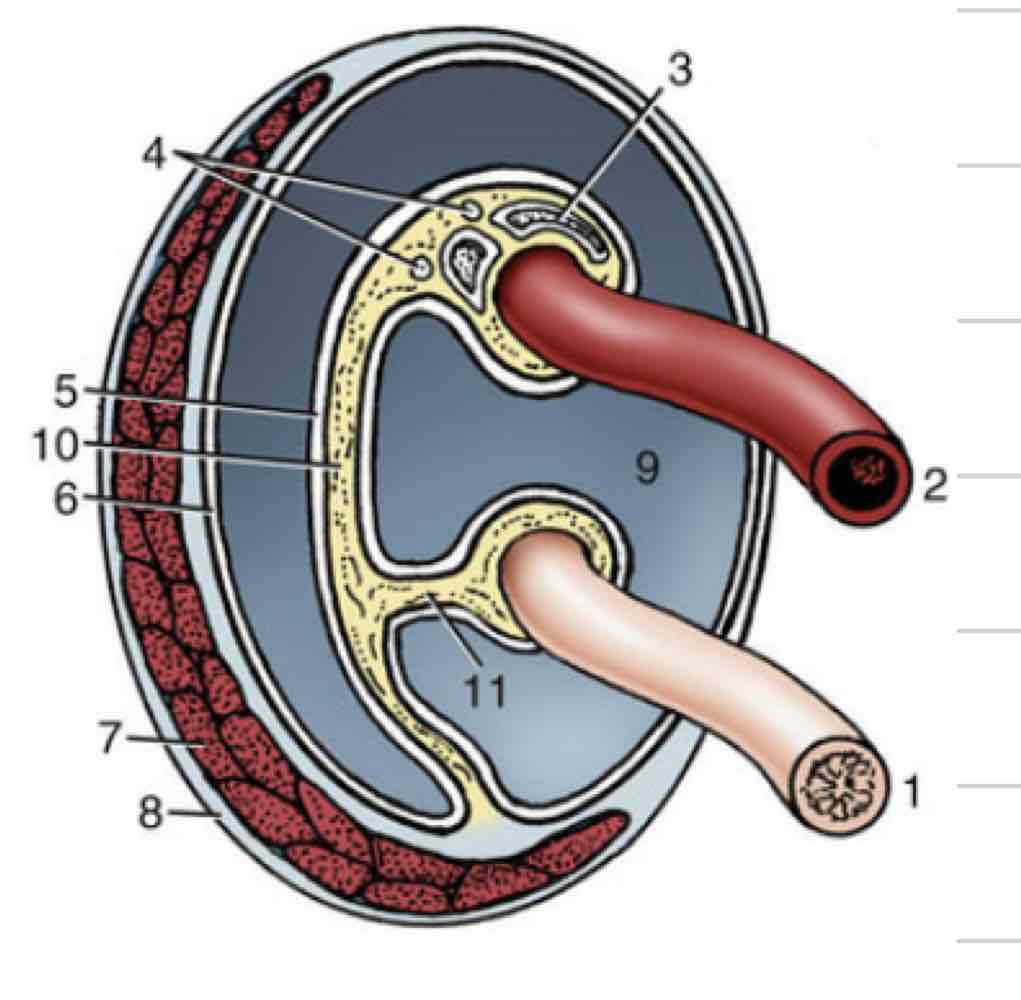
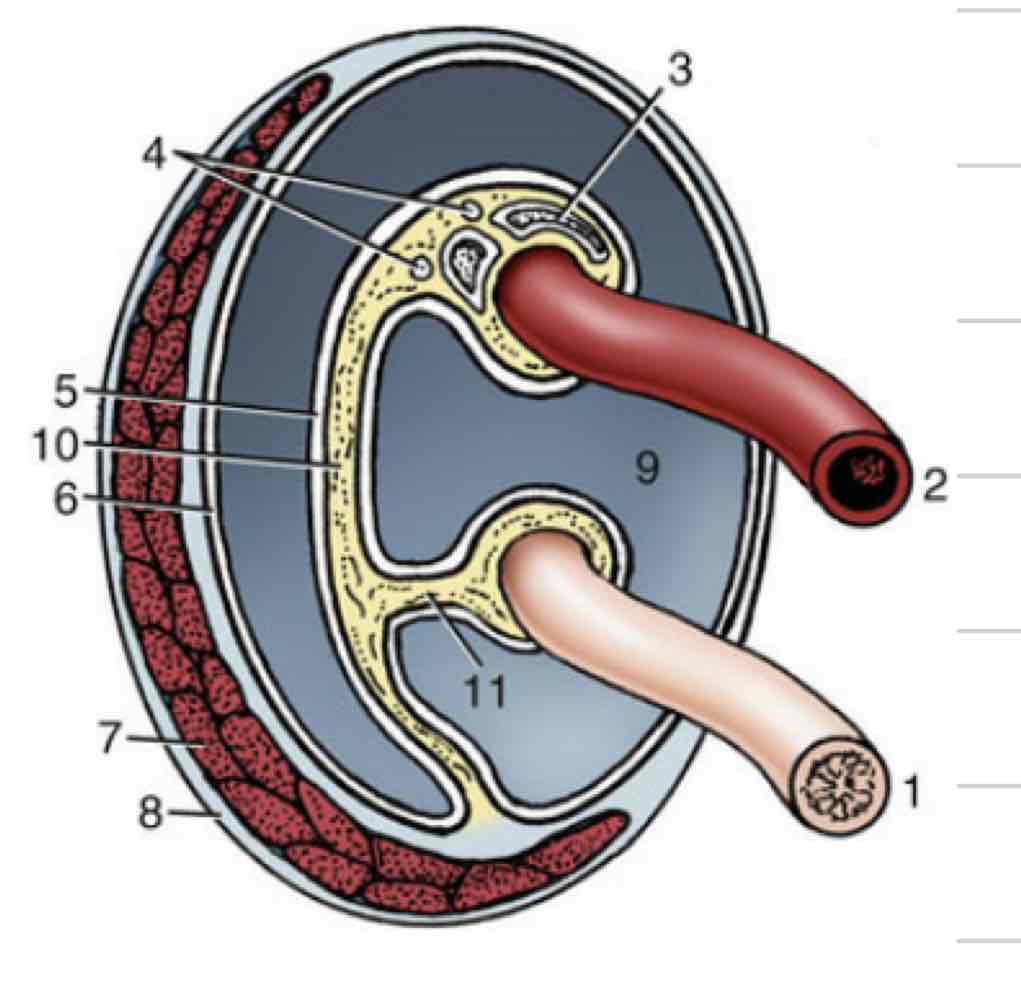
Corpus spongiosum
(Orange) erectile tissue directly enclosing urethra
allows urethra to remain patent when tissue is engorged
forms bulb and glans of penis
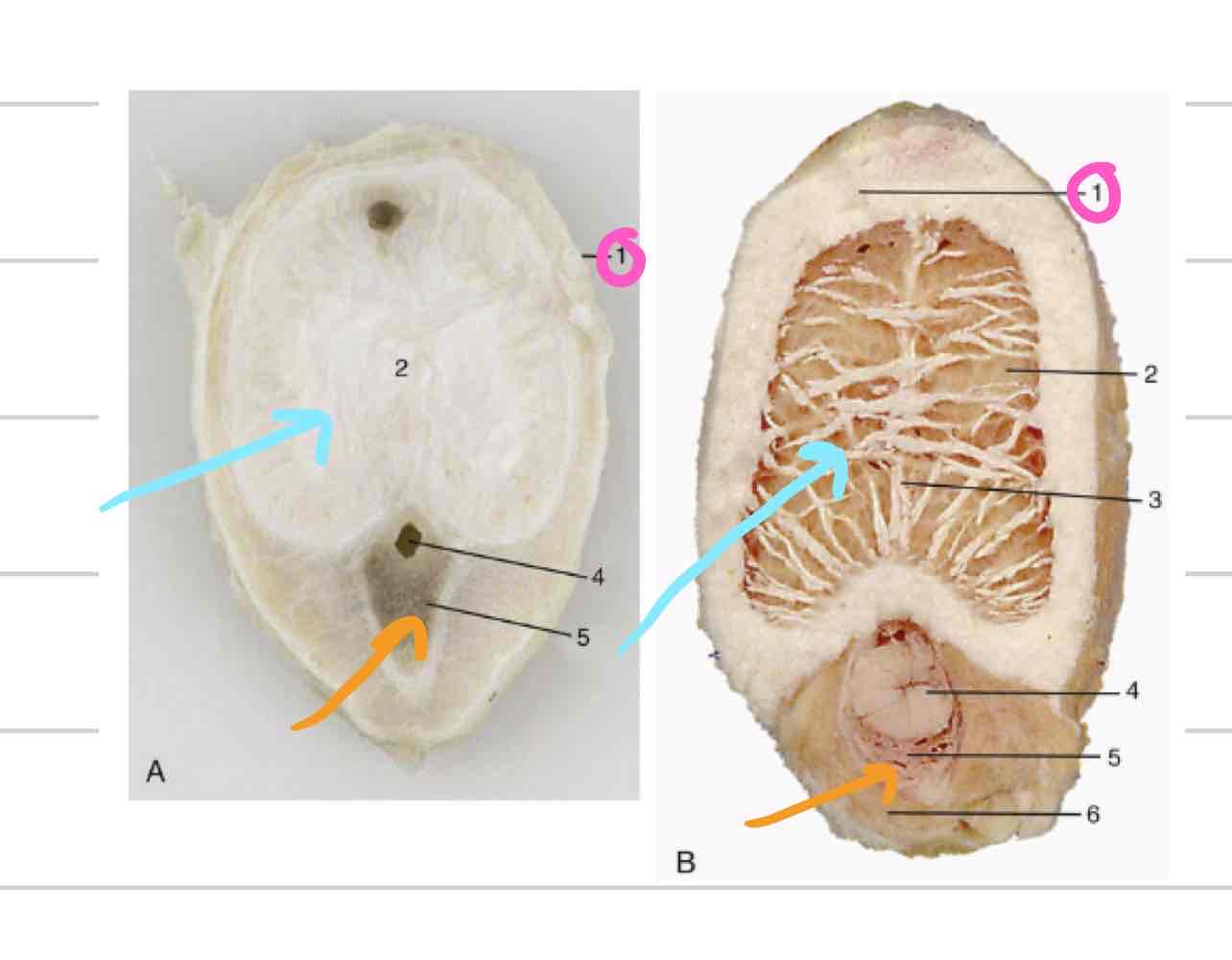
Corpus cavernosum
(Blue) paired erectile tissue that comprises bulk of the body of the penis
tapers off at glans
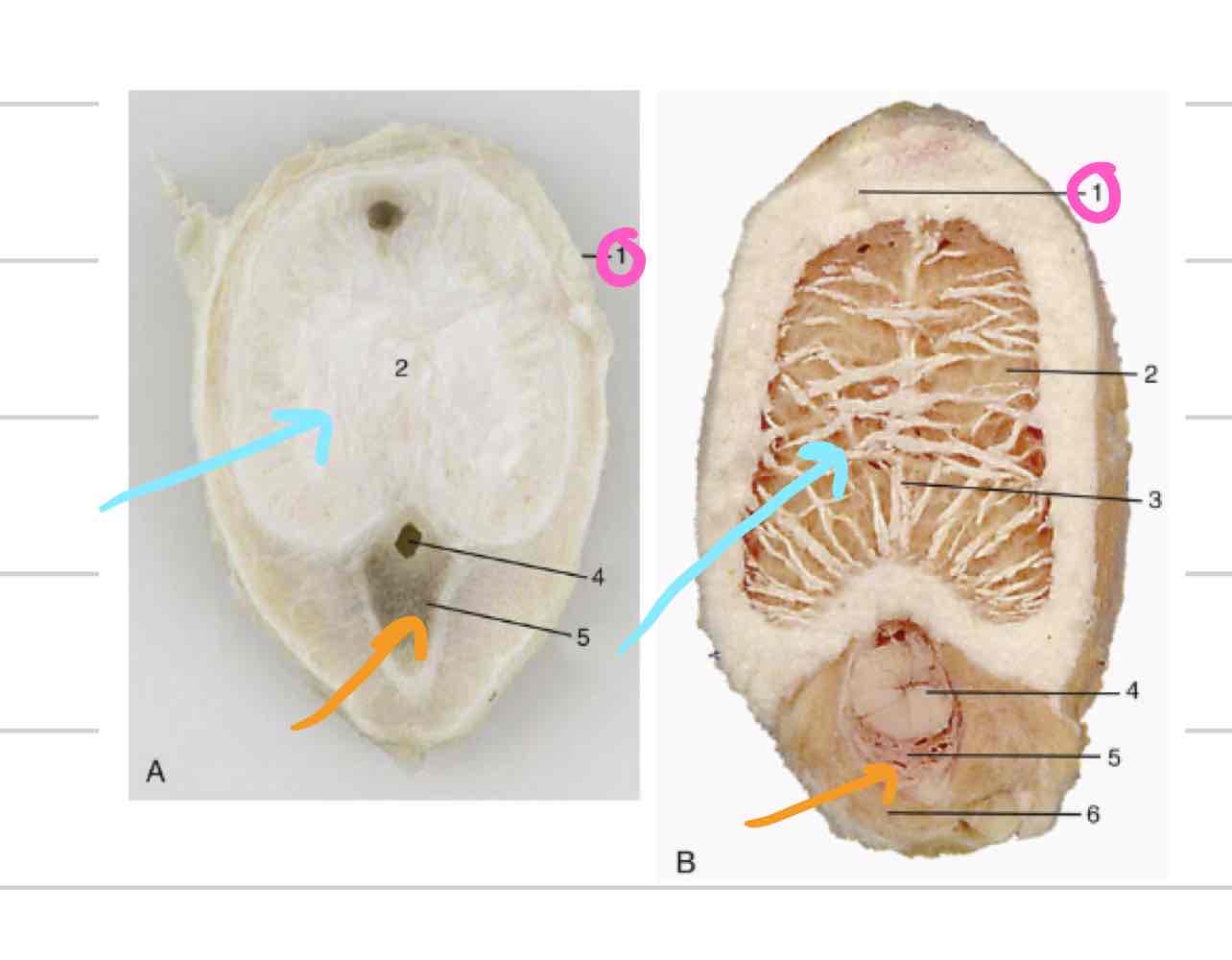
Tunica albuginea (penis)
(Pink) tough outer casing that surrounds corpus cavernosum
Retractor penis muscle
retracts penis back into abdomen or prepuce (11)
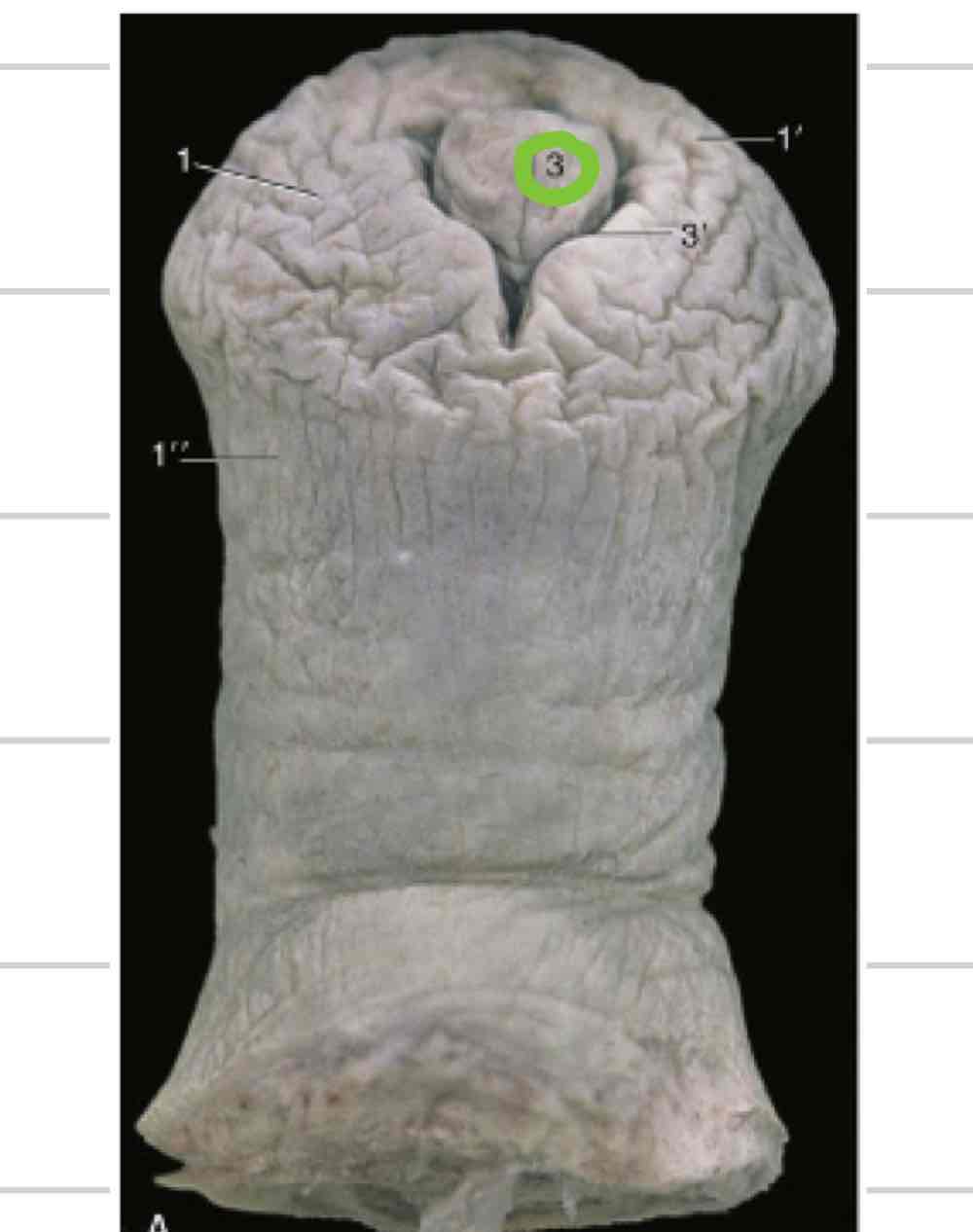
Urethral process
extension of urethra beyond glans
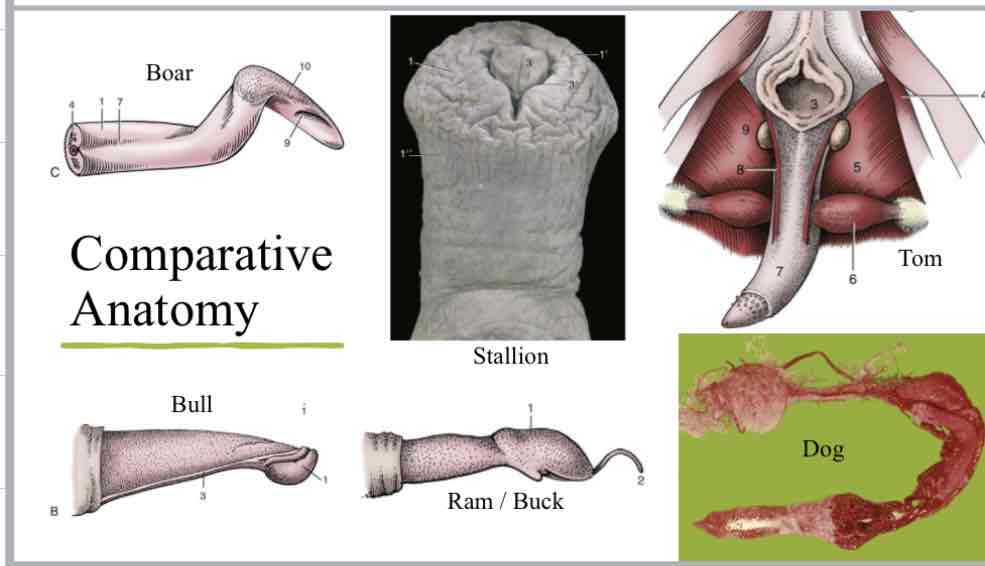
Penis comparative anatomy
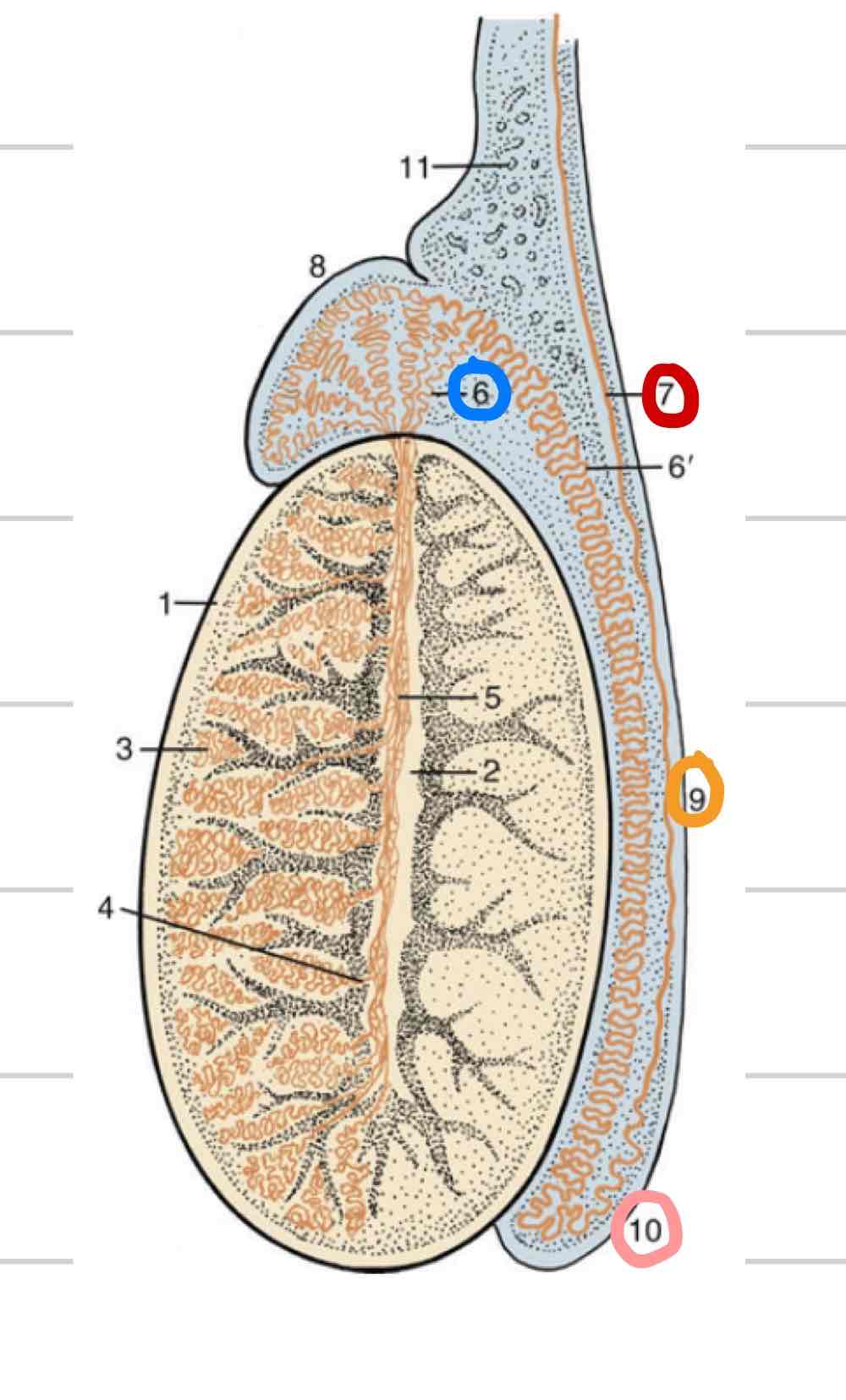
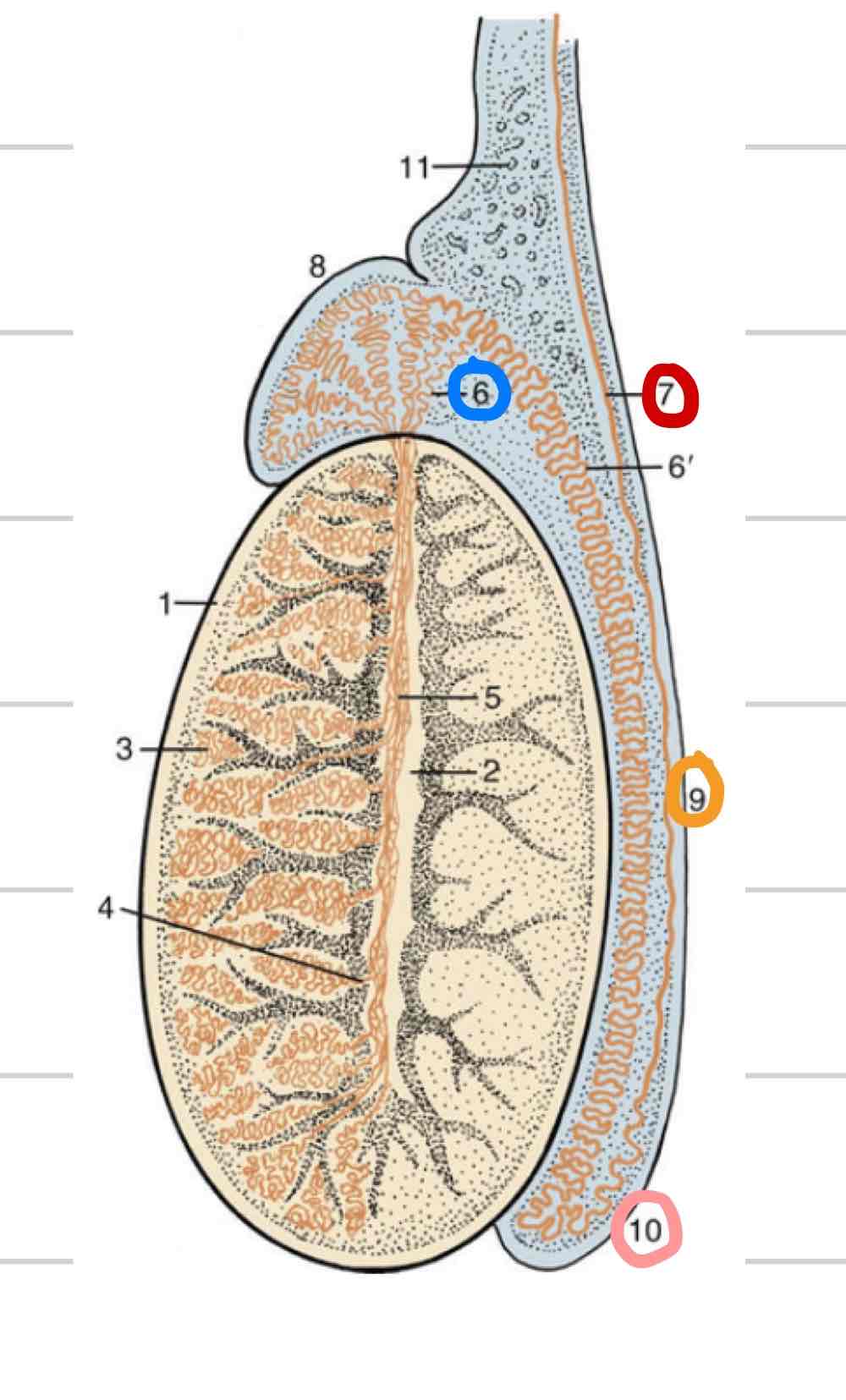
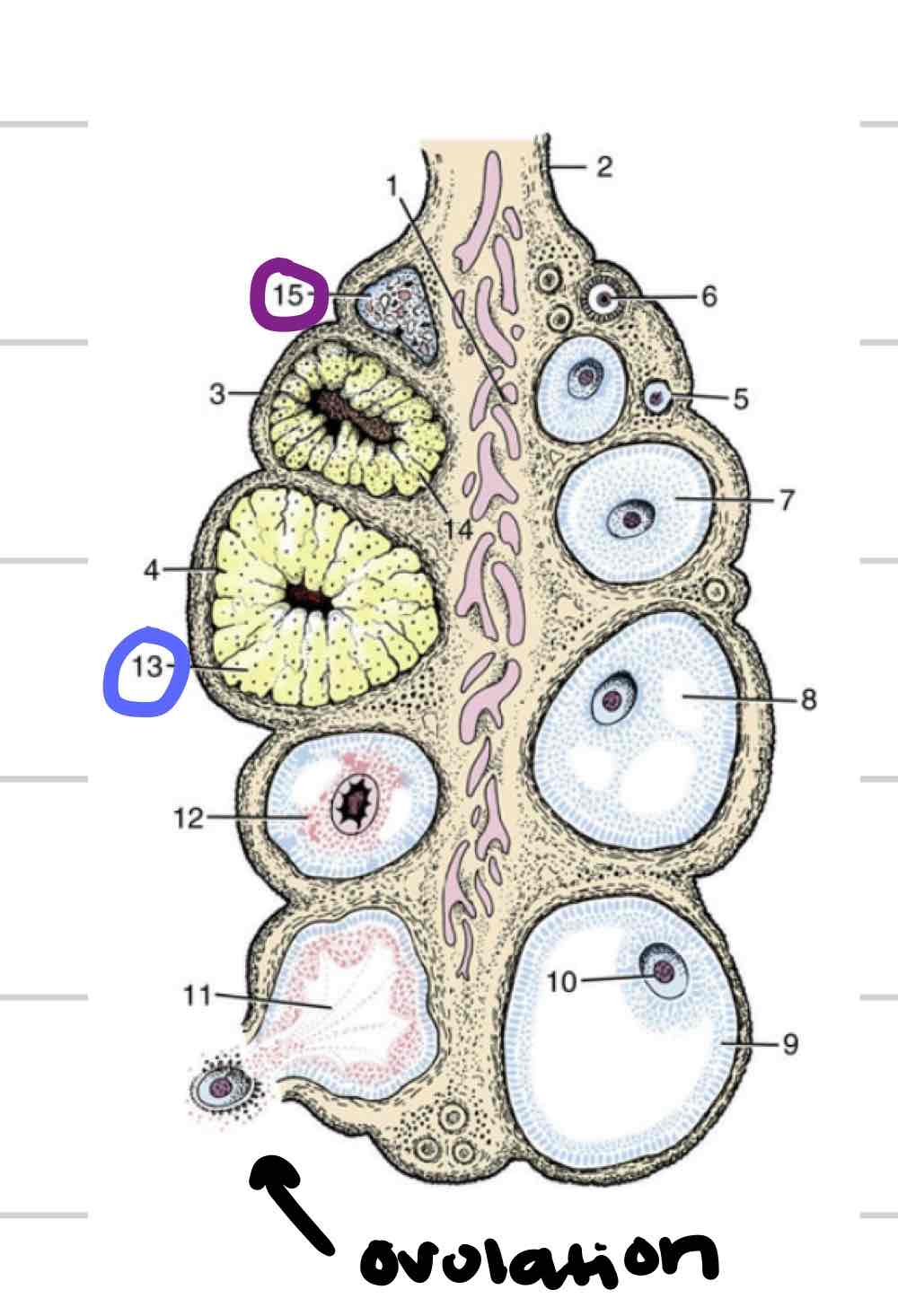
Ovaries
(Blue) Paired female gonads where gametes are produced
endocrine function, where sex hormones are produced and released
typically in dorsal and caudal half of abdomen
surrounded by tunica albuginea
Ovarian cortex
Outer layer of ovary
structures at different stages and levels of development
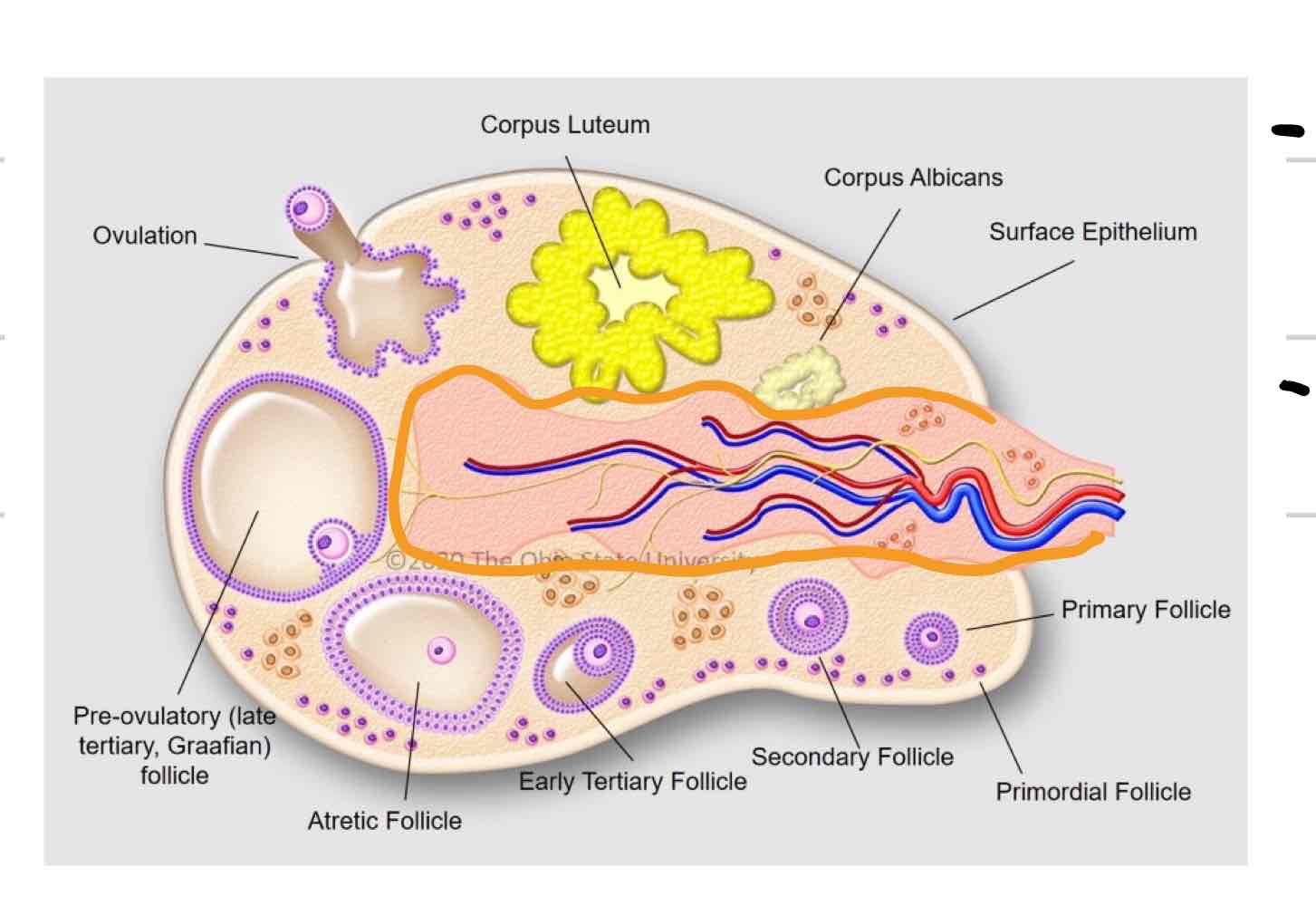
Ovarian medulla
Central layer of ovary (outlined in orange)
Mainly blood vessels, nerves, tissue, etc
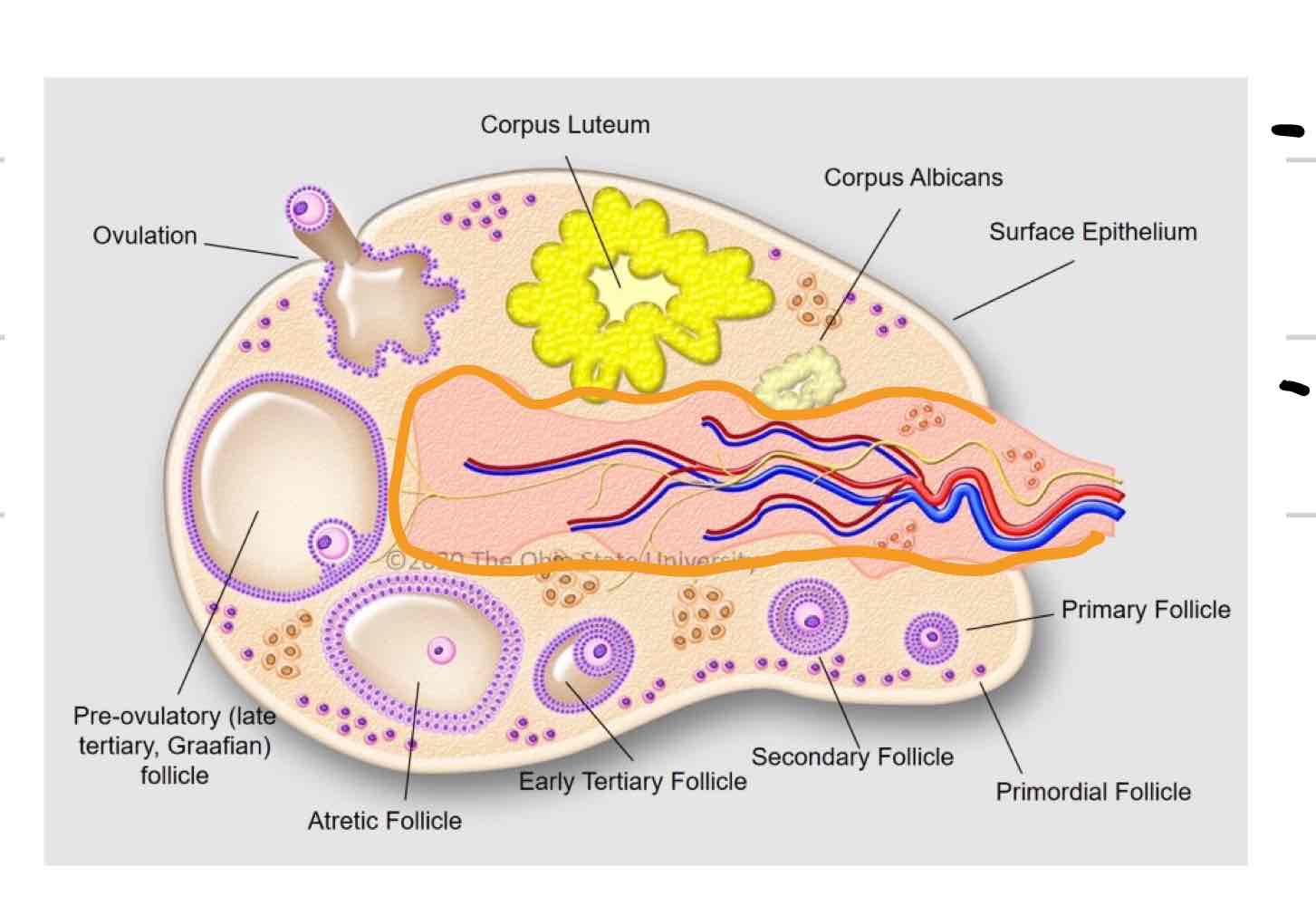
Follicle
thin-walled fluid filled structure that contains oocyte
expand in size as mature
Ovulation- release of oocyte
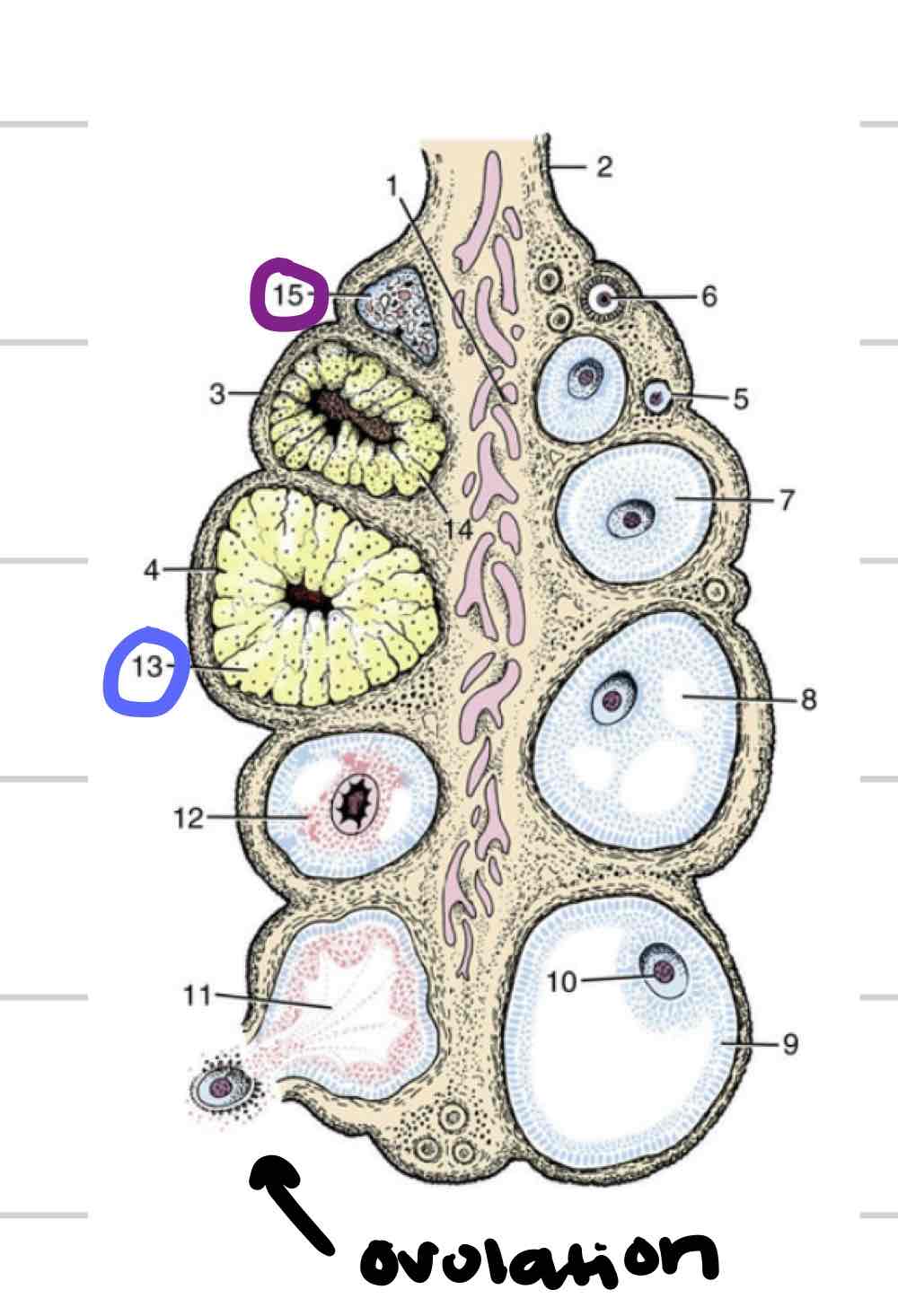
Corpus Luteum
tissue that forms where follicle ruptured (blue)
“yellow body”
secretes hormones that are required to maintain early pregnancy
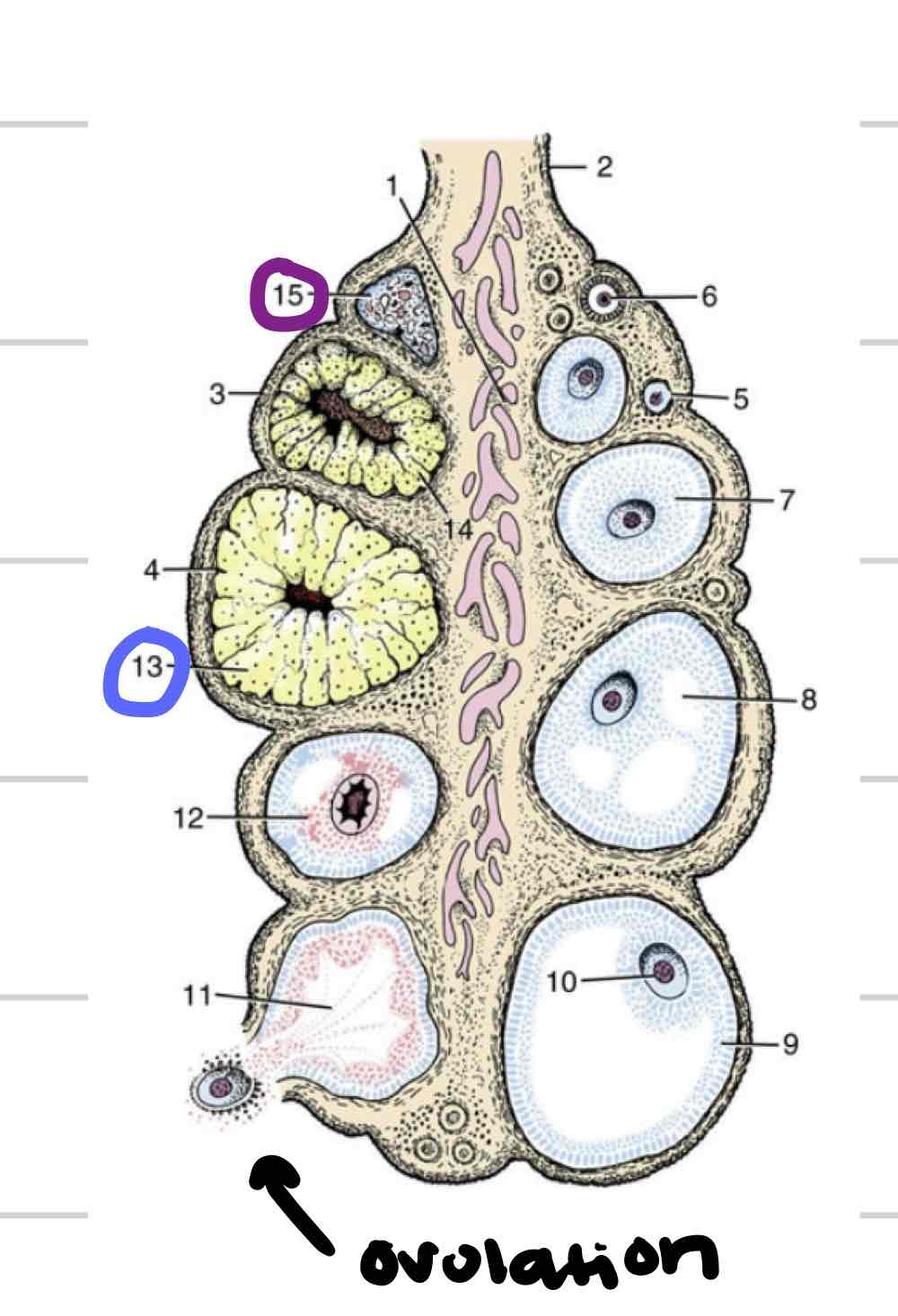
Corpus Albicans
Scar tissue remnant of CL (purple)
“white body”
Oviduct
Uterine tubes (green)
Carry ovulated oocyte to uterus
where fertilization occurs
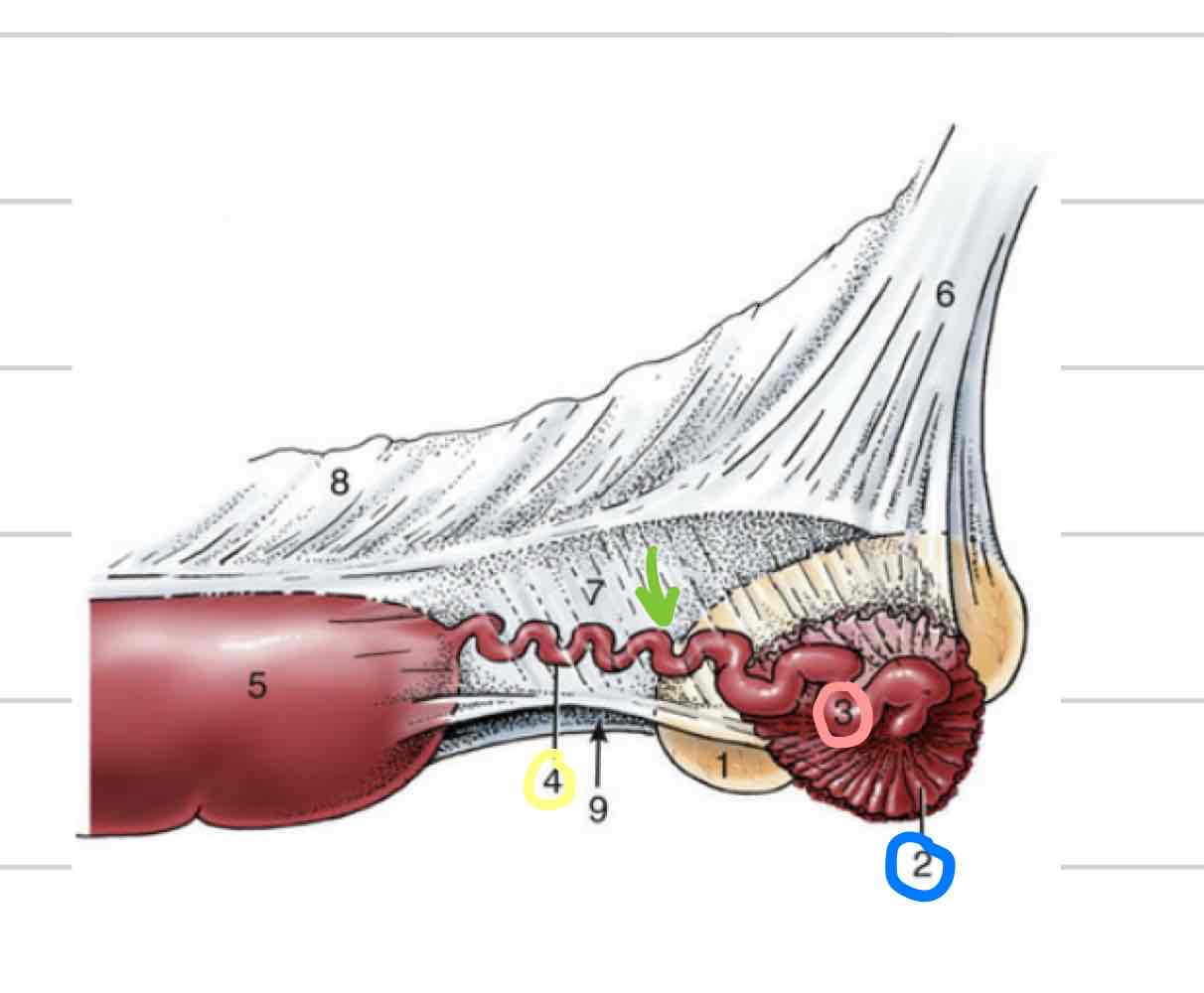
Infundibulum
Funnel/ “catcher’s mitt” (blue)
Part of uterine tube closest to ovary
Very thin walled with fingerlike projections called fimbriae
come into contact with ovary to collect ovum
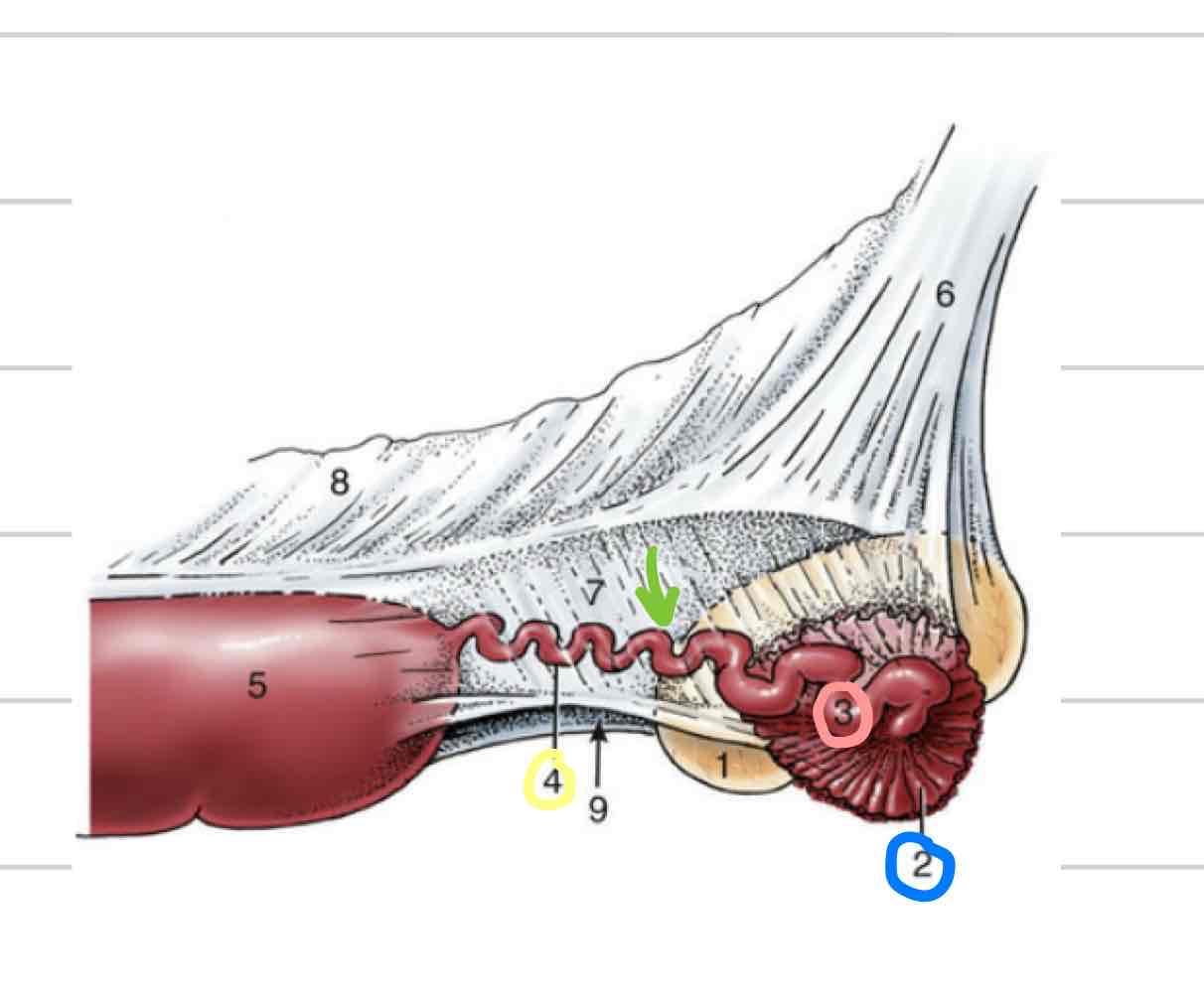
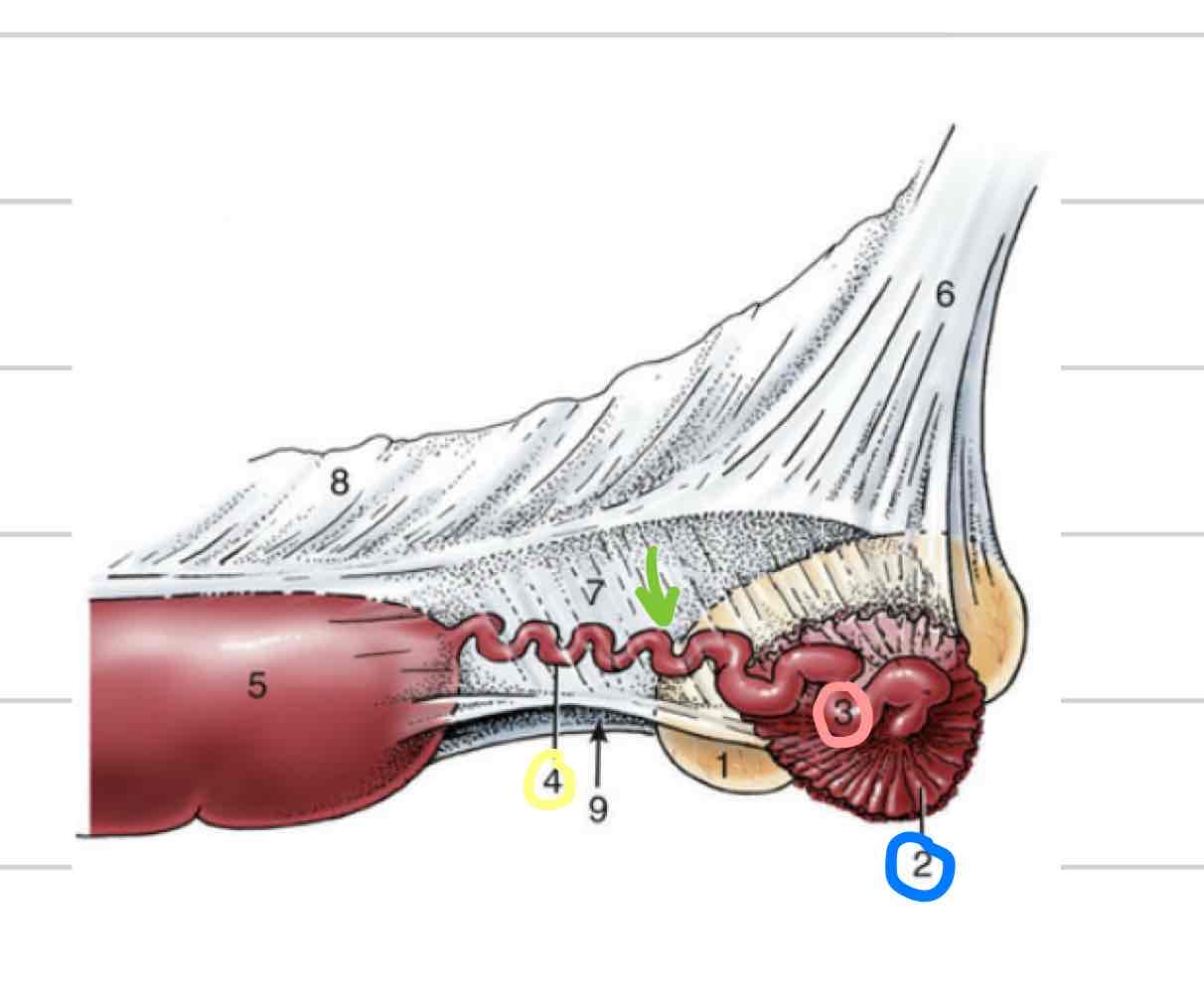
Ampulla
proximal segment closer to infundibulum (pink)
larger in diameter than isthmus
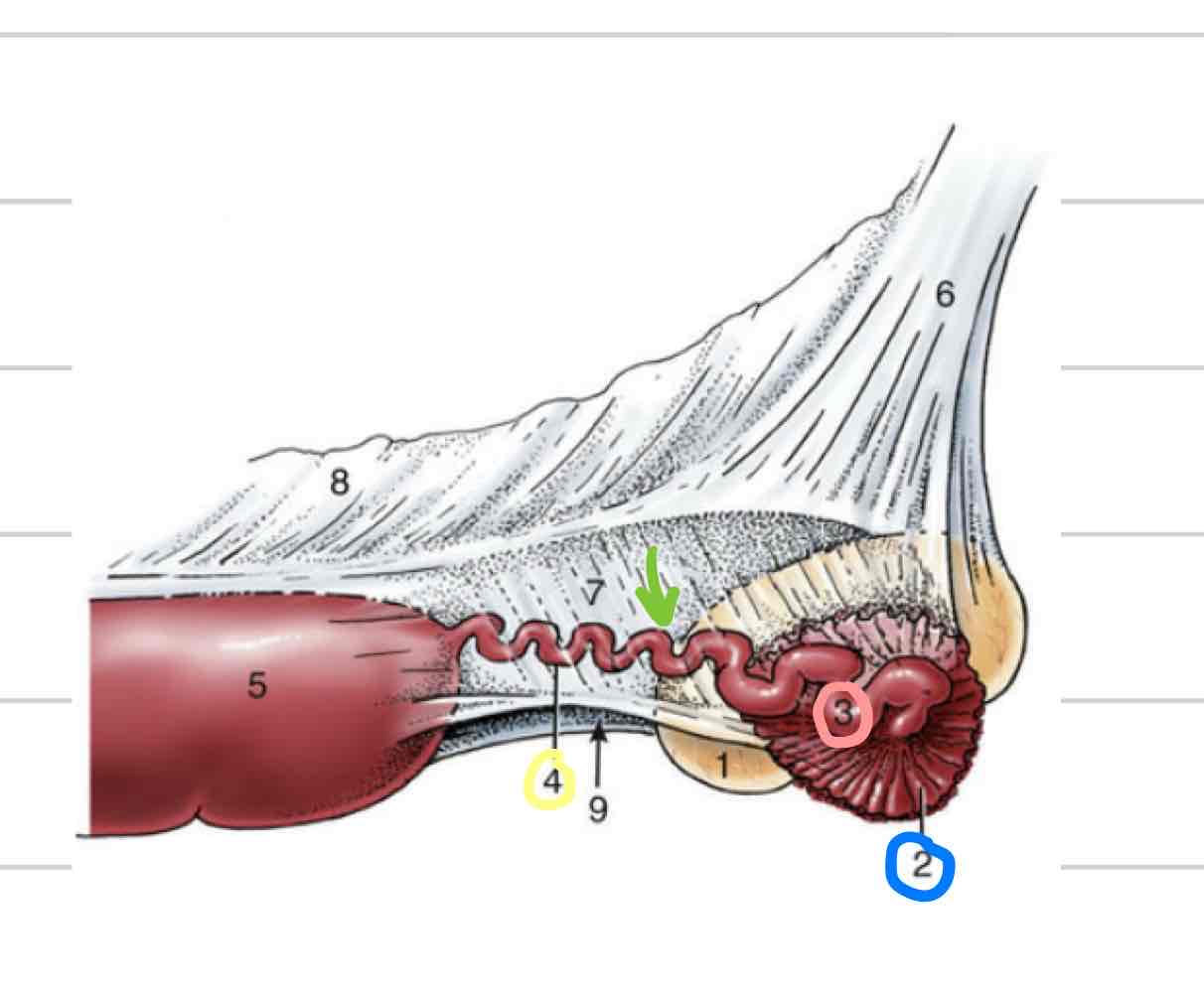
Isthmus
segment that follows ampulla (yellow)
Part of uterine tube that connects to uterine horn
Longer, thinner, convoluted (twisted)
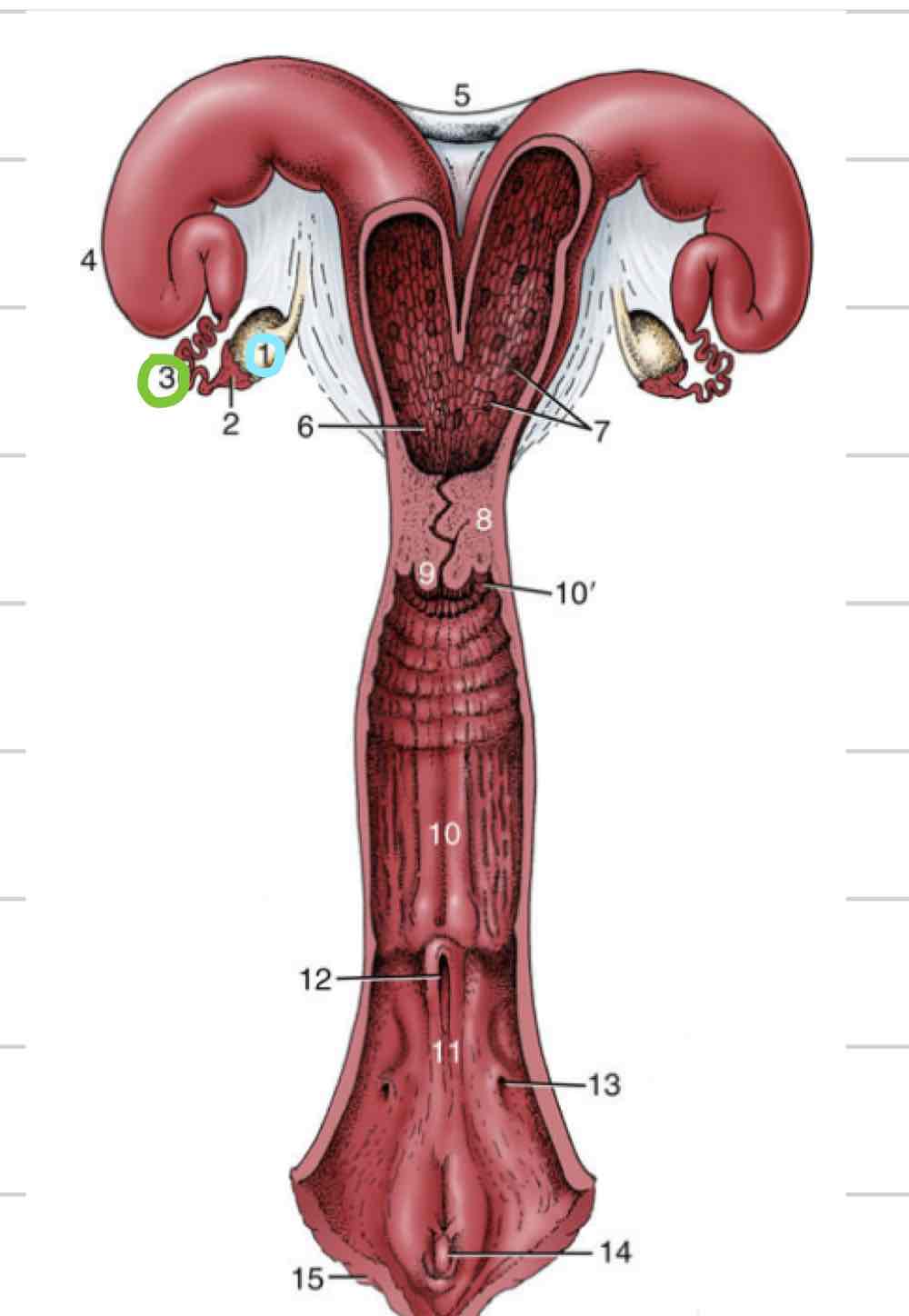
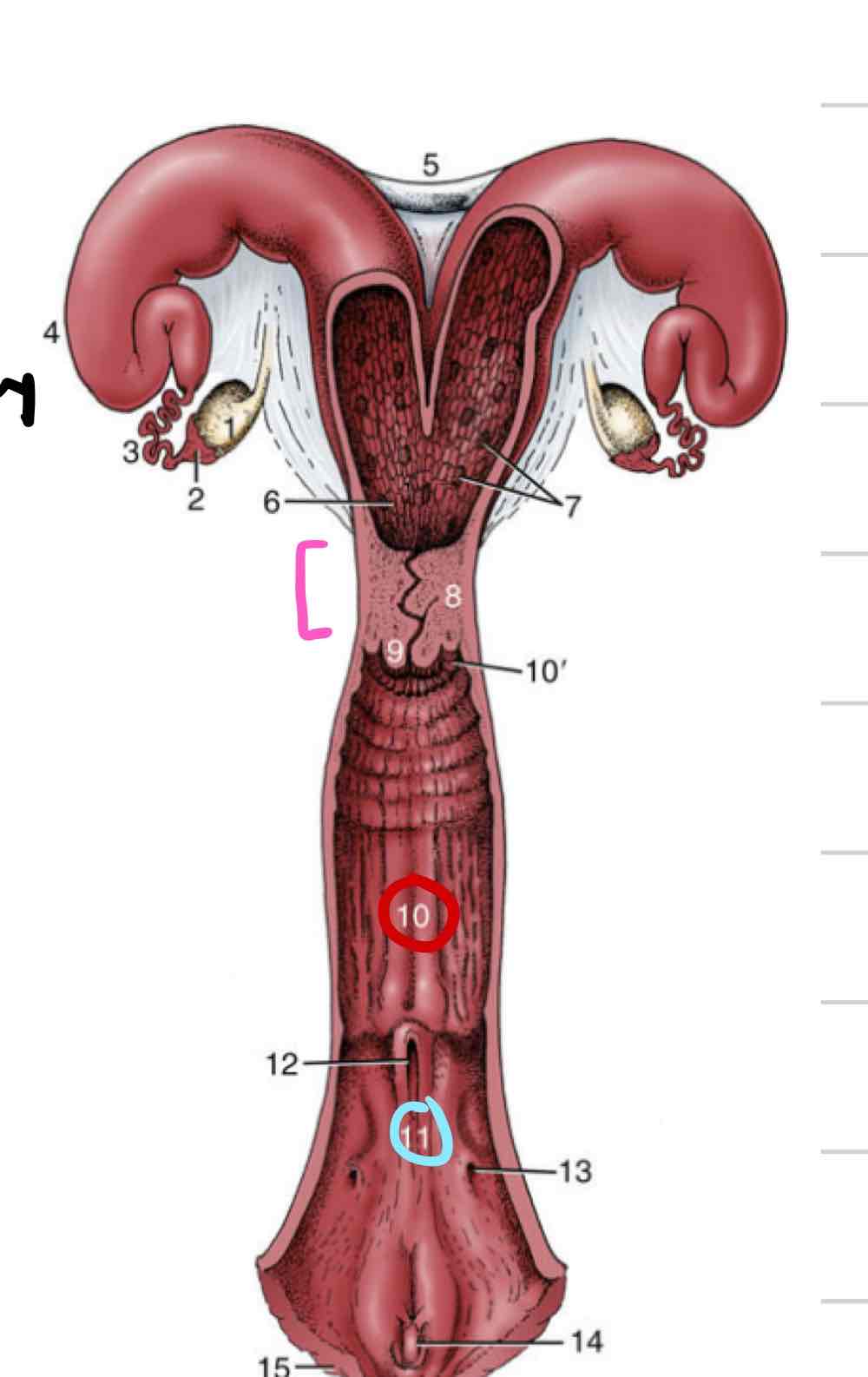
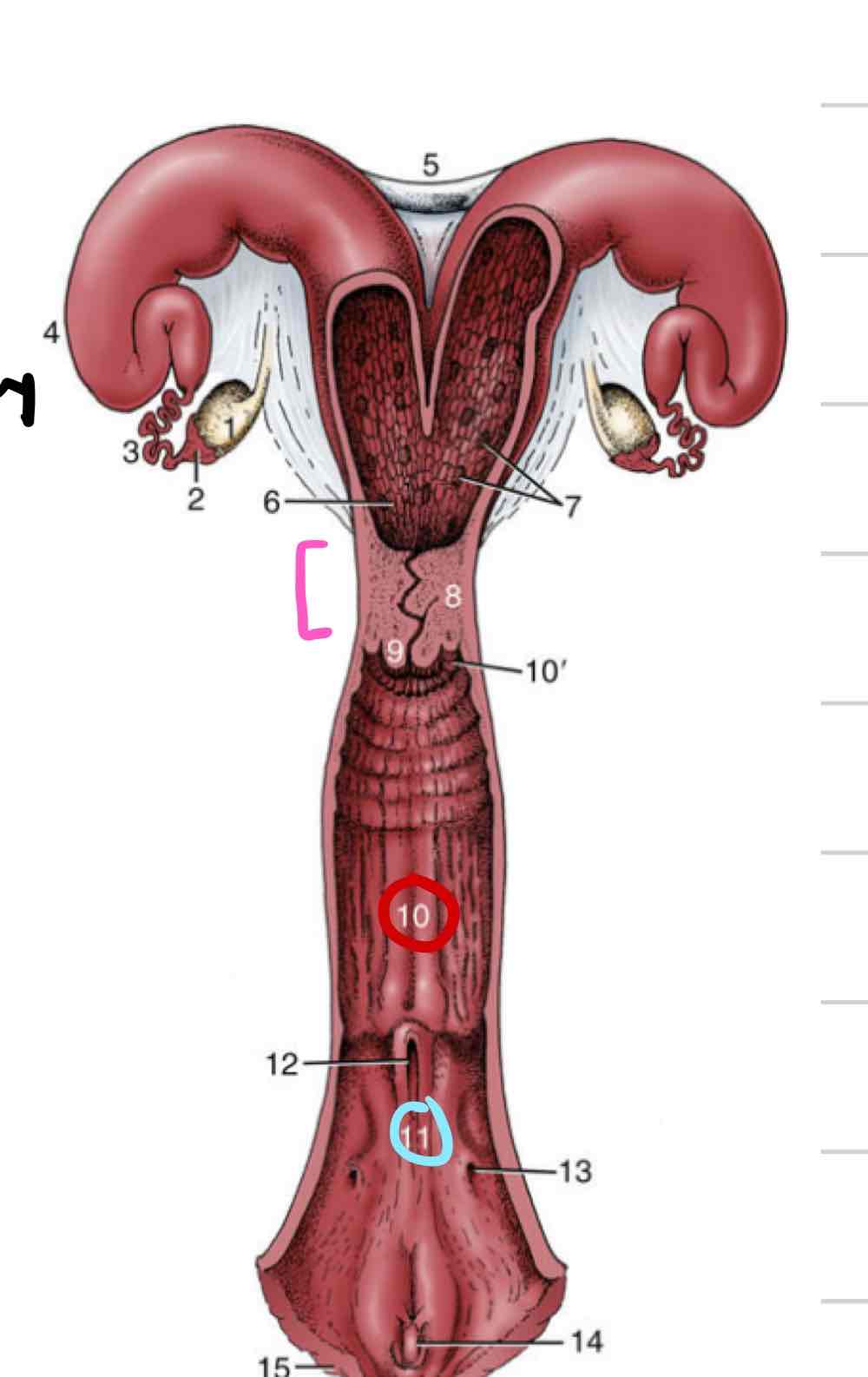
Uterus
enlarged portion of repro tract where fetus attaches and grows
Most variation between species
Two parts- uterine horns and uterine body
Layers of uterus
Perimetrium- serosal outer layer
Myometrium- muscular middle layer
Endometrium- inner mucosal layer, very glandular
Uterine horns
(4) shorter horns in species with 1 or 2 babies
Very prominent horns in litter bearing species
Uterus comparative anatomy
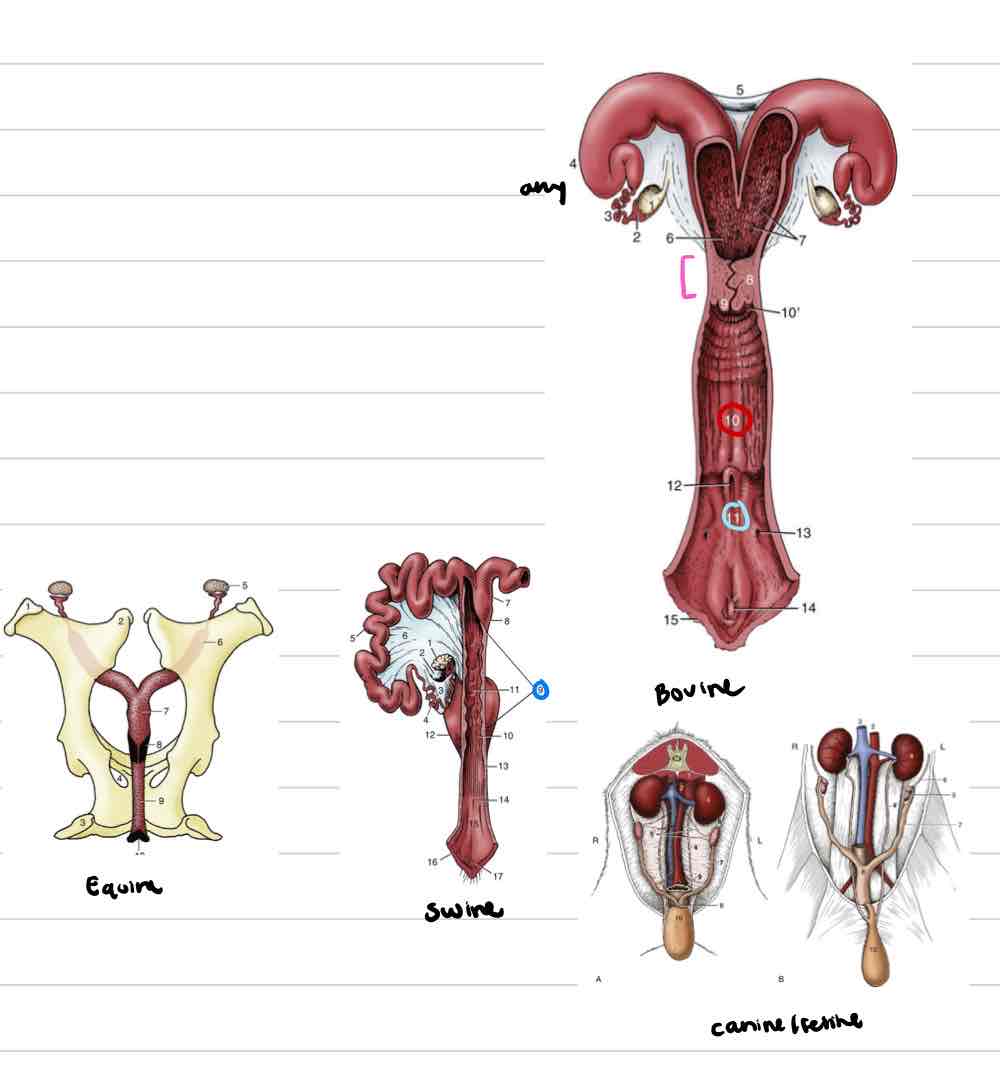
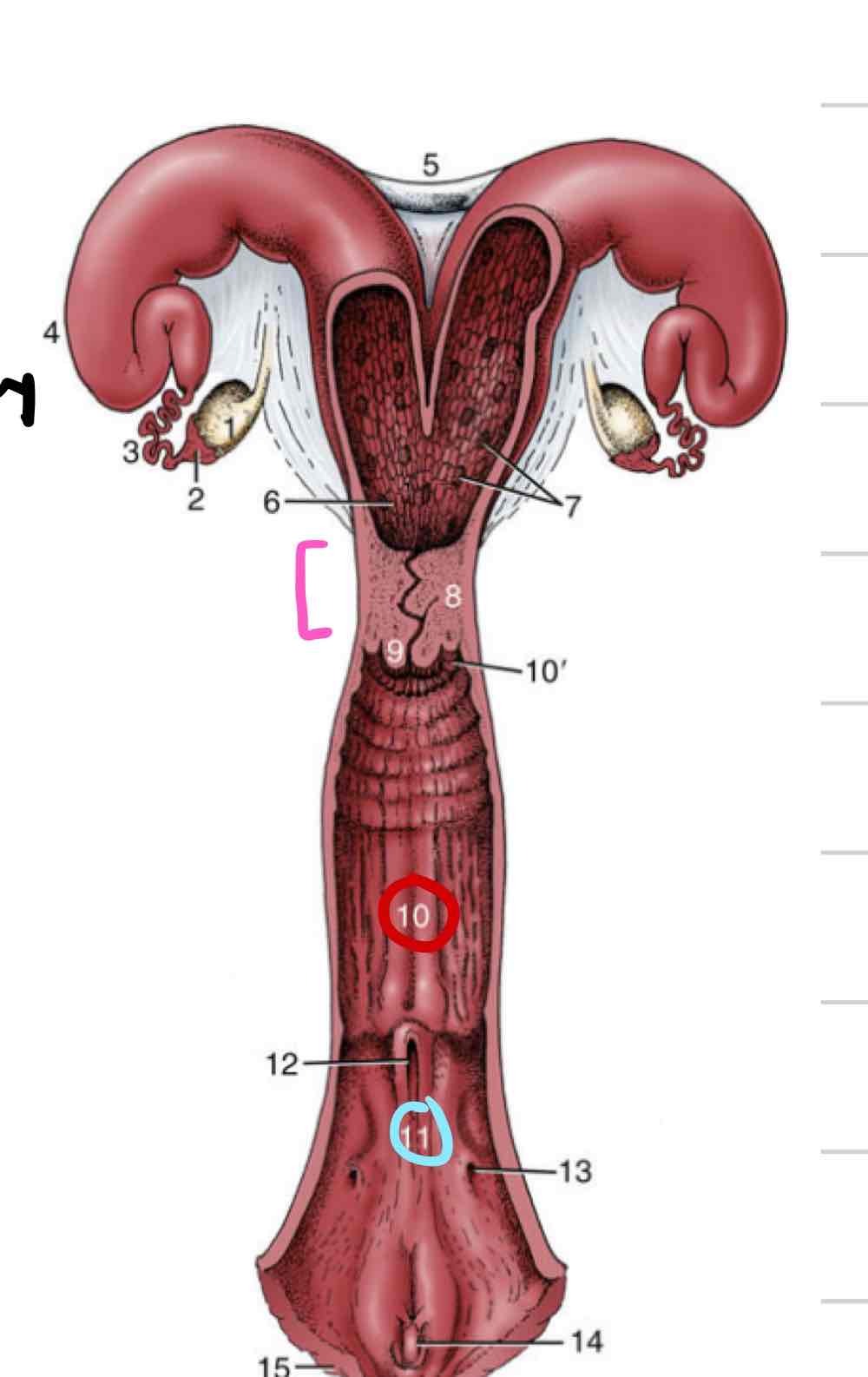
Cervix
sphincter that acts as a barrier, physical and chemical (pink)
Fibrous elastic tissue and muscle
Responsive to hormones that fluctuate through estrous cycle
Pelvic cavity
Cervix comparative anatomy
Cow/ewe/doe- firm, fibrous, several rings
Fornix formed by vaginal part of cervix bulging out into vagina
Mare/bitch/queen- simple muscular cervix with vagina part and fornix
No annular rings
Sow- very long and complicated, mucosal projections that come together to close lumen
No fornix, hard to tell where vagina begins and cervix ends
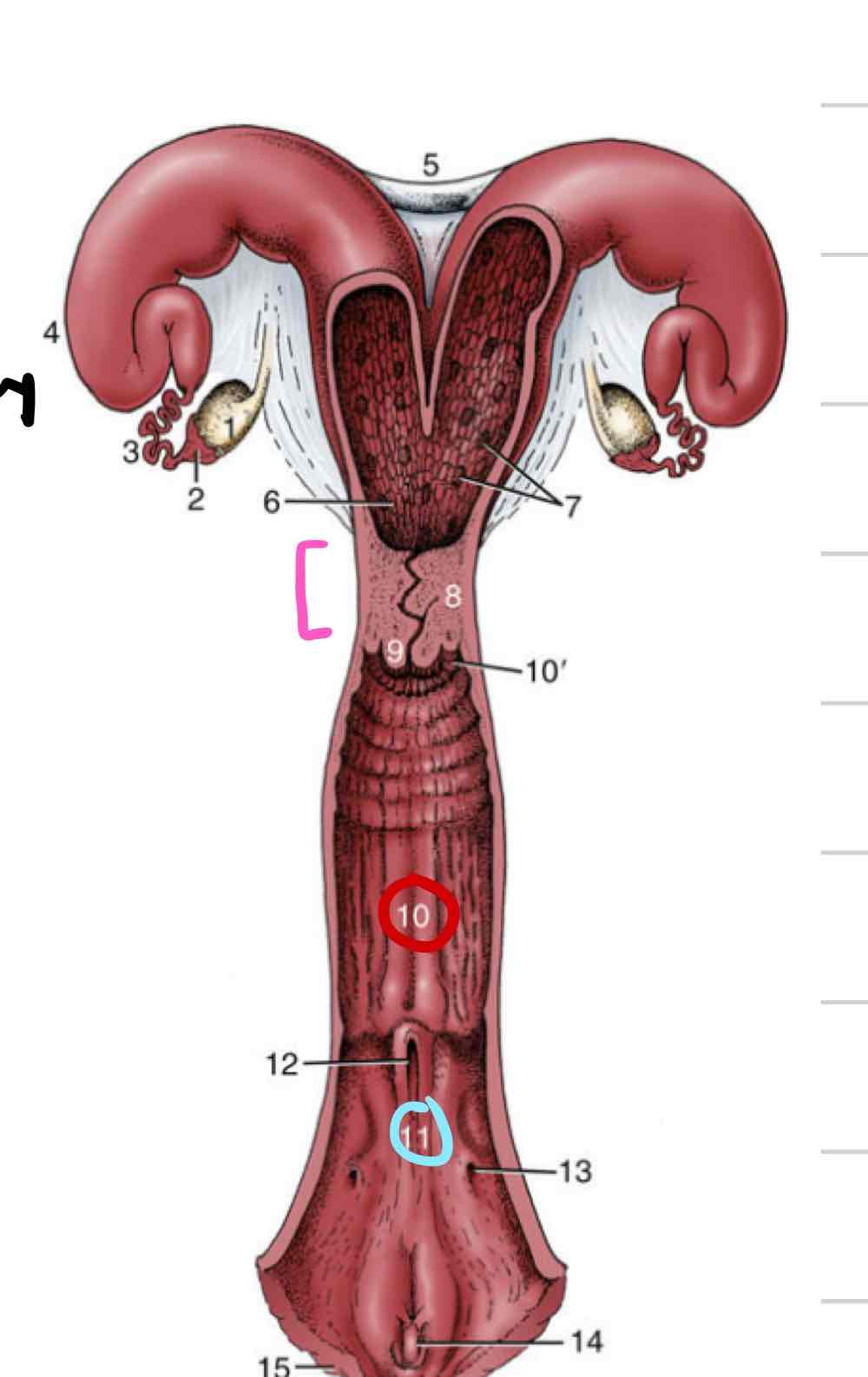
Vagina
(10) Distal to cervix
Thinner walls
Less muscular and glandular
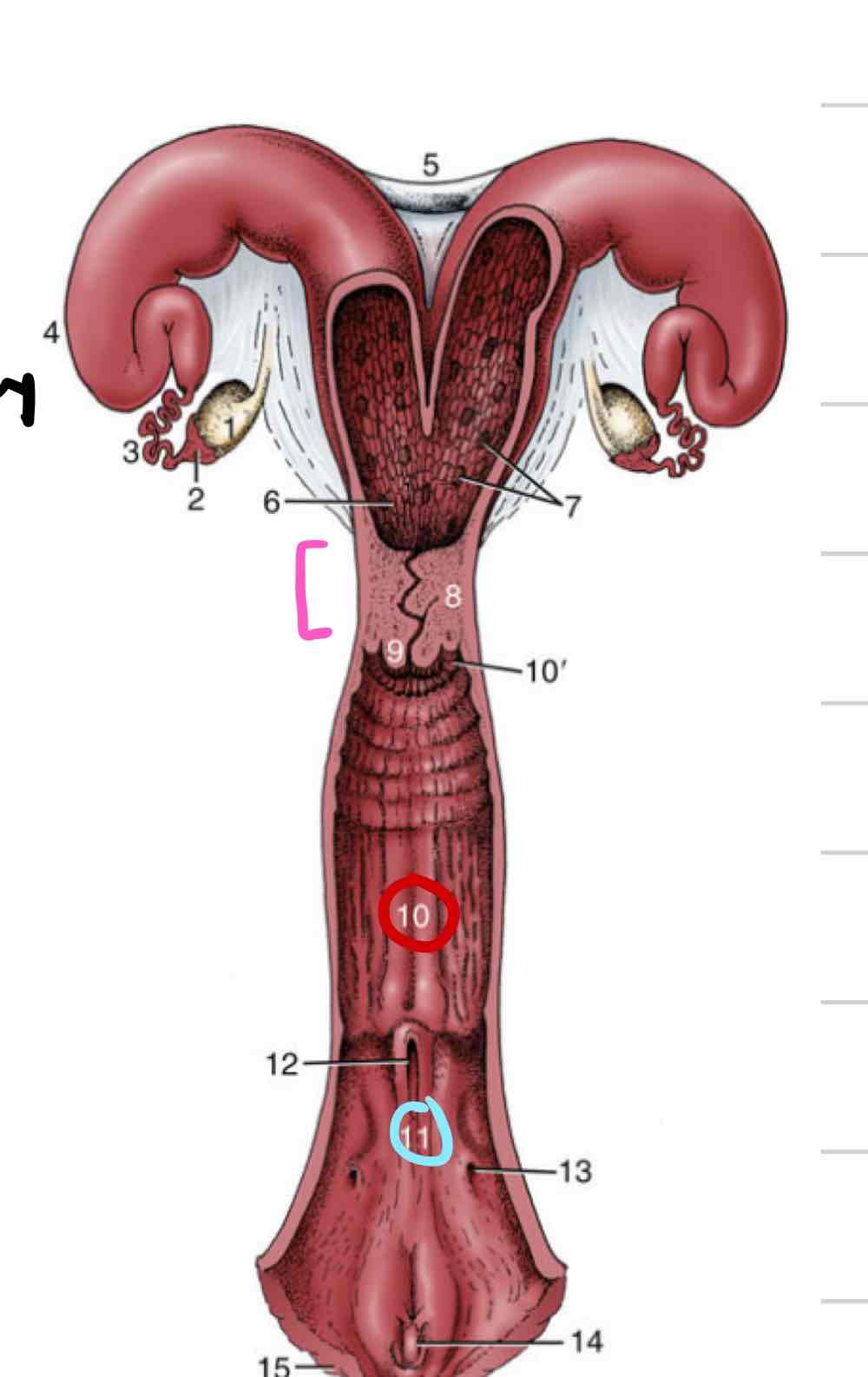
Vestibule
(11) shared repro and urinary space
somewhere in between cloaca and human tracts
urethral opening and vaginal opening
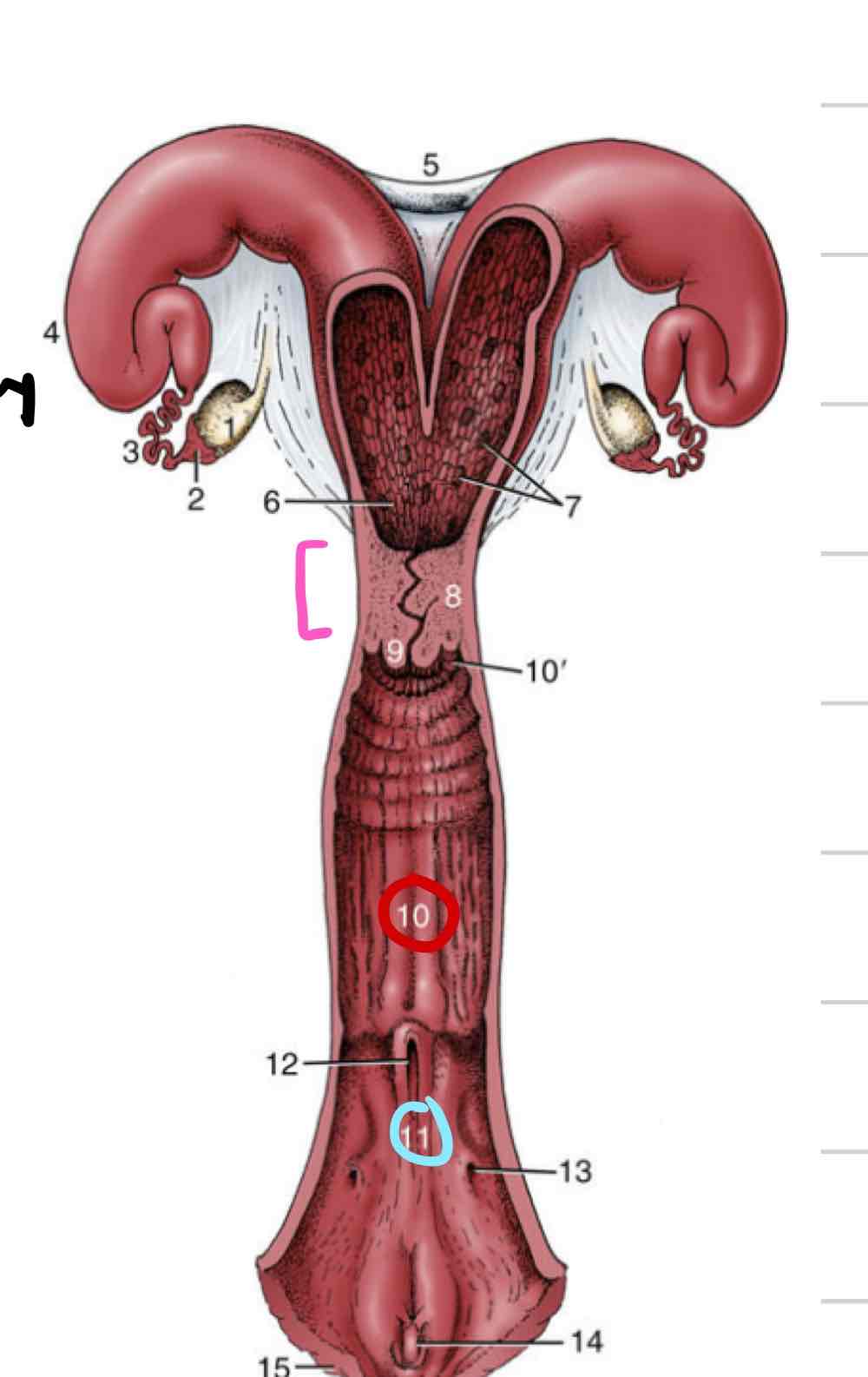
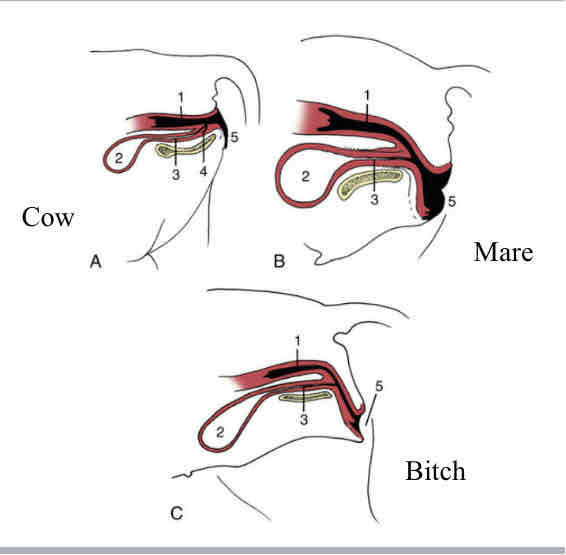
Vestibule comparative anatomy
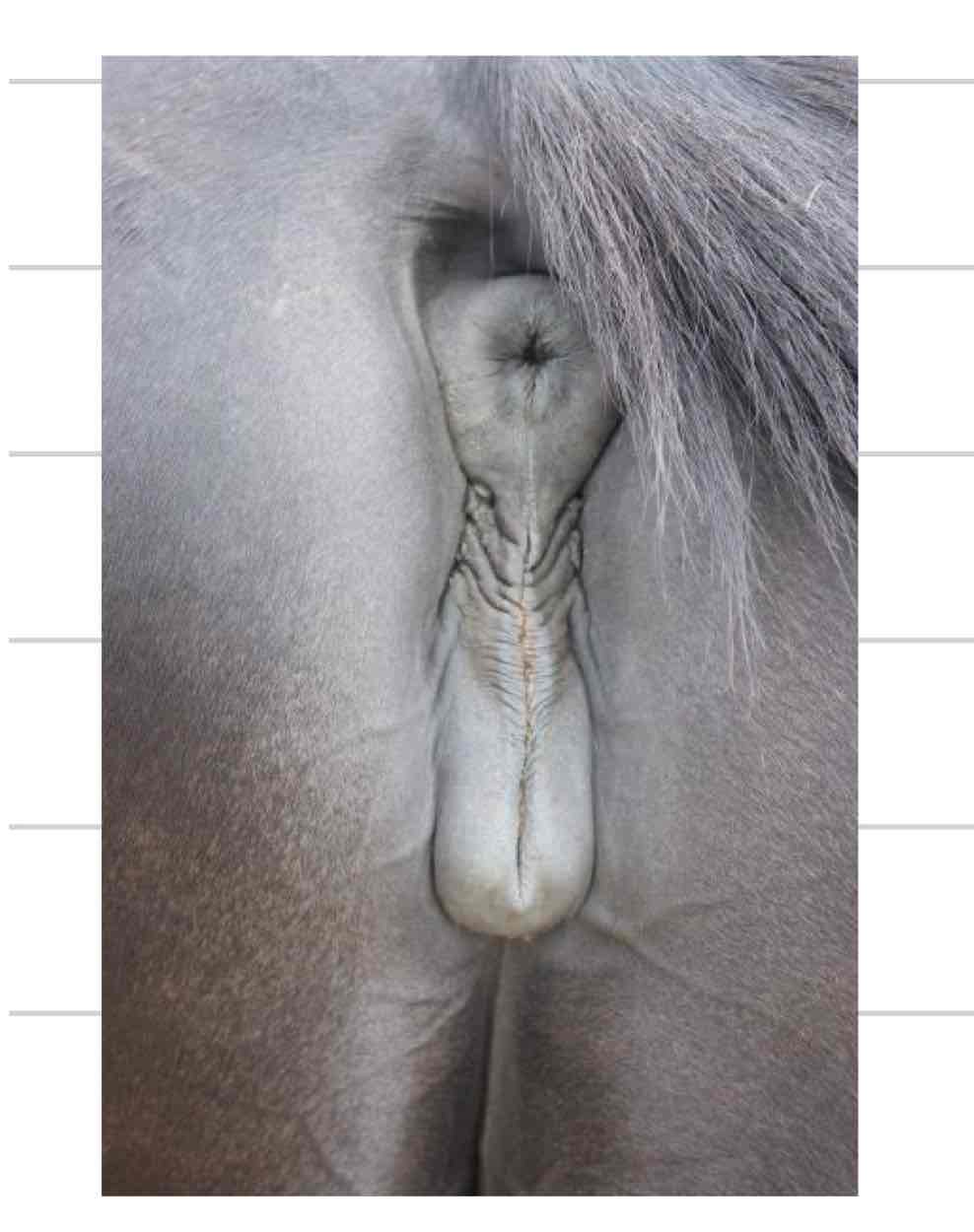
Vulva
external portion of repro tract
two vertically oriented labia meet at dorsal and ventral commissures
In most species dorsal commissure is rounded and ventral is pointed
Inverse in mare
Clitoris
analogous to male penis (14)
Consists of 2 crura, a body, and a glans
only glans visible externally
Found within ventral commissure of vulva
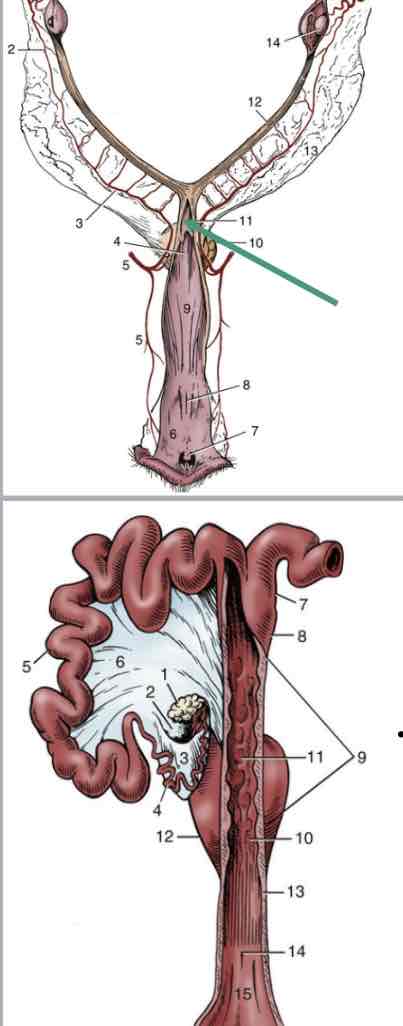
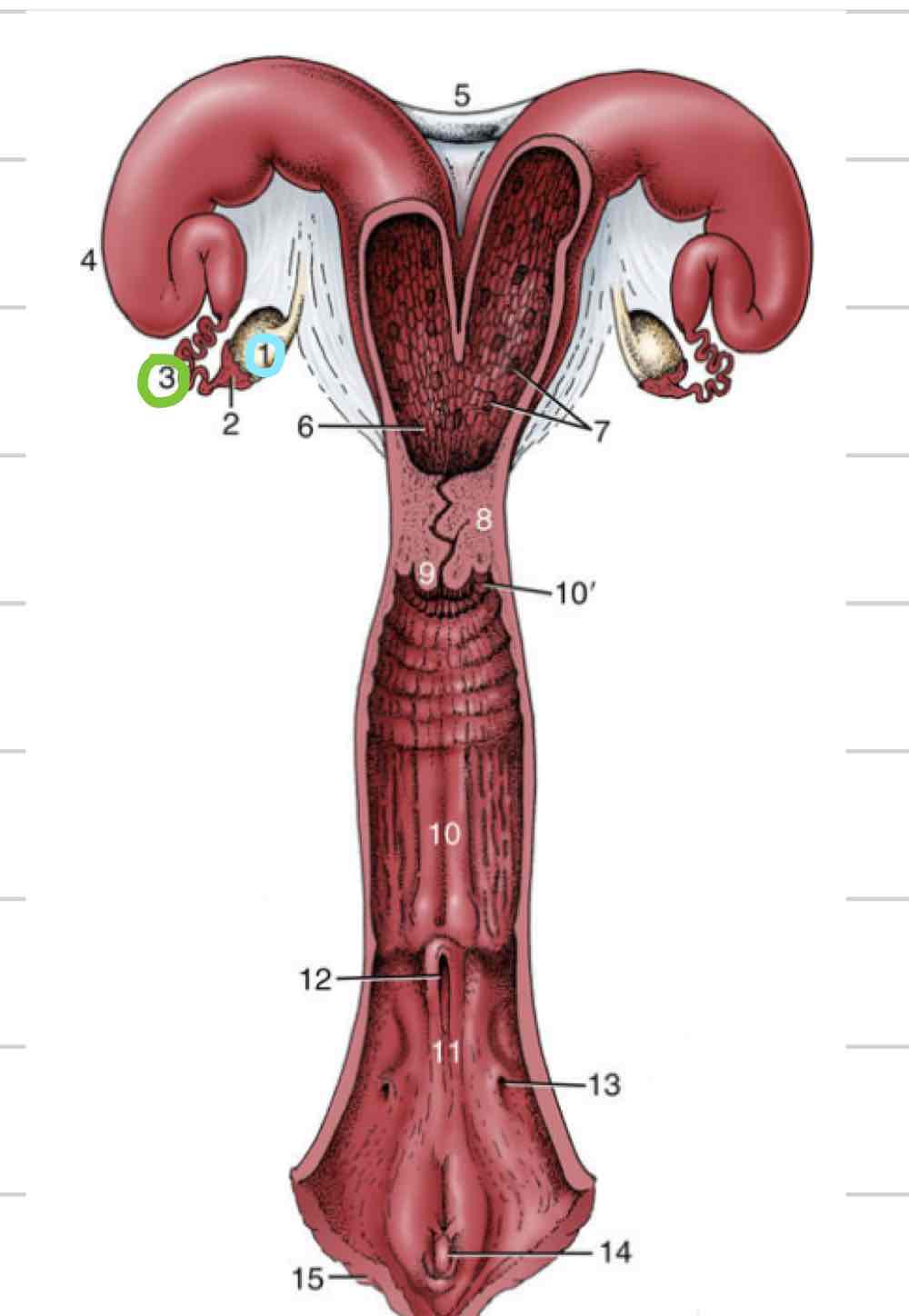
Broad ligament
Suspensory apparatus for entire female repro tract
Fold of peritoneum from dorsal body wall
3 parts
Mesovarium
(6) Connects ovaries to body wall
Mesosalpinx
(7) connects oviducts to body wall
Mesometrium
(8) connects uterine horns and body to the body wall
Proper ligament of ovary
strong cord of fibromuscular tissue (9)
connects ovary to uterine horn
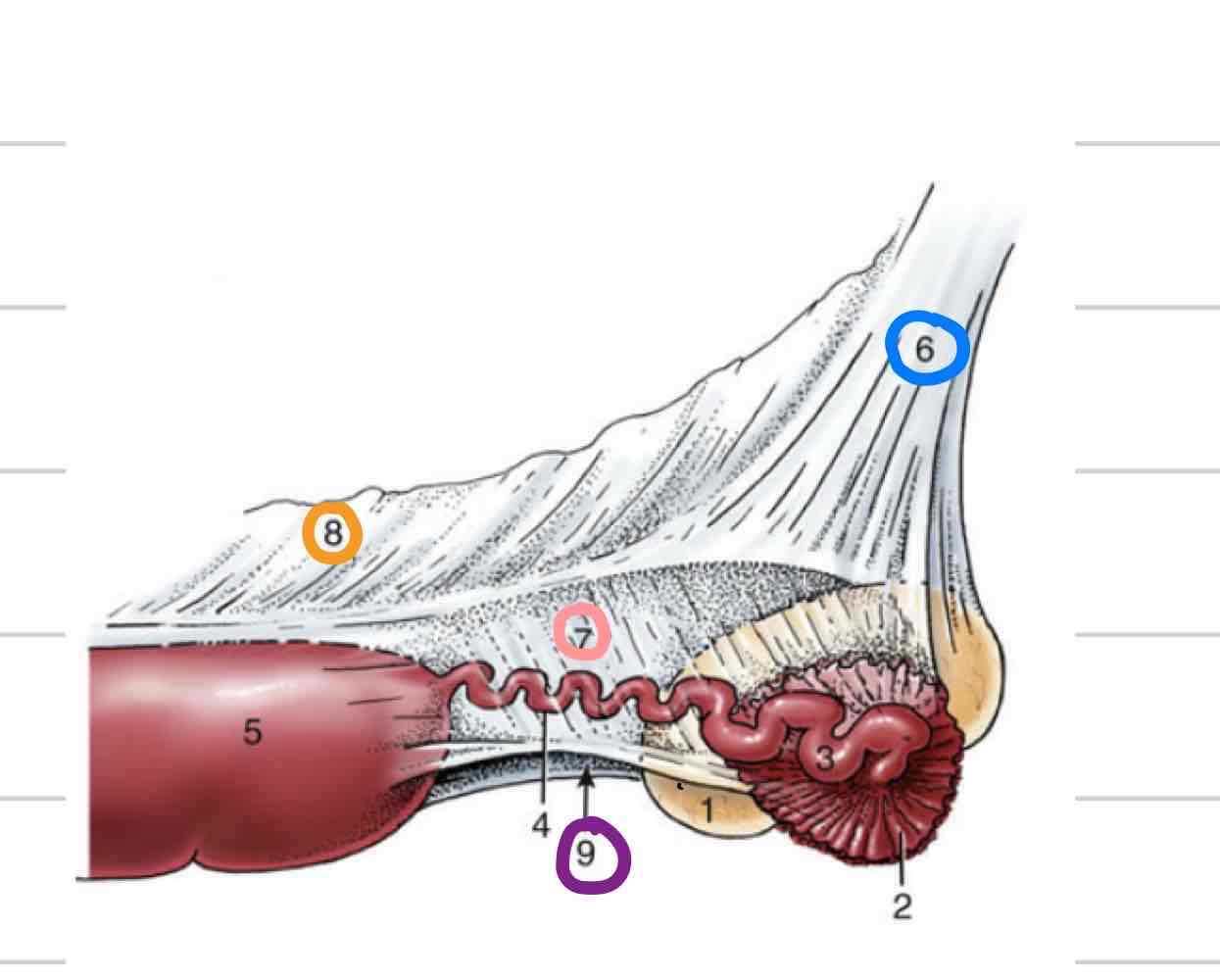
Intercornual ligament
connects uterine horns to one another (5)
dorsal and ventral ligaments
important in diagnosis pregnancy in bovine (allows for manipulation of uterus)
Placenta
Facilitates waste and nutrient exchange
Hormone production for maintaining pregnancy
No direct exposure of fetal/maternal blood
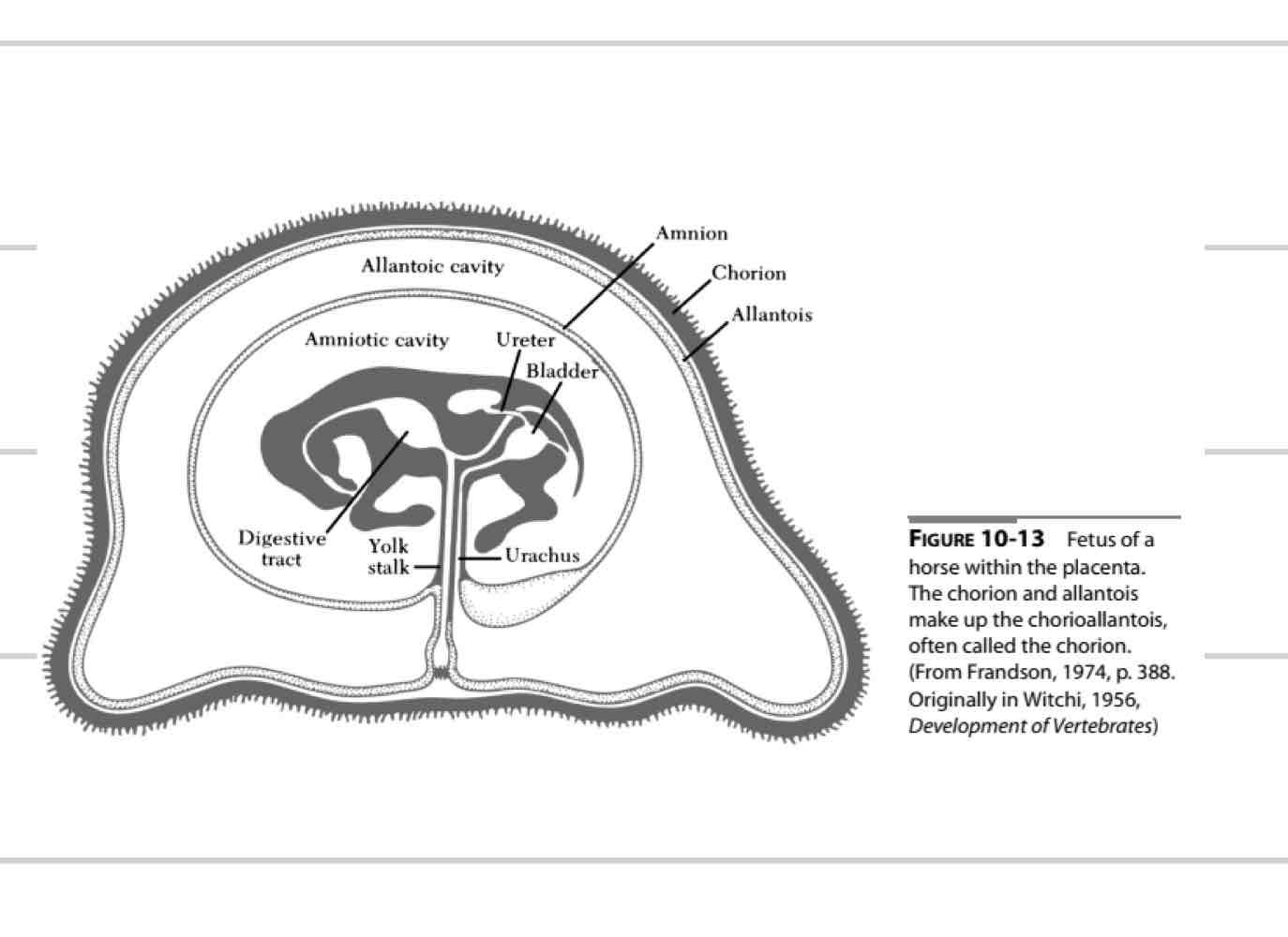
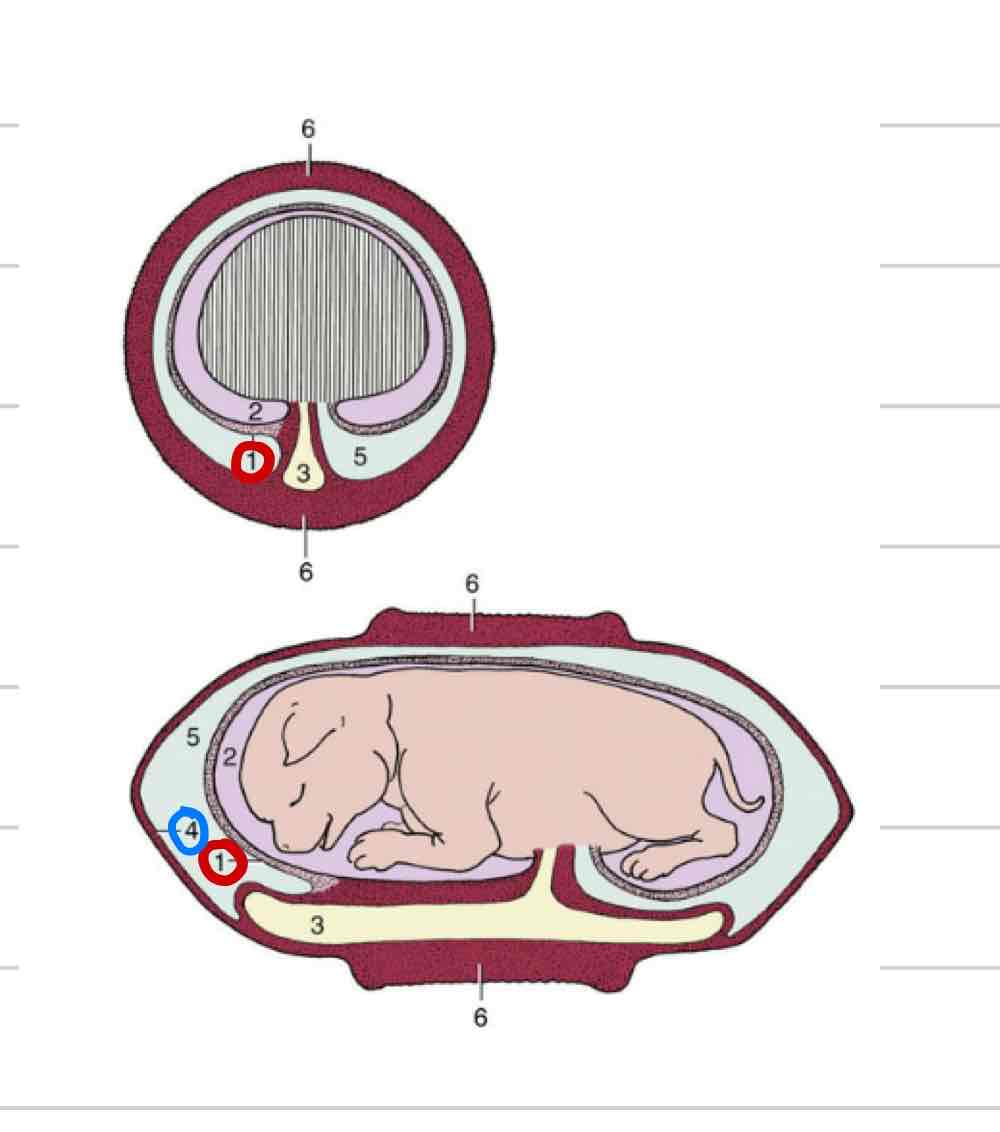
Fetal membranes
form around embryo to protect
transfer of nutrients and waste
Amnion
Allantois
Chorion
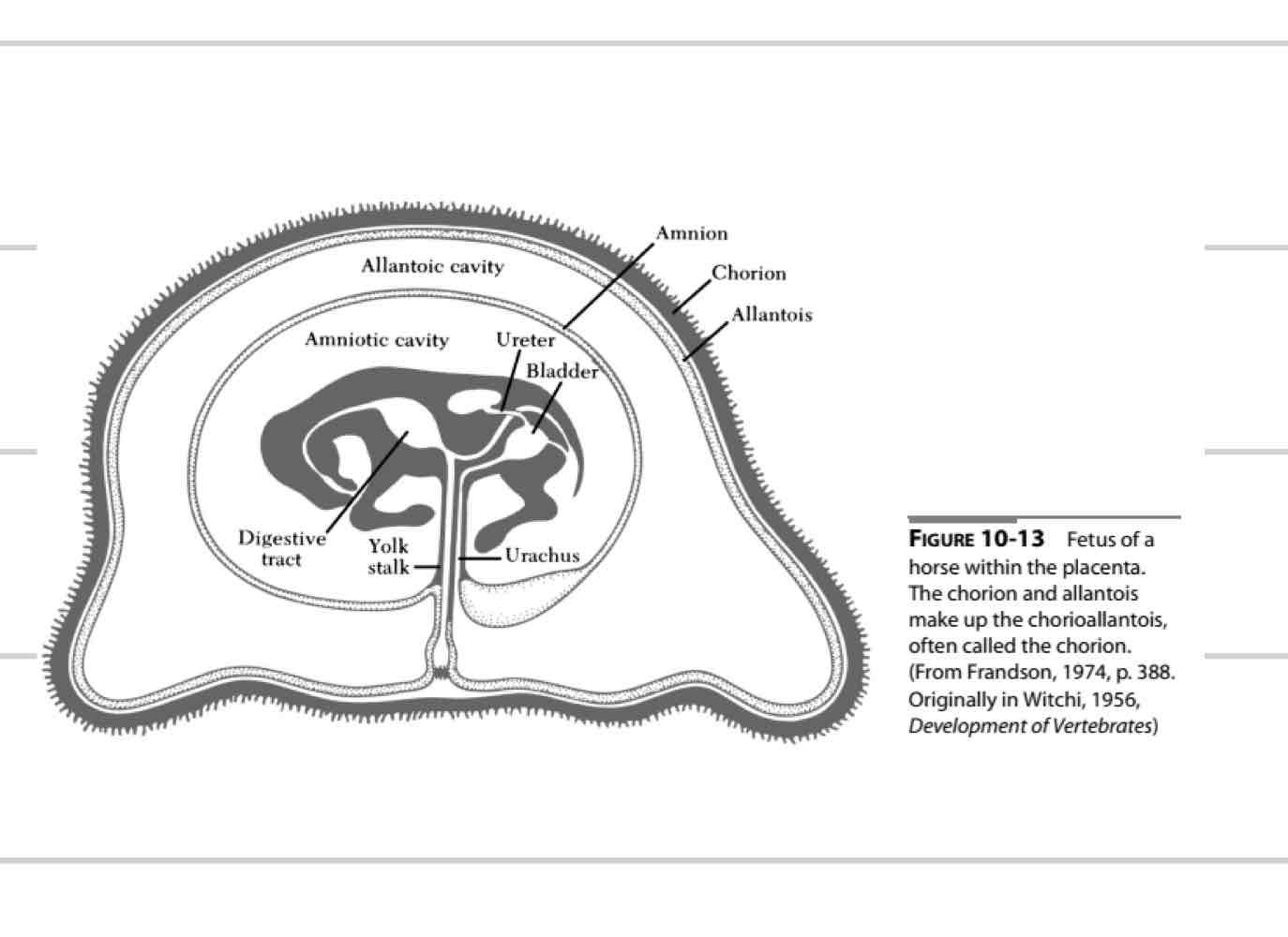
Amniotic membrane
Innermost membrane (1)
Surrounds amniotic cavity
Fluid that directly surrounds fetus
“clean”
Shock absorber
fetal development
Thin, clear/white
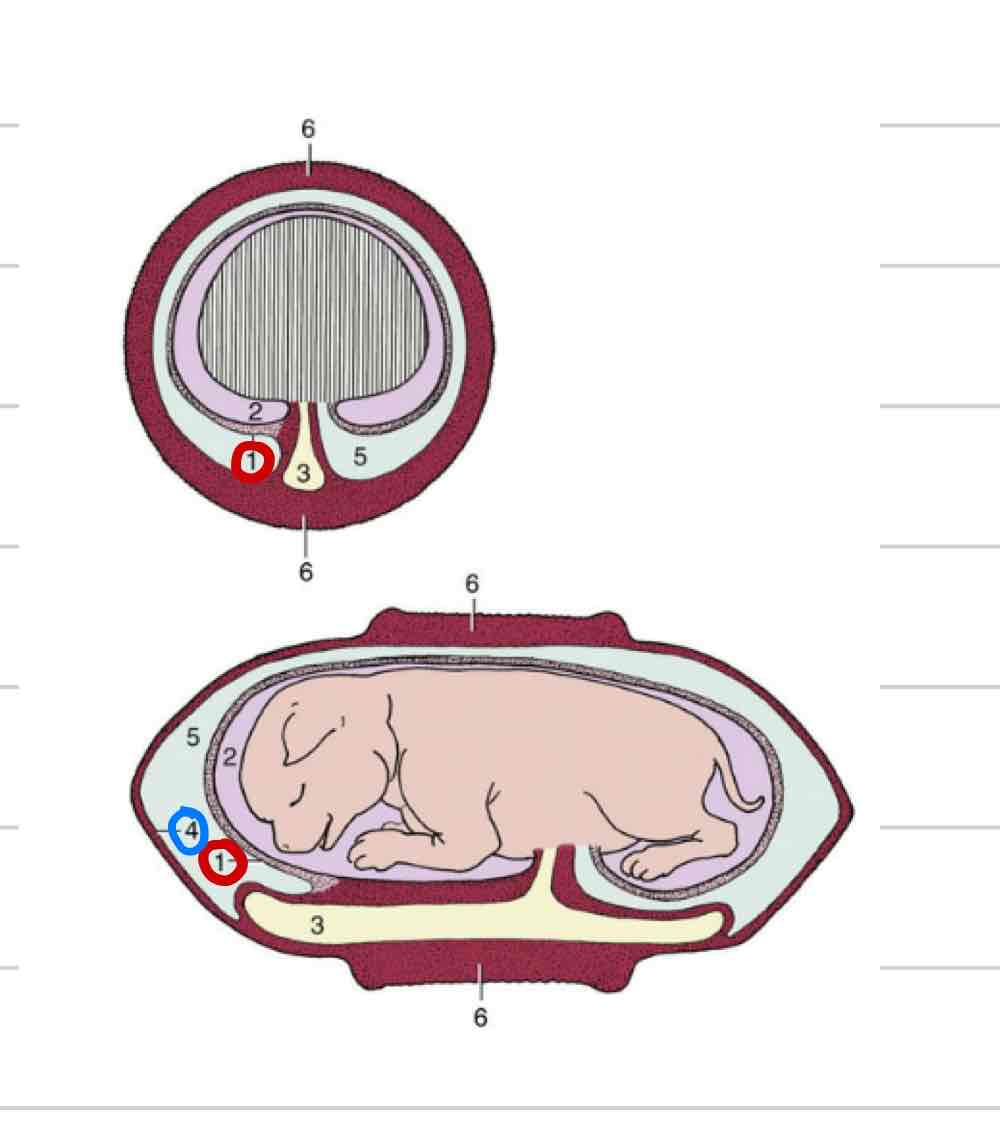
Allantoic membrane
Middle membrane (4)
surrounds allantoic cavity
Dirty cavity
Communicates with urachus
carries waste away
Fused with chorion
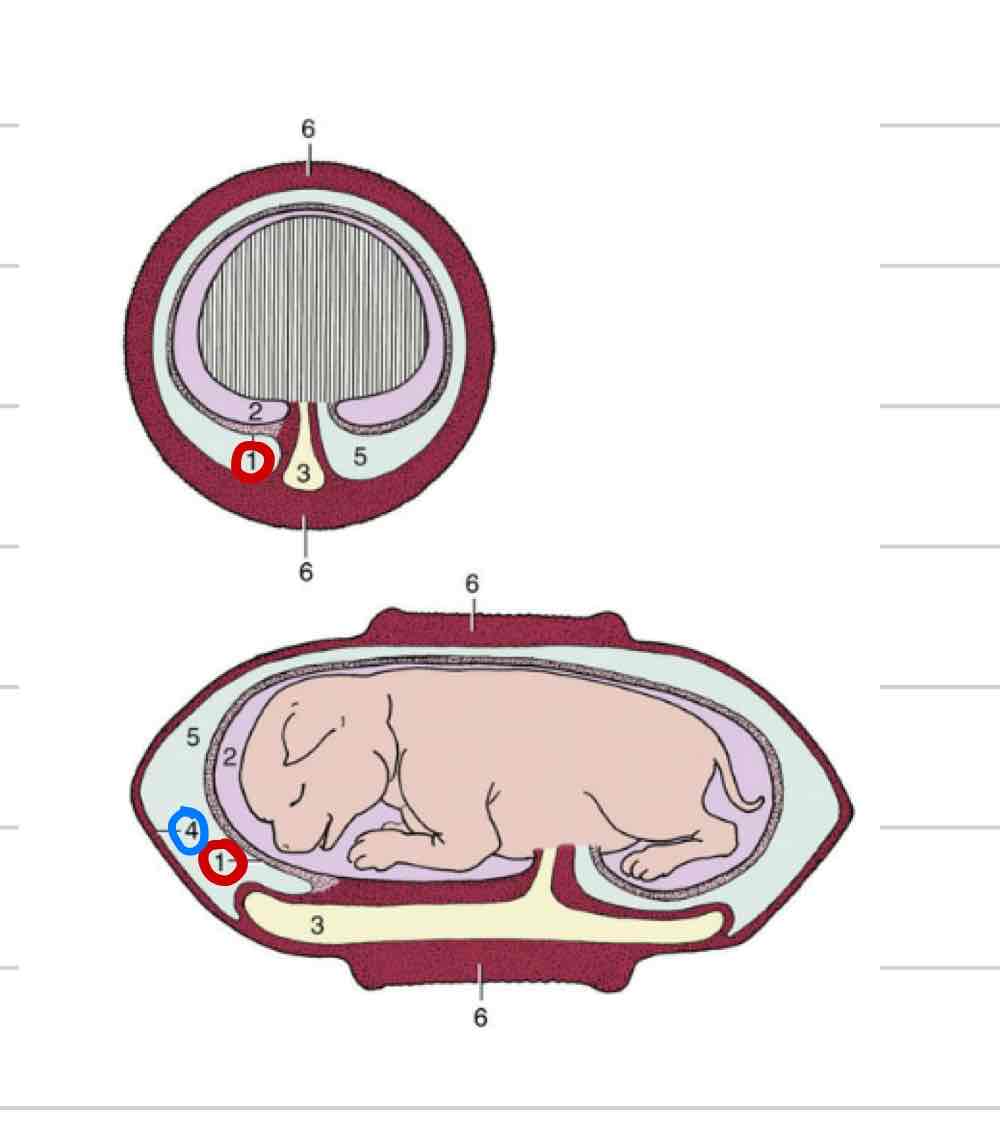
Chorionic membrane
Most external membrane (4)
Fused to allantois
Chorioallantois
Communicates with endometrium
Placental attachment
not a smooth interface
Villi on both surfaces
Chorionic villi- extend from chorioallantois
Endometrial villi- extend from maternal endometrium
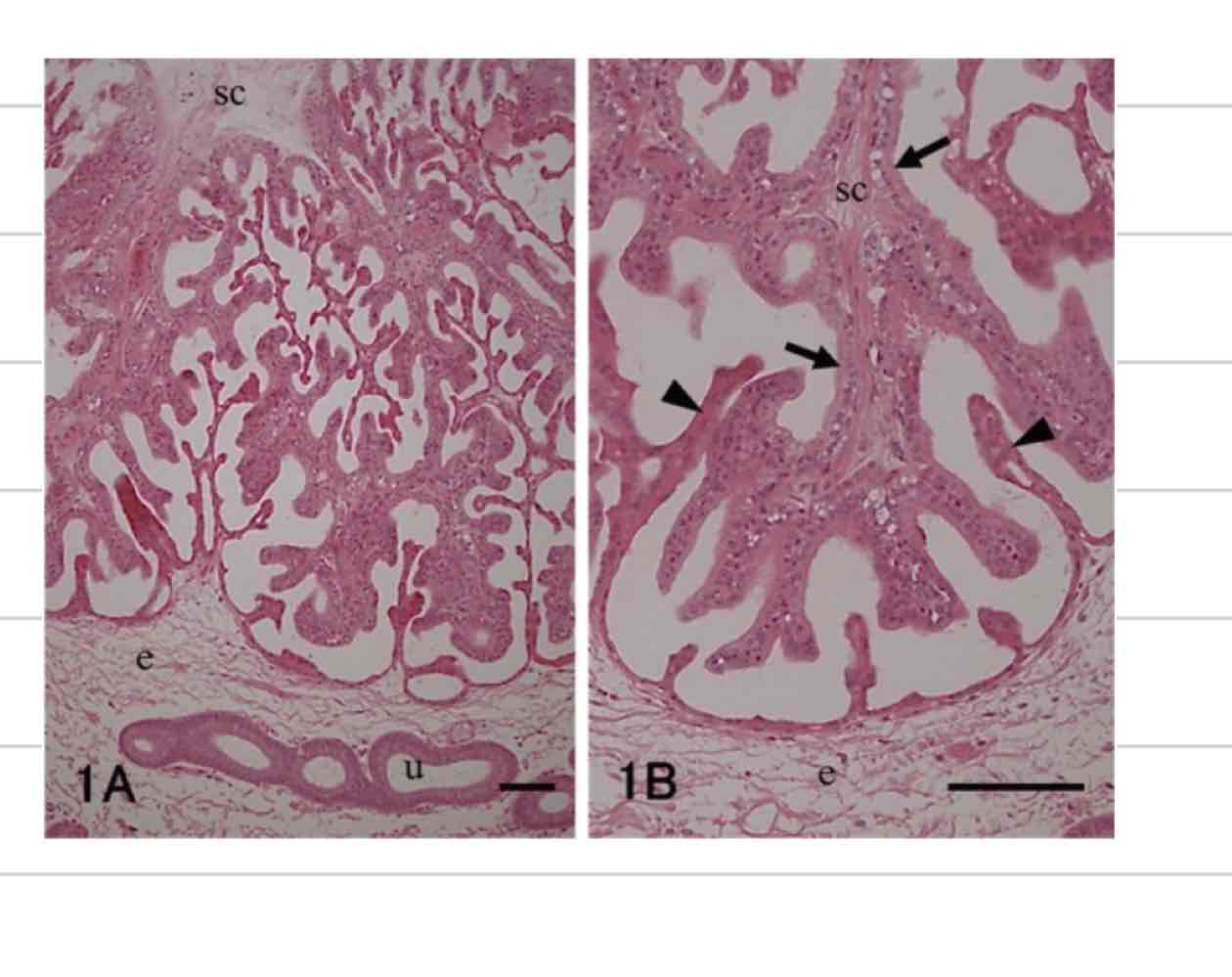
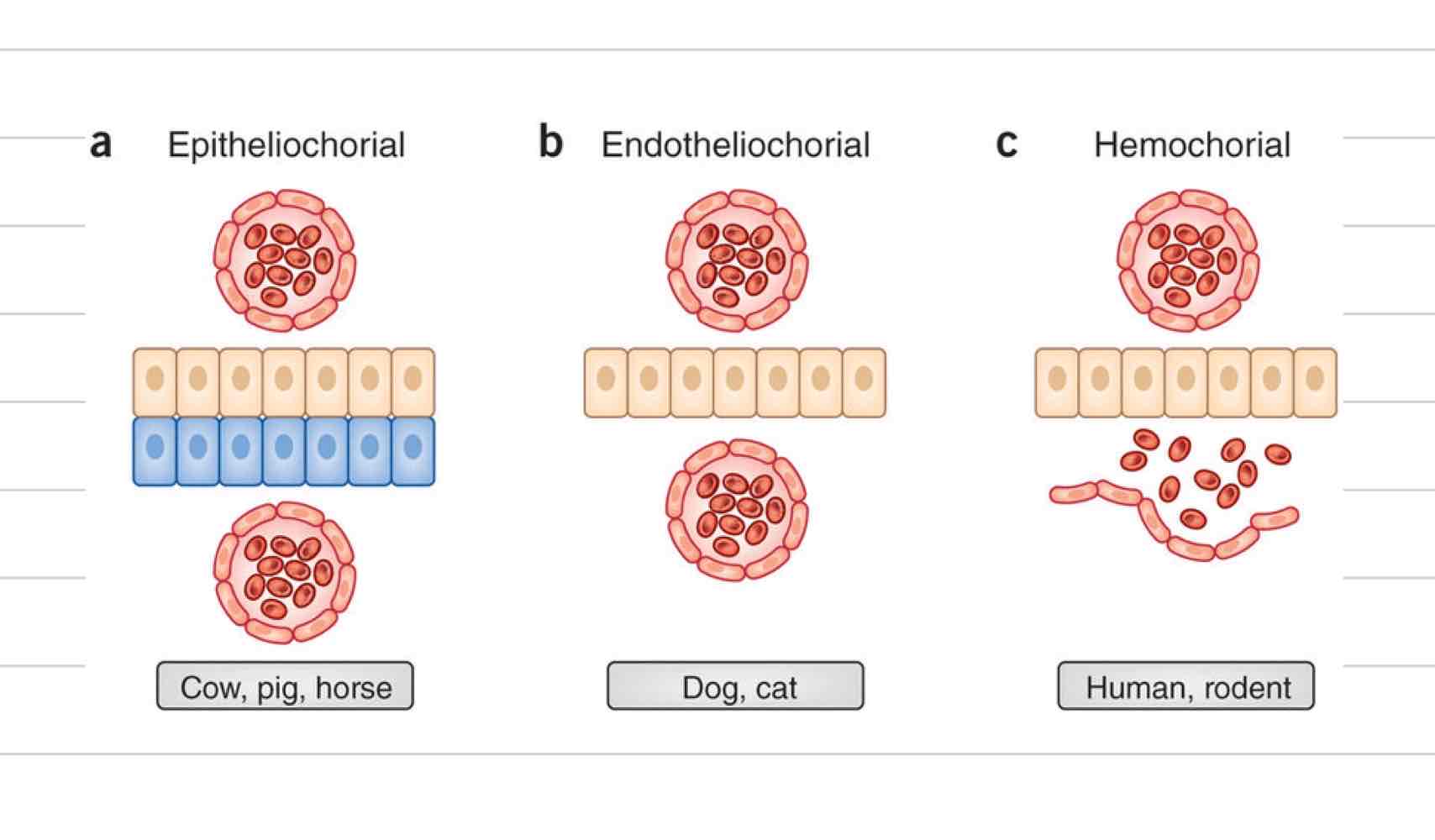
Epitheliochorial placentation
Least invasive, 6 layers
Fetal layers
Fetal endothelium
fetal connective tissue
chorionic epithelium
Maternal Layers
maternal epithelium
maternal connective tissues
maternal endothelium
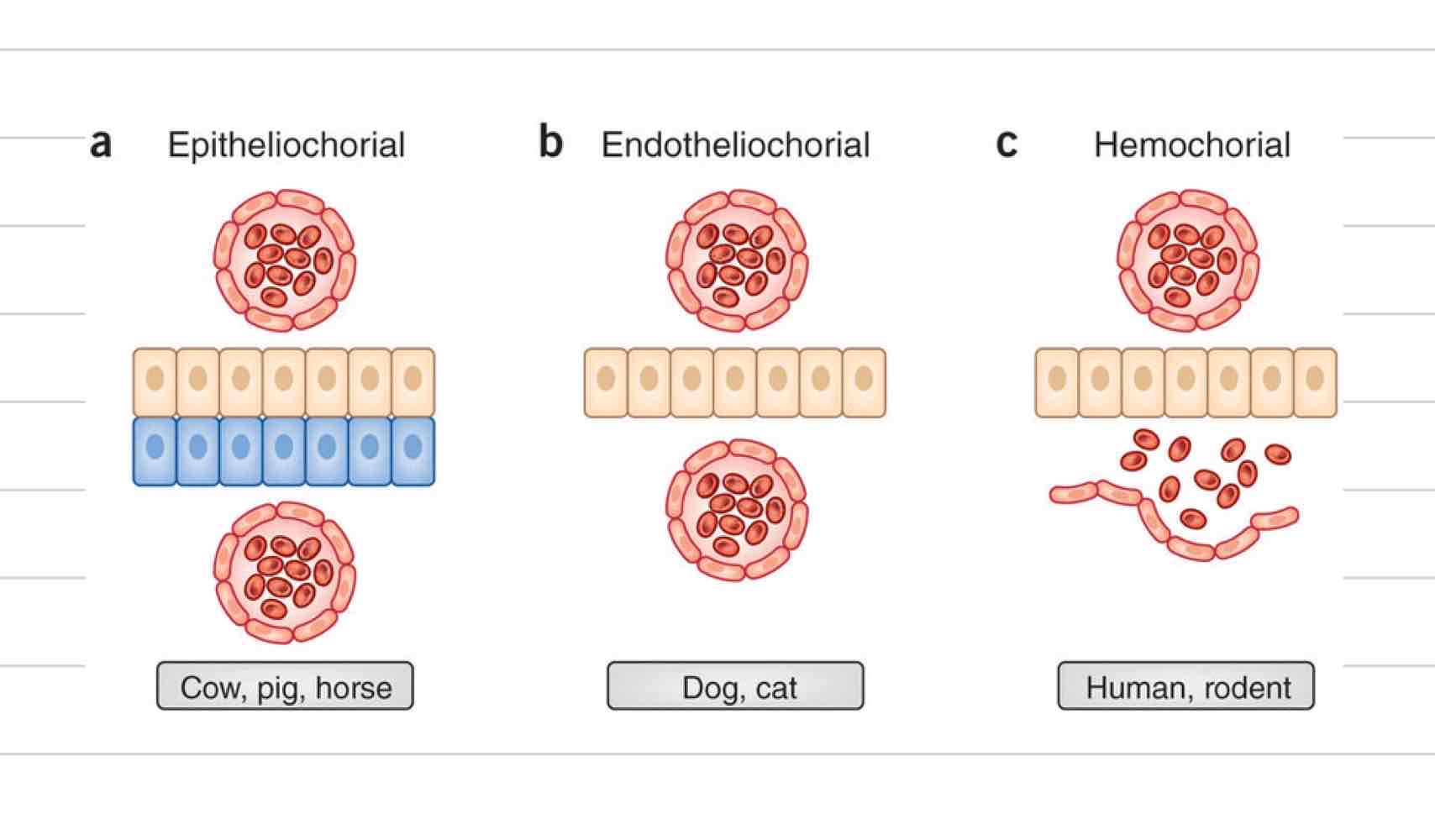
Endothelialchorial placentation
Somewhat invasive, 4 layers
Fetal layers
Fetal endothelium
fetal connective tissue
chorionic epithelium
Maternal Layers
maternal endothelium
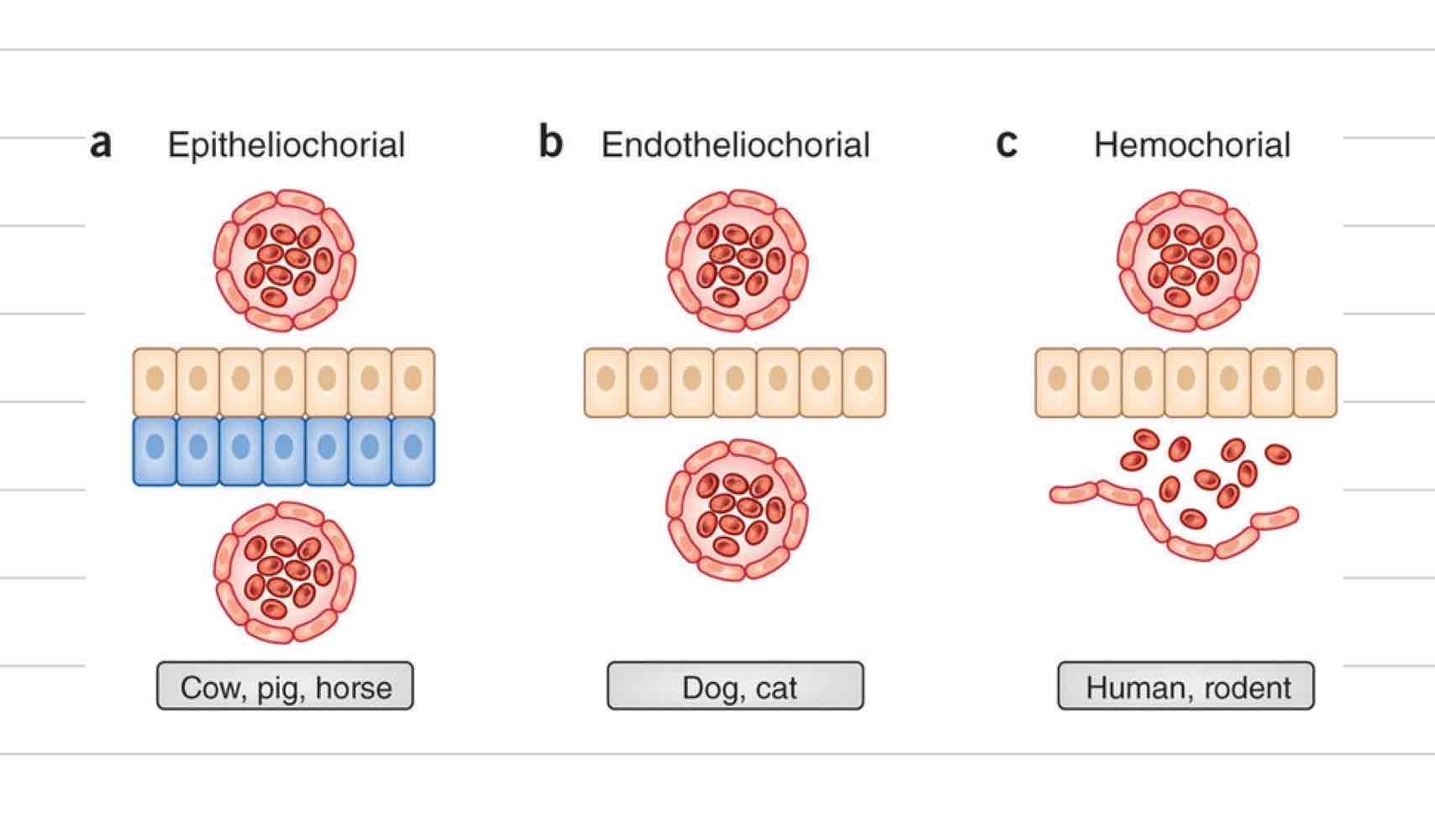
Hemochorial placentation
Most invasive, 3 layers
Fetal layers
Fetal endothelium
fetal connective tissue
chorionic epithelium
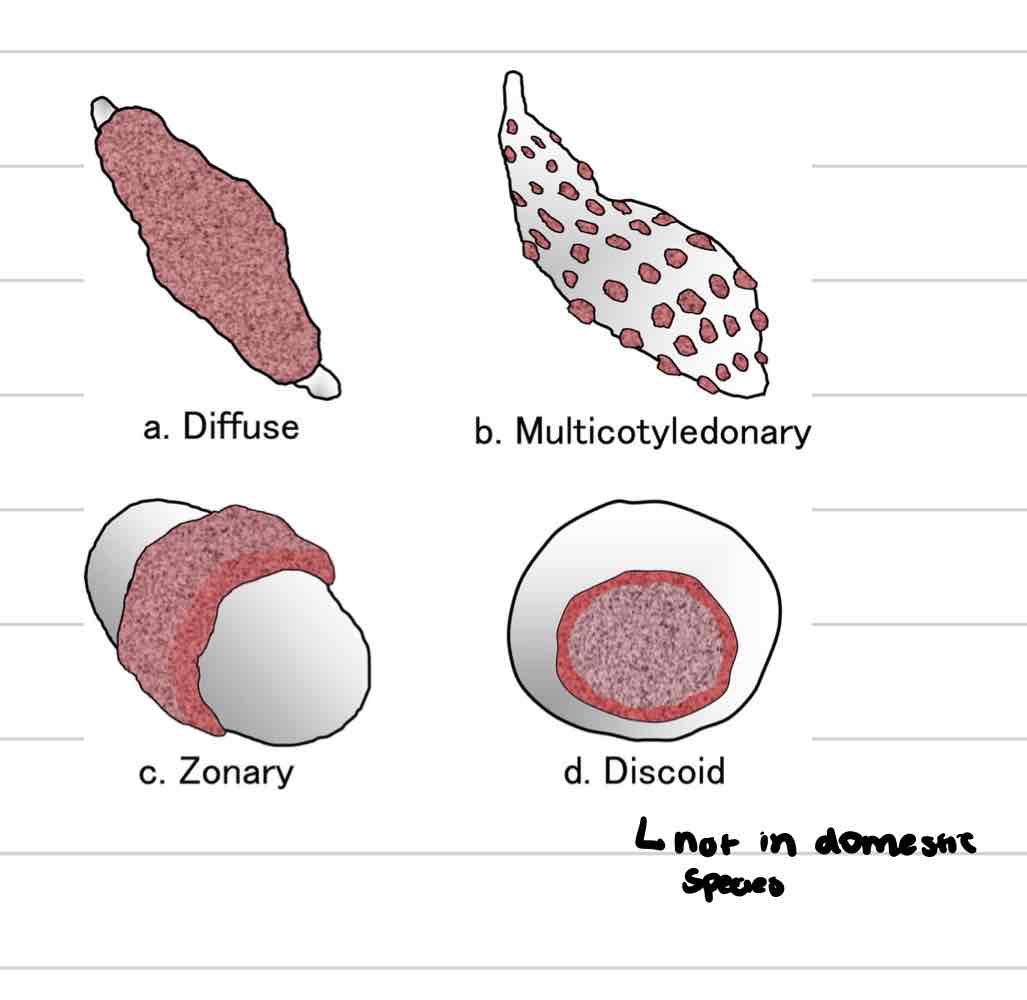
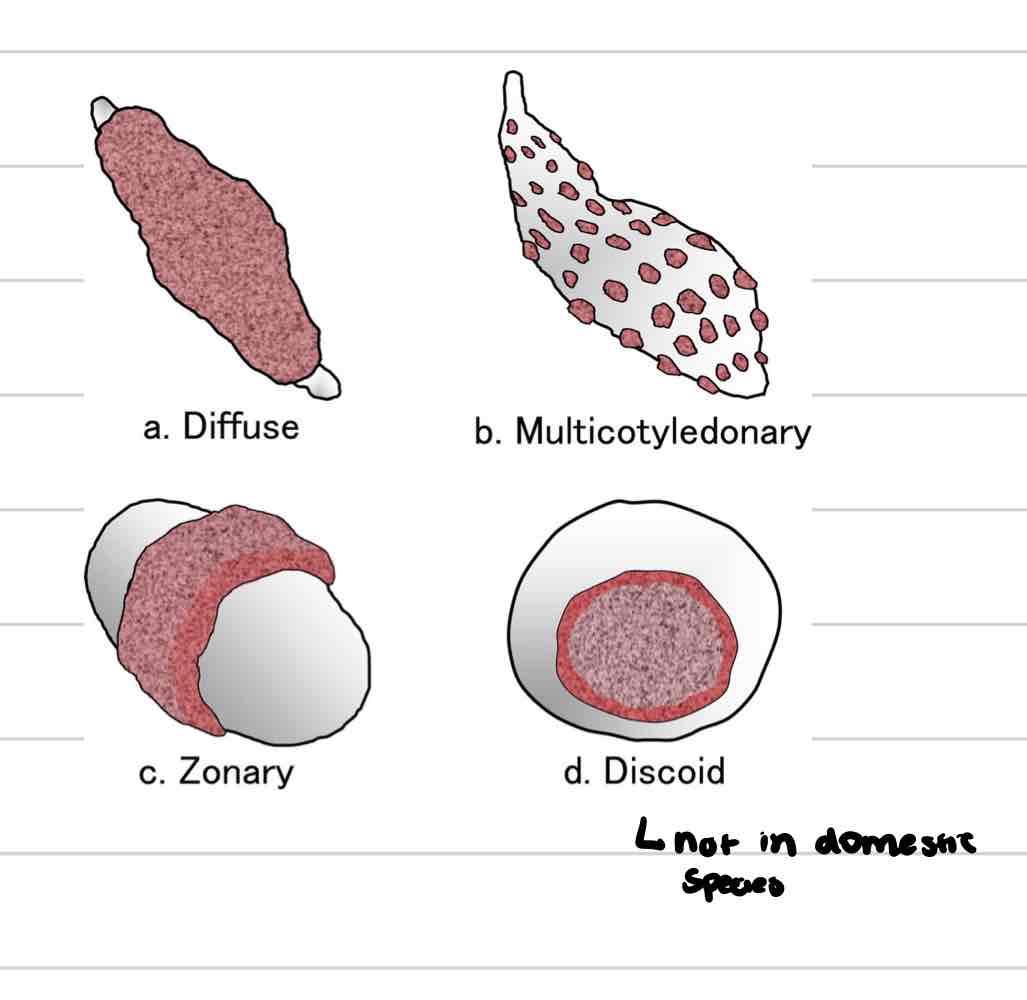
Diffuse placenta
villi spread in small clumps over entire surface of chorion
pigs, horses
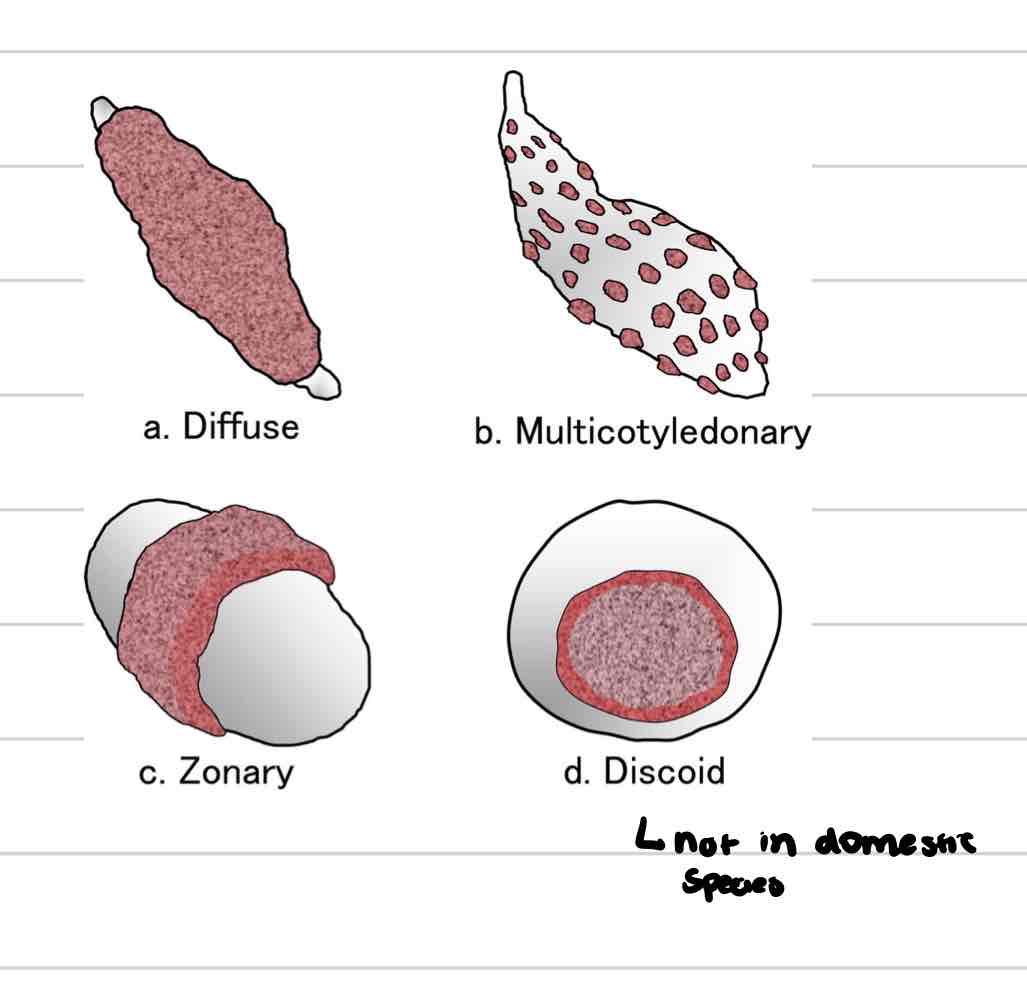
Cotyledonary placenta
Villi in scattered patches (cotyledons) across chorion
Associated with maternal caruncles found on uterine endometrium
ruminants
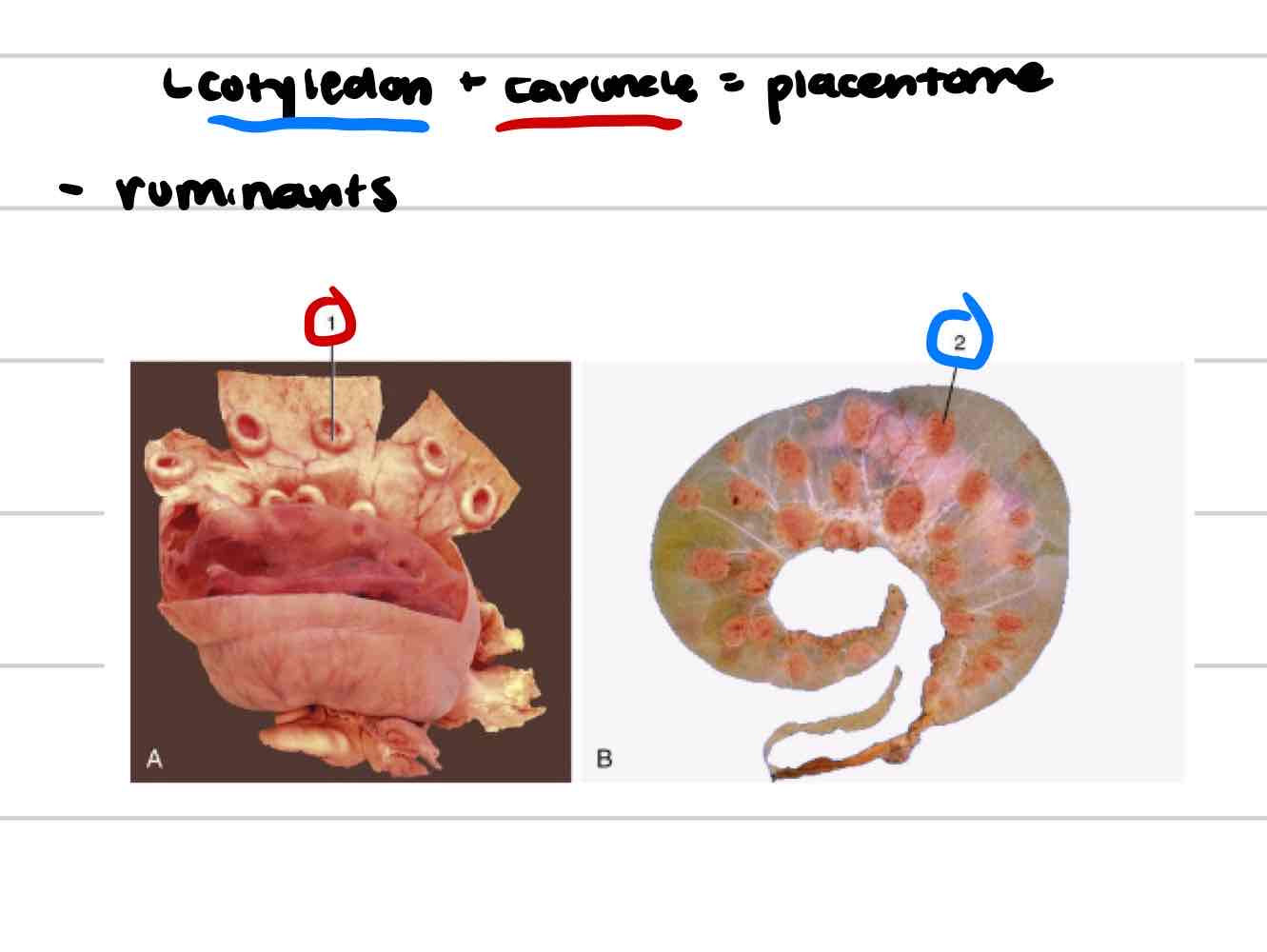
Placentome
functional unit
cotyledon+caruncle
Zonary placenta
villi develop along band of chorion that encircles trunk of embryo
dogs and cats
Umbilical cord
Connection between fetus and placenta
2 umbilical arteries
1 umbilical vein (2 in placenta)
Urachus
wharton’s jelly
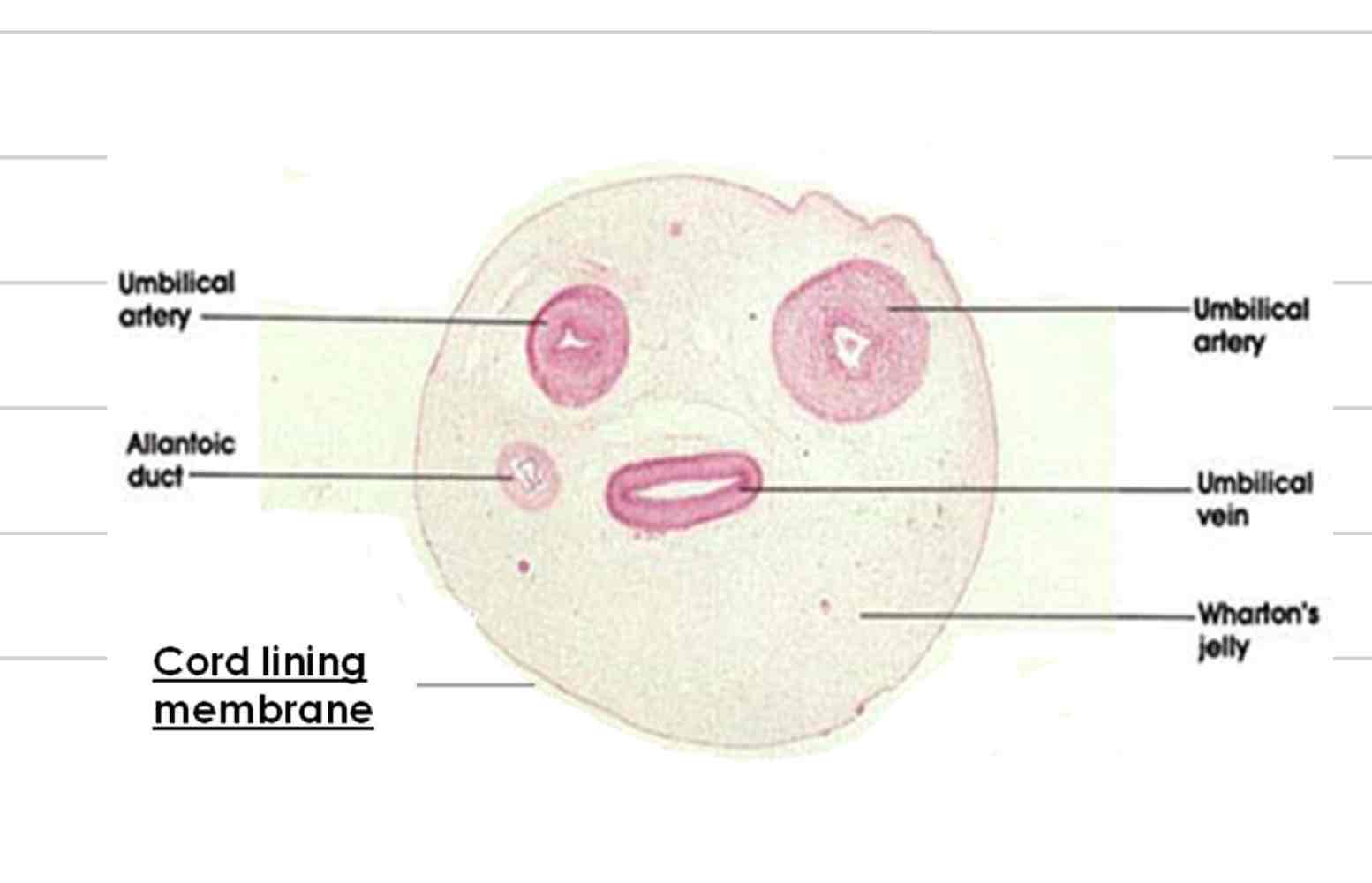
Umbilical arteries
Deoxygenated blood
bring blood from fetal caudal abdominal aorta to placenta
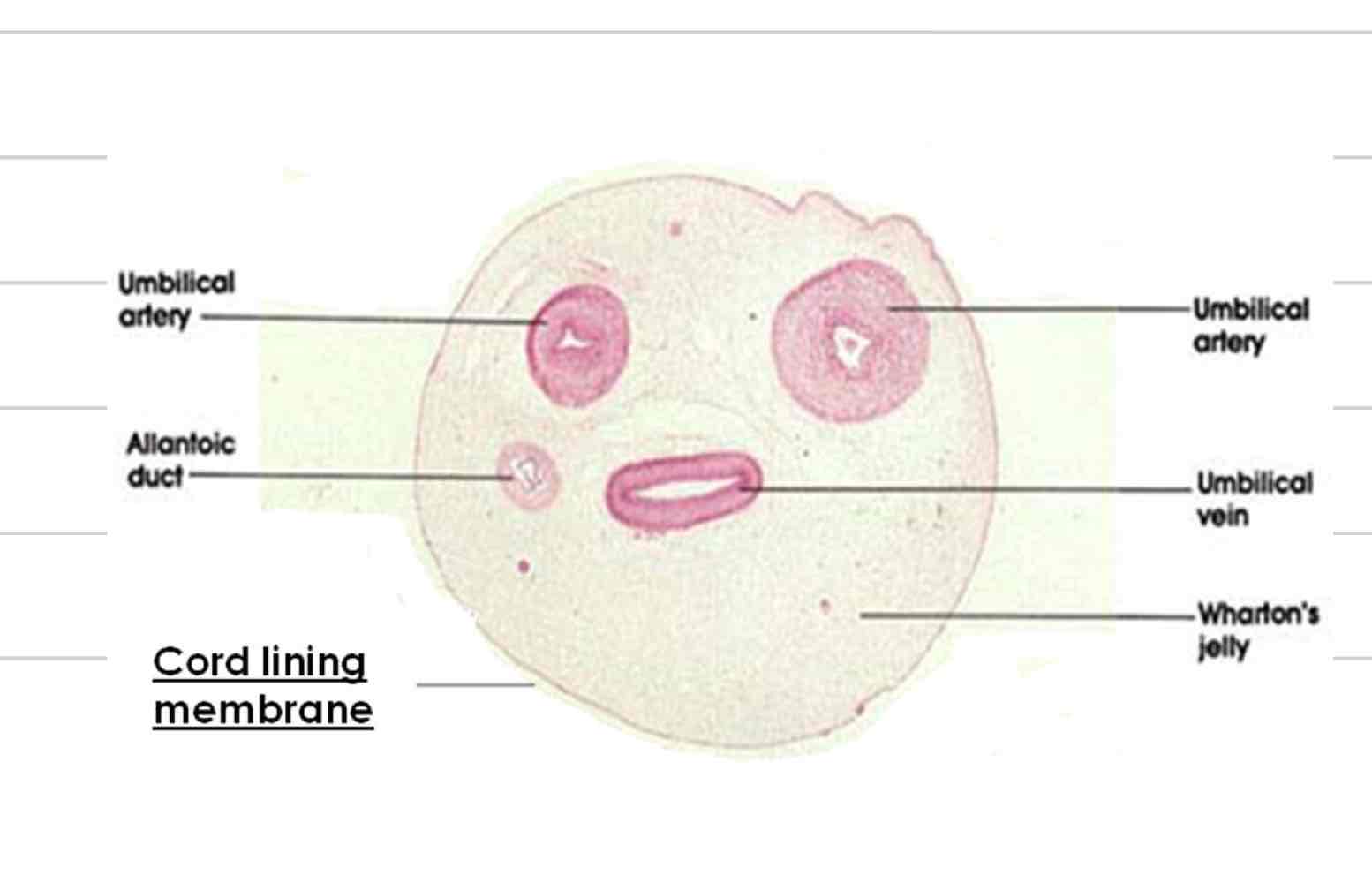
Umbilical veins
Oxygenated blood
bring blood from placenta to hepatic portal vein and ductus venosus
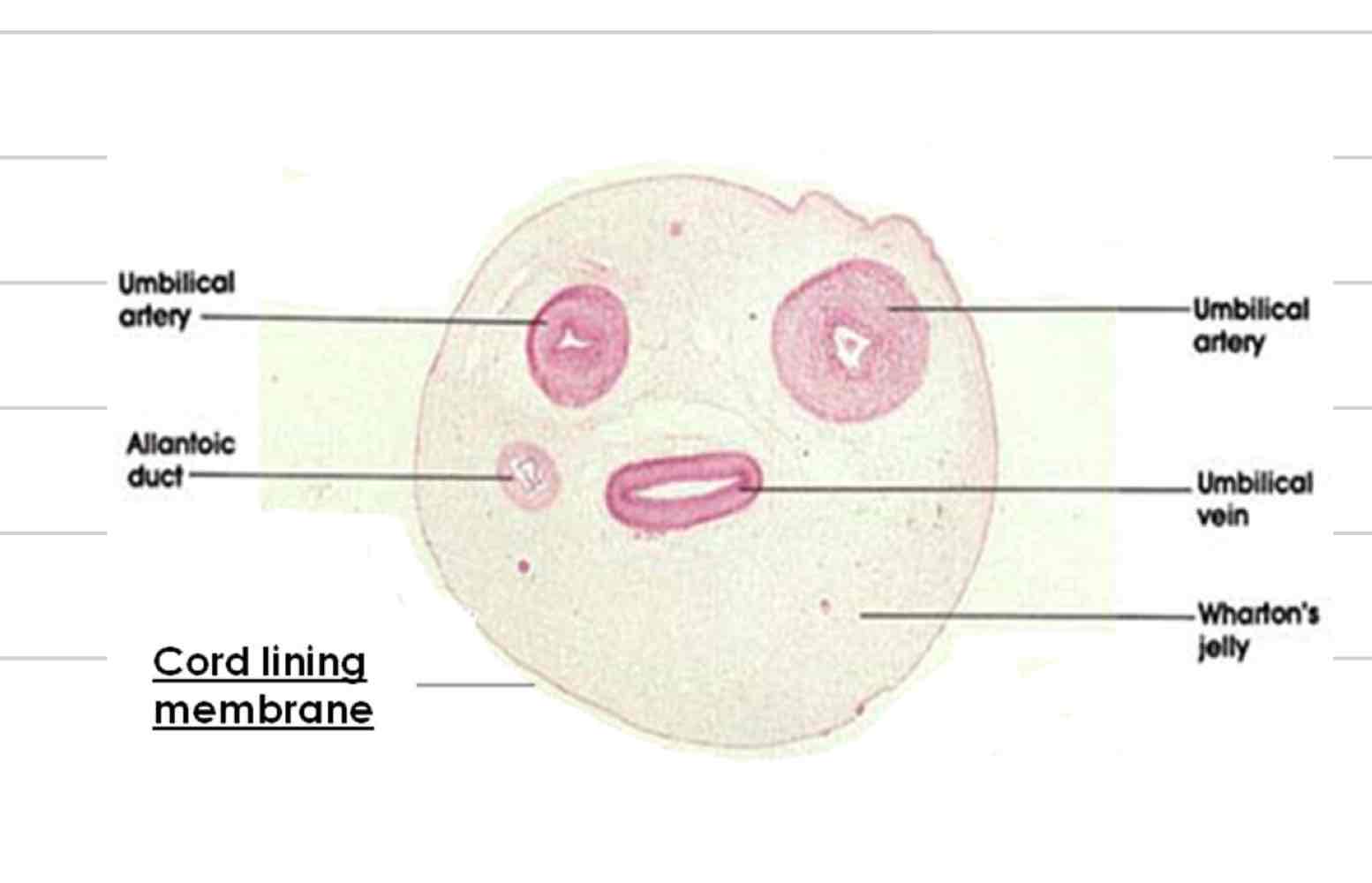
Urachus
Carries waste from bladder to allantoic cavity
Ductus venosus
Shunt the bypasses liver
goes directly from umbilical vein to caudal vena cava
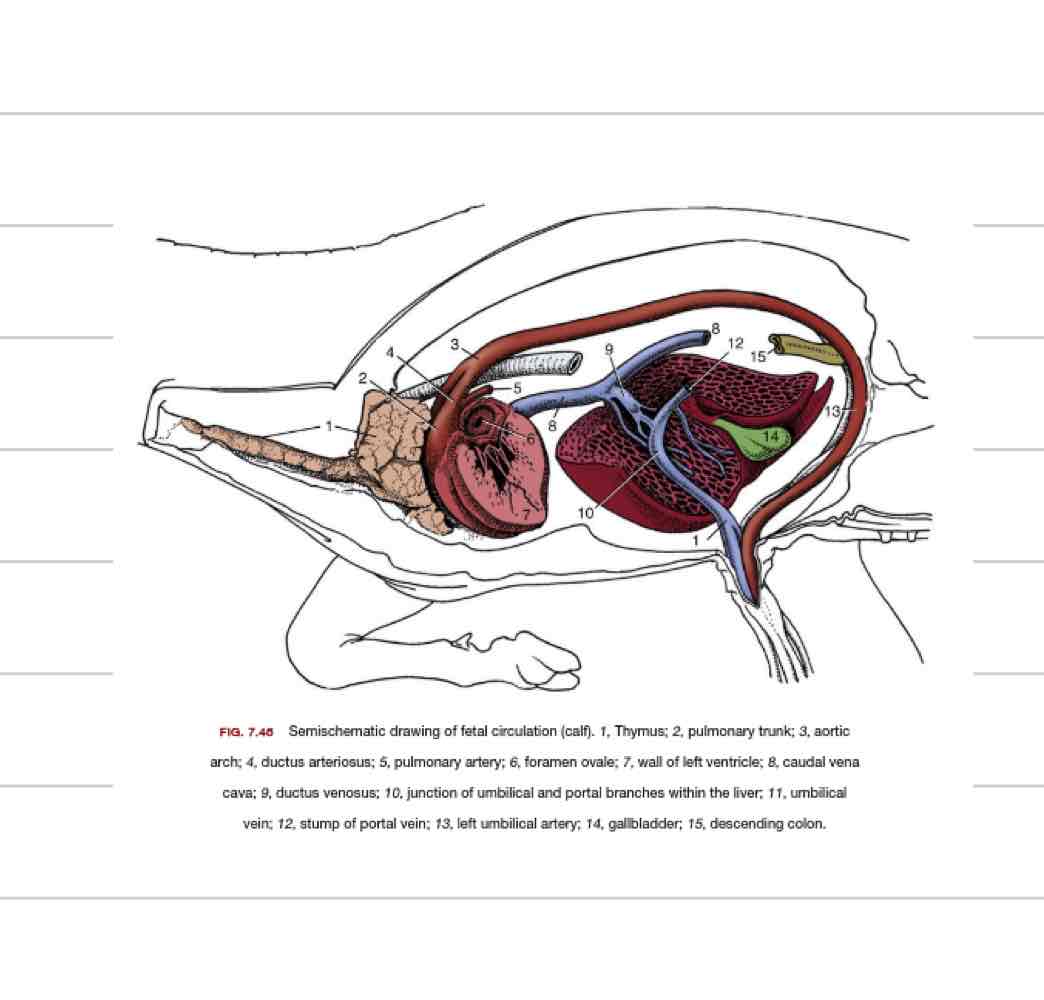
Ductus arteriosus
Shunt that bypasses the lungs
goes directly from pulmonary artery to aorta
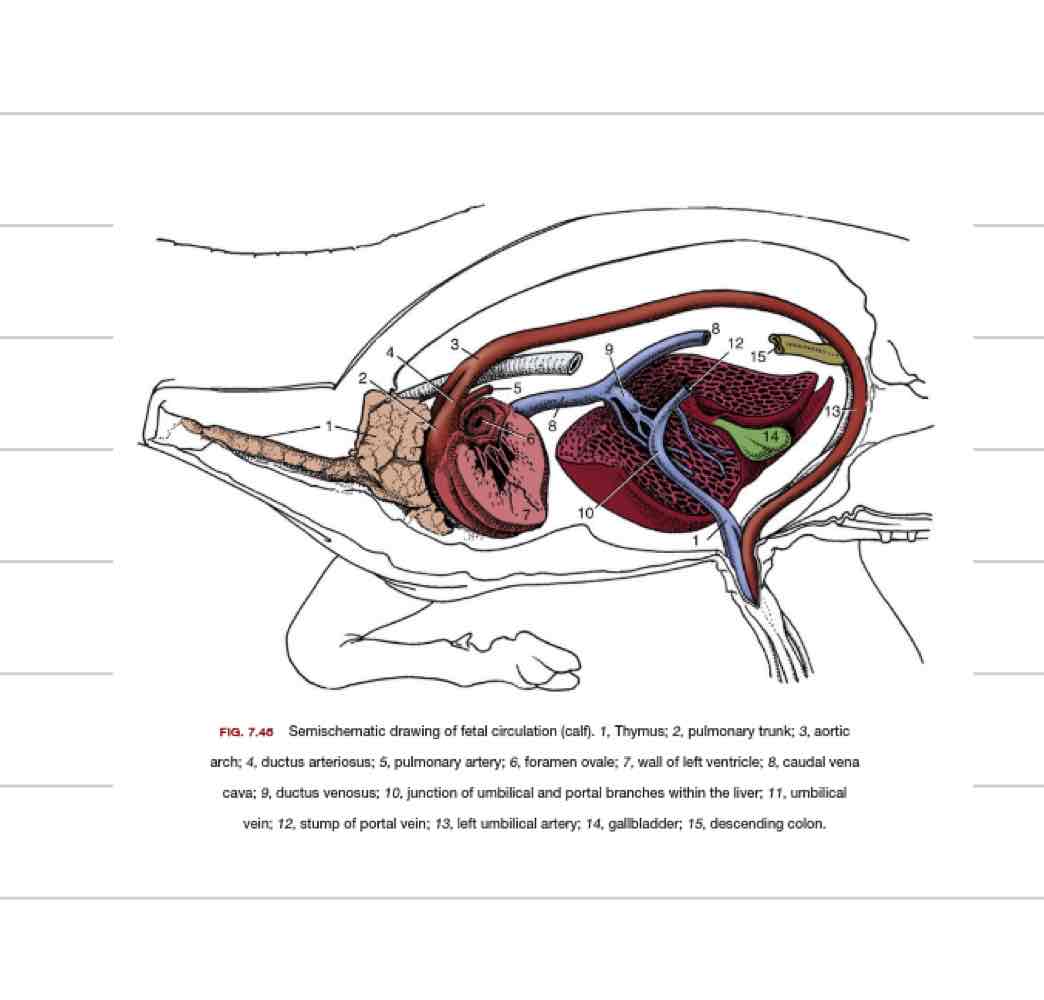
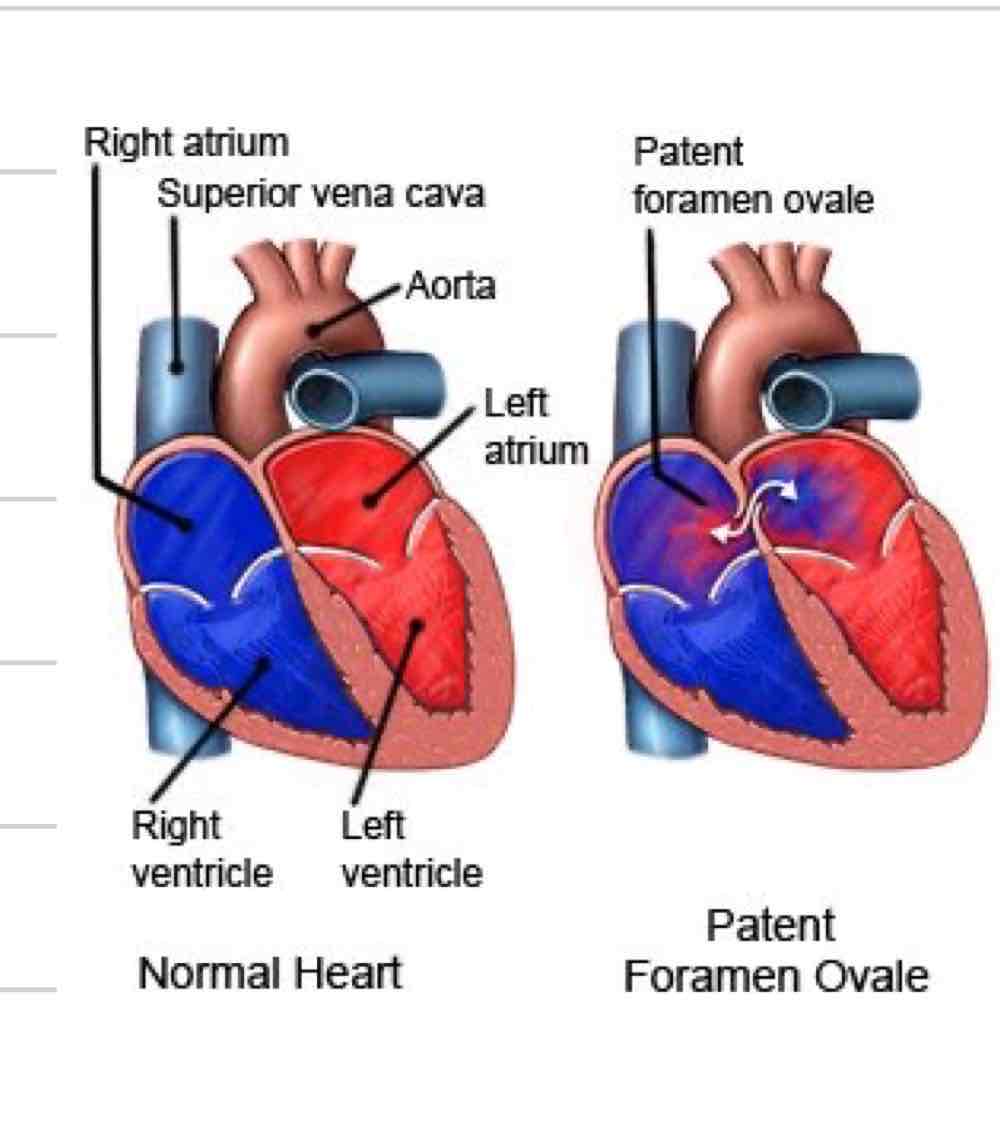
Foramen ovale
Opening between R and L atrium
Some blood still flows from R atrium to ventricle and out pulmonary artery
Changes at parturition
ductus venosus closes within hours to days
foramen ovale closes in days due to decreased left atrial pressure
urachus closes when cord broken
ductus arteriosus closes within a few days
Eponychium
Fairy fingers
outer epidermal layer covering hooves
protects uterus from damage
helps tell if they have walked
Mammary gland function
secrete milk to nourish offspring
colostrum (first milk)
enlarged modified sweat glands
Glandular portion of mammary gland
Structure that creates and stores the milk
Teat
protrusion that allows offspring to obtain milk
Alveoli
grape-like clusters of milk secreting cells
Mlik ducts
large ducts in glandular portion that carry milk from alveoli to cistern
Cistern
storage cavity
gland cistern and teat cistern
Teat canal
duct that leads from teat sinus to teat opening
Teat sphincter
exit point for milk
keeps milk in and pathogens out
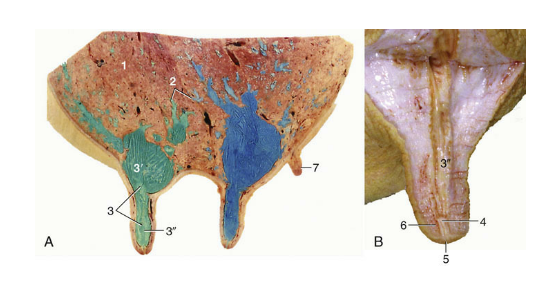
Mammary gland comparative anatomy
Cow/doe/ewe- single teat canal and single teat opening
Mare/sow- two teat canals, two teat openings per teat
Bitch/cat- multiple teat canals, multiple teat openings per teat
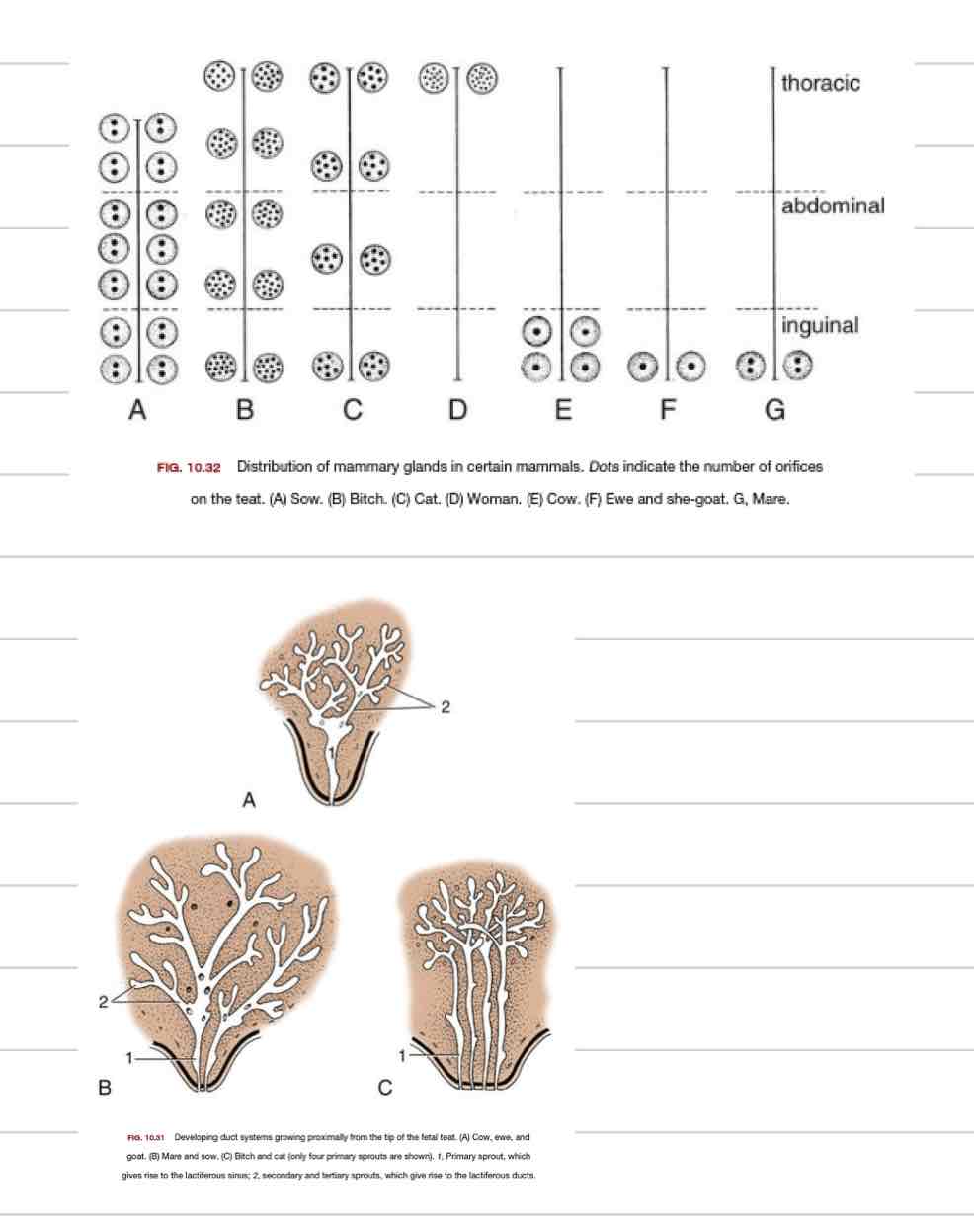
Functions of nervous system
Perception of environment
Integration and processing of environmental information
Response to environment
Voluntary and involuntary
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord
Integration and processing of information
Incapable of true regeneration
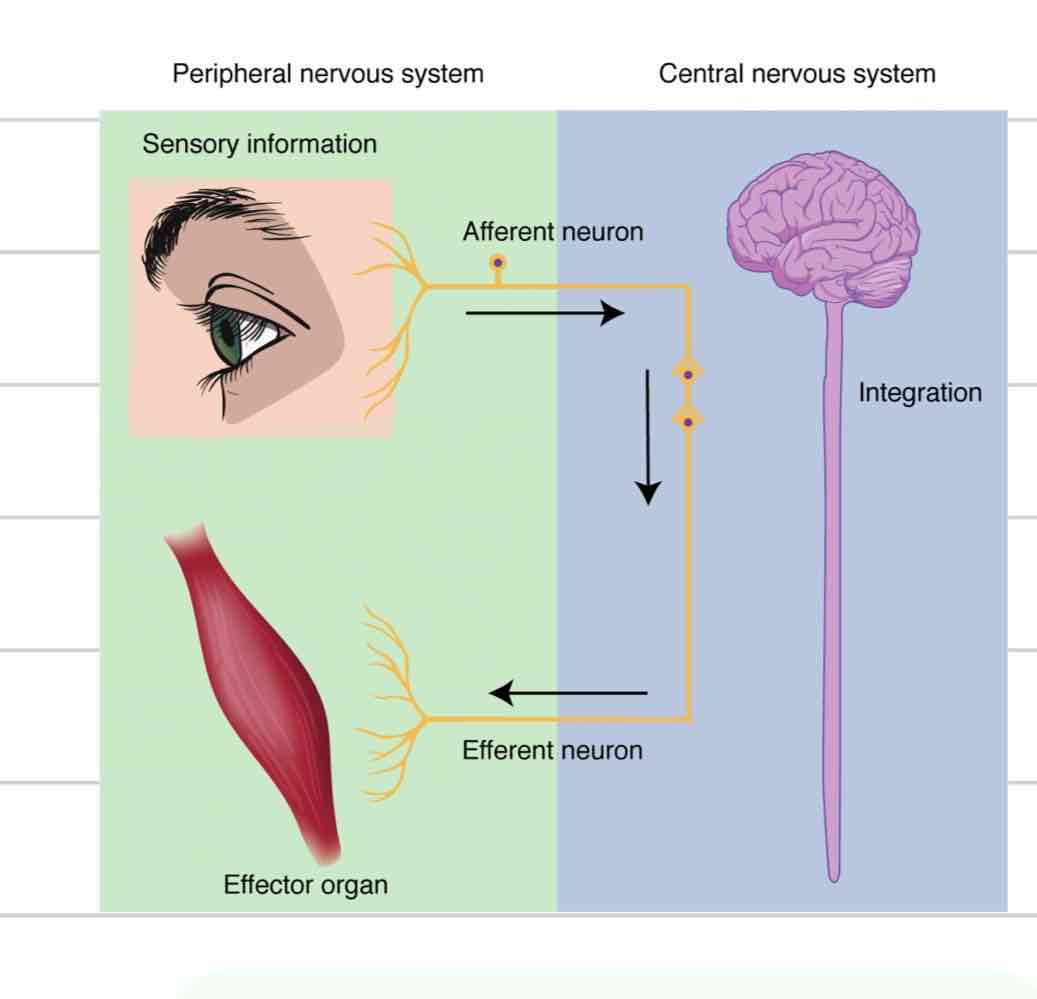
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Cranial and spinal nerves that spread to rest of body
Sensation and movement
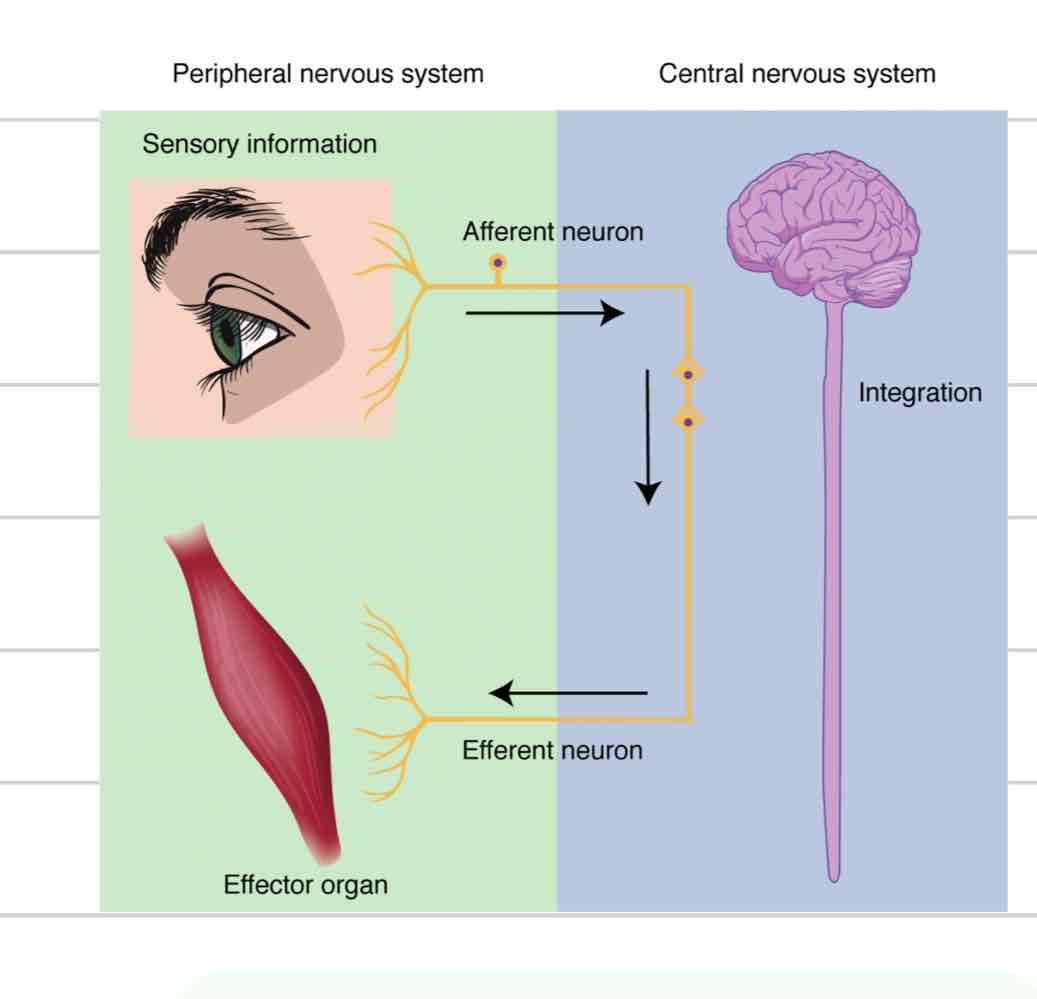
Afferent component of PNS
Sensory
Carries info from extremities to spinal cord and brain
Efferent component of PNS
Motor
Carries info away from spinal cord and brain, to extremities
Somatic Nervous System
Conscious activity
Nerves of skin and muscles
Sensory and motor function
Autonomic Nervous system
Unconscious activity
Heart, GI tract, etc
Sensory and motor function
Functions of afferent system
Sensation of different categories of stimuli
Pressure
Stretch
Temperature
Noxious (discomfort, pain)
Special categories limited to the head
Vision
Audition
Taste
Olfaction
Balance
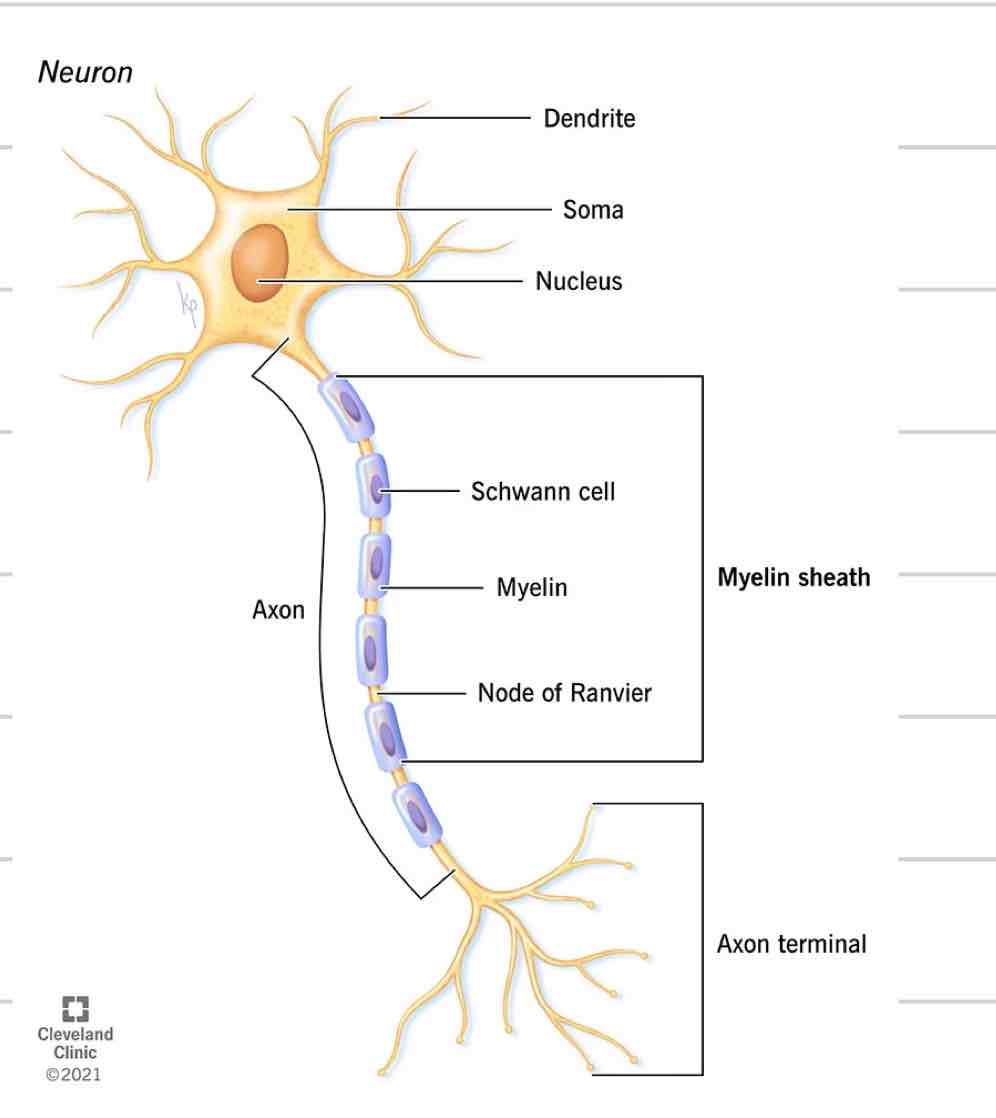
Neuron
Nerve cell
Just like every other cell with a nucleus, cell membrane, etc
4 distinct parts
Soma
Dendrites
Axon
Axon Terminals/ Synaptic knobs
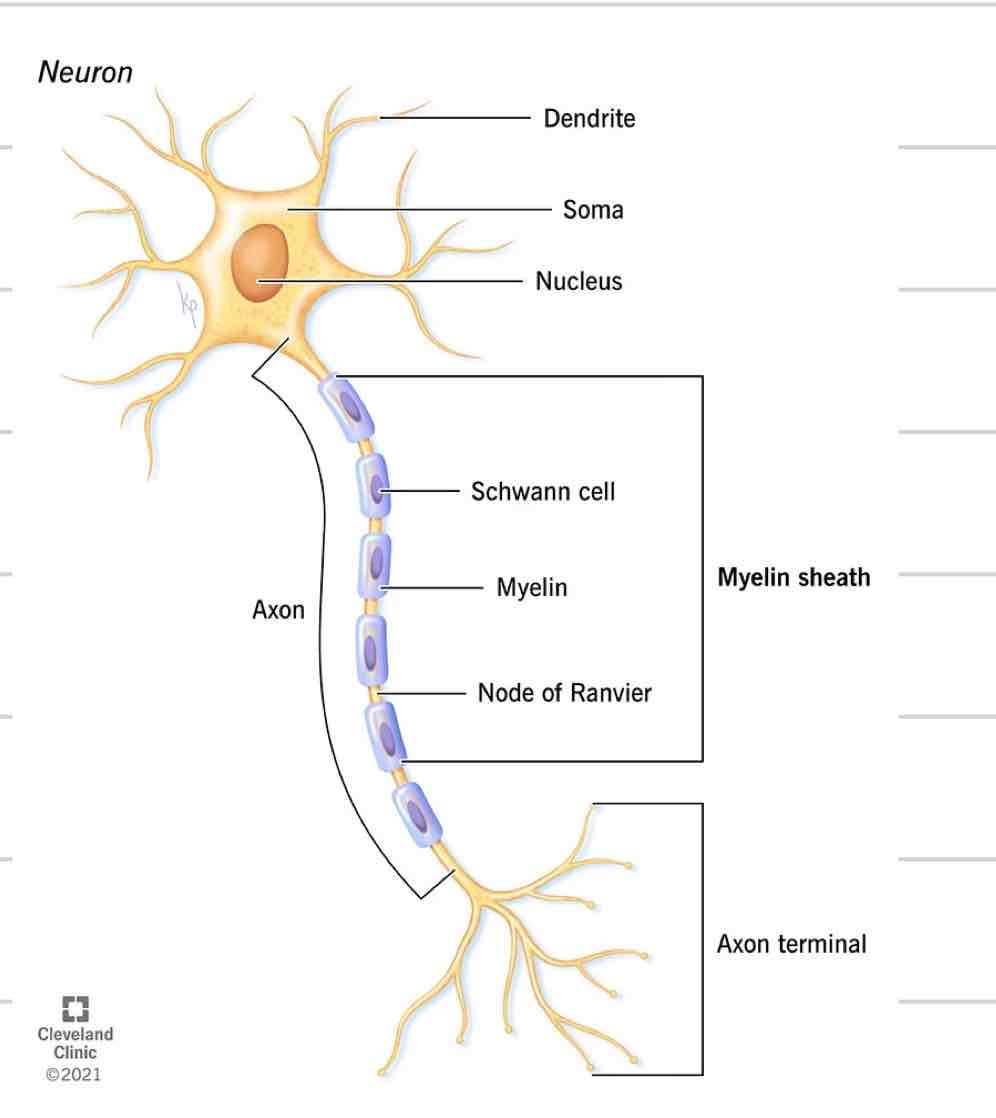
Soma
Cell body where nucleus and other organelles are contained
Sends and receives information
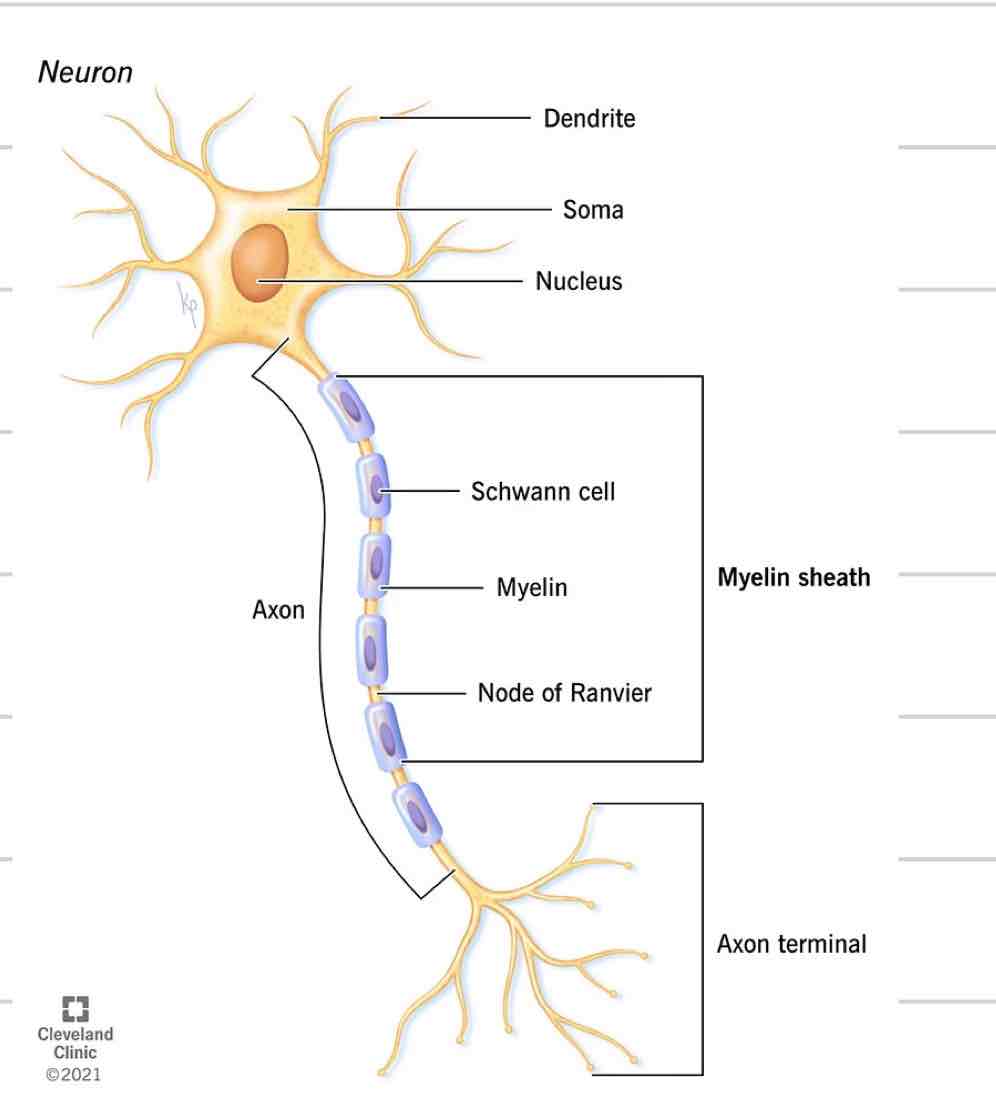
Dendrites
Projections from soma
Receives and transmits electrical impulses, brings to soma
Where they come together at the soma is where info is processed
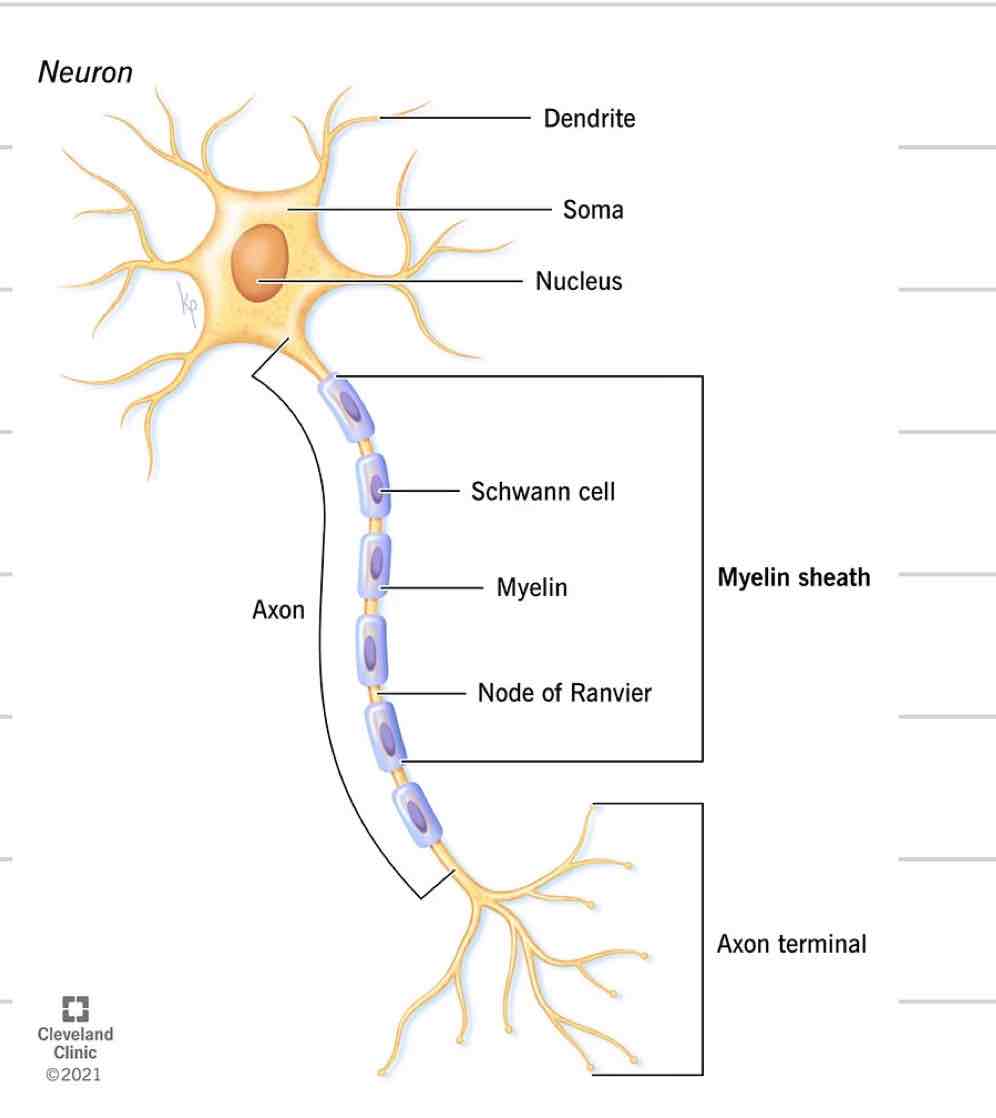
Axon
single projection from soma
Transmit signals away from soma, to another cell
New impulses generated at spot where soma and axon come together
Covered in myelin
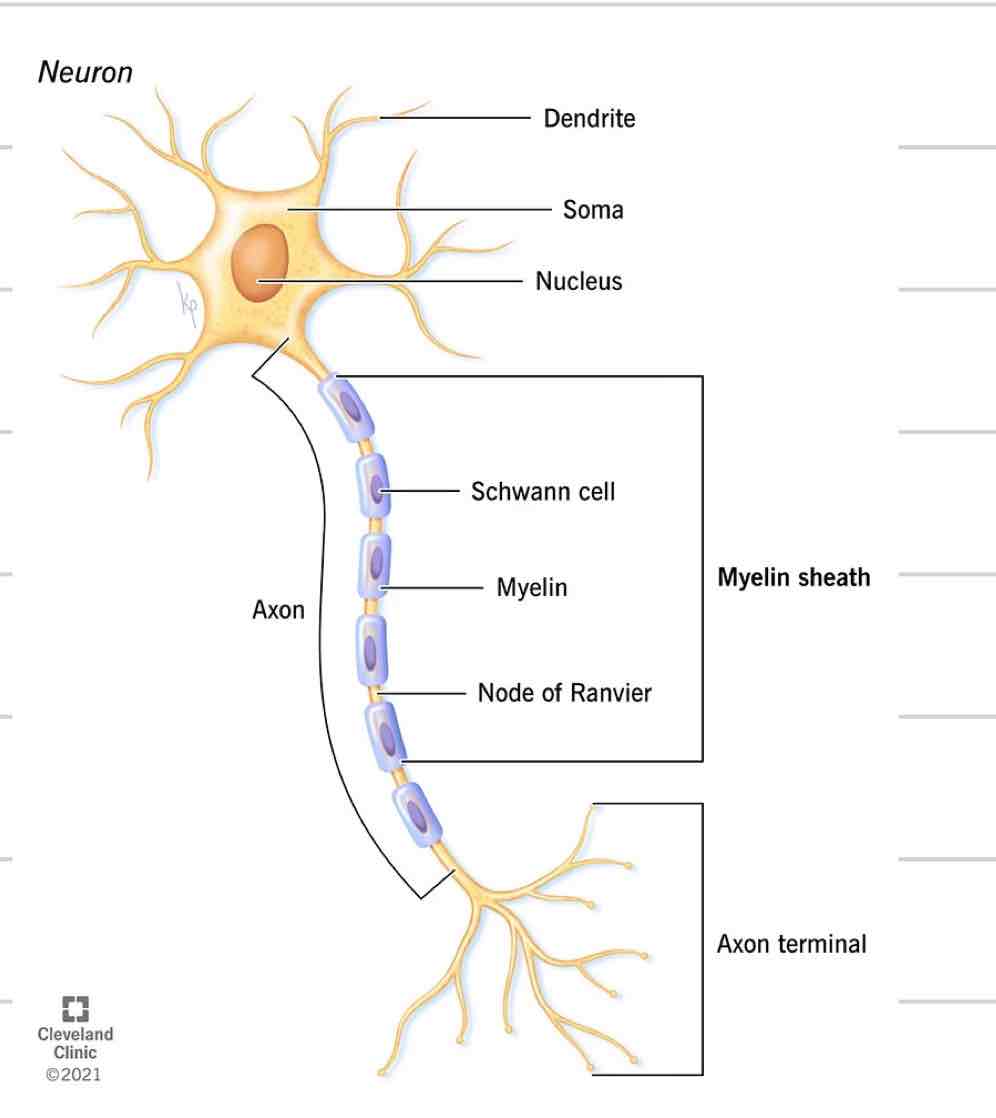
Axon Terminal/ synaptic bulbs
Specialized ending of axon
Interacts with next cell to transmit information
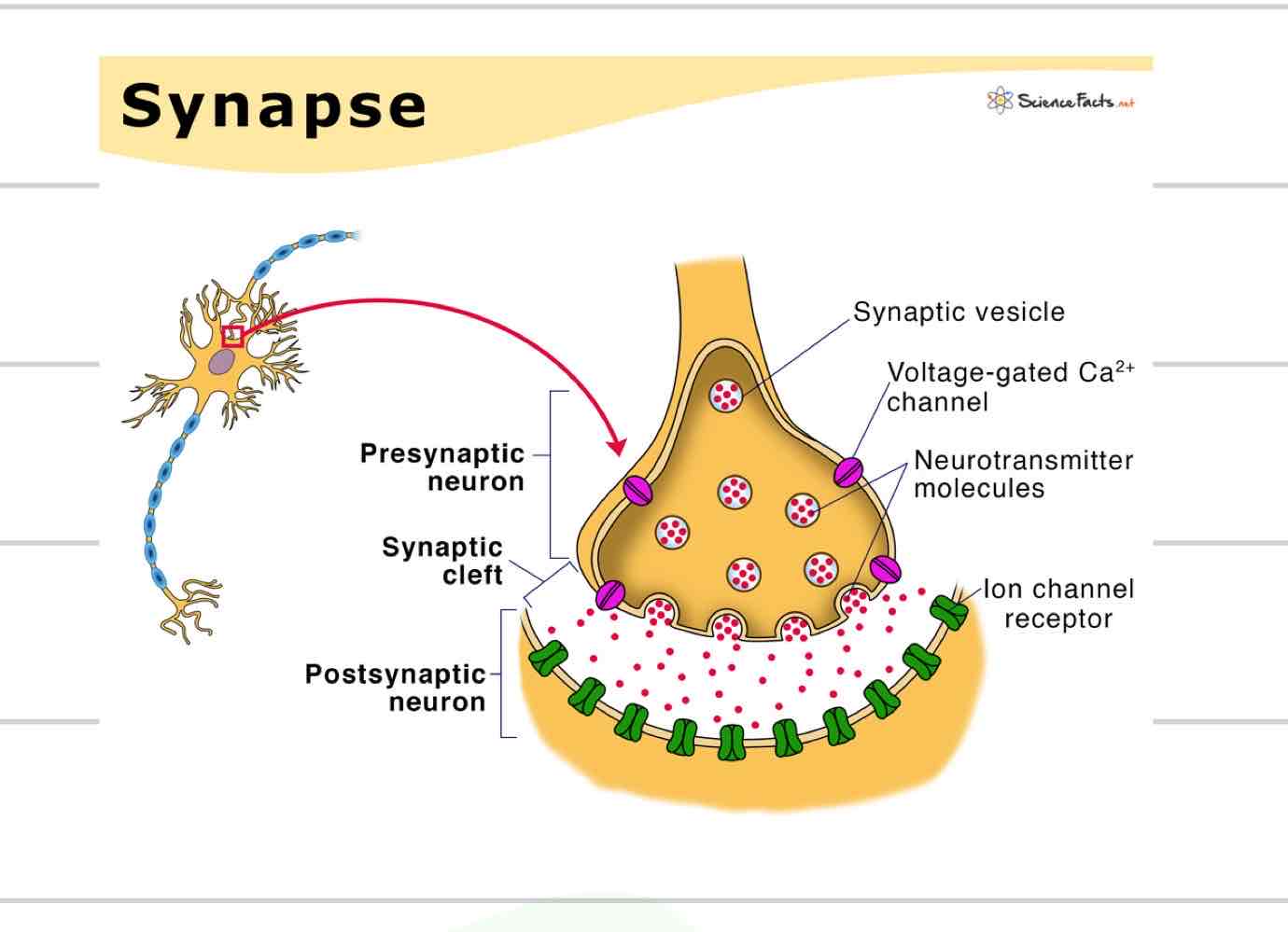
Synapse
Axon terminal converts electrical signal to a chemical signal- a neurotransmitter
Pre-synaptic neuron releases neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft
Neurotransmitter received by post-synaptic neuron or other type of cell
Myelin
Insulated sheath formed around nerve projections
Axon
Dendrites
Provided by supportive cells which differ based on location
Oligodendrocytes- CNS
Schwann Cells- PNS
Increase speed of electrical impulses
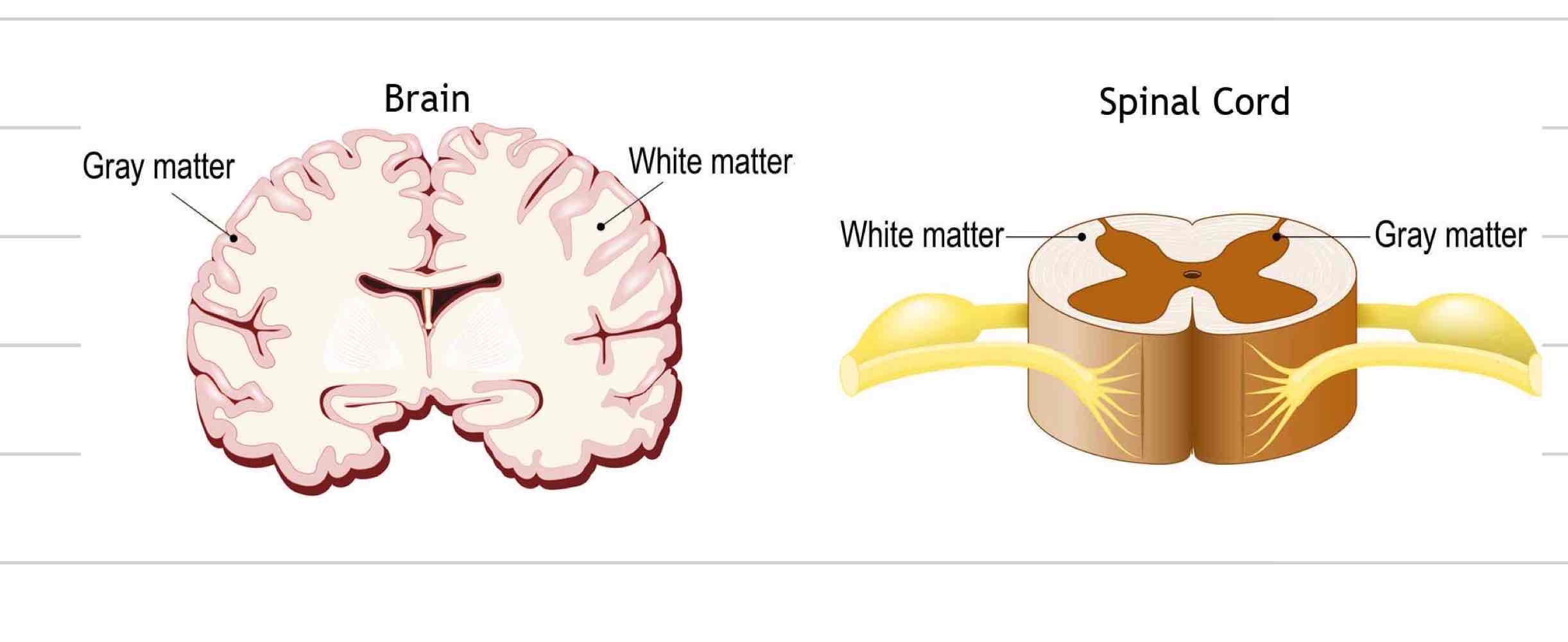
White matter
Regions of CNS where nerves are myelinated
Internal region of brain
External region of spinal cord
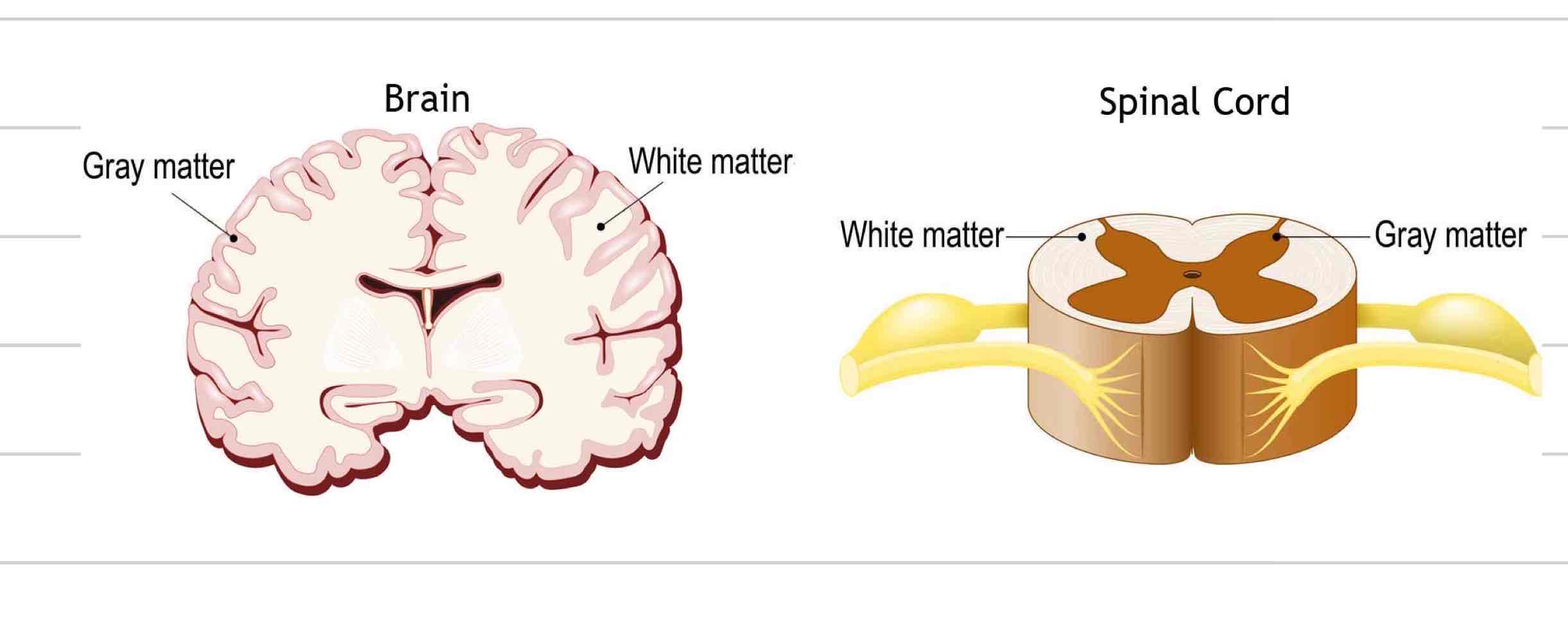
Gray matter
Region of CNS where nerves are not myelinated
External region of brain
Internal region of spinal cord