Exploring Sex, Gender, and Sexuality in Society
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Sexuality
Refers to a person's sexual attractions, in terms of sexual orientation eg heterosexual, homosexual, bisexual.
Sex
A person's genetic makeup —specifically whether the sex chromosome is XX (female), XY (male) or in an extremely small %: X, XXY, XXYY, etc.
Gender
Refers to the socially constructed expectations associated with a given sex category.
Sexual orientation
Refers to a person's pattern of physical, romantic, sexual and emotional attraction to, and/or intimate relationships with, to individuals based on the sex/gender.
Heteronormativity
The normative practice and belief that sexual activity between people of the 'opposite' sex is the natural expression of sexuality.
Heterosexuality
The normative or predominant preference for members of the opposite sex as sexual partners.
Gender roles
Behaviours that conform to widely shared expectations about how males and females are supposed to act, think, feel, etc.
Essentialism
The view that gender differences are due to biological differences between women and men. E.g. hormonal, physiological, chromosomal, genetic, etc.
Social constructionism
Gender differences are 'constructed' as a reflection of the different social positions occupied by women and men.
Gender
Constructed or invented by people living in historically specific social structures and cultures.
Essentialism
Biosocial theories that suggest all humans instinctively try to ensure their genes are passed on to future generations.
Gender Strategies
Different strategies developed by women and men for passing on genes.
Biological Basis of Behavior
Behavior has a biological basis due to the difference in men's and women's reproductive capacities.
Traditional Gender Roles
Roles that are essential for integrating society and allowing it to function properly, reflecting the status quo.
Essence of Masculinity
Viewed as a series of 'instrumental' traits, such as strength, rationality, confidence, and competitiveness.
Essence of Femininity
Viewed as a series of 'expressive' traits, such as gentleness, nurturance, and sensitivity to others.
Breadwinner
An example of an instrumental trait associated with masculinity.
Mothering
An example of an expressive trait associated with femininity.
Critique of Essentialism
Argues that essentialism ignores historical and cultural variability regarding sex, gender, and sexuality.
Generalization from the Average
A critique that essentialism tends to ignore variations within gender groups.
Lack of Evidence for Essentialism
Critique that argues little or no evidence directly supports essentialists' major claims.
Role of Social Power
Critique that essentialism ignores the role of social power.
Male Domination
Located in class inequality, developed when societies began producing surpluses.
Control of Surpluses
Men controlled surpluses and imposed rules that only men could own property.
Control over Women's Sexuality
A rule imposed by men to control women's sexuality.
Feminist Perspective
Argues that male domination is rooted in patriarchal authority relations, family structures, and patterns of socialization.
Social Constructionism
Features of life that appear natural or innate are sustained by social processes that vary historically and culturally.
Gender as Social Construction
Gender is considered a social construction.
Gender Socialization
Various ways in which meanings of gender are taught.
Gender Socialization
The process through which individuals learn to become masculine or feminine.
Girls' Toys
Toys that stress nurturing, physical attractiveness, and indoor activities.
Boys' Toys
Toys that stress aggression, competition, and outdoor activities.
Gender Socialization and Parenting
Parents shape resources and opportunities for their children, influencing their gender roles.
Father's Play Style
Fathers are more likely to play boisterously and competitively with their sons than with their daughters.
Encouragement of Girls
Parents tend to encourage girls to participate in cooperative, role-playing games.
Gender Socialization in Schools
The influence of educational materials and teacher perceptions on gender roles.
Science Textbooks
Textbooks that disproportionately feature the contributions and awards of males.
Teacher Attribution
Teachers attributing success in math and science to males' innate ability and females' hard work.
Sex Segregation in Sports
Sports being divided by gender and associated with specific gender roles.
Gender Socialization in the Workplace
The perception of women as less competent in leadership positions due to gendered interaction styles.
Female and Male Scholars
Comparison of co-authored versus sole-authored articles and publications between genders.
Department Heads
A comparison of department heads with no PhD versus women faculty who hold PhDs.
Mass Media Representation
Women are generally underrepresented as characters on television and in movies.
Stereotypical Portrayal of Women
Women in the media tend to be portrayed in stereotypical ways.
Hypersexualization of Women
Images of women in the media are often hypersexualized.
Global Gender Gap Index
A measure of inequality between men and women in terms of participation in the paid labor force, educational attainment, health and life expectancy, and political influence.
Canada's Global Gender Gap Rank
Canada ranks 25th out of 146 countries in the Global Gender Gap Index.
First Wave of the Women's Movement
Emerged during the late nineteenth century focused on the right to vote and to be considered persons.
Second Wave of the Women's Movement
Developed in the mid-1960s focused on equal rights with men in education and employment, elimination of sexual violence, and control over reproduction.
Third Wave of the Women's Movement
Began in the 1990s recognizing that women were oppressed in different ways and to varying degrees.
The Feminist Movement
A social movement aimed at establishing equal rights for women.
Liberal feminism
The main sources of women's subordination are learned gender roles and the denial of opportunities to women.
Socialist feminism
Women's relationship to the economy is the main source of women's disadvantages.
Radical feminism
Patriarchy is the main source of women's disadvantages.
Gender Wage Gap
The ratio of male wage to female wage among employees ages 25 to 54 in Canada, from 1998 to 2021.
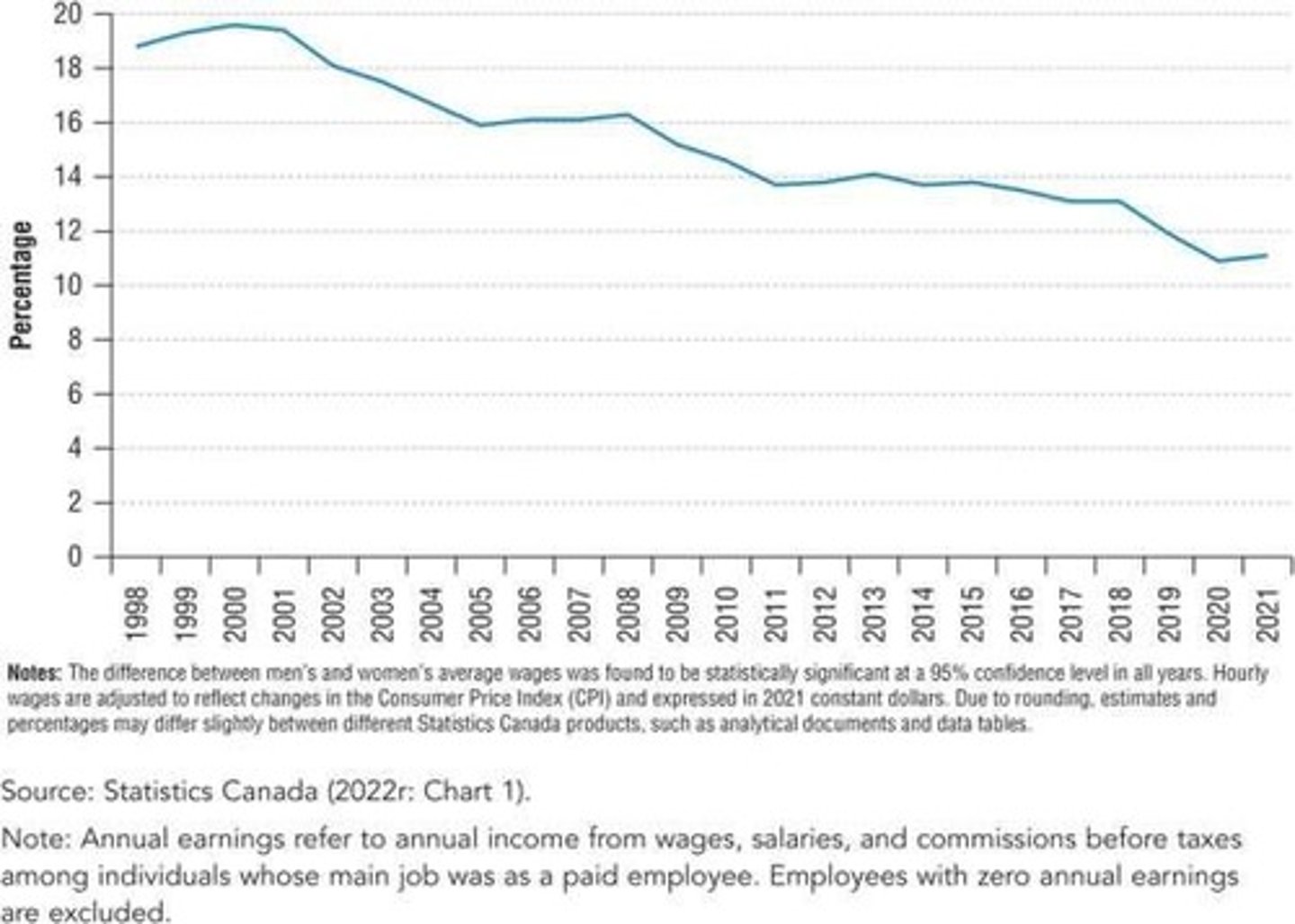
Horizontal occupational sex segregation
The unequal sex distribution of workers across occupations.
Vertical occupational sex segregation
The unequal sex distribution of workers within occupations.
Motherhood Penalty
The tendency for women who become mothers to experience a drop in earnings.
Fatherhood Premium
The tendency for men who become fathers to experience a boost in earnings.
Childrearing responsibility
Women shoulder greater responsibility for childrearing relative to men.
Child care system improvement
Development of a better child care system to eliminate the gender gap in the labour market.
Pay equity policy
'Equal pay for work of equal value': refers to the equal dollar value of different jobs.
Sexual Harassment
Any conduct, comment, gesture, or contact of a sexual nature likely to cause offence or humiliation to an employee.
Sexual assault
Approximately one in three women over the age of 14 experienced some form of unwanted sexual behaviour in the previous 12 months.
Sexual assault conviction rate
Less than 1 percent of all sexual assaults result in jail time.
Unfounded sexual assault complaints
One in five sexual assault complaints reported to the police are categorized as unfounded.
Victim credibility issues
Defence attorneys raise doubt about victims' credibility and status as victims.
Judicial bias
Bias on the part of the judge or the jury can affect sexual assault cases.
Incarceration guarantee
When a conviction is obtained for sexual assault, incarceration is not guaranteed.
Intimate partner abuse
About 30 percent of police-reported violent crime in Canada involves intimate partner violence.
Victims of intimate partner violence
About 80 percent of the victims of intimate partner violence are women.