PSY140 Exam 2 Part II Study Guide
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is the difference between endocrine glands and exocrine glands.
1. Exocrine glands secrete things locally through ducts
2. Endocrine glands secrete hormones into the blood, which have long lasting effects on the body.
Name an example of both endocrine and exocrine glands.
1. Exocrine: sweat glands
2. Endocrine:
- hypothalamus
- pituitary gland,
- adrenal gland
- ovaries/testes.
How do hormones work?
Hormones are transmitted in the blood and have long lasting effects
How do neurotransmitters work?
they are transmitted through the synaptic clefts and have local short-lived effects.
How do steroid hormones work?
they diffuse across the cell membrane and attach to receptors in the cytoplasm
How do non-steroid hormones work?
they attach to the cell membrane and activate the second messenger systems within cells.
What are the two main types of steroid hormones and where are they synthesized?
1. cortisol which is synthesized in the adrenal cortex
2. sex hormones(Androgens and Estrogens) which are synthesized in the gonads.
What is the process by which cortisol is converted to estradiol?
Cortisol -> TTT then TTT -> to Estradiol by enzyme aromatase.
What are the male and female gonads called and what do they do?
- the male gonads (testes) secrete TTT and produce sperm.
- female gonads (ovaries) secrete estradiol and produce ovum.
What is genitalia?
the non-endocrine parts of the reproductive organs.
What does TTT do to genitalia in utero?
- testes in the male fetus secrete TTT -> causes male genitalia to develop.
- without TTT female genitals develop
What do the twin studies tell us about homosexuality?
this study tells us there is a genetic competent to homosexuality, but there is a nurture component as well.
What are secondary gender characteristics?
- caused by estradiol: broad hips and breast development.
- caused by TTT: beards, broad shoulders, and muscles.
- for both male and female: pubic hair and underarm hair.
What are the 10 emotions?
1. Distress
2. Anger
3. Disgust
4. Contempt
5. Fear
6. Shame
7. Guilt
8. Interest
9. Happiness
10. Surprise
What are the three emotional behaviors mentioned in class?
1. Avoidance
2. Aggression
3. Reinforced behavior
Name the structures of the limbic system.
- cingulate gyrus
- septal nuclei
- nucleus accumbens
- amygdala
How are they important for rewarding behavior?
they are involved in learning and memory, where the nucleus accumbens produces dopamine.
What is positive reinforcement?
when the reinforcer increases the likelihood that a behavior will occur.
Give an example of positive reinforcement.
when a rat presses a lever a food reward is delivered, the resulting behavior is that the rat continues to press the lever to receive the food reward.
What will a rat choose to do when presented with the opportunity to deliver stimulation directly to its nucleus accumbens?
Rats will choose direct stimulation of the nucleus accumbens over caring for their own pups.
What is the amygdala involved in?
it is involved in the emotions fear and anger and the behaviors avoidance and aggression.
What are the inputs to the amygdala?
- visual
- auditory cortex
- thalamus
List the stimuli the amygdala responds to.
responds to facial expressions of emotion, vocal emotions, and subliminal stimuli.
What are the outputs of the amygdala and how do they affect behavior?
1. Amygdala to Hypothalamus: causes a sympathetic autonomic response, increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate.
2. Midbrain to the pons: causes freezing/flinching behaviors.
What happens to animals with lesioned amygdala's?
they cannot learn new fear associations and lose old fear associations.
Recap the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems roles.
The sympathetic system is our fight/flight system, while our parasympathetic system is the "rest/relax" system. The sympathetic system gets input from the hypothalamus which increases heart and breathing rate, and sends signals to the adrenal medulla.
What does the adrenal medulla do and which system is it innervated by?
it secretes the hormones, adrenaline and noradrenaline into the bloodstream.
What are the effects of adrenaline/noradrenaline?
- increase heart and breathing rate and blood pressure,
- stimulate the liver to break down glycogen into glucose.
Define and explain the HPA axis.
is the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal cortex axis.
What does the HPA axis do?
1. hypothalamus secretes CRF into the pituitary
2. the pituitary releases ACTH into the blood
3. ACTH activates the adrenal cortex which releases cortisol.
What are the effects of cortisol?
1. stimulates liver to breakdown GLYCOGEN
2. increases heart rate and blood pressure
3. increases metabolic rate - (Krebs cycle)
What is the Krebs cycle?
glucose + oxygen -> ATP energy
Is our body tuned for chronic stress or just for acute stress (i.e. running from a predator), why?
Our bodies were made for acute stress (like running from a predator), but todays world brings many chronic stressors that can adversely affect our health.
What is a psychosomatic illness?
A psychosomatic illness is a real illness brought on by a negative psychological state.
Name some psychosomatic illnesses brought on by chronic stress.
High blood pressure, memory loss, and ulcers.
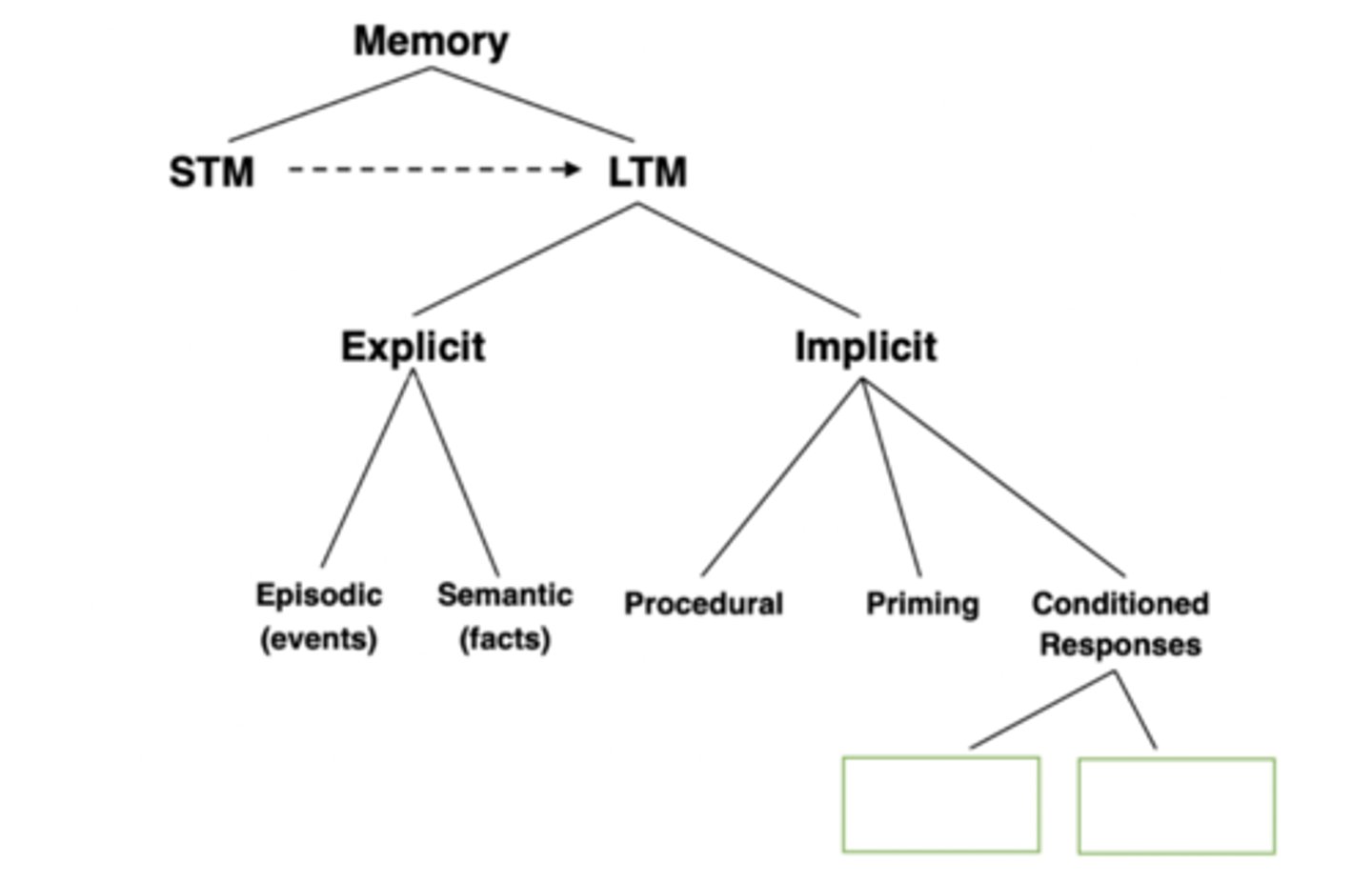
Fill out this memory diagram:
1. STM
2. LTM
- A. Explicit
- i) Episodic (events)
- ii) Semantic (facts)
- B. Implicit
- i) Procedural
- ii) Priming
- iii) Conditional Responses
- a) Operant
- b) Classical
Define encoding.
processing new information into a form that can be stored
Define storage.
retaining/maintaining a memory
Define retrieval.
getting information out of storage into conscious awareness
What are the two components of retrieval?
A) Recall: to bring back to mind
B) Recognition: to perceive something as previously known (familiar)
Define short term memory.
memories that are for things that just happened
Define long term memory
memory for things that don't currently occupy your attention and must be retrieved.
How do memories become permanent?
must be consolidated from STM to LTM.
How do you consolidate memories?
You need glucose to consolidate memories from STM to LTM.
What are the two types of Explicit long term memories?
1. semantic memories: facts
2. episodic memories: are things that you've experienced
What may help with consolidating memories?
sleep and alcohol
What are the three types of Implicit long term memories?
1. procedural: skills, procedures or habits
2. priming: exposure to stimulus
3. conditioned responses. Procedural memories are those that are procedures, skills, or habits, like solving a rubix cube. Priming occurs when the exposure to a stimulus influences behavior without you being aware of it, like subliminal advertising. There are two types of conditioned responses, operant and classical.
Explain Operant Conditioning.
1. Reward (or "Reinforcement")-> increase the likelihood of behavior X
- i) positive: do X -> give reward
- ii) negative: do X -> reward is removing something
2. Punishment -> decrease the likelihood of behavior Y
- i) positive: do Y -> give punishment
- ii) negative do Y -> remove reward
Explain Classical Conditioning.
- uses "natural", automatic response ("When I do this, you'll do that")
Explain the Pavlov's dogs experiment.
A bell is paired with the presentation of food which causes the dogs to salivate. But even when the bell is rang and there is no food, the dogs still salivate.
Damage to what structure causes amnesia?
The hippocampus
What are the two types of amnesia?
1. Retrograde Amnesia
2. Anterograde Amnesia
Define retrograde amnesia.
loss of events prior to injury
Define anterograde amnesia
inability to create new memories after the injury
Patient HM had damage to his hippocampus, what type of amnesia did he have, what kind of memories was he able to maintain?
HM had severe explicit LTM anterograde amnesia but not implicit LTM so he was still able to access procedural memories