FIVS 210 Forensic Photography Exam 2
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Anthropometry
the scientific study of the measurements and proportions of the body created by Alphonse Bertillon
began in France in 1883 and was in use until 1903
purposes of crime scene photography
record details of scene and surrounding areas
document initial appearance and location of physical evidence with respect to the crime scene
provide investigators, witnesses, and others to a permanent visual record
refresh memory of crime scene
review details
provide evidence
document an injury
quality crime scene qualifications
correct exposure
maximum depth of field
in focus
how to document a crime scene
long range, medium range, and close ups
long range photographs
used to establish an overall view of the crime scene location and potential evidence
overlap photographs to make connection between images
capture scene as initially found
medium range photos
establish location of evidence with respect to other items at crime scene
transition from distant to close range
evidence is obvious
close up images
ID evidence and establish location
fill the frame with evidence
90* angle - use a tripod
cardinal rules of crime scene photography
fill the frame
maximize depth of field
keep the film plane parallel
the three rules of investigative photography
if its worth looking at, its worth photographing
photograph everything before its moved or altered
document evidence with long, mid, and close up shots
photo log
records general info about the case, jogs memories, explains lighting, and specific settings
case identifier tag
the first photo in a set at a new case showing case number, photographer name, investigator name
inverse square laws
how fast light falls off and how far it spreads as the distance from the light source increases
Light Close for sharper shadows, bigger catchlights and darker backgrounds. Light Far for softer shadows, smaller catchlights and brighter backgrounds.
built in flash
convenient but weak
can cause red-eye
flash synchronization
built-in flash is timed to the exposure by the camera
the speed of the exposure must be slow enough to allow for the benefit of the flash
fill flash
lightens the shadows and reduces image contrast
reduces “hotspots”
bounce flash
bouncing the light off an object other than the subject to light up an area
diffused flash
softens and spreads out harsh, concentrated flash
painting with light
slow shutter speed used to lighten an entire area
takes a long time and uses an assistant
tripod components
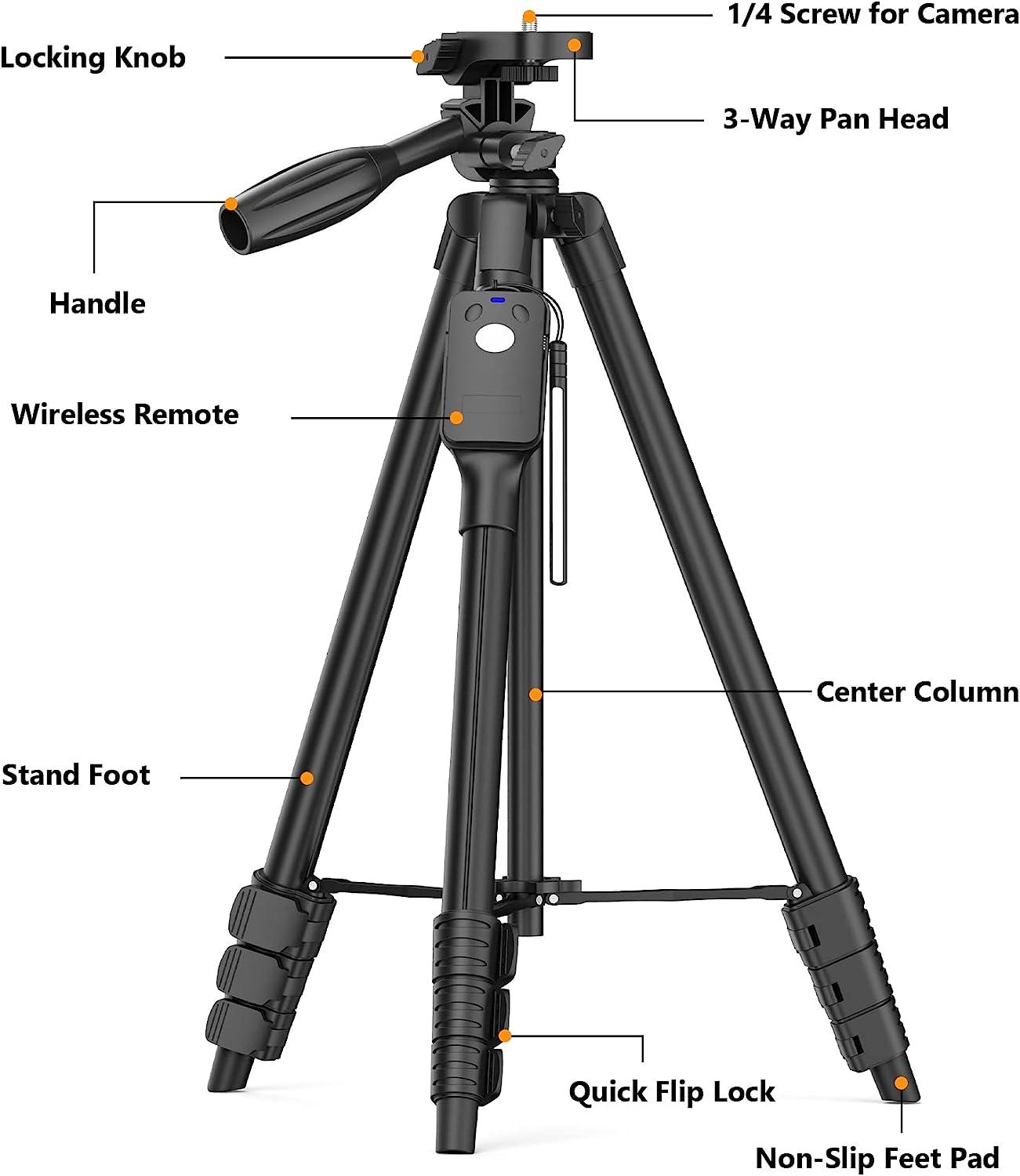
SWIGIT
Scientific Working Group on Imaging Terchnology
provides guidelines and recommendations for use of imaging technologies
Category One Image
used to record a time, place or event
includes:
general crime scene images, including evidence
surveillance images
autopsy images
documentation of evidence in lab
arrest photos/mug shots
category two images
used for specific analysis and comparison
includes:
latent prints
bloodstain patterns
questioned documents
tool mark images
gunshot residue
impression evidence
bits of data
each 1 bit DOUBLES the number of combinations
meta data
additional information is embedded within the image file that provides more details
info includes:
caption info
photographer information
IPTC
camera data
image data
video/audio data
DICOM, XMP, EXIF
history
to view metadata
file info
history/photoshop tab
to enhance category 1 images
a detailed history is not required
adjust brightness/contrast
adjust color balance
adjust hue/saturation
adjust white balance
image sharpening
cropping
rotating
enhancement of category 2 images
the image MUST be RAW OR TIF and a detailed history must be maintained
includes:
tonal range corrections
color channel selection and subtraction
fourier analysis
noise reduction
image sharpening
how to start a history log
edit tab
preferences
history log
turn it on by saving log items to metadata and editing log items to detailed
dynamic range
values that span the entire histogram
the output if very intense at one setting
diopter
glass filters that can be added onto the end of a camera lens and stacked to zoom in further
+1, +2 or +4
when stacked, can soften the image and make focusing difficult
extension tubes
expensive, but can get close to the object without distortion
sharper images
shutter speed and exposure are effected
reversing rings
allows you to mount the lens backwards, making it a magnifying glass
macro lens
allows you to focus extremely close to a subject
true sensors will be 1:1
magnification ratio
the relationship between the size of the in-focus subjects projection on the imaging sensor and the subject’s size in reality
minimum focus distance: 18”
what is the purpose of evidence w/ and w/out a scale
a scale is utilized to capture important dimension info and a photo w/out can be used to show no modifications were made
with respect to photographs, what does the phrase “true and accurate representation” mean
refers to a photo documentation of the scene as it originally appeared
you are asked to determine the size of an item from a photo. explain the process
by utilizing the scale in the photo, a relative dimension can be obtained on any item in the image. the easiest way is to enlarge the item and print the scale to its natural size
what are the three series of photographs which should be taken to completely document a crime scene
overall, midrange, and closeup
what are 2 considerations when utilizing a scale?
scale at the same height as the subject
scale should be a similar shade as the subject/background
camera film plane should be parallel to the subject
scale should be an appropriate length
take a photo before the scale is placed
why utilize a flash fill
to lighten up a dark/shadowy area
why utilize a bounce flash
to avoid “hot spots” in the imane
why use an external flash?
it is more powerful and can be angled for bouncing light
why should you use flash from 3 different angles?
when directing light at oblique angles, you get better images, but there may be shadowing produced
what does examination quality photograph mean?
photos taken at proper resolution, angle, lighting, and scale
the rules of evidence provide 2 legal principles for digital imaging process. they may be used if
nothing material or essential has been added
nothing material or essential has been removed
when using the levels function, what should you be careful of
clipping