Fundamental of amines and amides
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
We can prepare an amine by reacting a halogenoalkane with…
ammonia
The reaction of a halogenoalkane with ammonia to prepare an amine requires…(3)
heat.
high pressure
excess ammonia
To produce an amide, we can react an amine with a(n)…(2)
acyl chloride.
acid anhydride
What functional group do amines contain?
NH2
We can prepare an amine by heating excess ammonia with a(n)
haloalkane
We can react an amine with either an acyl chloride or acid anhydride to produce a(n)
amide
amide functiional group
RONH2
Classify the following amines as either primary, secondary or tertiary.
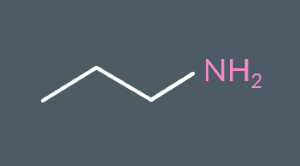
Primary
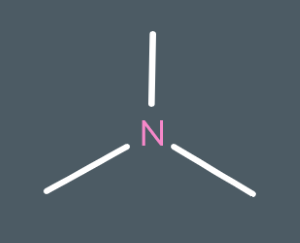
Classify the following amines as either primary, secondary or tertiary.
tertiary
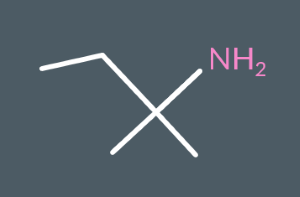
Classify the following amines as either primary, secondary or tertiary.
primary
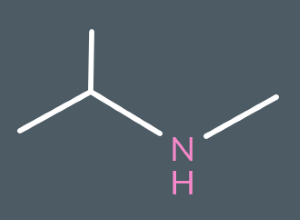
Classify the following amines as either primary, secondary or tertiary.
secondary
What’s the name of this molecule?
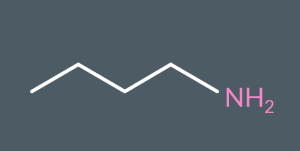
Butylamine
We call this molecule…
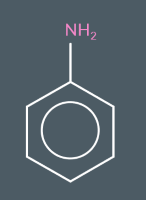
phenylamine
What’s the name of this molecule?
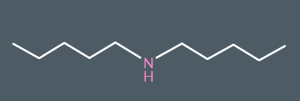
Dipentylamine
What do we call this molecule?
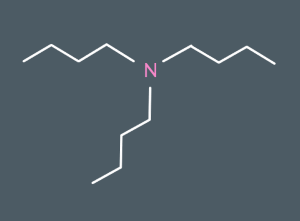
tributylamine
To name secondary amines with identical groups, we add the multiplier
di
To name tertiary amines with identical groups, we add the multiplier
tri
What’s the name of this molecule?
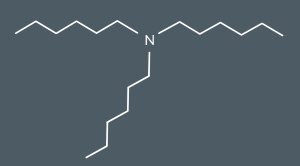
trihexylamine
What’s the name of this molecule?
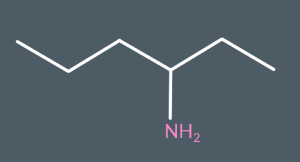
Hexan-3-amine
What’s the name of this molecule?
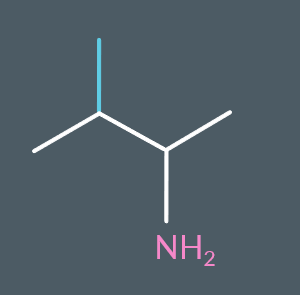
3-methylbutan-2-amine
What’s the name of this molecule?
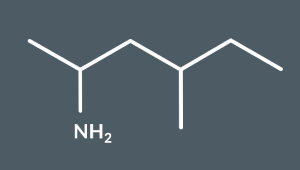
4-methylhexan-2-amine
What’s the name of this molecule?
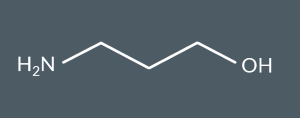
3-aminopropan-1-ol
What’s the name of this molecule?
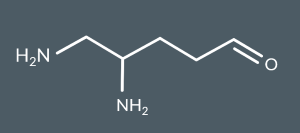
4,5-diaminopentanal
When the amine is the highest priority functional group, we write the suffix…
amine
When the amine isn’t the highest priority functional group, we write the prefix…
amino
What’s the name of this molecule?
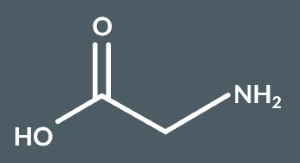
2-aminoethanoic acid
What’s the name of this molecule?
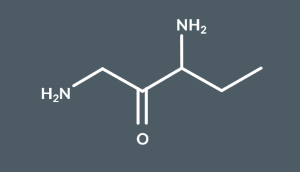
1,3-Diaminopentan-2-one
What’s the name of this molecule?
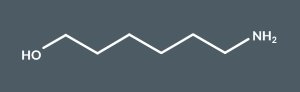
6-Aminohexan-1-ol
What’s the IUPAC name of this molecule?
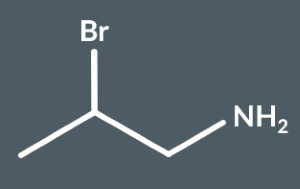
2-Bromopropan-1-amine
We classify an amine as either aliphatic or aromatic according to whether…
a benzene ring is directly bonded to nitrogen.
What’s the name of this molecule?
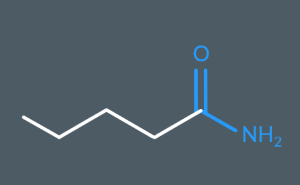
Pentanamide
What’s the name of this molecule?
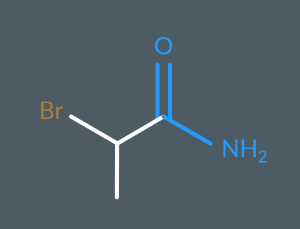
2-bromopropanamide
What’s the name of this molecule?
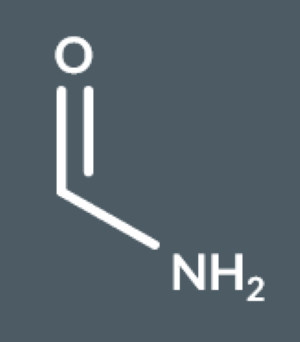
methanamide
What’s the name of this molecule?
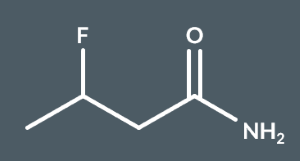
3-fluorobutanamide
What’s the name of this molecule?
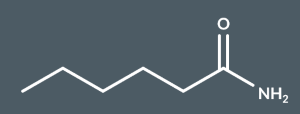
hexanamide
What’s the name of this molecule?
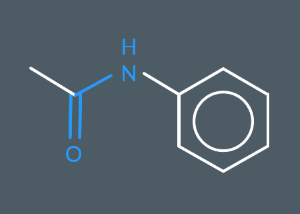
N-Phenylethanamide
What’s the name of this molecule?
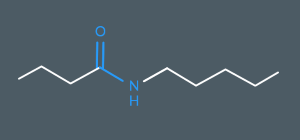
N-pentylbutanamide
What’s the name of this molecule?
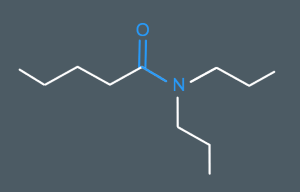
N,N-Dipropylpentanamide
What’s the name of this molecule?
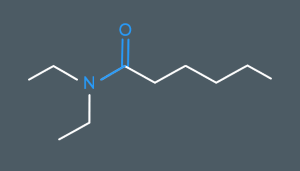
N,N-diethylhexanamide
What’s the name of this molecule?
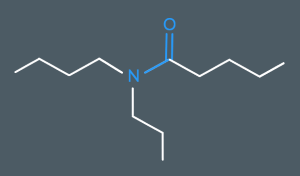
N-Butyl-N-propylpentanamide
What’s the name of this molecule?
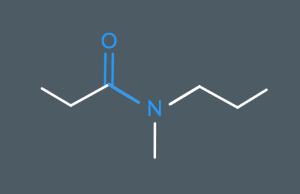
N-methyl-N-propylpropanamide
What’s the name of this molecule?
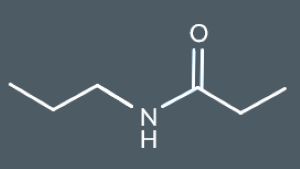
N-propylpropanamide
The solubility of amines and amides decreases as their size increases because…
a greater region of the molecule is nonpolar.
nonpolar molecules are highly insoluble in water.
Because amines have a lone pair of electrons, they can act as…(2)
bases.
nucleophiles.
can amines and amides form bonds with water?
All amines and amides can form hydrogen bonds with water
What happens to the solubility of amines and amides and their size increases?
The solubility of amines and amides in water decreases as the size of the molecule increases.
product of amine+acid?
salt
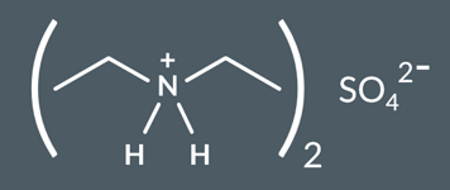
What salt do we form in this reaction?
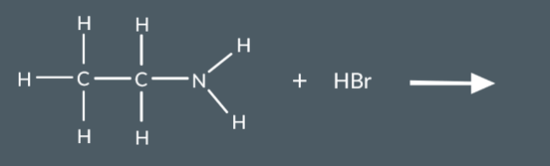
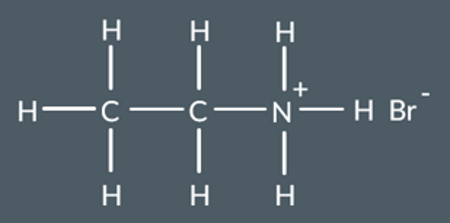
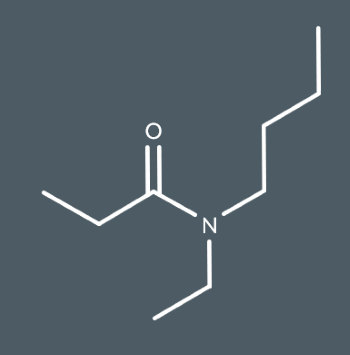
Draw the skeletal formula of N-butyl-N-ethylpropanamide.
A chemist reacts diethylamine,(CH3CH2)2NH, with sulfuric acid.
Draw the salt that forms in this reaction.