Physiology Exam 1
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Pathology
the study of disease, its causes, processes, development, and consequences.
Physiology
the scientific study of normal living functions within an organism, organ, tissue, or cell, focusing on how these parts work together to maintain life and respond to internal and external changes
Anatomy
the scientific study of the structure of living organisms and their parts
Circadian Rhythm
your body's internal, 24-hour clock that regulates your sleep-wake cycle, hormone release, body temperature, and other crucial functions
Effector
responding unit
Emergent properties
characteristics that arise from the interactions of simpler components within a complex system. Ex. organ→ organ system
Extracellular fluid
all body fluid located outside of cells, primarily composed of blood plasma and interstitial fluid
Intracellular membranes
the water and solutes (like potassium, phosphate, and proteins) contained inside the cell membranes
Homeostasis is a ___, not a static,
process
dynamic
receptor
detects change in some variable in internal environment
control center
processes information and directs an appropriate response
Response
what occurs from the output signal
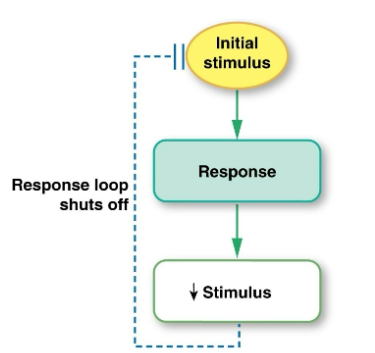
Negative feedback
the response counteracts the stimulus, shutting off the loop
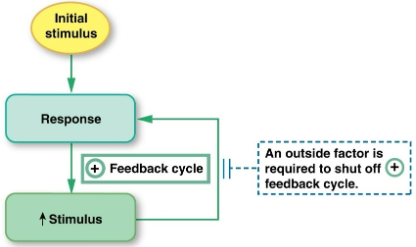
Positive feedback
the response reinforces the stimulus, sending the variable farther back from its set point
Mechanistic approach
describes the “how”, Oxygen binds to hemoglobin molecules contained in the red blood cells
Teleological approach
explains the “why”, because cells need oxygen and red blood cells bring it to them
Mass flow
the measure of the mass of a substance passing through a given point or cross-section per unit of time
Homeostasis
the automatic process by which living organisms maintain a stable internal environment, keeping variables like temperature, blood sugar, and fluid levels within a narrow, healthy range despite changes in the external environment
reflex control
is a more widespread, coordinated response involving long-distance signaling through the nervous and/or endocrine systems
local control
is a self-contained regulation within a specific tissue or cell, often using paracrine or autocrine signals
4 key themes in Physiology
Structure and Function Relationships, Energy needs, Information Flow, Homeostasis
Acid
A substance that donates hydrogen ions (H⁺) in solution, lowering pH
Amino acid
The building block of proteins, consisting of an amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen atom, and variable R group attached to a central carbon
Amphipathic
A molecule that has both hydrophilic (water-loving) and hydrophobic (water-fearing) regions.
Base
A substance that accepts hydrogen ions (H⁺) in solution, raising pH
Carbohydrate
Organic molecule made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (usually in a 1:2:1 ratio); includes sugars and starches used for energy and structure.
Cellulose
A polysaccharide made of glucose units that forms plant cell walls and provides structural support.
Covalent bond
A chemical bond formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons.
Denaturation
Loss of a protein’s shape (and function) due to heat, pH changes, or other stressors.
Disaccharide
A carbohydrate made of two monosaccharides linked by a covalent bond (e.g., sucrose, lactose).
Electronegativity
The tendency of an atom to attract electrons toward itself in a chemical bond
Fatty acid
A long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group at one end; building blocks of many lipids.
Free radical
An unstable molecule with an unpaired electron that can damage cells.
Glucose
A monosaccharide (C₆H₁₂O₆) that is the primary energy source for cells.
Glycerol
A three-carbon molecule that forms the backbone of fats and phospholipids.
Glycogen
A polysaccharide made of glucose that serves as energy storage in animals.
Glycolipid
A lipid with one or more carbohydrate groups attached, important in cell recognition
Glycoprotein
A protein with carbohydrate groups attached, often found on cell membranes for signaling.
High energy electron
An electron that carries extra energy, often transferred in redox reactions or stored in molecules like NADH.
Hydrogen bond
A weak bond between a hydrogen atom (covalently bound to an electronegative atom) and another electronegative atom.
Hydrophilic
“Water-loving”; molecules that dissolve easily in water (polar or charged).
Hydrophobic
“Water-fearing”; molecules that do not dissolve in water (nonpolar)
Induced fit
Enzyme model where the active site changes shape slightly to better fit the substrate.
Ionic bond
A bond formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another, creating charged ions that attract each other.
Ligand
A molecule that binds specifically to a receptor or protein
Lipid
Hydrophobic biomolecule including fats, oils, phospholipids, and steroids; used for energy storage and membranes.
Lock and key
Enzyme model where the active site has a fixed shape that matches only a specific substrate.
Monosaccharide
The simplest carbohydrate (sugar unit), e.g., glucose, fructose, galactose.
Nonpolar
A molecule with no significant charge separation; does not mix with water.
Nucleotides
Building blocks of nucleic acids (DNA, RNA); consist of a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base.
pH scale
A measure of hydrogen ion concentration in a solution; ranges from 0 (acidic) to 14 (basic).
Phospholipid
A lipid with two fatty acids and a phosphate group attached to glycerol; main component of cell membranes.
Polar
A molecule with partial positive and negative charges due to unequal electron sharing.
Polysaccharide
A carbohydrate made of many monosaccharides linked together (e.g., starch, glycogen, cellulose).
Proteins
Large biomolecules made of amino acids; perform structural, enzymatic, transport, and signaling functions.
Primary protein structure
The linear sequence of amino acids in a protein.
Secondary protein structure
Local folding of a protein chain into alpha-helices or beta-sheets due to hydrogen bonding.
Purine
A double-ring nitrogenous base (adenine and guanine in DNA/RNA).
Pyrimidine
A single-ring nitrogenous base (cytosine, thymine in DNA, uracil in RNA).
Quaternary protein structure
The arrangement of multiple protein subunits into a larger complex.
Saturation
Refers to fatty acids; “saturated” means all single bonds (no double bonds), while “unsaturated” has one or more double bonds.
Steroid
A type of lipid with four fused carbon rings; includes cholesterol, testosterone, estrogen.
Tertiary protein structure
The overall 3D folding of a single protein chain, stabilized by various bonds and interactions.
Van der Waals forces
Weak attractions between molecules due to temporary shifts in electron distribution.
What are the 4 biomolecules
lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids
What are the 4 biological roles of e-
Form covalent and ionic bonds, store energy, redox reactions
Factors contributing to protein shape
H-bonds, ionic bonds, van der Waals forces