Intro to Management Exam 2
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Ethics
standards of right and wrong. May vary among countries and cultures
Ethical behavior
actions that are accepted as right and wrong according to standards
ethical dilemma
a situation in which you have to decide to pursue a course of action that may benefit you or your organization but is unethical or even illegal
Two conflicting value systems an organization may have
the value system stressing financial performance and the value system stressing cohesion and solidarity in employee relationships
Five most common unethical behaviors at work
1. misusing company time
2. abusive behavior
3. employee theft
4. workplace cheating
5. violating corporate internet policies
The utilitarian approach
guided by what will result in the greatest good for the greatest number of people
The individual approach
guided by what will result in the individual's best long-term interests
The moral-rights approach
guided by respect for the fundamental rights for humans shared by everyone
The justice approach
guided by respect for impartial standards of fairness and equity
The rock star theory hypothesis
variation in outcomes will primarily be a result of expectations endowments engagement or environments meaning differences will arise due to initial conditions
Feedforward control
focuses on preventing future issues
Concurrent control
Entails collecting performance information in real time
Feedback control
Uses information about the past results to identify and fix issues
Total Quality Management (TQM)
the philosophy that everyone in the organization is concerned about quality, throughout all of the firm's activities, to better serve customer needs
ISO 9000
ethical procedures a company must adhere to but doesn't include environment
ISO 14000
extends ISO 9000 concept by identifying standards for the environmentterm-45
The four developmental processes
1. New strategy
2. New capabilities
3. New business development
4. New product development
Balance Scorecard
strategy implementation tool that harnesses multiple internal and external performance metrics in order to balance financial and strategic goals
The four types of balance scorecards
1. Customer satisfaction
2. Internal processes
3. Innovation and improvement activities
4. Financial measures
The four growth strategies
market penetration, market development, product development, diversification
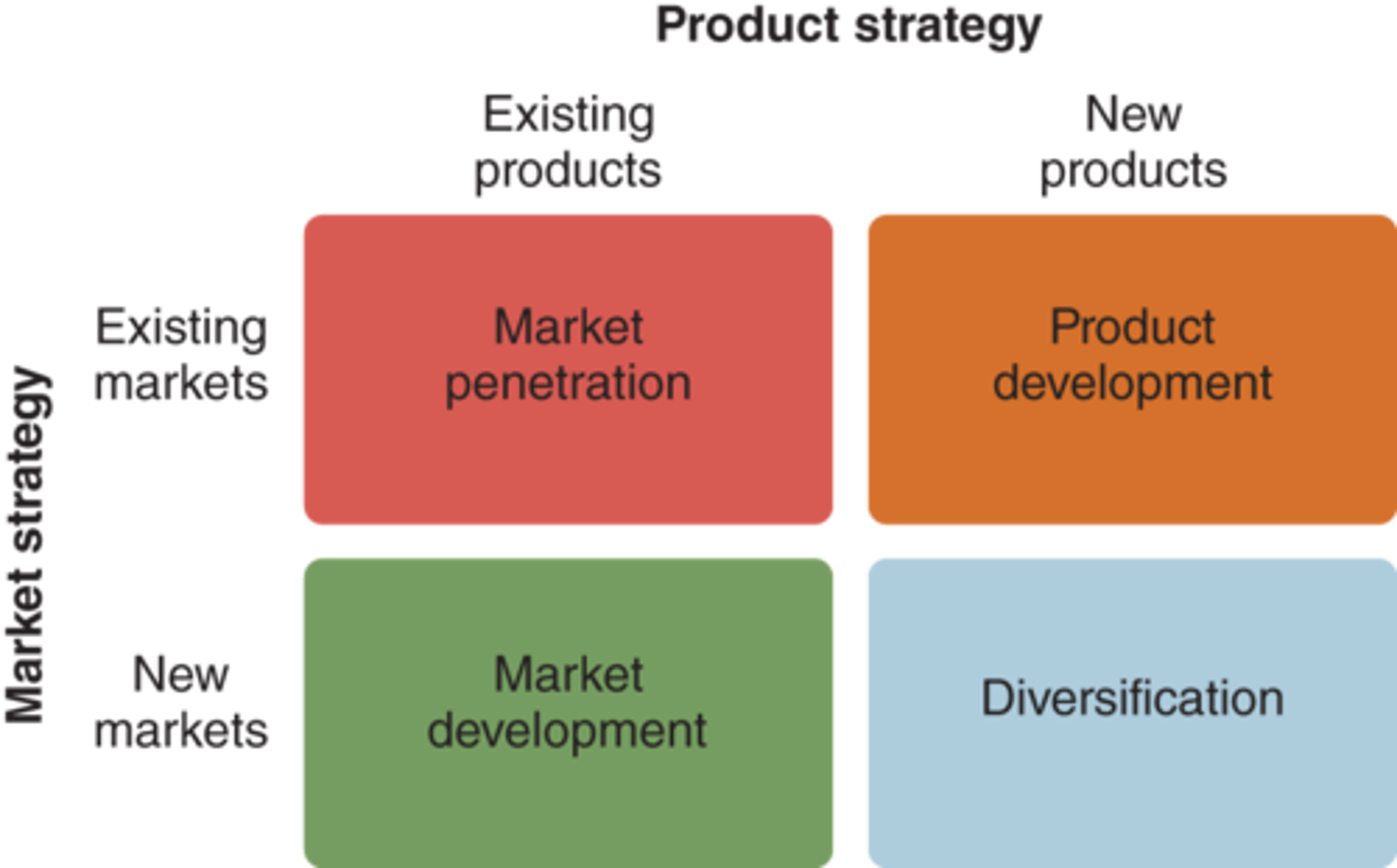
Managing Cooperative Strategies
Cost minimization
Opportunity maximization
cost minimization
a firm's goal of producing a specific quantity of output at minimum cost
opportunity maximization
Intended to maximize value-creating opportunities by sharing of ideas and resources
Less formal contracts and fewer constraints on partners' behaviors
Based on values of trust, respect, and transparency (open and truthful sharing of information)
Three kinds of change from least to most threatening:
Adaptive - innovative - radically innovative
Lewin's Change Model for the individual
1. Unfreezing
2. Changing
3. Refreezing
4. Feedback loop
Lewin's Change Model for development
1. diagnosis
2. intervention
3. evaluation
4. feedback loop
To be innovative a product must:
Be commercialized and make a profit
code of values
standards a company abides by
Value Chain
The steps it takes to develop a code of values
Joint Venture
a way for a company to form a strategic alliance with a foreign company to share risks and rewards if starting new business in a foreign country
strategic alliance
firms combine some resources for the purpose of creating a competitive advantage
Franchising
firm using contract relationship to describe and control sharing of resources with its franchises
Licensing
allows foreign companies to pay a fee to make and sell its products/services
Globalization
trend of world economy toward becoming a more interdependent system
Rise of globalization is due to:
1. Rise of global village and ecommerce
2. World becoming one market
3. Rise of megafirms and internet minifirms worldwide
Global village
the "shrinking" of time and space as air travel and the electronic media have made it easier for the people around the globe to communicate with one another
Ecommerce
the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet
Ethnocentric
Belief in the superiority of one's nation or ethnic group.
Polycentric
Belief that managers in the host country know the best approaches
Geocentric
Belief that both countries have valid ideas and the best approaches vary between the home and foreign nation based on the circumstance.
Free trade
international trade free of government interference
Proectionism
national policies designed to restrict international trade, usually with the goal of protecting domestic businesses
World Trade Organization (WTO)
designed to monitor and enforce trade agreements
World Bank
an international bank that offers low-interest loans, advice, and information to developing nations
Trading blocs
A group of neighboring countries that promote trade with each other and erect barriers to limit trade with other blocs. Most relevant to us is NAFTA
low-context culture
shared meanings are primarily derived from written and spoken words. includes the USA
high-context culture
people rely heavily on situational cterm-45ues for meaning when communicating with others
Stakeholders
the people whose interests are affected by an organization's activities
Stakeholders exist in 3 organizational environments
1. Internal (owners, employees, board of directors)
2. External- task
3.External- general
Social Responsibility
the manager's duty for ethics and corporate social responsibility is corporate duty for ethics
Benchmarking
a process by which a company compares its performance with that of high-performing organizations
Control Chart
a time-ordered diagram that is used to determine whether observed variations are abnormal
control process steps
1. establish standards
2. measure performance
3. compare performance to standards
4. take corrective action, if necessary
control standard
the desired performance level for a given goal
Deming management
proposed ideas for making organizations more responsive, more democratic, and less wasteful
Financial Ratios
calculations typically used to track a business's liquidity (cash), efficiency, and profitability over time compared to other businesses in its industry
incremental budgeting
a method of budget making that involves adding new funds (an increment) onto the amount previously budgeted (in last year's budget)
backward/forward integration
occurs when a firm owns or controls the inputs it uses
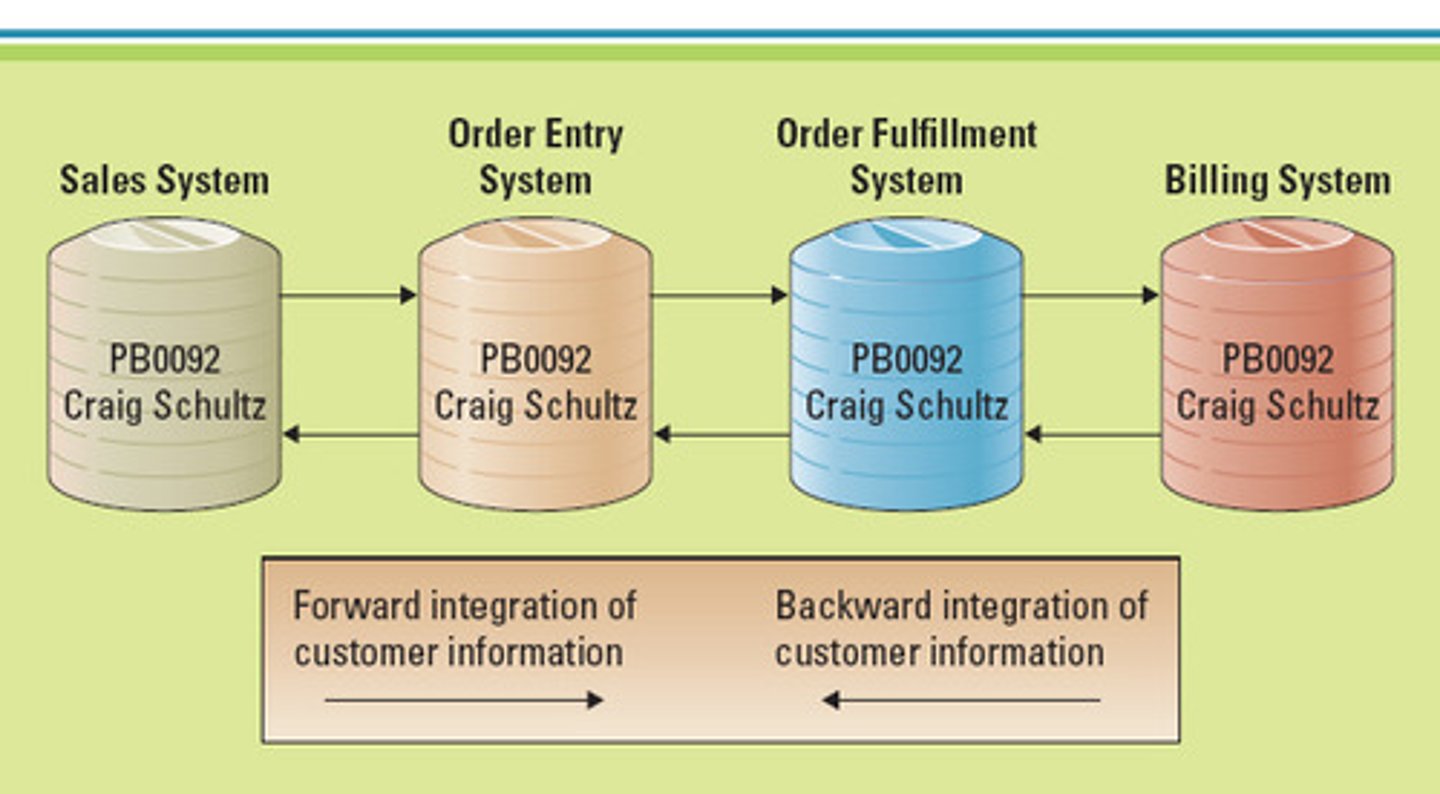
market power
the ability of a single economic actor (or small group of actors) to have a substantial influence on market prices
diseconomies of scale
the situation in which a firm's long-run average costs rise as the firm increases output
economies of scale
a proportionate saving in costs gained by an increased level of production.
diversification strategies
emphasize both new products and new markets to achieve growth
Organic growth
growth achieved through the expansion of current business activities
unrelated diversification
a growth strategy whereby a new business lacks any common elements with the present business
Countertrading
a complex form of bartering in which several countries may be involved, each trading goods for goods or services for services
cross-cultural awareness
ability to interact effectively and appropriately with people from different language and cultural backgrounds
Dumping
selling products in a foreign country at lower prices than those charged in the producing country
Embargo
an official ban on trade or other commercial activity with a particular country.
exchange rate
The measure of how much one currency is worth in relation to another.
expatriate
a migrant worker who is a professional or skilled worker in his or her profession.
Expropriation
Forced transfer of assets from a company to the government with compensation
Foreign Corrupt Practices Act
a law that prohibits U.S. corporations from making illegal payments to public officials of foreign governments to obtain business rights or to enhance their business dealings in those countries
global outsourcing
using suppliers outside the US to provide labor, goods, or services
GLOBE project
a massive and ongoing cross-cultural investigation of 9 cultural dimensions involved in leadership and organizational processes
greenfield venture
establishes a foreign subsidiary by building an entirely new operation in a foreign country
Hofstede model of four cultural dimensions
power distance, uncertainty avoidance, individualism, masculinity