Intro to Radiology
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Who discovered X-rays? When?
William Roentgen; November 8, 1895
How did Roentgen accidentally discover x-rays?
when he evacuated a cathode ray tube of air, filled it with special gas, and passed a high voltage through it, it produced invisible rays capable of passing through heavy paper and causing a fluorescent glow, which he named X-rays
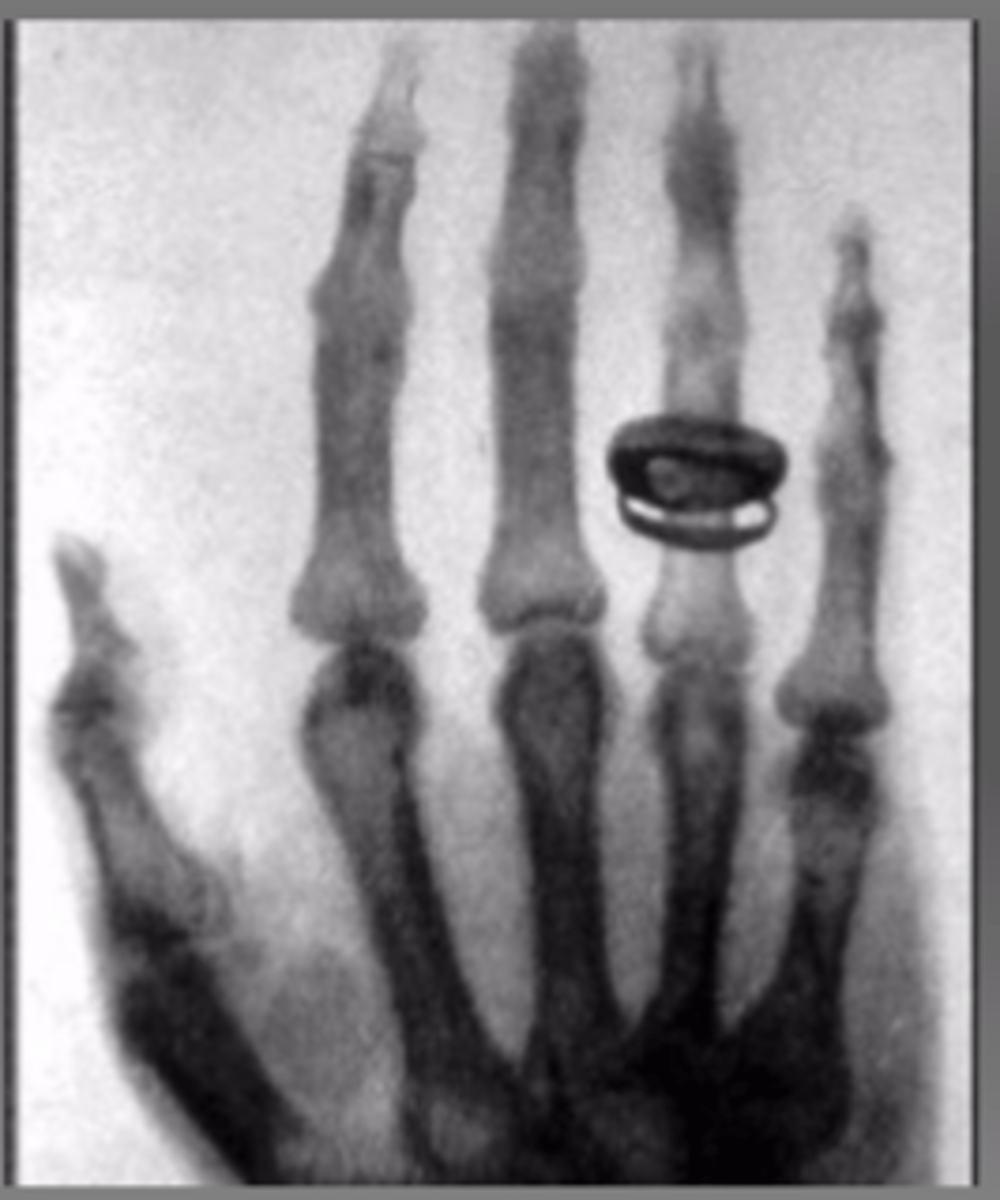
First human radiograph
of Roentgen's wife!
What did JJ Thompson discover?
it was discovered that cathode rays were made of tiny negatively charged "corpuscles" (later called electrons), particles less than 1/1000th the mass of a hydrogen atom, earning the Nobel Prize for revealing that they were not waves or ions but a new fundamental particle
Otto Walkoff
Made the first dental radiograph - 25 minute exposure
C. Edmund Kells
first practical use of dental radiographs in the U.S. on a living person, but years of daily x-ray exposure cost him his fingers, then his hands, and eventually his arms
William Coolidge
Invented the first x-ray tube in 1913 - "Coolidge tube" with tungsten filament to create heat
Why do we take radiographs?
to detect and confirm oral diseases or conditions, locate lesions or foreign objects, guide procedures, evaluate growth, monitor changes, document patient status, and aid in treatment planning
Dental radiology
use of radiant energy (ionizing and non-ionizing) in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the head and neck
What was dental radiology originally called?
roentgenology
X-Ray
BEAM of energy that has the power to penetrate substances and record image shadows on receptors (photographic film or digital sensors)
Radiograph
IMAGE/PICTURE produced on a receptor (Radiation-sensitive film, phosphor plate, or digital sensor) by exposure to ionizing radiation
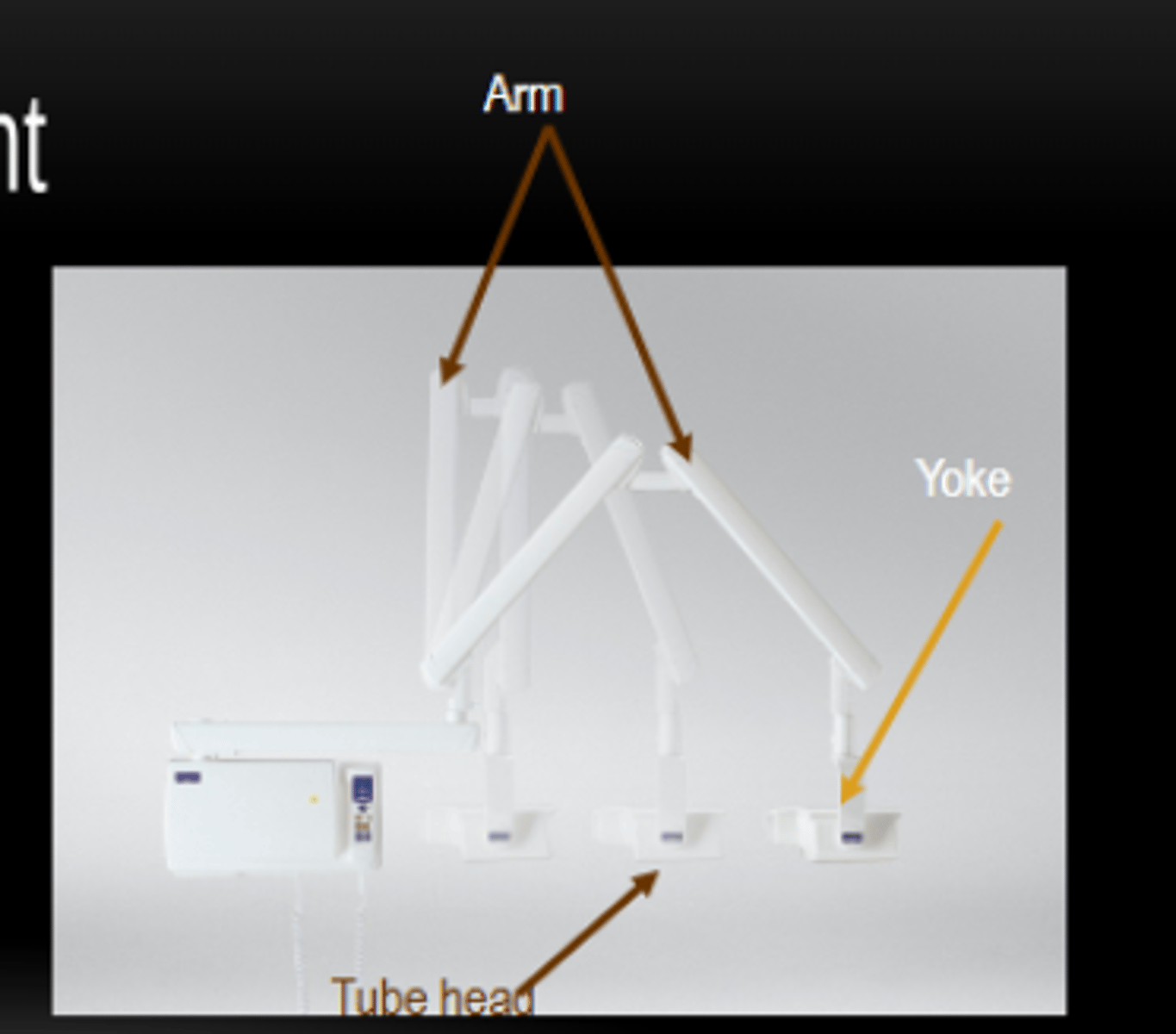
X-ray Arm
Attaches the tube head and allows for positioning.
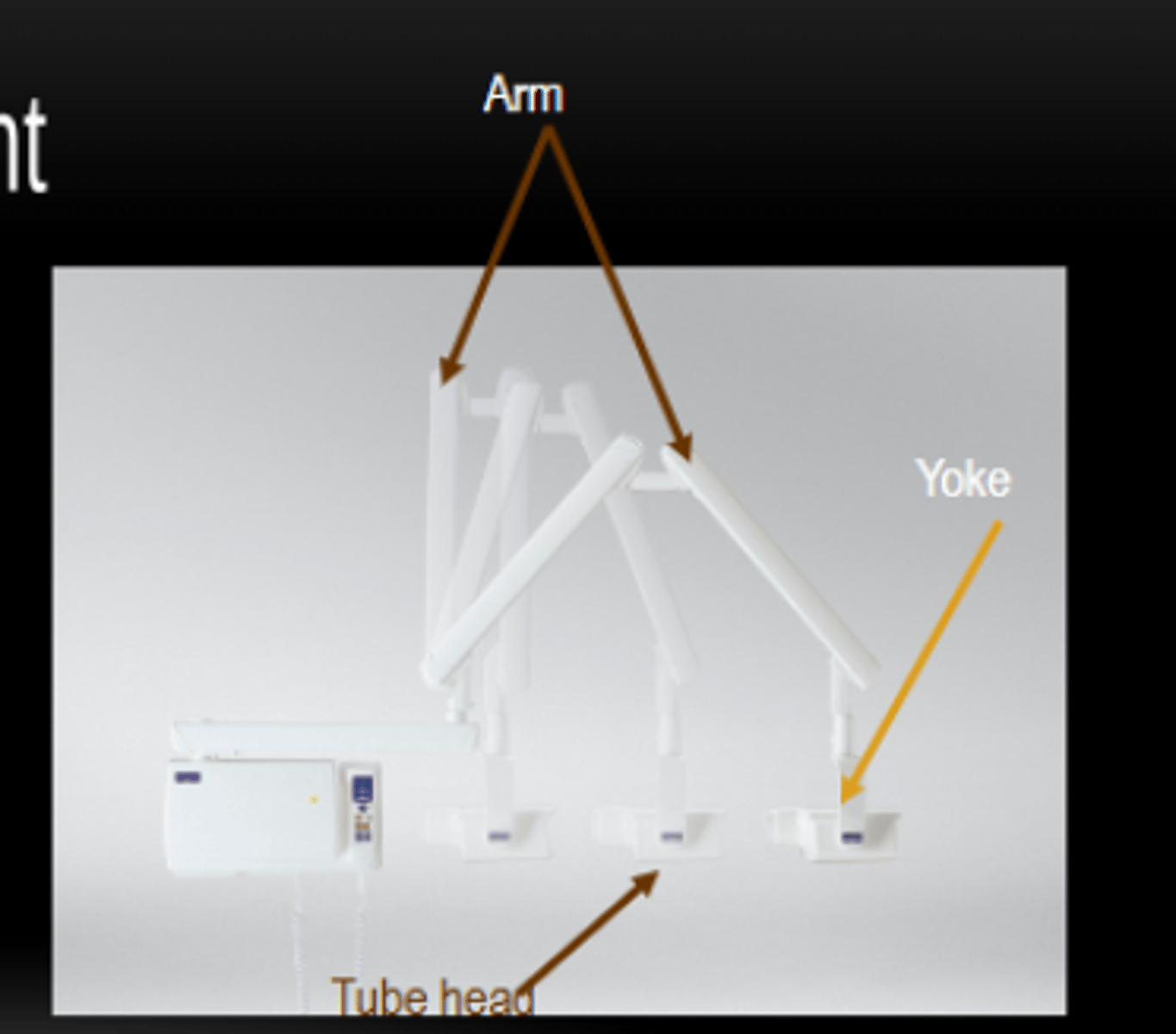
X-ray Wall Mount bracket
supporting and positioning X-ray equipment and accessories
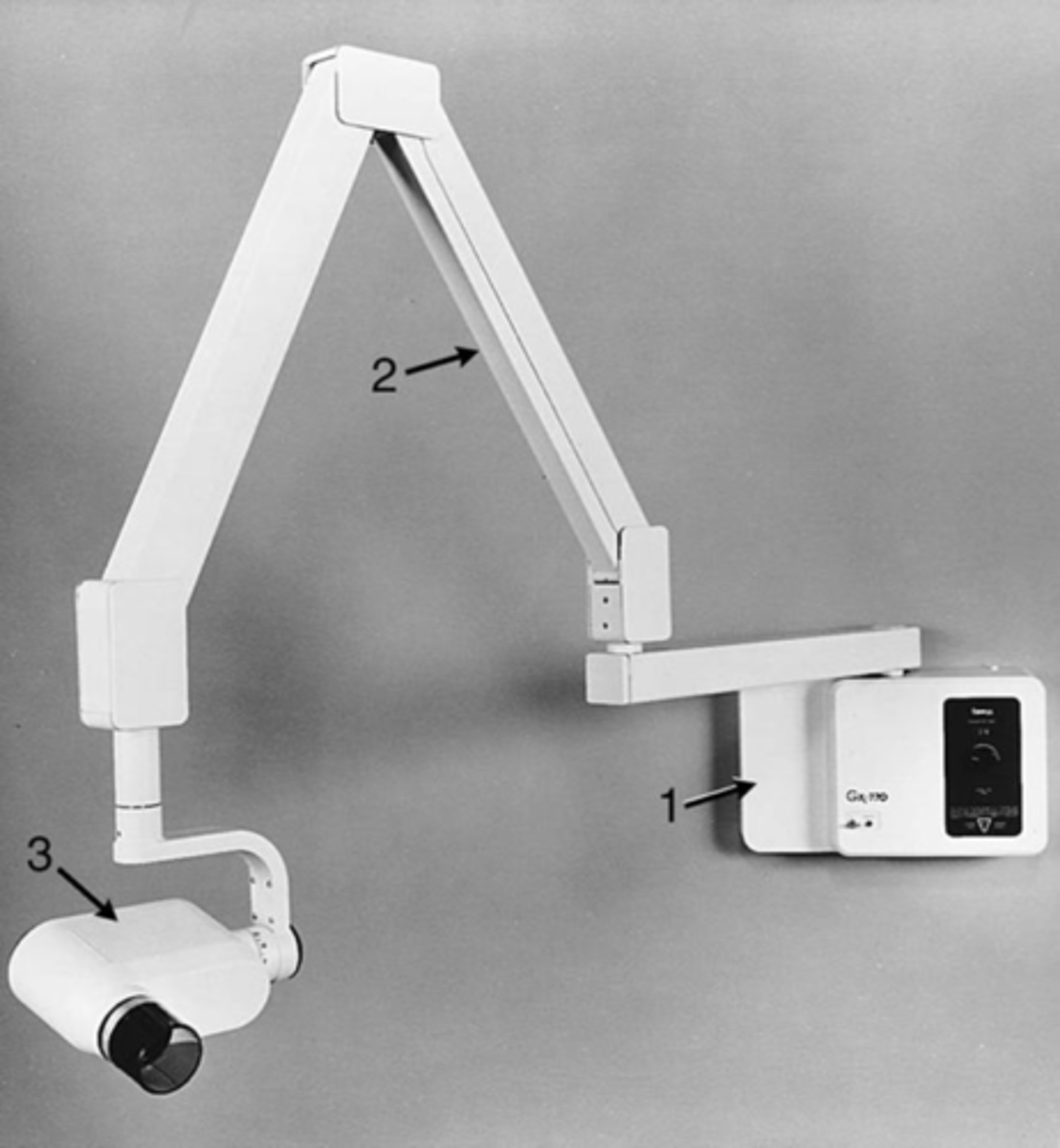

Beaming indicating device (BID) or Position indicating device (PID)
guides the direction of the x-ray beam
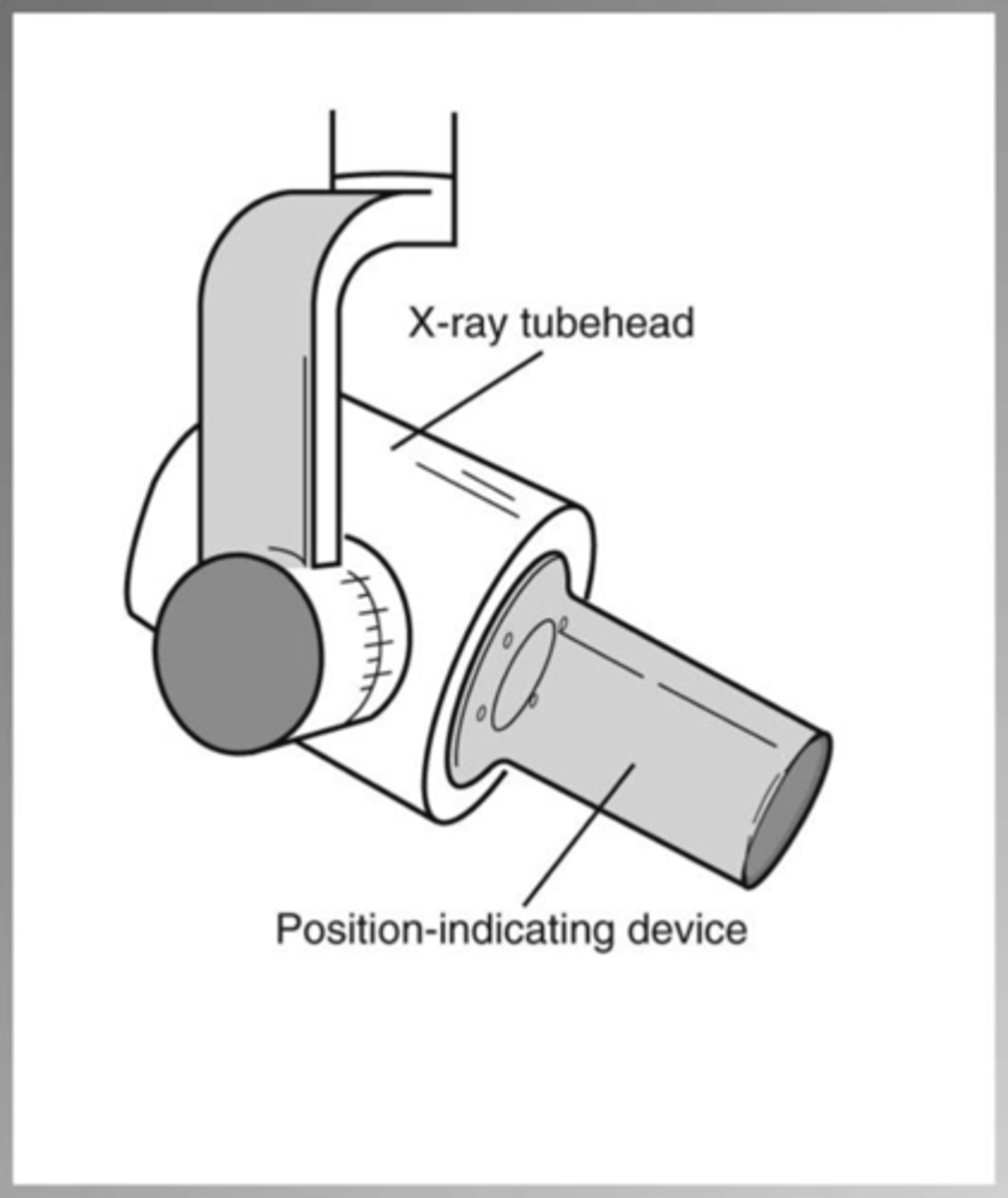
X-Ray Tube head
generating X-rays - through housing the x-ray tube
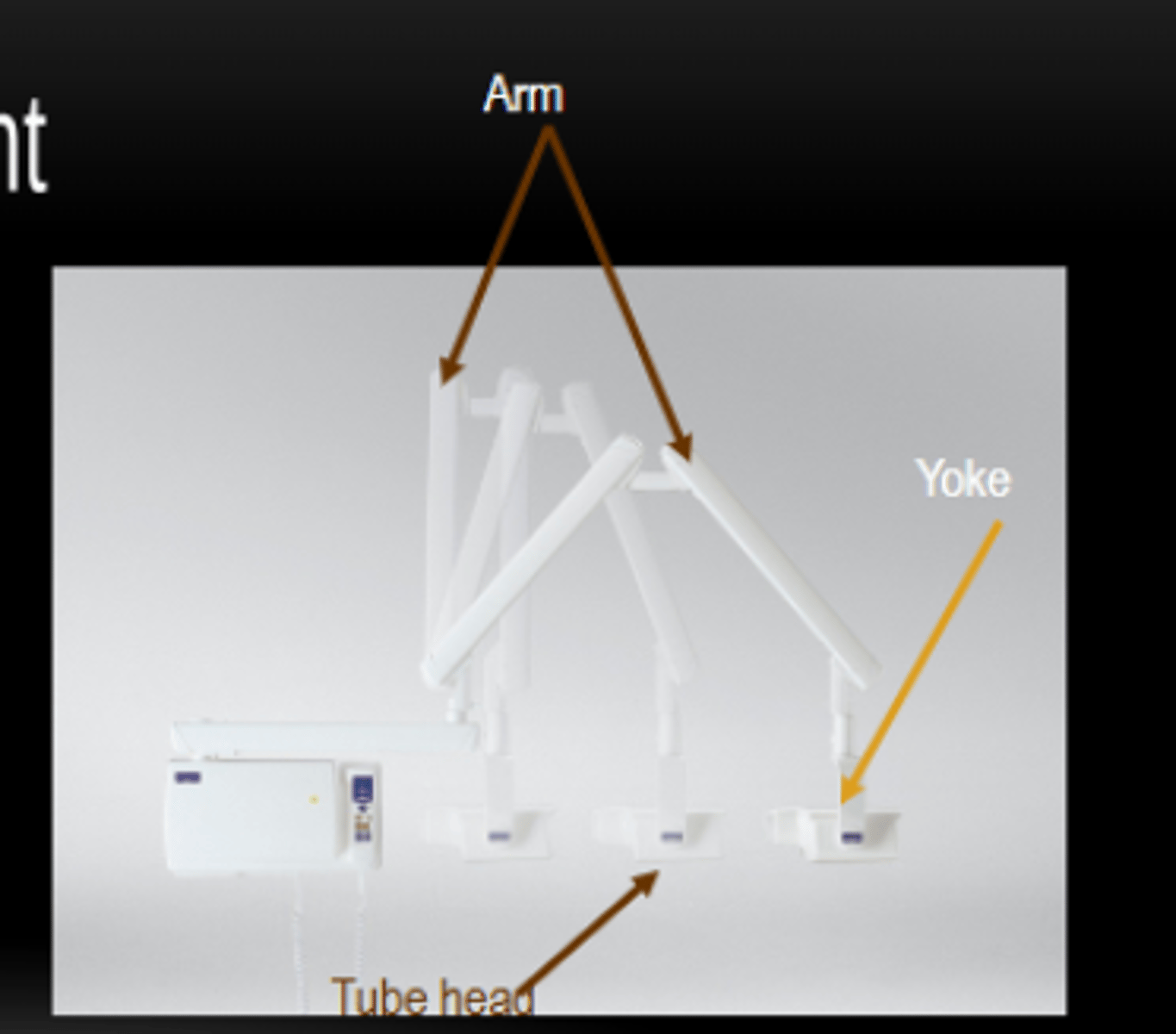
X-ray Yoke
the handle
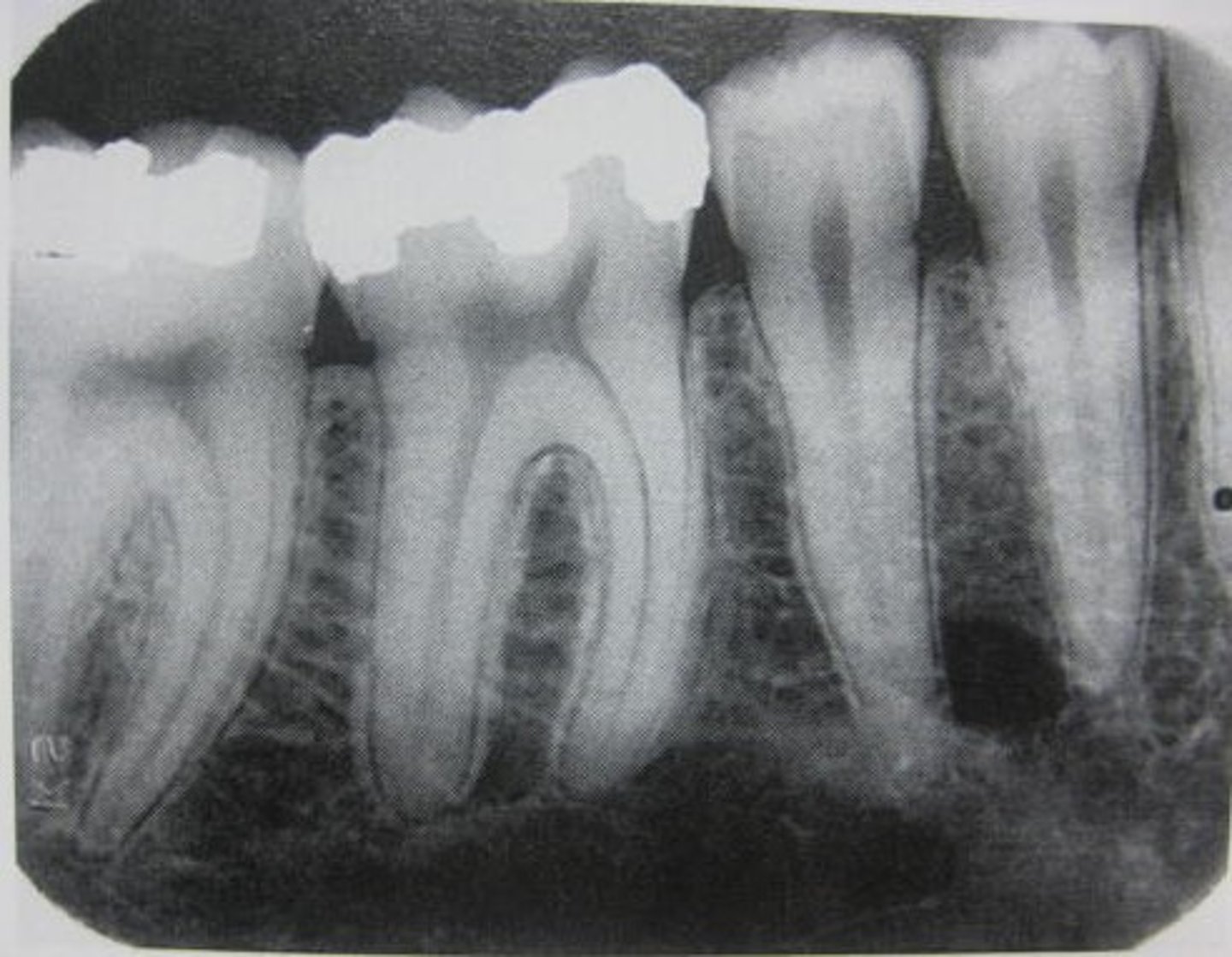
Intraoral images
means inside mouth
What are the 3 types of intraoral images?
periapical, bitewing, occlusal
Periapical
"around the root" to see entire tooth and surrounding bone
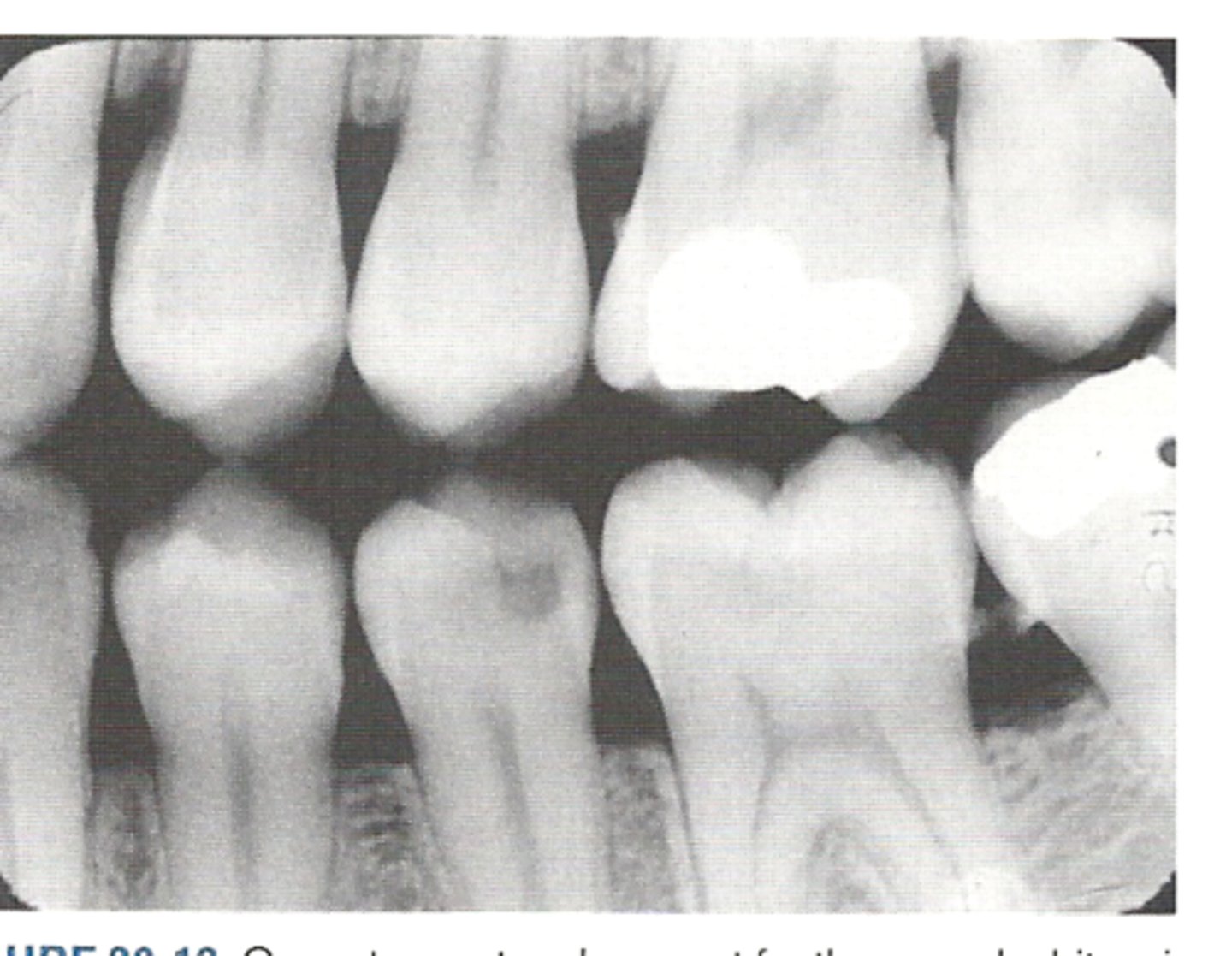
Bitewing
upper and lower crowns together and bone levels
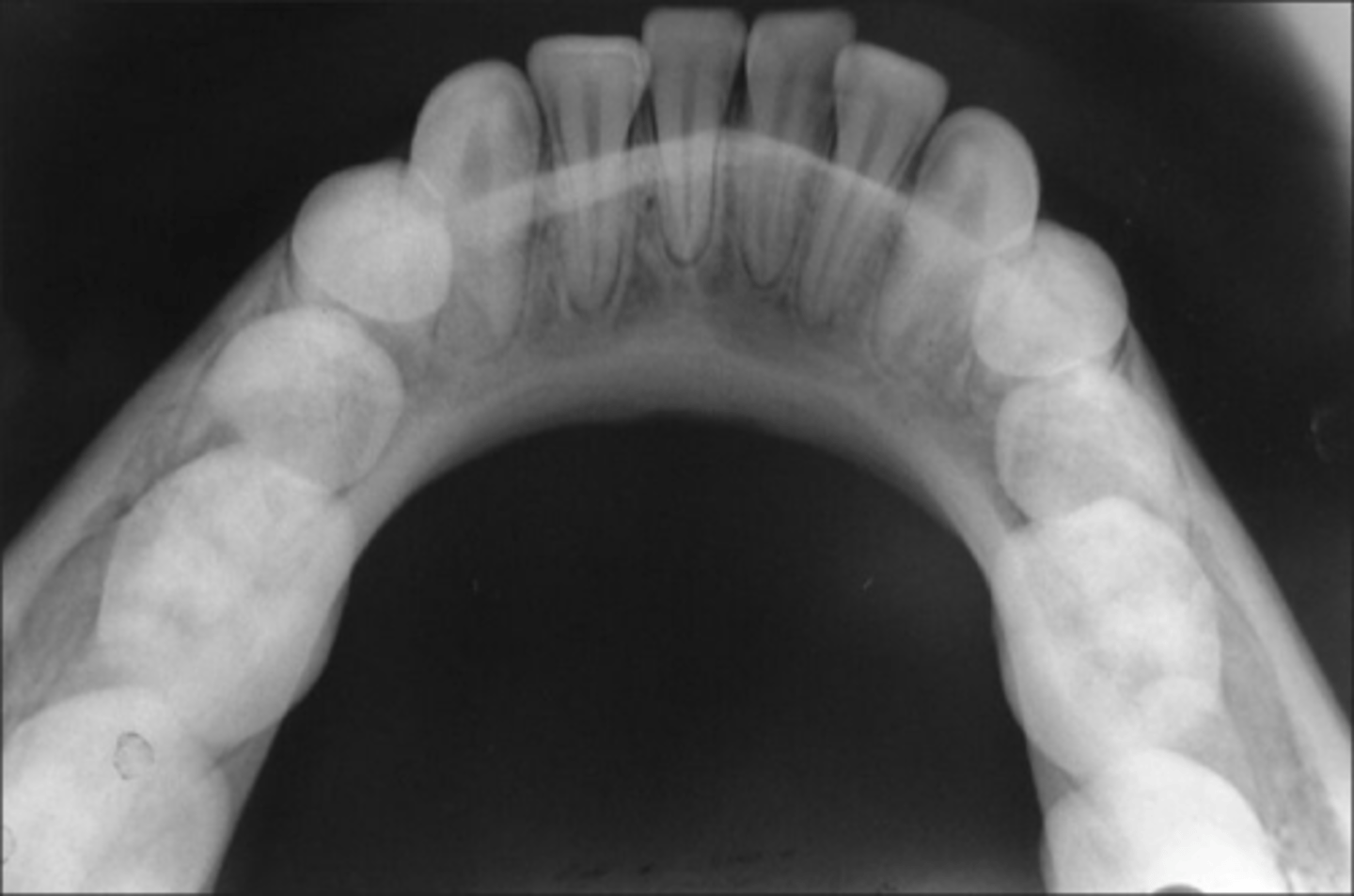
Occlusal
larger area of the arch
What is method is used for looking for interproximal decay?
bitewing
Which method is used a lot in Peds dentistry? And why?
occlusal, helps see development of teeth
FMX
full mouth series of radiographs
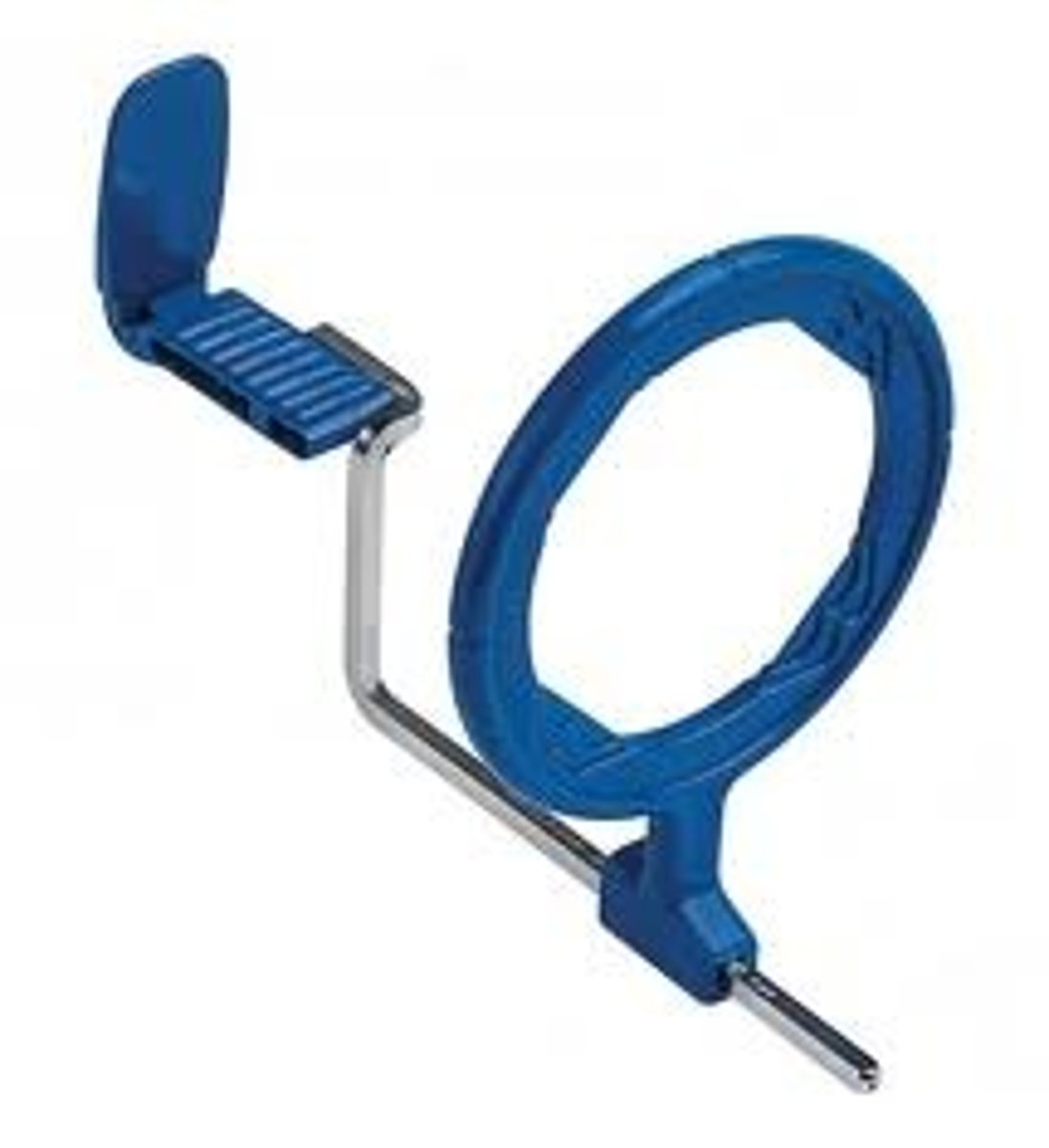
Beam alignment device/XCP kit
helps to angle where to place the beam

Extraoral
outside of the mouth
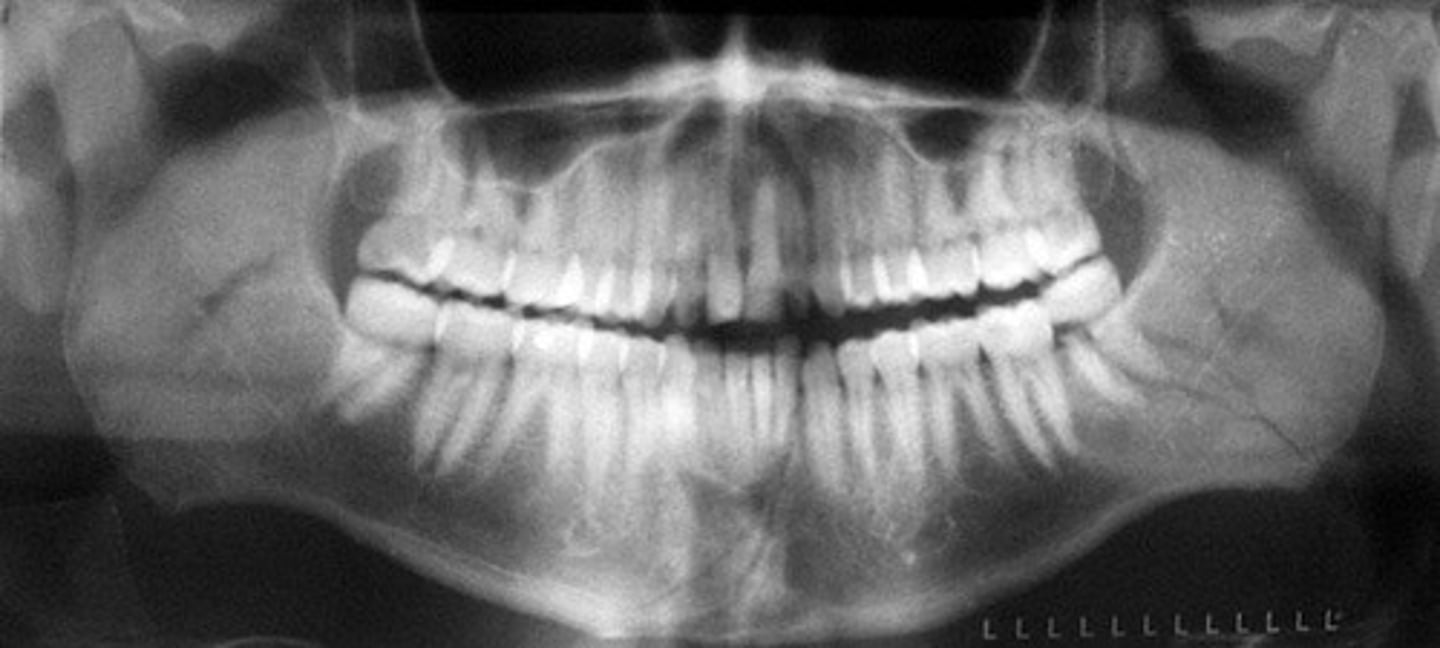
Panoramic x-ray
to identify various issues including impacted teeth, jaw and sinus problems, cysts, tumors, and gum disease
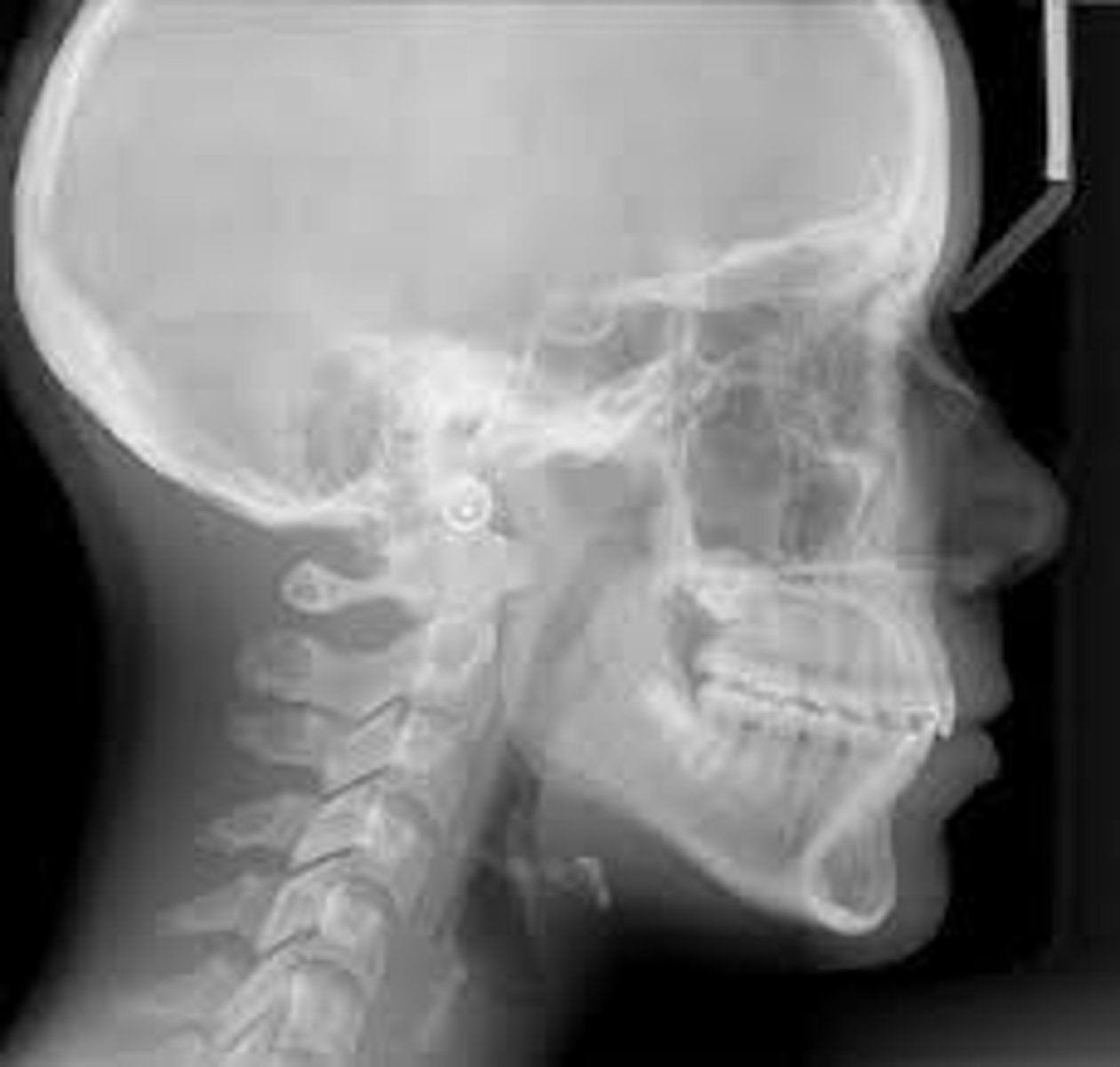
Cephalometric
mainly used in ortho but it helps to see development
Anterior teeth
maxillary and mandibular centrals, laterals, and canines
Posterior teeth
maxillary and mandibular premolars and molars
Radiopaque
"bright" or "white" structures - something you cannot see through and thick structure block x-rays from going through
Radiolucent
"dark"
Is a enamel going to be radiolucent or radiopaque?
radiopaque
Is a DEJ going to be radiolucent or radiopaque?
radiopaque
Is a dentin going to be radiolucent or radiopaque?
radiopaque
Is a pulp chamber going to be radiolucent or radiopaque?
radiolucent
Is a furcation going to be radiolucent or radiopaque?
radiopaque
Is a root canal going to be radiolucent or radiopaque?
radiolucent
Is a cementum going to be radiolucent or radiopaque?
radiopaque
Is a soft tissue going to be radiolucent or radiopaque?
radiolucent
Is a CEJ going to be radiolucent or radiopaque?
radiopaque
What makes a good radiograph
clear image, good detail, correct posture, correct teeth and structures in image
How many total images do we take for a full mouth radiographic series?
14-20
What do we need to make sure we get with Periapicals?
entire length of the tooth and surrounding bone
Why do we take PAs?
show roots and surrounding bone
What do we need to make sure we get with Bitewings?
crowns of both maxillary and mandibular teeth on same radiograph
Why do we take bitewings?
show caries, margins of restoratios, and alveolar crest better
Why do we take a Occlusal?
evaluating extent of disease in jaw, showing development of jaw
Intraoral equipment
x-ray unit, computer, digital sensor, and beam alignment device
Central ray
beam as it exits directly from the PID
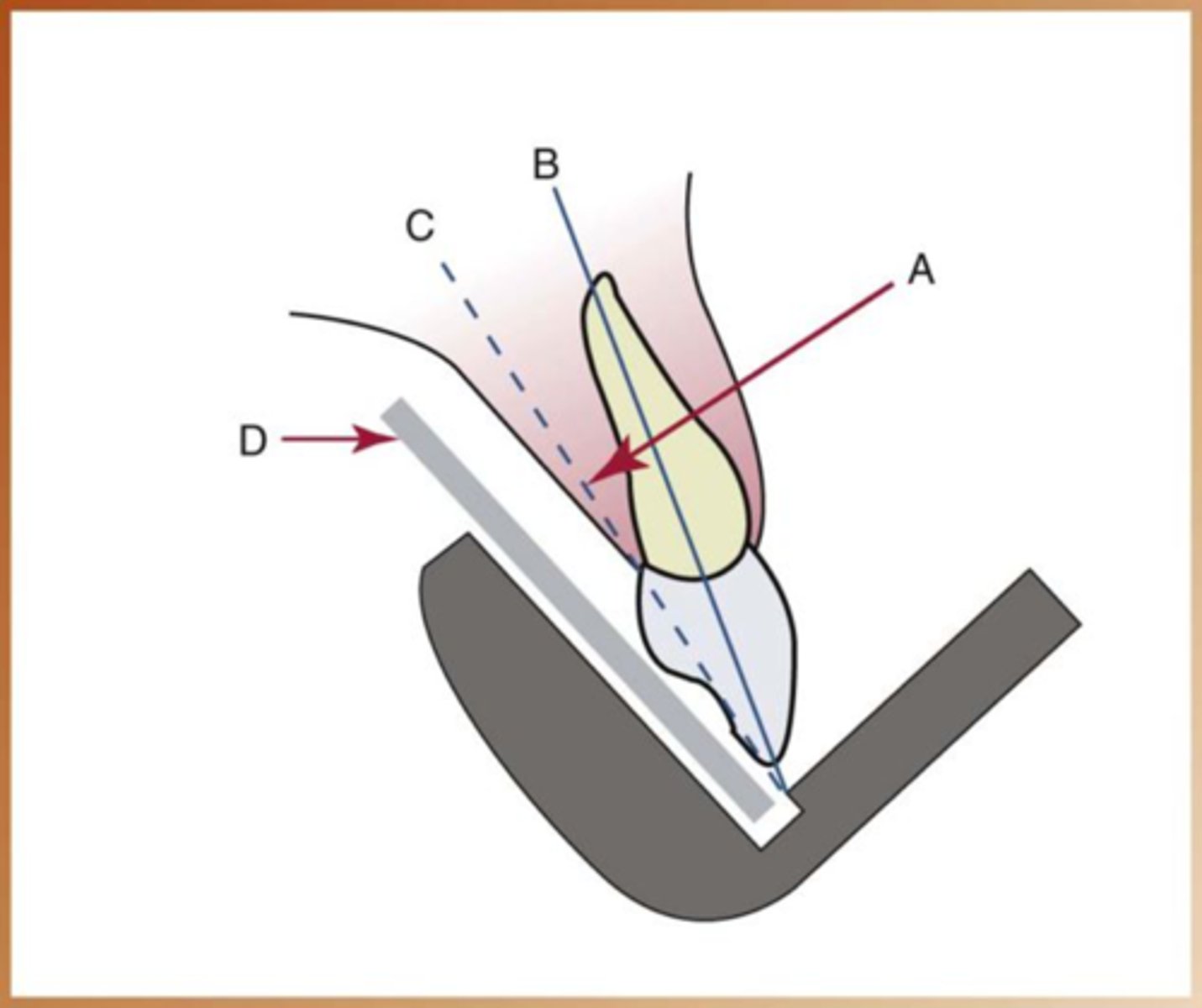
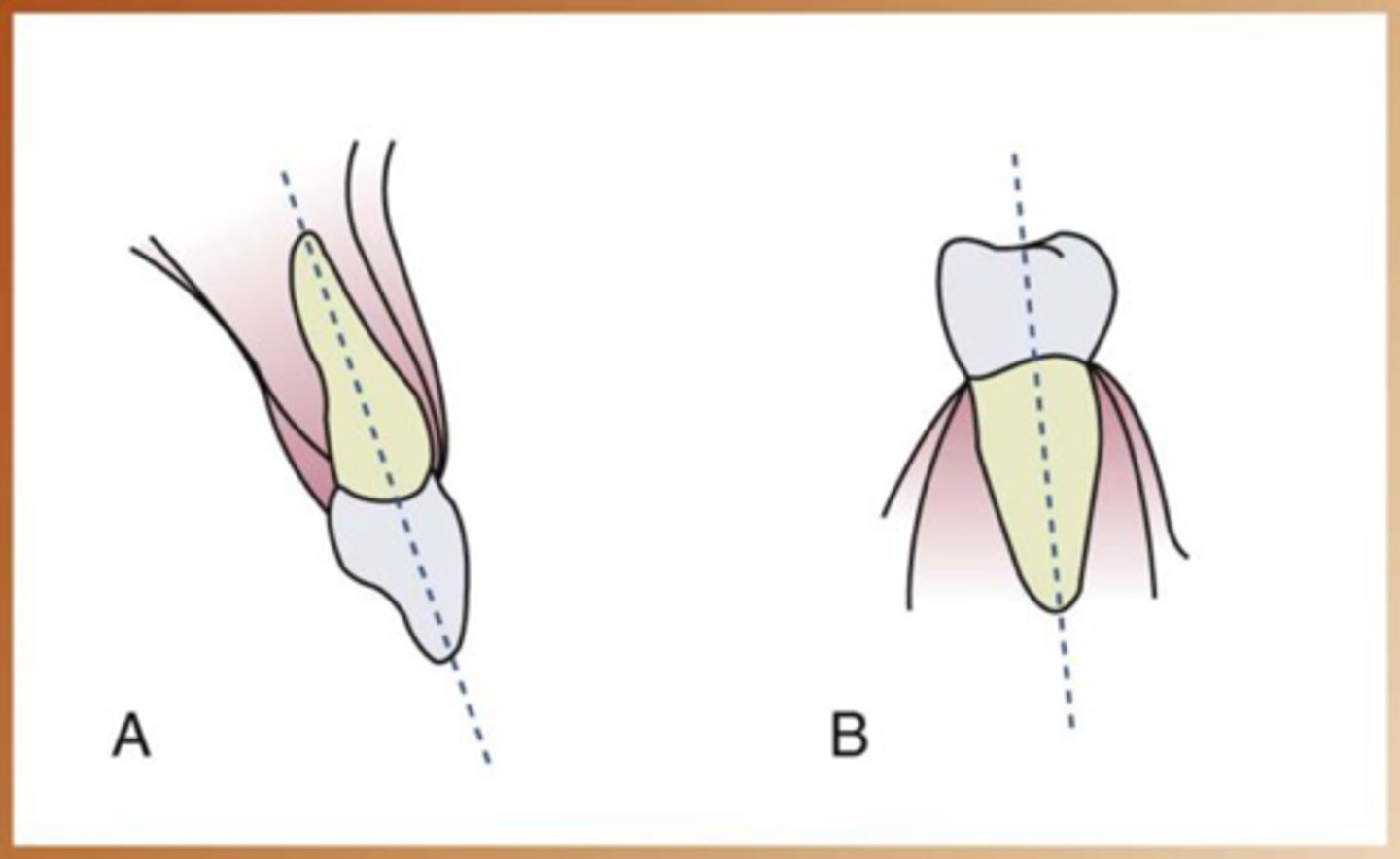
Long axis of the tooth
imaginary line of the tooth that divides in two equal parts
receptor
digital sensor or film

What are the two principle techniques of intraoral imaging?
paralleling and bisecting
Paralleling
preferred method, less distortion
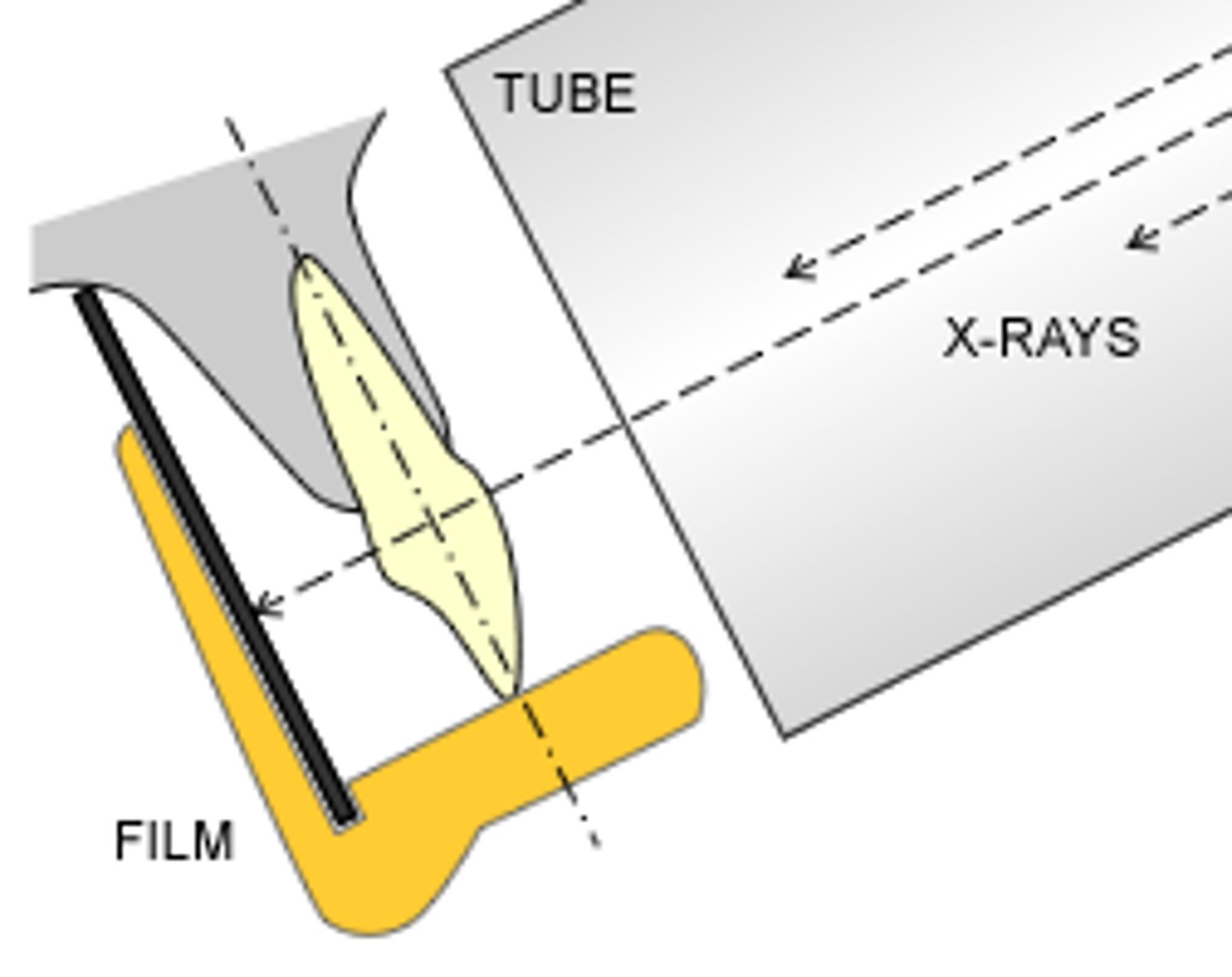
Bisecting the angle
used when parallel position is not possible (anatomical limitations)
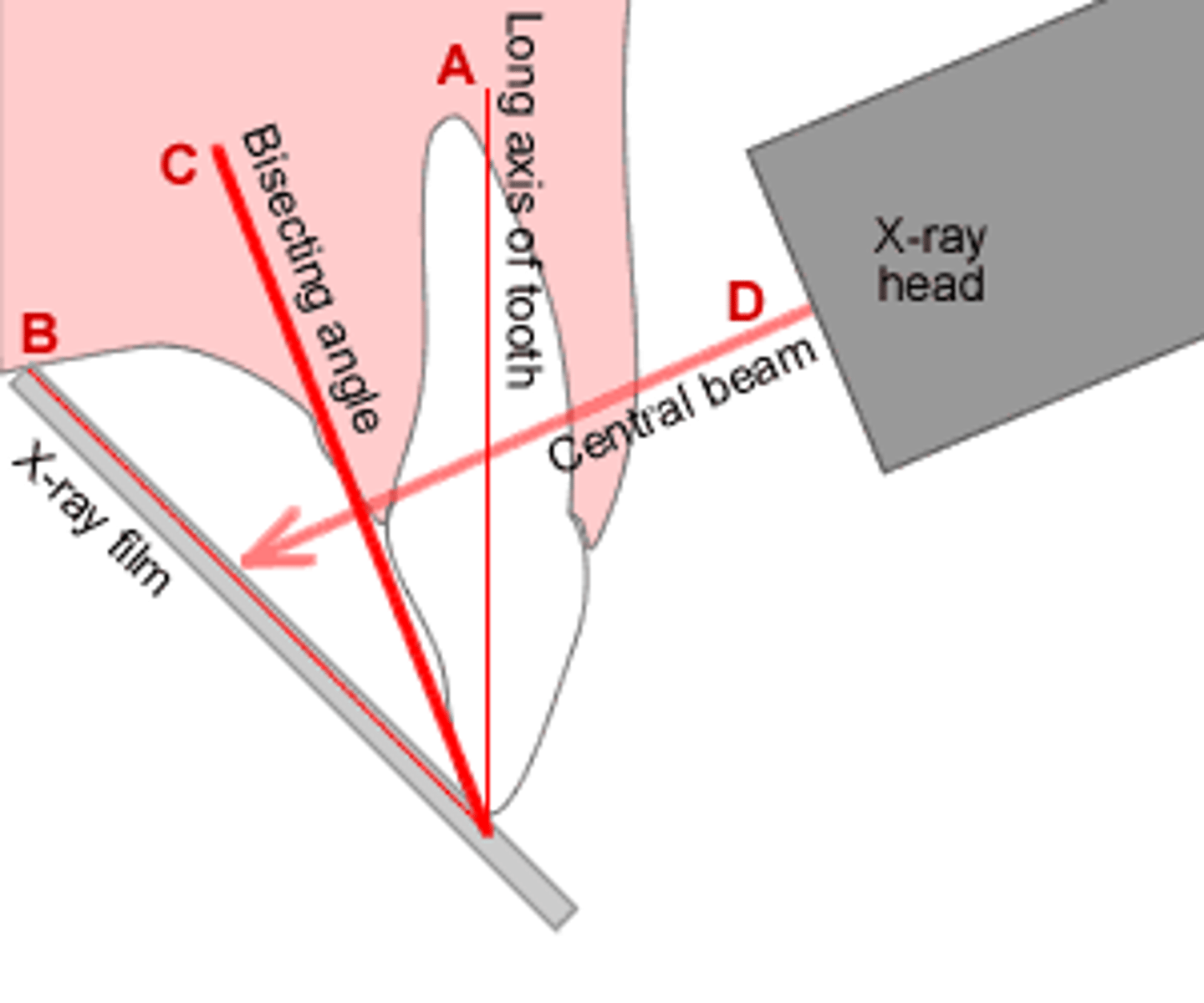
How do we place the receptor when we use the bisecting angle?
as close to the tooth as possible
How should the central xray beam be when using bisecting angle?
directed perpendicular to an imaginary line that bisects or divides the angle formed by the long axis of the tooth and the plane of the image receptor