Chapter 7: Business to Business Marketing
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
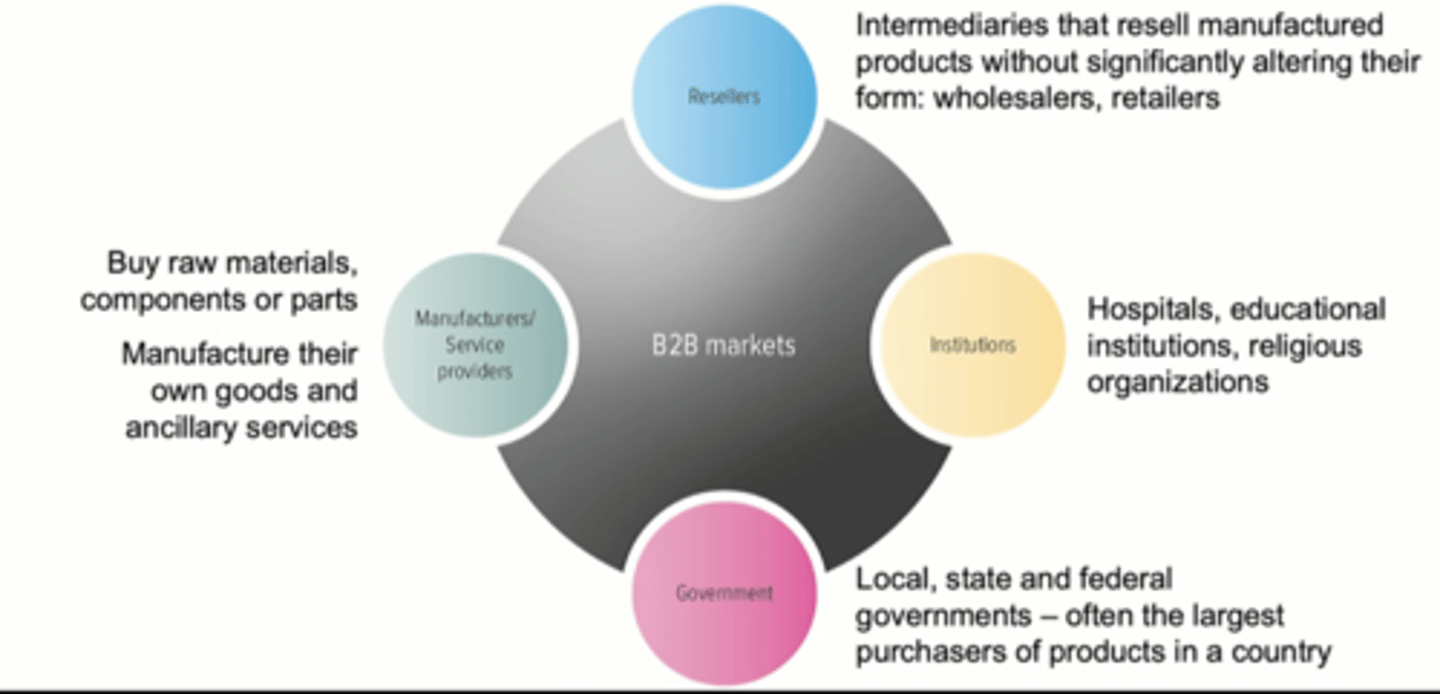
B2B Markets
B2B Markets: Manufacturers and Service Providers
- manuf. buy raw materials, components, and parts that allow them to make and market their own goods and ancillary services
- ex: (not necessary to know for exam) Volkswagen makes Audi, Bentley, Bugatti, etc.
B2B Markets: Resellers
- Resellers: marketing intermediaries hat resell manufactured products without significantly altering their form
- manuf->wholesallers and distributors->retailers
- candy is largest reseller segment in U.S
B2B Markets: Resellers: Wholesalers, distributers, and retailers
- Wholesalers: firm engaged in buying, taking little title to, often storing, and physically handling goods in large quantities, then reselling the goods (usually in smaller quantities) to retailers or industrial or business users
- Distributers: A type of reseller or marketing intermediary that resells manufactured products without significantly altering their form. Distributors often buy from manufacturers and sell to other businesses like retailers in B2B transaction
- Retailers: represent resellers and engage in B2B transactions when they buy fixtures, capital investments, leasing locations, financing operations, and merch for their stores
B2B Markets: Institutions
- hospitals, educational orgs, religious orgs also purchase all kinds of goods and services
- public institutions also engage in B2B relationships to fulfill their needs for capital construction, equipment, supplies, food, and janitorial services
B2B Markets: Gov't
- in most countries, the central govt is one of the largest purchasers of goods and services
- local, state, and federal
- the U.S. govt spends 4 trillion dollars annually; dept of defense works with cybersecurity firms
B2B buying Process
- info search and alternative evaluation steps are more formal and structures in the B2B process
- typically, B2B buyers specify their needs in writing and ask potential suppliers to submit formal proposals, whereas B2C buying decisions are usually made by indiv or families and do not need formal proposals
- for schools to buy their laptops and tablets, it must complete requisition forms, accept bids from manuf, and obtain approval for the expenditure. The final decision rests with a committee, which demands a great deal of consideration
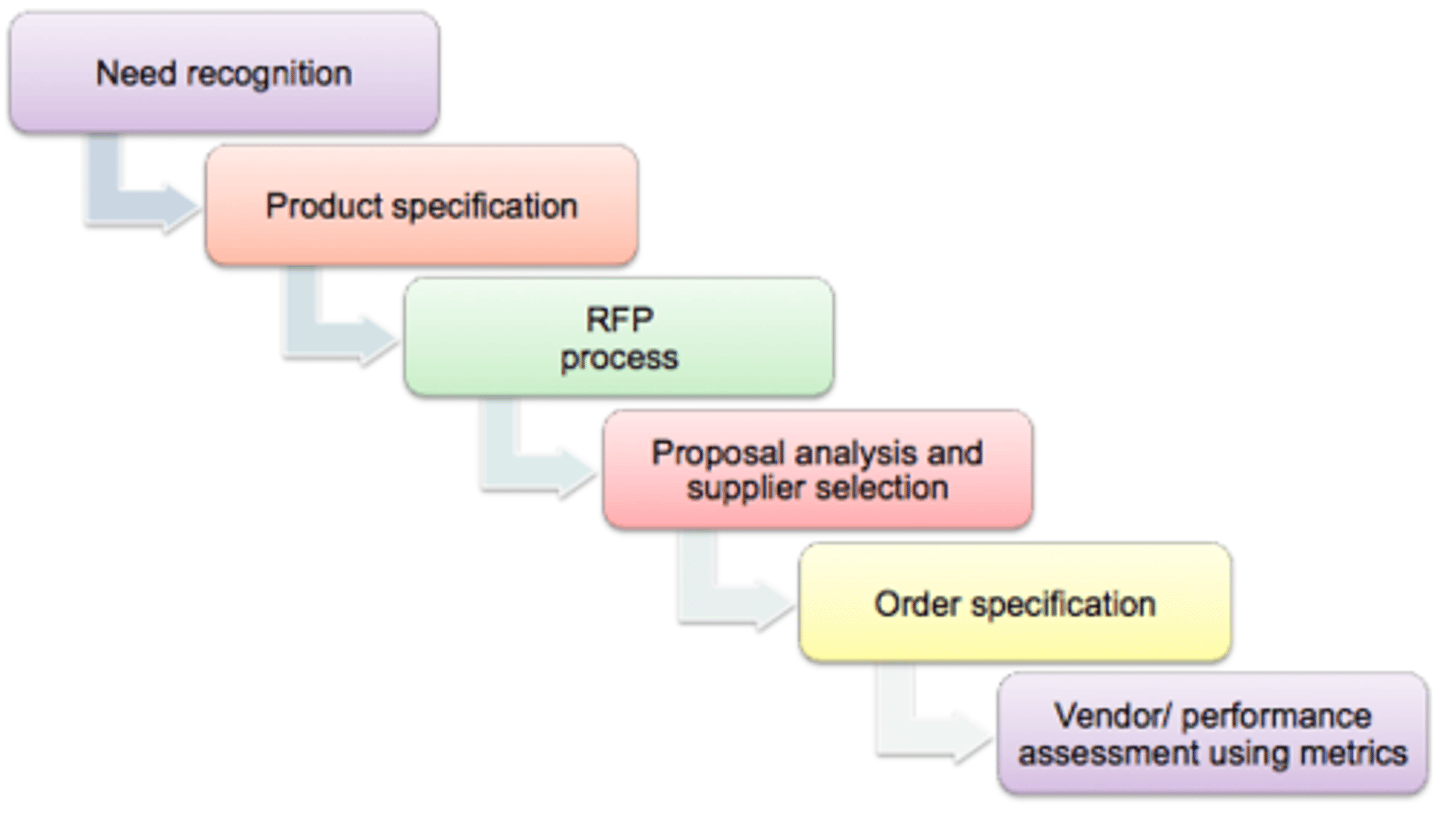
B2B Buying Process: Stage One: Need Recognition
- the buying organization recognizes, though either internal or external sources, that it has an unfilled need. Considers alternative solutions
B2B Buying Process: Stage Two: Product Specification
- list of potential specifications that vendors might use to develop their proposal (screen size, battery life, processor speed)
- used by suppliers/vendors to develop proposals
B2B Buying Process: Stage Three: RFP Process
- Request for Proposals (RFP): a process through which buying organizations invite alternative suppliers to bid on supplying their required components or specifications
- the purchasing company may simply post its RFP on its website, work through various web portals, or inform its preferred vendors directly
B2B Buying Process: Stage Three: RFP Process: Web Portals
- small companies may lack the ability to attract broad attention to their requests, so they may turn to a web portal (an internet site whose purpose is to be a major starting point for users when they connect to the web)
--- there are general portals, like yahoo!, B2B partners connect to specialized or niche portals to participate in online info exchanges and transactions. These help streamline procurement or distribution processes.
- Portals can be cost saving bc they eliminate periodic negotiations and routine paperwork, and they offer the means to forma a supply chain that can respond quickly to buyer needs
- Small to med sized companies looking for skilled service workers can also se portals such as Guru.com to facilitate the RFP process. Guru helps freelance professionals connect with companies that need their services
B2B Buying Process: Stage Four: Proposal Analysis, Vendor Negotiation, and Selection
- the buying org, in conjunction with its critical decision makers, evaluates all the proposals it receives in response to its RFP
- many firms narrow the process to a few suppliers, often those with which they have existing relationships, and discuss key terms of the sale, such as price, quality, delivery, and financing
- some firms have a policy that requires them to negotiate with several suppliers, particularly if the product or service represents a critical component or aspect of the business--- policy makes the suppliers know that the buying firm can always shift a greater portion of its business to an alternative supplier of it offers better terms
B2B Buying Process: Stage Five: Order Specification
- firm places its order with the preferred supplier(s)
- the order includes a detailed description of the goods, prices, delivery dates, and, in some cases, penalties for noncompliance
- the supplier then sends an acknowledgement that it has received the order and fills it by the specified date
B2B Buying Process: Stage Six: Vendor Performance Assessment Using Metrics
- firms analyze their vendor's performance so they can make decisions about their future purchases
- this analysis is more formal and objective
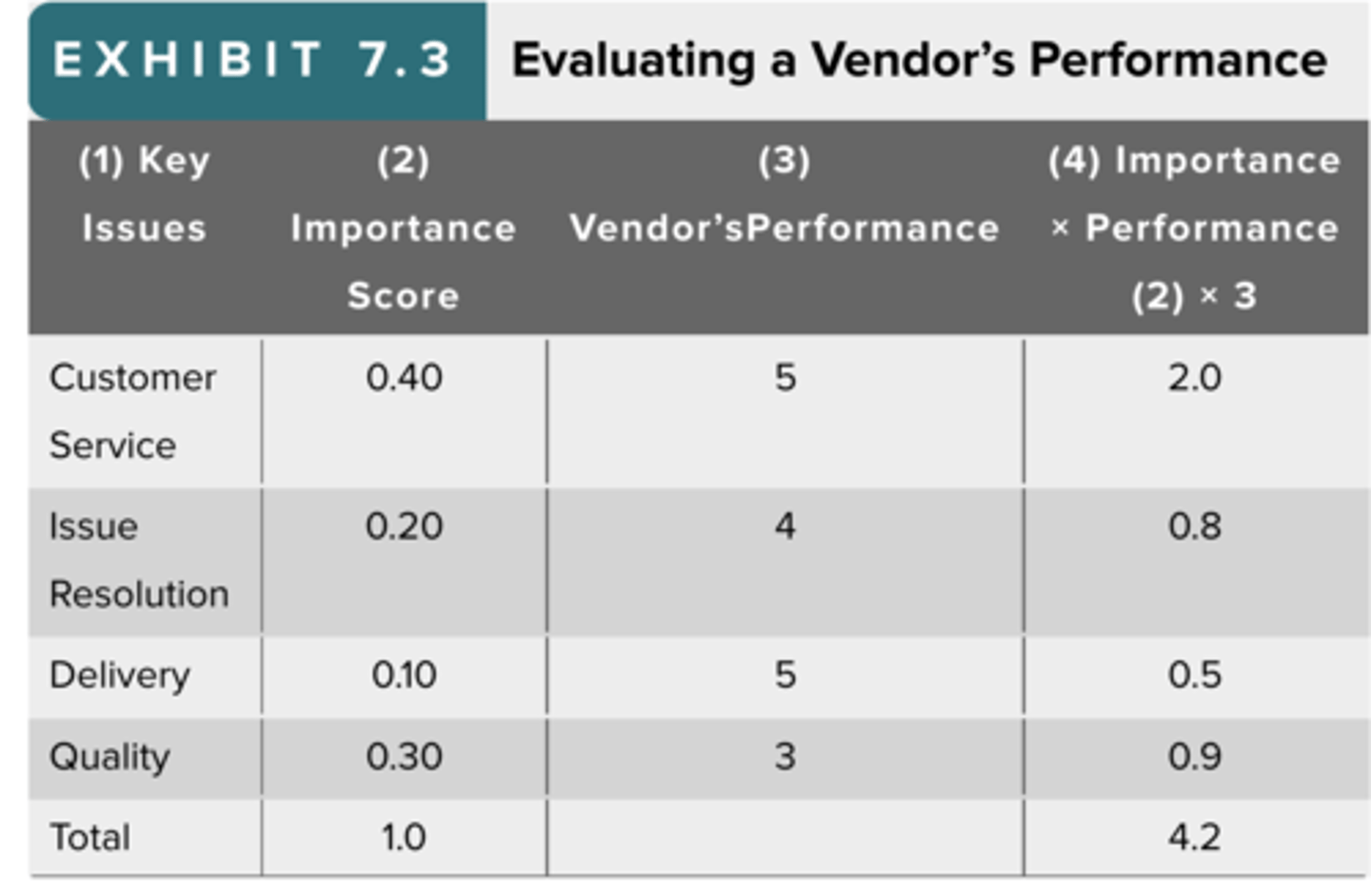
1) The buying team develops a list of issues that it believes are important to consider in the vendor evaluation.
To determine the importance of each issue (column 1), the buying team assigns an importance score to each (column 2). The more important the issue, the higher its score, but the importance scores must add up to 1. In this case, the buying team believes that customer service and quality are most important, whereas issue resolution and delivery are comparatively less important.
3) In the third column, the buying team assigns numbers that reflect its judgments about how well the vendor performs. Using a 5-point scale, where 1 equals poor performance and 5 equals excellent performance, the university decides that the tablet vendor performs quite well on all issues except product quality.
4) To calculate an overall performance score in the fourth column, the team combines the importance of each issue and the vendor's performance scores by multiplying them. Because the tablet vendor performed well on the most important issues, when we add the importance/performance scores in column 4, we find that the overall evaluation is pretty good—4.2 on a 5-point scale.
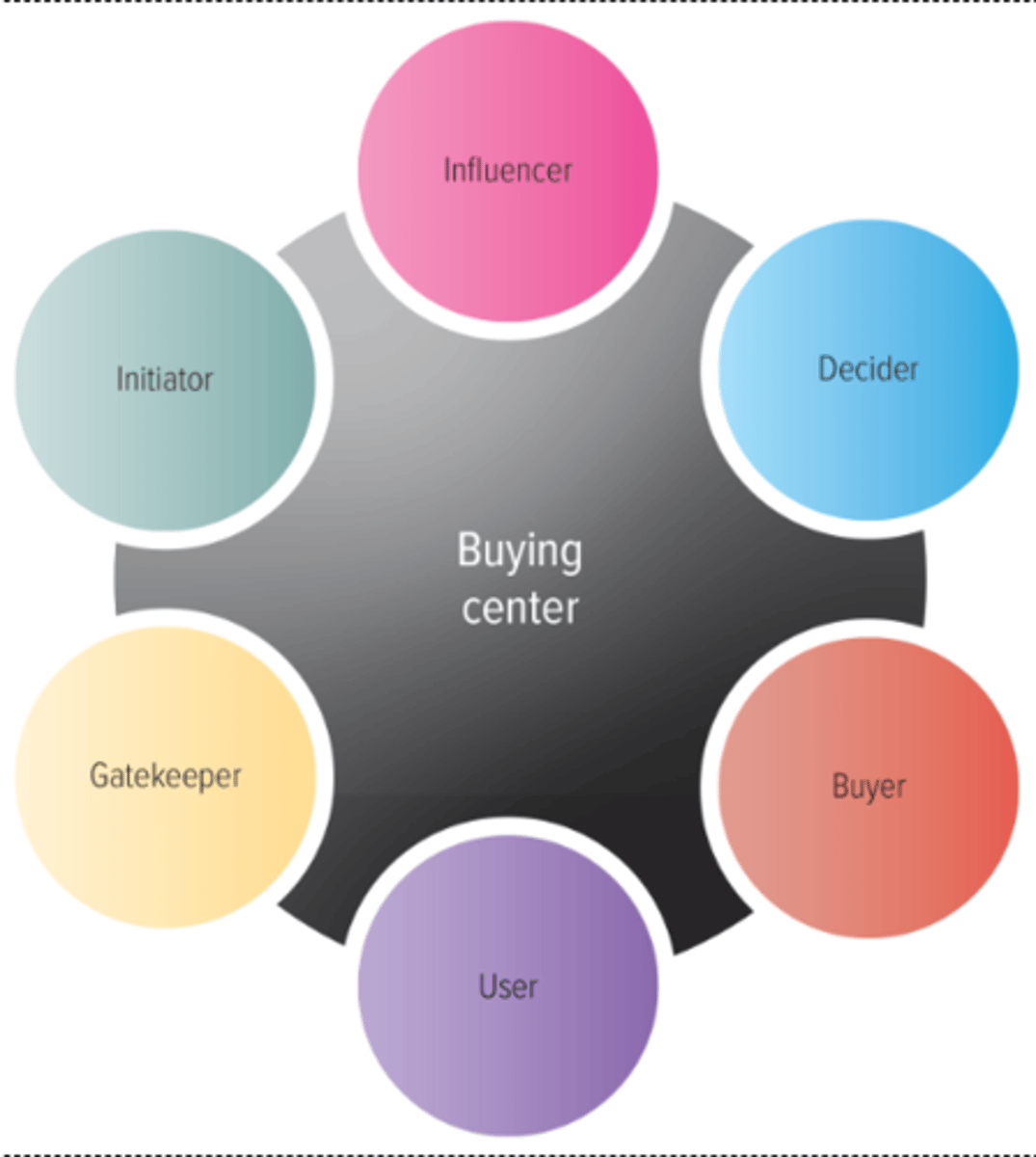
Buying Center Roles (use the setting of a hospital for examples)
- Buying Center: the groups of ppl typically responsible for the buying decisions in a large organization
1. Initiator: (your doctor)The buying center participant who first suggests buying the particular product or service
2. Influencer: (the medical device supplier) the person whose views influence other members of the buying center in making the final decision
3. Decider: (the hospital) the person who ultimately determines any part of or the entire buying decision- whether to buy, what to buy, how to buy, or where to buy
4. Buyer: (the hospitals materials manager) the person who handles the paperwork for the actual purchase
5. User: (the patient) the person who consumes or uses the product or service
6. Gatekeeper: (the insurance company) the person who controls information or access, or both to decision and influencers
Organizational Culture
- set of values, traditions. and customs that guide its employees' behavior
- comprises as a set of unspoken guidelines that employees share with one another through various work situations
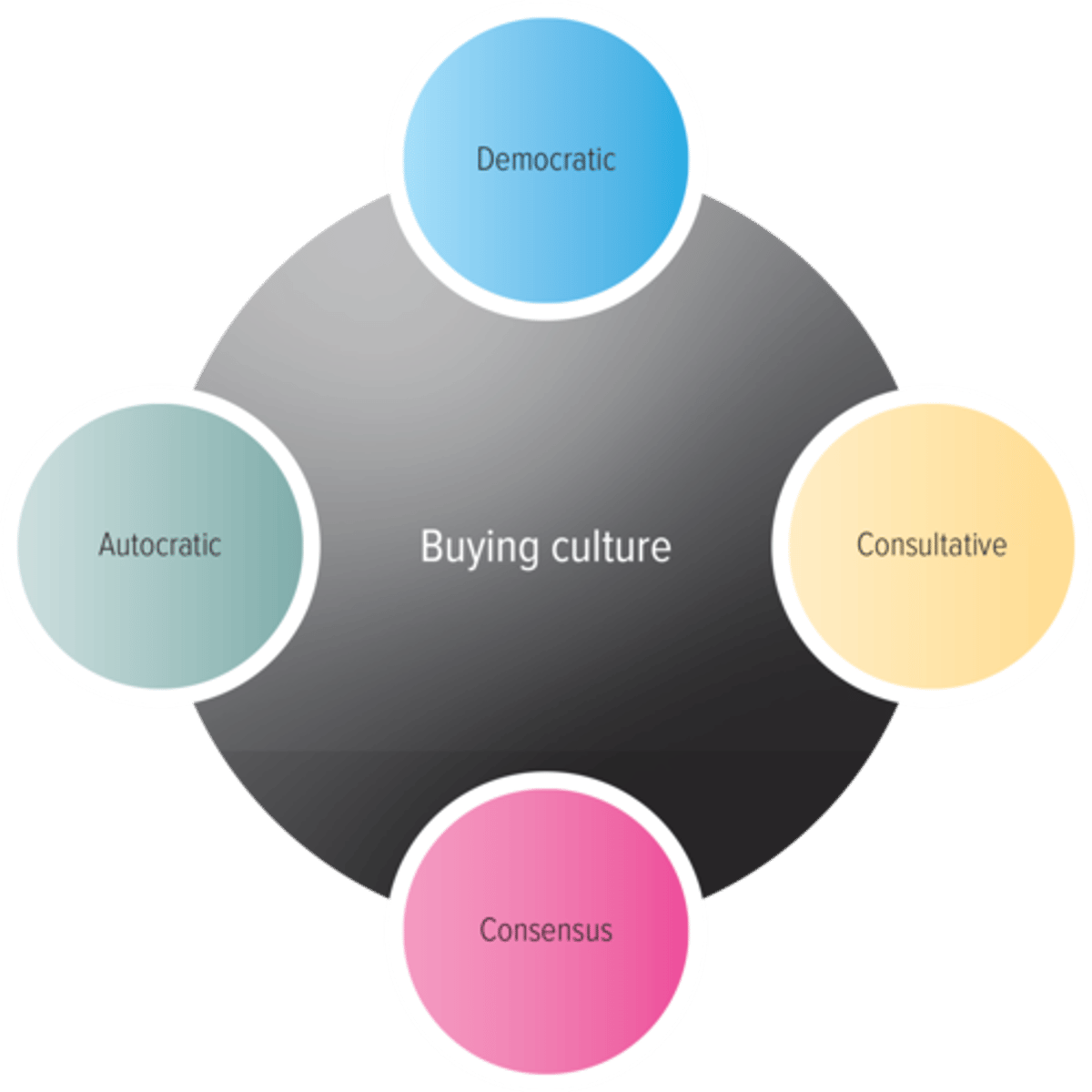
Organizational Buying Culture
- knowing which buying center culture is prevalent in a given organization helps the seller decide how to approach that particular client, how and to whom to deliver pertinent information, and to whom to make sales presentation
- Autocratic BC: one person makes the decision alone, though there may be multiple participants
- Democratic BC: majority rules in making decisions
- Consultative BC: one person makes the decision, but they solicit input from others before doing so
- Consensus BC: all members of the team must reach a collective agreement that they can support a particular purchase
Building B2B Relationships
-a multitude of ways to enhance relationships, and these methods seem to be advancing and evolving by the minute.
-ex: blogs and social media can build awareness, provide search engine results, educate potential and existing clients about products or services, and warm up a seemingly cold corporate culture
-Web analytics, like traffic on the website and the number of comments, can offer tangible evaluations, but a better measure is how often the blog gets mentioned elsewhere, the media attention it receives, and the interaction, involvement, intimacy, and influence that it promotes.
-ex: Twitter, the micro-blogging site, is valuable for B2B markets, because they can communicate with other businesses as often as they want.
- White papers: promotional technique used by B2B sellers to provide info abt a product or service in an educational context, thereby not appearing like promotion and propaganda (subject matter expert)
Buying Situations
- New Buy: a purchase of a good or service for the first time; the buying decision is likely to be quite involved because the buyer or the buying organization does not have any experience with the item; goes thru all 6 steps in buying process and involve new ppl
- Modified Rebuy: when the buyer has purchased a similar product in the past but has decided to change some specifications, such as the desired price, quality level, customer service level, options, and so forth; current vendors are more likely to have an advantage in acquiring modified rebuy
- Straight Rebuy: when the buyer or buying organization simply buys additional units of products that have previously been purchased; buyers is only involved