OCR B Geography GCSE Changing Climate
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Climate change
changes in long-term temperature and precipitation patterns that can either be natural or linked to human activities
Quaternary period
the most recent geological period covering the last 2.6 million years, during which time there were several cold or warm periods
glacial periods
historic cold periods associated with the build-up of snow and ice and the growth of ice sheets and glaciers
inter-glacial periods
historic warm periods in-between glacial periods where conditions were much the same as they are today
global warming
a trend associated with climate change involving a warming trend (0.85°C since 1880)
Geological fossil evidence
plant and animal fossils provide a good indicator of what past climates were like.
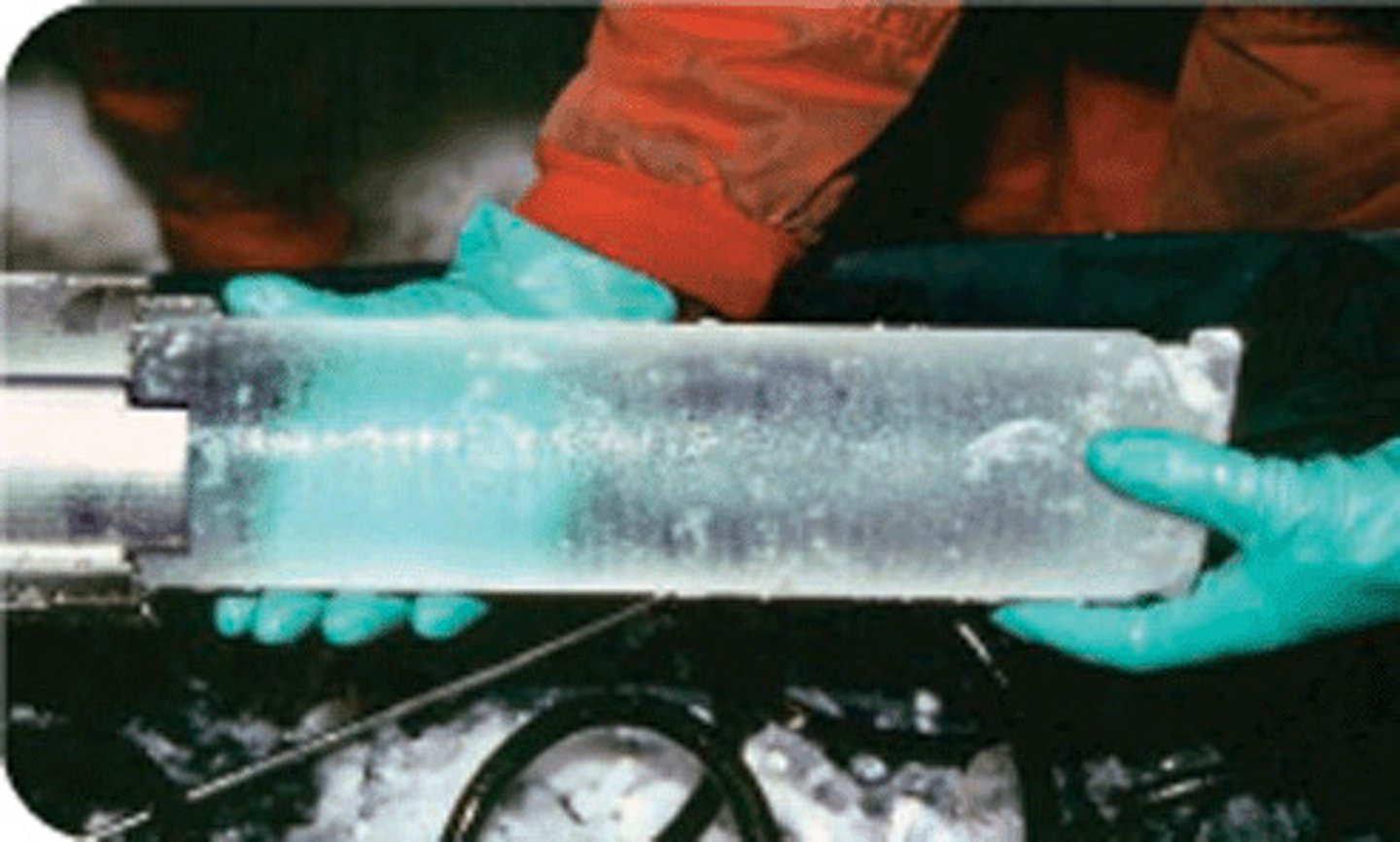
ice core
a cylinder of ice drilled from an ice cap which contains a continuous record of past climatic conditions. It can be analysed to model past climate and help predict conditions in the future.

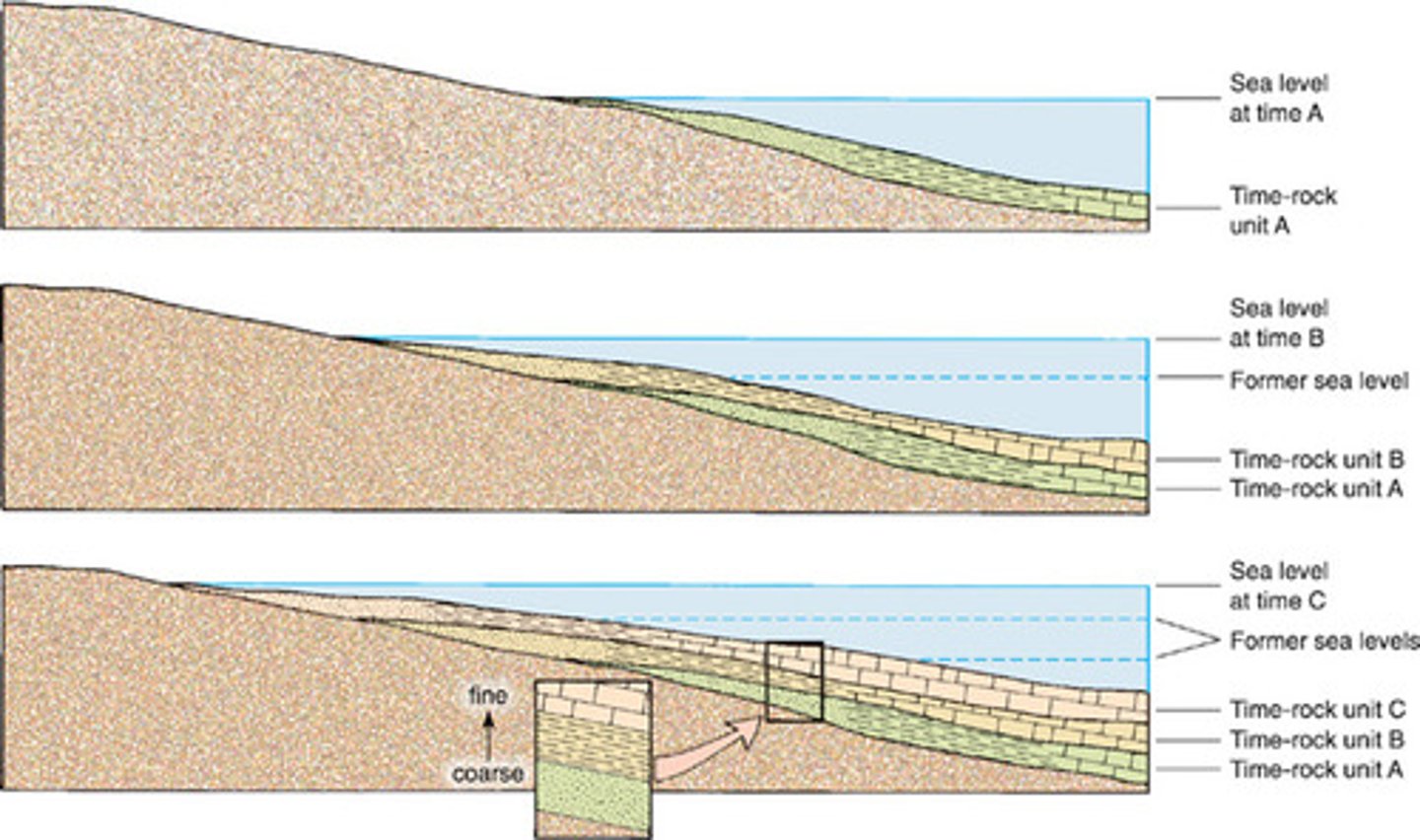
Ocean sediments
layers of sediment build up trapping evidence of past climates which can be drilled into and analysed to investigate past climatic conditions
The little ice age
a period between 1300-1870 during which winter temperatures were colder than today

Megafauna
large animals greater than 50kg e.g. giant beaver
Mastodons
an elephant like mammal with woolly coats

Milankovitch cycles
orbital variations (eccentricity, precession and tilt) which lead to natural climate change.
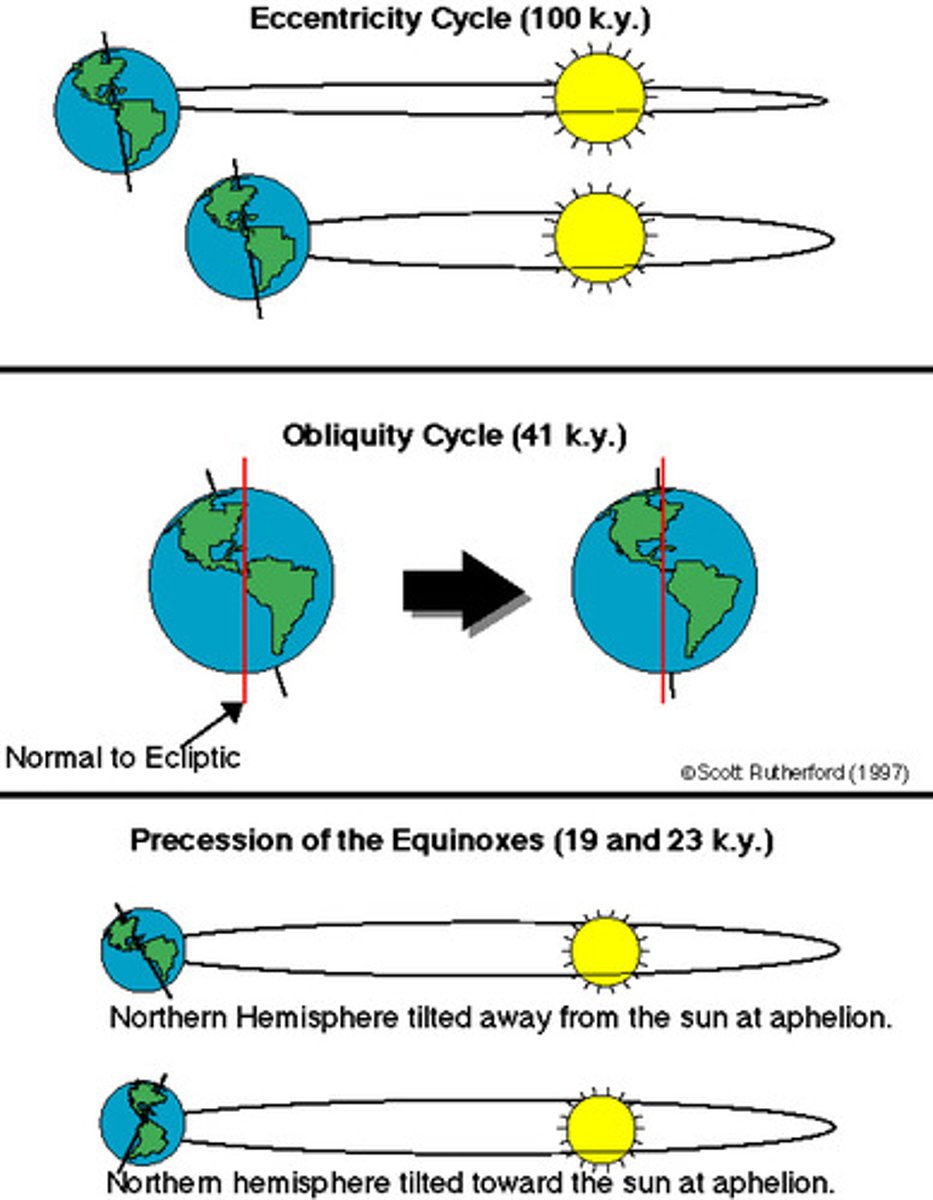
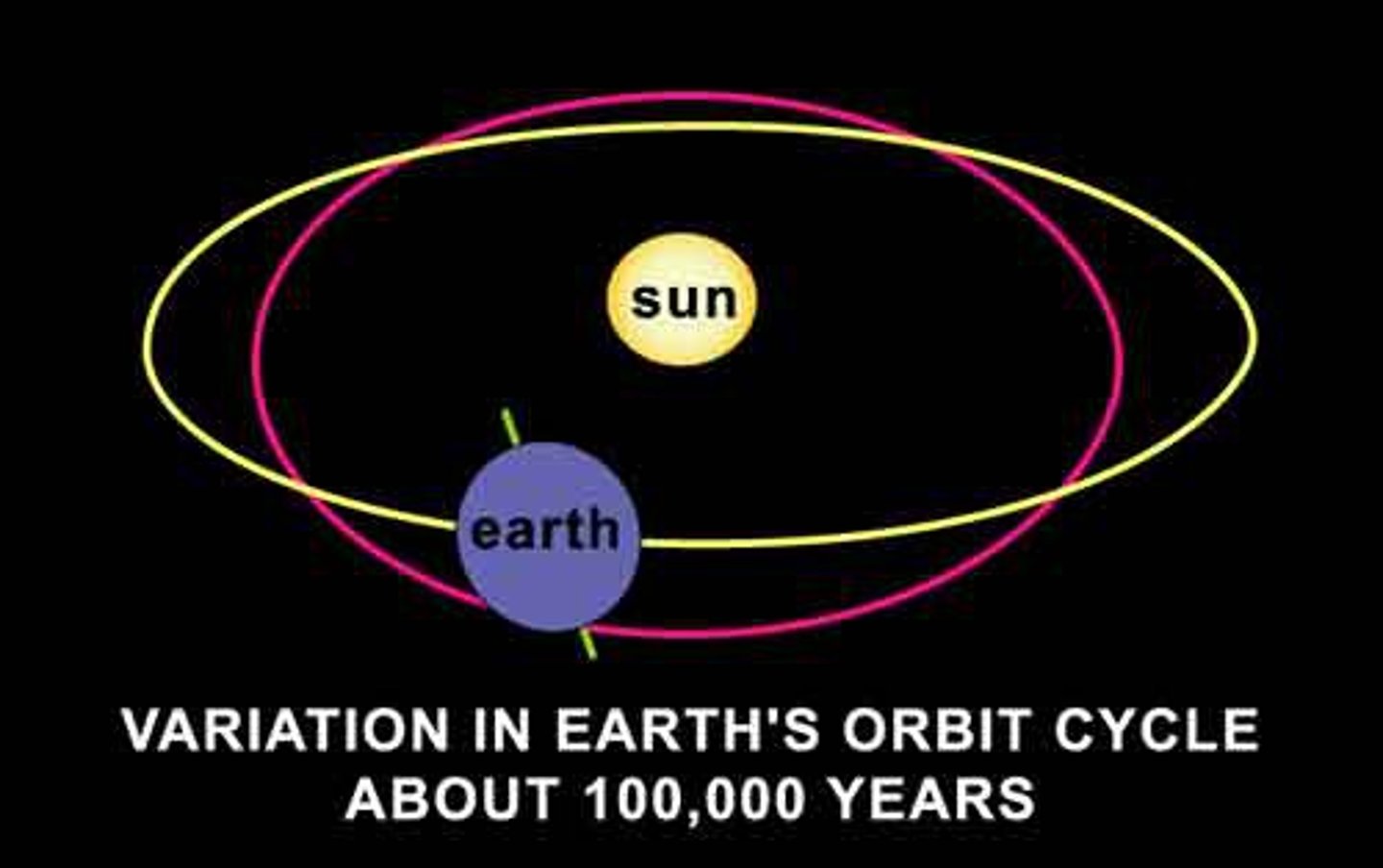
Eccentricity
100,000 year cycle during which the Earth's orbit changes from circular to elliptical and back to circular again. Colder periods occur when the orbit is more circular.
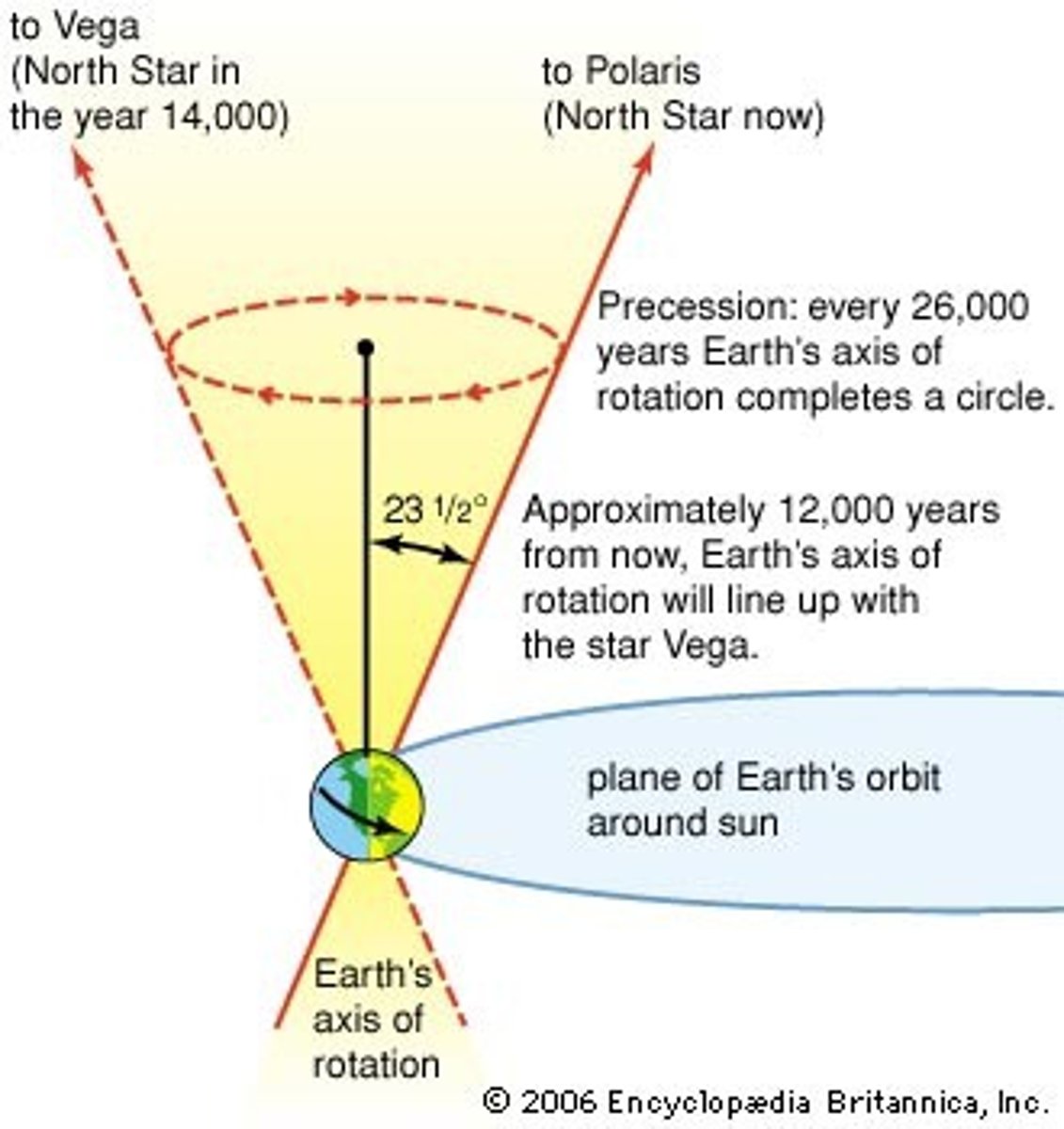
Precession
26,000 year cycle during which the 'wobble' of the Earth shifts
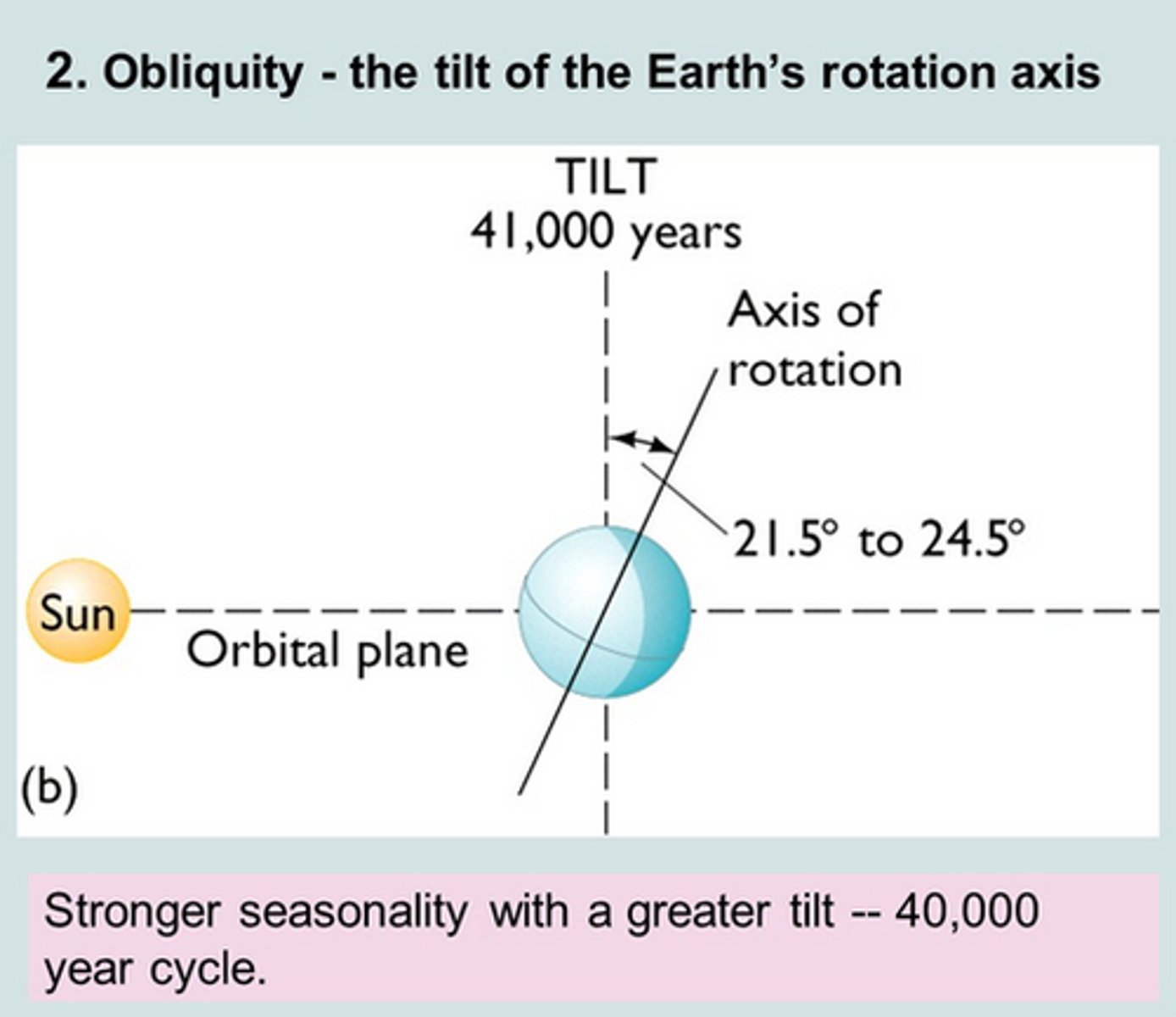
Axial tilt
a 41,000 year cycle during which the tilt of the earth cycles from 21.5 degrees to 24.5 degrees and back again
volcanic winter
colling trend caused by volcanic particules in the atmosphere blocking out some of the Sun's radiation
sunspot
a spot or dark patch that appears on the surface of the sunand is associated with an outburst of energy from the Sun.
sunspot cycle
a period lasting 11 years during which sunspot activity increases from a minimum to a maximum and then back to a minimum
greenhouse effect
natural warming of the atmosphere as heat given off from the Earth is absorbed by liquids and gasses, such as carbon dioxide
enhanced greenhouse effect
the increased greenhouse effect as a result of human activity
Sea level rise
an increase in sea levels attributed to increased amounts of water in oceans (due to less being stored on land in ice caps and glaciers) and thermal expansion of water
Thermal expansion
An increase in the volume of a substance when the temperature is increased