C2.1 Chemical Signalling
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Quorum Sensing
A change in the behaviour of a colony when its population density reaches a certain threshold
Endocrine glands
Secrete hormones into the bloodstream throughout body
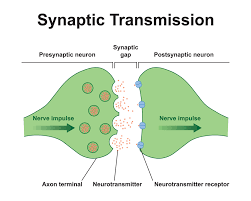
State where neurotransmitters travel in
Only in small space between neurons
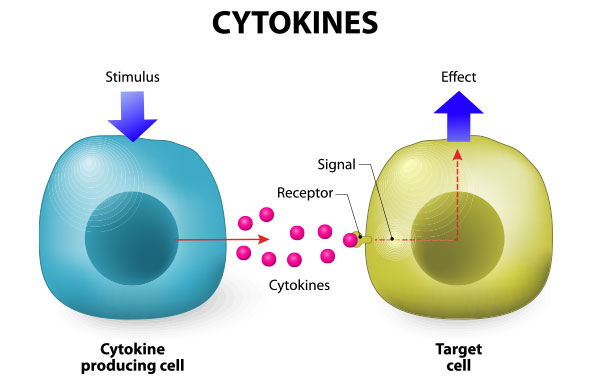
Cytokines
Proteins that act as chemical messages within cells
Muscle fibres
Calcium ions bind to a protein on actin to allow myosin heads to attach
Neurons
Causes the release of neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron
Similarities between hormones and neurotransmitters
small
water soluble
have a shape compatible with its receptor
Outline what hormones can consist of
Steroids
Amines
Peptides
Outline what neurotransmitters can consist of
Amines
Amino Acids
Esters
Gases
Esters
Organic compounds that react with water to produce alcohols
Localised Effect
Molecules are closer together
Distant Effect
Molecules are far away from each other
State some structural characteristics of a signalling molecule being able to enter a cell
Receptor protein is located in cytoplasm/nucleus (inside the cell)
Intracellular
Surface of receptor is covered in hydrophilic amino acids
State some structural characteristics of a signalling molecule being unable to enter a cell
Receptor protein located on the plasma membrane
Transmembrane
It has hydrophilic (heads) and hydrophobic (tails) amino acids
Transduction pathway
Sequence of interactions initiated by the ligand binding to the receptor
Intracellular pathways
Ligand enters the cell, binds to receptor
Transmembrane pathway
Ligand binds with the receptor, receptor changes shape
GPCR
G-protein couples receptors (transmembrane receptor proteins)
GDP
Guanosine diphosphate
GTP
Guanosine triphosphate
Explain the binding of the Gs
When GDP is bound to a G protein, it is inactive
When a ligand binds to the receptor, GDP is replaced by GTP
Epinephrine =
Adrenaline
Explain the formation of Epinephrine
Hormone produced by the adrenal glands
Binds with a G protein
ATP converted into secondary messenger molecule
Amplifies the effect
Kinase
Enzyme that removes a phosphate group from ATP and adds it to molecule
Tyrosine kinase
Enzyme that transfers a phosphate from ATP to tyrosine in a protein
Explain how oestradiol affects target cells
Hypothalamus releases GnRH to pituitary glands
Pituitary glands releases LH and FSH
Oestradiol travels through cells of hypothalamus
Positive feedback
Characteristics of negative feedback loop
Maintains stable internal conditions (homeostasis)
Opposes initial stimulus to restore balance
Automatically adjusts body processes
Characteristic of positive feedback loop
Final product triggers even more production of the product