The Lymphatic System
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about the lymphatic system, covering its components, functions, and related concepts, based on lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Lymph
Clear, colorless fluid lacking red blood cells but containing white blood cells.
Lymphatic Capillaries
Smallest vessels that transport lymph.
-large diameter
-Endothelial cells are overlapping (allows fluid to get in)
-no basement membrane
-valves
Trunks and Ducts
Largest vessels that transport lymph.
Lymphatic Tissue
Clusters of immune cells within the lymphatic system.
Lymphatic Organs
Collections of lymphatic tissues.
Fluid Recovery
Recovery of fluid in systemic circulation performed by the lymphatic system.
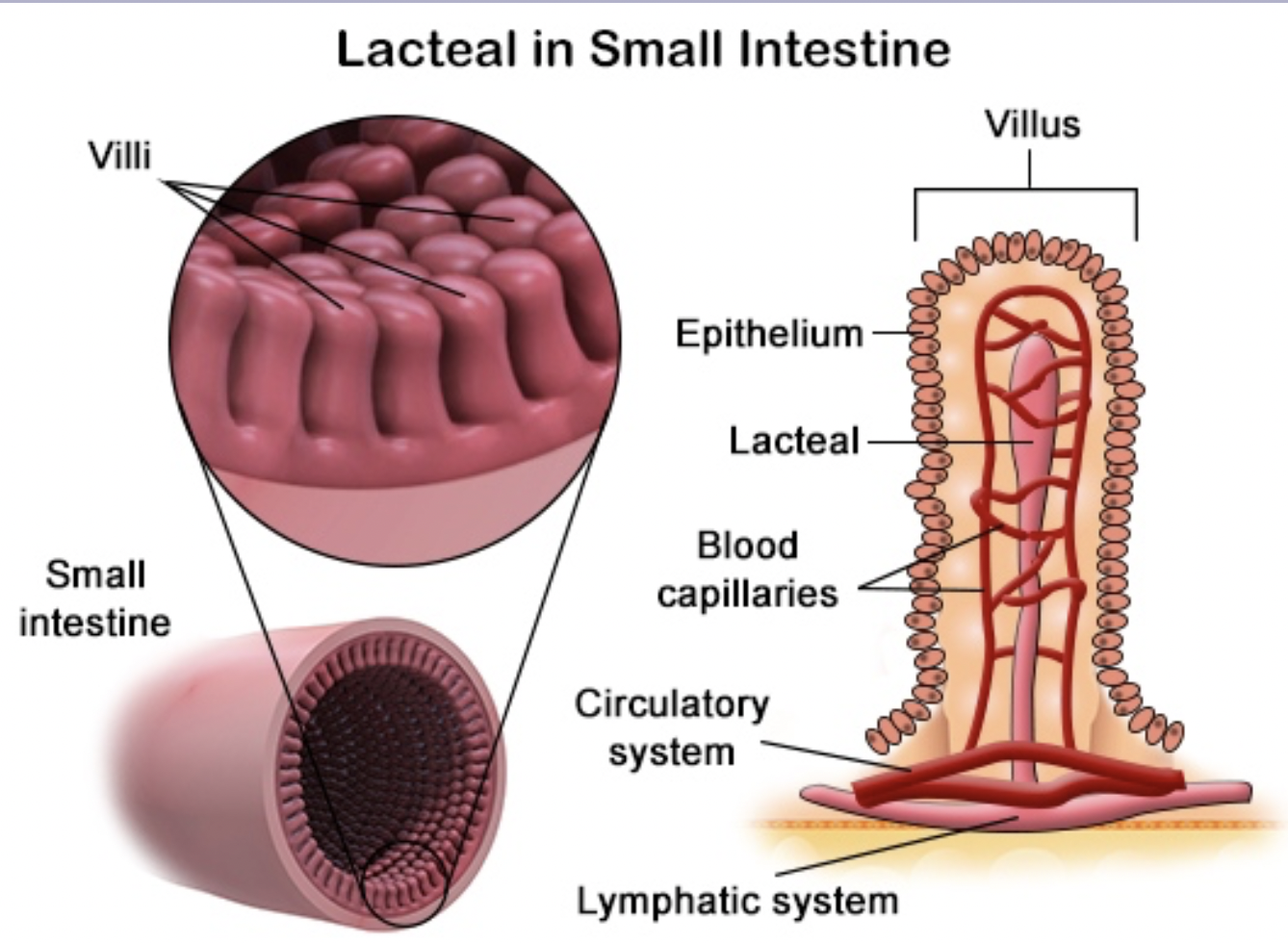
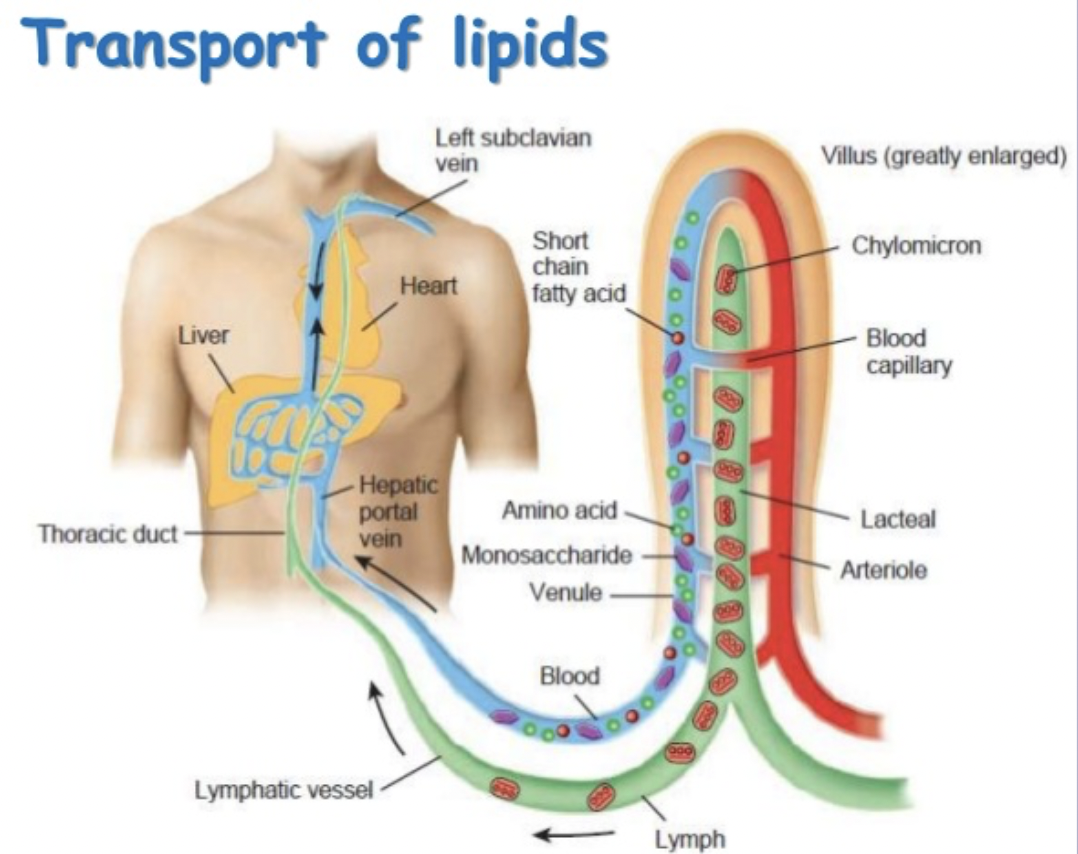
Lipid absorption
Connection to our digestive system.
the small intestines absorbs 95% of nutrients but a significant fraction of lipids is absorbed into lymphatic capillaries and transported to the top of your heart
Lacteals
Connects to the digestive system and used to absorb lipids and lymphatic fluids. loc. large intestines
Immunity
process of detecting foreign pathogens and mounting an immune response.
Lymphatic Fluid
Interstitial fluid that enters lymphatic capillaries.
Chyle
Lymph that is lipid-rich and transported through lacteals from the GI tract to the heart.
Cisterna Chyli
Sac that collects lymph from the lumbar and intestinal trunks; located posterior to the abdominal aorta; contains lipid-rich lymph.
Right Lymphatic Trunk
Collects lymph from the right side of the body above the diaphragm, right arm, neck, and head; drains into the right subclavian vein.
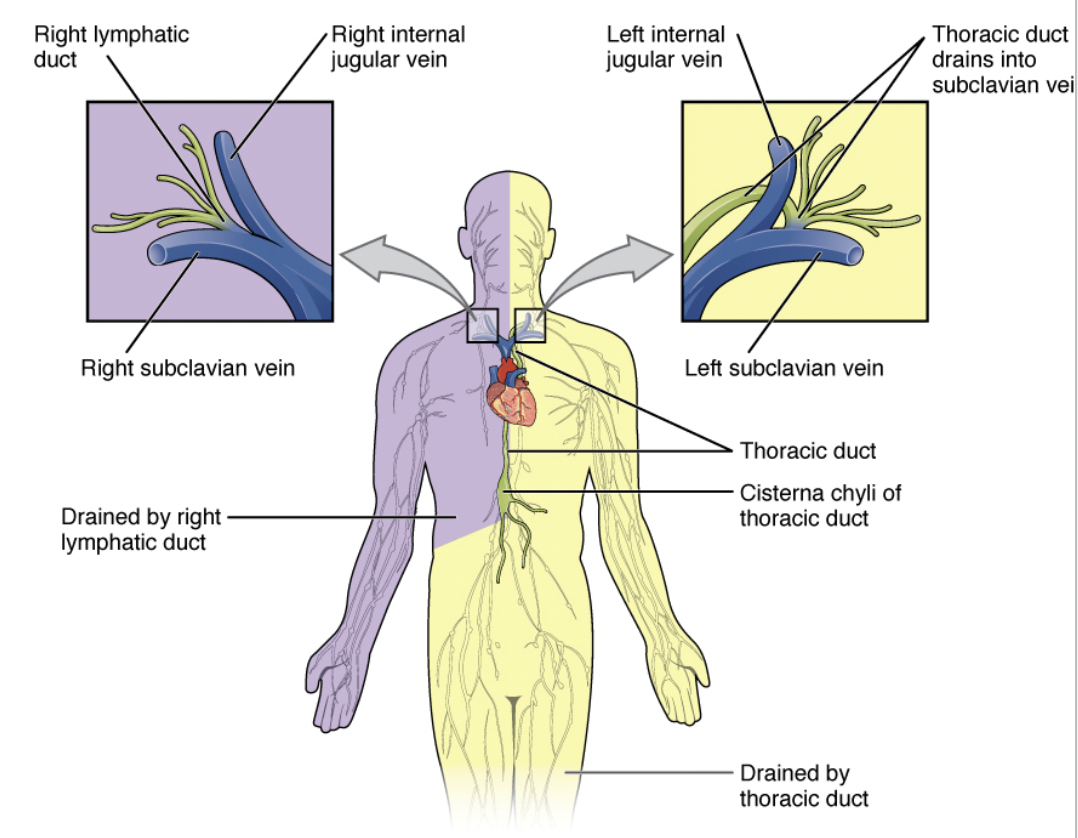
Left Lymphatic Trunk
Drains into the left subclavian vein.
collects from everywhere other than right side
Lymphatic Fluid Movement Control
Movement of lymphatic fluid controlled by valves, skeletal muscle pump, and respiratory pump (above the diaphragm)
Lymphatic Tissue- MALT
Mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue; diffused through the intestines.
-70% scattered through the intestines dissued through systems
lymphatic tissue- Lymphatic Nodules
Concentrated lymphatic tissue; functionally the same as diffused tissue; found on the surface of the digestive system.
Primary Lymphatic Organs
Organs producing and maturing immune cells (bone marrow, thymus)
Secondary Lymphatic Organs
Organs carrying out specific immune functions (lymph nodes)
Thymus:
Thymic Involution & Anamtomy
Thymic Involution- Shrinking of the thymus gland with age due to sex hormones (starts with puberty)
Outer Cortex- uneducated
immune cells —these cells die
and atrophy eventually
Inner Medulla- educated
immune cells recognize self
and non-self
-the educated survive
Spleen
Largest lymphatic organ; functions in recycling red blood cells
Spleen- Red Pulp
Phagocytosing old RBCs, contains sinusoids, recycles components.
spleen- White Pulp
WBCs, immune responses are carried out here.
spleen- Spleenomegaly
Enlarged spleen.
-can be removed
-not essential for life
associated with diabetes
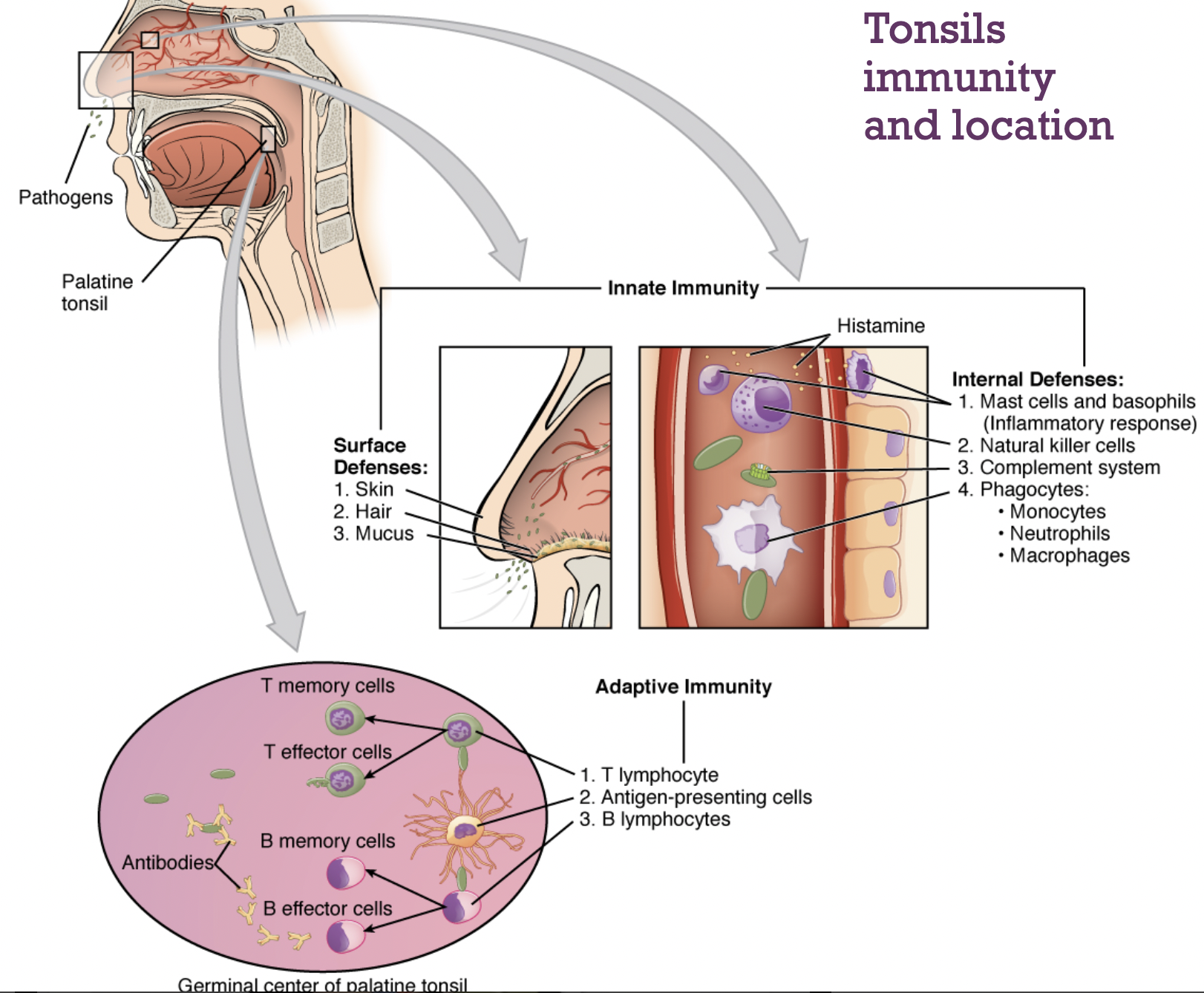
Tonsils-
Pharyngeal Tonsil & more
found near the pharynx behind uvula
Also known as the adenoid, nose breathing is a better immunological filter.
-palantine tonsil, linguinal tonsil
-large tonsilar cyst- open to the exterior and catches large things
-Lymphatic nodules
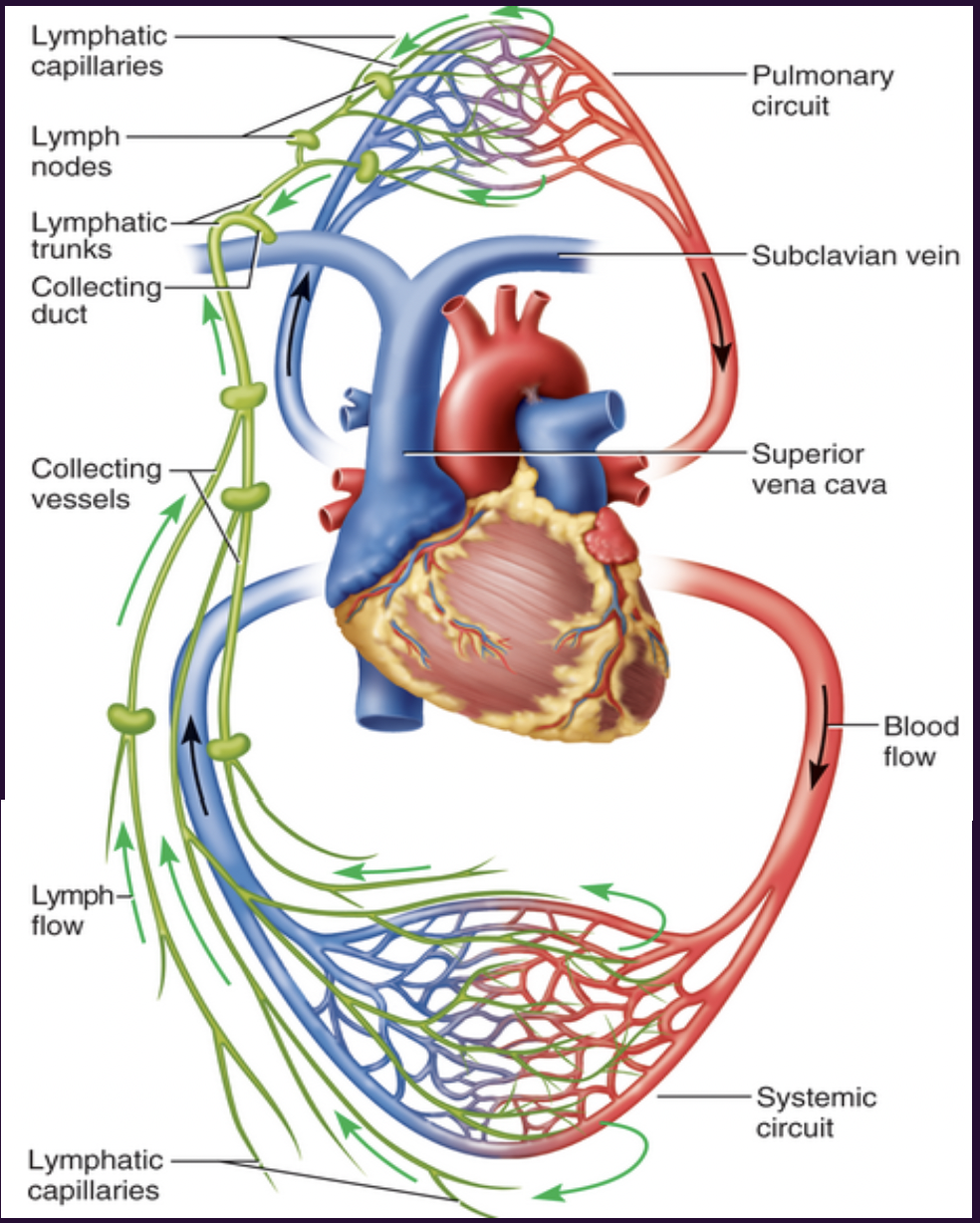
cardiovascular vs. lymphatic system
direction of bloodflow:
cs- carries blood away from the heart versus
ls- carries lymph back to the heart.
Type of fluid:
cs- blood (plasma and cells)
ls- lymph
Pump:
cs-yes(heart)
ls-no
direction of lymph flow
lymphatic capillaries (millions)—→collecting vessels—→ lymphatic trunks—→collecting ducts (2)—→heart
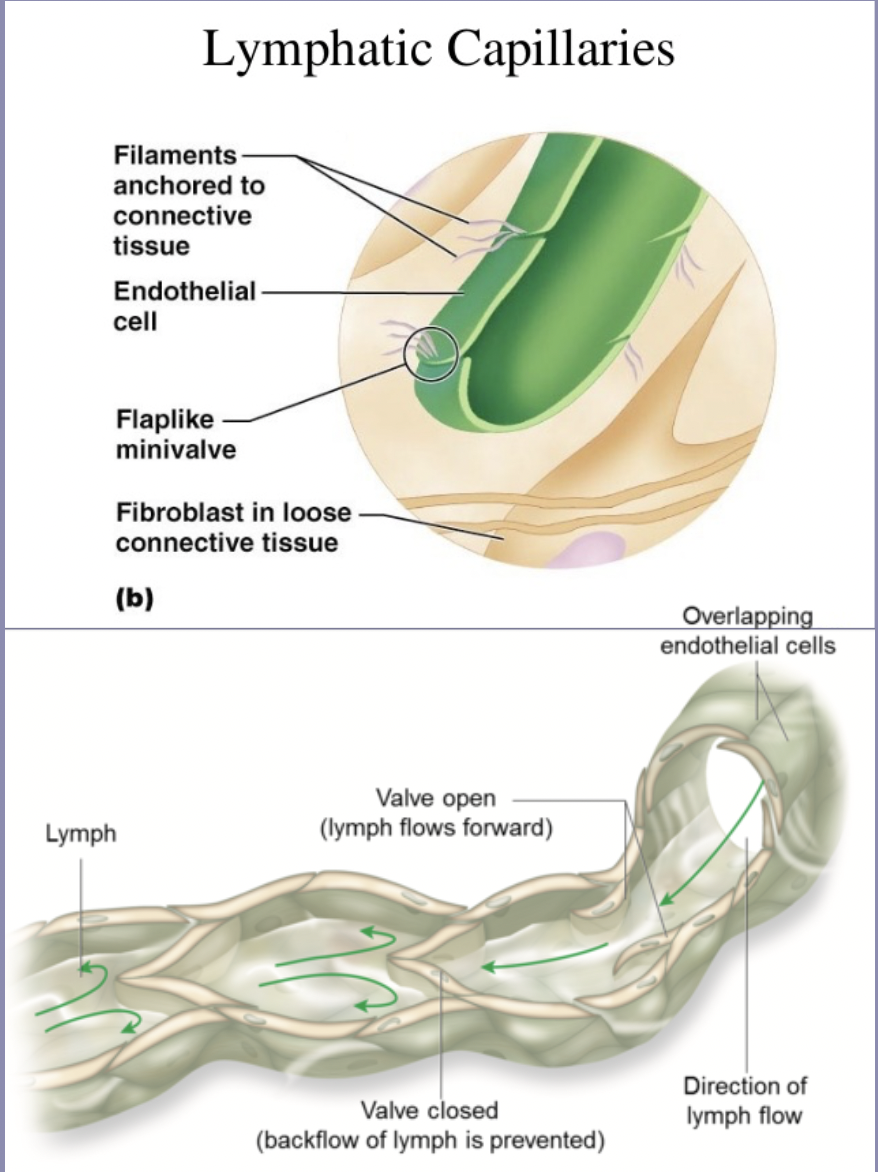
blood capillaries
small diameter
tunica interna- endothelium + basement membrane
endothelial cells arranged end to end
transport of lipids
Lymph Node Image
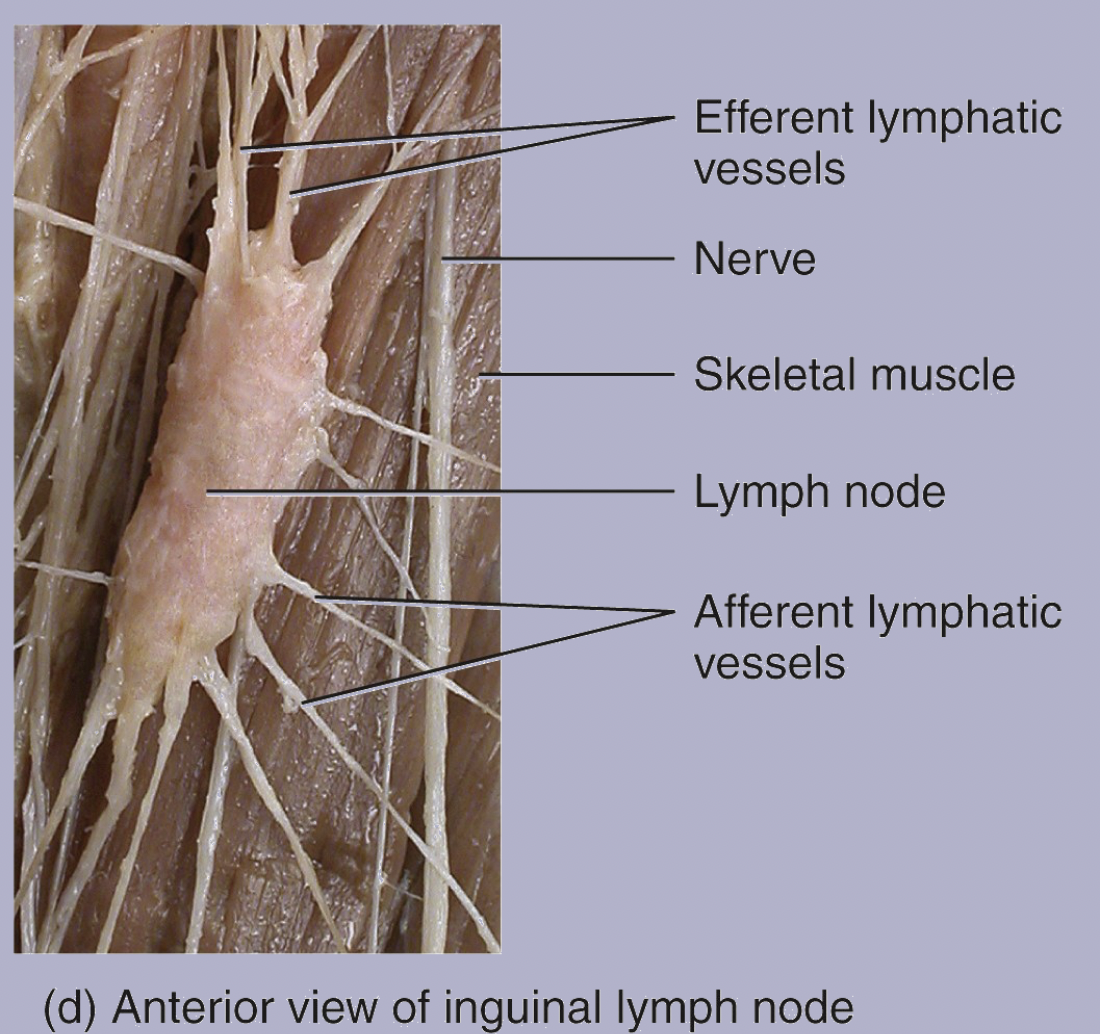
Structural Classification: Encapsulated vs. non-capsulated
encapsulated- bone marrow, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus
non-encapsulated- tonsils
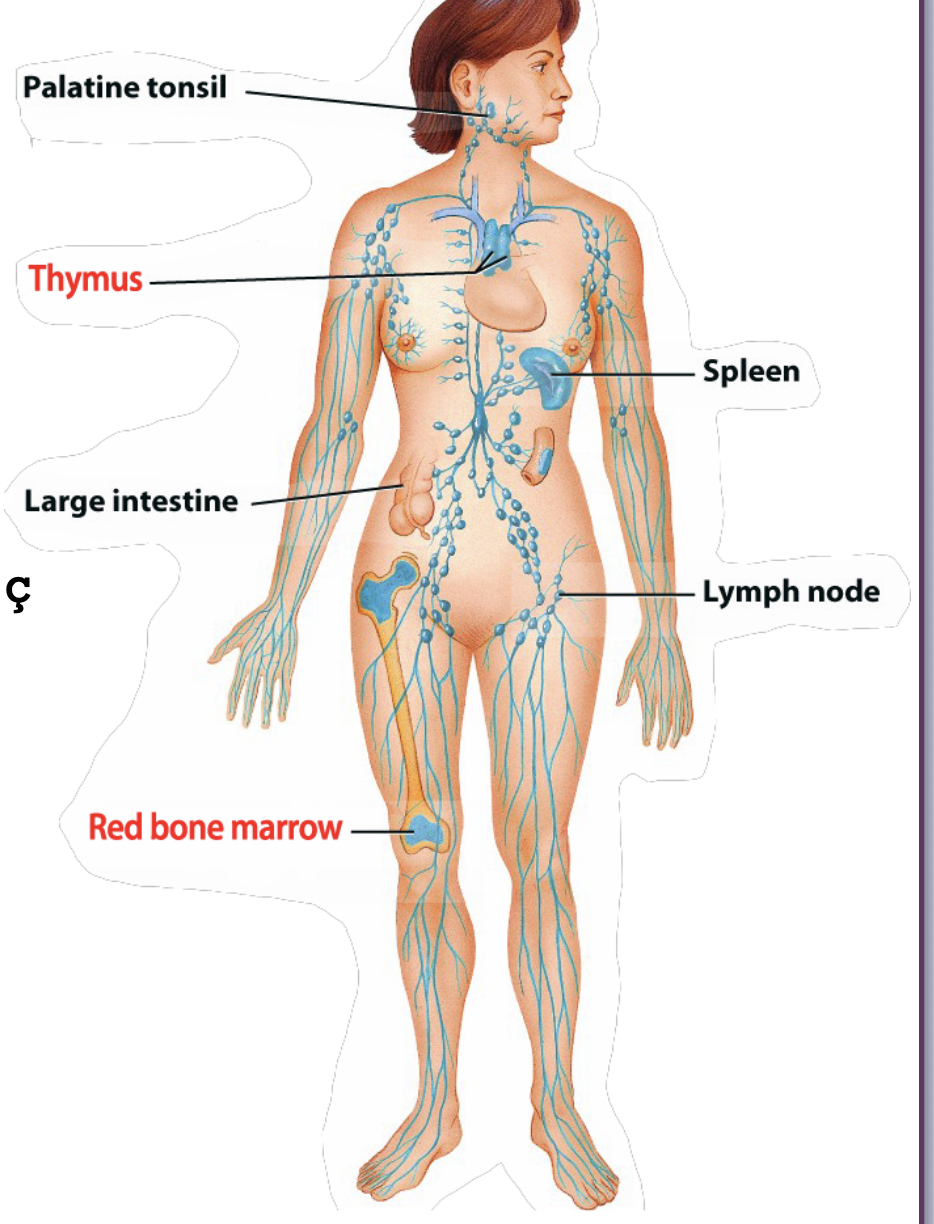
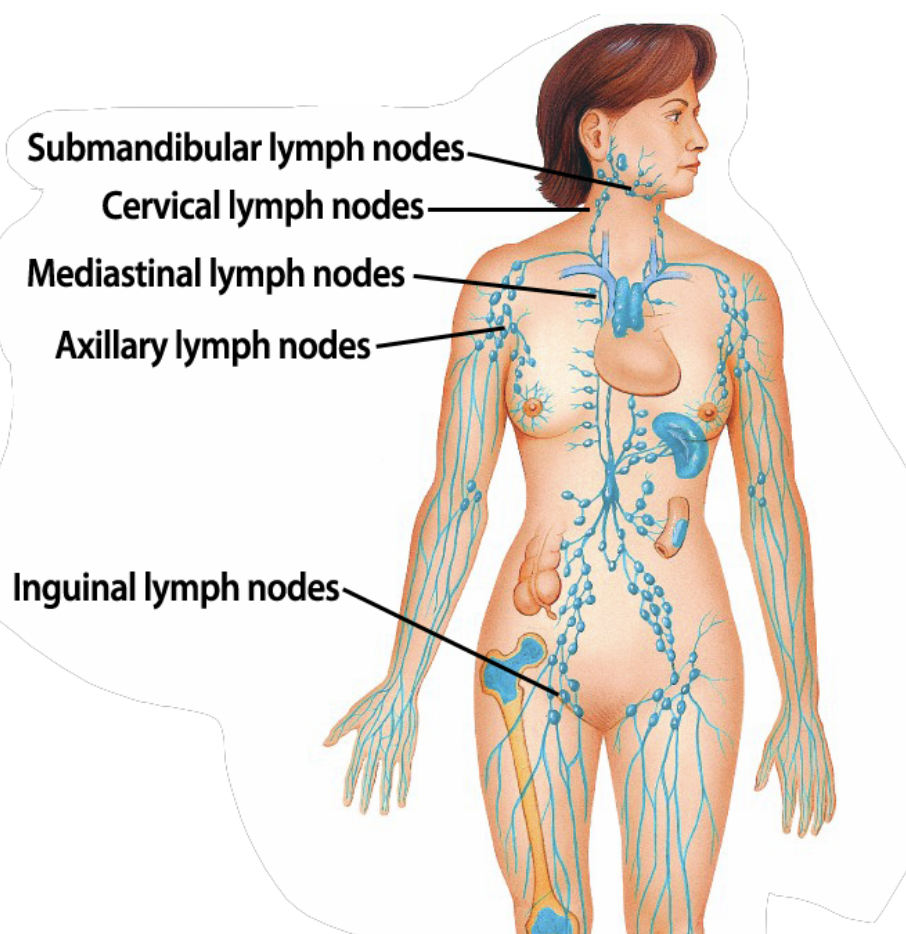
lymph nodes overview
-600-700 lymph nodes
-act as filters
loc. GI
Lungs
Inguinal
Missing or sparse in
lower regions