Unit 11-renal system
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
functions of the renal/urinary system
removal of waste products from body fluids= excretion
elimination of organ waste materials from body(nitrogenous wastes-urea, uric acid, creatinine)
homeostatic regulation in the urinary system
regulating blood volume and blood pressure by adjusting water lost in the urine
works to preserve water/concentration urine
hormonal response(aldosterone, ADH, renin, erythropoietin)
regulating plasma ion concentrations(NA+, K+, Cl-, H+, etc)
regulation of blood pH
preservation of valuable nutrients
the kidneys-external anatomy
at level T12-L3
left kidney higher than right due to location of liver
3 layers of supportive tissue around each kidney:
inner fibrous capsule
middle adipose tissue layer(cushions and protects)
outer renal fascia(anchors to surrounding structures)
the adrenal gland is on the superior surface of each kidney(aka suprarenal gland)
hilum
area where blood vessels, lymphatics, nerve fibers enter the kidney
runs at the proximal end of the ureters
blood supply:
renal arteries and veins
kidneys receive 20% of cardiac output, liver receives 25%
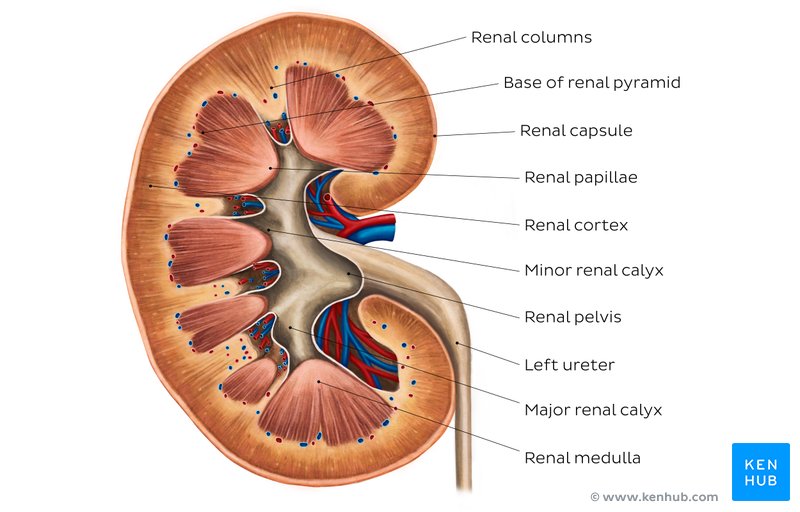
renal medulla
divided into 6-19 renal pyramids separated by renal columns
base of each pyramid at the apex(renal papilla) projections into renal sinus
at the renal papilla are calyces(singular calyx)= site of urine collection
urine moves from renal medulla→ minor calyx→ major calyx→ renal pelvis → ureter
kidney lobe
blood vessels run around the pyramid
includes a renal pyramid
this is where urine is made
blood flow in the kidneys
blood travels to the kidneys via Left and right renal arteries
renal artery
branches to
segmental arteries
branches to
interlobar arteries
arcuate arteries
radiate arteries
afferent arterioles that feed capillaries supplying individual nephrons
the nephron
it is the functional unit of the kidney
2 kinds
cortical nephron(85%)→ in the outer cortex of the kidney
juxtamedullary nephron→ deeper down in the kidneys(concentrate liver)
Each nephron has a renal corpuscle and renal tubule
renal corpsule
includes the glomerulus(capillary network)capsule aka bowman’s capsule
where filtrate is produced
renal tubule
includes the proximal convoluted tubule(PCT), nephron loop-loop of henle,distal convoluted tubule(DCT)
From the glomerular capsule to collecting tube
Functions:
reabsorption and secretion of water and solutes to maintain homeostasis and produce urine
reabsorption and secretion varies along the renal tubule due to variation in tissues and membrane permeability
ureters
pair of muscular tubules extending from renal pelvis of kidney to urinary bladder(about 30mcm)
path of ureters depend on presence of reproductive organs
enter posterior wall of bladder at an oblique angle(slit-like opening called ureteric orifices
ureteric orifices→ prevent backflow from the bladder if it is overfilled
peristaltic contractions sweep across ureters every 30 secs→ force urine toward the bladder
urethra
extends from the internal urethral sphincter and carries urine out of body
5x longer in males than females
male urethras have 3 sections prostatic, membranous, and spongy urethra
female urethras are shorter and more prone to infection
external urtheral sphincter is under voluntary control
resting tone of the external urtheral sphincter must be voluntarily relaxed to allow urination
glomerulus
includes 50 intertwined capillaries(within the glomerular capsule)
receives blood from afferent arterioles and blood exits via efferent arterioles
the outer layer is made up of simple squamous epithelium
extraglomerular mesangial cells→ muscular cells that contract to decrease the size of the vessel lumen(only in juxtamedullary nephrons)
they impact filtration and change constriction
filtration membrane
filtration slits at the visceral membrane created by gaps between unique podocyte cells
glomerular capillaries are fenestrated capillaries meaning they have pores that allow the rapid movement of more fluids and solutes
filtration happens in the renal corpuscles with water and small solutes being pushes out of glomerular capillaries into the capsular space
the end product of filtration=filtrate
filtrate leaves the glomerular capsule and enters the renal tubule(starting at the proximal convoluted tubule)
3 types:
macula densa cells
juxtaglomerular cells
mesangial cell
s
juxtaglomerular complex(JGC)
has a critical role in the regulation of blood pressure and the formation of filtrate
found in all nephrons→ it is the structure where afferent arterioles make contact with distal convoluted tubule
3 types:
macula densa cells
juxtaglomerular cells
mesangial cell
3 cells of the juxtaglomerular complex(JGC)
Macula densa- epithelial cells in distal tubule(chemoreceptors and baroreceptors)
juxtaglomerular cells- in wall of afferent arterioles and secrete renin- activates angiotensin I
mesangial cells-in the space between afferent and efferent arterioles
feedback station for the macula densa and juxtaglomerular
collecting system
function is to move tubular fluid from the nephron to the renal pelvis (this further adjusts its composition as needed to create the final product=urine)
a number of nephrons will empty into one collecting duct
several collecting ducts converge into larger papillary duct
papillary ducts empty into minor calyx
principal cells of the collecting duct
reabsorb water and secrete potassium
made of cuboidal epithelium without microvilli
intercalated cells
maintain acid base balance
made of cuboidal epithelium with microvilli
vasa recta
long straight capillary running beside the nephron loop
carries solutes and water reabsorbed in the renal medulla back to the systemic circulation(countercurrent exchange)
formation of urine-filtration
blood pressure forces fluid across the glomerulus into glomerular capsule(aka bowman’s capsule)
the main driver of filtration is hydrostatic pressure
if the blood pressure decreases, filtration also decreases(creates a risk of renal fialure)
large molecules cannot fit through the glomerulus because it is selectively permeable
eg. colloid= plasma protein that cannot fit through the glomerular membrane
formation of urine-reabsorption
moving water and solutes from the tubular fluid back into circulation
reabsorption is selective and passive
fluid goes from the filtrate into the peritubular fluid '
regulated by hormones
90% of filtrate from glomerular capsule will be reabsorbed
formation of urine-secretion
secretion of solutes back into the tubular fluid(filtrate) before excretion
depends on permeability and availability of other transport mechanisms
proximal convoluted tubule
reabsorption of water, ions, and all organic nutrients
distal convoluted tubule
active secretion of ions, acids, drugs, toxins to the tubular fluid
selective reabsorption of Na+ ions and water
active transportation of chloride and water
aldosterone is in control of Na+ ion channel and pumps
some reabsorption of water, sodium ions, and calcium ions→ under hormonal control
Plays a key role in acid-base balance and secretion of ions like potassium and hydrogen.
Lacks a brush border, as less absorption occurs compared to the PCT
can be influenced by ADH to reabsorb more water
nephron loop
thin descending limb:
further reabsorption of water
not very permeable to solutes(Na+, Cl-)
Thick ascending limb:
reabsorption of Na+ and Cl- ions
impermeable to water
collecting duct
some reabsorption of water
reabsorption and or secretion of sodium, potassium, hydrogen , and bicarbonate ions
papillary duct
delivery of urine to minor calyx
glomerular filtration
the first step in kidney function mainly due to hydrostatic pressure in the glomerular capillaries
influenced by blood colloid osmotic pressure(BCOP)
net filtration pressure=difference between hydrostatic pressure and BCOP
glomerular filtration rate(GFR)→ the amount of filtrate that the kidneys produce in 1 minute(average=125 mL/min)
glomerular filtration rate
the amount of filtrate that the kidneys produce in 1 minute(average=125 mL/min)
controlled by autoregulation, hormonal regulation, and autonomic regulation
autoregulation
control of local blood flow via vasoconstriction and vasodilation
hormonal regulation
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system(RAAS)
lower BP(or GFR) triggers the release of renin
renin converts angiotensinogen into inactive angiotensin I
Angiotensin converting enzyme(ACE) converts angiotensin I→ angiotensin II
angiotensin II promotes vasoconstriction aldosterone production, and stimulates the sympathetic nervous system to increase blood pressure and restore GFR
natriuretic peptides have the opposite effect
autonomic regulation
sympathetic nervous system can cause powerful vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles to decrease GFR
slow down production of filtrate which allows the retention of fluids in response to low BP
less blood going to the glomerulus= less pee is produced
tubular reabsorption
returns nutrients from tubular fluid back to blood
tubular secretion takes unwanted substances in the blood and assds substances from the blood to the tubular fluid
involves mechanisms of diffusion, osmosis, channel mediated diffusion, and carrier mediated transport
carrier mediated transport→ can be saturated
carrier mediated transport
2 characteristics
specificity→ what it will bind with
saturation: capacity of carrier protein to move substances
once saturated it cannot take anything else
saturation point of transport maximum determines renal threshold(plasma concentration at which a certain substance or ion will begin to appear in urine)
renal threshold
the plasma concentration at which a specific substance or ion will begin to appear in urine
varies between substances
glucose over the threshold will be seen in a urinalysis
eg. diabetes→ increased glucose in urine test shows that the body does not have enough insulin to bring down glucose levels
if tubular threshold is surpassed the substance will be found in urine
tubular secretion
involves transfer of selective substances from the peritubular capillaries(blood) into tubular lumen(tubular fluid)
most import secretory systems are for:
H+:
important in regulating acid-base balance
secreted in proximal, distal, and collecting tubules
K+: keeps plasma K+ concentration at appropriate level to maintain normal membrane excitability in muscles and nerve
secreted only in the distal and collecting tubules under the control of aldosterone
Organic ions:
more efficient elimination of foreign organic compounds from the body
secreted only in the proximal tubule
regulating urine volume and concentration
urine volume and osmotic concentration are controlled by water reabsorption
volume is very dependent on amount of water reabsorbed in the DCT and collecting system which depends on ADH
as ADH rises, DCT and collecting system become more permeable to water→ water reabsorption increases
under maximum ADH, osmotic concentration of urine can equal that of the surrounding medulla
urea
a byproduct of amino acid breakdown that is the most abundant organic waste
always have a certain level in the blood
raised levels can indicate kidney failure
excreted only in urine
creatinine
generated during skeletal muscle activity and is a byproduct of the breakdown of creatine phosphate
monitored the most to detect kidney function(benchmark for kidney function)
continually excreted in the urine only
uric acid
formed as the body recycles nitrogenous bases from RNA
urine osmality
measure of the osmotic concentration of urine(mOsm/Kg of water)
urinalysis
analysis of chemical and physical properties of urine
looks at the color, clarity, and presence of unexpected substances
creatinine clearance
compares creatinine levels in urine with creatinine levels in the blood, estimation GFR
lower kidney function= increased creatinine levels in the blood = lower GFR
GFR is always an estimate but provides important info on kidney function
GFR= creatinine excreted in urine(mg/h) /plasma concentration of creatinine
blood urea nitrogen(BUN)
measures amount of urea in the blood
increased Blood urea nitrogen(BUN)= lower kidney function
urinary bladder
hollow muscular organ that temporarily stores urine
rugae in the mucosal lining allow for expansion
longitudial and circular muscles form the detrusor muscles
when detrusor muscles contract, the bladder is compressed and urine is squeezed into the urethra
trigone area as thick smooth mucous layer that acts to funnel urine into urethra when bladder contracts(urethral opening at the apex of the trigone)
neck of the bladder houses the internal urethral sphincter(involuntary)
urine storage reflex
spinal reflex and pontine storage center
stretch receptors stimulate sympathetic activity that inhibits contraction of detrusor muscles and promote contraction of internal and external sphincter
decrease parasympathetic function
urine voiding reflex
spinal reflex and micturition center
micturition center stimulates increased parasympathetic activity and decreases sympathetic activity
sphincters relax and detrusor muscles contract
regulation of urination
urge to urinate or void begins when there is about 200 mL of urine in the bladder
peristaltic contractions bring urine from kidneys to bladder
urination involves 2 spinal reflexes:
→ urine storage reflex
→urine voiding reflex
infants and urination
infants lack a voluntary control of urination
necessary corticospinal connections are not yet developed
18-36 months the voluntary control is gained
changes in renal system in older age
decrease in number of functional nephrons
nephrolithiasis(formation of renal calculi)
decreases sensitivity to ADH
loss of muscle tone and sphincter'
urinary retention related to prostate enlargement