BIOL 3000 Genetics and Crime
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms (RFLP)
Molecular technique used to identify variations in DNA sequences.
RFLP Process
Cell sample → DNA is extracted → Cleavage of DNA by restriction enzyme → Separation of DNA fragments by electrophoresis → Transfer to a membrane (Southern blatt) → Binding of radioactive DNA probe to specific DNA fragments → Membrane washed free of excess probe → X-Ray film used to detect radioactive pattern → DNA comparison
Restriction enzymes
An enzyme produced chiefly by certain bacteria, having the property of cleaving DNA molecules at or near a specific sequence of bases. Bacterial proteins such as palindromic sequences
Cleave ae specific DNA (Palindromic Sequences)
Found in prokaryotic organisms as a part of the bacterial immune system
Restriction Sites can be protected from digestion by the addition of Methyl groups
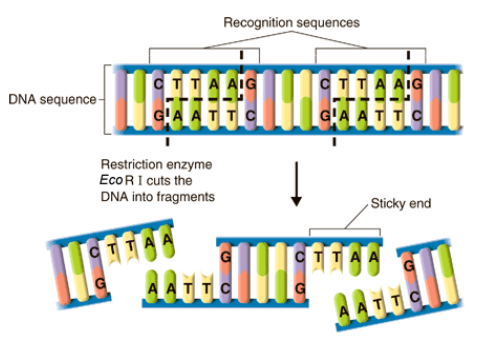
RFLP Analysis
Isolate DNA samples from crime scene and suspects → Treat DNA with Restriction Enzymes → Label DNA with radioactive markers → Electrophorese labeled DNA → Expose to X-Ray film
Variable Number Tandem Repeat (VNTR)
Any location in the genome where a short nucleotide sequence is arranged as a tandem repeat, like microsatellite repeats
Similarities of Restriction Enzymes and VNTR
Isolates DNA from a sample
Electrophorese
Number of specific cut sites in DNA yielding different band patterns
Differences of Restriction Enzymes vs. VNTR
Restriction Enzymes: Cut with enzymes, requires a lot of DNA, longer time to perform and expensive
VNTR: Specific primers to access region of interest (PCR), can use PCR to increase the DNA amount, and it is much quicker and cheaper
DNA Fingerprinting
Most often used to exclude a suspect
Victim vs. Suspects
Short Tandem Repeats (STR)
A microsatellite consisting of a unit of two to thirteen nucleotides repeated several to dozen of times in a row on the DNA strand
STR Analysis
Used to compare specific loci on DNA from two or more samples.
Strand Slippage
Misalignment of repeating STRs → Resulting in the addition or deletion of Repeats (microsatellites) or bases
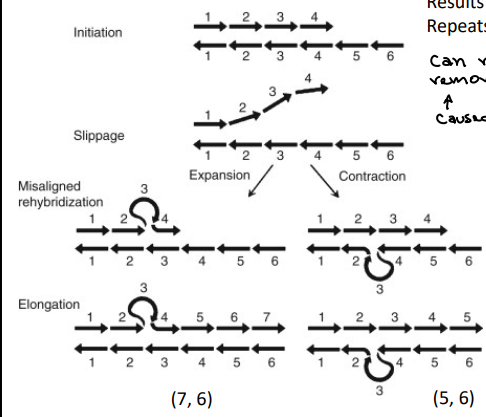
DNA Fingerprinting - STR
Isolate DNA samples from crime scene and suspects → Amplify DNA using PCR → Label DNA with fluorescent markers → Capillary-Electrophoresis → Laser Detection
Differences of VNTR vs. STR
VNTR: Repeats are 10-100 bp in length, DNA sequence 50-5000 bp in length, many different alleles, found often in heterochromatin, cumbersome and time consuming, hard to tell lots of alleles apart, tend to occur at the end of chromosomes, requires a lot of DNA
STR: Repeats are 2-6 bp in length, DNA sequence < 500 bp in length, Occur all over the chromosome especially in euchromatin, Lend very well to PCR, Number of Repeats is highly variable, Small size allows separation from other areas of the chromosome, Quicker results because Smaller
Combined DNA Index System (CODIS)
A nationwide database managed by the FBI that helps state and local crime labs compare DNA profiles electronically.
DNA Profile
Consists of ONE or TWO alleles for each individual profile at the 13 CODIS Core Loci (+7 recently added). Only data from STR, Y-STR or mtDNA technologies are stored in CODIS.
Loci refers to where the microsatellites happen to be
How CODIS works
Collect DNA evidence → Generate DNA profile → Submit PROFILE to CODIS → Search indices for match
Y-Chromosome STR
All paternally linked males have the same Y-STR profile
Very useful when analyzing evidence with high amounts of female DNA and low amount of Male DNA (sexual assaults)
Application in paternity cases
PARABON DNA Phenotyping
The process of predicting an organism’s phenotype using only genetic information collected from genotyping or DNA sequencing
Test 100,000’s of SNPs based off single nucleotide polymorphisms
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)
Most common type of genetic variation found in humans
Differences at one specific place
One SNP may occur in ~1% of the population
Almost always biallelic
Are a measure of genetic similarity
Forensic DNA Phenotyping
Prediction of appearance traits of unknown sample donors based upon DNA samples.
Current Externally Visible Characteristics (EVCs): eye, hair, and skin color
Future Externally Visible Characteristics (EVCs): body height/stature, hair vs. baldness, age predictions
Exceptions to DNA Phenotyping
Artificial alterations in appearance
Legal issues
Idea is in its infancy