Biology 30 Nervou system
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Homeostasis
Maintaining a stable internal environment
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord.
It is surrounded by a 3-layered protective membrane known as the meninges.
Pheripheral Nervous System (PNS)
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body. Divided into sensory pathways and motor pathways.
Motor Pathways
Somatic nervous system (SNS): Under conscious control
Automatic nervous system (ANS): Under unconscious control.
Automatic Nervous System (ANS)
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms.
parasympathetic nervous system
The division of the autonomic nervous system that restores the body after stress.
Ex: Stimulates flow of saliva, peristalsis and secretion, release of bile, slows heartbeat, constricts bronchi, and contracts bladder.
"Rest and digest"
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for stress
Ex: Dilates pupil, bronchi, inhibits flow of saliva, peristalsis and secretion, bladder contraction, accelerates heartbeat, converts glycogen to glucose, and secrets adrenaline to nor adrenaline.
"Fight, flight, or freeze"
Neurons
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system.
A bundle of neurons is called a nerve.
Glial cells
Non-conducting support cells of the nervous system.
Dendrites
Cytoplasmic projections that carry the nerve impulse to the cell of the body. Some neurons have special dendrites called sensory receptors.
Cell Body
Houses the nucleus and the orgenelles of the neuron. The position of the cell body in a reflex arc will determine the type of neuron it is.
Axon
Cytoplasmic extension that carries the nerve impulse away from the cell body. Most axons are almost entirely covered by Shawann cells.
Shawann cells
Glial cells that surround the axon and secrete the myelin sheath. Myelin is the cytoplasm of the shawann cells which wraps around the axon.
Myelin Sheath
It insulates the axon, enabling for faster nerve impulse transmission.
Neurillema
A thin layer surrounding the shawann cell and axon. Repairs damage to axons.
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath where nerve impulses occur. Allows for saltatory conduction.
Saltatory conduction
Rapid transmission of a nerve impulse along an axon, resulting from the action potential jumping from one node of Ranvier to another, skipping the myelin-sheathed regions of membrane.
Axon terminal
The point where the nerve impulse is passed to another neuron. Contains synaptic vesicles that contain neurotransmitters.
3 types of neurons
sensory, motor, interneurons
sensory neuron
Carries impulse recieved by sensory receptors to CNS. Can have cell body wherever
Interneuron
Found in CNS(spine) and signals to brain or motor neurons. Contains no shawann cells
Motor neurons
Carries impulse to effectors(muscles, organs, galnds). Can only have a cell body at the start of the neuron.
Reflex arc
An involuntary/unconsious response to a stimulus. It is a simple nerve pathway that does not involve the brain.
Pathway: Stimulus, sensory neuron(afferent), interneuron(spinal cord), motor neuron(efferent), muscle/body response, pain.
Reflex arcs have few synapses, accounting for the rapid response. More synapses = slower signal.
Thee most time ccomsuming part of the process of nerve impulse transition is diffusion.
action potential
Known as the nerve impulse, it is an eletrochemical charge along the length of the neuron and is due to the movement of K+ and Na+ channels opening and closing.
Ion channels
These ensure ions do not move down their concentration gradients at the wrong time. Na+ and K+. Their opening and closing depends on the membrane potential.
Resting potential
the state of the neuron when not firing a neural impulse. Na+ ions are high in concentration outside the neuron whereas K+ ions are high in concentration inside the neuron. Membrane potential is negative, inside more negative then outside. It is polarized.
Depolarization
The process during the action potential when sodium is rushing into the cell causing the interior to become more positive. High concentration of Na+ and K+ ions inside the neuron. Must reach a threshold level to produce an action potential. The influx of Na+ ion channels propagates the impulse along the neuron.
Repolarization
Period during which potassium ions diffuse out of the neuron, high concentration of Na+ ions inside and high concentration of ions outside the neuron. Propagates so much K+ ions outside the neuron it becomes very negative and overshoots resting potential. Hyperpolarized.
Refractor period
K+ ion channel closes, high concentration of Na+ inside and K+ outside neuron. Na/K+ Pump opens, 3 Na+ out, 2 K+ in which uses 1 ATP. Eventually returns neuron to resting potential.
Saltatory Conduction
Rapid transmission of a nerve impulse along an axon, resulting from the action potential jumping from one node of Ranvier to another, skipping the myelin-sheathed regions of membrane. Myelinated axons transits nerve impulse faster then unmyelinated axon.
multiple sclerosis
myelin sheath destruction. disruptions in nerve impulse conduction
Threshold levels
minimum level of a stimulus required to produce a response. Different neurons have different threshold levels and more intense stimulus will fire higher thresholds. Once threshold stimulus is reached, it will completely fire. Higher intensity stimuli do not result in bigger action potentials. The more intense a stimulus, the more frequent the neuron fires.
How does the brain interpret a stimulus
1. The number of neurons firing
2. The neurons respective threshold level
3. The frequency of action potential
Summation
When 2 or more neurons fire together onto another neuron with higher threshold causing it to fire.
Inhibition
When a neuron fires onto another and inhibits the subsequent neuron from firing.
Synapse
The region between a axon terminal and another neuron's dendrites. The space between the pre-synaptic neuron and post-synaptic neuron is called the neuromuscular junction (Only between a motor neuron and a muscle).
Neurotransmitters
Transmission of a nerve impulse across the membrane involves neurotransmitters. They are chemical messengers released by the pre-synaptic neuron that bind to receptors on the post-synaptic neuron.
Synaptic transmission
1. The wave of depolarization reaches the pre-synaptic axon terminal and Ca2+ ion channels open in response.
2. Ca2+ ions bind to vesicles containing neurotransmitters which stimulates these vesicles to fuse with the axon terminal membrane.
3. The vesicles then release the neurotransmitters into the synapse(synaptic cleft). The neurotrnsmitters then diffuse across the synapse and bind to receptors on the dendrites pf the post-synaptic neuron.
4. Ion channels on the post-synaptic neuron open in response to the neurotransmitter which will cause either depolarozation or hyperpolarization in the post-synaptic neuron
5. Enzymes in the synaptic cleft break down the neurotransmitter which is then recycled by the pre-synaptic neuron.
Excitatory neurotransmitters
Make the post-synaptic neuron more permeable to Na+
Inhibitory neurotransmiters
Make the post-synaptic neuron more permeable to K+
Acetylcholine
-Results in muscle contraction.
- Acetylcholinesterase breaks down acetylcholine in the synapse.
-In fainting coats video they stiffen because they get excited/nervous and acetylcholine causes heir muscles to stiffen and they "faint".
Addiction theory
Neurons may respond to excess neurotransmitter by producing more receptors. The effect of this response is that it increases the threshold of the neuron to depolarization. The body becomes physiologically addicted.
Parkinson's disease
Not enough of the neurotransmitter dopamine.
Causes involuntary movements and tremors.
Alzheimer's disease
Decreased production of acetylcholine.
Results in deterioration of memory and mental capacity.
Multiple Sclerosis
The immune system kills Shwann cells.
Results in deterioration of myelin sheath and less efficient nerve impulse.
Frontal Lobe
Controls higher mental functioning. Ex: Rational decision making, right vs wrong, socially acceptable behavior.

Parietal Lobe
Involved with integrating sensory(somatosensory) information. Different parts of the parietal lobe control and respond to specific body areas.
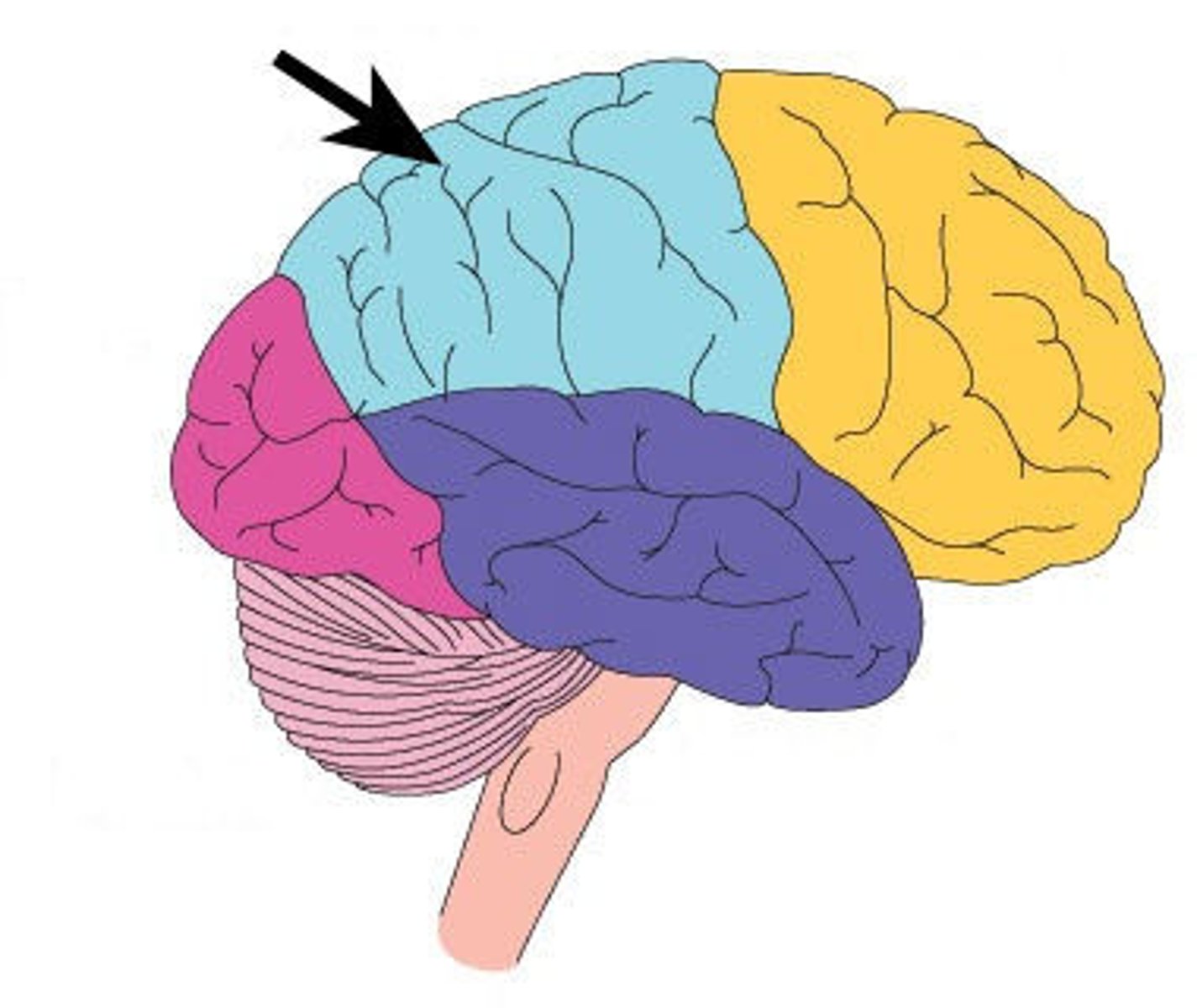
Occipital lobe
Involved in processing visual information. Nerves from eyes will lead to this lobe.
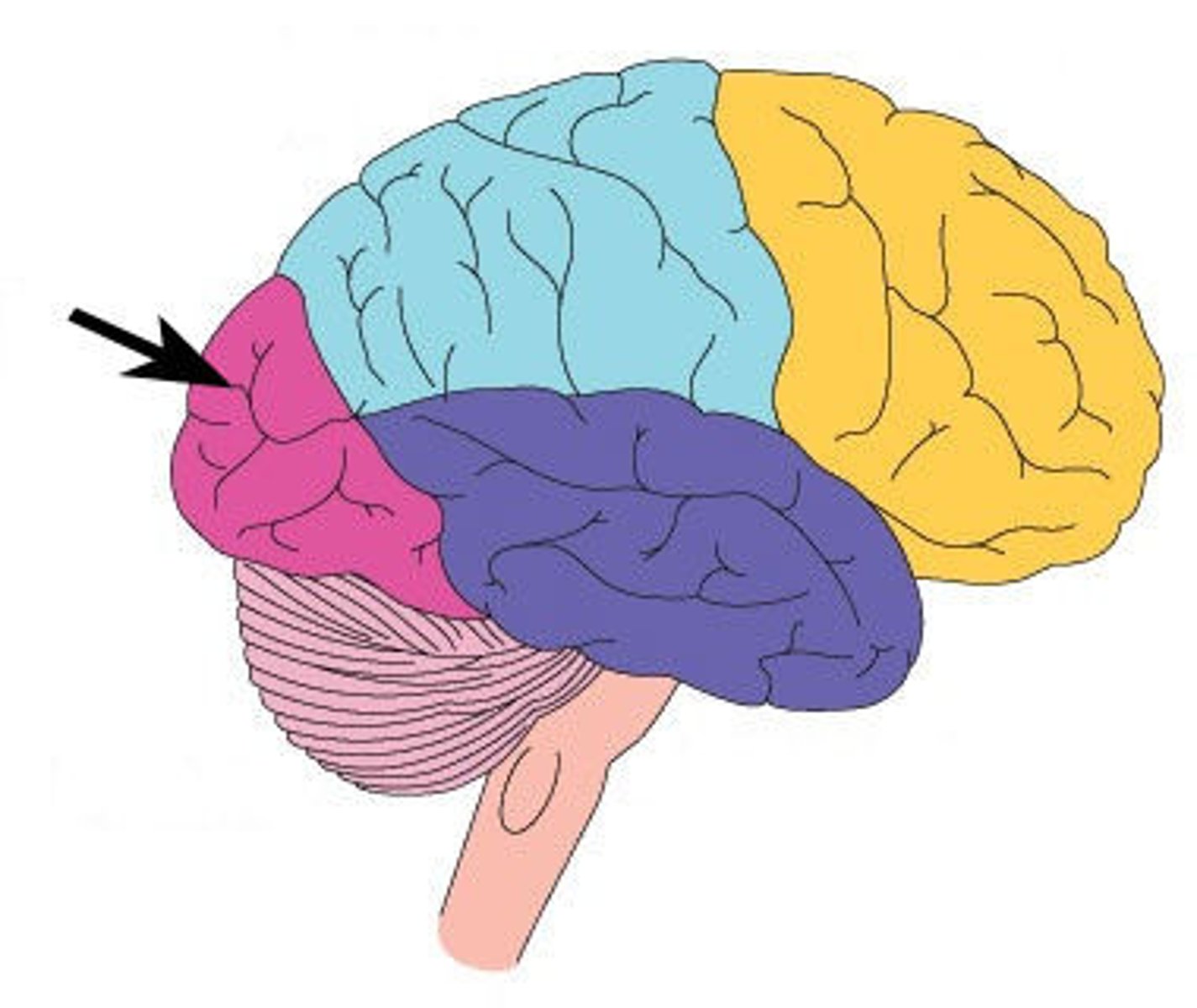
Temporal lobe
Involved in processing auditory information and some long and short term memory.
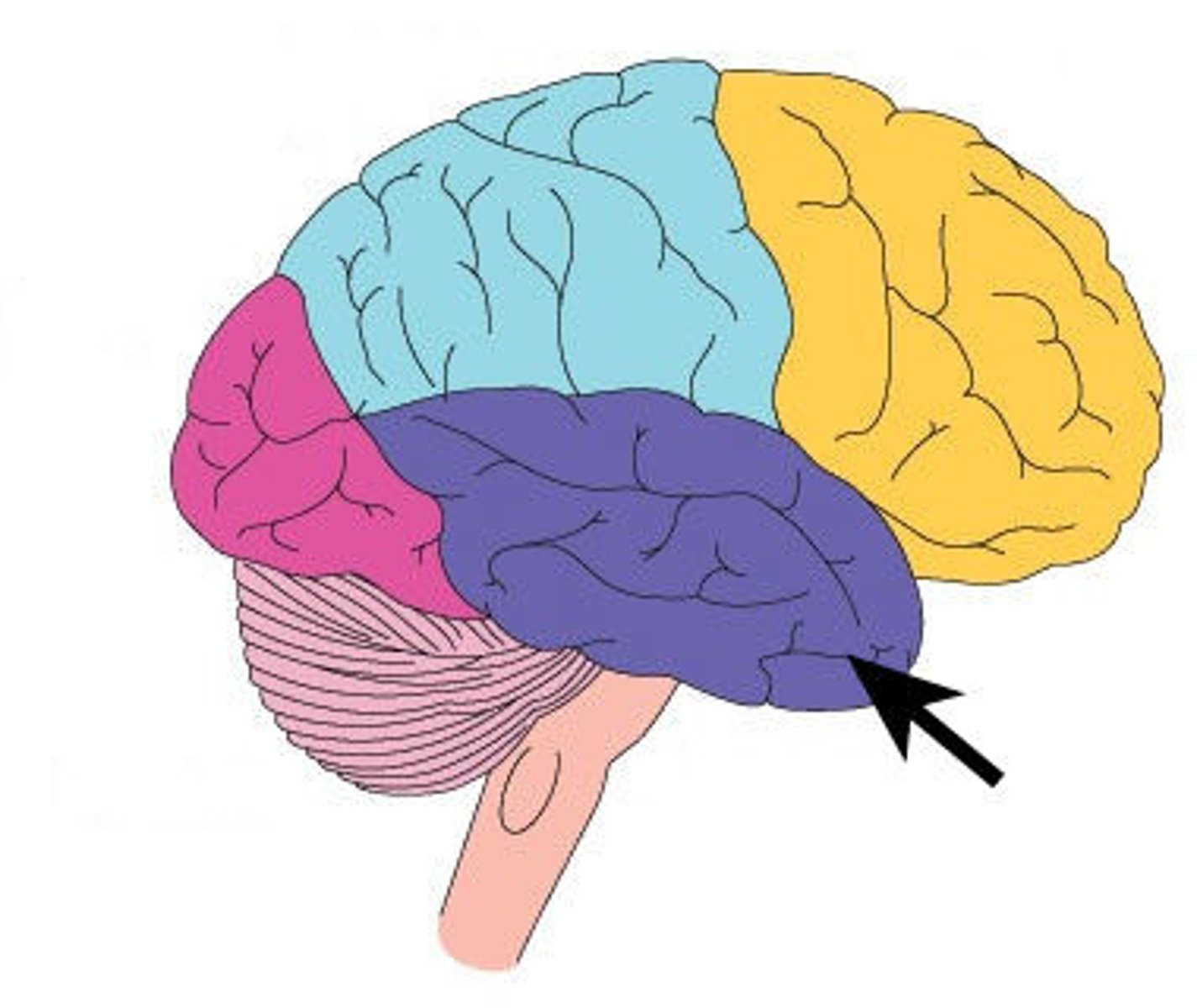
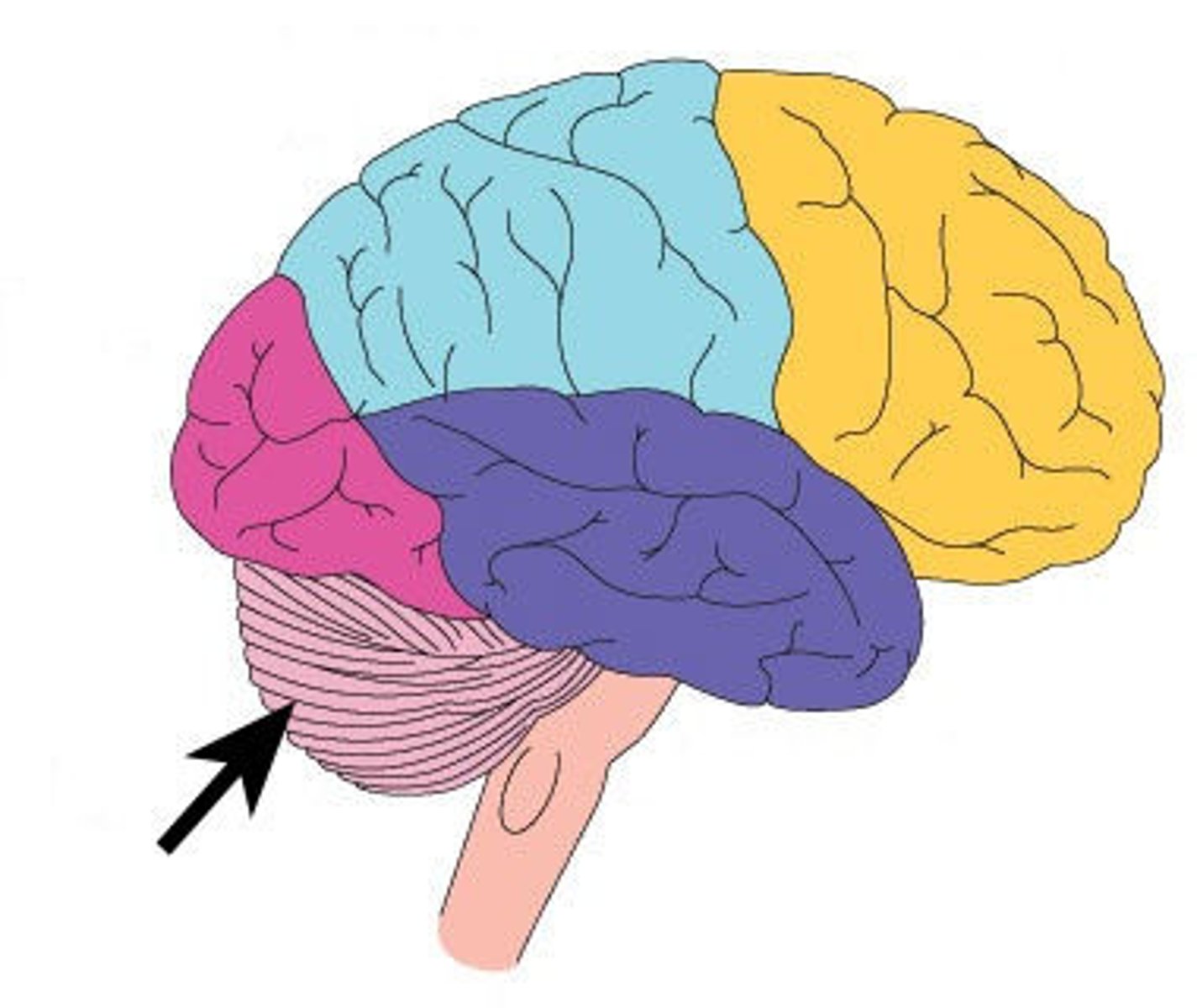
Cerebellum
Involved in coordinating muscle movement. Strongly involved in balance and body awareness.
Cerebrum (Cerebral cortex)
-Stores sensory info
-Initiates voluntary actions
-Involved in intellectual abilities
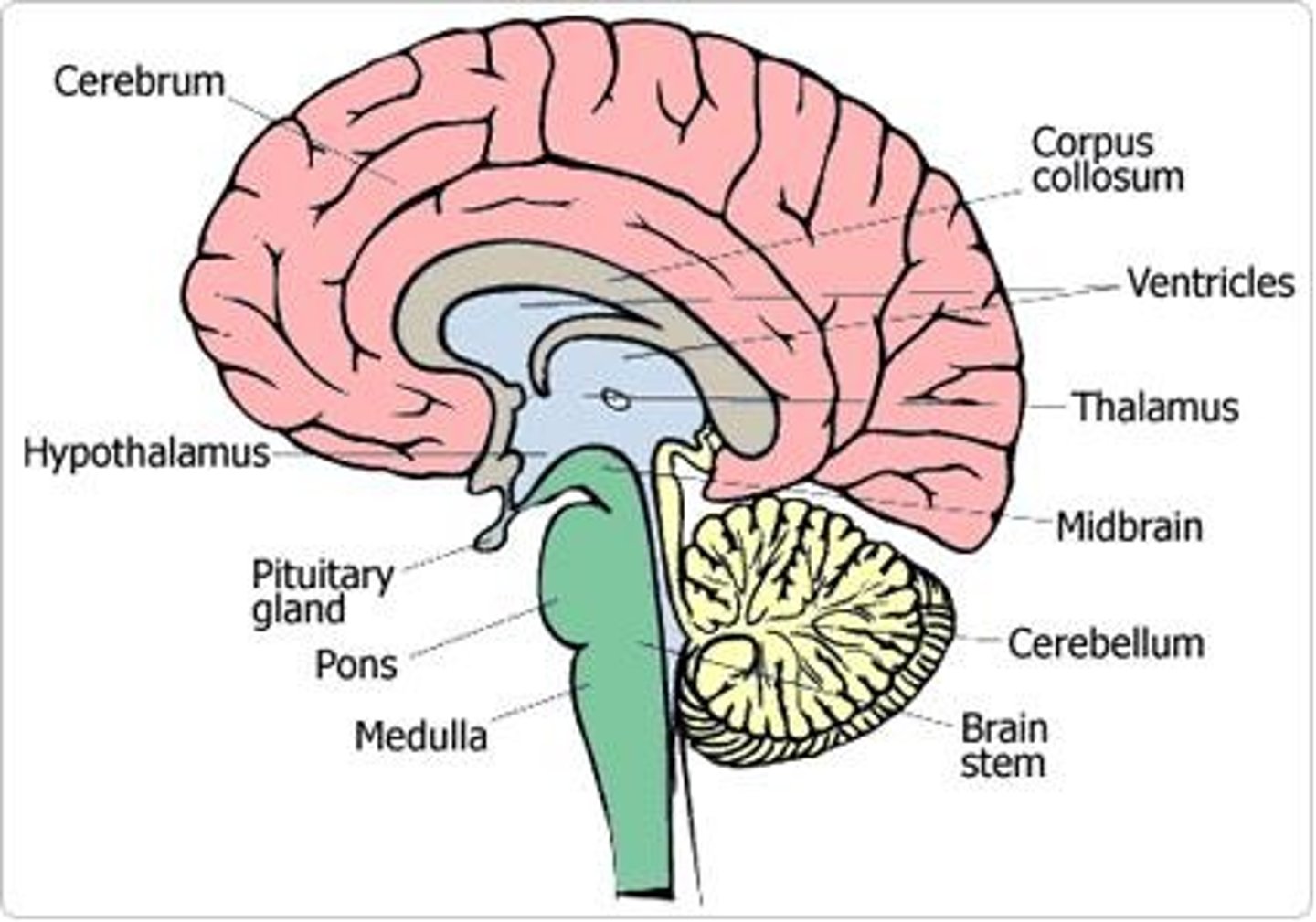
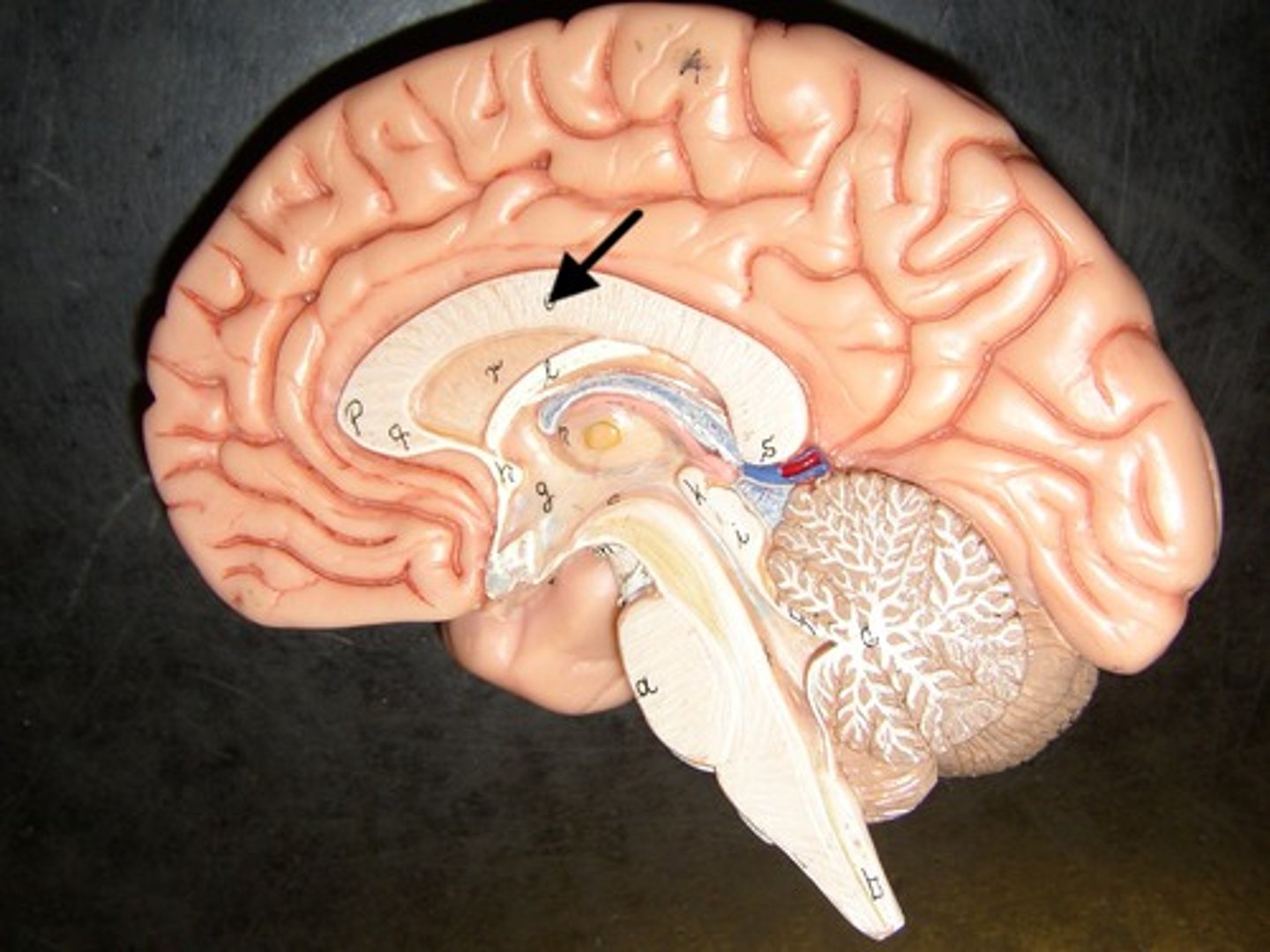
Corpus Callosum
-Connects two parts of brain
-Allows for communication between two parts.
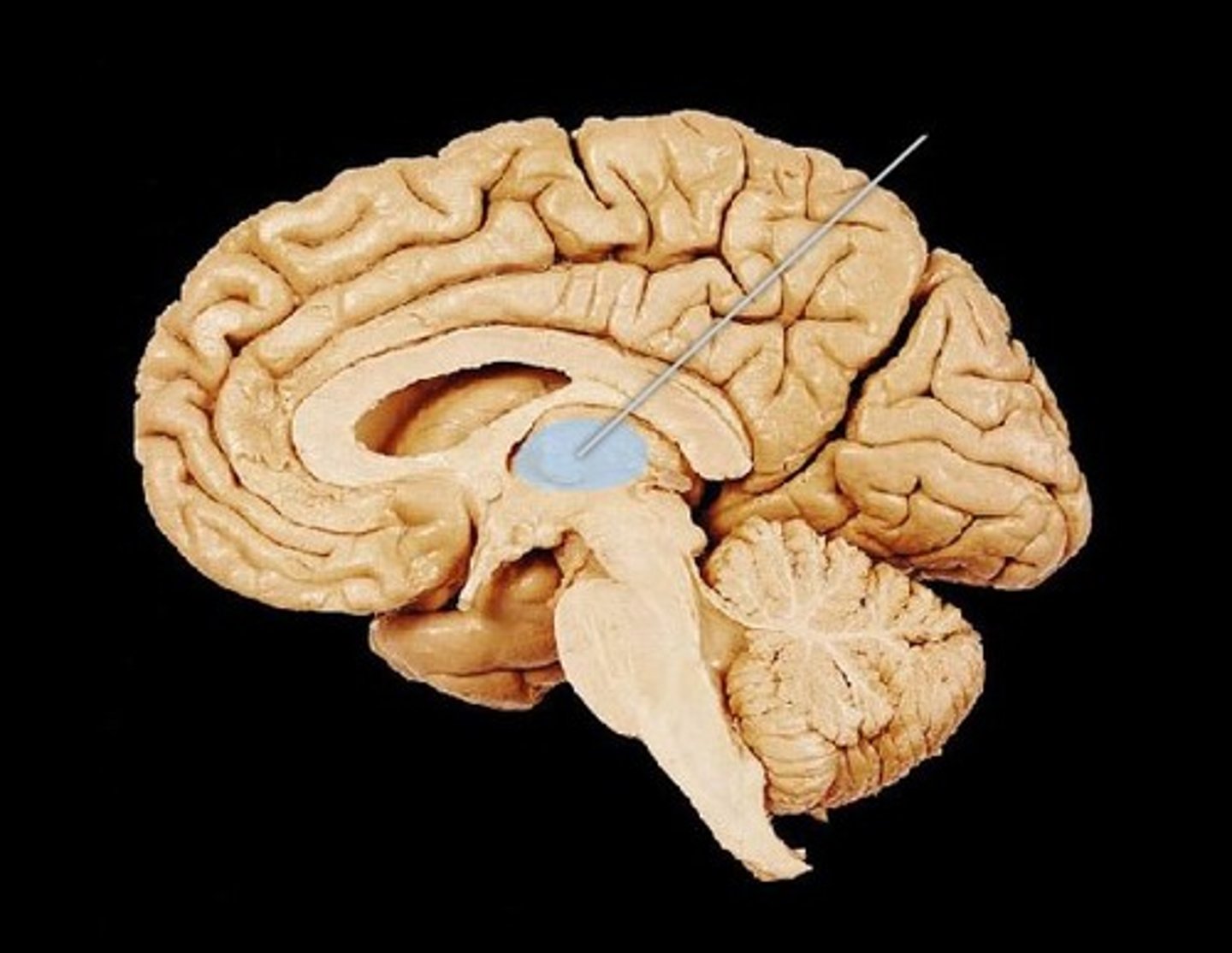
Thalamus
Coordinates various sensory info from the cerebrum to the cerebellum.
Hypothalamus
-Largely maintains homeostasis
- Coordinates communication between nervous system and endocrine system
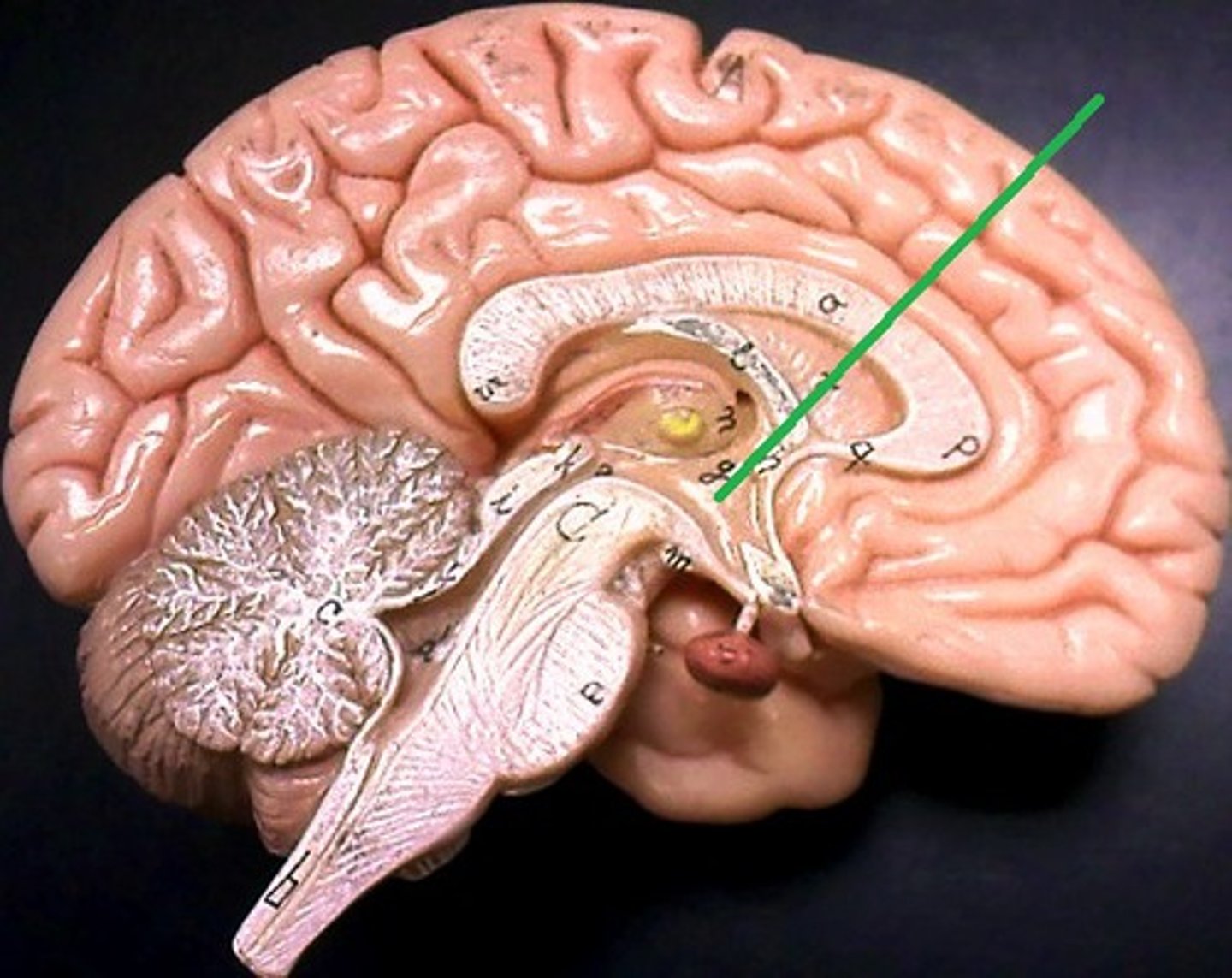
Olfactory Bulb
Processes info about smell
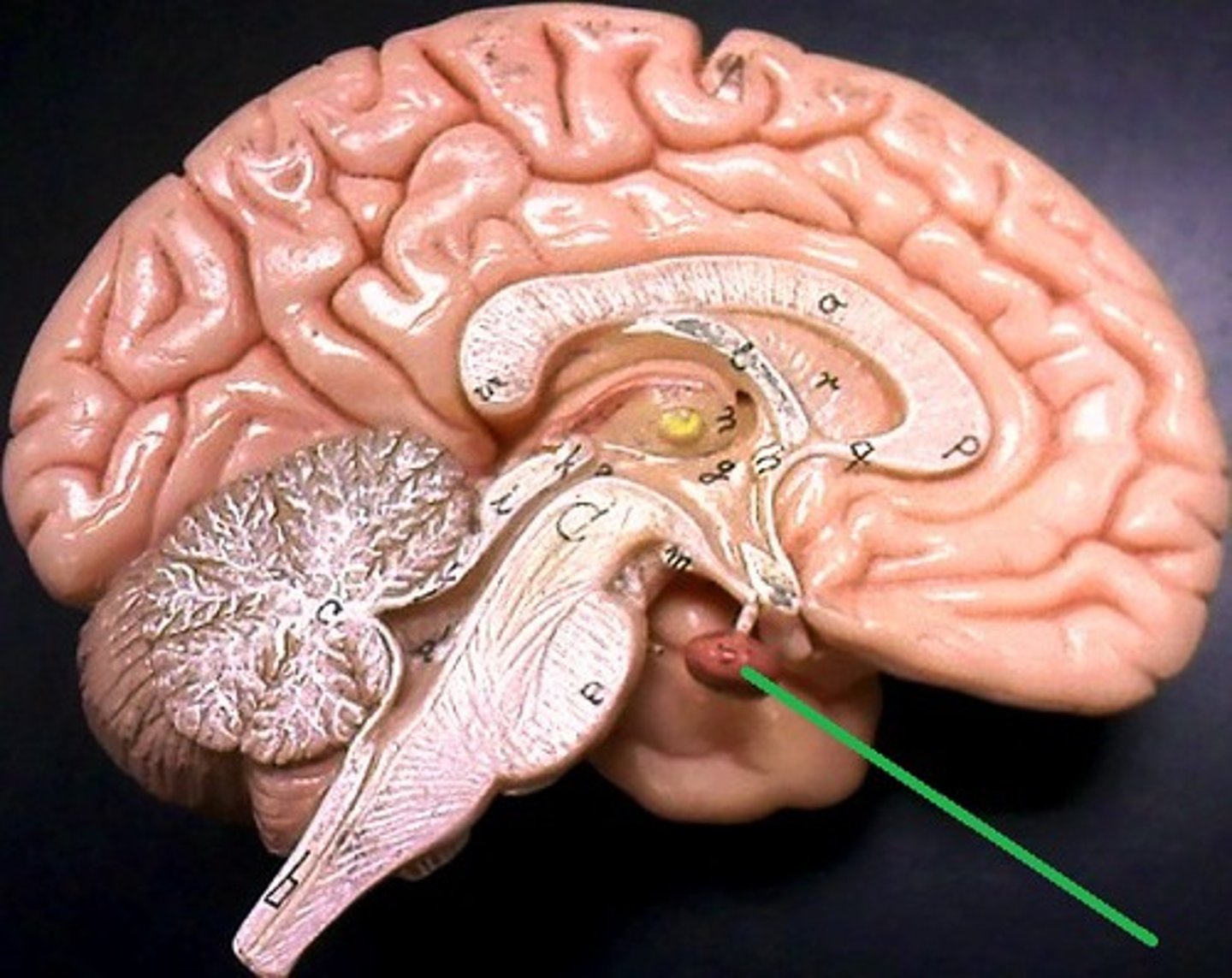
Pituitary gland
Major site of hormone production
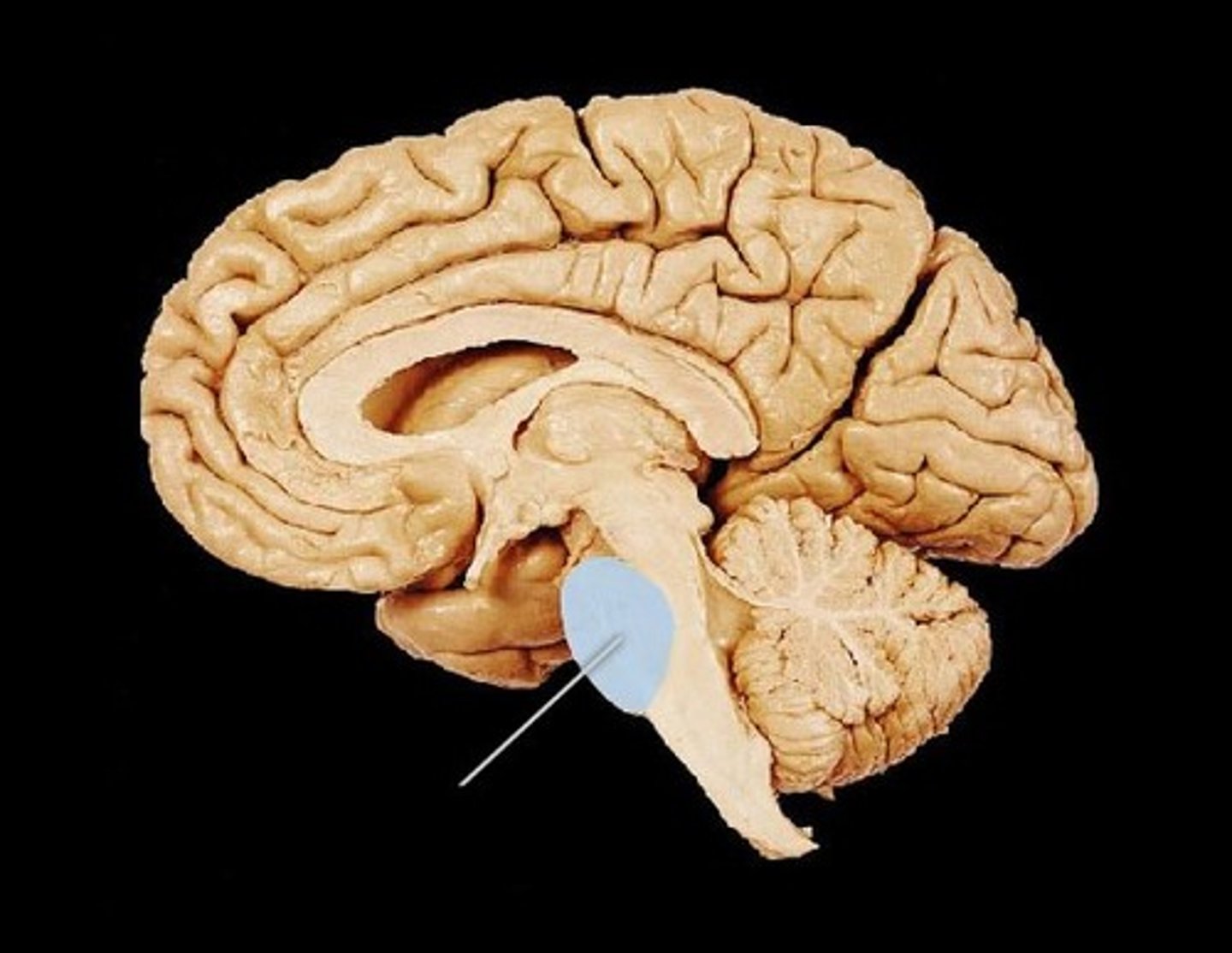
Pons
Majorly involved in relaying signals from cerebrum to the cerebellum and medulla oblongata.
Medulla Oblongata
Site of automatic nerve control. Controls activities like breathing, heart contraction, digestive movements, etc.
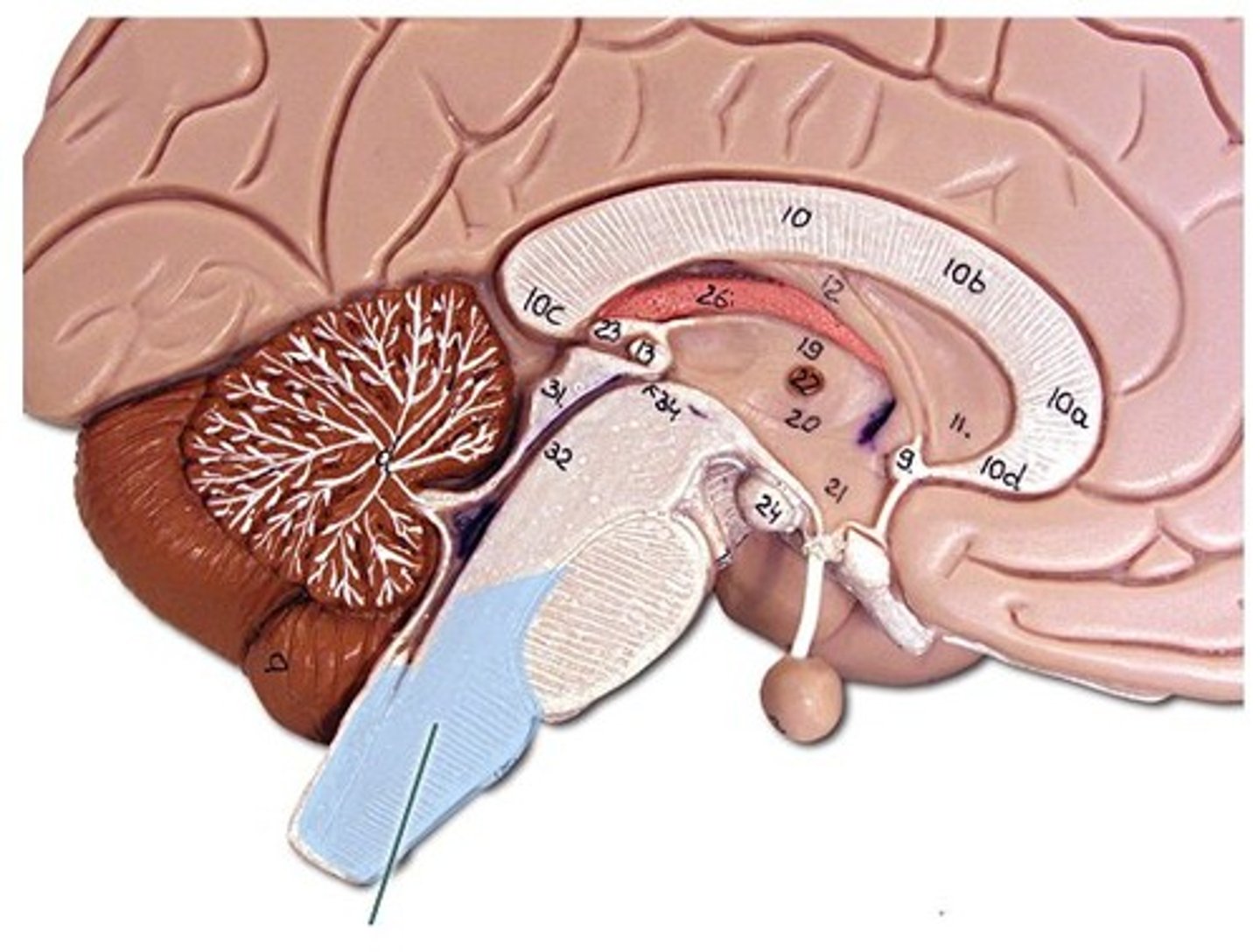
Mid brain
-Largely a relay center for various ear and eye functions.
- Also involved in the sleep/wake cycle.
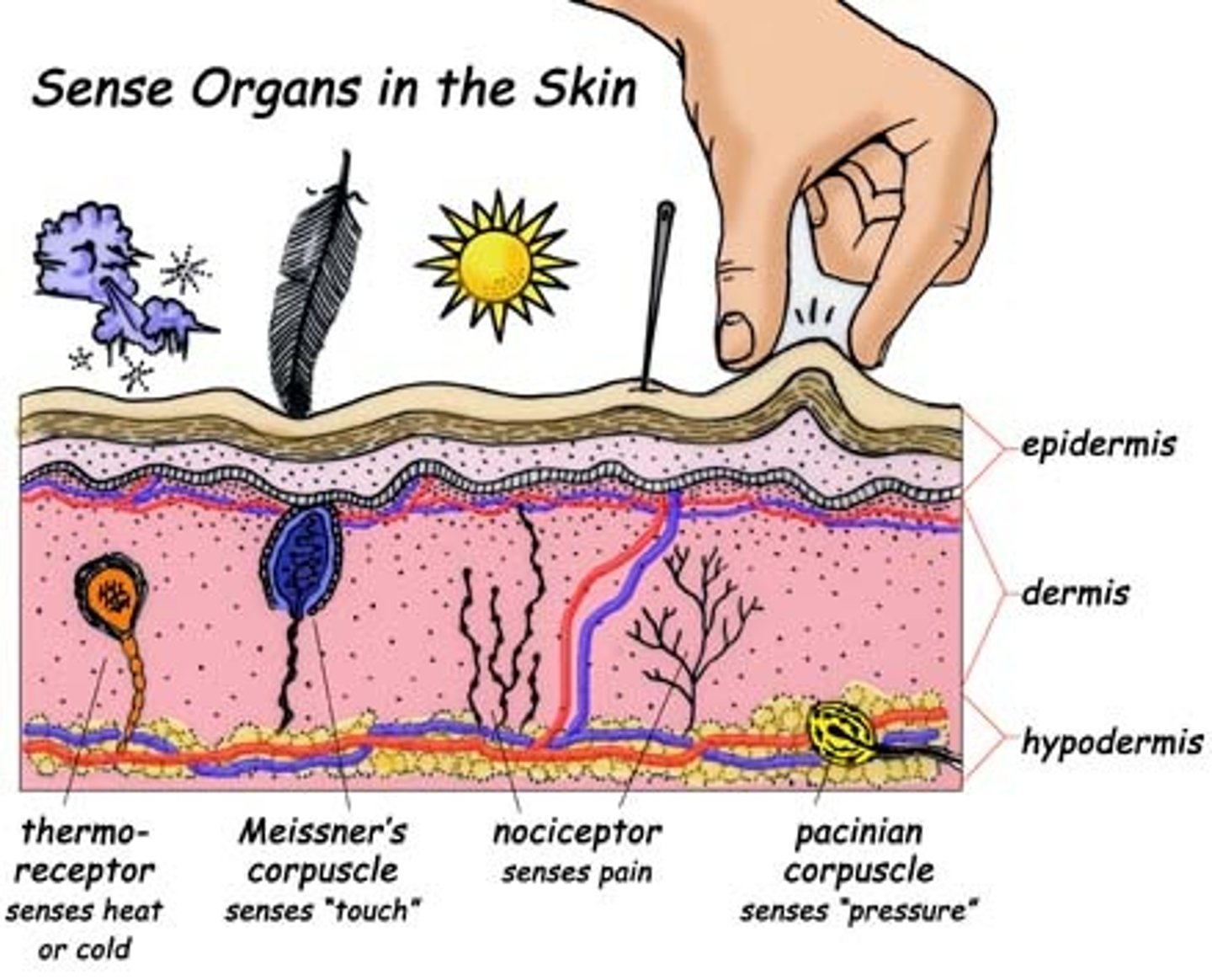
Sense Organs in the skin
Proprioceptors
Found in muscles, tendons, joints, and ears. Respond to limb and body movement.
Taste receptors
Found in tongue, respond to taste
Olfactory receptors
Found in nasal cavity, responds to chemicals in air.
Photorecetors
Found in eye, responds to wavelengths of lights.
Mechanoreceptors
Found in ear. responds to wavelengths if sound.
Multiple inputs
The brain relies on multiple sensory information to make associations with objects. The brain uses multiple inputs to make associations between for example, taste and smell receptors and can determine the taste of the object.
Sensory adaptation
Process by which a sensory receptor becomes accustomed to a stimulus.
Sclera
-The white layer that surrounds the eye.
-It is a thick and tough layer.
-Functions to protect the inner sensitive parts of the eye.

Choroid
-Located beneath the sclera
- Contains a network of blood vessels
-Functions to provide retina with nutrients and oxygen as well as remove metabolic waste.
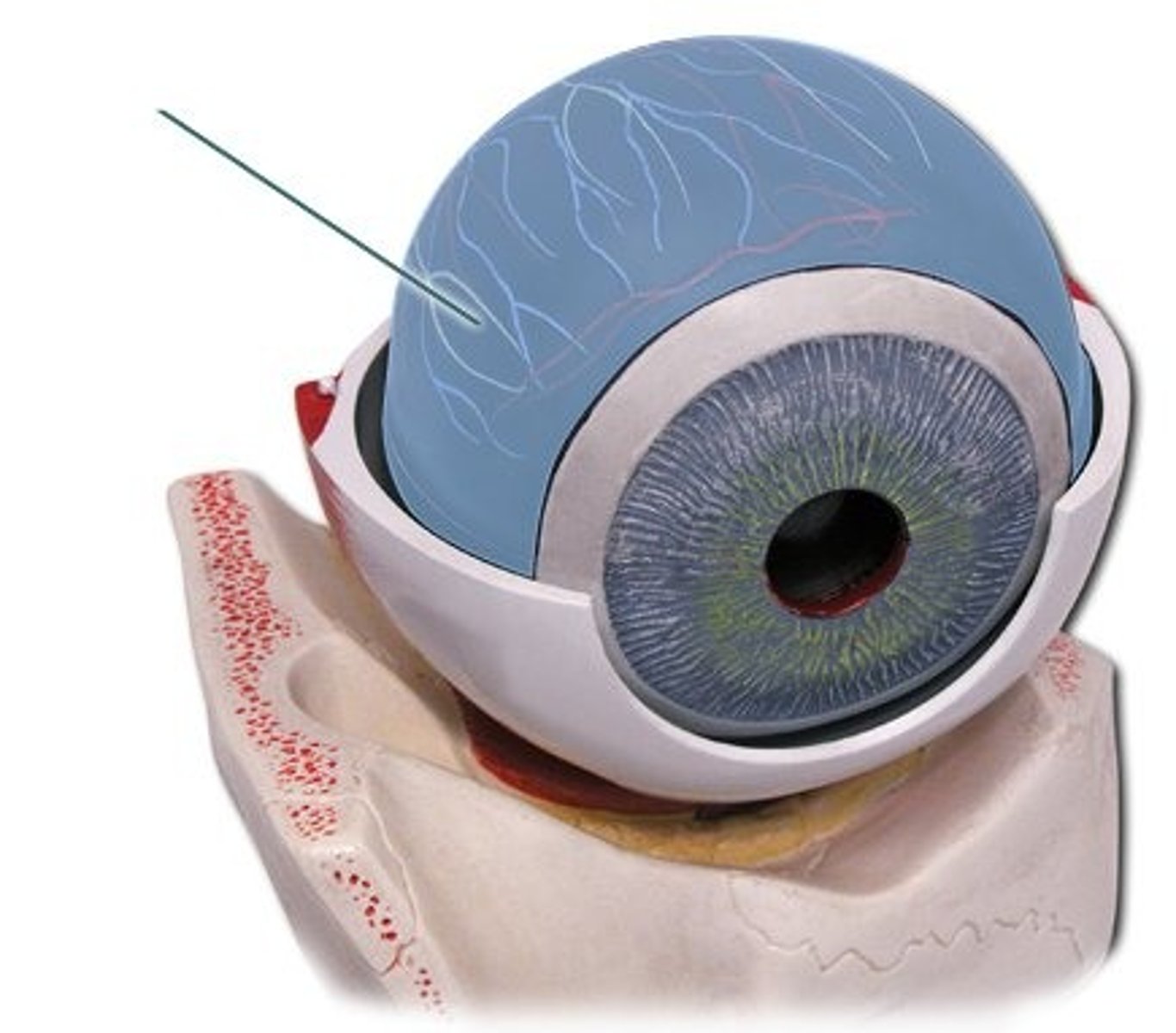
Retina
-The innermost layer of the eye
-Contains two types of light receptors(cones and rods)
-Functions to absorb light and ultimately generate nerve impulses that are sent to the brain.
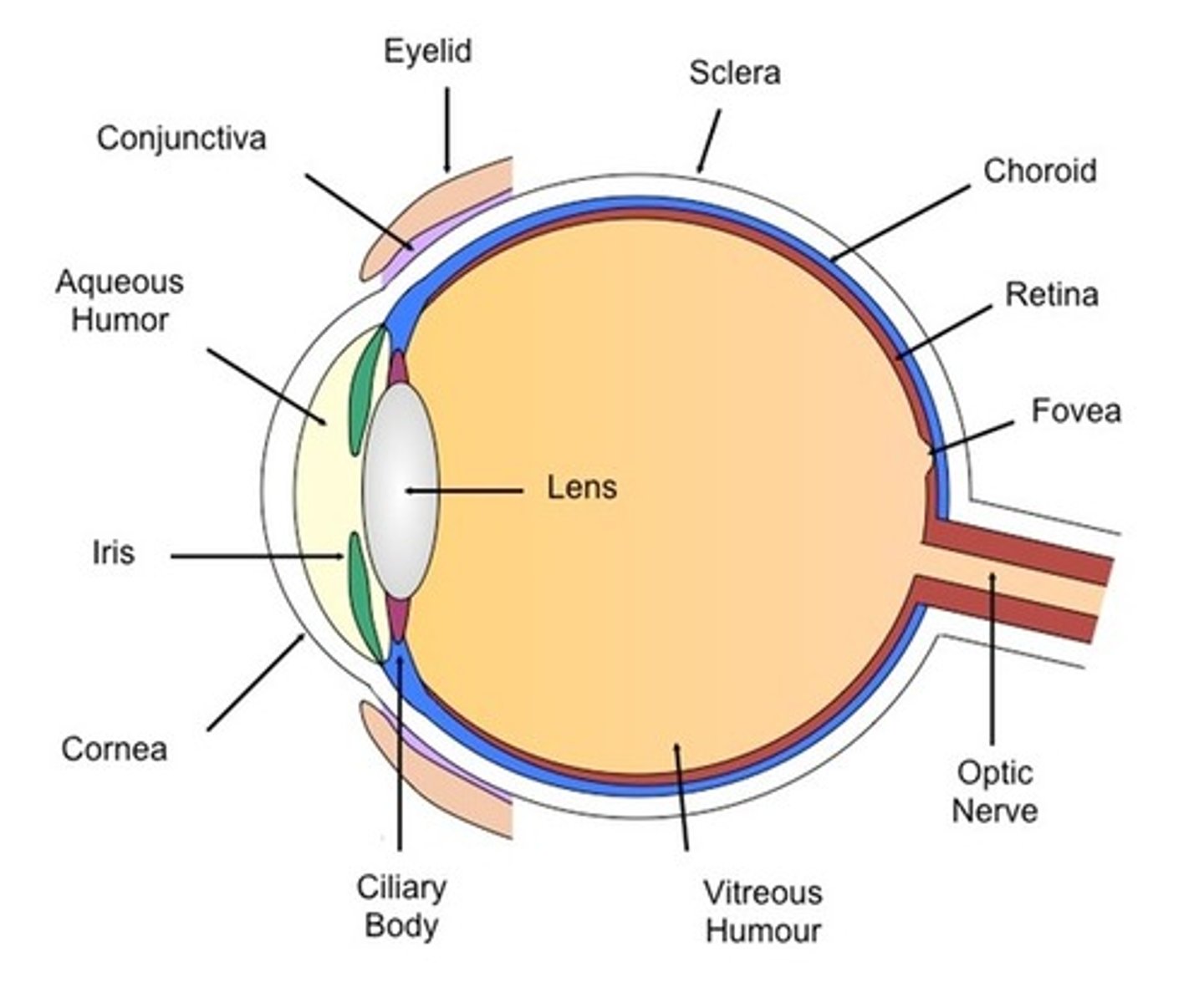
Vitreous Humor
-A clear, gel like substance filling the eyeball
- Located behind the lens
-Functions to maintain the shape and allow light to pass through the eye to the retina.
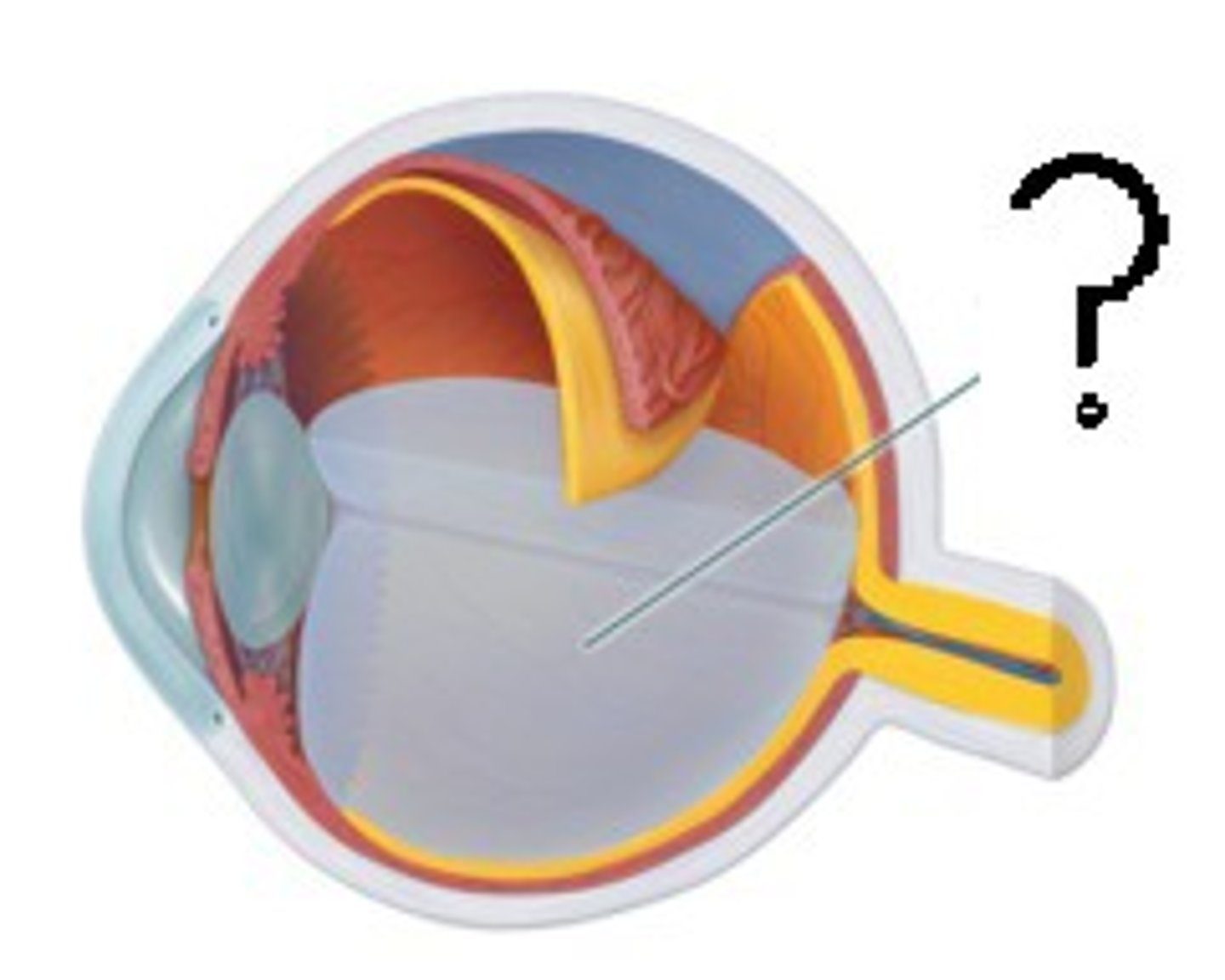
Fovea Centralis
-A section of the retina located above the optic nerve
-Contains densely packed light sensitive cells.
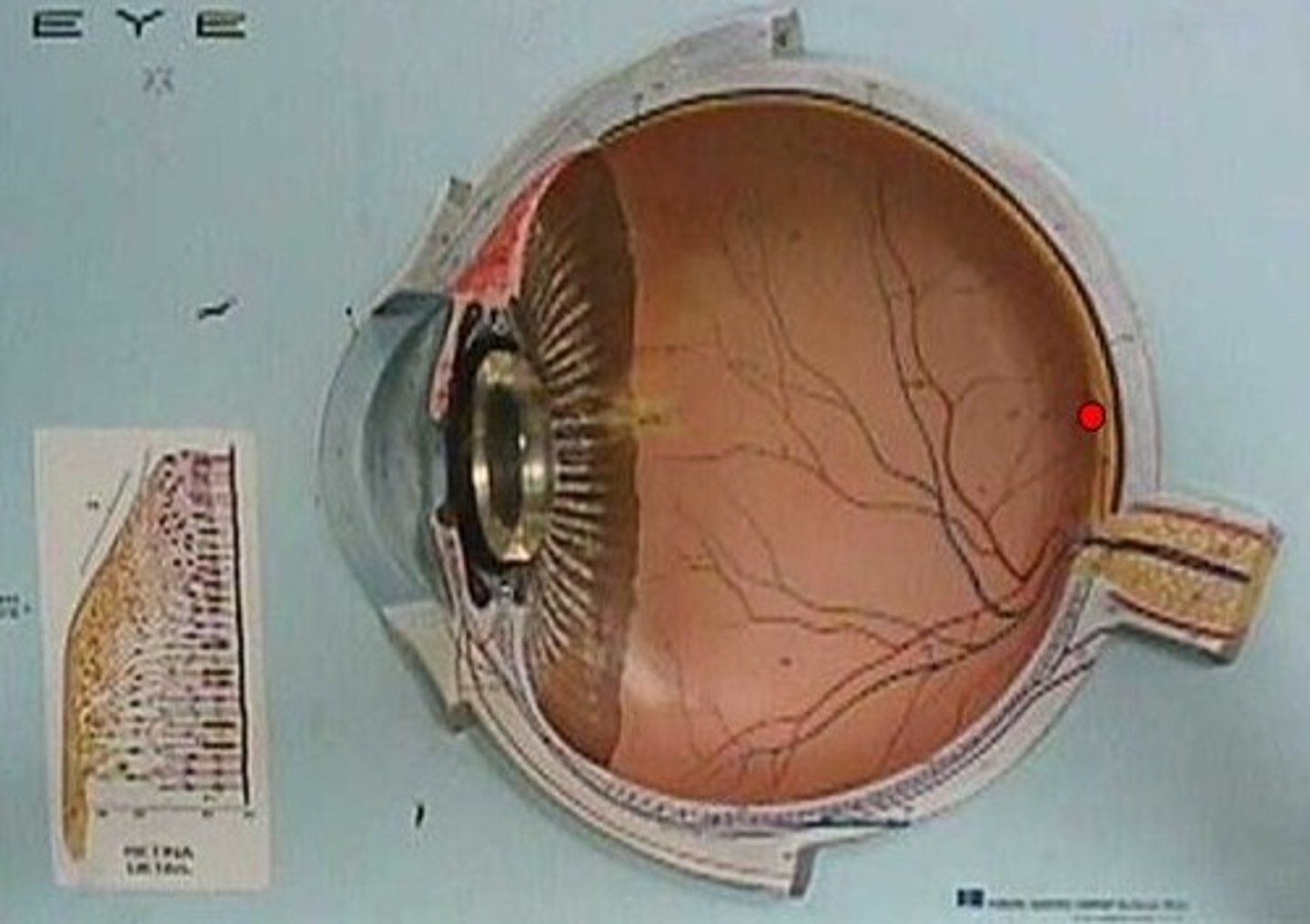
Blind spot
-Located where the optic nerve attaches to the eye
-Blood vessels and neuron axons are present in this area

Optic nerve
-Attaches to the bottom rear of the eye
-Consists of over 1000000 axons
-Functions to carry nerve signals from the eye to the brain
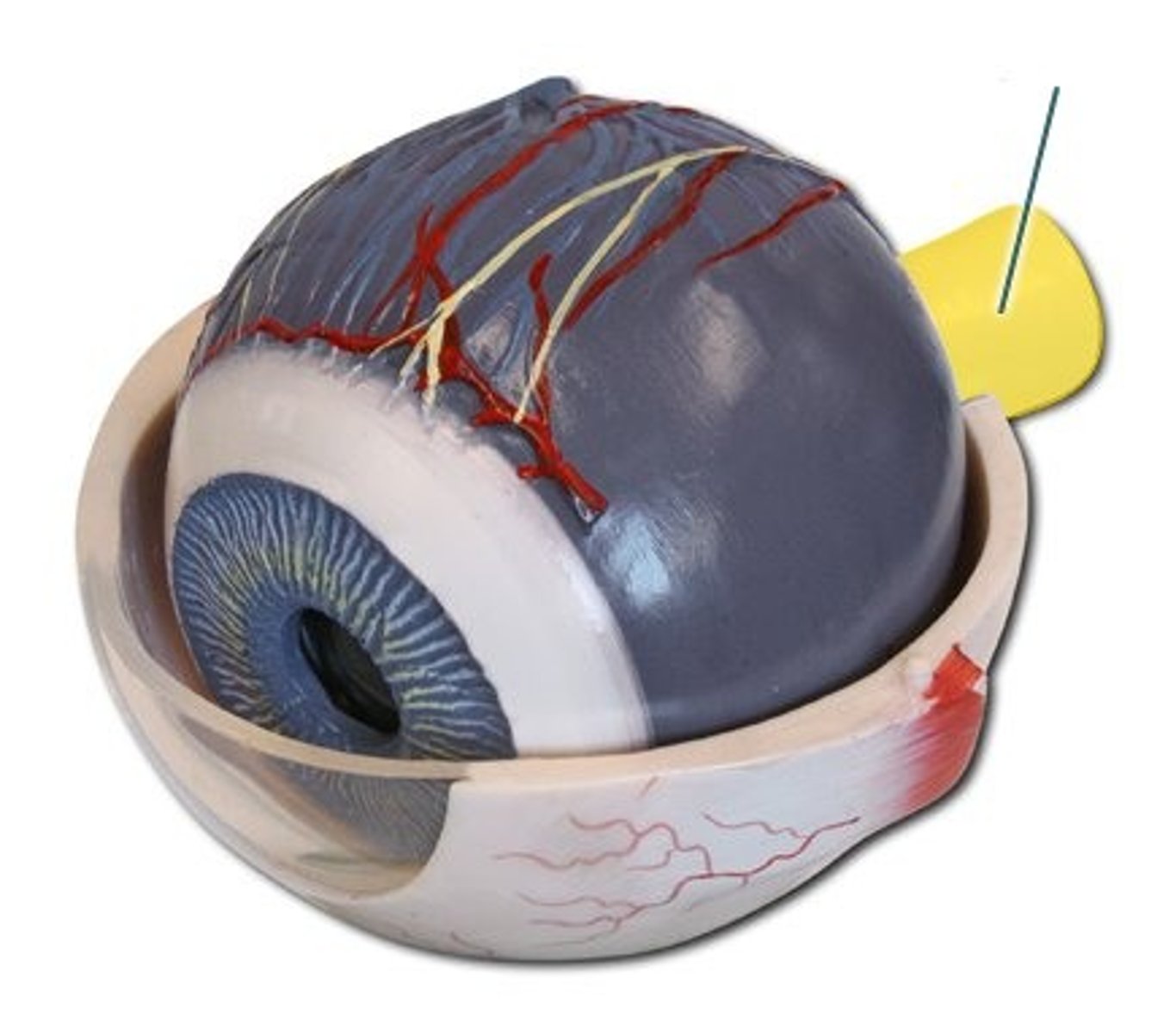
Cornea
-Located in front of the iris and pupil
-A clear, transparent layer
-Functions to retract(bend) light entering the eye

Iris
-The colored structure of the eye
Capable of expending and contracting
-Functions to control the amount of light passing through the pupil.
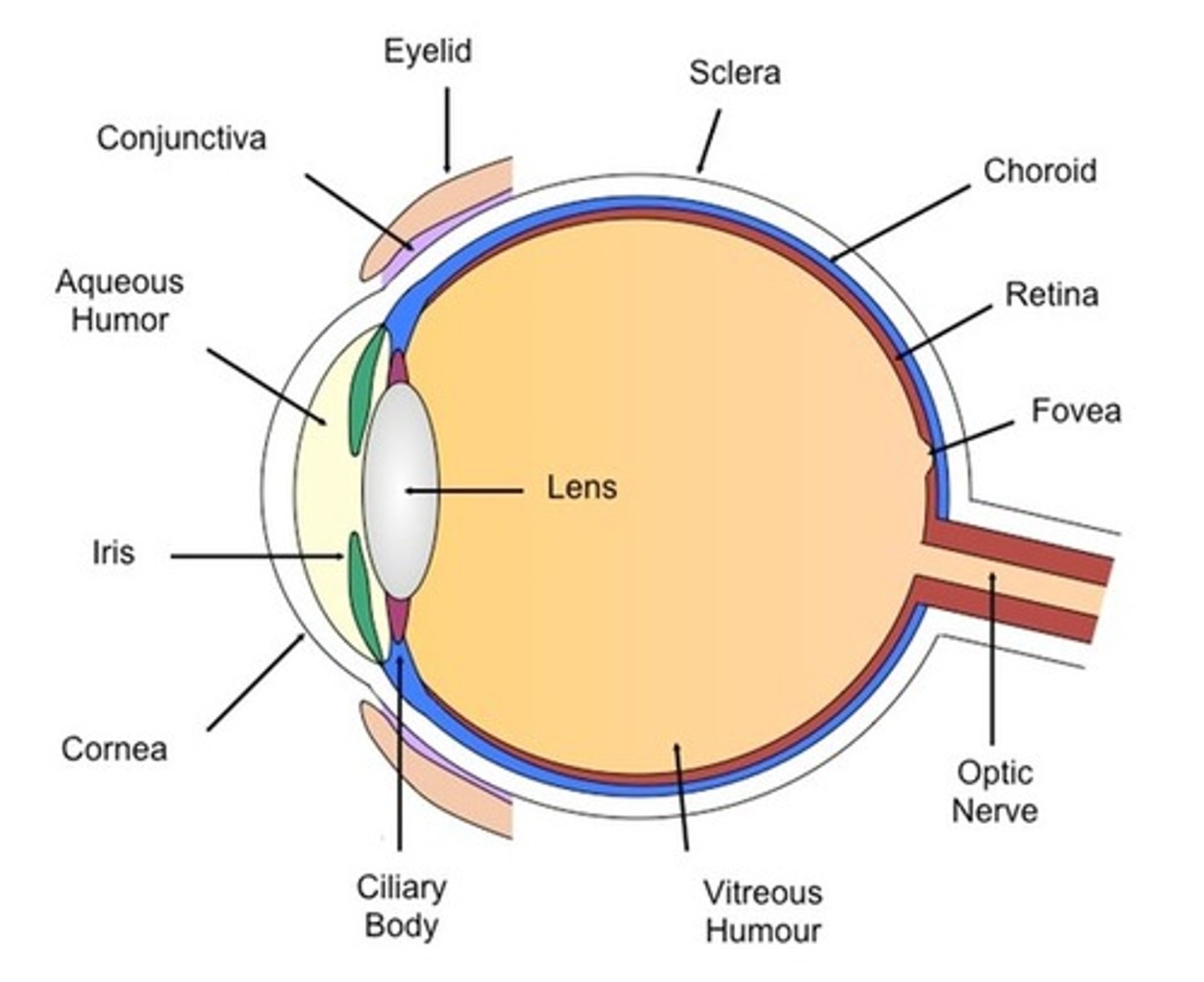
Pupil
-The hole that is formed by the iris
-The iris expanding/constricting results in the pupil constricting/dilating.
-Functions to allow light to enter the eye
Lens
-A crystalline structure located behind the pupil
-Its shape is capable of being altered
-Functions to refract light such that it is focused on the retina
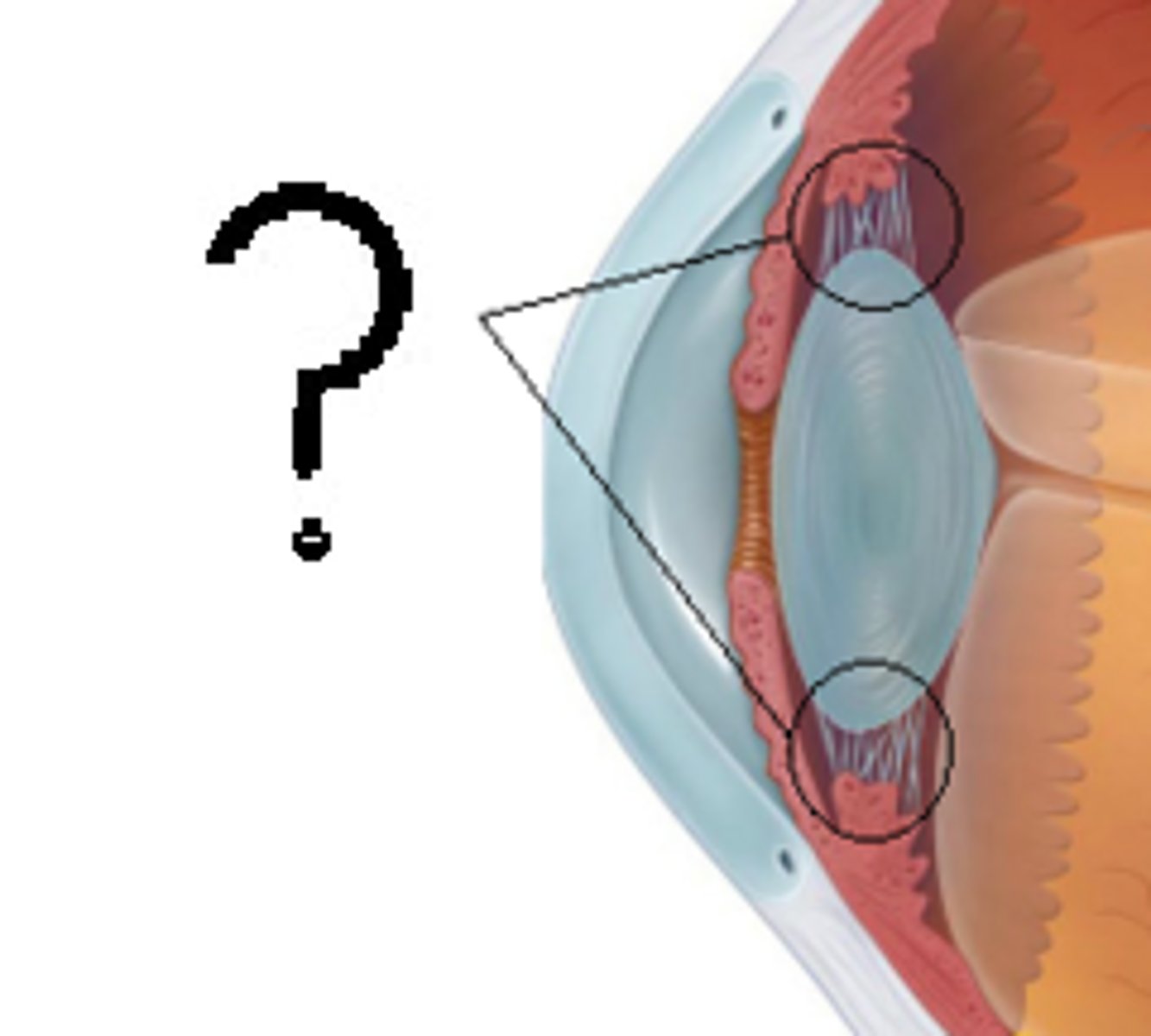
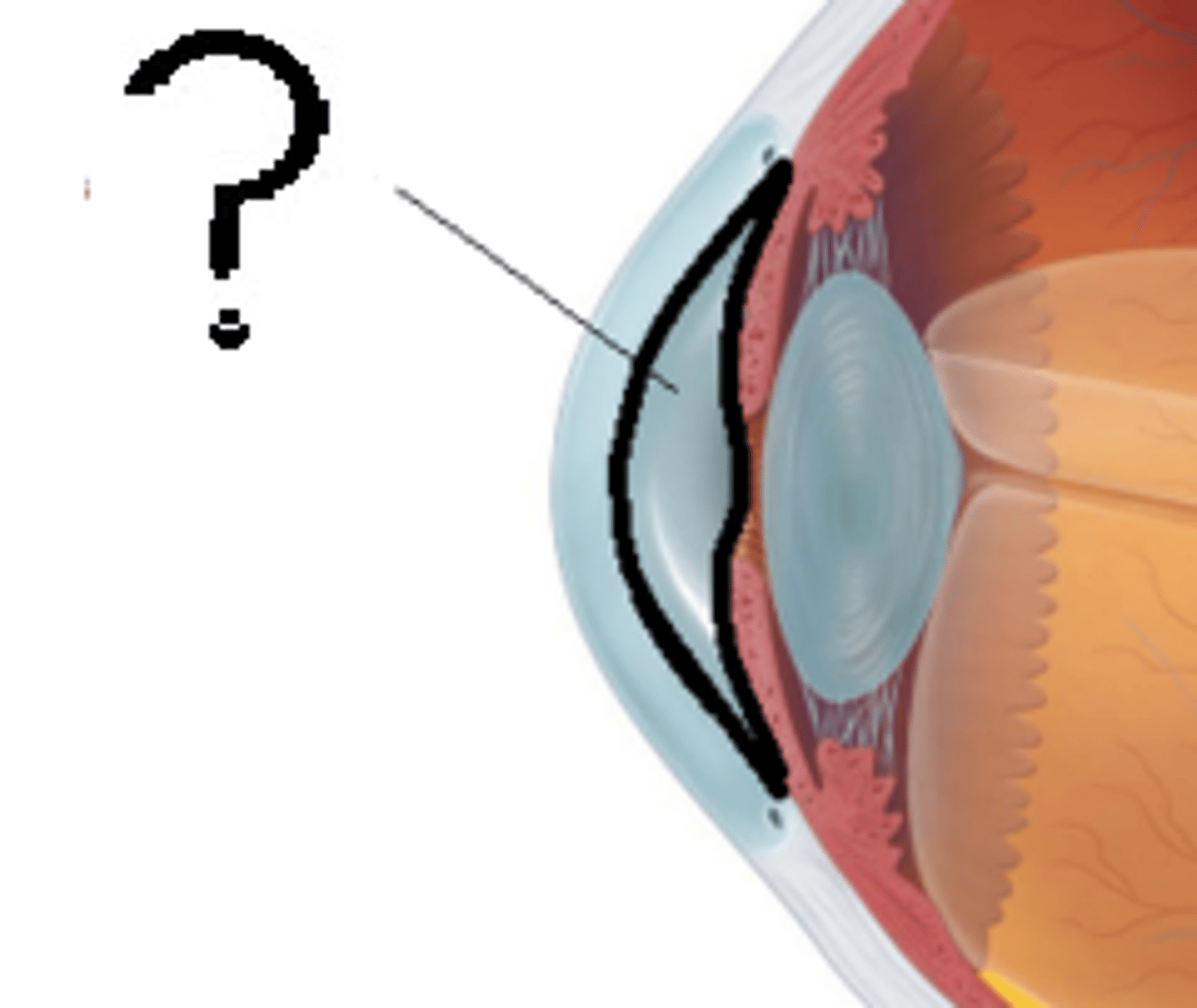
Ciliary body
-Attaches to the lens
-Contains suspensory ligaments and ciliary muscles
-Functions to control the shape of the lens and produces the aqueous humor
Aqueous humor
-The fluid that fills the space between the lens and the cornea
-Functions to supply the cells of the cornea and lens with nutrients and oxygen
pigmented epithelium of retina
-Firmly attached to the underlying choroid
-Its pigment depends on the animal type
-Shield retina from excess incoming light by reflecting light out of the eye
-Back of the eye, light hits this part of the retina first
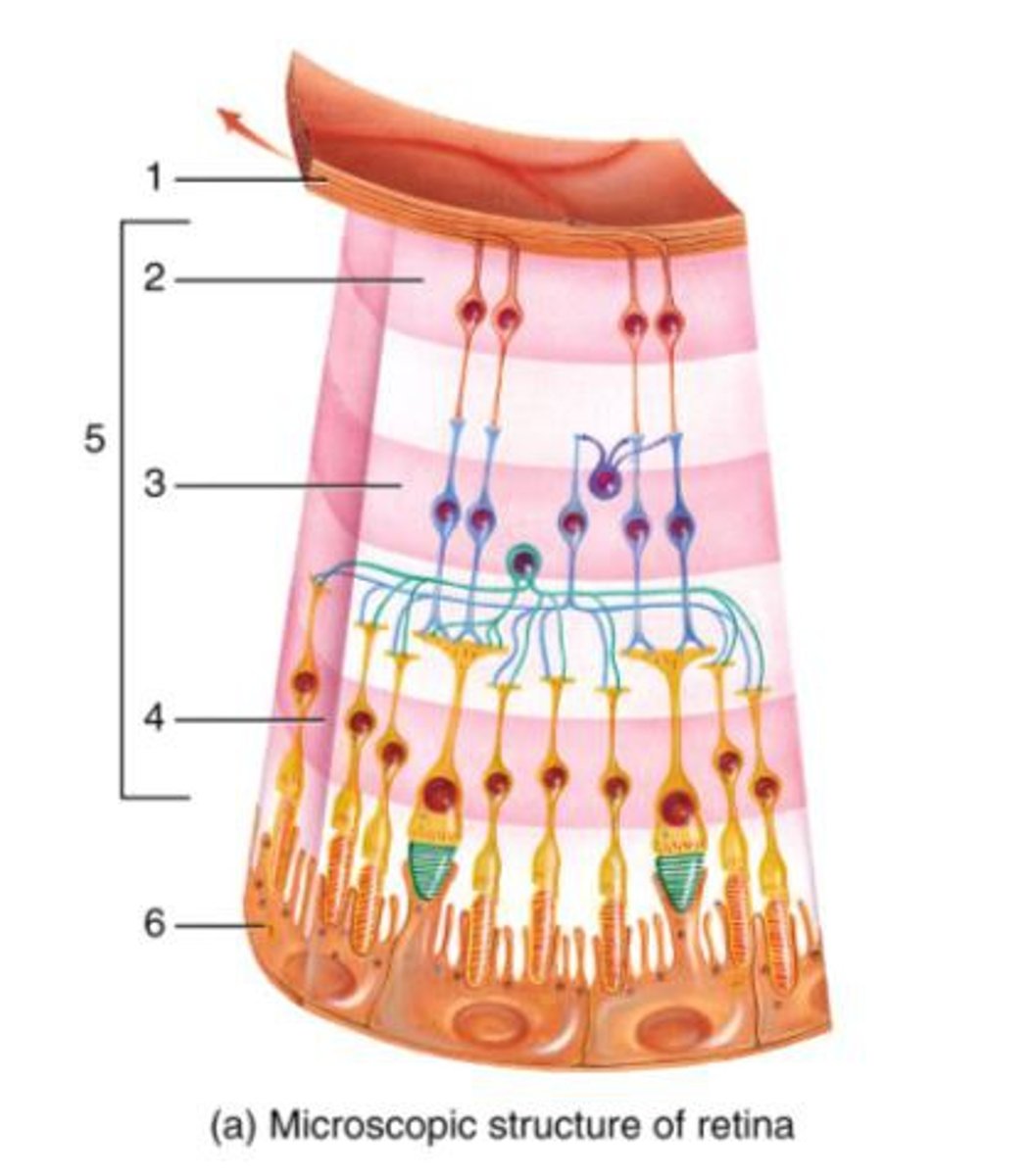
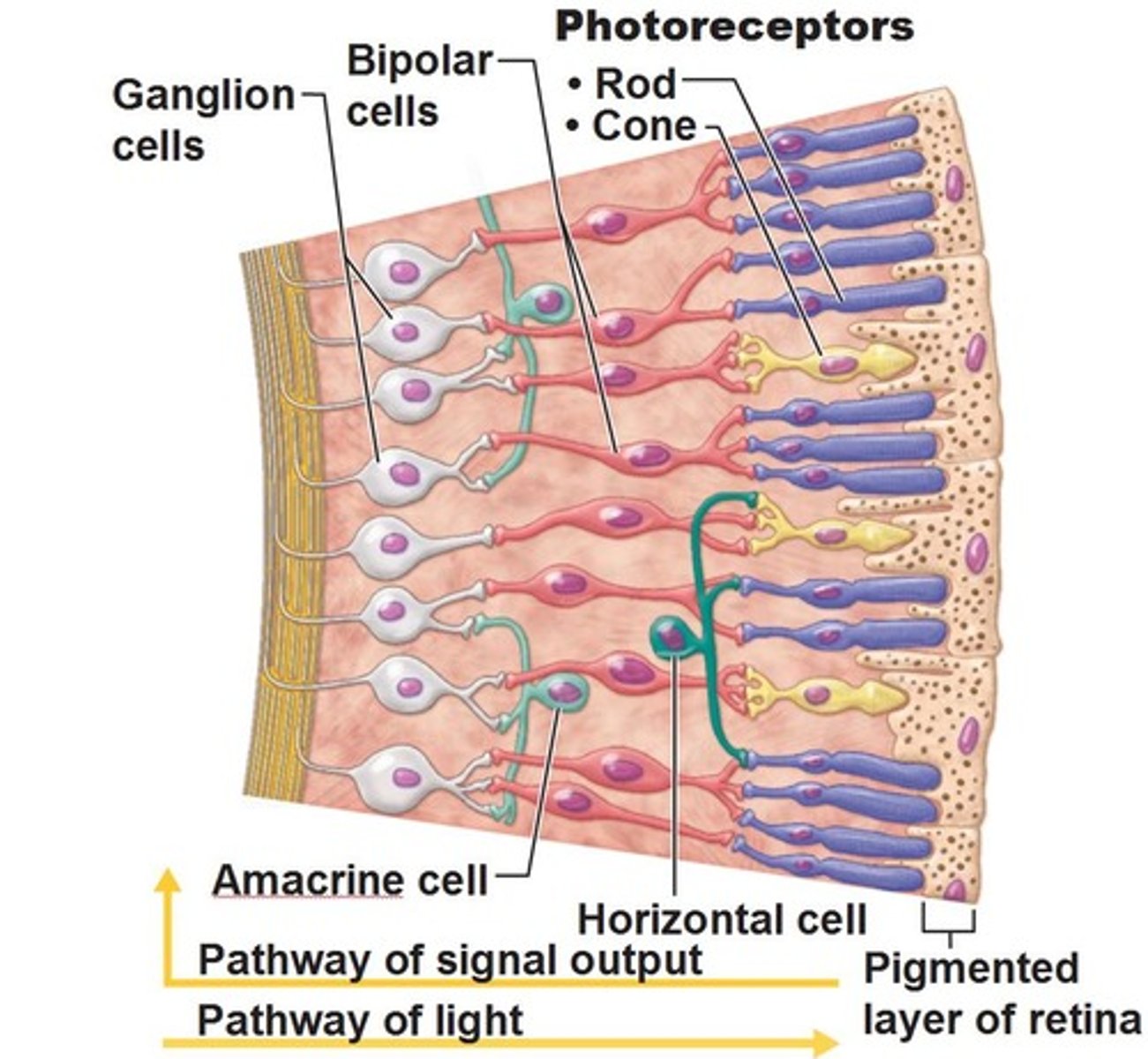
Photoreceptors
-Light sensitive cells
-Known as rods and cones
-Respond to light and generates nerve impulse
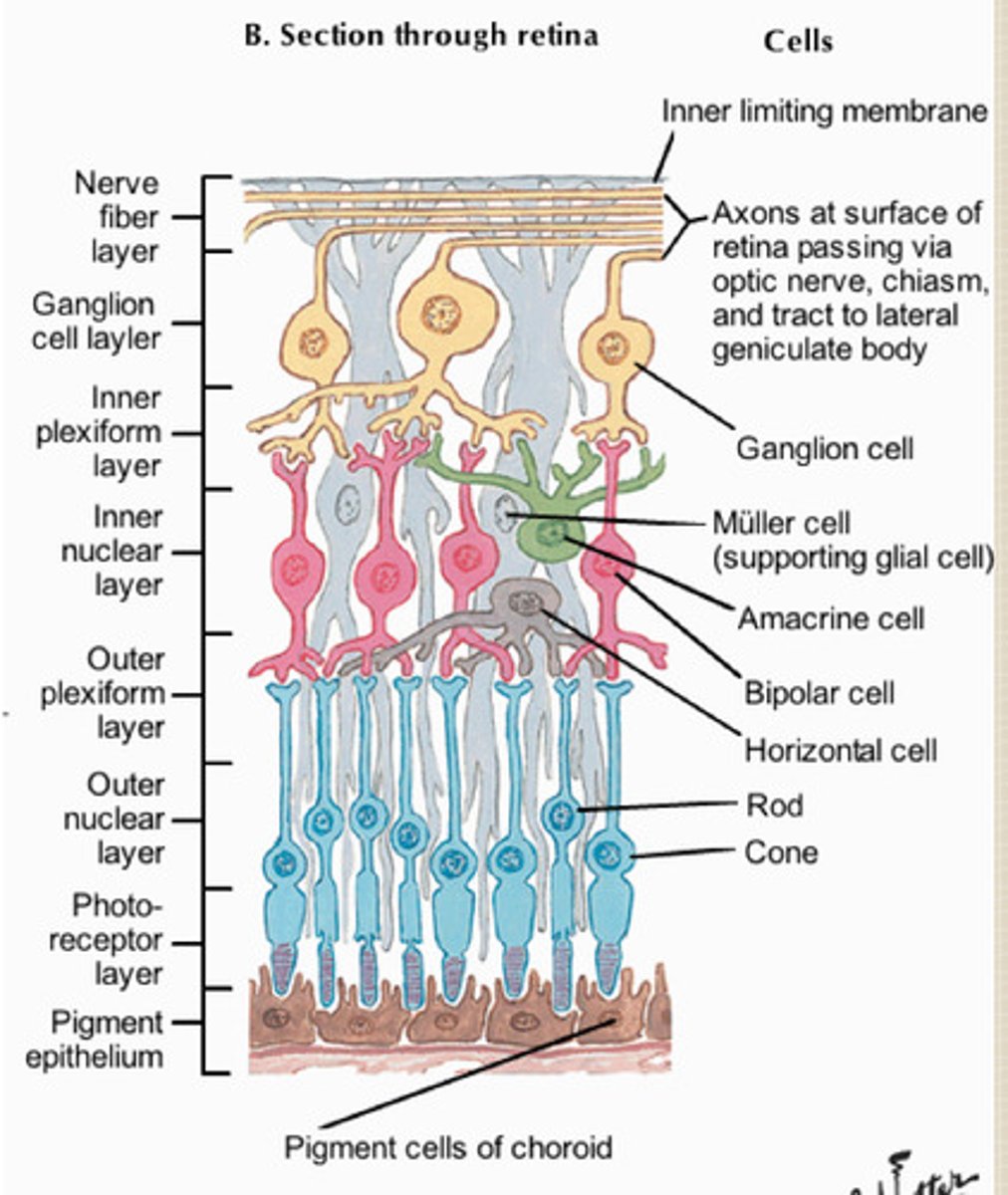
Bipolar cells
-Located in front of the photoreceptors
-Carry nerve impulse
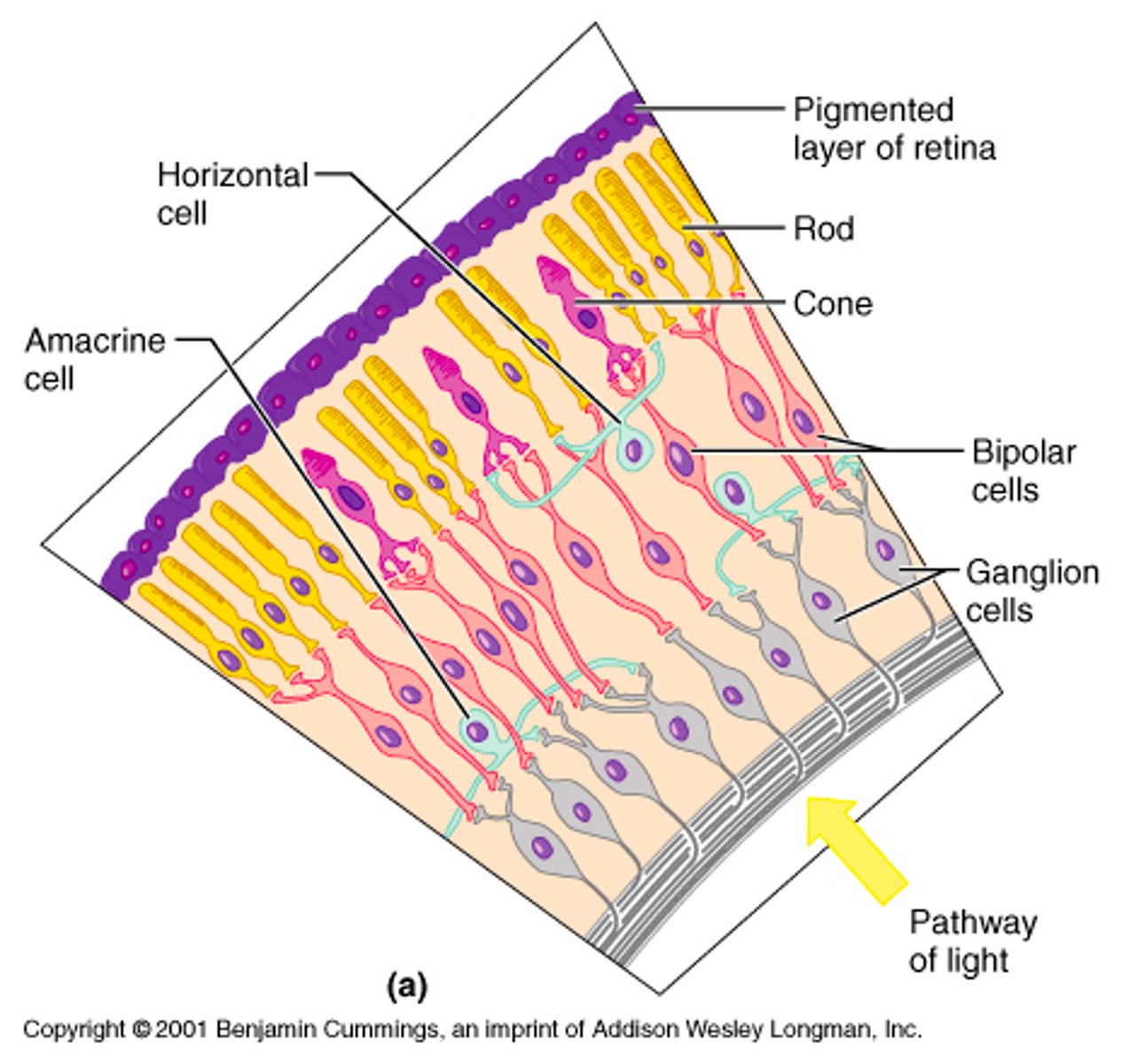
Optic nerve cells/ganglion
The foremost layer of the retina
-Carries nerve impulse
Rods
-Responds to low-intensity light
-Shades
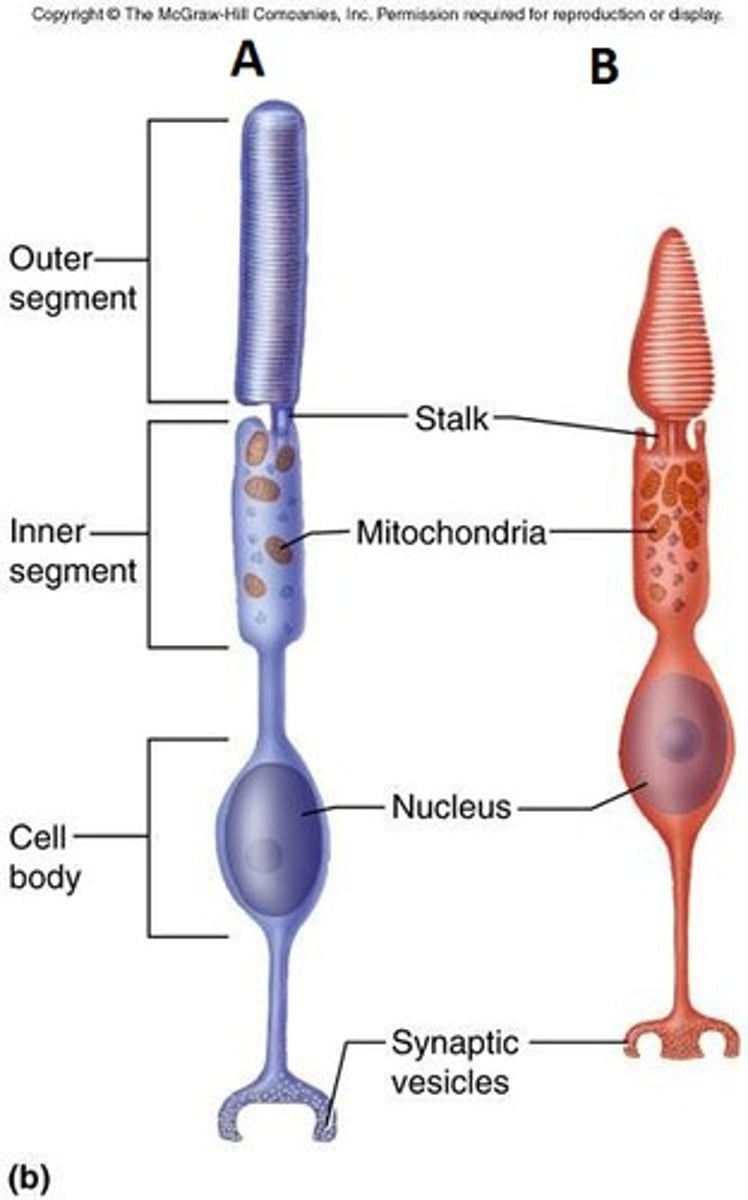
Cones
-Responds to high-intensity light and color
-Blue, green, red
-Mainly found in the fovea centralis
Nerve impulse generation
-Impulse generation in a rod is due to the light-sensitive pigment known as rhodopsin
Nerve impulse with rhodopsin hitting eye
1. light enters the eyes and strikes the rhodopsin pigment
2. Rhodopsin splits into pigment portion and opsin
3. This splitting changes the memebrane chemistry of a rod and generates a nerve imsulse
Accommodation
-This is when adjustments are made to the lens to fucus objects that are near or far
-This is due to the ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments
Near object lens
1. Ciliary muscles contract
2. Suspensory ligaments slacken
3. Lens becomes more round
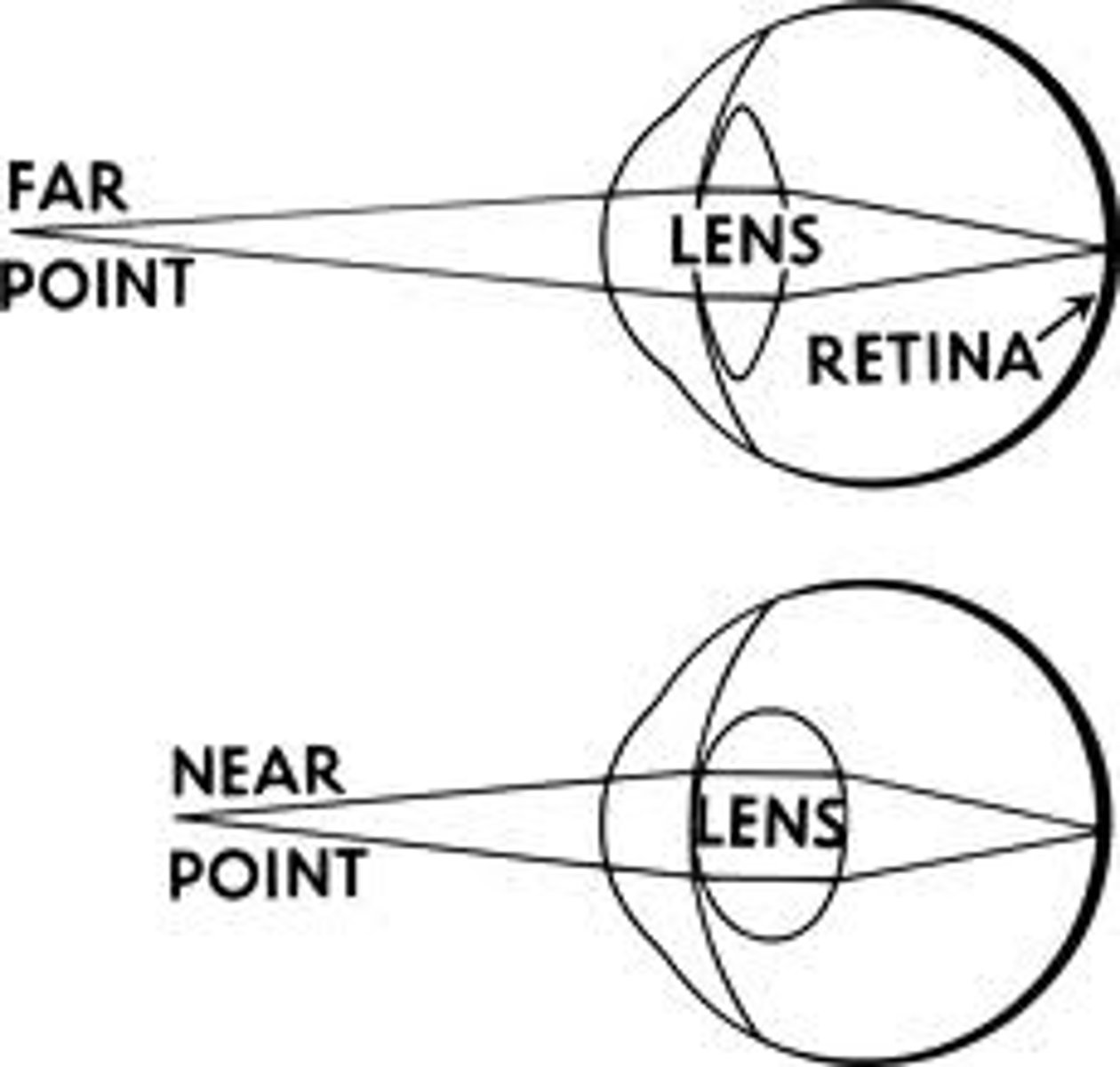
Far objects lens
1. Ciliary muscles relax
2. Sensory ligaments tighten
3. Lens becomes more flat
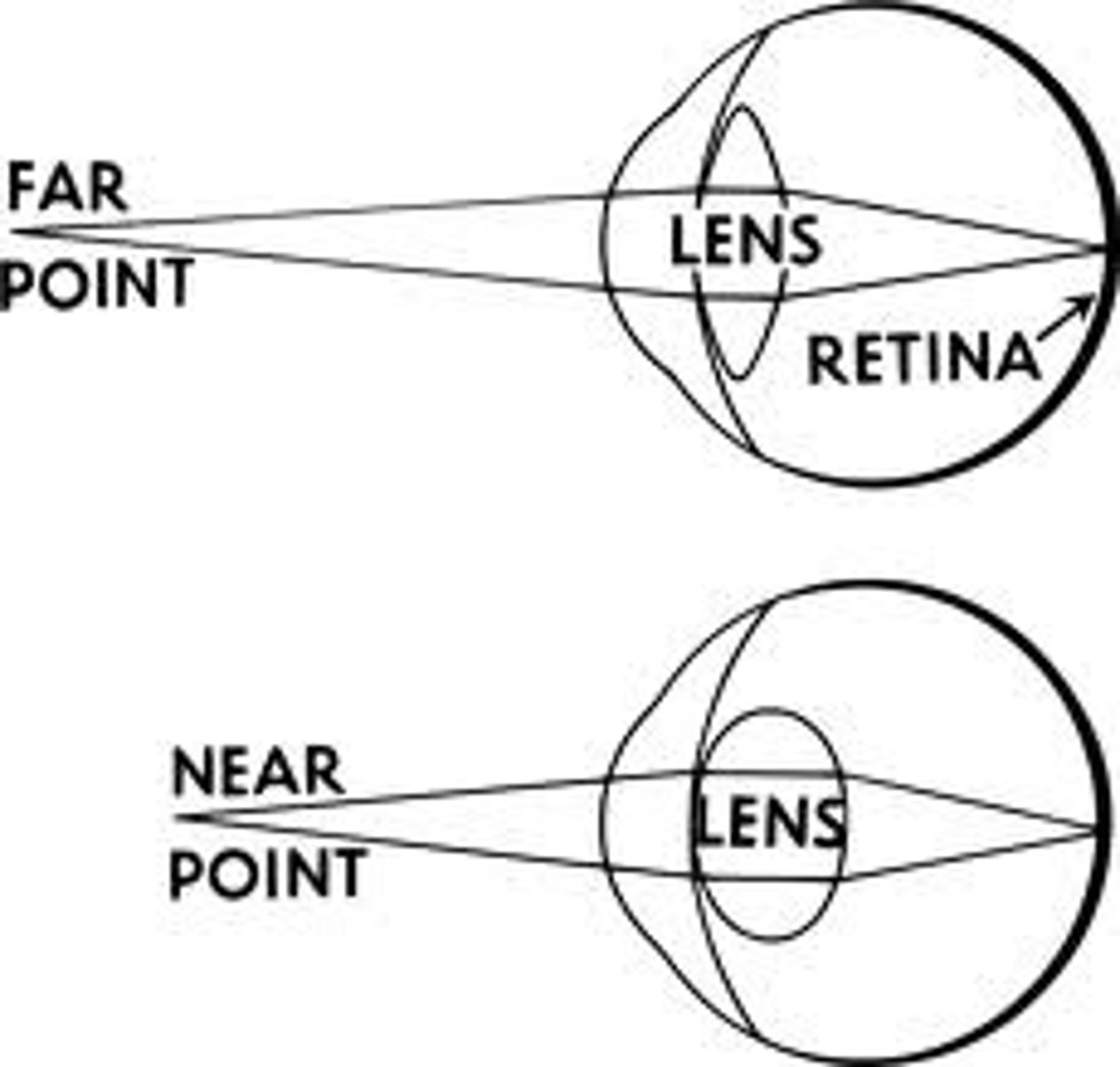
Myopia
-Nearsightedness
-The image is focused in front of the retina
-Difficulty focusing on far objects
-Treated with concave lens
-Could be caused by cornea being too round
Hyperopia
-Farsightedness
-Image focused behind retina
-Could be caused by cornea being too flat
- Will have trouble focusing on near obejcts
-Treated with convexe lens
Astigmatism
-An irregular shape of the cornea or lens
-Prevents light from properly focusing on the retina
-Treat with proper corrective lens
Glaucoma
-A build up of aqueous humor due to blocked drainage ducts
-Creates pressure in the eye and can damage retina cells
-Treated with chemicals to open blocked ducts or laser surgery
Cataracts
-The lens of the eye becomes opaque
-Prevents light from passing through to the retina
-Can be removed with sound vibrations
Lasik surgery can also be used to treat
1. Cornea flap is created with a microkeratome
2. Cornea flap is folded back
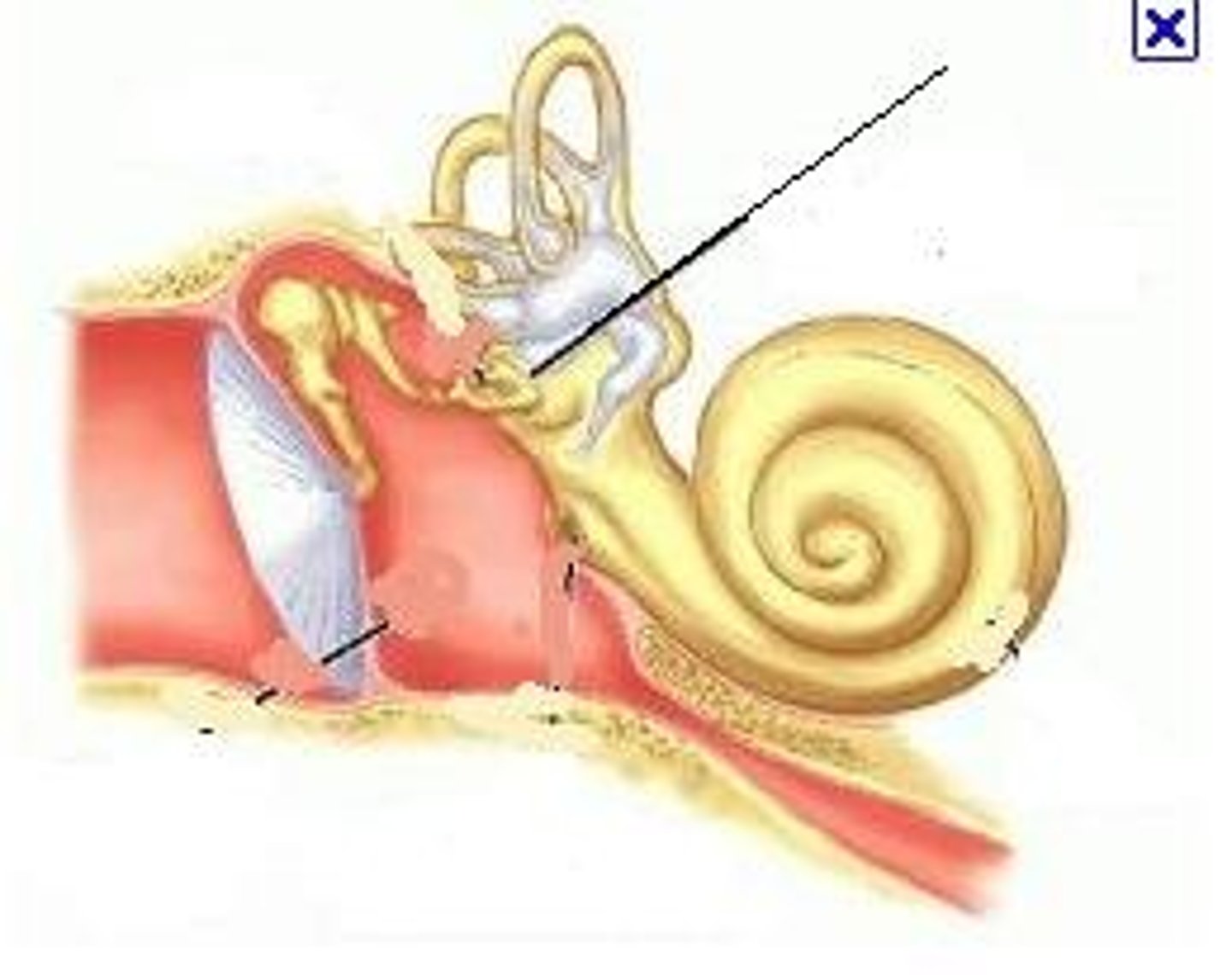
Outer ear
Pinna
-Gathers sound waves and directs them into the auditory canal
Auditory Canal
-Directs sound waves to the lymphatic membrane (ear drum)
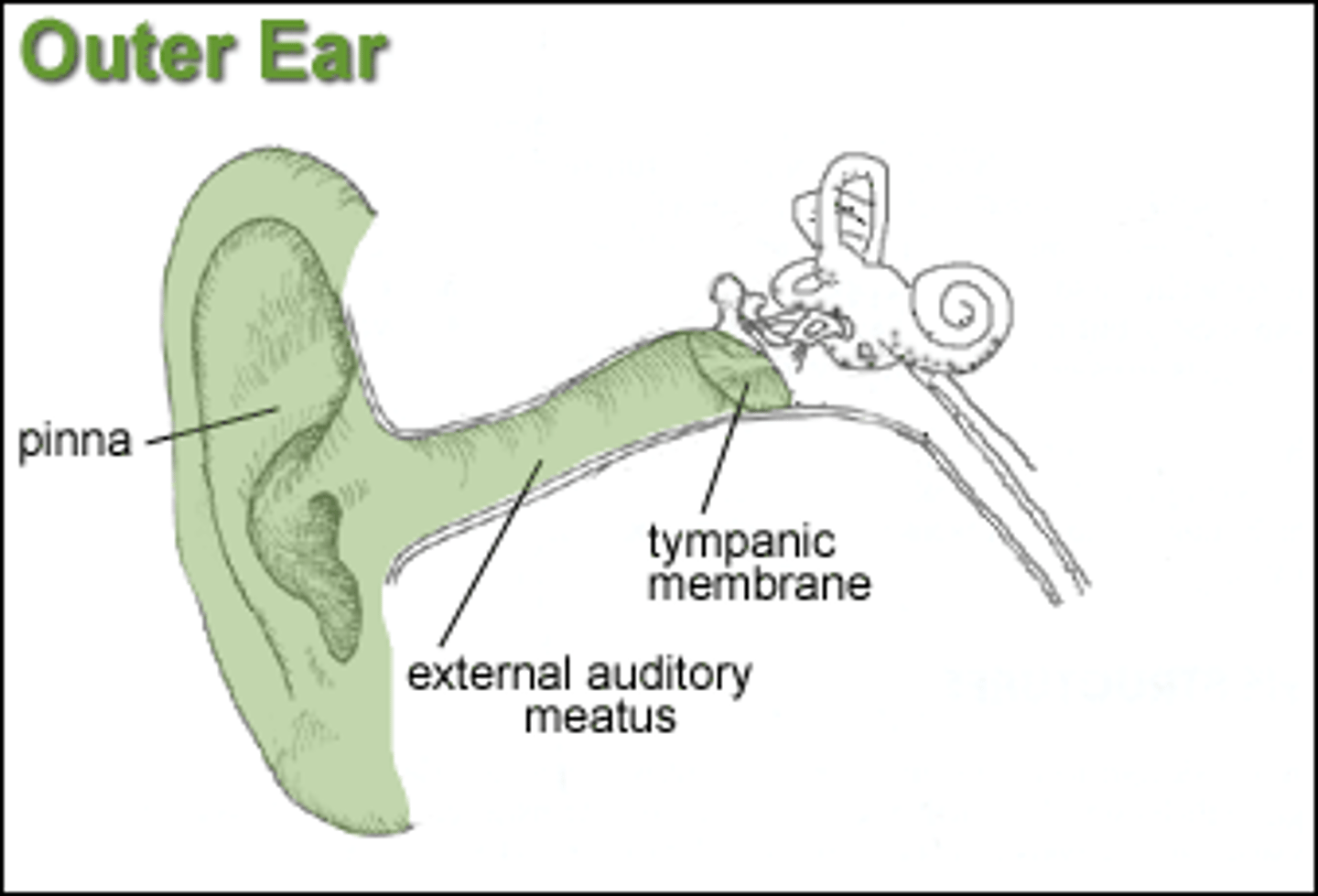
Tympanic membrane
-Converts sound energy into mechanical energy(movement of ossicles)
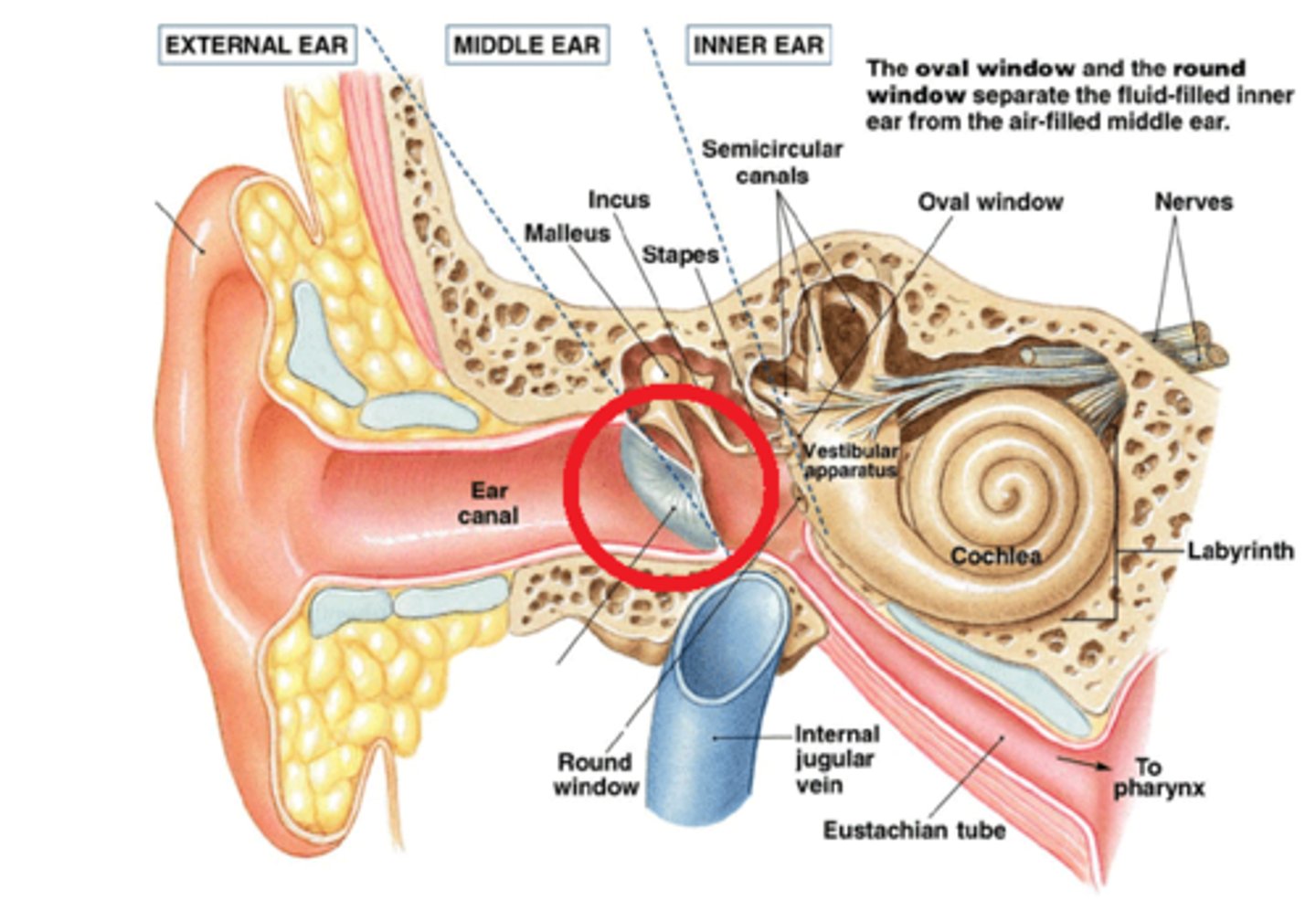
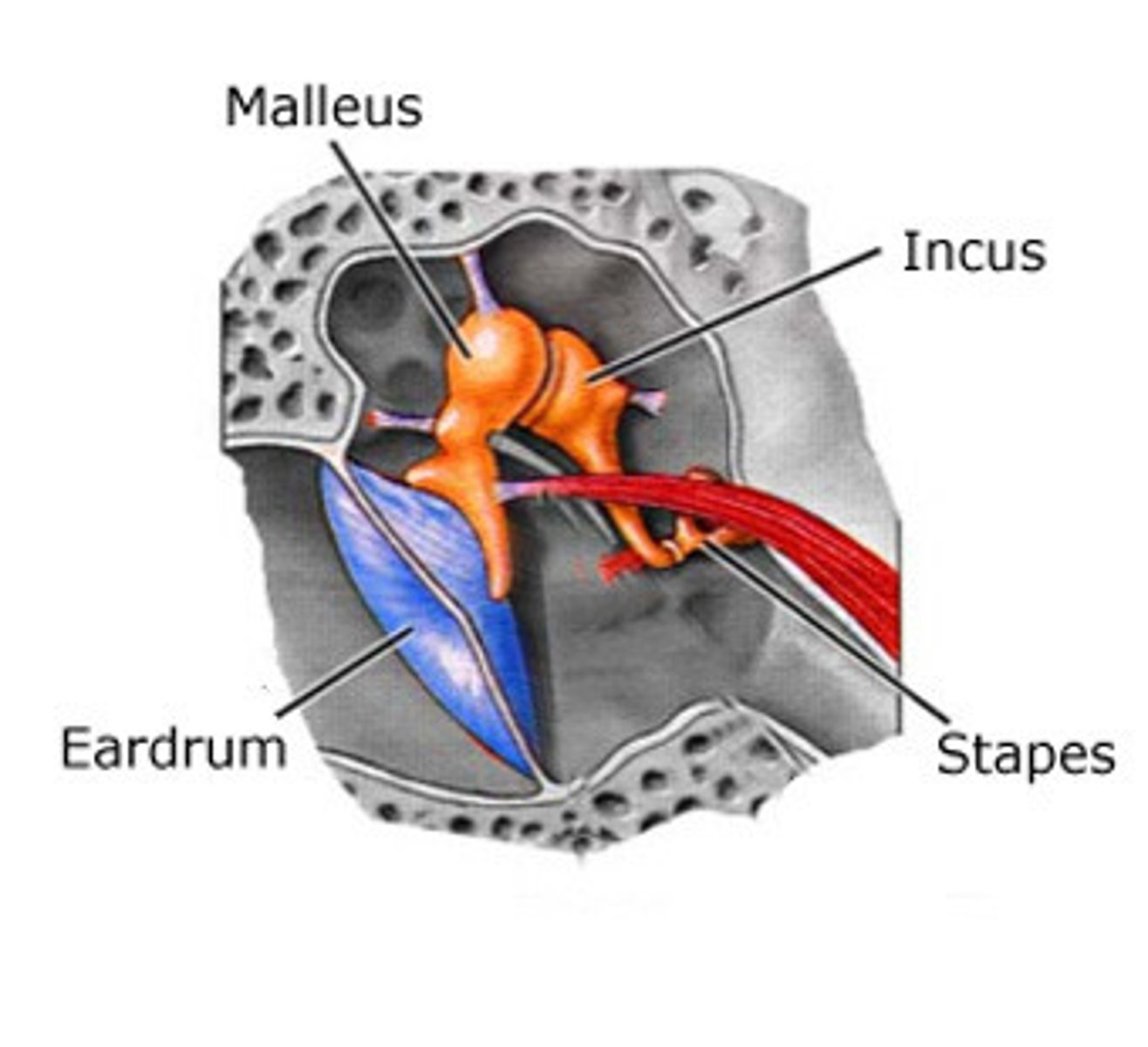
Ossicles
Transfer and amplify tympanic membrane vibrations to the oval window
Malleus(hammer) -> Incus(anvil) -> Stapes(Sturip)
Oval window
Transfers vibrations from ossicles to the cochlea in the major act of amplification