UNIT 1 diagrams
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
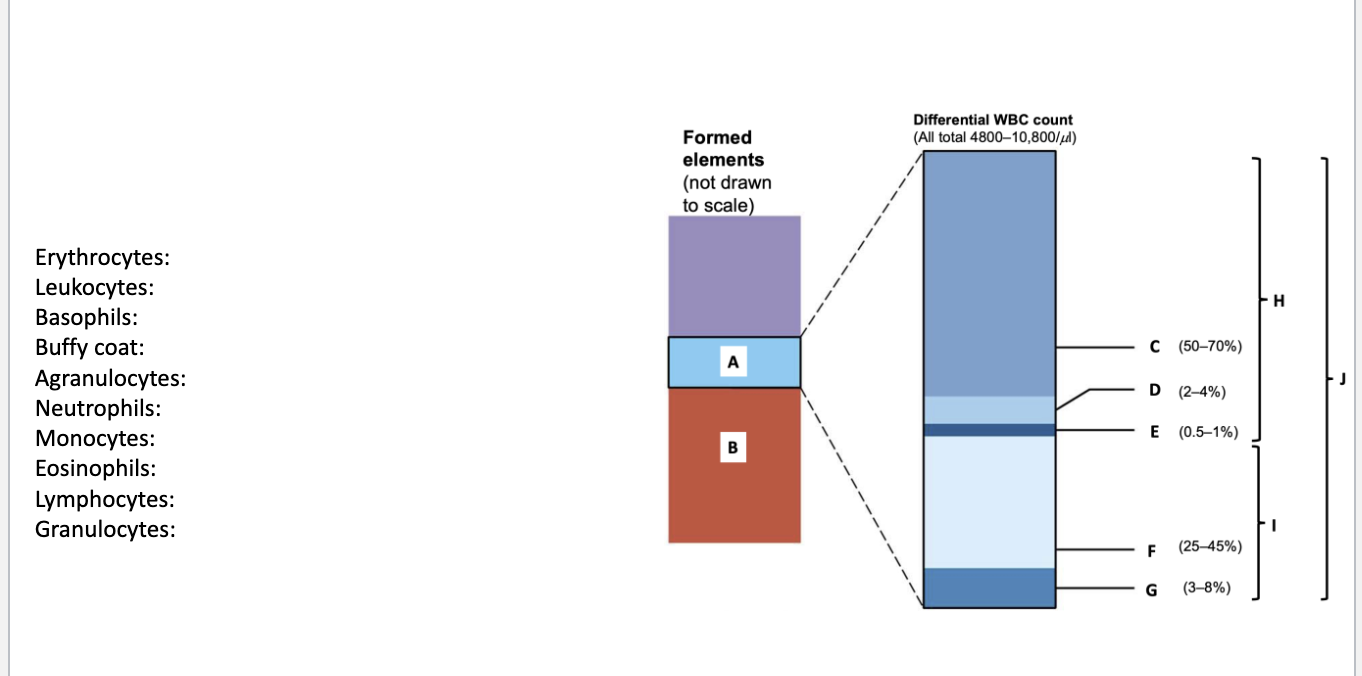
Erythrocytes: B
Leukocytes: J
Basophils: E
Buffy coat: A
Agranulocytes: I
Neutrophils: C
Monocytes: G
Eosinophils: D
Lymphocytes: F
Granulocytes: H
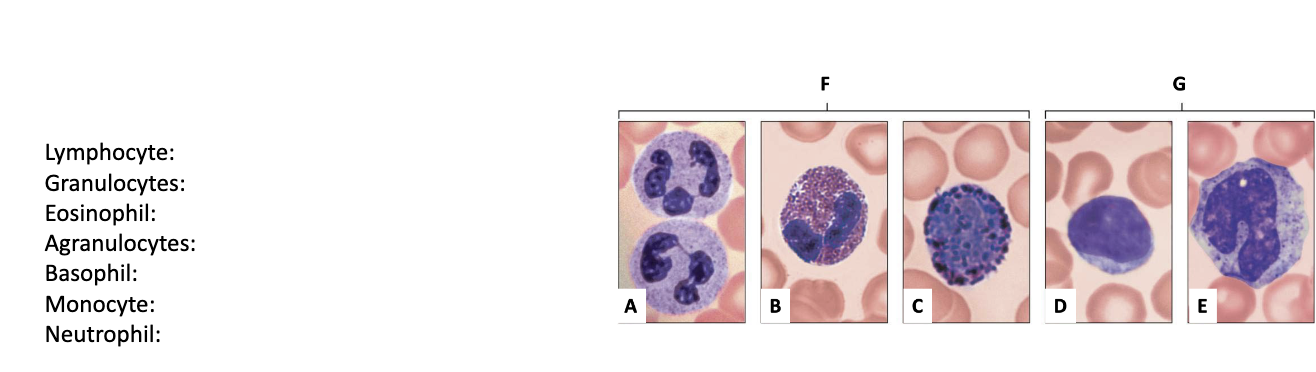
Lymphocyte: D
Granulocytes: F
Eosinophil: B
Agranulocytes: G
Basophil: C
Monocyte: E
Neutrophil: A
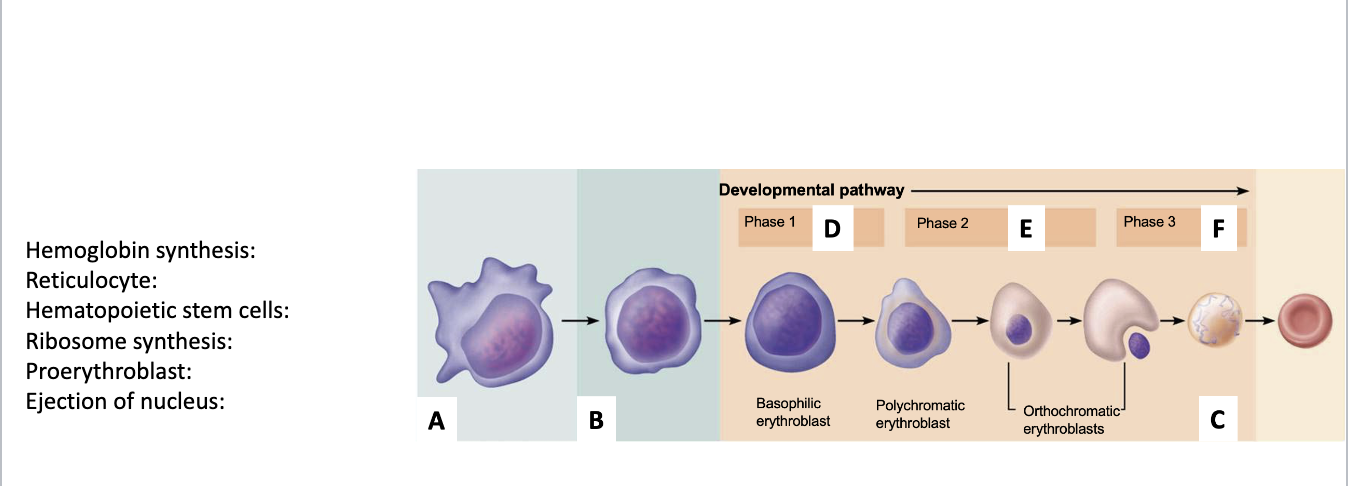
Hemoglobin synthesis: E
Reticulocyte: C
Hematopoietic stem cells: A
Ribosome synthesis: D
Proerythroblast: B
Ejection of nucleus: F
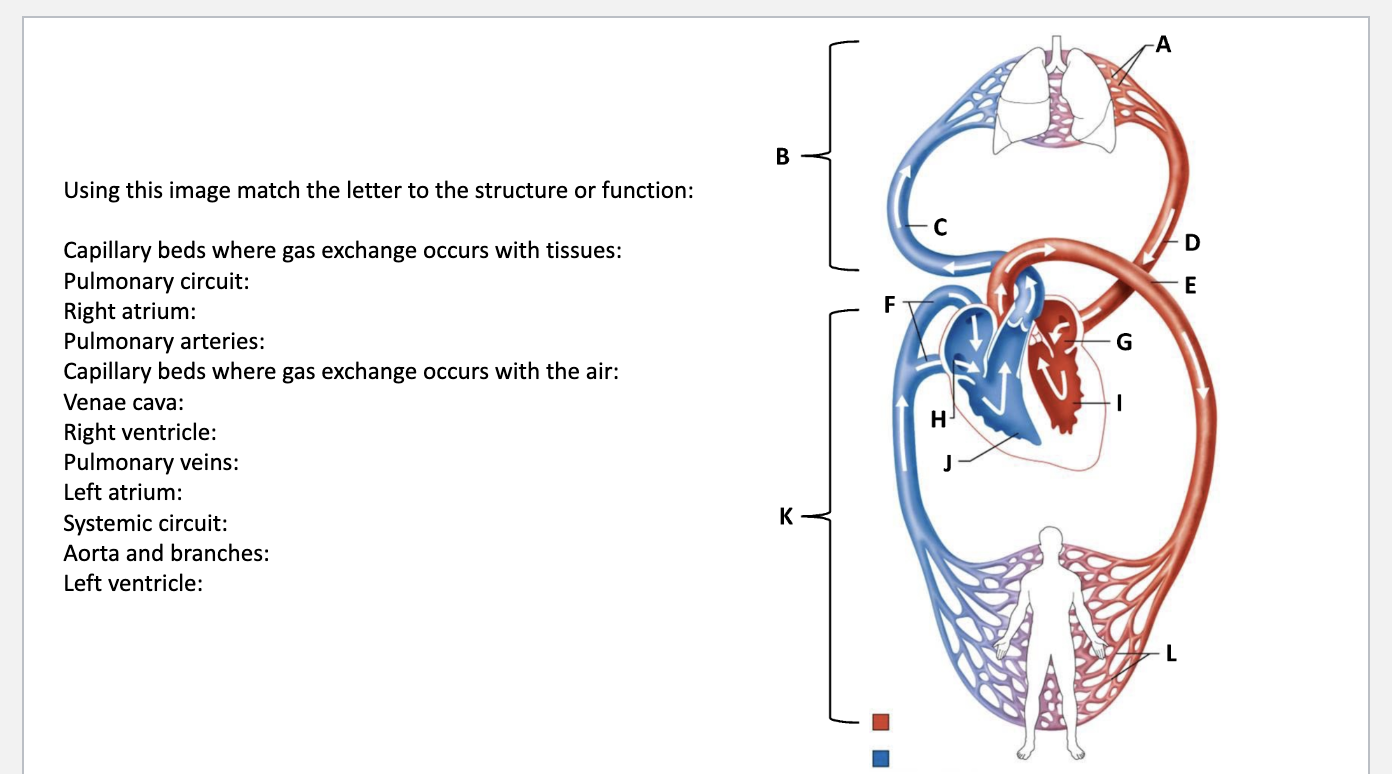
Capillary beds where gas exchange occurs with tissues: L
Pulmonary circuit: B
Right atrium: H
Pulmonary arteries: C
Capillary beds where gas exchange occurs with the air: A
Venae cava: F
Right ventricle: J
Pulmonary veins: D
Left atrium: G
Systemic circuit: K
Aorta and branches: E
Left ventricle: I

Delayed spread of depolarization at the AV node: B
Completion of ventricular depolarization: D
Atrial depolarization initiated at the SA node: A
Ventricular depolarization through the bundle of His and to the Purkinje fibers and atrial repolarization: C
Completion of ventricular repolarization: F
Ventricular repolarization: E
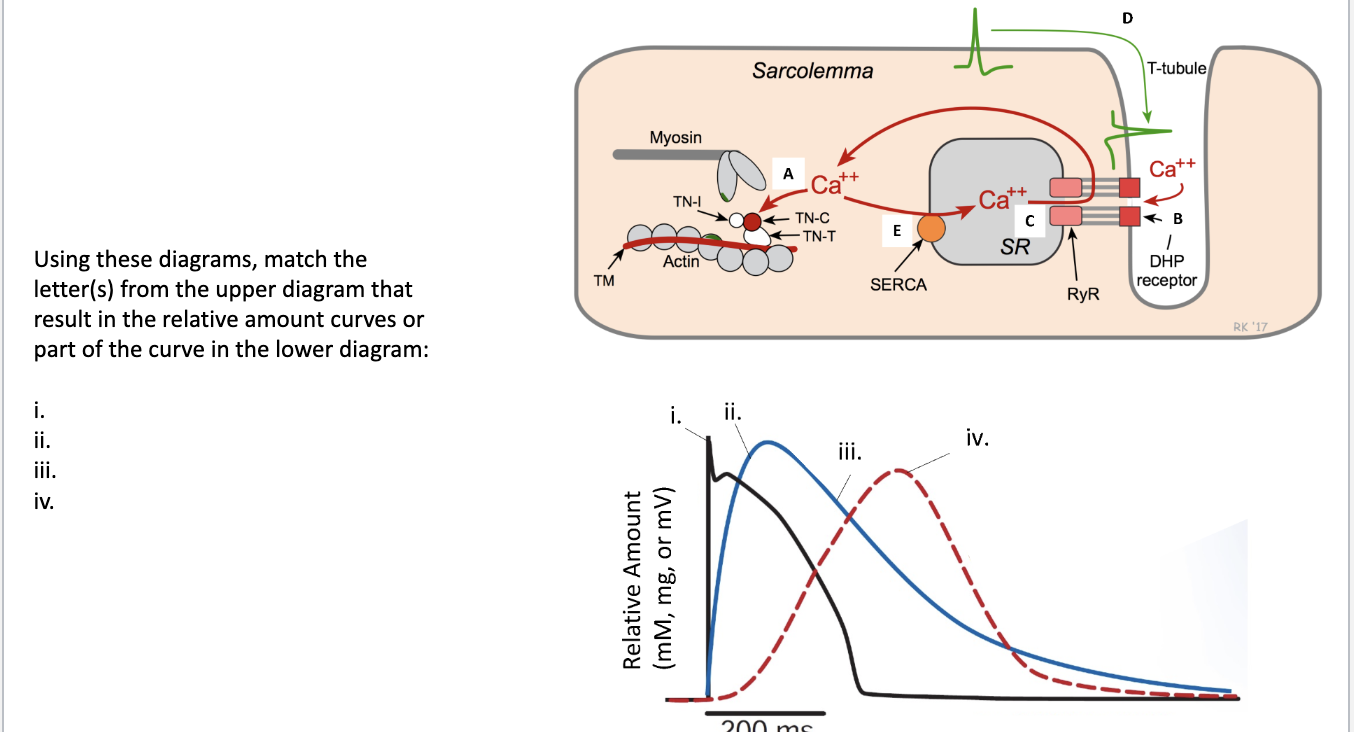
i. D
ii. B or C
iii. E
iv. A
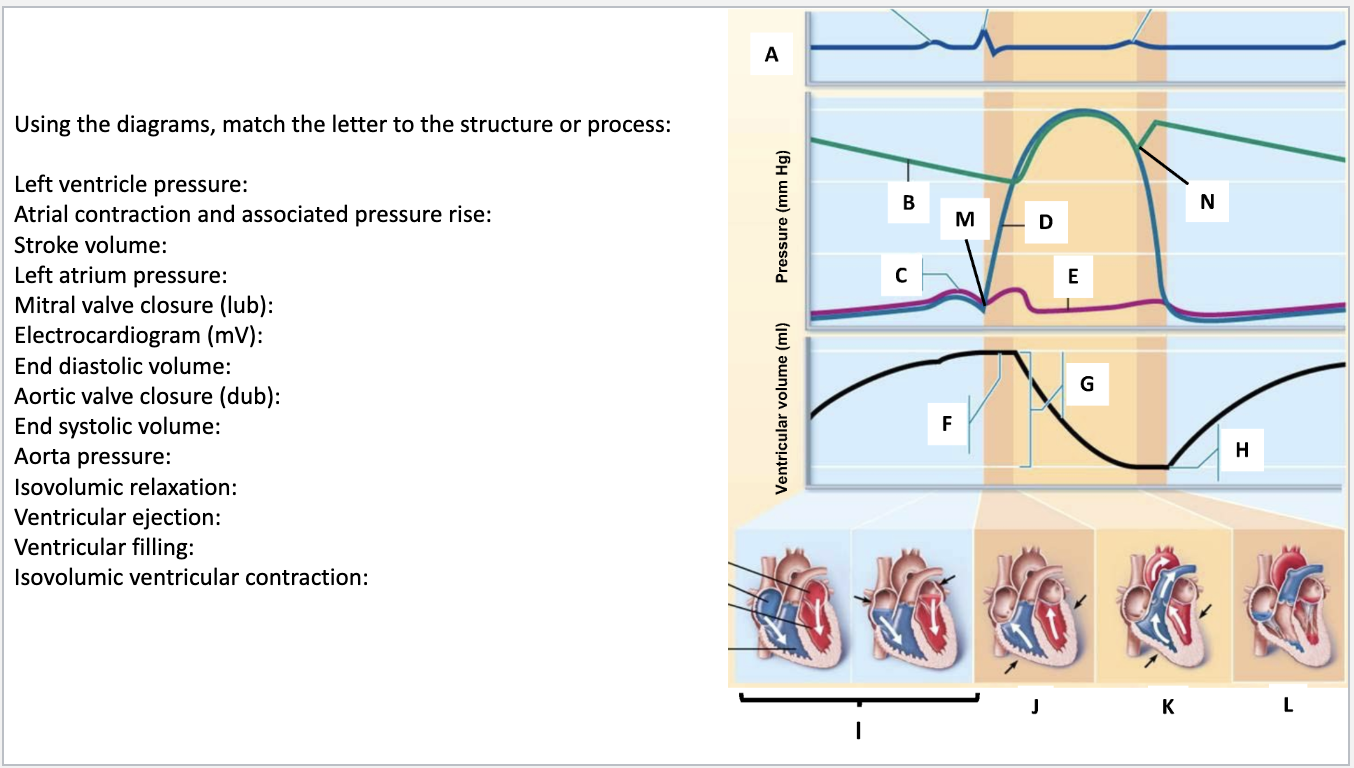
Left ventricle pressure: D
Atrial contraction and associated pressure rise: C
Stroke volume: G
Left atrium pressure: E
Mitral valve closure (lub): M
Electrocardiogram (mV): A
End diastolic volume: F
Aortic valve closure (dub): N
End systolic volume: H
Aorta pressure: B
Isovolumic relaxation: L
Ventricular ejection: K
Ventricular filling: I
Isovolumic ventricular contraction: J
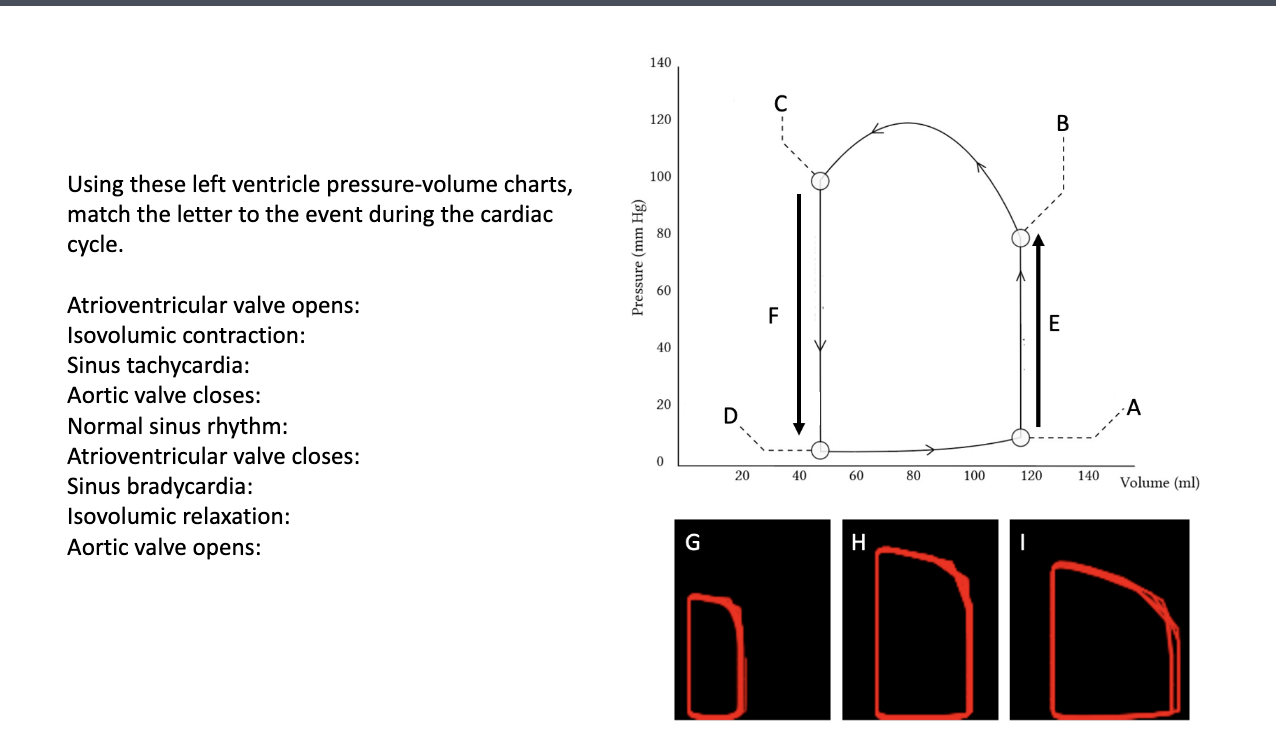
Atrioventricular valve opens: D
Isovolumic contraction: E
Sinus tachycardia: G
Aortic valve closes: C
Normal sinus rhythm: H
Atrioventricular valve closes: A
Sinus bradycardia: I
Isovolumic relaxation: F
Aortic valve opens: B
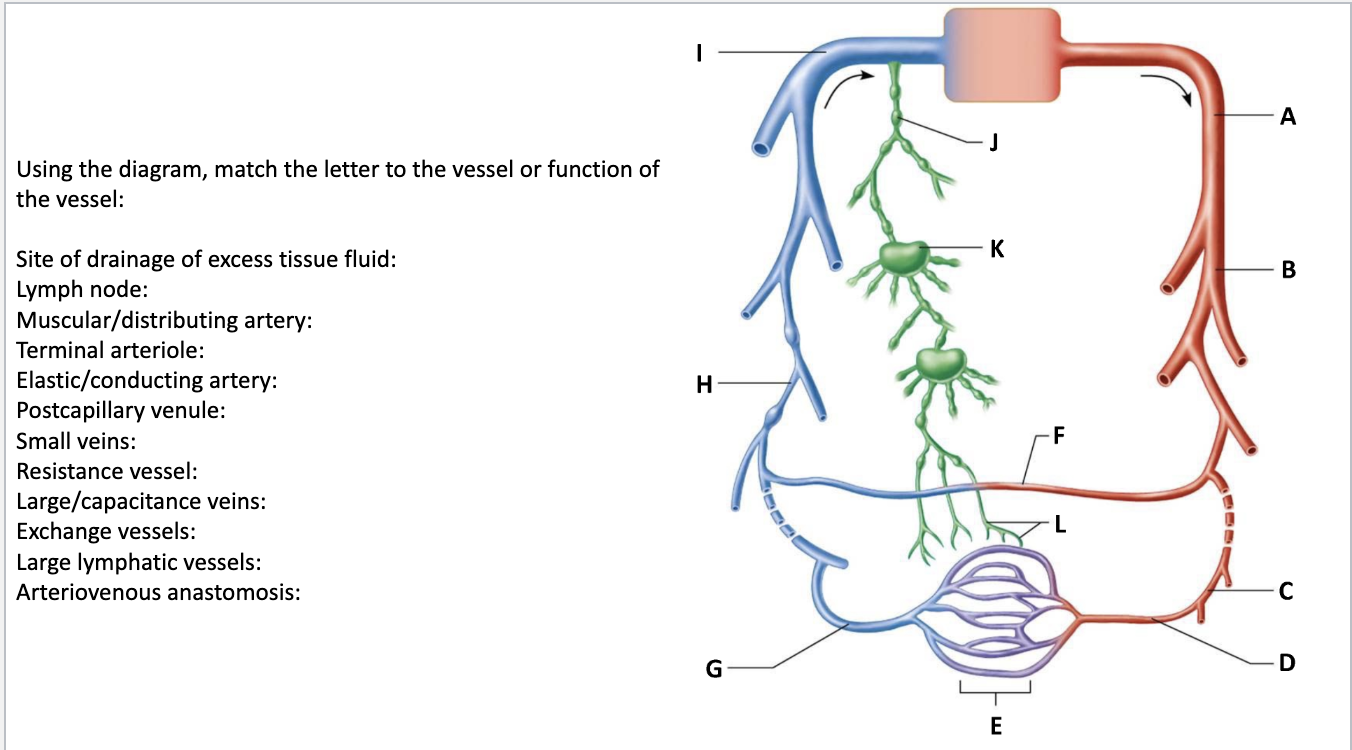
Site of drainage of excess tissue fluid: L
Lymph node: K
Muscular/distributing artery: B
Terminal arteriole: D
Elastic/conducting artery: A
Postcapillary venule: G
Small veins: H
Resistance vessel: C
Large/capacitance veins: I
Exchange vessels: E
Large lymphatic vessels: J
Arteriovenous anastomosis: F
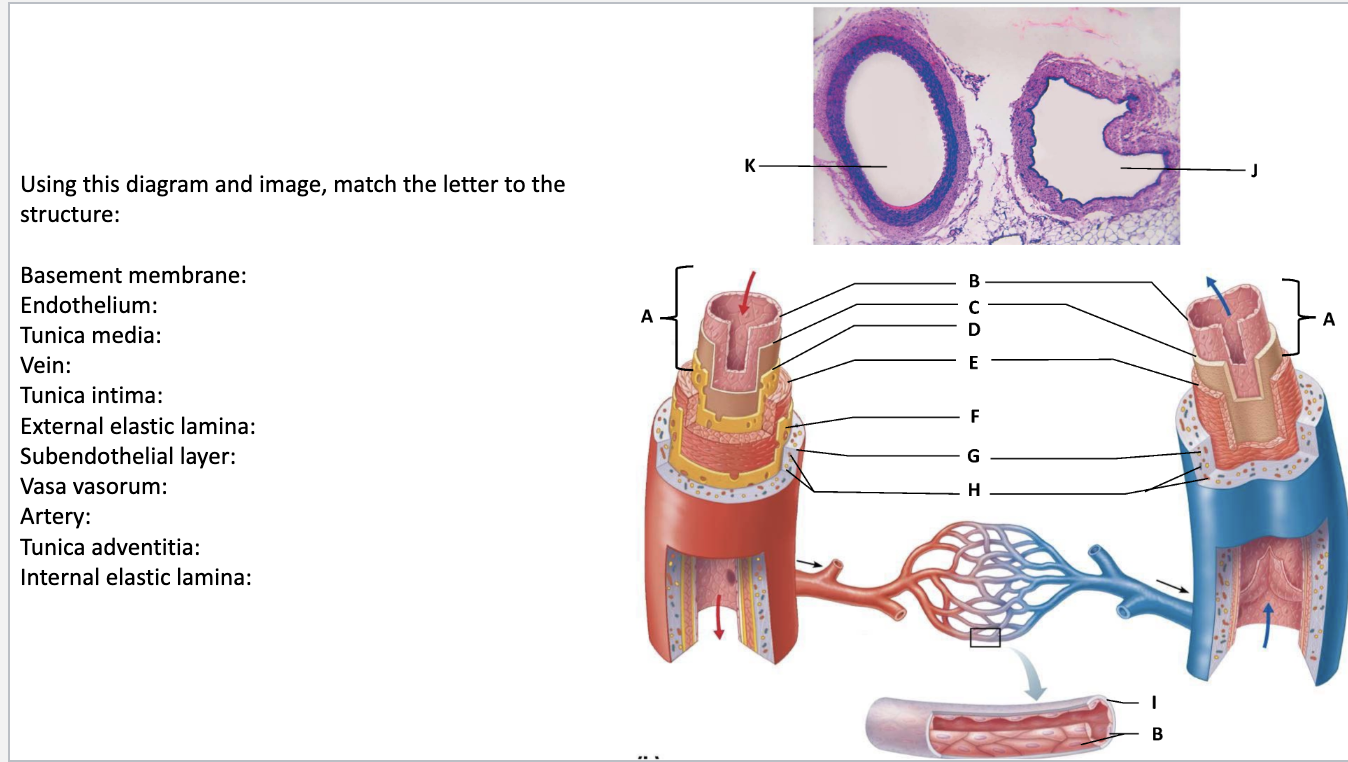
Basement membrane: I
Endothelium: B
Tunica media: E
Vein: J
Tunica intima:
A External elastic lamina: F
Subendothelial layer: C
Vasa vasorum: H
Artery: K
Tunica adventitia: G
Internal elastic lamina: D

Intestines: B
Sinusoidal/discontinuous capillary: C
Continuous capillary: A
Liver: C
Fenestrated capillary: B
Brain: A
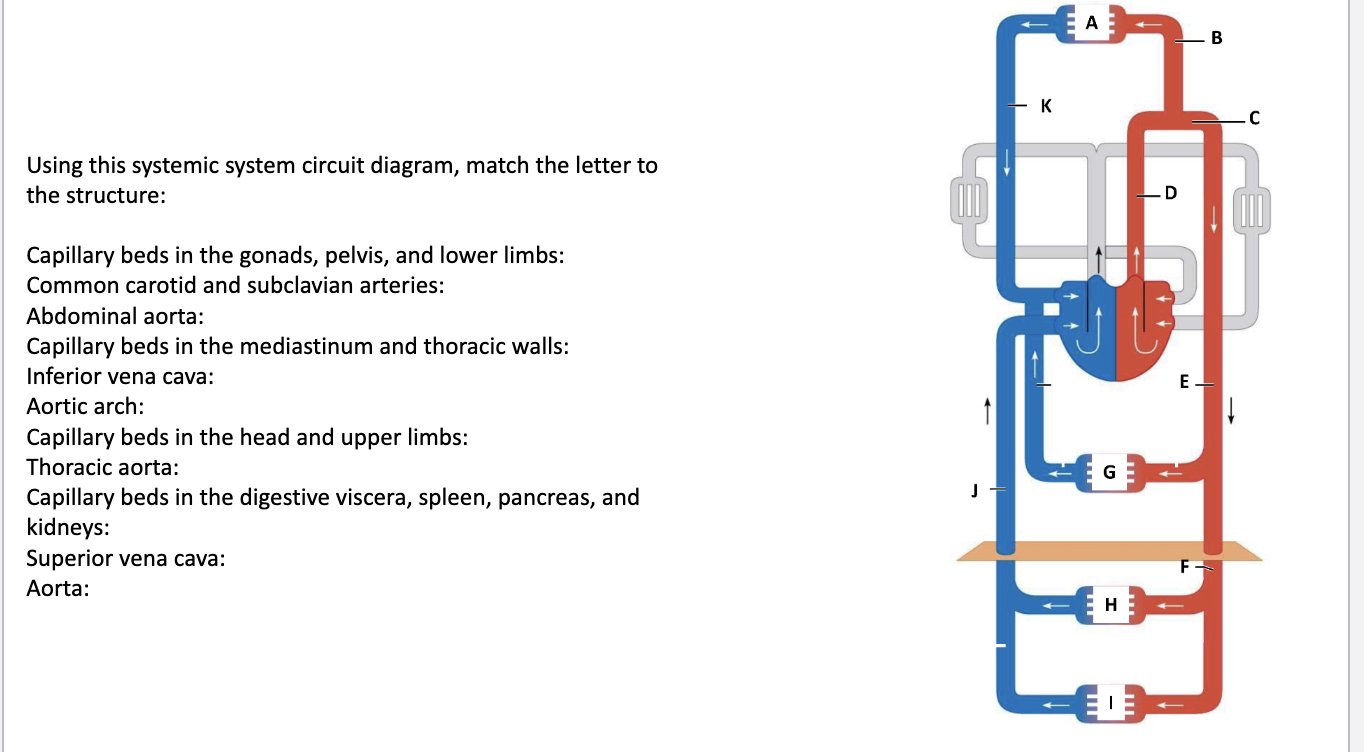
Capillary beds in the gonads, pelvis, and lower limbs: I
Common carotid and subclavian arteries: B
Abdominal aorta: F
Capillary beds in the mediastinum and thoracic walls: G
Inferior vena cava: J
Aortic arch: C
Capillary beds in the head and upper limbs: A
Thoracic aorta: E
Capillary beds in the digestive viscera, spleen, pancreas, and kidneys: H
Superior vena cava: K
Aorta: D
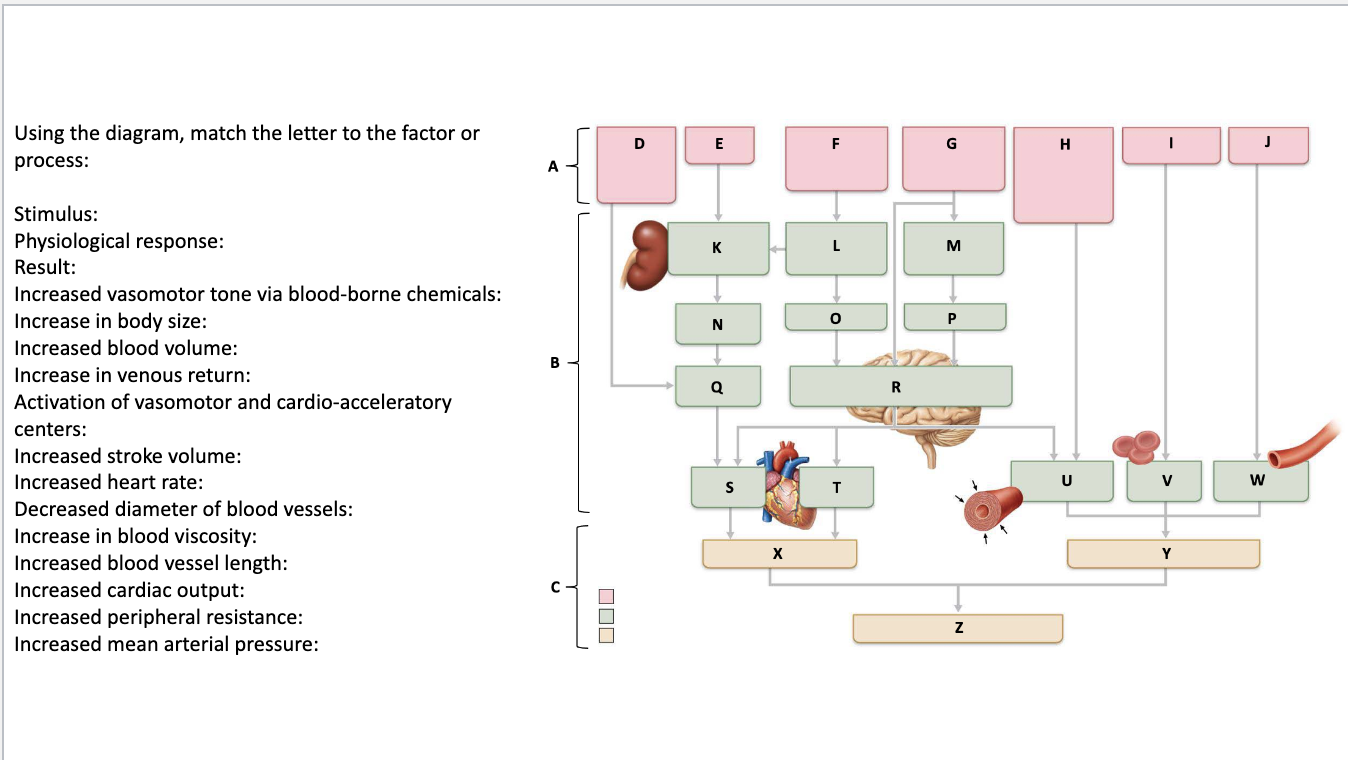
Stimulus: A
Physiological response: B
Result: C
Increased vasomotor tone via blood-borne chemicals: H
Increase in body size: J
Increased blood volume: N
Increase in venous return: Q
Activation of vasomotor and cardio-acceleratory centers: R
Increased stroke volume: S
Increased heart rate: T
Decreased diameter of blood vessels: U
Increase in blood viscosity: V
Increased blood vessel length: W
Increased cardiac output: X
Increased peripheral resistance: Y
Increased mean arterial pressure: Z