Chapter 9: Immunity Mediated by B Cells and Antibodies
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
B cell receptor (BCR)
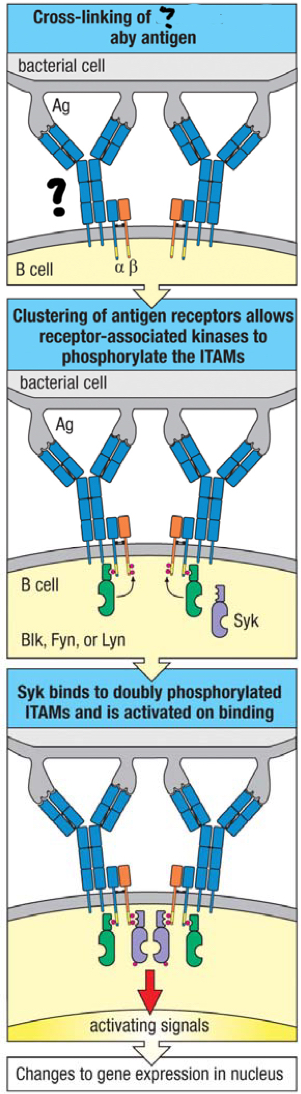
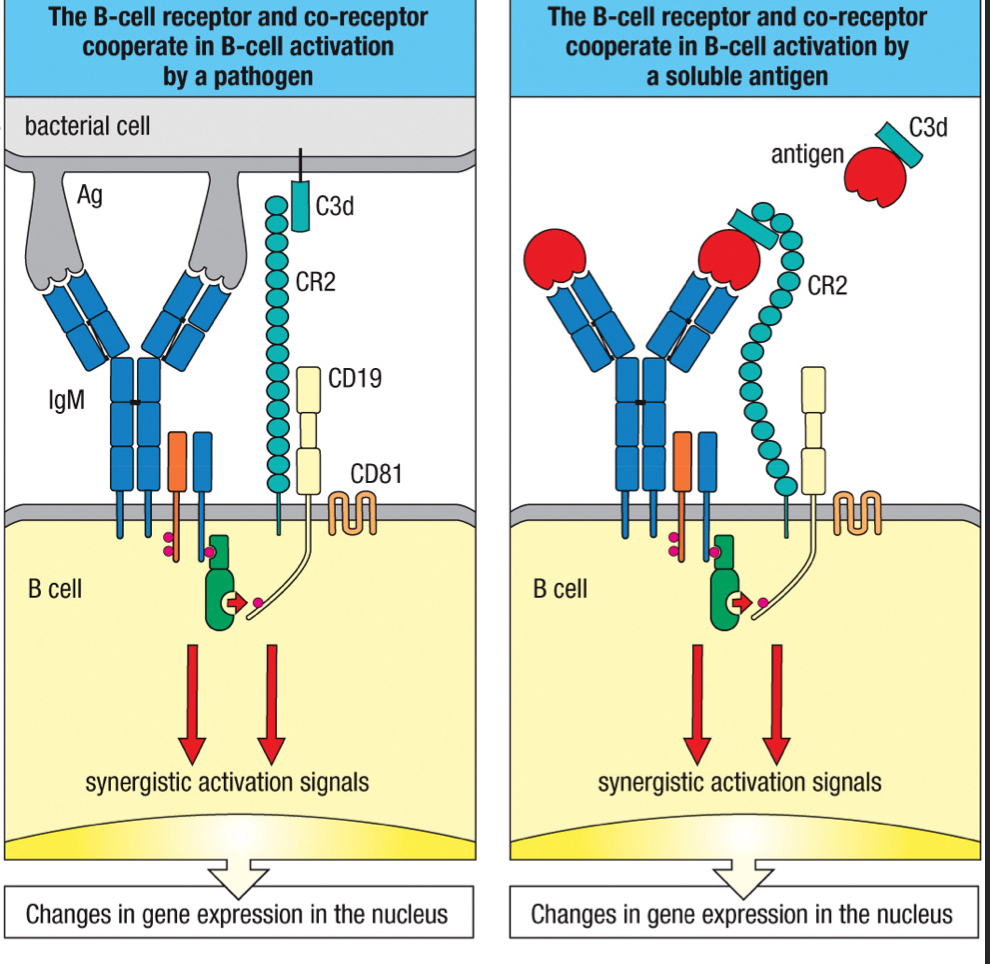
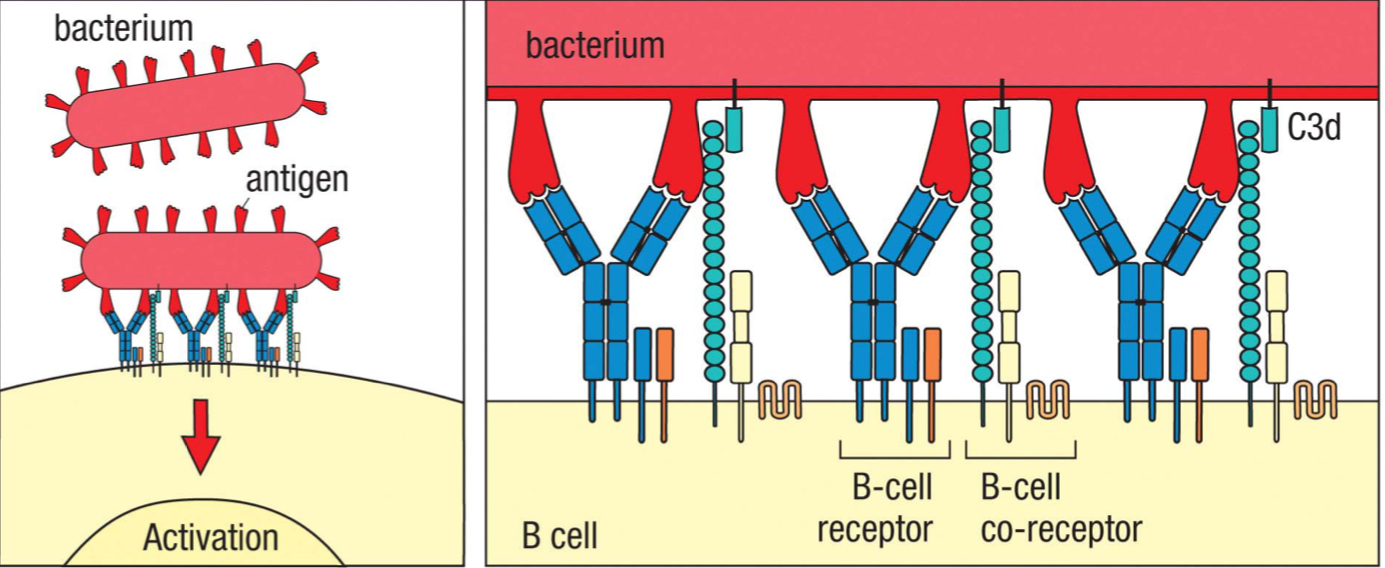
membrane bound IgM on a mature naive B cells that receives an antigens and triggers B cell activation; upon binding to multiple identical epitopes, it’s crosslinked to each other and clustered together, triggering a phosphorylation cascade of signal transduction
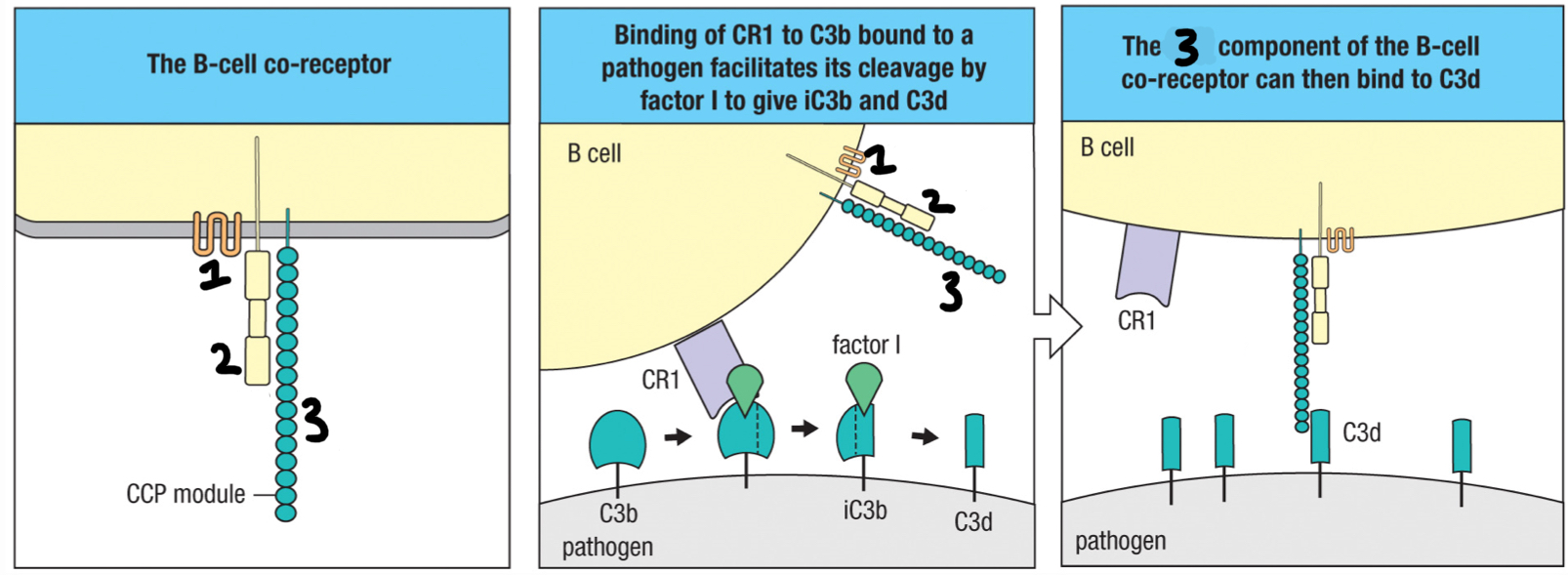
complement receptor 2 (CR2)
3; part of B cell co-receptor that recognizes iC3b and C3d deposited on the pathogen and brings the BCR and co-receptor close to each other
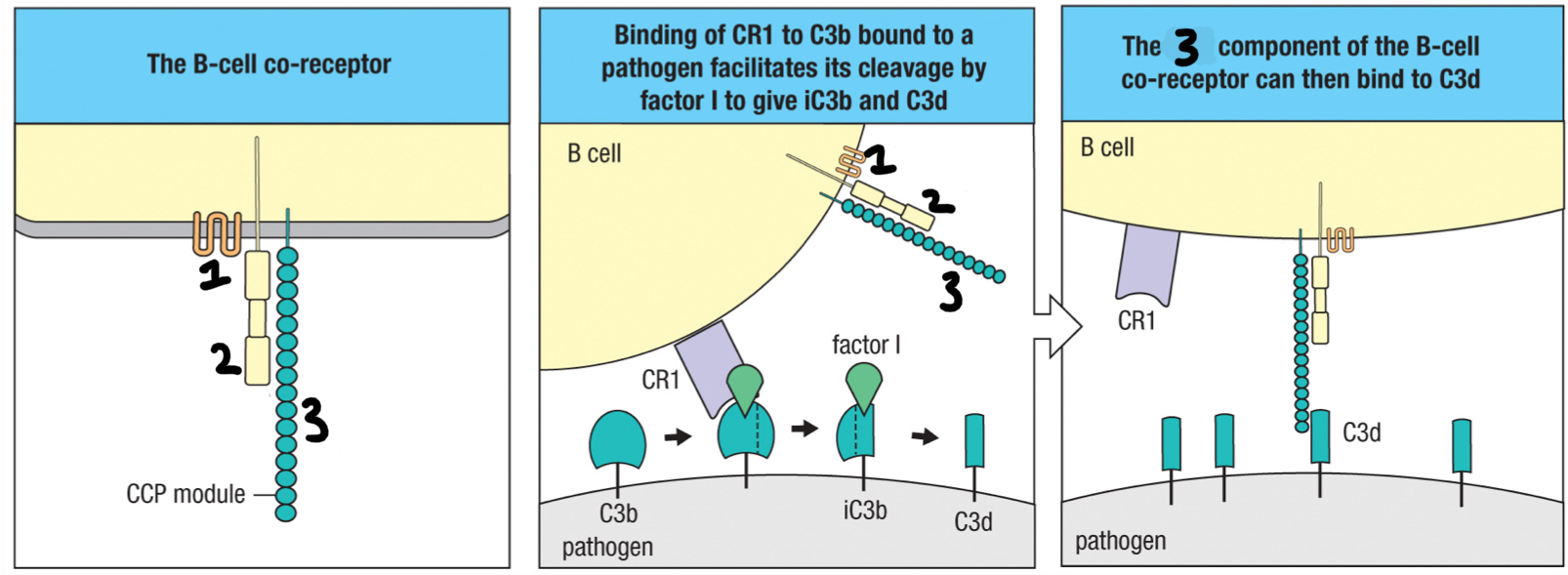
CD19
2; signaling chain of the B cell co-receptor
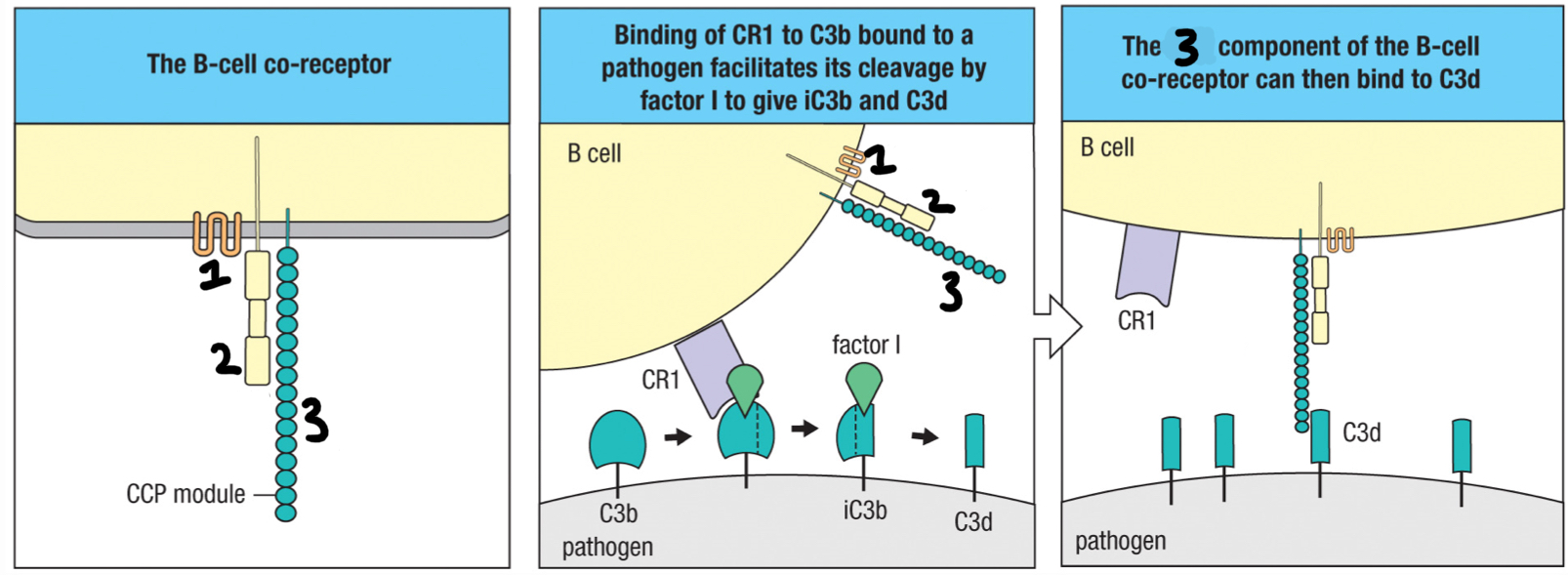
CD81
1; part of B cell co-receptor that binds to CD19
increase
Simultaneous interactions by the BCR and co-receptor greatly increase or decrease the B cell sensitivity, which initiates signal transduction?
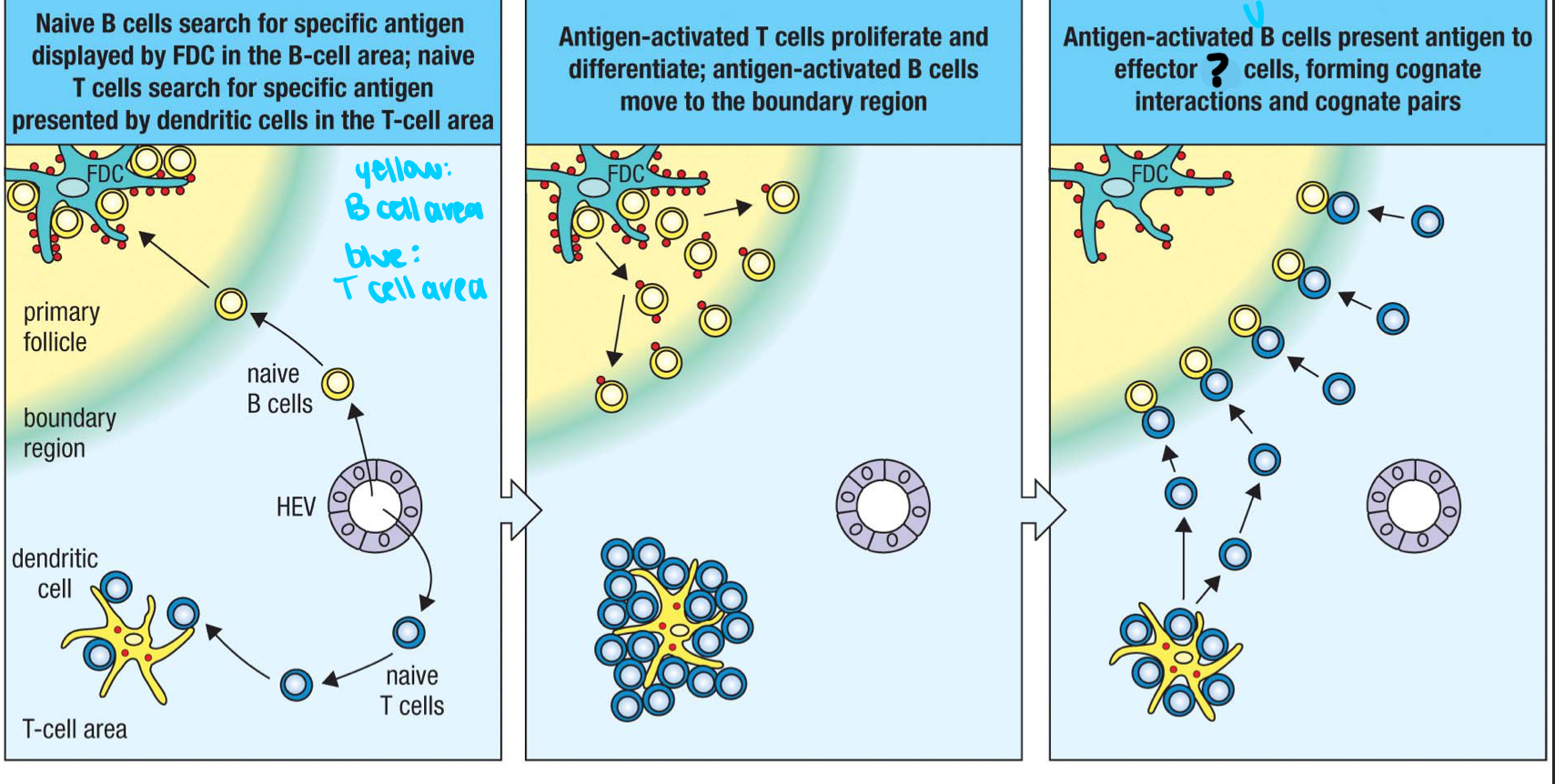
afferent lymphatic vessel
1; where lymph and other cells enter the lymph node
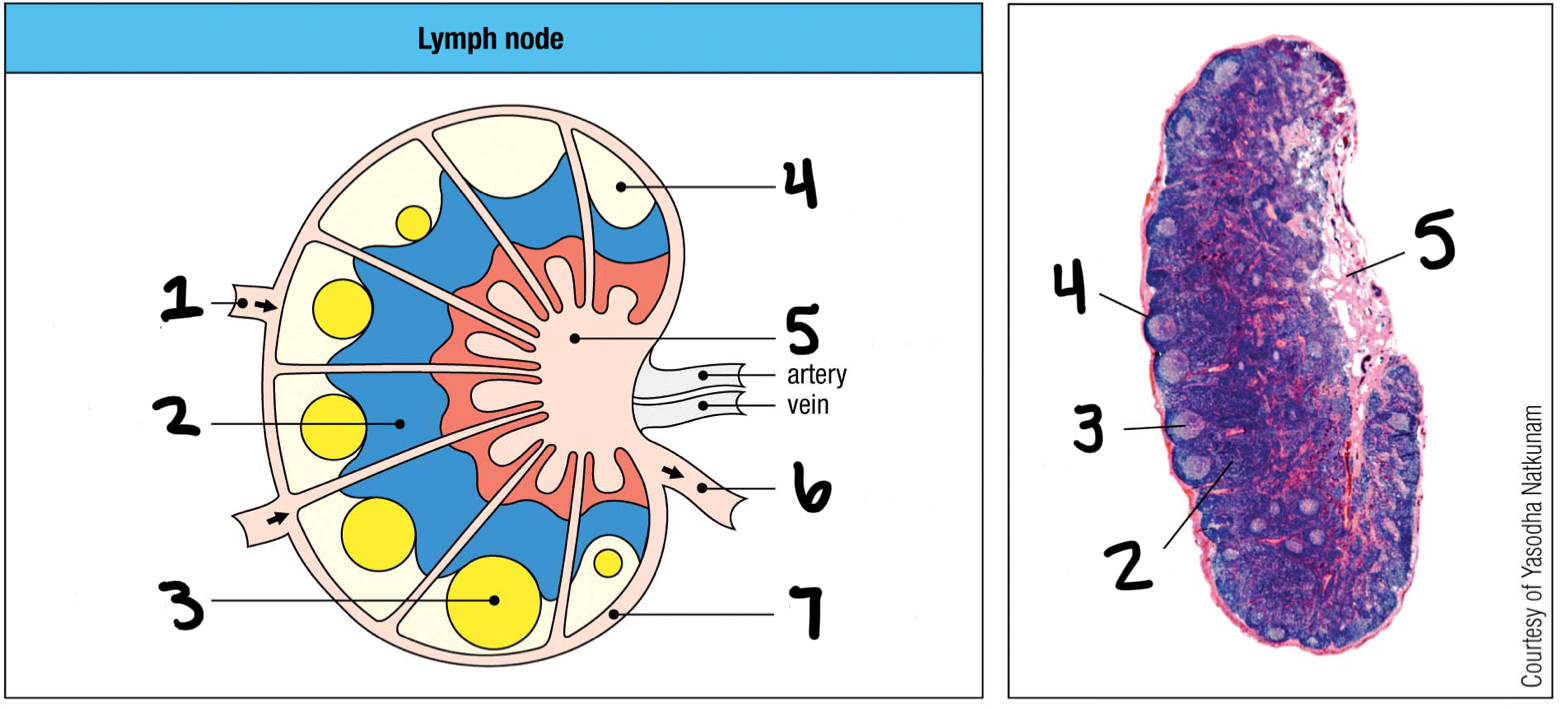
T cell area
2
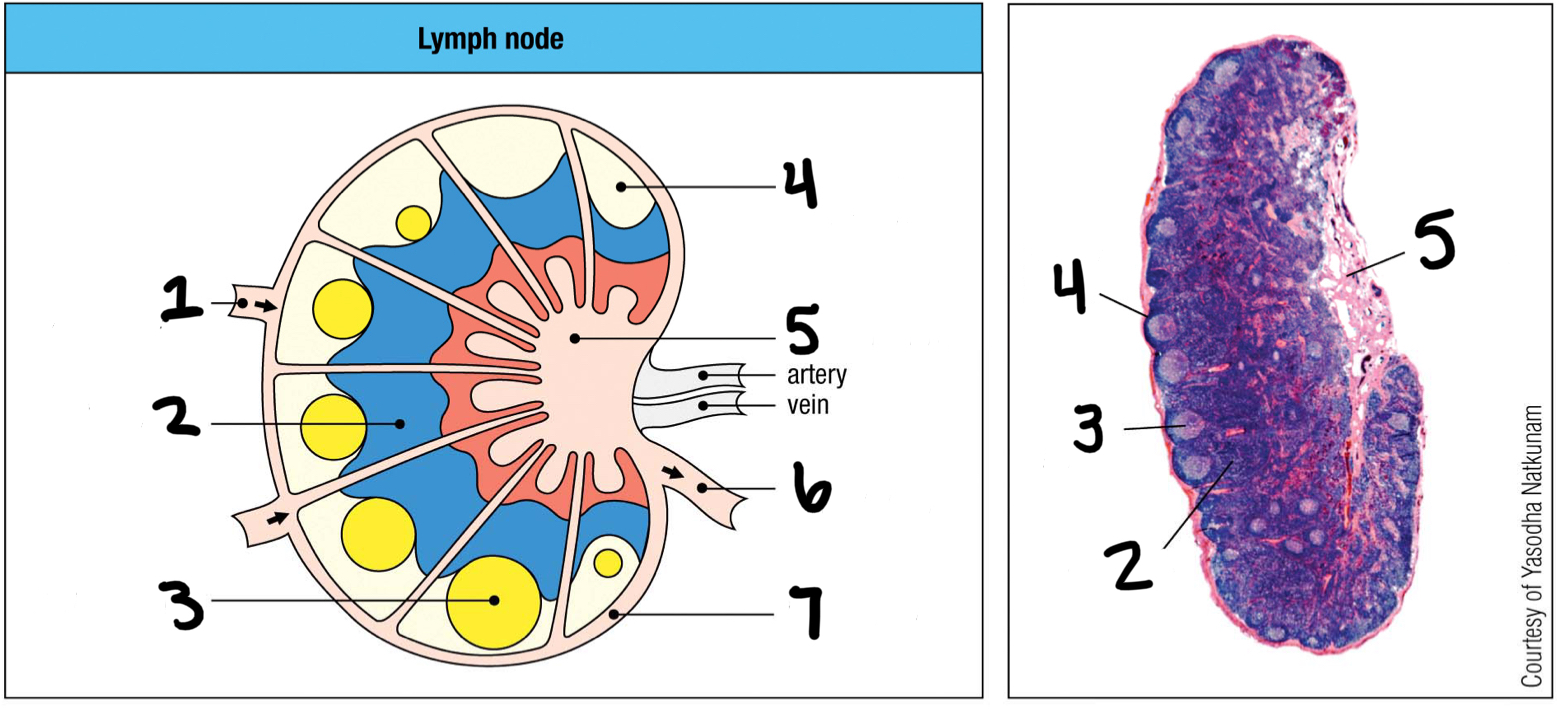
germinal center
3; where B cells proliferate
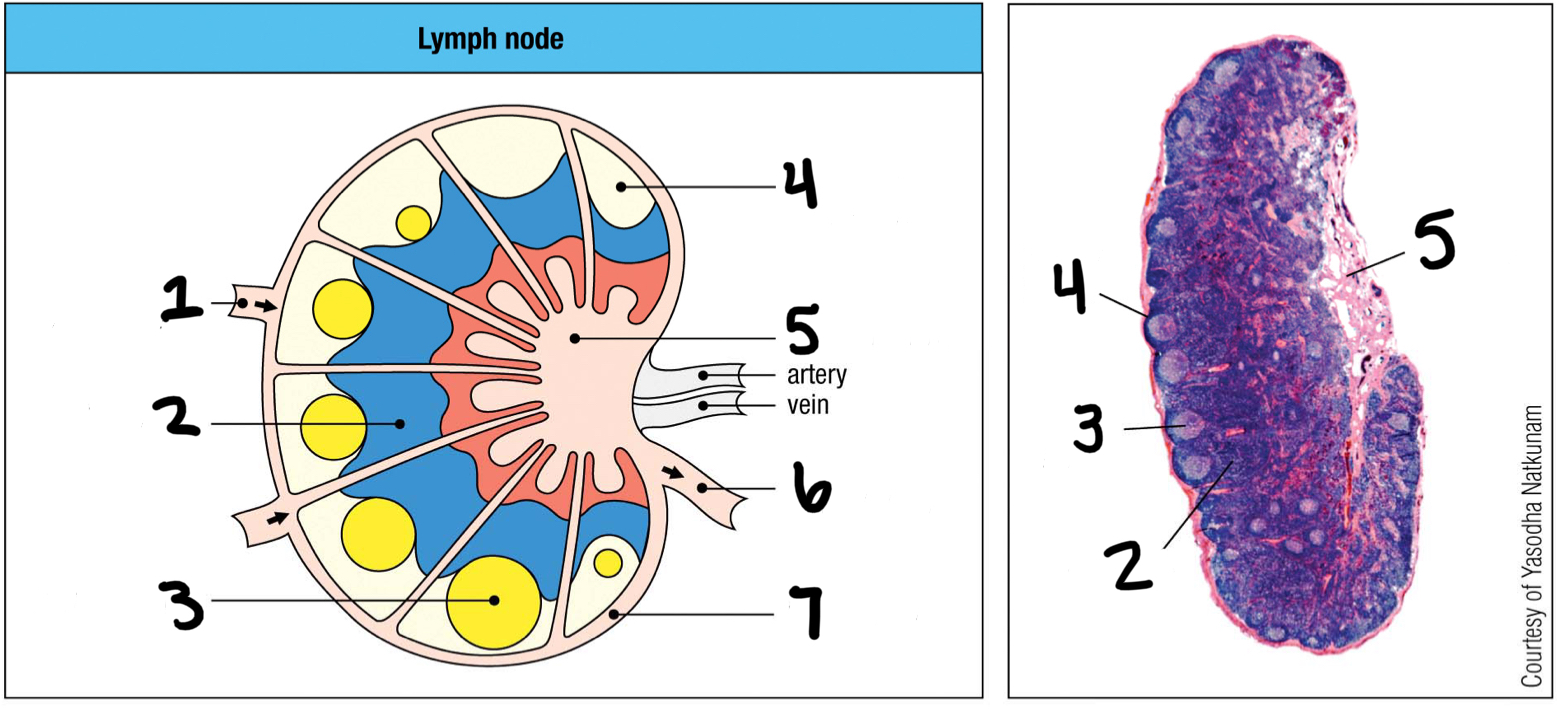
lymphoid follice
4; mostly B cells
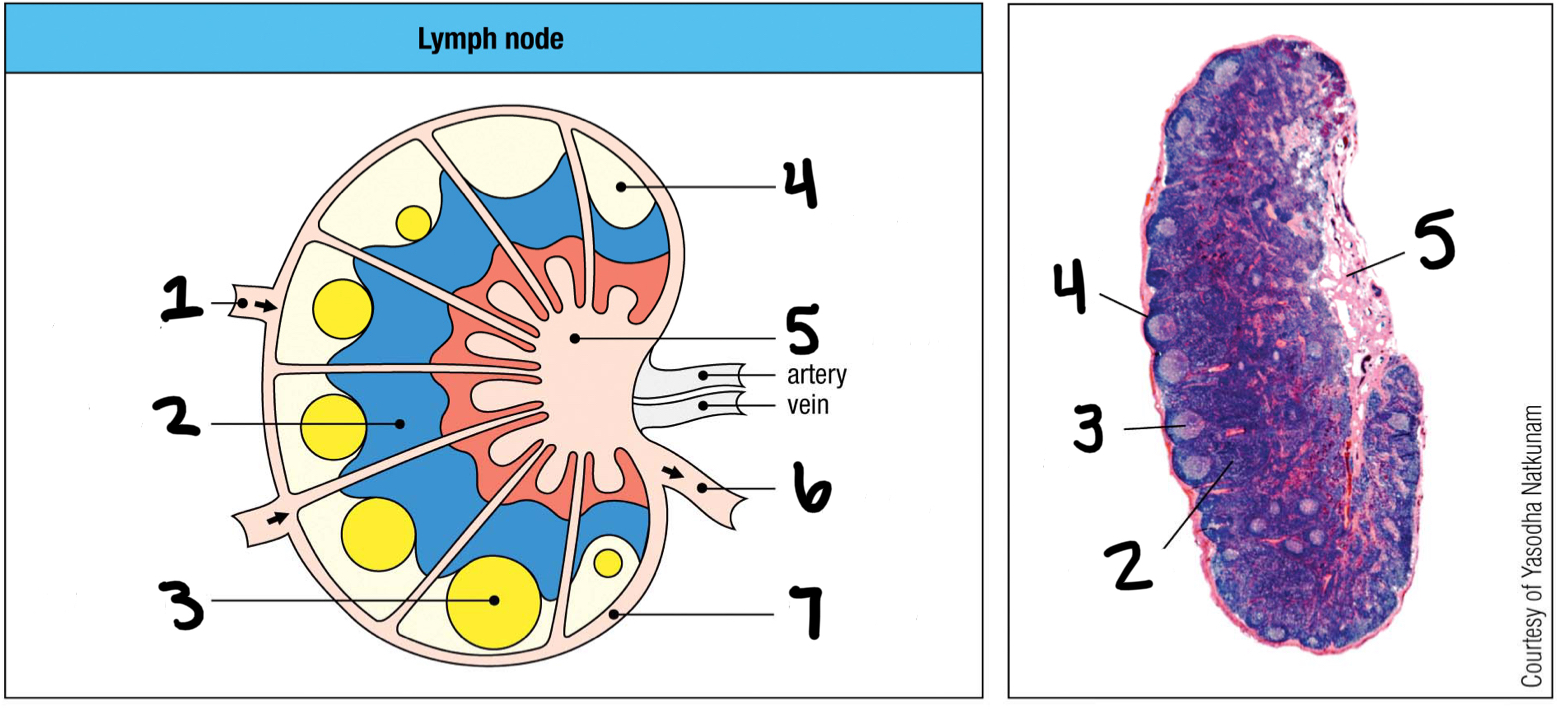
medullary sinus
5
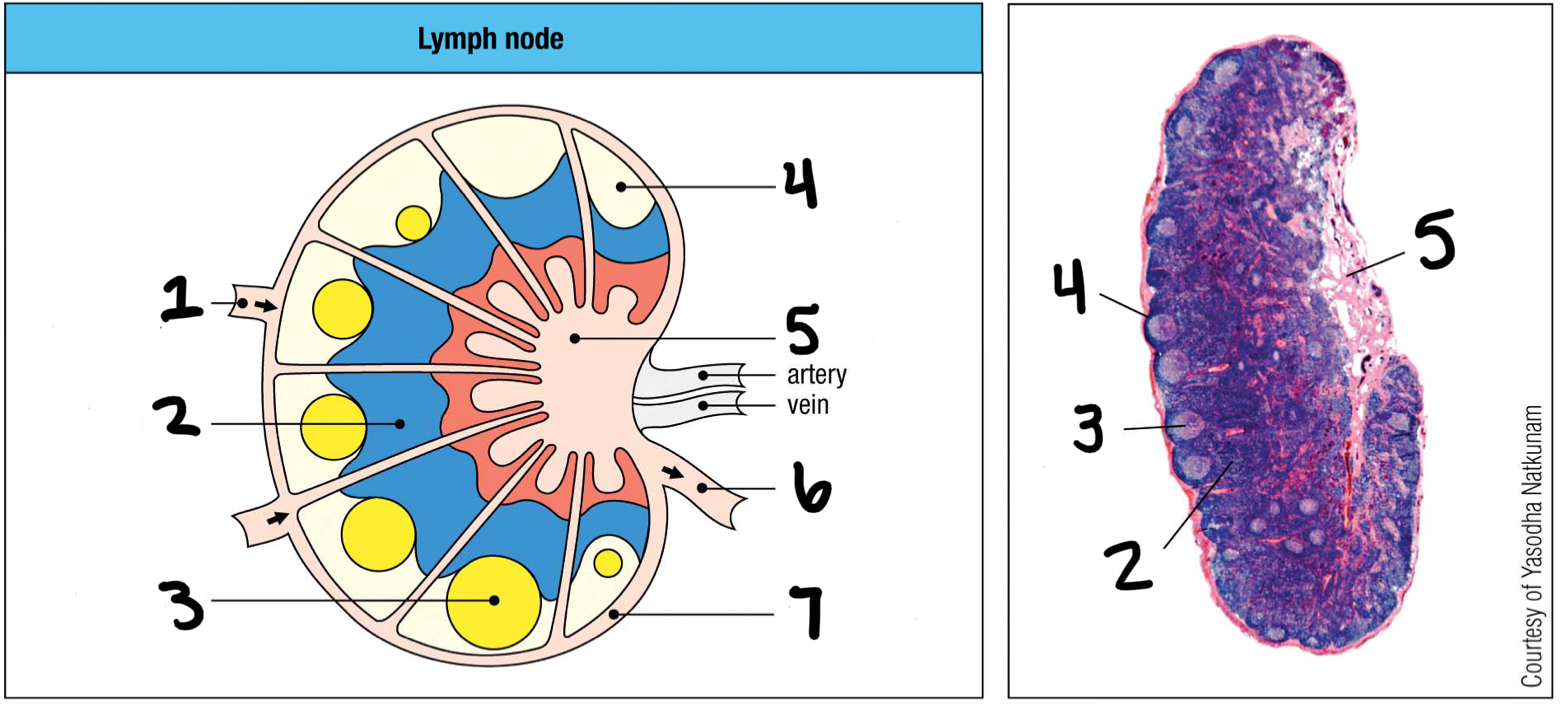
efferent lymphatic vessel
6; where lymph and other cells exit the lymph node
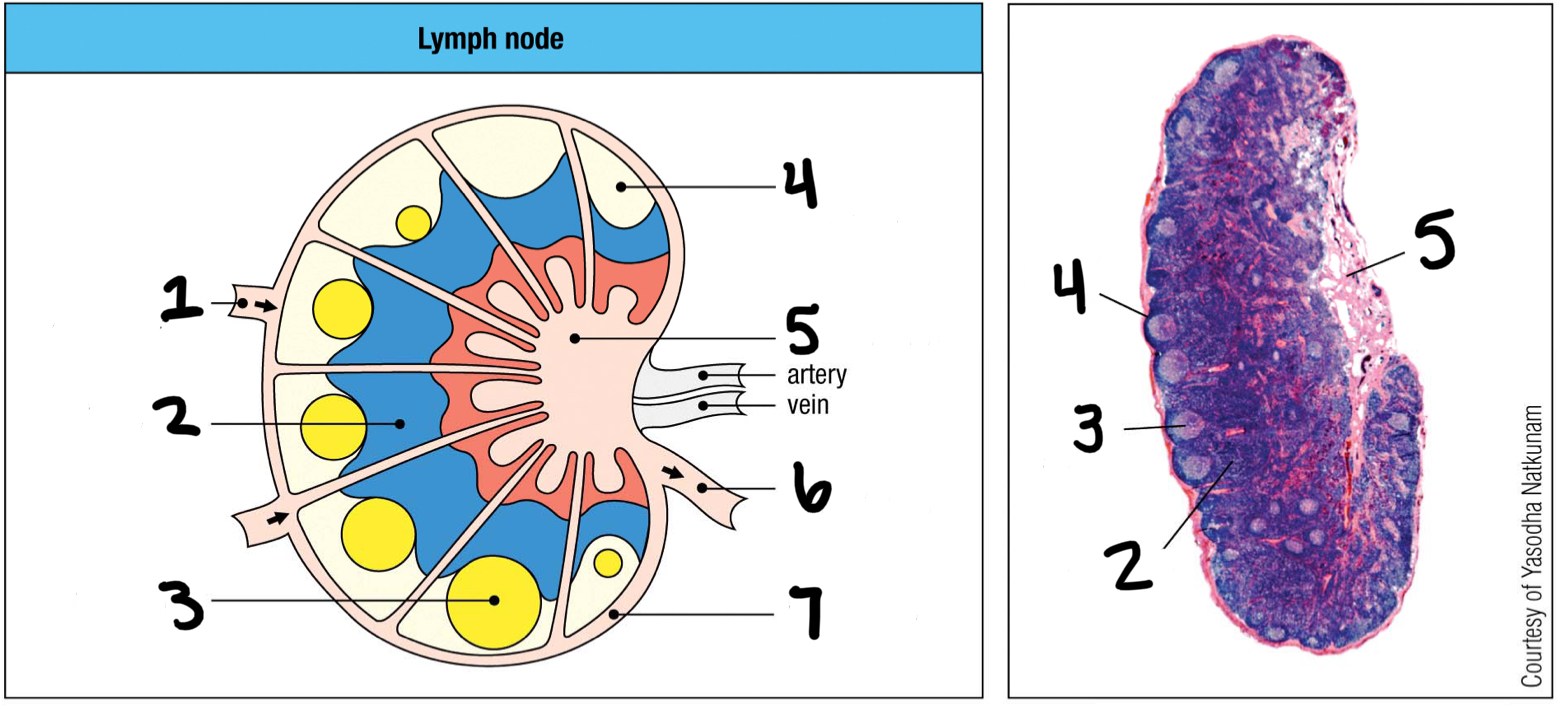
marginal sinus
7
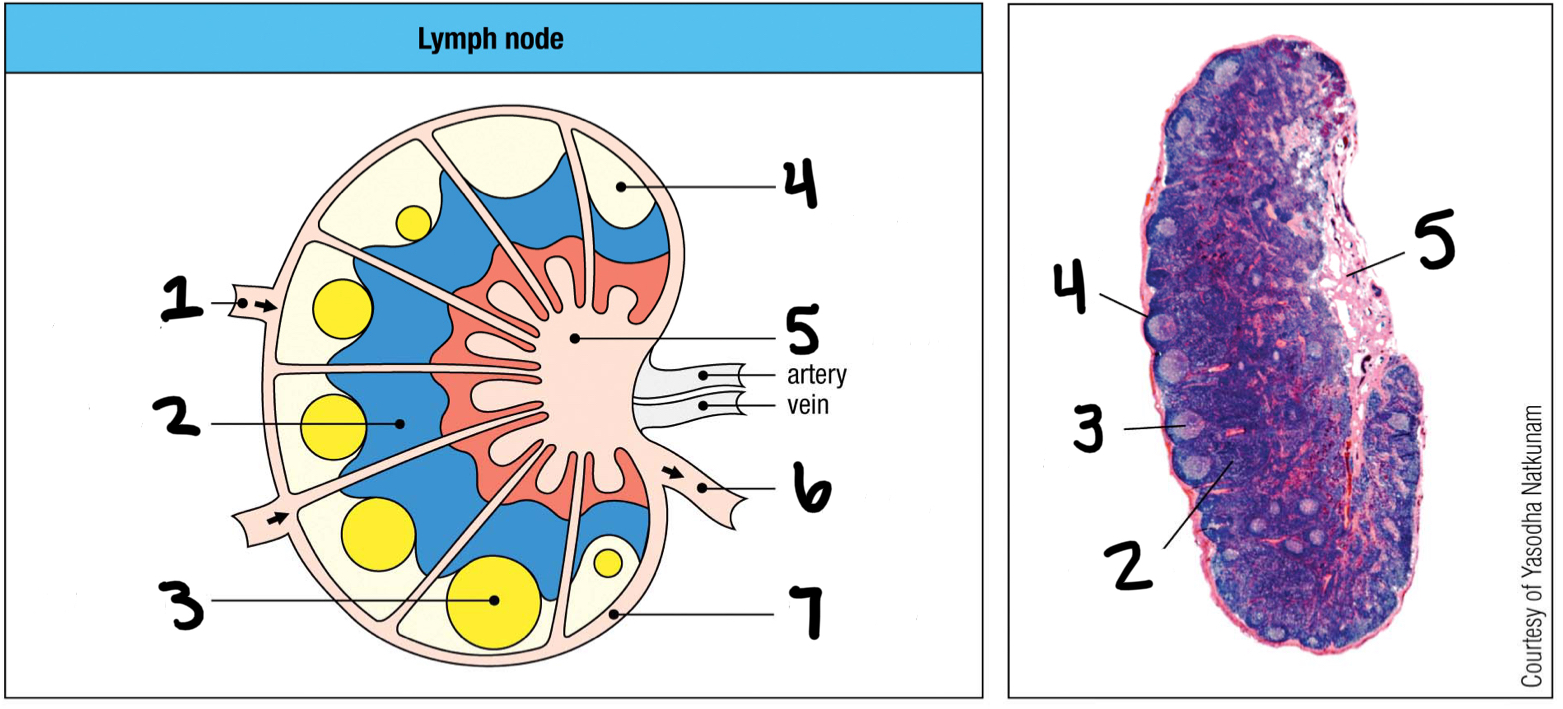
inner
Are T cells populated in the inner or outer cortex of the lymph nodes?
outer
Are B cells populated in the inner or outer cortex of the lymph nodes?
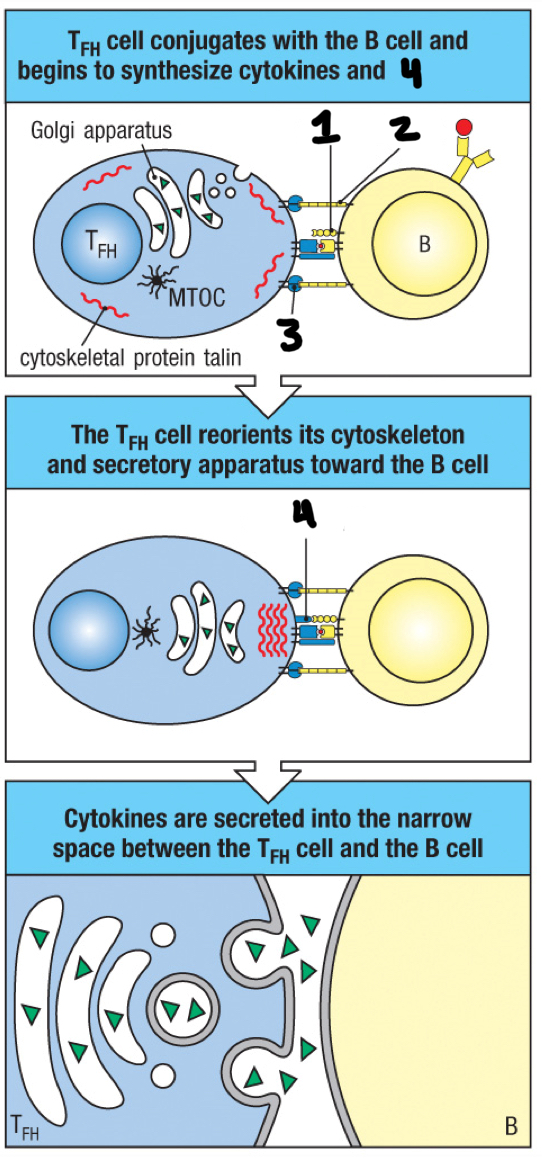
TFH cell
effector T cell that helps activate B cells; moves to follicle boundary to meet with antigen-activated B cells and delivers cytokines to the B cell surface
immunological synapse
space between TFH cell and antigen-activated B cell
CD40
1
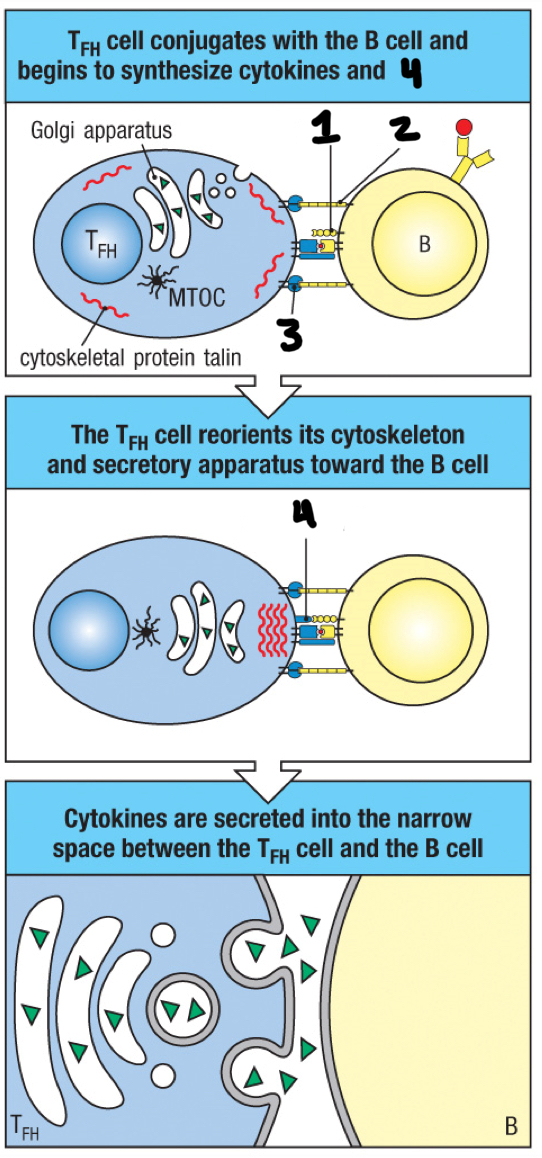
ICAM-1
2
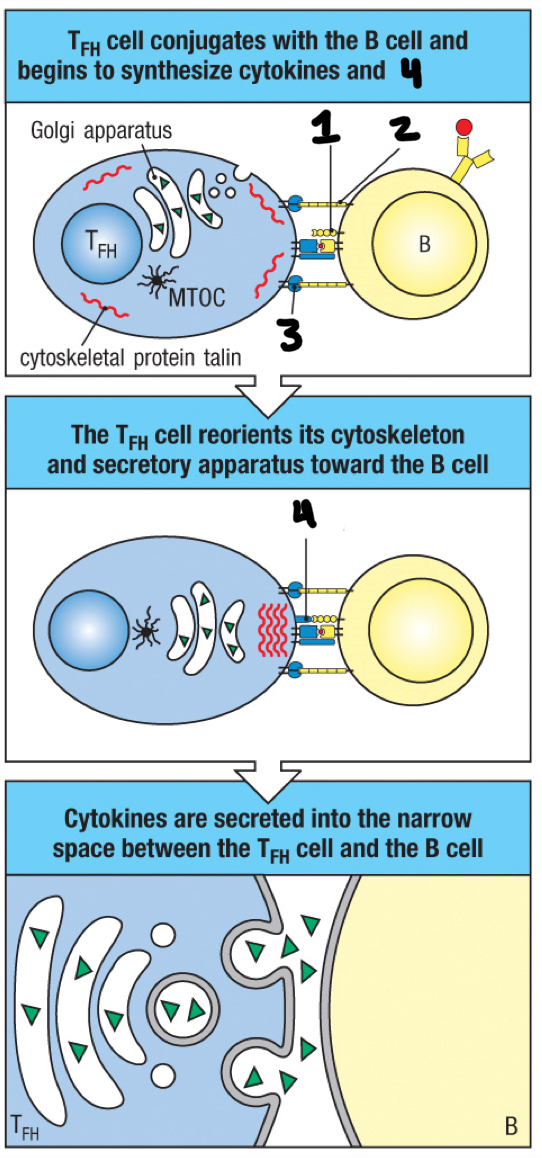
LFA-1
3
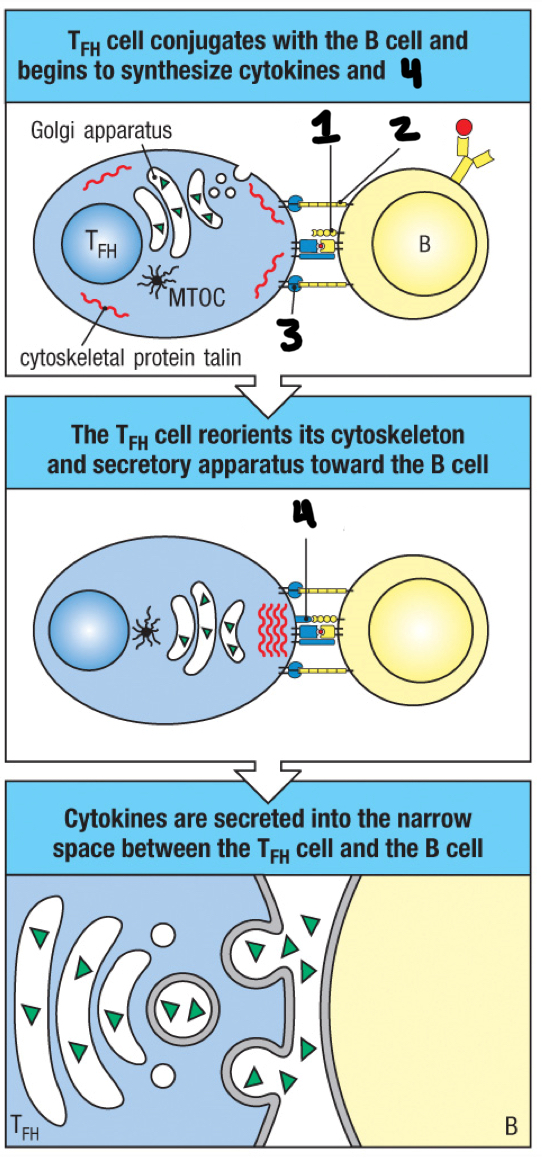
CD40 ligand
4
plasmablast
dividing B cells that secrete IgM
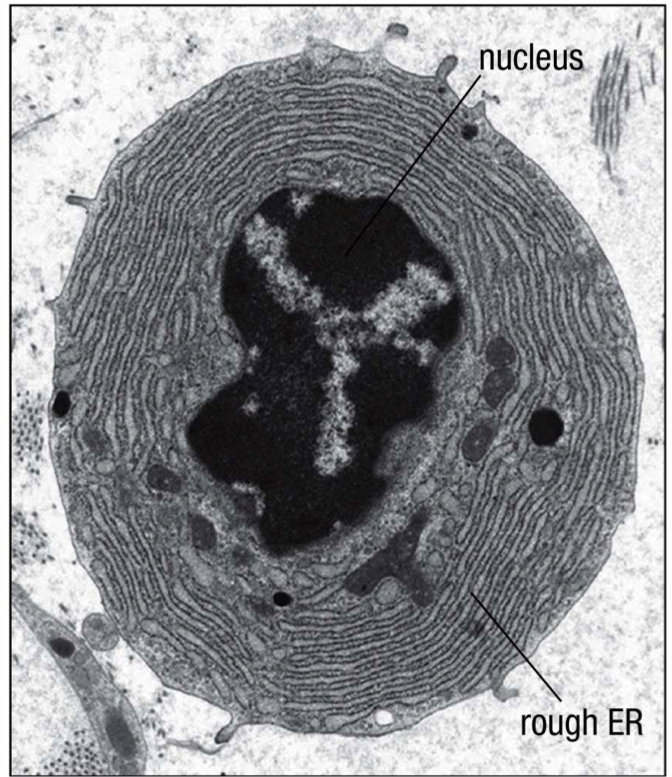
plasma cell
the terminally differentiated B cell; contains a large cytoplasm packed with rough ER, where antibodies are made
IL-5 and IL-6
Which cytokines do TFH cells secrete to induce terminal differentiation of B cells into plasma cells?
true
T/F: the TFH cell/B cell cognate pair move together into the medullary cords and proliferate together, forming the primary focus of clonal expansion
medullary cords
3; The TFH cell/B cell cognate pair move together into the __ and proliferate together?
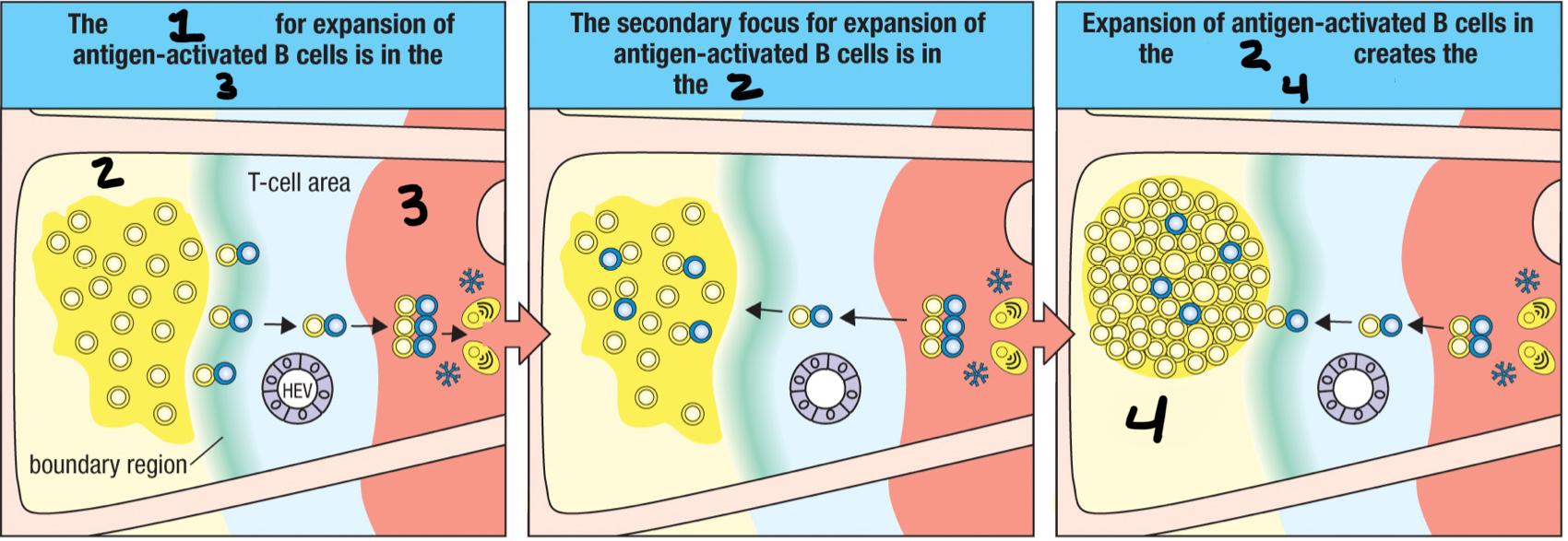
primary focus of clonal expansion
1; formed when the TFH cell/B cell cognate pair move together into the medullary cords and proliferate together; temporary aggregate of proliferating activated antigen-specific B cells and T cells that forms in a secondary lymphoid tissue at the beginning of an adaptive immune response
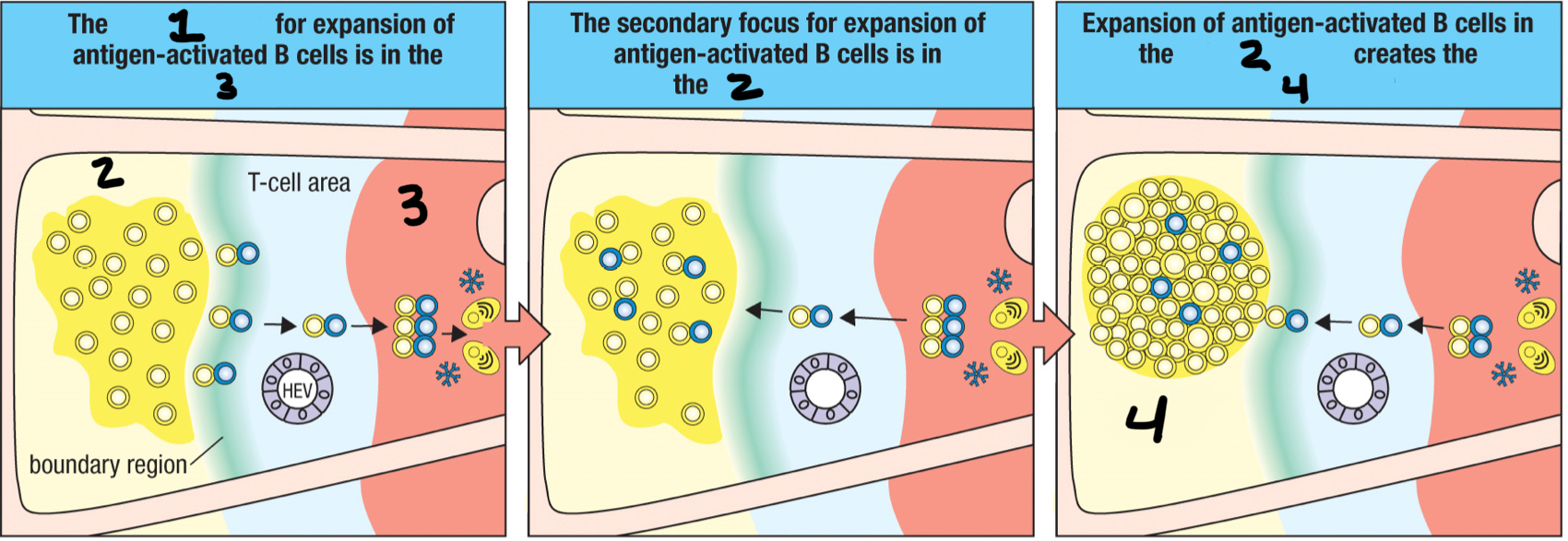
primary follicle
2; When the TFH/B cell cognate pair leave the primary focus, it enters the __ to proliferate into the germinal center?
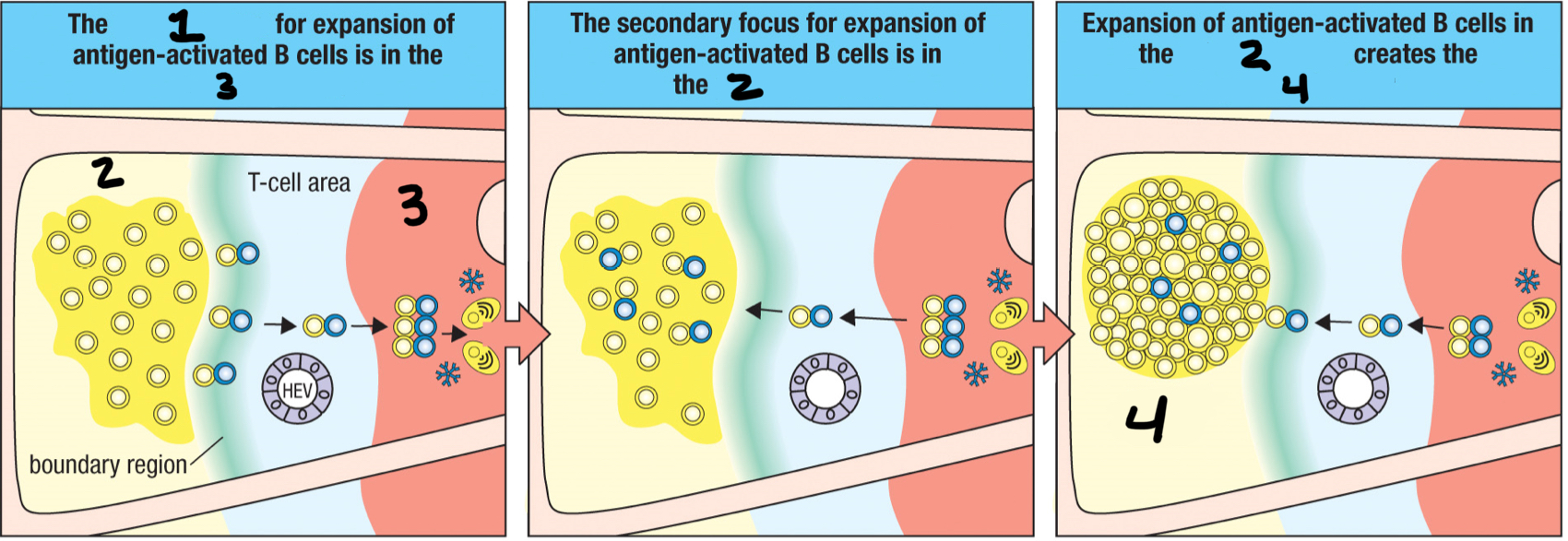
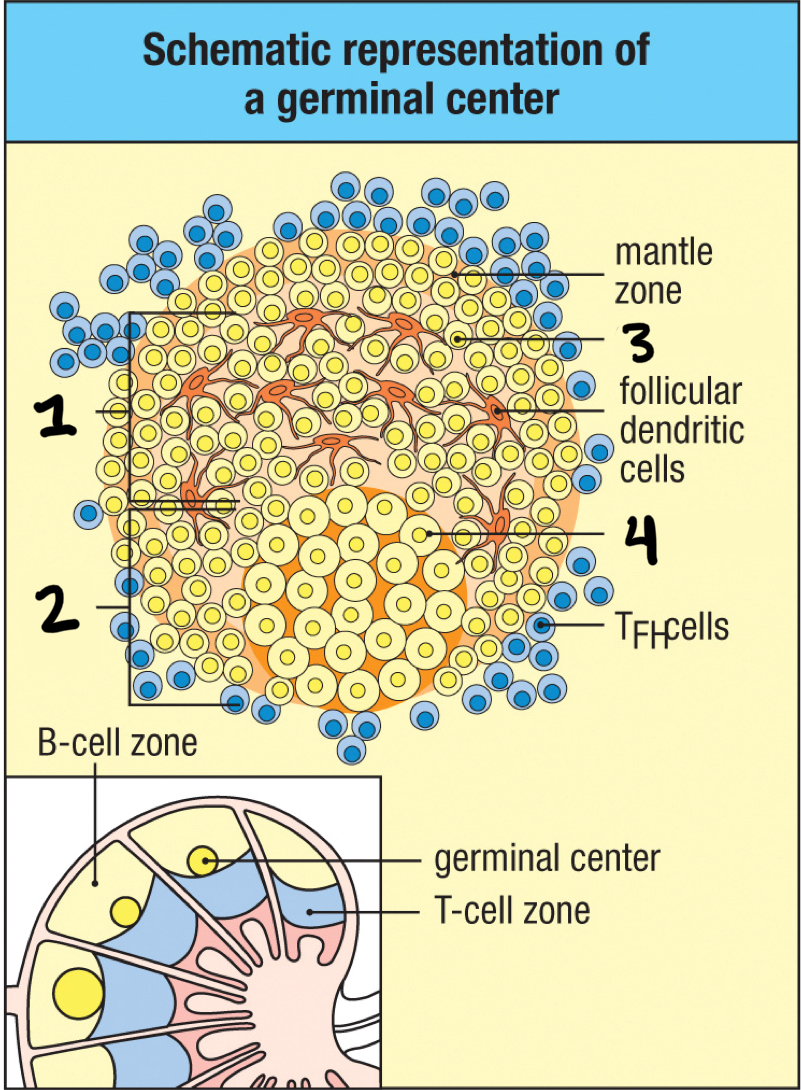
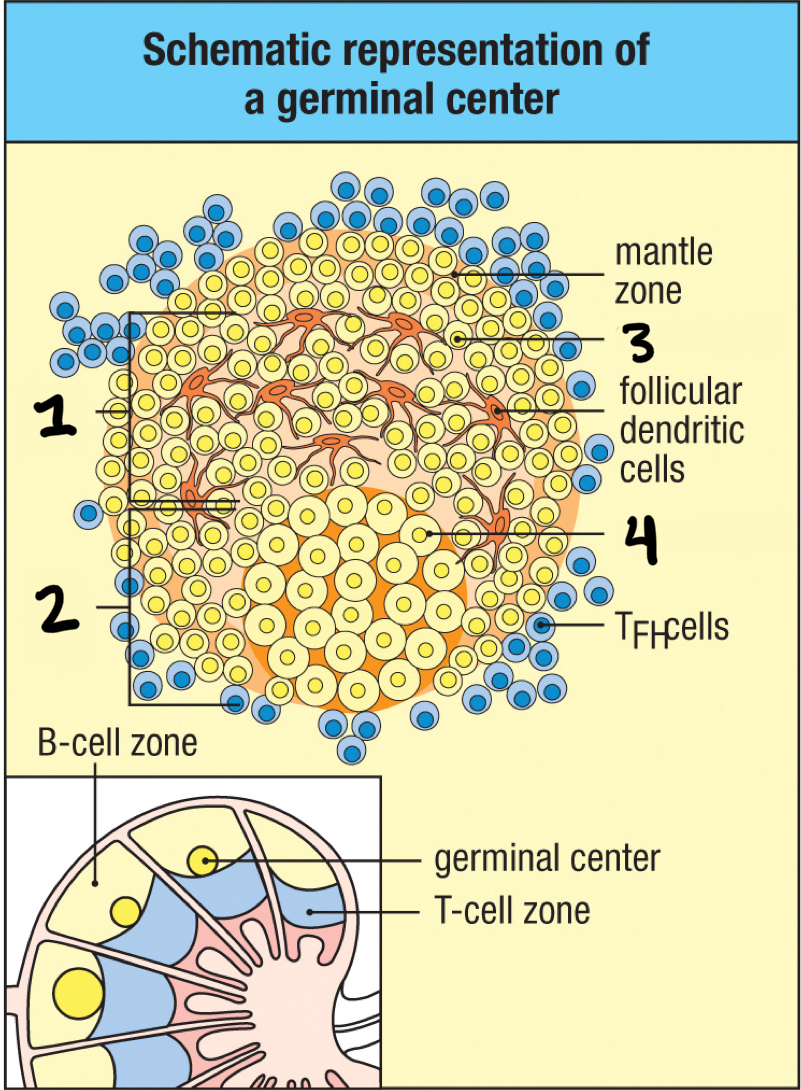
germinal center
4; where B cells divide rapidly to become large and active centroblasts; where both hypermutation and isotype switching occur
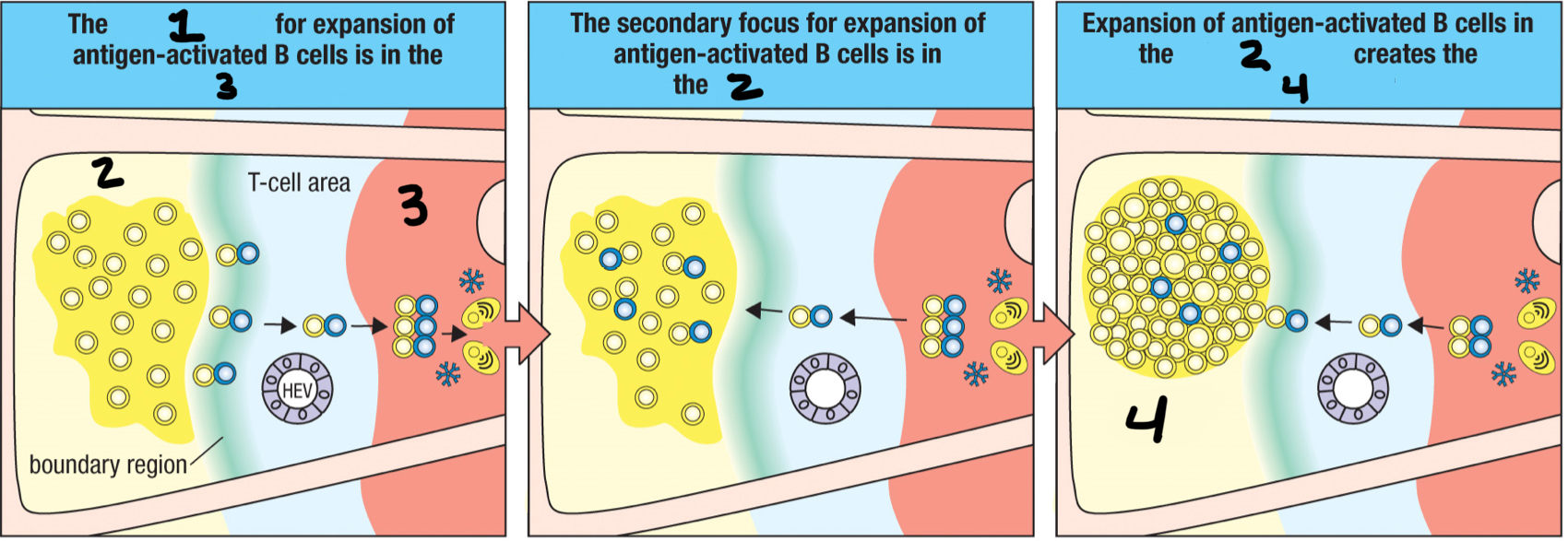
centroblast
4; fully divided and active B cell that can now undergo hypermutation and isotype switching
dark zone
2; part of a germinal center that contains dividing centroblasts increasingly packed together.
centrocytes
3; centroblasts become this after hypermutation and isotype switching is done; divide slowly and leave the dark zone and move into the light zone; compete for binding to TFH and follicular dendritic cell
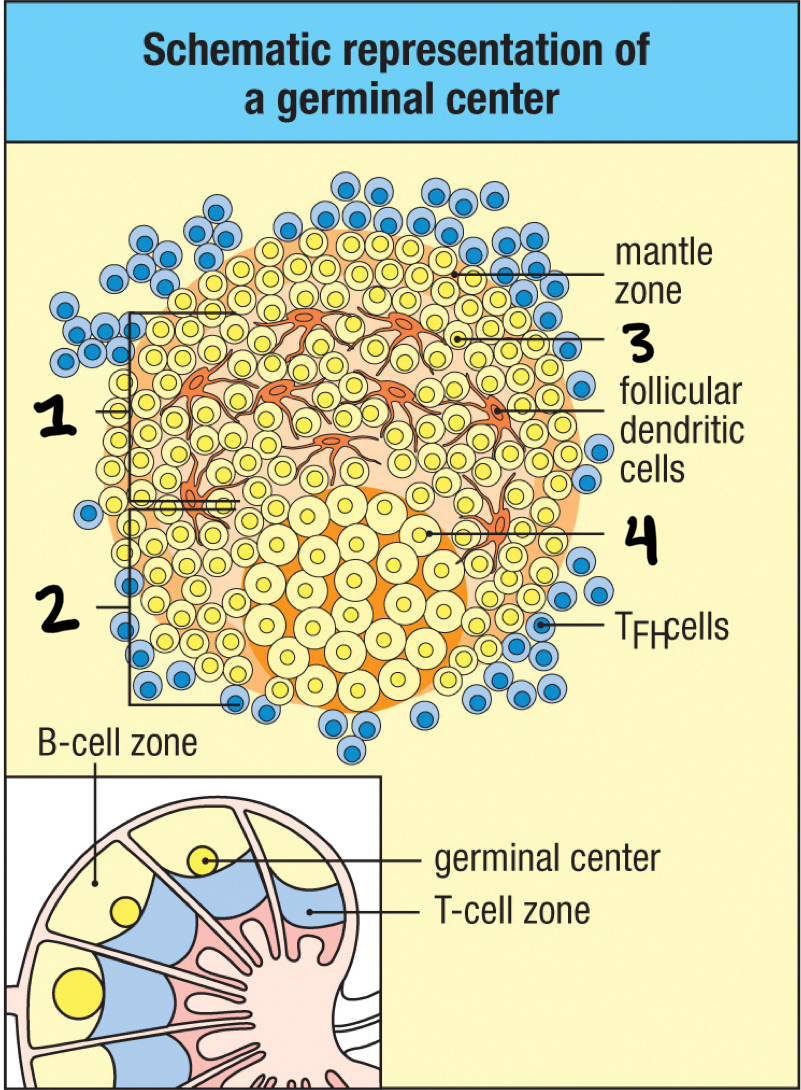
light zone
1; part of germinal center where B cell density is lower; contains nondividing centrocytes interacting with follicular dendritic cells
true
T/F: after the somatic hypermutation, the B cells compete for the access of the limited amount of antigen displayed by FDCs in the light zone
affinity maturation
during the competition after somatic hypermutation, the antibody with high affinity is selected
Bcl-XL
protects the cell from apoptosis
true
T/F: only the centrocytes with high affinity to the antigen are induced to express Bcl-XL
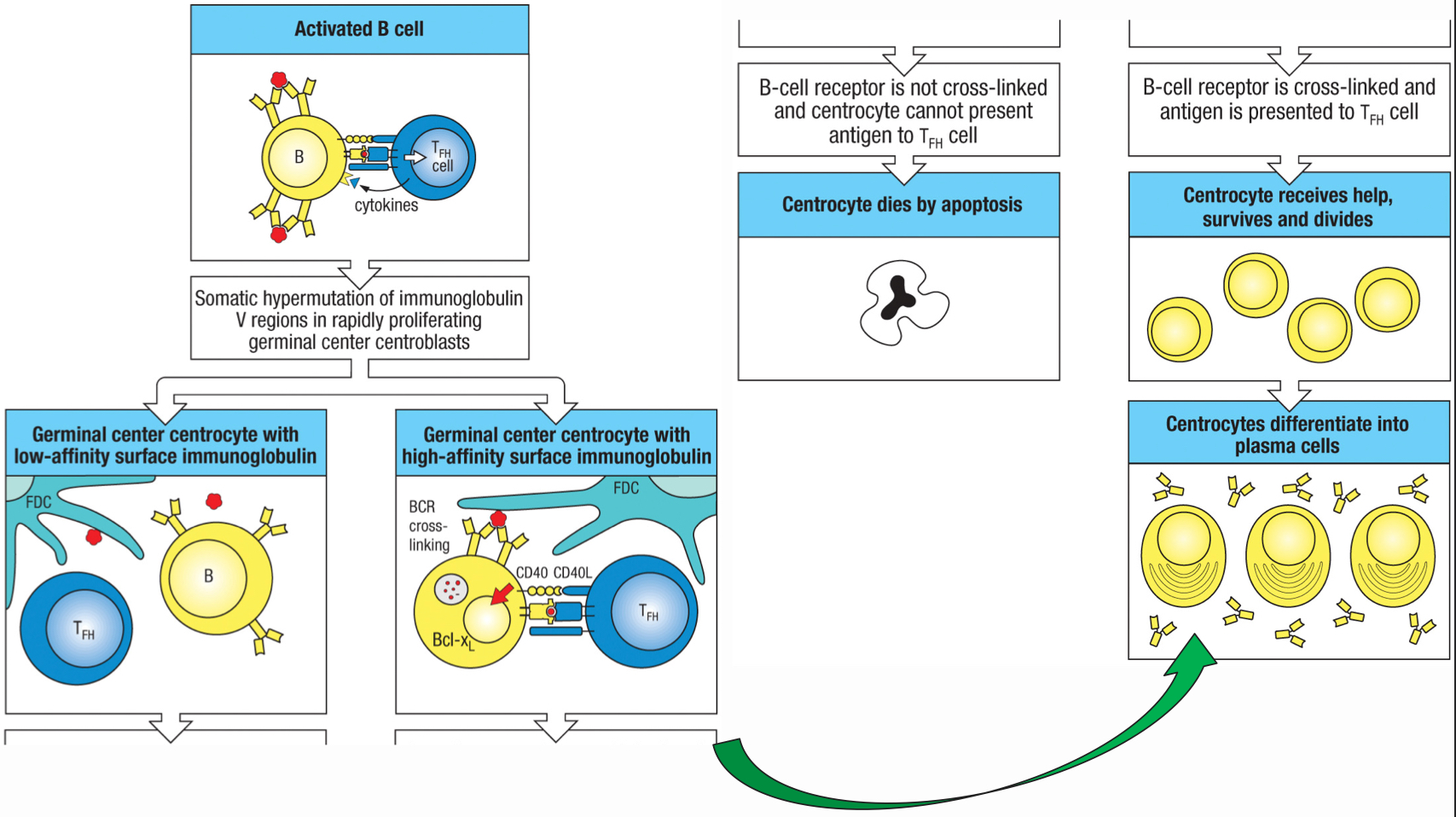
true
T/F: TFH cells drive B cell expansion, somatic hypermutation, affinity maturation, isotype switching and memory
false
T/F: autoreactive B cells can be propogated without TFH cells
true
T/F: in the absence of T cell help, antigen-activated B cells are deleted or anergized
surface Ig
Do naive B cells have surface Ig or secreted Ig?
secreted Ig
Do plasma cells have surface Ig or secreted Ig?
yes
Do naive B cells have surface MHC class 2?
no
Do plasma cells have surface MHC class 2?
isotype switching
process accomplished by homologous recombination within the cluster of the C gene; the antigen specificity remains the same, but the isotype of the antibody is changed; the recombination loops out the expressed C genes and brings another C gene to juxtaposition with the assembled V region
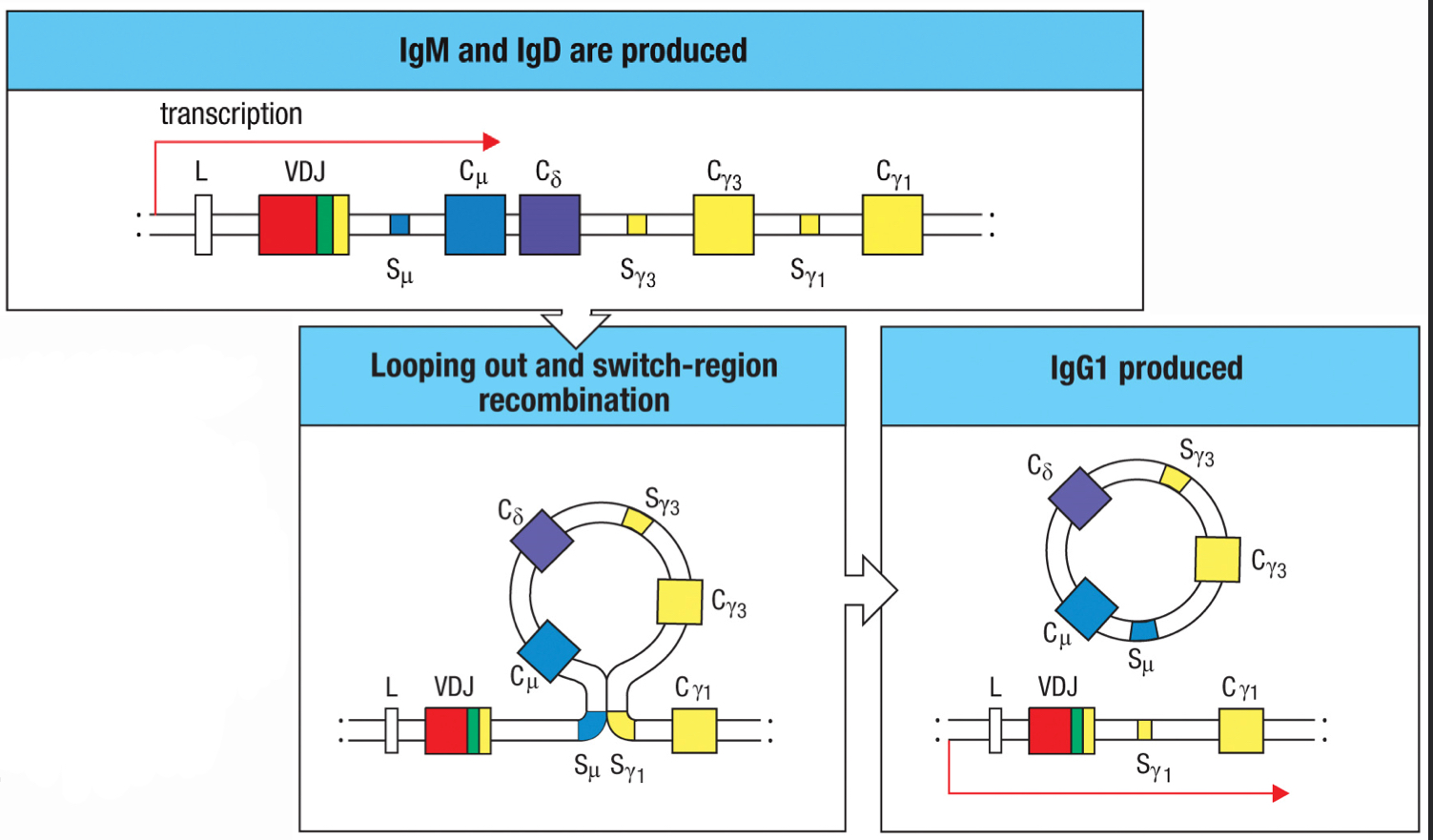
T-cell independent antibody production
occurs due to a lack of a thymus; the B cells are activated when epitopes are in dense arrays on pathogens surfaces and the dense clustering of BCRs and co-receptors can generate sufficient signaling to trigger B-cell proliferation and differentiation; IgM is produced, but no somatic hypermutation, isotype switching or memory is generated
true
T/F: the different Ig classes have the same binding site, but different constant regions
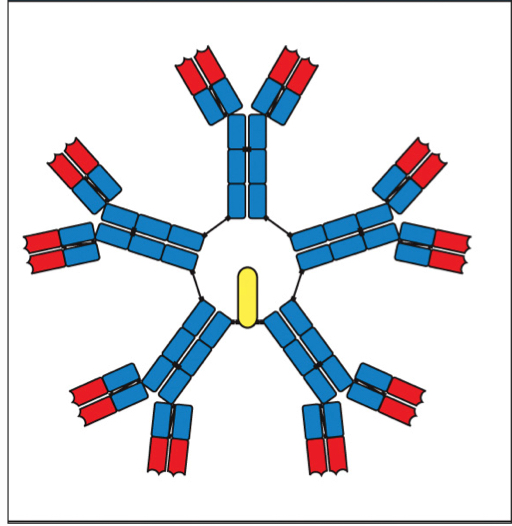
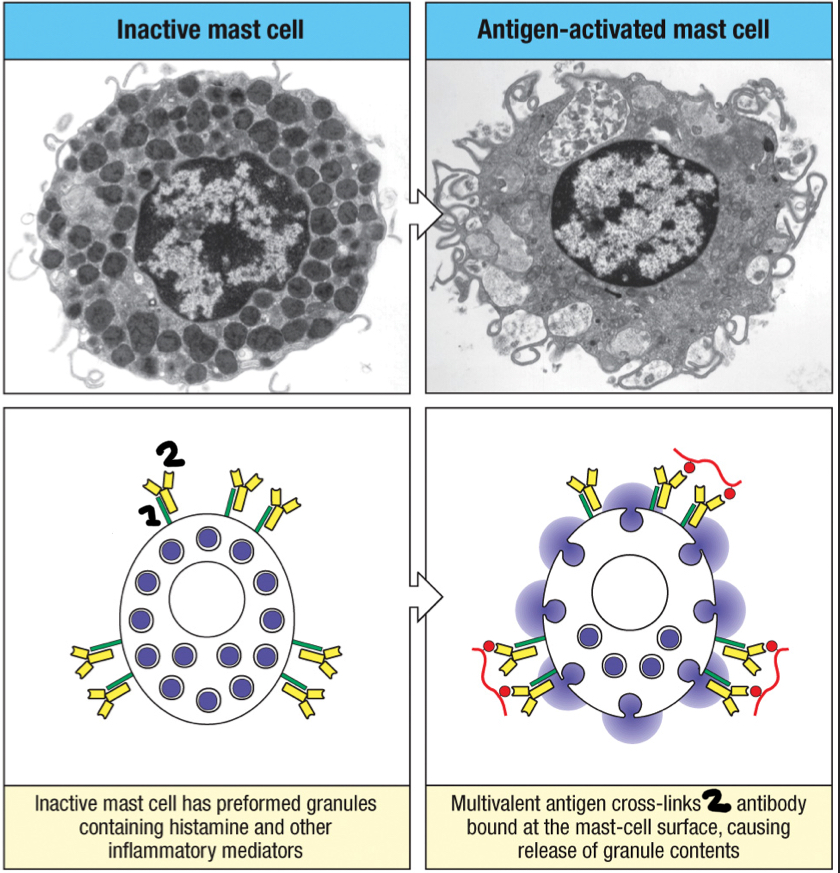
IgM
the first antibody class produced and secreted as a pentamer, creating 10 antigen-binding sites; helps the complement cascade and phagocytosis; disadvantaged because of it’s bulky size, so it limits its penetration of infected tissues; can be secreted before hypermutation occurs
transcytosis
a receptor mediated process that transports macromolecules from one side of the cell to the other
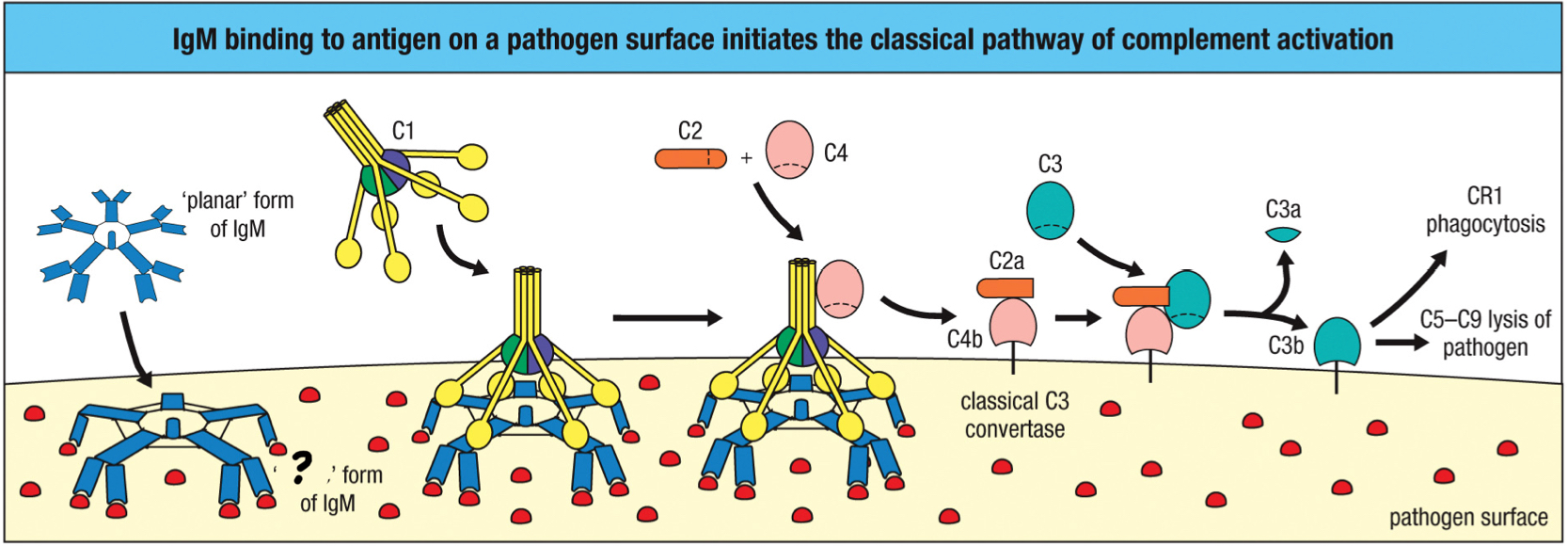
IgG
antibody class that penetrates the tissue via the Fc receptor; transports through the tissue via transcytosis; forms stable immune complex with soluble multivalent antigens to activate the classical complement pathway; major type is serum; aids in neutralization
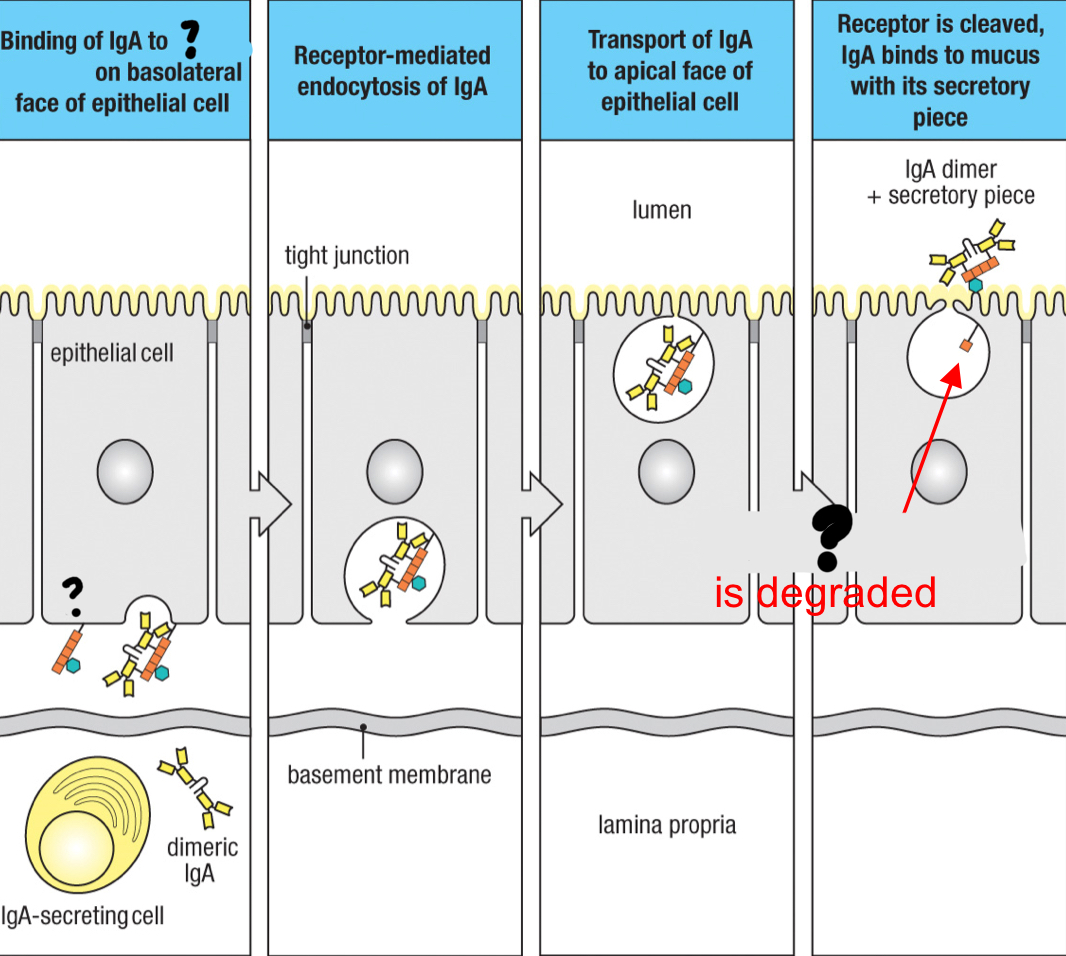
poly-Ig receptor
receptor found on mucosal epithelial cells that specifically binds to the IgA dimer and IgM pentamer via the J chain leading to transcytosis to transport them across the epithelium
true
T/F: polymeric antibody is brought to mucosal surface by transcytosis to protect the body
IgA
dimeric antibody class that’s secreted and uses the poly-Ig receptor to cross the epithelia by transcytosis
IgE
2; antibody class that tightly binds to FcεRI present on the surface of mast cells, basophils and activated eosinophils to trigger the quick release of large granules in mast cells that contain inflammatory mediators such as histamine
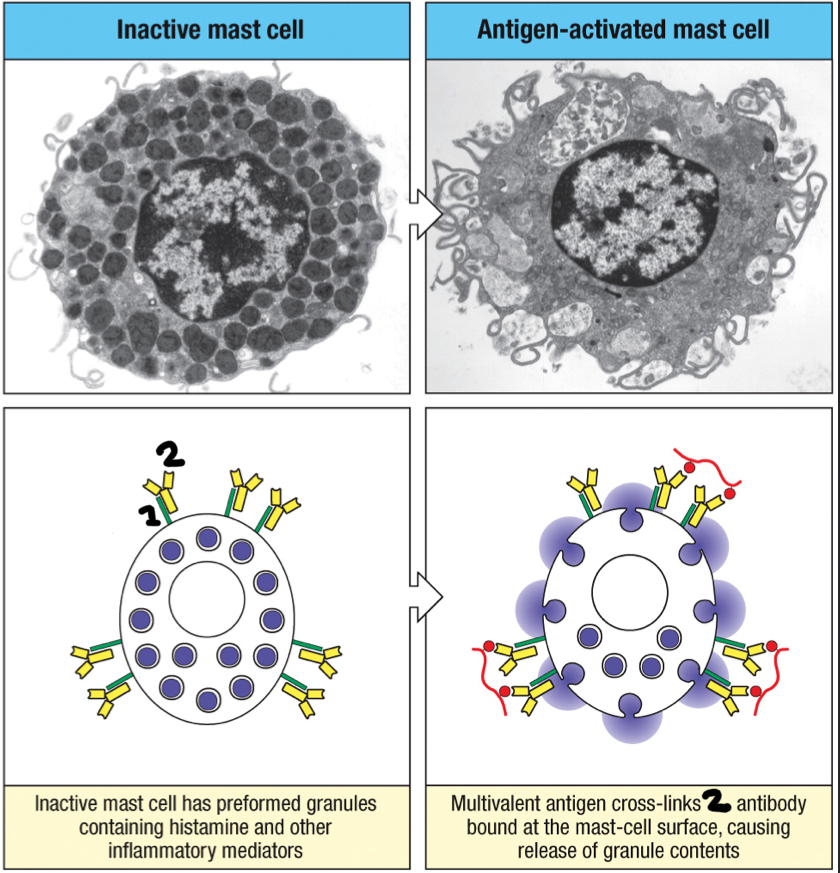
false
T/F: IgE is very present in circulation
FcεRI
1; Fc receptor found on the surface of mast cells, basophils and activated eosinophils that binds to IgE; binding triggers the quick release of large granules in mast cells that contain inflammatory mediators like histamine
neutralizing antibodies
high affinity antibodies that bind to the microbial surface and can prevent the microbe from attaching and binding to human cells; block microbial entry
toxin
microbial protein that disrupts normal cell functions in the human body; antibodies bind to these to prevent the effects
toxoid
a toxin that has been deliberately inactivated so that it’s no longer toxic, but still provokes a protective immune response as a vaccine
staple
Upon binding to a pathogen surface, IgM takes a __ conformation that exposes the C1q binding site in the Fc region
true
T/F: multiple attachments of C1q binding sites to IgM is easily achieved, which triggers the activation of the classical complement pathway
multiple
Does IgM have single or multiple C1q binding sites?
single
Does IgG have single or multiple C1q binding sites?
false
T/F: IgG’s single C1q binding site is sufficient to activate C1
true
T/F: Crosslinking of two or more IgG by the antigen on the pathogen surface activates the classical pathway
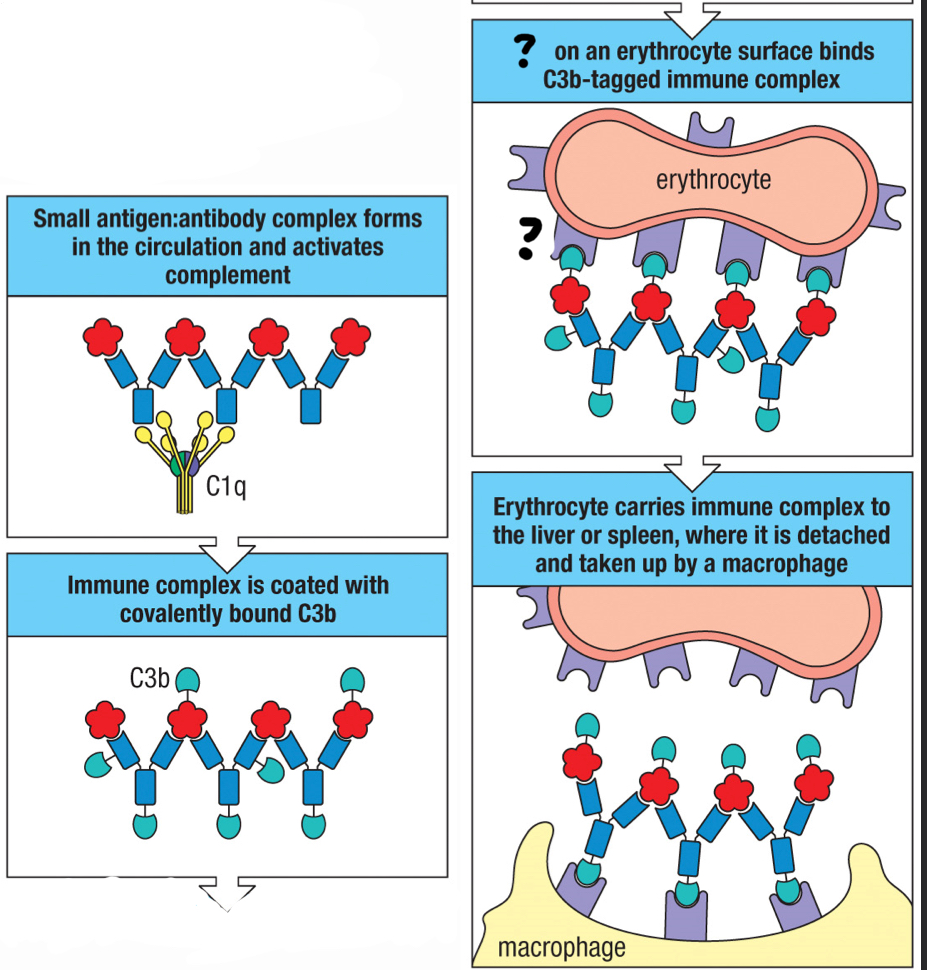
CR1
complement receptor found on erythocytes and help move large amounts of immune complexes to macrophages throughout the body for opsonization; helps clear out pathogens once antibodies are formed; interacts with C3b fragment
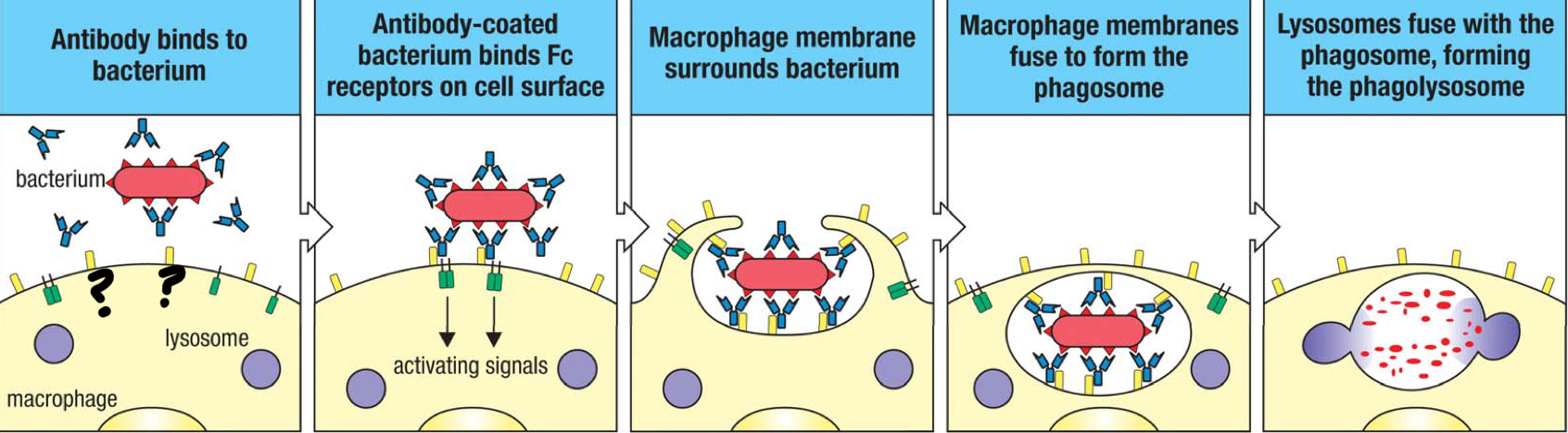
Fcγ receptor
receptor that interacts with IgG, tethering the pathogen to the surface of the macrophage, which enhances the engulfment of the antibody-coated pathogen; facilitates phagocytosis
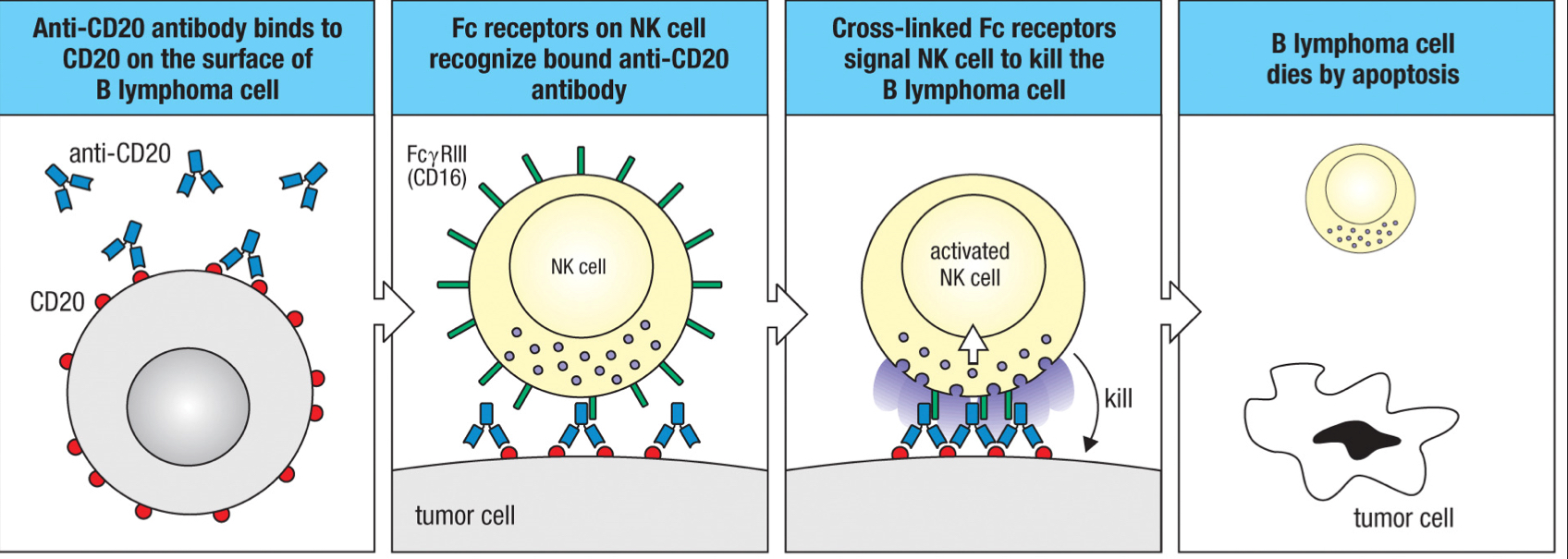
FcγRIII/CD16 receptor
receptor expressed by natural killer cells that recognizes the Fc region of the bound antibody and leads to ADCC
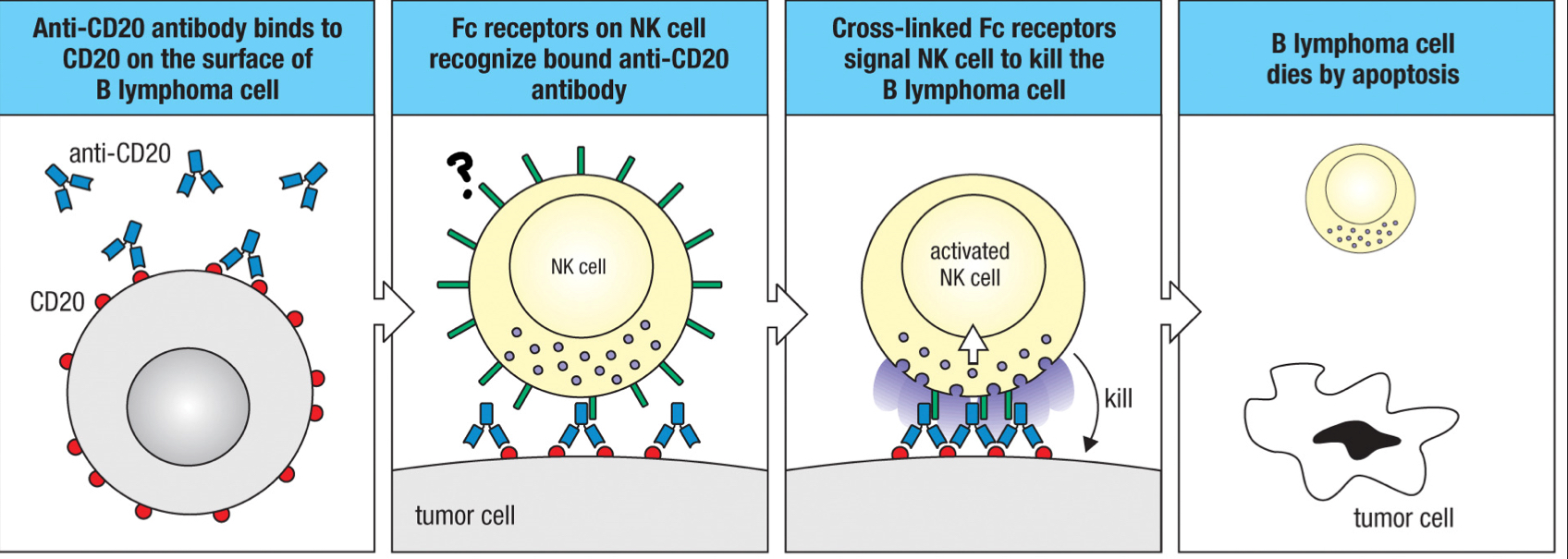
antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
the mechanism of killing infected cells; natural killer cells recognize human cells coated by IgG1 or IgG3 that binds to cell surface components and kill those cells
IgG
Which antibody class goes with γ (gamma)?
IgM
Which antibody class goes with μ (mu)?
IgD
Which antibody class goes with δ (delta)?
IgA
Which antibody class goes with 𝛼?
IgE
Which antibody class goes with ε?
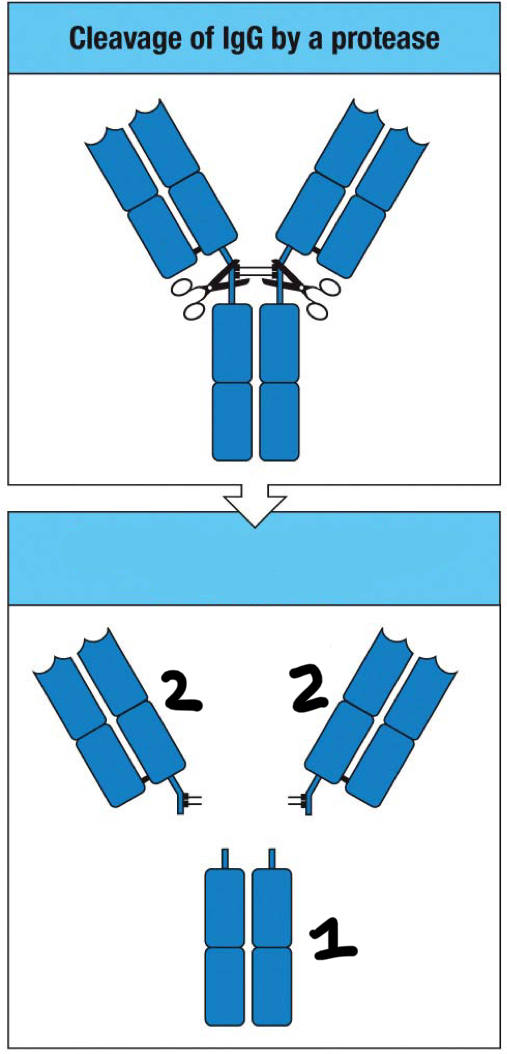
Fab fragment
2
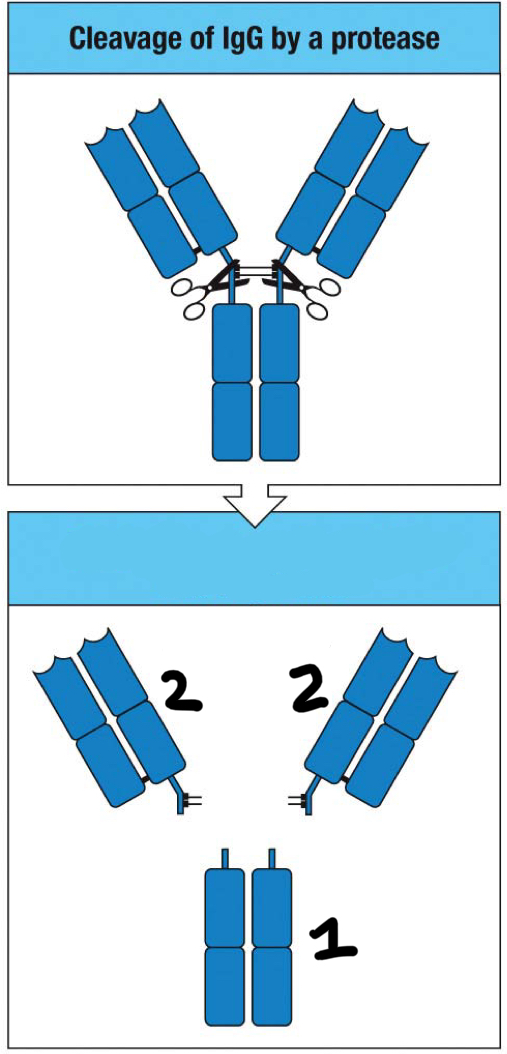
Fc fragment
1
secondary focus of clonal expansion
the TFH cell/B cell cognate pair moves to primary follicles and develop into germinal centers
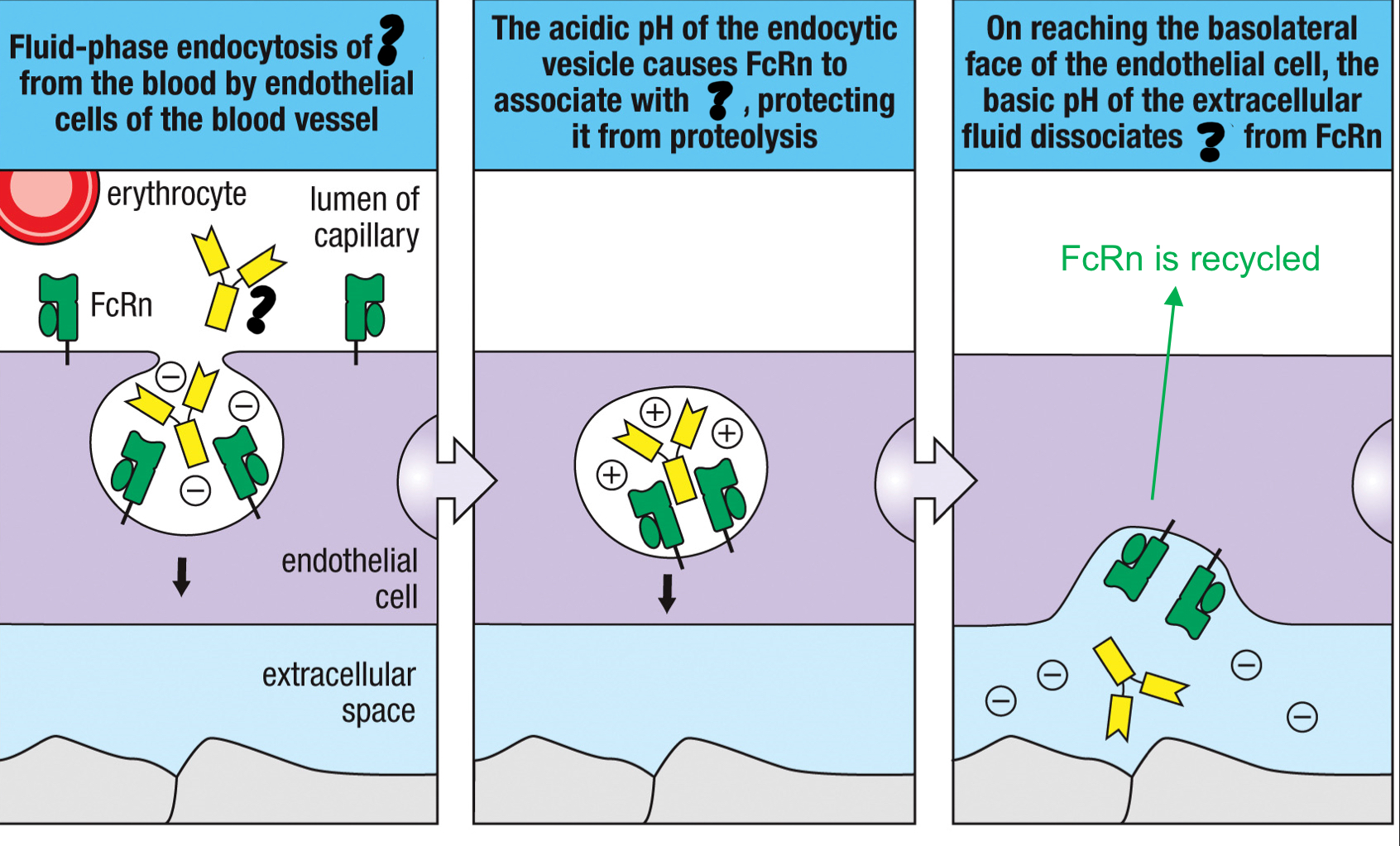
FcRn
Fc receptor that aids in transcytosis of IgG; transports IgG across epithelia; similar structure to MHC class 1
B cell co-receptor
complex of CD19, CD81 and CR2 that binds to complement on the antigen-bearing target cell and so augments the BCR’s response to the specific antigen
true
T/F: clustering of surface antibodies is associated with B cell activation
true
T/F: germinal centers contain apoptotic cells
false
T/F: germinal centers exist prior to antigen exposure
false
T/F: follicular dendritic cells are excluded from the germinal center
true
T/F: affinity maturation occurs in the germinal center
false
T/F: the germinal center is composed primarily of nondividing B cells
true
T/F: germinal centers are the site where B cells differentiate into memory cells
true
T/F: individuals born without a thymus don’t mediate effective isotype switching in their B cells
IgA
Mucosal epithelia of the GI tract, eyes, nose, throat, respiratory, urinary and genital tracts and the mammary glands are protected by which class of antibodies?
false
T/F: neutralizing antibodies often have low affinity for antigen
true
T/F: neutralizing antibodies that provide protection in the gut are typically of the IgA isotype
false
T/F: neutralizing antibodies require complement to be effective
true
T/F: IgE is primarily effective against viral infections
true
T/F: IgE is rapidly phagocytosed by neutrophils whether or not it’s bound to an antigen
Complexes of IgG bound to soluble multivalent antigens can activate the classical pathway of complement, resulting in the deposition of __ on the complex, targeting it for endocytic uptake by cells bearing __?
C3b; CR1 and Fc receptors
Erythrocytes are equipped to facilitate the removal of small immune complexes from the circulation using receptors that bind to __?
C3b