DPT 744 Lecture 1
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
The skins function is what?
Protection, temp control, and sensation
What are the the 2 layers of the skin?
Epidermis and dermis
What provides protective outer serface (that is tough, horny superficial layer
Keratinized epithelium
Does the epidermis have blood vessels or lymphatics?
NOOO
What is the avascular?
nourishes by underlying vascularized dermis(no or few vessels)
What does the Dense layer of the Dermis contain
Collagen and Elastic fibers
After the Dermis what kind of tissue does it consist of?
(Subcutaneous tissue) loose, fatty connective tissue
The basil layer consist of what?
Epidermis
Deep fascia
form compartment, which helps to stabilize muscular and prevent spread of infection
How does skin thermally regulates through evaperation of water on skin?
Sweat glands
What gland is usually associated with hair follicle and uses oil to keep the skin fresh?
Sebaceous glands
Hair follicles?
Hair grows from the base of a slanted follicle formed by the growth of epidermal cells into the dermis. Each follicle is connected to an arrector pili muscle, which contracts in response to autonomic or sensory stimuli, causing the hair to stand upright.
What is the axial skeleton
Head, neck, and trunk
Appendicular skeleton?
Limbs, including formation of pectoral and pelvic girdles
Cartilage
is flexiable, semi rigid form of connective tissue, and forms where more flexibility is requires
what provides smooth, low friction, and gliding surface and is not flexiable
Articular Cartilage
What is avascular (no blood vessles enter) and is important to be compressed and decompressed
Cartilage
What is a hard form if connective tissue
Bone
If it covers bone?
Periosteum
If it covers cartilage?
Perichondrium
What provides attachment for tendons and ligaments
Bones
Tubular in form, femur
Long bones
Cuboidal, ankle wrist
short bones
proective function (ex: skull, scapula, ribs)
Flat bones
Different shapes, vertebrae
Irregular bones
Where tendons cross the ends of bones, protects tendons from exccesive wear
Sesamoid bone (ex Patella)
rounded articular area? (End of the bone and reduces friction between bone that slide past each other to create movement)
Condyle
Ridge of bone(can provide attachments for muscles,ligaments, and other tissue)
Crest
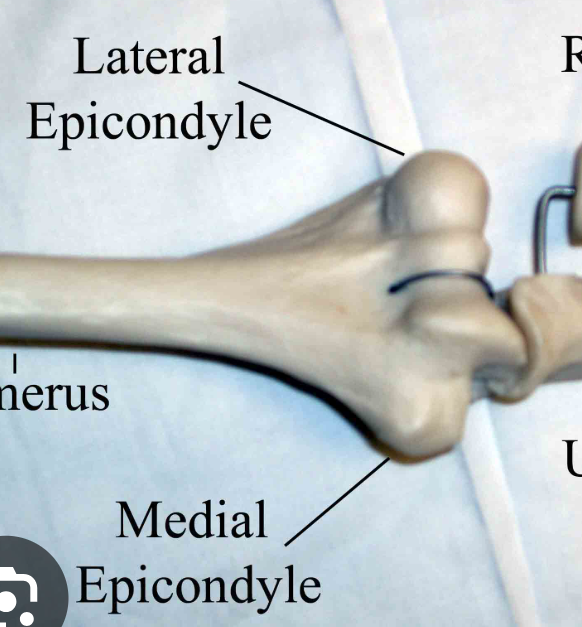
Eminence superior to a condyle(place of attachments for muscles, ligaments, and tendons)
Epicondyle
Smooth flat area, usually covered with cartilage, where bone aticulates(help with movement and absorb load)
facet
Passage through a bone(allows spinal cord, nerves and blood vessels to pass through)
Foramen
Hollowed or depresses area
Fossa
Elongated depression
Groove
Linear elevation
Line
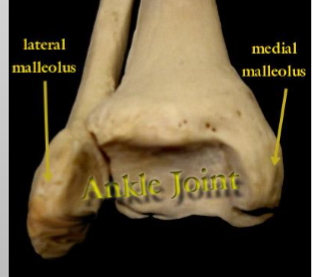
Rounded process
Malleolus
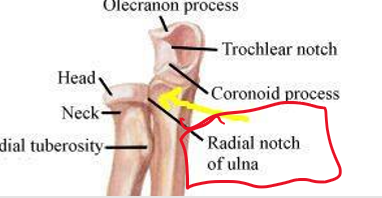
Indentation at the edge of a bone
Notch
Projection of bone
Protuberance
Thorn like process
Spine
large blunt elevation(upper part of femur, serves as an attachment point for hip and thigh muscles)
Trochanter
small raised eminence
Tubercle
Large rounded elevation (deltoid)
Tuberosity
What begins to ossify at 8 weeks
Humerus
When does ossification complete itself in the humerus?
20 years old
All bones are derive from what?
Mesenchyme (embryonic connectife tissue)
What are the 2 processes of the bone ossification?
Intramembranous and Endochondral ossification
Intramembranous Ossification
Known as membranous bone formation
Endochondral Ossification
Known as cartilaginous bone formation
What oasses through the periosteum via nutrient foramina?
Nutrient arteries
Skeletal joints are recognized by their what?
Fibrous
Cartilaginous
Synovial
Fibrous Joints
united by fibrous tissue
- sutures(skull)
- Syndesmosis type (keep bone together)
What is united by hyaline or fibrocartilage
Cartilaginous Joints
- Hyaline (particular cartilage)
- Fibrocartilage ( more motions)
What are the 4 Characteristcs of the Synovial Joints (CAFS)
Cavity
Synovial membrane and fuid
Articular cartilage
Fibrous capsule
What joint is gliding over the other (carpal bone)
Plane or gliding
what joint allows rotation (ex: Atlanto-axial joint)
Pivot
The fibrous capsule is strength by ligaments what are they?
Intrinsic ligaments (between carpal bones)
Extrinsic ligaments (between carpals and metacarpals)-outside wrist
Intra-articular (in knee joint)
Extra-articular (out the knee joint)
What cartilage is found lining articular surfaces; nasal septum, tracheal rings
Hyaline
What cartilage is found in the ear and epiglottis, is rigid
Elastic
What cartilage is found in intervertebral discs and often occurs where tendon and ligament are joined to bones
Fibrocartilage (allows more motion)
What arise from vessels around the joint?
Articular arteries
How do arteries form networks to ensure a blood supply in any position is assumed by the joint?
Anastomose
What communicated to the veins that accompany arteries?
Articular veins
what arise from branches of cutaneous nerves suppying overlying skin?
Articular nerves
What law states nerves supplying a joint also supply the muscles moving the joint and the skin covering their distal attachments
Hilton’s Law