Unit 4 Questions
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
All of the following could be virulence factors except:
Fimbriae
Capsule
Cell membrane
Flagella
Toxin
Cell membrane
A-E all contribute to a pathogen’s ability to penetrate and/or hide from a host’s defenses except:
Invasins
Capsule
antigenic variation (phase variation)
hyaluronidase
coagulases
There are no exceptions, A-E are all correct
There are no exceptions, A-E are all correct
Which of the following virulence factors among A-E is correctly matched with its definition or characterization?
Invasins: prevents opsonization of pathogen
Transcytosis: mechanism by which a pathogen might pass through tissues
OPA protein or M protein: type of exotoxins
Hyaluronidase or coagulase: used for attachment to cells, a type of adhesin
All are correctly mathced
Transcytosis: mechanism by which a pathogen might pass through tissues
If a vaccine to a specific viral disease only a viral envelope protein, this would be called
A live attenuated vaccine
a nucleic acid vaccine
a recombinant vector vaccine
a subunit vaccine
an inactivated killed vaccine
a conjugated vaccine
none of the above
a subunit vaccine
If a vaccine contained an avirulent form of a whole virus, capable of replicating, this would be called
a live attenuated vaccine
a nucleic acid vaccine
a recombinant vector vaccine
a subunit vaccine
an inactivated killed vaccine
a conjugated vaccine
possibly two of the above
a live attenuated vaccine
The most selective antimicrobial activity would be exhibited by a drug that
inhibits cell wall synthesis
inhibits protein synthesis
injures the plasma membrane
inhibits nucleic acid synthesis
all of the above
inhibits cell wall synthesis
All of the following are modes of action of antiviral drugs except
inhibition of protein synthesis
inhibition of DNA synthesis
inhibition of RNA synthesis
inhibition of uncoating
All of the above are modes of action of antiviral drugs
inhibition of protein synthesis
Within a few weeks of treatment with teh drug 3TC, a patient’s HIV population consists entirely of 3TC-resistant viruses. How can this result best be explained
The drug caused the HIV RNA genome to change
A few drug resistant viruses were present at the start of treatment and natural selection increased their frequency
HIV began making drug resistant versions of reverse transcriptase (a viral enzyme) in response to the drug
A few drug resistant viruses were present at the start of treatment and natural selection increased their frequency
Which among A-F is incorrect?
Streptococcus pathogen: necrotizing fasciitis
Staphylococcus pathogen: boils
Streptococcus pathogen: strep throat
Staphylococcus pathogen: scalded skin syndrome
Streptococcus pathogen: shingles
Staphylococcus pathogen: folliculitis & impetigo
A-F are all correct
Streptococcus pathogen: shingles
All of these typically could potentially cause meningitis EXCEPT
Listeria monocytogenes
Neisseria meningitidis
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Rabies virus
All of these can cause meningitis
Rabies virus

Regarding the pathogen presented thus far, what would be the reservoir of those microbes
Soil
Water
Humans
Animals
None of the above
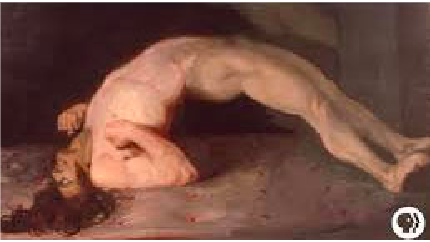
This person is suffering from
A bad back
Meningitis
Botulism
Listeriosis
Tetanus
Tetanus
Humans most frequently contract rabies from the bite of a
Rat
Cat
Bat
Dog
Other
Bat
Which of A-F is not correctly matched?
Infectious disease initially appears in one form, then years later can assume a different form: Herpes-Zoster virus
Intracellular foodborne pathogen that can grow at 4ºC: Listeria monocytogenes
Toxin blocks ability of muscles to contract: Botulism
Gram-negative diplococci able to cross the blood-brain barrier: Neisseria sp.
Lesser virulent member of this group of Gram-positive cocci arranged in grape-like cluster: Staphylococcus epidermidis
Vaccine can be given for treatment following infection: rabies
A-F are all correctly matched
A-F are all correctly matched
Most respiratory infections and gastrointestinal infections are _____ in nature
Bacterial
Fungal
Protozoal
Viral
Viral
Which of A-F is not correctly matched?
Pneumonic form of the disease caused by this pathogen is the most contagious: Yersinia pestis
Common protozoal pathogen causing GI tract infections: Giardia lamblia
One of its toxins kills ciliated cells in the trachea: Treponema pallidum
Facultative intracellular foodborne pathogen: Salmonella enteritidis
Can be the cause of pneumonia and meningitis: Streptococcus pneumonia
In nature, often found in amoebas: Legionella peumophila
A-F are all correctly matched
One of its toxins kills ciliated cells in the trachea: Treponema pallidum
Which of A-E is not considered an obligate or facultative type of intracellular pathogen?
Legionella pneumophila
Listeria monocytogenes
Rabies virus
Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC)
Neisseria meningitidis
All are considered either obligate or facultative type of intracellular pathogen
All are considered either obligate or facultative type of intracellular pathogen
Bacteria
are totally awesome
my best friends
are part of my innate immune system
are my reason for living
All the above
All the above
Which of the following represents a DNA vaccine?
attenuated measles virus
a plasmid containing genes for influenza type A protein
hepatitis B antigen produced in yeast cells
tetanus toxoid
a plasmid containing genes for influenza type A protein
The administration of infectious material into the skin as done with smallpox to generate immunity is termed
variolation
agglutination
phagocytosis
endotoxin effect
variolation
Which of the following among A-D is false?
Gram-negative bacteria: possess endotoxin
Syncytium formation: cytocidal effect of a virus
Subunit vaccine: contains live, attenuated organisms
A-B toxins: exotoxins possessing a targeting binding component and a component that disrupts cell function
None of A-D are false, all are true
Subunit vaccine: contains live, attenuated organisms
All of the following are modes of action of antiviral drugs except:
inhibition of adherence to a cell
inhibition of DNA synthesis
Inhibition of RNA synthesis
Inhibition of uncoating
All of the above are modes of action of antiviral drugs
All of the above are modes of action of antiviral drugs
Within a few weeks of treatment for herpes virus with the drug isoniazid, a patient’s herpes virus population consists entirely of isoniazid-resistant viruses. How can this be best explained?
The drug caused the HIV RNA genome to change
The isoniazid drug spontaneously converted to a form ineffective against the virus
HIV began making drug-resistant versions of reverse transcriptase (a viral enzyme) in response to the drug
None of the above
None of the above
In the presence of penicillin, a cell dies because
it lacks a cell wall
it undergoes lysis
it lacks a cell membrane
it shrinks
it undergoes lysis
Which of the following virulence factors among A-D is correctly matched with its definition or characterization?
Invasins: prevents opsonization of pathogen
Antigenic variation: allows pathogen to switch between different forms of an extracellular antigen (e.g., flagellum)
opa protein or M protein: type of exotoxins
Hyaluronidase or coagulase: used for attachment to cells, a type of adhesin
All are correctly matched
Antigenic variation: allows pathogen to switch between different forms of an extracellular antigen (e.g., flagellum)
Superantigen type toxins lead to the release of excessive amounts of _____ stimulating a hyperactive immune response that can lead to shock and death in teh affected individual
antibodies
Antigenic variation: allows pathogen to switch between different forms of an extracellular antigen (e.g., flagellum)
water
antigen
interferon
cytokines
All of the following contribute to a pathogen’s ability to penetrate host defenses or hide from host defenses EXCEPT:
toxins
capsules
antigenic variation
hyaluronidase
coagulases
toxins
M protein, hyaluronidase, collagenase, and often a capsule, can be virulence factors for certain pathogenic strains of
Listeria
Streptococcus
Neisseria
Staphylococcus
Yersinia
Streptococcus
Respiratory pathogen characterized by pseudomembrane formation in the pharynx and toxin production
Bordetella pertussis
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Streptococcus pyogenes
Legionella pneumonia
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Which of the following virulence factors among A-D is correctly matched with its definition or characterization?
Invasins: prevents opsonization of pathogen
Antigenic variation: allows pathogen to switch between different forms of an extracellular antigen (e.g., flagellum)
Opa protein or M protein: type of exotoxins
Hyaluronidase or coagulase: used for attachment to cells, a type of adhesin
All are correctly matched
Antigenic variation: allows pathogen to switch between different forms of an extracellular antigen (e.g., flagellum)
Which pathogen description pair among A-E is incorrectly matched?
Treponema pallidum: can become a latent infection that later results in shingles
Staphylococcus aureus: some strains form exotoxins that cause gastroenteritis
Streptococcus mutans: Gram-positive, alpha-hemolytic pathogen that can cause cavities in your teeth
Streptococcus pneumoniae: primary cause of bacterial pneumonia among humans
Yersinia pestis: vector borne disease that causes a sytemic infection
A-E are all correctly matched
Treponema pallidum: can become a latent infection that later results in shingles
Which is false among A-C regarding sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)?
Treponema pallidum: causative agent of syphilis
Since STD pathogens are susceptible to drying out, they require direct contact with mucous membranes for transmission
Tertiary syphilis: presence of chancres at site of infection caontaining pathogen
None of A-C are false; all are true statement
Tertiary syphilis: presence of chancres at site of infection caontaining pathogen
Which of A-F is not correctly matched?
More likely to cause GI tract upset than any other microbe: virus, e.g., rotavirus
Spirochete-causing STD: Treponema pallidum
Intracellular foodborne pathogen that can cause meningitis: Listeria monocytogenes
Gram-negative vector borne pathogen that is at its most contagious if it enters the lungs: Yersinia pestis
This Gram positive causes GI problems without being in your gut: Staphylococcus aureus
An intracellular pathogen; disease outbreaks associated with contaminated water used for commercial AC ventilation systems: Legionella
A-F are all correctly matched
A-F are all correctly matched
All of the following are modes of action of antiviral drugs except
inhibition of protein synthesis at 70s ribosomes
inhibition of DNA synthesis
inhibition of RNA synthesis
inhibition of uncoating
All of the above are modes of action of antiviral drugs
inhibition of protein synthesis at 70s ribosomes
For which diseases listed below does the pathogen responsible have to cross the blood-brain barrier in order to produce the disease?
Necrotizing fasciitis
meningococcal meningitis
dysentery
tetanus
plague
meningococcal meningitis
For which disease listed below might treatment include vaccination after the individual has already acquired the pathogen; this is possible due to the slow nature of growth of the agent and the resulting slow progress of the disease.
Necrotizing fasciitis
meningococcal meningitis
rabies
tetanus
plague
rabies
Superantigen type toxins lead to the release of excessive amounts of _______ stimulating a hyperactive immune response that can lead to shock and death in the affected individual.
antibodies
cytokines
water
antigen
interferon
cytokines
In the presence of penicillin, a cell dies because
it lacks a cell wall
it undergoes lysis
it lacks a cell membrane
it shrinks
it undergoes lysis
Within a few weeks of treatment with the drug 3TC, a patient’s HIV population consists entirely of 3TC-resistant viruses. How can this result best be explained?
The drug caused the HIV RNA genome to change
A few drug-resistant viruses were present at the start of treatment and natural selection increased their frequency
HIV began making drug-resistant versions of reverse transcriptase (a viral enzyme) in response to the drug
None of the above
A few drug-resistant viruses were present at the start of treatment and natural selection increased their frequency
Which of the following represents a toxoid vaccine?
attenuated measles virus
a plasmid containing genes for influenza type A protein
hepatitis B antigen produced in yeast cells
tetanus vaccine
tetanus vaccine
If a vaccine to a specific viral disease contained only a virus envelope protein, this would be called
a live attenuated vaccine
a nucleic acid vaccine
a recombinant vector vaccine
a subunit vaccine
a conjugated vaccine
an inactivated killed vaccine
a subunit vaccine
Use of antibiotics in animal feed leads to antibiotic-resistant bacteria because
bacteria from other animals replace those killed by the antibiotics
the few surviving bacteria that are affected by the antibiotics develop immunity to the antibiotics, which they pass on their progeny
teh antibiotics cause new mutations to occur in the surviving bacteria, which results in resistance to antibiotics
the antibiotics kill susceptible bacteria, but the few that are naturally resistant live and reproduce, and their progeny repopulate the host animal
the antibiotics persist in soil and water
the antibiotics kill susceptible bacteria, but the few that are naturally resistant live and reproduce, and their progeny repopulate the host animal
All of the following contribute to a pathogen’s ability to penetrate host defenses or hide from host defenses, EXCEPT
toxins
capsules
antigenic variation
hyaluronidase
coagulases
toxins
For which disease, or diseases, are humans the primary reservoirs?
plague
tetanus
meningitis
listeriosis
none of the above
meningitis
The group contains pathogens that can be differentiated by reactions observed on blood agar
Staphylococcus
Listeria
Streptococcus
Neisseria
E coli
Streptococcus
Botulism differs from tetanus in that
botulism causes flaccid paralysis and tetanus causes spastic paralysis
tetanus is a food-borne disease and botulism is airborne
botulism is due to an exotoxin and tetanus is due to an endotoxin
botulism toxin acts directly on muscle cells
two of the above are correct
botulism causes flaccid paralysis and tetanus causes spastic paralysis
The gram stain would not be an effective tool to assist in the identification of this pathogen
Listeria monocytogenes
Giardia lamblia
Yersinia pestis
Clostridium tetani
Shigella dysenteriae
The identification of all the above can be aided by performing a Gram stain
Giardia lamblia
The presence of Gram-negative diplococci in cerebrospinal fluid is generally diagnostic for
gonorrhea
tetanus
meningococcal meningitis
syphilis
listeriosis
meningococcal meningitis
Which characteristic or feature among A-D is not applicable to the listeriosis pathogen
capable of multiplying within a cell
ability to grow at 4ºC
polymerization of actin for cellular movement
is widespread in soil, water, animals
all are applicable
all are applicable
Botulism toxin, tetanus toxin, and vibrio enterotoxin are all examples of
endotoxin
exotoxin
A-B type toxins
membrane-disrupting toxins
two of the above are correct
two of the above are correct
Endotoxins
caused by gram-negatives
Exotoxins
Cell membrane disruptors
protein synthesis disrupters
second messenger pathway disrupters
superantigen
proteases
Adhesins
Fimbriae/pili; glycoproteins
M protein; Opa protein
Intracellular pathogens
Invade host cell → invasins; membrane ruffling of host cell; actin rockets
Ingestion via phagosome → break out; survive in phagolysosome; prevent fusion w/ lysosome
Extracellular pathogens
Capsule
Bind/degrade antibodies → Proteins A (Staph); IgA protease (Neisseria)
Bind complement → M protein (Strep)
Phase variation