ch. 11 : exercise and sport psychology
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
exercise psychology
the application of psychology to the promoting, explaining, maintaining, and enhancing of the parameters of physical activity (how cognition, emotions and behaviors relate in strength and endurance)
sport psychology
application of psychological principles to sport (more on a competitive level)
academic exercise and sport psychologists
expand knowledge through teaching and critical research
applied exercise and sport psychologists
apply knowledge to real world situations; provide information on the role of psychological factors on exercise, PA
clinical exercise and sport psychologists
help athletes solve issues related to mental health, anxiety and drug dependence
beginnings of exercise and sports psychology ?
late 19th and early 20th centuries
Norman Triplett
conducted the first true experimental study in exercise psychology; study found that anxiety effects competition (competition fueled some and impaired others)
Coleman Griffith
father of American sport psychology
1960s & 1970s (exercise and sports psychology)
matures into a true discipline
1980s and 1990’s (exercise and sports psychology)
developmental and growth of research
parent disciplines (exercise & sports psychology)
psychology (study of human behavior)
physical education (improve and enhance performance during PA)
exercise psychology
area of study that involves applying psychology to the promotion, explanation, maintenance, and enhancement of physical activity
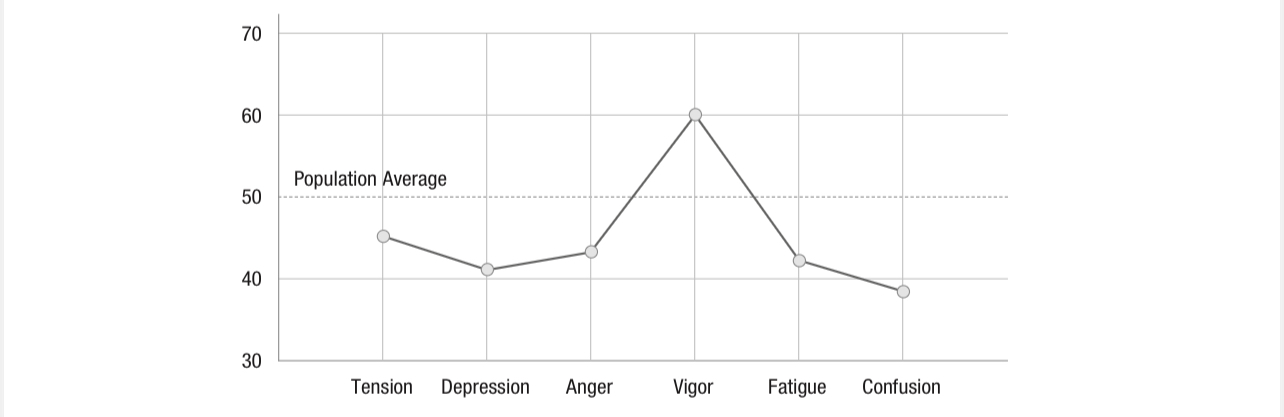
iceberg profile (Morgan et al.)
used to predict or assess mood state of athletes; score high on variable vigor
exercise adherence
degree to which an individual follows the recommended frequency, intensity, and duration in any given program or activity. (how well someone sticks to their recommended program or activity)
percentage of people who drop out of an exercise program within the first 6 months
50%
factors affecting exercise adherence
Physiological factors (body weight, body fat, angina pectoris)
psychological factors (self-motivation, attitudes toward exercise, and health knowledge and beliefs)
social factors (marital status, spousal and family social support, peer social support, and work demands)
program factors (enjoyment, convenience, quality of the exercise facility and equipment, program social support, group versus individual programs, program leadership, and program intensity)
exercise dependence syndrome
an addiction to exercise that can cause depression and withdrawal
primary exercise dependence: being addicted to exercise itself; increasing exercise intensity, duration, or frequency of exercise; lying to a spouse about exercising
secondary exercise dependence: using exercise to control body composition
Selye’s 3 stages of general adaptation syndrome
Alarm stage: initial stage, occurring at the onset of stress. (body mobilizes its mechanisms to meet the demands of the stress)
resistance stage: second stage; stress syndrome disappears, body becomes more resistant to the stressor
exhaustion stage: final stage; stress syndrome reappears and body enters a state of decline
exercise and mood states
A researched area in exercise psychology focusing on the effect of acute and chronic exercise on mood states
Monoamine Hypothesis
Holds that increased levels of central monoamine neurotransmitters give rise to feelings of positive affect
Thermogenic Hypothesis
Holds that elevation in body temperature accompanying exercise contributes to the perception of positive affect
distraction hypothesis
Holds that the psychological distraction or break from daily life provided by exercise is responsible for changes in affect, rather than the exercise itself
mastery hypothesis
Holds that exercise may increase one’s sense of self-mastery or accomplishment, thereby leading to improved affect
trait theory
Trait measurements are concerned with a more stable long-term characteristic within the individual; In sport psychology, this relates to the idea that individuals in different sports might have differing, potentially stable, personality profiles
situational approach
this hypothesis assumes that individuals have different situation-specific anxiety levels and a repertoire of coping options available to them from which they can choose, depending on the situation's characteristics
overtraining
incorrect dose of frequency, intensity, duration, and mode in a training and conditioning program
staleness
increased negative mental health and decreased performance
burnout
An unresponsive stagnation or a debilitating withdrawal from the sport. It is a psychological syndrome characterized by emotional exhaustion, reduced accomplishment, and depersonalization
behavioral theoretical approach
participants are viewed as being primarily motivated by factors external to themselves
Psychophysiological approach
examine the physiological processes of the brain and their influences on the physical activity
Cognitive–Behavioral
assumes that the behavior of individuals is determined by their cognitive mental (or “thinking”) processes
Global positioning systems (GPS)
transmit continuous microwave signals via satellites to
a GPS receiver that computes estimated energy expenditure by tracking speed, slope, and duration of physical activity
fitness and wellness field
includes personal trainers, directors of corporate fitness and wellness programs; having the ability to apply motivational techniques and adherence strategies would be particularly valuable
rehabilitation field
athletic trainers, physical therapists, and cardiac rehabilitation staff; The ability to increase confidence and reduce stress in an individual participating in rehabilitation
consulting field
developing cognitive behavioral strategies or imagery training schema to enhance performance