Classes of Compounds - Ochem1
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Hydrocarbons
compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen
alkanes
cycloalkanes
alkenes
cycloalkenes
alkynes
aromatic/ benzene ring
alkanes
single bonds between the carbons
all carbons are sp3
cycloalkanes: sp3 carbons form a ring
alkenes
double bonds are present in the molecule
sp2 carbons
cycloalkenes: double bond present in ring
alkynes
triple bonds are present
sp carbons
Aromatic
Contain a benzene ring
benzene ring: 6 membered ring with alternating single and double bonds.
Alcohols
Contain Hydroxyl group (—OH) as main functional group
R— OH
Ethers
Contain two alkyl groups bonded to an oxygen
R —O— R
no hydrogen bonding ( low bp than alcohols)
Aldehyde and Ketones
Contain Carbonyl group
C=O
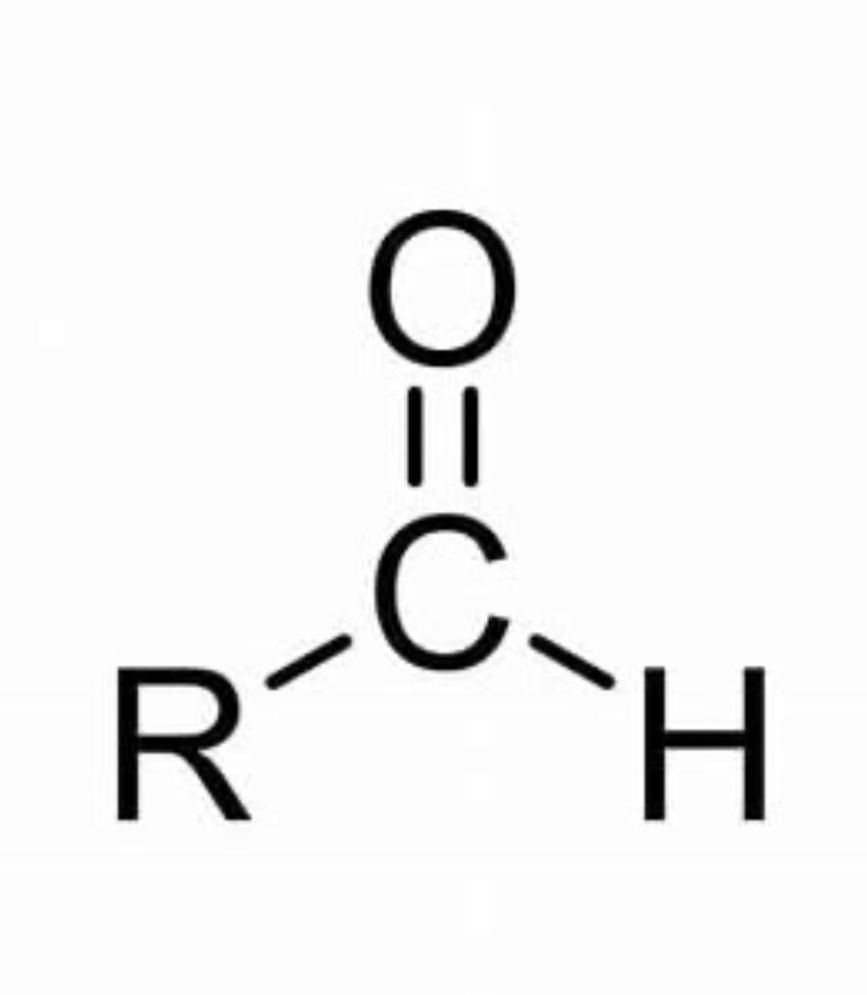
Aldehyde
Carbonyl group- one of R groups is an H
Carbon double bonded to O and bonded to 2 R groups
RCHO
Ketone
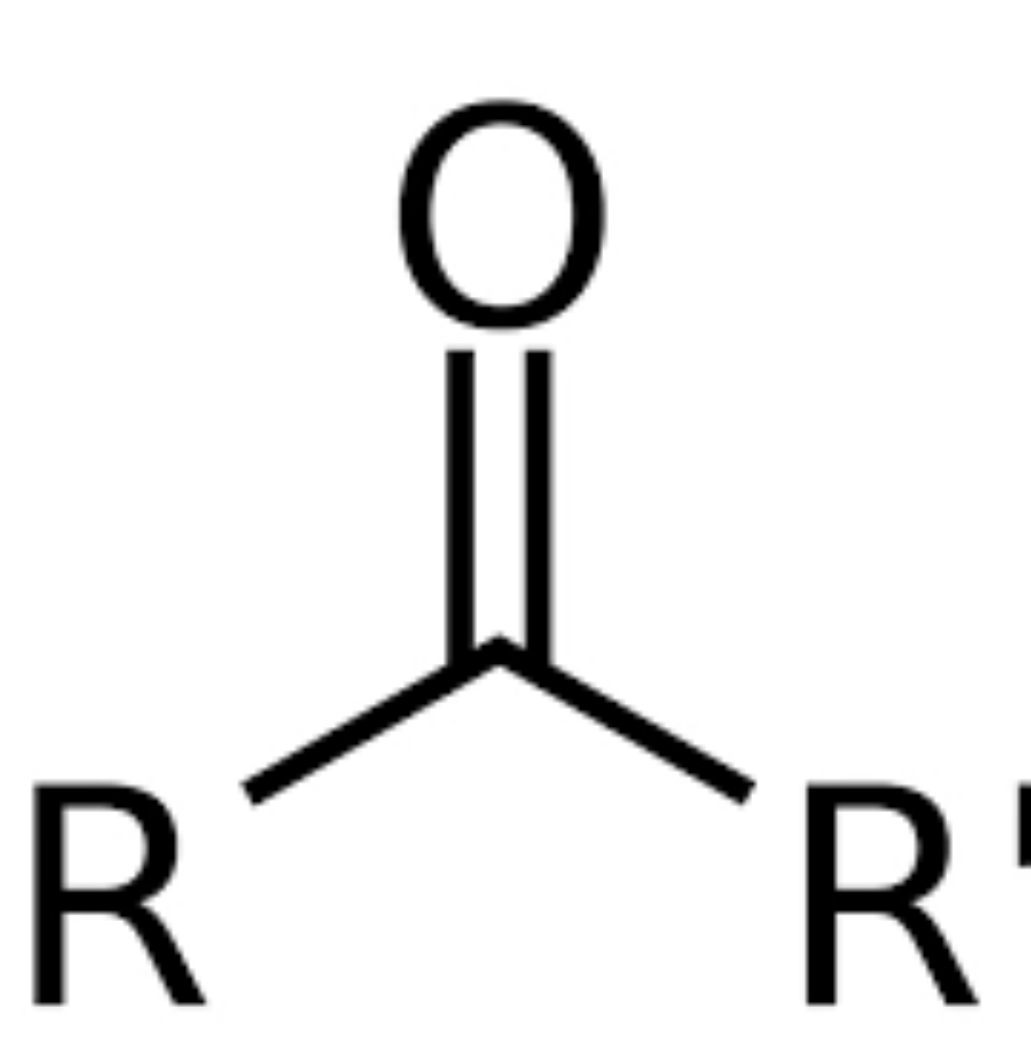
Carbonyl group- 2 R groups
carbon double bonded to O and bonded to 2 R groups
RCOR
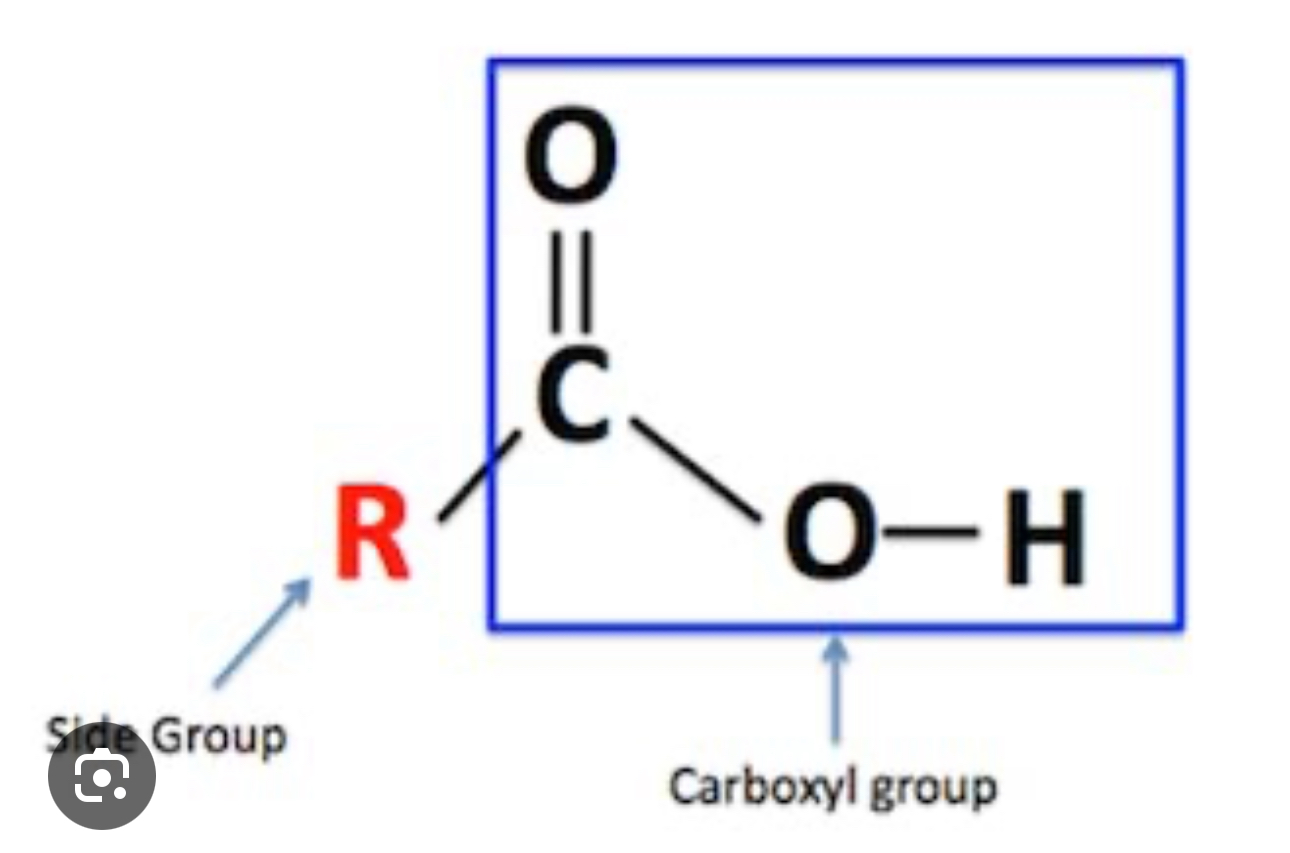
Carboxylic Acids
Contain Carboxyl group —COOH
Caroboxylic Acid Derivatives
Carboxylic Acid is easily converted to a variety of acid derivatives:
Acid Chlorides
Esters
Amides
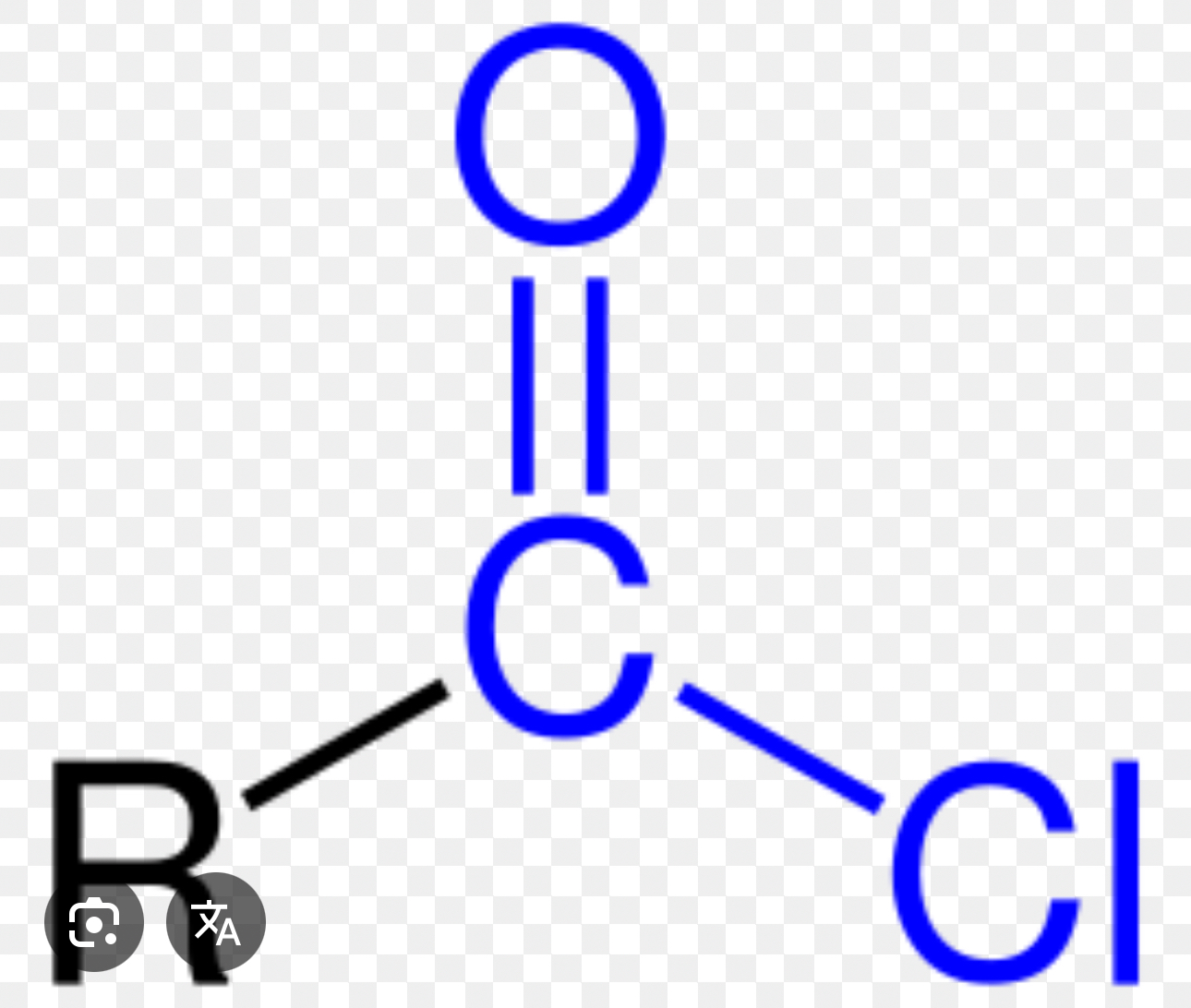
Acid Chlorides
R— COCl
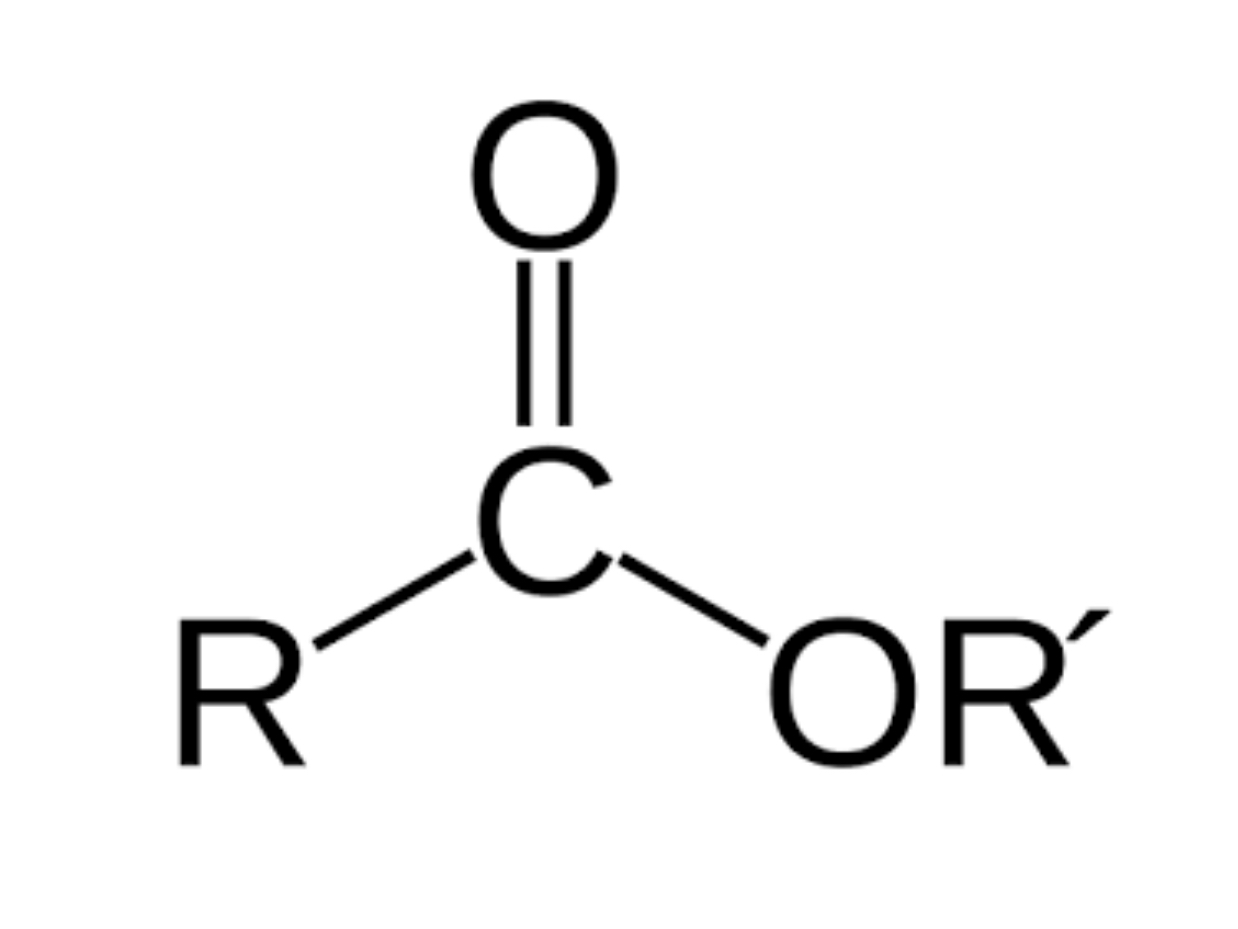
Esters
R— COOR
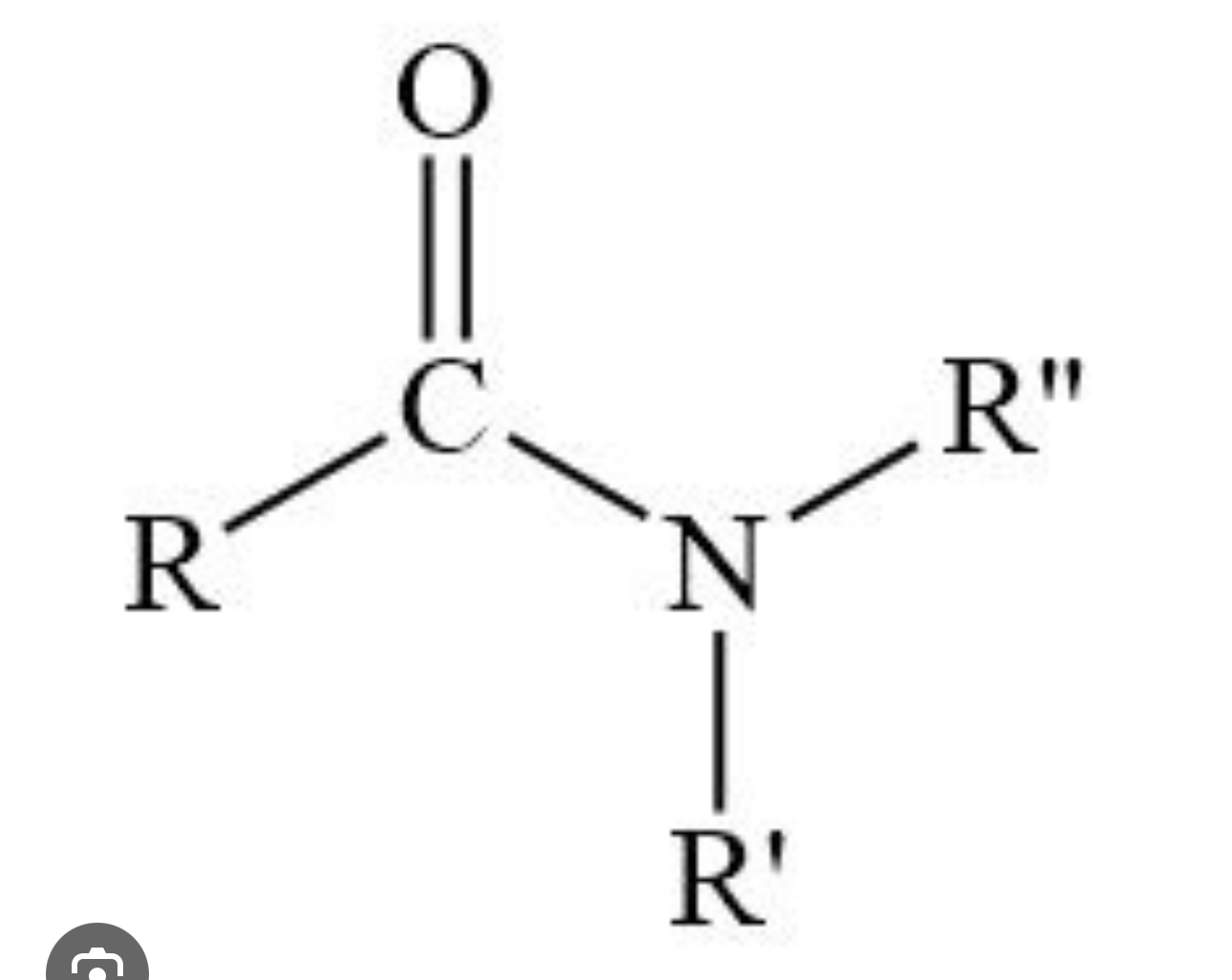
Amides
R— CONH2
Derivatives that result from a combination of an acid with ammonia or an amine
R— CONHR
R— CONR2
Amides have carboxyl group (C=O) unlike Amine
C=O + Ammonia(NH2) or Amine (N)
Compounds Contaning Nitrogen
Amines
Amides
Nitriles
Amines
Alkylated derivatives of ammonia
nitrogen bonded to one or more carbons.
At least 1 C—N connection:
R—NH2
R—NH—R
R—N(—R)—R
Nitriles
Compound containing a cyano group
Cyano group: C ≡ N
dipole moment (partial neg N)
Highly polar solvent
R—C≡N: CH3—C≡N: CH3CH2—C≡N: