Biological molecules Chapters 1 and 2
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
What is a monomer?
A small, basic molecular unit that can form a polymer
What is a polymer?
They are large, complex molecules composed of long chains of monomers joined together
What is a condensation reaction?
It forms a chemical bond between monomers, releasing a molecule of water
What is a hydrolysis reaction?
It involves breaking the chemical bonds between monomers using a water molecule
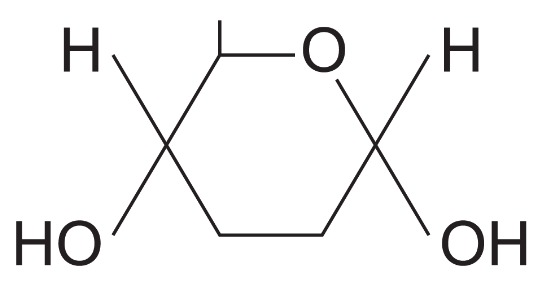
What isomer of glucose is this?
Alpha glucose
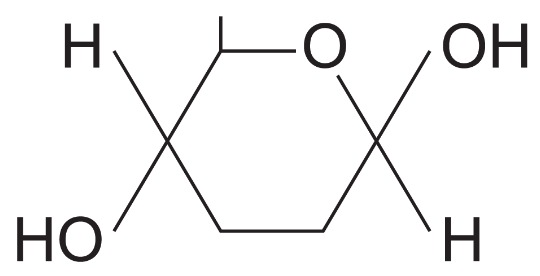
What isomer of glucose is this?
Beta glucose
What are the four isomers of glucose?
Alpha glucose, Beta glucose, fructose and galactose
What is a disaccharide?
When two monosaccharides join together by condensation reactions
What is a glycosidic bond?
It forms between the two monosaccharides as a molecule of water is released
What does alpha glucose + alpha glucose make?
Maltose
What two monomers make sucrose?
Alpha glucose + fructose
What two monomers make lactose?
Alpha glucose + galactose
How do you test for reducing sugars?
Add Benedict’s reagent to a sample and heat it in a water bath
Sample forms green → yellow →Orange →brick red precipitate
If it remains blue then theres no reducing sugar present
How do you test for non-reducing sugars?
Heat sample with Benedict’s reagent
Sample will stay blue
Heat a new sample with dilute hydrochloric acid then neutralise the sample by adding sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Heat sample with Benedict’s reagent
Sample forms green → yellow →Orange →brick red precipitate
If it remains blue then theres no reducing sugar present
What is a polysaccharide?
It is formed when more than two monosaccharides are joined together by condensation reactions
What is starch?
It is a mixture of two polysaccharides of alpha-glucose — amylose and amylopectin
What is the structure of Amylose?
It is a long, unbranched chain of alpha-glucose. The angles of glycosidic bonds give it a coiled structure, almost like a cylinder
What is the structure of Amylopectin?
It is a long, branched chain of alpha-glucose.
What does the structure of amylose do to help it?
It is compact, so it is a good storage molecule because you can fit more in a small space
What does the structure of amylopectin do to help it?
Its side branches allow the enzymes that break down the molecule to get at the glycosidic bonds easily. This means that glucose can be released quickly.
What makes starch good for storage?
It is insoluble in water and doesn’t affect water potential.
It doesn’t cause water to enter the cells by osmosis
It is a large molecule so it can’t leave the cell
Where is starch found?
Plants only:
Starch grains
Seeds
Storage organs
What is the the structure of Glycogen?
Its structure is very similar to that of amylopectin, except that it has loads more side branches
How does the structure of Glycogen help it for its function?
Loads of branches means that stored glucose can be released quickly
It is compact so it’s good for storage
What is the structure of Cellulose?
It is made of long, unbranched chains of Beta-glucose in parallel to each other
When beta-glucose molecules bond, they form straight cellulose chains.
These cellulose chains are linked by hydrogen bonds to form strong fibres called micofibrils
How does the structure of cellulose it for its function?
The strong fibres mean it provides structural support for cells
What test is used for starch?
Iodine
the test sample and iodine is dissolved in potassium iodide solution
What colours shows starch is present?
Browny-orange colour shows no starch
Dark,blue-black colour shows starch
What are the properties of Lipids?
Contain Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen
The proportion of carbon to oxygen and hydrogen is smaller than in carbs
They are insoluble in water
They are soluble in organic solvents such as alcohols and acetone
What are roles of lipids?
Flexible cell membranes
Source of energy
Waterproofing
Insulation
Protection
How do you test for lipids?
Add 2cm³ of the sample being tested and 5cm³ of ethanol
Shake tube
Add 5cm³ of water and shake
A white emulsion should appear if it is present
What is the structure of triglycerides?
They have 3 fatty acids combined with glycerol
What bond is made in Triglycerides?
Ester bond
What does unsaturated fat mean?
When there is a double bond between two carbons
What is the structure of phospholipids?
One fatty acid is replaced by a phosphate group
Fatty acid molecules repel water and phosphate molecules attract water
How does the structure of phospholipids help its function?
They form a bilayer with cell-surface membrane
Form glycolipids important in cell recognition
What makes up polypeptides?
Amino acids
What is the general formula for amino acids?
NH2.RCH.COOH
How many essential amino acids are there?
8
What is the primary structure of proteins?
The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
What is the secondary structure of proteins?
Polypeptide chains are either coiled into a spiral alpha-helix or linked to form beta-pleated sheets
What is the structure of alpha-helixs?
The coils of the chain are held together by hydrogen bonds that form between the amine group and carboxyl group of different amino acids
What is the structure of beta-pleated sheets and what does it do to help its function?
Hydrogen bonds form between the CO and NH group of one chain and the NH and CO groups of neighboring chains.
This gives it high tensile strength
What is the tertiary structure of proteins?
The alpha-helices of the secondary structure can be twisted and folded to give 3D structures of each protein
What bonds are formed in the tertiary structure of proteins?
Disulfide bridges - Which are fairly strong and therefore not broken easily.
Ionic bonds - Formed between any CO and NH groups that are not involved in the forming of peptide bonds. These can be broken easier by changes in pH.
Hydrogen bonds - Which are numerous and easily broken.
There are also hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions
What is the quaternary structure of proteins?
They consist of more than one polypeptide chain and has other inorganic substances incorporated
What is Haemoglobin made of?
Made of 4 polypeptide chains held together by disulfide bridges
Each chain has an Iron-containing haem group
How much oxygen can each haemoglobin carry?
8
How do you classify proteins and what are the differences between them?
Fibrous | Globular |
|---|---|
-Secondary structure | -Tertiary structure |
-Insoluble in water | -Soluble in water |
What type of proteins are enzymes?
Globular
What is a enzyme?
An enzyme is a biological catalyst, it speeds up the biochemical process but they remain unchanged at the end of the process
How do enzymes work in catabolic reactions and name a example?
Enzymes active sites affect the bonds in substrates so they are easier to break
These are exothermic reactions
A example is respiration
Often involves oxidation of hydrolysis
How do enzymes work in anabolic reactions and name a example?
Enzymes bring the substrate molecules together
These are endothermic reactions
A example is photosynthesis
Often involves condensation reactions
What is the active site of a enzyme?
The part of the enzyme where the substrate binds to
Specific shape due to its tertiary structure
What is the enzyme substrate complex?
The intermediate bond formed when a substrate binds to the active site of an enzyme
What is the lock and key model?
The active site of the enzyme is complementary to the specific shape of the substrate
What is the induced fit model?
Activation energy of a substrate is lowered due to the distortion of bonds in the enzyme-substrate complex
The active site is flexible and fits around the substrate molecule
Before returning to its original shape
How does concentration of substrate and product change over time?
High concentration of substrate, means there is no products
This makes it easy for the substrate to come into contact with the active site
As all the active sites are filled, the reaction happens quickly
This means Substrate concentration decreases and product concentration increases
This makes it more difficult for successful collisions to take place between the substrate and enzymes
This makes the rate of reaction slows down
Eventually so little substrate that there is no change in concentration
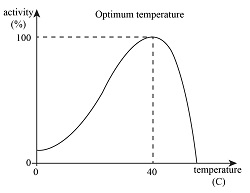
What happens at low temps, optimum temps and high temps?
At low temperature there is a low rate due to kinetic energy. There are few successful collisions between enzymes and substrates lead to slow rates
At optimum temperatures there are lots of collisions.
At high temperatures, bonds in the tertiary structure of enzymes are broken so the active site changes shape
What is enzyme inhibition?
Enzyme inhibitors are substances that directly or indirectly interfere with the active site of the enzyme
What are the two categories of enzyme inhibitors?
Competitive inhibitors: Which bind to the active site of the enzyme
Non-competitive inhibitors: Which bind to the enzyme at a position than the active site
What are some examples of enzyme inhibitors?
Heavy metals which are irreversible non-competitive inhibitors
Cyanide is a irreversible inhibitor preventing ATP synthesis
Toxins/Venoms contain inhibitor that block enzymes
Antibiotics penicillin inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis
How do competitive inhibitors work?
They have a similar shape to that of the substrate and can occupy the active site
The inhibitor is not permanently bound so will get released
How do non-competitive inhibitors work?
Attach themselves to the enzyme at a binding site which isn’t the active site
Upon attaching this alters the shape of the enzyme’s active site
Describe the chemical reactions involved in the conversion of polymers to monomers and monomers to polymers.
Give two named examples of polymers and their associated monomers to illustrate your answer. (5)
A condensation reaction joins monomers together and forms a (chemical) bond and releases water
A hydrolysis reaction breaks a (chemical) bond between monomers and uses water
A suitable example of polymers and the monomers from which they are made
A second suitable example of polymers and the monomers from which they are made
Reference to a correct bond within a named polymer
What is a monomer? (1)
(a monomer is a smaller / repeating) unit / molecules from which larger molecules / polymers are made
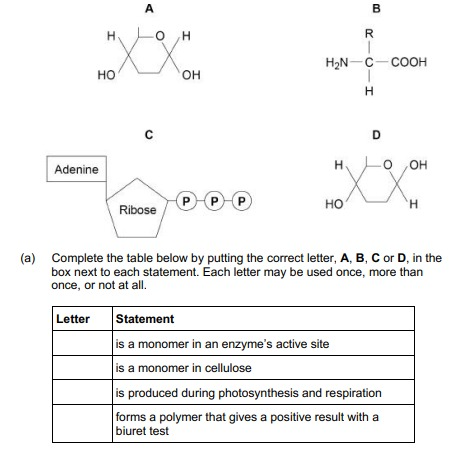
Complete the table below by putting the correct letter, A, B, C or D, in the box next to each statement. Each letter may be used once, more than once, or not at all. (4)
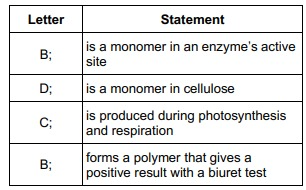
A biochemical test for reducing sugar produces a negative result with raffinose solution.
Describe a biochemical test to show that raffinose solution contains a non-reducing sugar. (3)
Heat with acid and neutralise
Heat with Benedict's (solution)
Red precipitate/colour
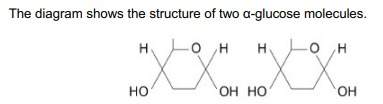
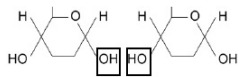
On the diagram, draw a box around one chemical group in each glucose molecule used to form a glycosidic bond. (1)
A precipitate is produced in a positive result for reducing sugar in a Benedict’s test. A precipitate is solid matter suspended in solution. A student carried out the Benedict’s test.
Suggest a method, other than using a colorimeter, that this student could use to measure the quantity of reducing sugar in a solution. (2)
Filter and dry (the precipitate)
Find mass/weight
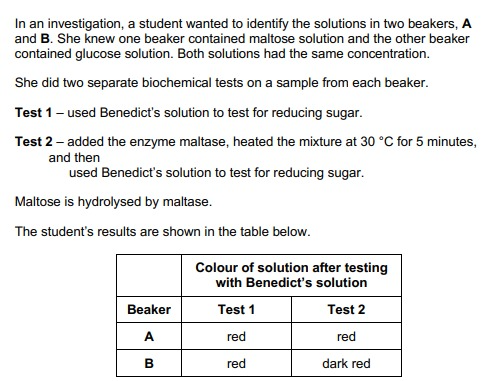
Explain the results for beakers A and B in the table. (2)
A = glucose and B = maltose
Because more sugar/precipitate after hydrolysis/maltase action
Use of a colorimeter in this investigation would improve the repeatability of the student’s results. Give one reason why (1)
Quantitative OR (Colour change is) subjective
In Test 1, the student used a measuring cylinder to measure 15 cm3 of solution from a beaker. The measuring cylinder gives a volume with an uncertainty of ±1 cm3. She used a graduated syringe to measure 5.0 cm3 of Benedict’s solution. The graduated syringe gives a volume with an uncertainty of ± 0.5 cm3. She mixed these volumes of liquid to do the biochemical test.
Calculate the percentage error for the measurements used to obtain a 20 cm3 mixture of the solution from the beaker and Benedict’s solution. Show your working. (2)
16.67 − 17 = 2 marks
Lactulose is a disaccharide formed from one molecule of galactose and one molecule of fructose.
Other than both being disaccharides, give one similarity and one difference between the structures of lactulose and lactose. (2)
Similarity
1. Both contain galactose / a glycosidic bond;
Difference
2. Lactulose contains fructose, whereas lactose contains glucose;
Starch is a carbohydrate often stored in plant cells. Describe and explain two features of starch that make it a good storage molecule. (2)
Insoluble (in water), so doesn’t affect water potential;
Branched / coiled / (α-)helix, so makes molecule compact
Polymer of (α-)glucose provides glucose for respiration
Large (molecule), so can’t cross the cell membrane
Glycogen and cellulose are both carbohydrates. Describe two differences between the structure of a cellulose molecule and a glycogen molecule. (2)
Cellulose is made up of β-glucose (monomers) and glycogen is made up of α-glucose (monomers)
Cellulose molecule has straight chain and glycogen is branched
Cellulose molecule has straight chain and glycogen is coiled
glycogen has 1,4- and 1,6- glycosidic bonds and cellulose has only 1,4- glycosidic bonds
Which box identifies the test which would be used to show the presence of starch.
C
Describe the structure of glycogen. (2)
Polysaccharide of α-glucose
(Joined by) glycosidic bonds
In mammals, in the early stages of pregnancy, a developing embryo exchanges substances with its mother via cells in the lining of the uterus. At this stage, there is a high concentration of glycogen in cells lining the uterus.
During early pregnancy, the glycogen in the cells lining the uterus is an important energy source for the embryo.
Suggest how glycogen acts as a source of energy.
Do not include transport across membranes in your answer (2)
Hydrolysed (to glucose);
Glucose used in respiration
Name the monomers from which a maltose molecule is made. (1)
Glucose (and glucose)
Name the type of chemical bond that joins the two monomers to form maltose. (1)
(α1,4) Glycosidic
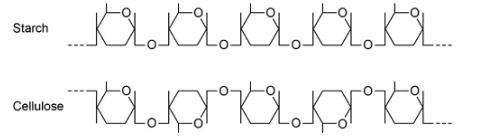
Explain the difference in the structure of the starch molecule and the cellulose molecule shown in the diagram above. (2)
Starch formed from α-glucose but cellulose formed from β-glucose;
Position of hydrogen and hydroxyl groups on carbon atom 1 inverted.
Starch molecules and cellulose molecules have different functions in plant cells. Each molecule is adapted for its function.
Explain one way in which starch molecules are adapted for their function in plant cells. (2)
Insoluble;
Don’t affect water potential;
Explain how cellulose molecules are adapted for their function in plant cells.(3)
Long and straight chains
Become linked together by many hydrogen bonds to form fibrils
Provide strength (to cell wall)
The general structure of a fatty acid is RCOOH.
Name the group represented by COOH. (1)
Carboxyl
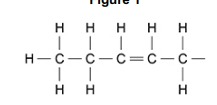
Name the type of R group shown in Figure 1. Explain your answer.
Type of R group 1:
Unsaturated (fatty acid/hydrocarbon)
Explanation:
Double bond (between carbons)
Describe how you would test for the presence of a lipid in a liquid sample of food. (2)
Add ethanol/alcohol then add water and shake/mix
White/milky (emulsion)
Describe how a triglyceride molecule is formed. (3)
One glycerol and three fatty acids
Condensation (reactions) and removal of three molecules of water
Ester bond(s) (formed)
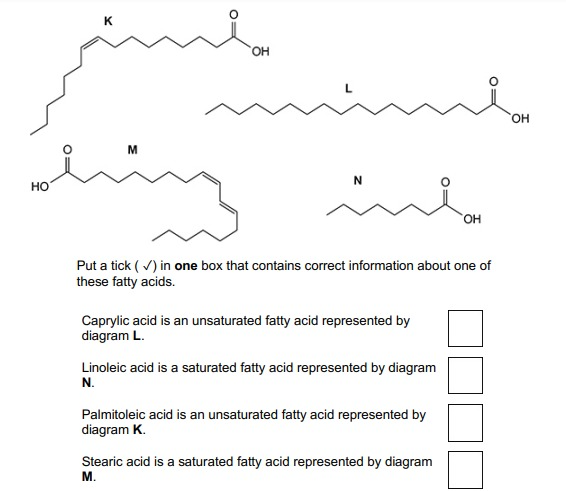
Put a tick ( ✓) in one box that contains correct information about one of these fatty acids.
Palmitoleic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid represented by diagram K
Describe how an ester bond is formed in a phospholipid molecule. (2)
Condensation (reaction)
Between of glycerol and fatty acid
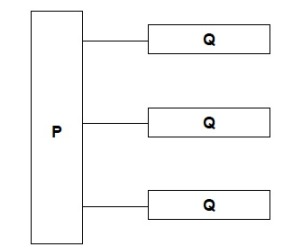
Name the molecules represented in the diagram by P and Q
P – glycerol
Q – fatty acid (chains)
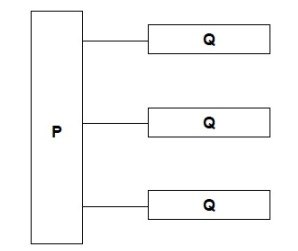
Name the type of bond between P and Q in the diagram.
Ester Bond
Describe how you would test a liquid sample for the presence of lipid and how you would recognise a positive result. (2)
(Mix / shake sample) with ethanol, then water
White / milky (emulsion)
Describe how you would test a piece of food for the presence of lipid (2)
Dissolve in alcohol, then add water
White emulsion shows presence of lipid.
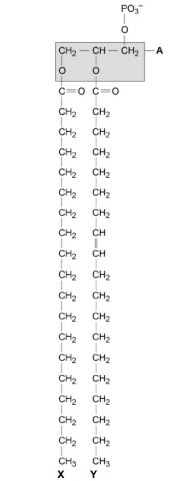
The part of the phospholipid labelled A is formed from a particular molecule. Name this molecule.
Glycerol
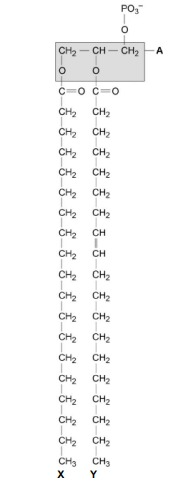
Name the type of bond between A and fatty acid X.
Ester.
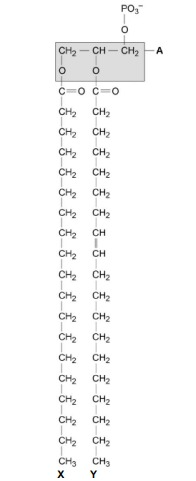
Which of the fatty acids, X or Y, in the figure above is unsaturated? Explain your answer.
Y (no mark)
Contains double bond between (adjacent) carbon atoms in hydrocarbon chain.
The scientists expressed their results as Percentage of lipid in plasma membrane by mass. Explain how they would find these values.
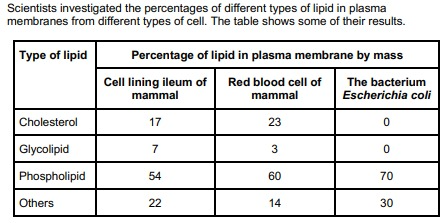
The scientists expressed their results as Percentage of lipid in plasma membrane by mass. Explain how they would find these values. (2)
Divide mass of each lipid by total mass of all lipids (in that type of cell);
Multiply answer by 100.